Abstract
This study investigates the roles of foreign direct investment (FDI) and technological innovation in influencing environmental sustainability across ten newly industrialized countries (NICs) over the period from 1990 to 2021. Using the wavelet quantile regression (WQR) approach, the analysis captures both the dynamic and heterogeneous relationships between FDI, technology, renewable energy, economic growth, financial development, and environmental outcomes across different quantiles and time scales. The results show that although economic expansion and foreign direct investment often help to lower CO2 emissions, their impact varies across countries and time horizons. Technological innovation has a dual impact—contributing to emission reductions in the short term while potentially leading to increased environmental degradation over the long term. These results underscore the importance of aligning FDI inflows and technological advancement with environmental policies to ensure sustainable growth in NICs. This study makes significant empirical and policy contributions to the ongoing discourse on reconciling economic development with ecological preservation in emerging markets.
1. Introduction
The link between economic growth, ecological sustainability, and technological progress has garnered considerable attention, especially in the context of developing nations like newly industrialized countries (NICs). These countries, transitioning from developing to developed economies, encounter distinct difficulties in reconciling industrial growth with environmental preservation [1]. As NICs undergo swift economic advancement, often fueled by foreign direct investment (FDI) and technological breakthroughs, their environmental sustainability becomes increasingly jeopardized [2]. Although these nations play a vital role in global economic progress, they also rank among the top contributors to CO2 emissions, underscoring the urgency of exploring the intricate relationship between economic growth and environmental consequences [3,4].
A central complexity in this discourse is the dual and conditional nature of both FDI and technological innovation. FDI is lauded for transferring capital, expertise, and cleaner technologies [5], but its net environmental impact is highly context-dependent. In the absence of robust environmental regulation and sufficient technological absorptive capacity, FDI can entrench pollution-heavy industrial practices [6,7]. Similarly, technological innovation may serve as both a solution and a risk: while advances in energy efficiency and renewable energy promise decarbonization [8], they can also drive rebound effects, where efficiency gains lead to expanded industrial activity and ultimately greater aggregate emissions [9].
The interplay of these forces cannot be fully understood without accounting for institutional and structural heterogeneity across NICs. The environmental consequences of economic growth and technological advancement are mediated by (1) the stage of financial development, which affects capital allocation and innovation financing; (2) technological readiness and infrastructure, which influence the diffusion of green technologies; and (3) the rigor and enforcement of environmental regulations, which shape firms’ behavioral responses [10]. These factors underscore the inadequacy of one-size-fits-all policy prescriptions and call for differentiated, evidence-based approaches.
Recognizing these complexities, this study advances the literature by applying the wavelet quantile regression (WQR) method—an innovative econometric tool that captures both the nonlinear and time-varying nature of relationships among FDI, technological innovation, and environmental outcomes. Unlike traditional panel techniques, WQR reveals how the strength and direction of these relationships shift across the distribution of CO2 emissions and over different periods. This allows for a more nuanced understanding of environmental dynamics in NICs and enables the formulation of targeted policy responses that are sensitive to both national context and temporal evolution.
The selection of 10 NICs is justified for several compelling reasons. First, NICs represent a critical stage in economic development, characterized by rapid industrialization and urbanization, which can significantly intensify environmental pressures. For example, NICs such as Malaysia, Turkey, and South Africa have experienced average industrial GDP growth rates of over 4% annually in the past decade, contributing to increased CO2 emissions and resource consumption [11]. Second, these countries often operate with constrained technological capacity and limited environmental management infrastructure. According to the UNIDO Industrial Development Report [12], more than 60% of NICs fall below the global median in the Environmental Performance Index (EPI), highlighting gaps in pollution control and sustainable practices. Third, the NIC group displays diverse economic structures and environmental outcomes, allowing for cross-country comparisons. For instance, while Turkey’s FDI inflows reached USD 10.5 billion in 2022, South Africa attracted USD 9 billion, with both countries channeling investments into energy, manufacturing, and technology sectors [13]. This diversity enables a more nuanced analysis of how FDI and technological innovation affect environmental sustainability under varying conditions. Therefore, studying NICs provides valuable insights into how emerging economies can balance economic growth with environmental protection.
This study makes three substantive contributions to the growing literature on the environmental externalities of technological diffusion and foreign capital inflows in newly industrialized countries (NICs). First, it offers empirical evidence based on a balanced panel of ten diverse NICs over the 1990–2021 period—a critical window that captures both the intensification of globalization and the evolution of environmental technologies. Unlike prior studies that treat this relationship statically, our approach reflects the dynamic and conditional nature of these interactions. Second, methodologically, the study employs a wavelet quantile regression (WQR) framework, which innovatively captures both time–frequency variations and distributional heterogeneity across emission quantiles. This enables us to identify how the effects of FDI and technological innovation vary not only over time but also across different levels of environmental pressure—an aspect largely overlooked in conventional panel models. Third, the analysis generates policy-relevant insights by differentiating between the environmental impacts of indigenous innovation and technology transferred via FDI under varying institutional, regulatory, and technological capacities. Collectively, the study provides a multidimensional analytical framework that integrates empirical rigor with theoretical nuance, enabling a deeper understanding of when and how FDI and innovation act as either drivers or deterrents of sustainability in transitional economies.
2. Literature Review
With global issues such as climate change and environmental degradation coming to the agenda, the examination of various factors affecting CO2 emissions emerges as a very important factor. The empirical literature of the study is constructed in this direction, and the literature is analyzed under five headings.
2.1. Technology (TECH) and CO2 Emissions
Human history shows that all industrial revolutions have been shaped by the adoption of innovative and transformative technologies for efficient production and more responsible consumption. In the modern world, these innovations have the potential to both optimize industrial processes and promote the adoption of ecologically friendly and sustainable consumer practices [14]. Nevertheless, even though technological advancements have improved industrial methods, it has also contributed to increased CO2 emissions, rapid depletion of natural resources, and climate change.
The theoretical basis of the link between technology and environmental sustainability can be explained by the “ecological modernization theory”. This theory argues that the transition of nations from low to medium levels of development increases environmental pollution. This is because, during this transition, the nation prioritizes increasing economic growth rather than environmental sustainability. However, the advanced stage of development results in the prioritization of environmentally friendly technological innovations. Thus, the second stage results in a quality environment. On the other hand, if innovations are purely growth-oriented, economic expansion results in poor environmental quality due to intensive energy consumption [15]. When technological innovations are implemented per environmental quality standards, they can reduce CO2 emissions. Nowadays, public institutions and industries in developing countries are making large R&D investments to improve energy efficiency and save energy. In recent years, technological innovation has gained an important place in both combating climate change and achieving sustainable development. Research shows that technological innovation is a critical mechanism for reducing GHG emissions. Clean energy use and research and development (R&D) investments play an important role in minimizing CO2 emissions [16].
Many studies reveal that technological innovation has environmental protection effects. For example, Ahmed [17] found that environmentally friendly technologies lead to less CO2 emissions in production processes by increasing energy efficiency. Similarly, Chu [14] confirmed that environmental technologies have a long-term positive impact on the ecological footprint in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) countries. On the other hand, technological innovations may also have negative impacts on the environment. Even if technological developments provide more energy savings, they may increase total energy consumption and emissions due to increased consumption trends. In this instance, also referred to as the rebound effect, new technology leads to increased use of energy and natural resources, which may result in increased trash production. This concept states that there are two ways that technological advancements can happen. First, technological advancements enhance energy-efficient manufacturing methods; second, they boost economic expansion. Growth increases energy demand in an economy, partly offset by the energy saved through energy-efficient production techniques. Economic growth may result in more energy use, which raises emissions of pollutants and ultimately degrades the environment [15]. In this regard, information and communication technologies (ICT) raise CO2 emissions even while they boost economic growth, according to Danish et al. [18] Park et al. [19] on the other hand, found that because of the development of internet infrastructure and the spread of digitalization in European Union (EU) countries, energy demand has increased, and thus, there is now more environmental pressure. R&D also helps lower CO2 emissions in Turkey, according to Kilinc-Ata [20].
2.2. FDI and CO2 Emissions
Although the relationship between FDI and CO2 emissions has been analyzed in many studies, no consensus has been reached on a common result. FDI is very important, especially for the economies of developing countries. Because FDI is one of the important sources of economic growth, employment increases, and modernization. At the same time, FDI contributes to higher living standards by making countries more competitive in international markets [21]. However, FDI may have some impacts on the environmental quality of host countries. Studies on the subject have examined the relationship between FDI and environmental quality through two main theories. These theories are the “pollution haven hypothesis” and the “pollution halo hypothesis”.
According to the pollution haven hypothesis, foreign direct investment (FDI) drives pollution-intensive industry activity from wealthy nations to those with laxer environmental rules. Hence, developed economies reduce the costs of complying with environmental regulations and benefit from cheap labor [22]. This theory is supported by numerous studies of different nations. For instance, He [23] found that industrial SO2 emissions will rise by 0.098% for every 1% increase in FDI capital stock in his analysis of 29 Chinese regions. Shahbaz et al. [24] discovered that FDI causes environmental damage in 110 developed and developing nations, supporting this theory. The pollution halo hypothesis states that there is a negative relationship between FDI inflows and environmental pollution. According to this hypothesis, FDI can reduce pollution in the host country by using environmentally friendly technology and less polluting production practices to operate under environmental regulations [25]. A similar result was found by Tang and Tan [26] for Vietnam using Johansen cointegration and Granger causality tests both in the short and long run. Alongside these studies, Chen et al. [27] examined the environmental effects of foreign direct investment (FDI) in 30 Chinese provinces and discovered that FDI improves air and water quality through production-oriented technological advancements and energy efficiency through environment-oriented technological advancements.
Beyond their impacts, FDI and technological innovation are increasingly recognized as interrelated factors that jointly influence environmental outcomes in host countries. FDI serves as a critical vehicle for the international transfer of advanced, often greener, technologies—especially in developing and newly industrialized countries that face constraints in domestic innovation capacity [28]. Multinational enterprises (MNEs), through their investments, can introduce cleaner production methods, energy-efficient technologies, and more stringent environmental management practices, thus potentially enhancing environmental performance in host economies [29]. This aligns with the pollution halo hypothesis, which emphasizes that the environmental impact of FDI depends not only on its scale but also on the environmental standards and technological content embedded in the investment. However, where institutional capacity and environmental regulations are weak or where domestic firms lack the absorptive capacity to adopt new technologies, FDI may reinforce existing pollution-intensive industrial practices [30,31]. Therefore, the interaction between FDI and technological readiness is critical in determining whether FDI contributes to environmental degradation or supports green transformation. Policymakers must adopt integrated strategies that not only attract environmentally sound FDI but also strengthen national innovation systems to better absorb and scale up imported green technologies.
2.3. Economic Growth and CO2 Emissions
The fact that environmental problems started to be seriously felt globally in the early 1990s paved the way for researchers to examine the possible effects of gross domestic product (GDP) on the environment. The relationship between these two variables has been intensively analyzed with the pioneering work of Grossman and Krueger [32]. Panayotou [33] proposed the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis, which postulates that environmental deterioration initially rises with per capita wealth but then reverses as the economy grows. Consequently, it is believed that the relationship between GDP and environmental deterioration is inverted U-shaped. There are three main effects behind this hypothesis. The first of these effects is the scale effect. Accordingly, under the assumption that economic structure and technology remain constant, increases in production in the early stages of economic growth require more inputs, which in turn means more emissions. Accordingly, when economic growth increases output, resource use, and energy consumption, waste and pollutant emissions will rise, and environmental quality will decline [34]. A structural change in the economy that has a favorable impact on the environment is shown by the technical effect that appears later in economic growth. The economic structure gradually changes as income levels rise in tandem with economic expansion, increasing the proportion of less polluting industries in overall production. In the advanced stages of this transformation, a shift from energy-intensive industrial sectors to knowledge and technology-oriented service sectors is observed. Since natural resources are consumed relatively less in technology-intensive sectors, the environmental impacts of these sectors are also more limited. In this context, the transformation of the economic structure is recognized as a crucial factor in achieving sustainable environmental quality [35]. The increase in income will lead to an increase in the funds that countries allocate for research and development initiatives. Consequently, this will facilitate the adoption of more environmentally friendly technologies instead of environmentally harmful technologies and thus improve environmental quality. This phenomenon is referred to as the technology effect. While the growing part of the EKC is associated with the scale effect, the decreasing part is associated with structural effects and technological factors [34].
Although much of the literature analyzes the relationship between GDP and environmental degradation, the results of the studies vary. This may be due to differences in the variables used, the period analyzed, the country/countries, the region, the model, and the methodology. For example, Pal and Mitra [36], using the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) method for India and China, found that the EKC hypothesis is not valid in both countries and that there is an N-shaped relationship between CO2 emissions and income. Similarly, Narcisse et al. [37], utilizing the ARDL method for China, found that there is an N-shaped relationship between GDP and environmental pollution. In contrast to these studies, Shahbaz et al. [24] conclude that the EKC hypothesis is valid in Pakistan using the Granger causality test. Similarly, Dong et al. [38] confirmed that the EKC hypothesis is valid in China according to their study with ARDL and the Granger causality approach for China. Finally, Mutascu [39] analyzed the non-linear dynamics and temporal changes of the EKC for the US with the WQC methodology.
2.4. Renewable Energy and CO2 Emissions
RE, also known as green energy, generally provides energy to four different sectors, including transport, electricity generation, water, air heating/cooling, and rural energy services [40]. Renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water are abundant in many regions, while fossil fuels are geographically spread over a more limited number of countries. Therefore, each country can utilize its RE potential. This may lead to more equitable energy production and utilization. In addition, with the increase in RE investments, the scale effect has started to come into play in this field, and there have been significant reductions in costs. The unit cost of electricity generation from solar and wind energy is cheaper than fossil fuels in most regions today. RE and its production have a positive impact on environmental quality. Therefore, RE sources, which include solid waste, wave, and tidal energy, in addition to solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, are attracting more and more attention. Energy authorities prioritize these renewable sources as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels [41]. Indeed, there are many studies supporting the positive impact of RE use on the environment. For example, Sharif et al. [40] analyzed the impact of disaggregated RE sources on CO2 emissions in the US using the quantile-on-quantile regression method and concluded that RE plays a very important role in reducing CO2 emissions. Chen and Lei [42] examined the effects of RE on the environment for 30 countries using the panel quantile regression method, and the results show that there is an inverse relationship between CO2 emissions and RE. At the same time, according to the study, in countries with high emission levels, the impact of RE on reducing CO2 emissions is limited, which is due to the low share of RE in total energy. Similarly, the effect of RE in maintaining environmental sustainability was examined by Alola et al. [43], and the results indicate that RE promotes environmental sustainability by raising the load capacity factor.
Although many studies support that RE has positive effects on environmental quality, some studies have contrary results. For example, Adebayo and Ozkan [44] analyzed the effect of energy efficiency and RE on CO2 emissions in G7 countries using the panel vector autoregressive (VAR) method and found a positive relationship between RE and CO2 emissions. However, some studies [45] concluded that RE is not effective on CO2 emissions.
2.5. Financial Development (FD) and CO2 Emissions
FD can have both negative and positive impacts on the environment. The direction of the impact depends on whether FD increases the use of fossil fuels or favors green technologies. FD can increase energy demand through both consumption and investment. FD promotes several changes within a country, such as reduced financial risk and borrowing costs, greater transparency between lenders and borrowers, greater access to financial capital and investment flow across borders, and access to the latest energy-efficient products and cutting-edge technology, all of which can affect energy demand by increasing consumption and business fixed investment. The consumption channel of this effect, together with FD, makes it easier and cheaper for consumers to purchase highly energy-consuming consumer durables. This increases energy demand across the country. In the investment channel, thanks to the FD, enterprises can access financial capital at lower costs. This may cause enterprises to engage in energy-intensive production [46]. Similarly, FD affects energy demand through two other effects known as ‘scale and technical effects’. When FD-led economic activities follow the scale effect, production based on fossil fuel energy increases, which negatively affects the environment. When the technical effect occurs, production becomes more energy-efficient and environmentally sound. Moreover, FD can also pave the way for the use of clean energy in the form of environmentally friendly appliances (e.g., cooking appliances, electric composters, dishwashers, and washing machines) and environmentally friendly instruments (e.g., green bonds and green insurance) [15].
Additionally, Zhang [47] concludes that the impact of FD on the environment is negative in his study on China. Using cointegration theory, the Granger causality test, and the variance decomposition method, the author proves that FD in China, especially the scale of financial intermediation, is an important driver of the increase in CO2 emissions. Similarly, Kihombo et al. [48] find that FD causes ecological degradation. Yang et al. [49] claim that FD significantly deteriorates environmental quality in Brazil, India, China, and South Africa (BICS) economies. Finally, Saqib et al. [50] in their study on the top ten countries with the highest ecological footprint, revealed that FD has a negative impact on environmental quality by restricting green growth. In contrast to these studies, Tamazian and Rao [51] find that because FD finances ecologically beneficial innovations, it enhances environmental quality. Dar and Asif [52] further stress that FD helps to improve the quality of the environment.
Despite a growing body of literature exploring the individual roles of technological innovation, FDI, economic growth, and RE in shaping environmental outcomes, important gaps remain. Notably, most existing studies tend to analyze these factors in isolation or rely on linear, mean-based methodologies that may overlook complex, non-linear, and distributional dynamics across different emission levels. Additionally, there is limited empirical evidence from newly industrialized countries (NICs) that captures the joint effects of technological diffusion and foreign capital flows on CO2 emissions, particularly during periods of structural economic transformation.
This paper contributes to the literature by addressing these gaps using a novel wavelet quantile regression (WQR) framework, which accounts for both time–frequency dynamics and heterogeneity across the CO2 emissions distribution. By focusing on a balanced panel of ten NICs over the 1990–2021 period, the study provides fresh empirical insights into how the environmental effects of technology and FDI vary across quantiles and over time. Furthermore, it offers a nuanced understanding of the conditional impact of innovation, both domestic and foreign, on sustainability, thereby informing more effective green industrial strategies for transitional economies.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
This study examines the time-quantile impact of technological innovation (TECH), foreign direct investment (FDI), economic growth (GDP), RE consumption (REC), and financial development (FD) on carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in newly industrialized economies which are Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, Turkey, and Mexico. The dataset spans the period from 1990 to 2021 to assess these interconnections. The study period of 1990 to 2021 was selected based on the consistent availability of data on technological innovation (TECH) across the NIC countries during these years. This timeframe ensures data continuity and comparability, allowing for a robust analysis of long-term trends in technological development and its interaction with FDI and environmental sustainability. Additionally, this period captures significant phases of industrial growth, globalization, and policy shifts in NICs, which are essential for understanding the dynamics under investigation. CO2 emissions serve as the dependent variable, while the primary independent variables are technological innovation and FDI. CO2 emissions serve as the dependent variable, while the primary independent variables are technological innovation and FDI. The description and source of the study variables are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Variables and possible effects of the study.
3.2. Method
The quantile regression (QR) approach proposed by Koenker and Bassett [56] establishes a statistical methodology that extends the traditional linear regression framework, offering a nuanced perspective on modeling the conditional quantiles of a dependent variable to an independent variable. QR presents numerous benefits in academic and practical applications. To begin with, it moves beyond the conventional average-centered viewpoint, delivering a more holistic representation of the conditional distribution of the response variable. Furthermore, its resilience to outliers and changing variance highlights its utility as an analytical instrument adept at managing data irregularities. Finally, quantile regression grants researchers the authority to explore and comprehend variations in the relationships between a factor variable across the range of quantiles in the distribution, thus providing a comprehensive view of the cases being studied. Nonetheless, the standard QR technique overlooks the possibility that the impact of the factor variable on the conditional attributes of the response variable may differ across multiple time frames [57]. This is a critical shortcoming in studies where relationships may evolve or exhibit nonlinear dynamics. In contrast, ARCH/GARCH models, while effective for modeling time-varying volatility in financial and economic time series, are primarily designed to capture second-moment dynamics (variance) and are less suited for analyzing distributional heterogeneity across quantiles. To address these limitations, we employed the wavelet quantile regression (WQR) approach, which integrates wavelet transforms with quantile regression to simultaneously capture both distributional and temporal dynamics. WQR decomposes time series data into different frequency components, allowing for the examination of relationships at various time scales, from short-term fluctuations to long-term trends. This enables a more granular analysis of how the effects of explanatory variables differ across quantiles and time horizons, offering a richer understanding of the underlying dynamics [58]. By leveraging WQR, our study overcomes the shortcomings of standard QR and ARCH/GARCH models, providing a robust framework for analyzing complex, nonlinear, and quantile-specific effects in the data, which are critical for deriving meaningful policy insights grounded in the empirical findings.
The present research utilized a novel WQR model proposed by Adebayo and Ozkan [44] WQR allows the relationship between two time series to be analyzed from both time and quantile perspectives. It analyses the effect of a factor variable on the quantiles of a dependent variable at various time intervals. In this study, five different WQR models are used to analyze the time-quantile effects of TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, and FD on CO2 in the context of NIC economies, respectively, as follows:
In Equations (1)–(5) Q emphasize the conditional quantiles of CO2 of the i-th NIC economies. In addition, , , , , , and represent the m-th decomposition (or time-period) of the i-th NIC economies’ CO2, TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, and FD, respectively. Moreover , , , , and represent the constant terms while , , , , and signify the slope coefficients that will be computed for all combinations of time-quantile pairs. This approach produces estimates that vary with quantities as well as time, thus providing more reliable results as opposed to traditional methods that focus only on the mean (or median) or only examine specific quantities or periods [59]. The empirical methodology used in this study is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Empirical flowchart.
4. Empirical Findings and Discussion
This section presents the empirical findings of the study. First, the variables were subjected to a unit root test. The results of this test, shown in Table A1 in Appendix A, were performed using the extended Dickey–Fuller (ADF) [60] and Phillips–Perron (PP) [61] unit root tests. The results indicate that when the first differences are collected for all NIC countries, the variables become stationary according to both unit root tests. In this context, the effects of the independent variables TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, and FD on the dependent variable CO2 emission in NIC countries can be analyzed with the WQR approach.
In the second stage, as suggested by Baz et al. [62] and Ramzan et al. [63] the BDS test proposed by Broock et al. [64] was utilized to test whether the relationship between CO2 emission, TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, and FD is linear. Empirically, the BDS test is performed on the residuals of all VAR (1) models for CO2-TECH, CO2-FDI, CO2-GDP, CO2-RE, and CO2-FD. The results reported in Table 2 reveal that the null hypothesis of nonlinearity is rejected for all NIC countries at the respective significance levels. This implies that the relationship between CO2 emission and TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, and FD is non-linear for NIC economies. In this context, the results of the BDS test confirm that it is appropriate to use the WQR approach for this study.

Table 2.
BDS results.
In the third stage, TECH, FDI, GDP, RE, RE, and FD were tested with the WQR approach on CO2 emissions in NIC countries and presented separately in the figures below. Figure 2 shows that while TECH has a negative effect on CO2 emission in Brazil in the short run, this effect turns positive in the medium and long run. For China, TECH has a negative effect on CO2 emissions in both the short and medium term, while it has a positive effect in low quintiles and a negative effect in high quintiles in the long term. In short, it is possible to say that TECH in China generally reduces emission levels. However, in Indonesia, while this situation follows a positive course in the short term, it follows a negative course in the medium and long term. In India, the short-term negative effect of TECH on CO2 emission turns positive in the medium and long term; in other words, the short-term reducing effect of TECH on CO2 emission disappears in the medium and long term. In Malaysia, the effect is positive in the short term and negative in the medium and long term. In Mexico and the Philippines, the short- and medium-term negative effect of TECH on CO2 emissions turns positive in the long run. In contrast to this finding, in South Africa and Thailand, the short- and medium-term positive effect of TECH on CO2 emission disappears and turns negative in the long run. Finally, while TECH has a relatively negative effect on CO2 emissions in Turkey in the short run, it has a positive effect in the medium and long run.
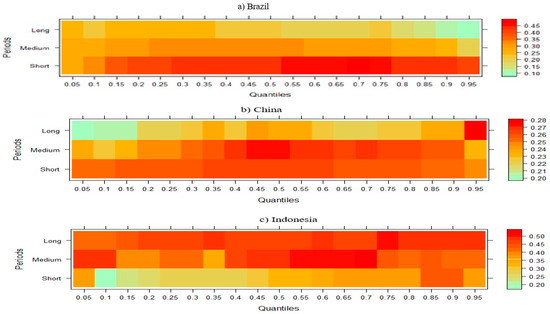
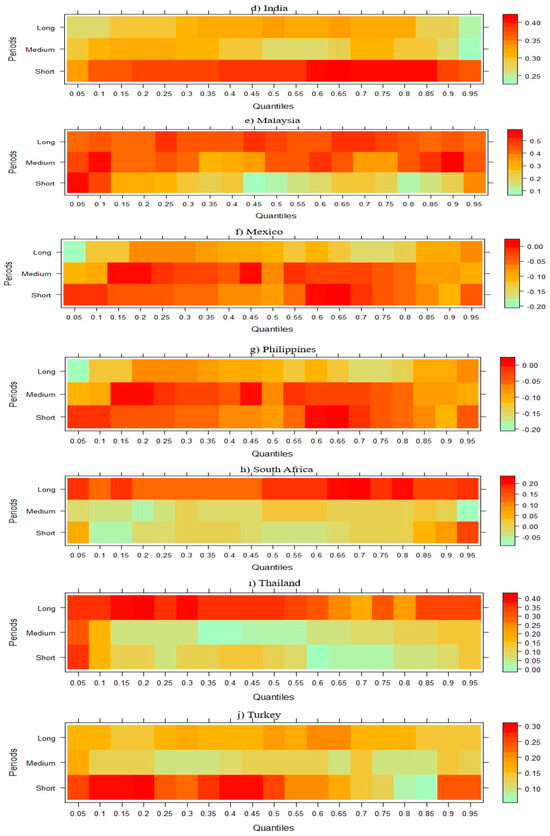
Figure 2.
Wavelet quantile regression between CO2 emissions and TECH.
According to Figure 2, the impact of TECH on CO2 emissions in NICs exhibits diverse patterns, as revealed by the WQR analysis. In China, TECH generally reduces emissions across various time frames, aligning with findings by Yu et al. [65], who observed that technological advancements significantly improve environmental quality in multiple countries. Conversely, in India, the initial negative effect of TECH on emissions reverses over time, suggesting that without supportive policies, technological progress may lead to increased emissions. This phenomenon is echoed by Udeagha and Ngepah [66], who found that in South Africa, innovation’s effectiveness in reducing emissions is contingent upon reaching a certain income threshold. Similarly, Malaysia and Indonesia display mixed results, with TECH’s impact on emissions varying over different periods. These inconsistencies underscore the importance of contextual factors, such as economic development stages and policy environments, in determining TECH’s environmental effects. Therefore, tailored strategies that consider each country’s unique circumstances are essential to maximize the environmental benefits of technological innovation.
The findings presented in Figure 3 show that FDI has a positive effect on CO2 emissions in Brazil, China, Indonesia, India, Malaysia, and Turkey in the short, medium, and long run in all quartiles. However, in Mexico, although FDI has a positive effect on CO2 emissions in the medium term, this situation turns negative in the short and especially in the long term. In the Philippines and Thailand, the short- and medium-term positive effect of FDI on CO2 emissions turns negative in the long term. Finally, it can be said that FDI has a decreasing effect on emission levels in almost all periods in South Africa.
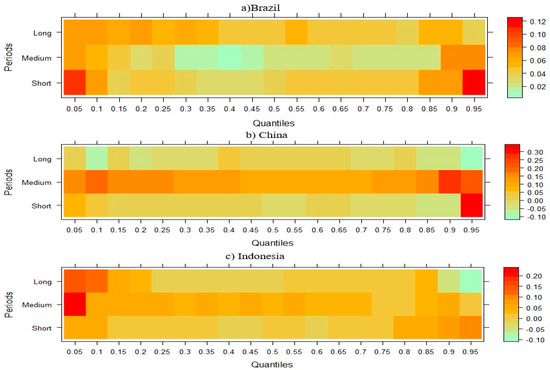
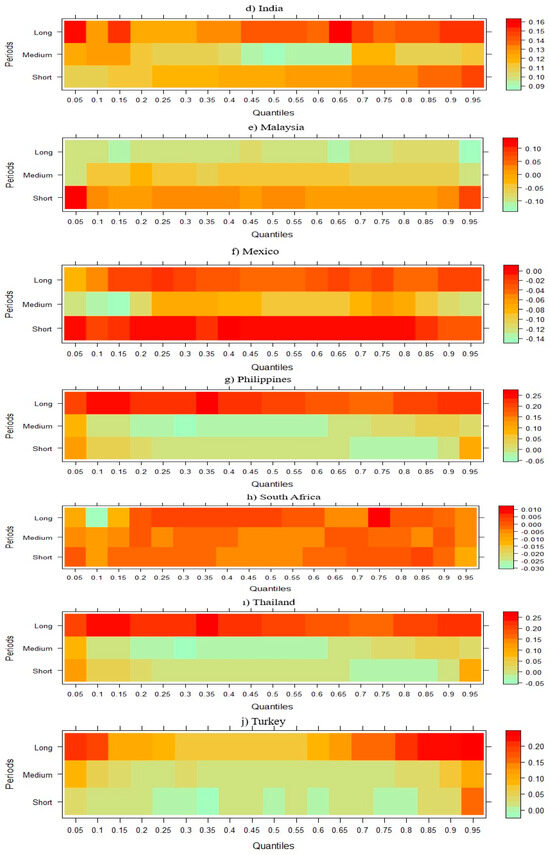
Figure 3.
Wavelet quantile regression between CO2 emissions and FDI.
Figure 3 illustrates that the relationship between FDI and CO2 emissions in NICs is time-varying and highly heterogeneous, reflecting both the environmental regulatory frameworks and the technological absorption capacities of individual countries. In economies such as Brazil, China, Indonesia, India, Malaysia, and Turkey, FDI is consistently associated with increased CO2 emissions across short-, medium-, and long-term horizons. This persistent positive relationship aligns with the pollution haven hypothesis (PHH), which suggests that multinational corporations relocate pollution-intensive operations to countries with weaker environmental regulations. Empirical studies reinforce this dynamic: for example, Baek [67] observed that FDI significantly increases CO2 emissions in developing countries, and Seker et al. [68] found a positive elasticity between FDI and emissions in Turkey, confirming that foreign investments often intensify industrial activity without corresponding environmental safeguards.
In contrast, countries such as Mexico, the Philippines, and Thailand reveal a transition in the impact of FDI over time, from a positive effect on emissions in the short run to a negative effect in the long run. This shift may reflect a delayed but eventually positive role of FDI in fostering cleaner technologies and improved environmental practices. This supports the pollution halo hypothesis, which argues that foreign investors can contribute to environmental improvements through the transfer of energy-efficient technologies, better environmental management systems, and higher operational standards. Huang et al. [69] found similar patterns, noting that the environmental impact of FDI is not uniform but conditioned by the host country’s absorptive capacity and the nature of the investment. Furthermore, Hille et al. [70] suggest that in countries with moderate to strong institutional quality, the long-term environmental benefits of FDI are more likely to materialize as regulatory frameworks and innovation systems help internalize environmental externalities.
Thus, the observed heterogeneity in FDI’s impact across NICs underscores the importance of country-specific factors, such as institutional strength, technological readiness, and environmental regulation stringency. It also highlights the dynamic nature of FDI’s influence, suggesting that the environmental consequences of foreign capital are not static but evolve in response to policy reforms, industry maturity, and technology adoption over time.
Figure 4 shows the effect of GDP on CO2 emissions in NIC countries. When this effect is analyzed, it is seen that the short-term negative effect of GDP on CO2 emission in Brazil, Indonesia, and India disappears and turns positive in the medium and long term. While this effect is negative in the short and medium term in China, it is positive in the long term in all quartiles. In the remaining six NICs, it can be said that GDP has a positive effect on CO2 emissions in all periods.
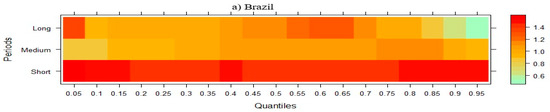
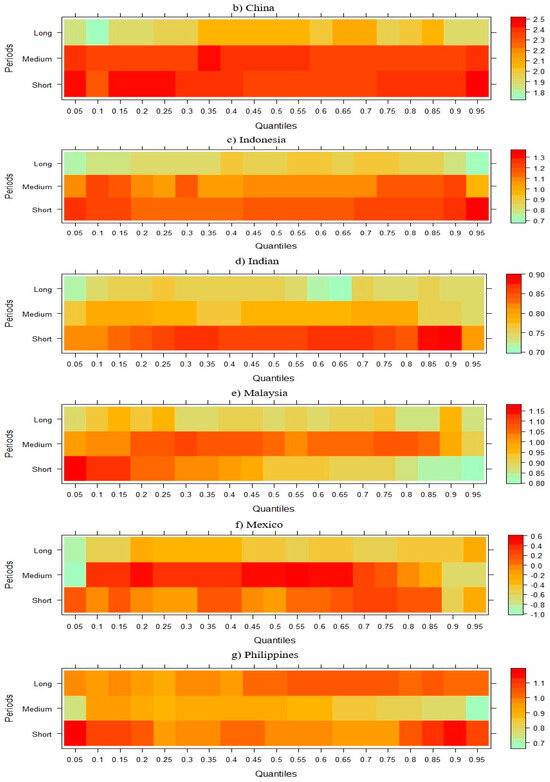
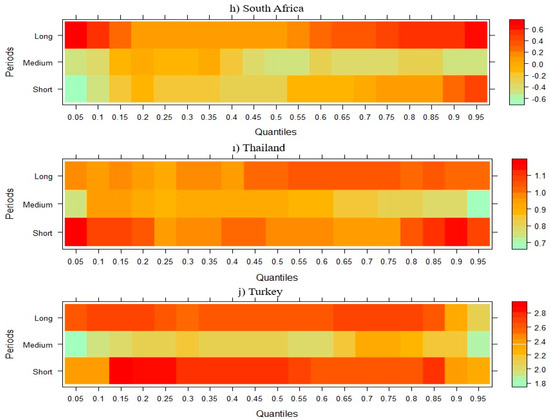
Figure 4.
Wavelet quantile regression between CO2 emissions and GDP.
The results from Figure 4 reveal that the relation between GDP and CO2 emissions in NICs varies significantly over time and between nations, indicating the environmental effects of growth as well as the intricacies of economic development. For instance, the short-term negative impact of GDP on emissions in Brazil, Indonesia, and India is reversed in the medium and long run. This pattern would suggest that while early growth is linked to cleaner energy use or structural improvements, as economies grow further, industrialization and rising energy demand push emissions higher. This aligns with the EKC hypothesis, which suggests that emissions initially rise with income but decline after reaching a certain threshold, an effect supported by recent findings from Wang et al. [71] who point out that environmental conditions may deteriorate during the initial phases of economic growth before improving as levels of development increase. Li and Wang [72], who highlight China’s uneven trajectory in balancing rapid economic expansion with environmental goals, speculate that early policy-driven gains in energy efficiency and renewable investment may be the cause of China’s GDP’s short- and medium-term negative impact on CO2 emissions turning to a positive long-term impact. In contrast, the constant upward correlation between GDP and CO2 emissions across all periods in the remaining NICs, including Mexico, the Philippines, and Malaysia, is in line with research by Miao et al. [73], which found that economic growth frequently prompts environmental degradation in nations with a high reliance on fossil fuels and little regulatory support. Given the present energy transition, findings emphasize the importance of tailored policy initiatives, whereby the adoption of RE, stricter environmental legislation, and investments in clean technologies can help separate emissions from economic growth [74]. Figure 5 illustrates the short-, medium-, and long-term effects of RE on CO2 emissions across different quantiles.
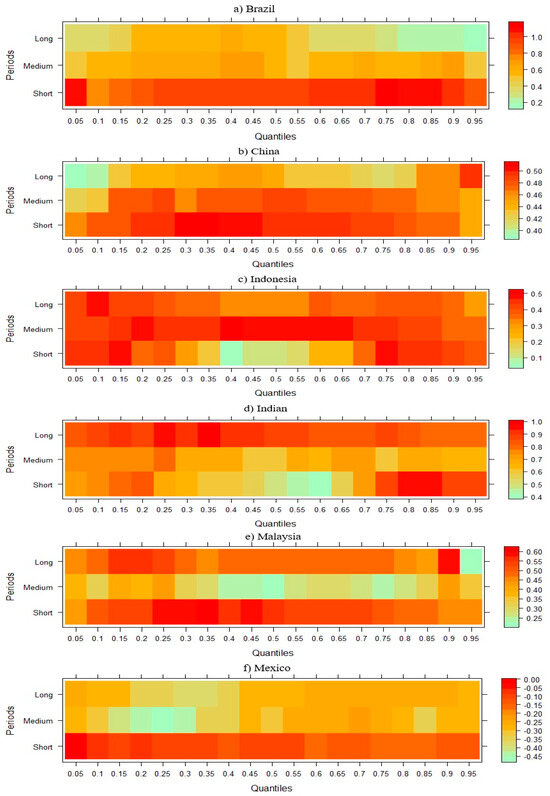
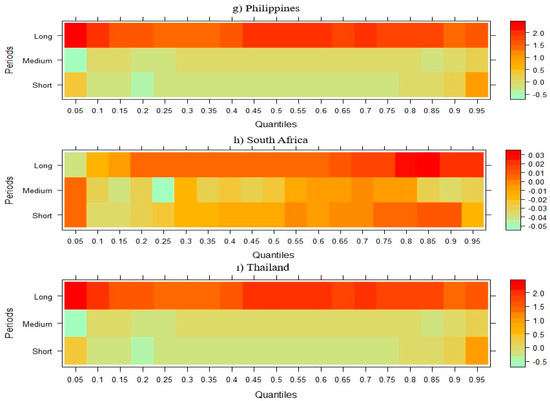
Figure 5.
Wavelet quantile regression between CO2 emissions and RE.
Figure 5 results indicate that, in Brazil and Mexico, short-term CO2 emissions are negatively impacted by RE; however, this effect diminishes and becomes positive in the medium and long term. In contrast, RE appears to consistently contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions in China, Indonesia, India, Malaysia, and South Africa across all periods. Finally, in the Philippines, Thailand, and Turkey, RE demonstrates a positive relationship with CO2 emissions in the short and medium term while transitioning to a negative effect in the long term, suggesting a delayed environmental benefit. A study by Silva et al. [75] highlights that while Brazil has made significant strides in RE adoption, issues such as deforestation and policy inconsistencies can offset initial emission reductions. Similarly, Jahanger et al. [76] observe that Mexico’s recent energy reforms aim to increase RE capacity; however, the effectiveness of these reforms is contingent upon consistent policy support and infrastructural advancements.
Figure 6 demonstrates the link between CO2 emissions and FD in NIC economies across short-, medium-, and long-term horizons.
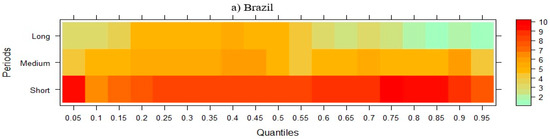
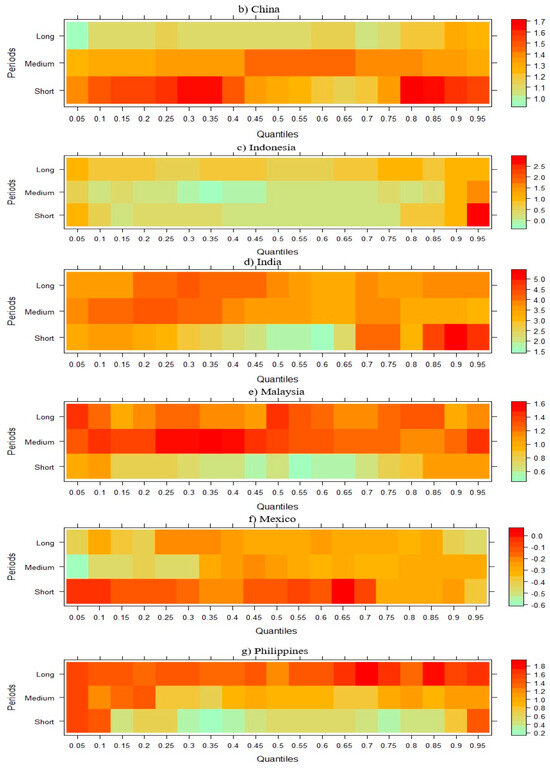
Figure 6.
Wavelet quantile regression between CO2 emissions and FD.
Figure 6 demonstrates that while FD initially lowers CO2 emissions for Brazil, China, and Mexico in the short term, it ultimately contributes to an increase in emissions over the medium and long term. FD typically results in higher CO2 emissions in India and Indonesia across periods. Short-term CO2 emissions in Malaysia are positively impacted by FD across all quartiles, while medium- and long-term effects are negative. In Thailand, South Africa, and the Philippines, FD has a short- and medium-term beneficial impact on CO2 emissions, but over time, this effect wanes and turns negative. These findings are consistent with those of Habiba and Xinbang [77], who demonstrate that FD has raised emissions and energy usage. However, depending on the level of economic growth and the focus of policy, FD can have both beneficial and negative effects on environmental quality, according to Fakher et al. [78].
For Turkey, FD shows a cyclical pattern, with short-term negative effects on CO2 emissions, medium-term positive effects, and long-term negative effects. This might be a sign of a stage of development where initial financial expansion raises emissions, and when financial institutions and regulations change, there is a shift towards sustainable behaviors. In other emerging economies, where there is a complicated and non-linear relationship between FD and environmental results, similar cyclical trends have been noted [79]. Table 2 below presents a summary of the findings derived from the WQR approach applied to NIC countries.
Table 3 presents a comparative analysis of how five key factors—technological innovation (TECH), foreign direct investment (FDI), economic growth (GDP), renewable energy (RE), adoption, and financial development (FD)—affect CO2 emissions across ten newly industrialized countries (NICs). The effects are categorized as “Negative” (reduces emissions), “Positive” (increases emissions), or “Mixed” (context-dependent outcomes).

Table 3.
Overview of empirical results.
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
In this study, we examined the impact of FDI and technological innovation on the economies of NICs from 1990 to 2021, employing the WQR approach. The findings indicate that FDI and economic growth generally help reduce CO2 emissions, though their effects vary across countries and over time. Technological innovation, while often associated with long-term emission reductions through cleaner and more efficient technologies, can also have a dual effect. In the short term, it contributes to emission reductions by fostering energy efficiency and promoting sustainable technologies. However, in certain contexts, especially when unsustainable technologies are scaled up or misused, it may inadvertently exacerbate environmental degradation in the long run. This highlights the complexity of technological diffusion and the need for careful consideration of the specific types of technologies being adopted, as well as their alignment with sustainability goals.
(1) Policymakers should develop technology- and region-specific RE transition plans tailored to each country’s resource base and grid capabilities, prioritizing sectors and regions with the highest emissions as identified in higher quantiles. For instance, Turkey could leverage its high solar irradiance for decentralized solar systems, Colombia could expand hydropower in rural areas, and South Africa could invest in utility-scale wind and storage solutions to address grid constraints. These plans should account for temporal dynamics, ensuring short-term deployment aligns with long-term decarbonization goals. (2) Governments should establish targeted innovation funds and sectoral R&D incentives to commercialize low-carbon technologies, focusing on industries with significant emission reduction potential, as revealed by quantile-specific effects. Countries with advanced manufacturing, such as Turkey and Mexico, should foster public-private partnerships to scale up clean production processes, while less mature innovation ecosystems, like those in Egypt or Peru, could prioritize international knowledge transfer and capacity-building to accelerate technology adoption. (3) Financial sector reforms should prioritize channeling capital into sustainable infrastructure, with a focus on high-emitting sectors identified in the WQR analysis. This includes implementing mandatory climate-risk disclosures, developing green bond frameworks, and offering interest rate subsidies for clean energy loans. For example, India and Indonesia could refine green finance taxonomies to support national decarbonization targets, while Vietnam and Nigeria could enhance access to concessional financing from multilateral institutions to address capital constraints in lower quantiles. (4) To address the emission-intensive nature of FDI, particularly in carbon-heavy sectors, NICs should impose quantile-informed environmental performance standards. These could include mandatory environmental impact assessments, technology benchmarking, and clean production certifications, with stricter thresholds for sectors and regions exhibiting higher emissions in the WQR results. Such measures ensure FDI aligns with sustainability goals without deterring investment. (5) Given the nonlinear impacts of technological and financial development, NICs should institutionalize robust, data-driven monitoring systems to evaluate green policy effectiveness across sectors and quantiles. These frameworks should incorporate periodic assessments to refine policy instruments over time, ensuring adaptability to temporal variations and promoting transparency and accountability in achieving emission reduction targets.
These recommendations leverage the WQR findings to provide actionable, evidence-based strategies that address the complex, quantile-specific, and time-varying dynamics of emissions in NICs, ensuring policies are both effective and contextually relevant. Furthermore, the study’s conclusions highlight how critical it is to go beyond broad recommendations. To balance economic competitiveness and environmental responsibility in a way that is both politically viable and socially inclusive, NICs must have precise, adaptable, and coordinated climate and energy policies. To further hone these suggestions and facilitate implementation, future research should build on this study by carrying out comprehensive, nation-specific case studies.
This study has several limitations. First, the analysis is restricted to the period from 1990 to 2021 due to challenges in accessing comprehensive data, as data for some NIC countries are not available through 2024. Additionally, the study focuses exclusively on newly industrialized countries, which limits the generalizability of the findings. Future research could address this by including a broader range of economies to enable comparative analysis and enhance the applicability of the results. Moreover, building on the study’s findings, future investigations should explore the mechanisms and policy interventions that can amplify the positive effects of technological innovation while mitigating the environmental drawbacks associated with FDI and energy consumption. This research highlights the importance of adopting a holistic approach that integrates technology, FDI, economic growth, and FD to promote environmental sustainability. Continued exploration in this area will be essential in shaping a more sustainable future for all economies. Finally, nonresidents’ and residents’ patent applications were selected as the TECH variable due to their consistent availability across the 10 NICs (Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, South Africa, Thailand, Turkey, and Mexico) from 1990 to 2021. This proxy enables a standardized and comparable measure of technological innovation, reflecting both domestic inventive activity (residents) and foreign technological contributions (nonresidents), which partially captures technology transfer through patenting activity within NICs. Although patent applications do not fully encompass all dimensions of technology transfer, such as tacit knowledge, licensing agreements, or non-patented innovations, they serve as a quantifiable indicator of technological progress relevant to the study’s focus on the time-quantile impacts on CO2 emissions. Future research could incorporate complementary proxies, such as R&D collaboration metrics or technology licensing data, to more comprehensively capture technology transfer dynamics in NICs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K.-A. and S.C.; methodology, S.C.; software, S.C.; validation, N.K.-A. and S.C.; formal analysis, S.C.; investigation, N.K.-A.; resources, S.C.; data curation, S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, N.K.-A., S.C. and S.T.; writing—review and editing, N.K.-A.; visualization, N.K.-A.; supervision, N.K.-A.; project administration, N.K.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide Emission |
| FD | Financial development |
| FDI | Foreign direct investment |
| GDP | Gross domestic product |
| NICs | Newly industrialized countries |
| R&D | Research and development |
| RE | Renewable energy |
| TECH | Technological innovation |
| WQR | Wavelet Quantile Regression |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Unit root test results.
Table A1.
Unit root test results.
| CO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Countries | ADF (level) | PP (level) | ADF (1.dif.) | PP (1.dif.) |
| BRA | −1.557 | −1.568 | −4.5167 a | −4.508 a |
| CHN | −0.219 | −0.017 | −5.844 a | −5.850 a |
| IND | 0.593 | 0.823 | −2.972 c | −5.801 a |
| IDN | −1.123 | −1.097 | −3.838 a | −6.667 a |
| MYS | −2.443 | −2.600 | −6.407 a | −6.408 a |
| MEX | −0.397 | −0.277 | −5.684 a | −5.685 a |
| PHL | −0.349 | −0.553 | −4.972 a | −5.046 a |
| ZAF | −1.710 | −1.628 | −6.220 a | −6.221 a |
| THA | −2.783 | −2.781 | −4.599 a | −4.590 a |
| TUR | −0.470 | −0.270 | −5.373 a | −5.465 a |
| TECH | ||||
| BRA | −1.365 | −1.363 | −4.379 a | −4.379 a |
| CHN | 1.115 | 1.625 | −3.682 b | −4.060 a |
| IND | 1.063 | 0.827 | −3.852 a | −3.853 a |
| IDN | −1.216 | −0.974 | −7.569 a | −9.065 a |
| MYS | −2.002 | −1.888 | −4.965 a | −5.967 a |
| MEX | −2.045 | −2.285 | −5.675 a | −6.099 a |
| PHL | −1.733 | −1.757 | −5.339 a | −5.302 a |
| ZAF | −2.122 | −1.868 | −4.907 a | −3.497 b |
| THA | −1.695 | −1.425 | −4.819 a | −7.023 a |
| TUR | 0.490 | 0.276 | −4.345 a | −4.345 a |
| FDI | ||||
| BRA | −1.613 | −1.590 | −5.838 a | −5.838 a |
| CHN | 0.232 | −0.248 | −4.145 a | −5.424 a |
| IND | −0.932 | −0.712 | −5.676 a | −5.940 a |
| IDN | −1.436 | −1.257 | −7.101 a | −8.167 a |
| MYS | −2.582 | −2.539 | −6.062 a | −7.168 a |
| MEX | −1.618 | −2.331 | −8.885 a | −10.112 a |
| PHL | 0.279 | 1.273 | −4.892 a | −4.668 a |
| ZAF | −1.281 | −1.079 | −3.732 a | −3.515 b |
| THA | −1.743 | −1.748 | −4.679 a | −8.598 a |
| TUR | −1.632 | −1.605 | −4.463 a | −4.332 a |
| GDP | ||||
| BRA | −0.912 | −0.938 | −4.182 a | −4.163 a |
| CHN | 7.527 | 6.151 | −8.158 a | −8.501 a |
| IND | 1.783 | 2.175 | −5.084 a | −5.095 a |
| IDN | 1.005 | 1.006 | −4.163 a | −4.164 a |
| MYS | −0.934 | −0.950 | −5.574 a | −5.607 a |
| MEX | −2.053 | −2.006 | −5.791 a | −5.891 a |
| PHL | 0.824 | 0.891 | −5.472 a | −5.473 a |
| ZAF | −0.844 | −0.898 | −3.931 a | −3.897 a |
| THA | 1.638 | 1.639 | −4.318 a | −4.319 a |
| TUR | 1.395 | 2.053 | −3.390 b | −4.201 a |
| RE | ||||
| BRA | −0.903 | −0.939 | −4.592 a | −4.566 a |
| CHN | 6.910 | 9.349 | −4.040 a | −3.137 b |
| IND | 1.716 | 3.381 | −5.033 a | −5.035 a |
| IDN | 3.377 | 3.404 | −2.843 c | −5.282 a |
| MYS | 2.162 | 3.196 | −3.443 b | −3.521 b |
| MEX | −1.611 | −1.412 | −7.026 a | −7.426 a |
| PHL | −2.471 | −2.409 | −5.632 a | −7.819 a |
| ZAF | 1.278 | 2.400 | −4.719 a | −4.740 a |
| THA | 4.278 | 1.127 | −3.932 a | −3.827 a |
| TUR | −0.330 | −0.403 | −4.612 a | −6.415 a |
| FD | ||||
| BRA | −1.878 | −2.074 | −4.963 a | −5.099 a |
| CHN | −0.904 | −0.866 | −6.435 a | −6.458 a |
| IND | −1.980 | −1.965 | −6.202 a | −6.156 a |
| IDN | −2.037 | −1.774 | −5.583 a | −8.309 a |
| MYS | −1.265 | −1.566 | −6.944 a | −9.787 a |
| MEX | −0.715 | −1.448 | −5.936 a | −7.371 a |
| PHL | −1.652 | −1.929 | −3.358 b | −6.710 a |
| ZAF | −1.759 | −1.173 | −4.068 a | −4.169 a |
| THA | −1.071 | −0.884 | −7.205 a | −7.651 a |
| TUR | −2.307 | −1.984 | −4.227 a | −6.531 a |
Note: a p ≤ 0.01, b p ≤ 0.05, c p ≤ 0.1.
References
- Chen, Z.; Paudel, K.P.; Zheng, R. Pollution halo or pollution haven: Assessing the role of foreign direct investment on energy conservation and emission reduction. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2022, 65, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, A. How environmental policy stringency, foreign direct investment, and eco-innovation supplement the energy transition: New evidence from NICs. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N. Investigation of the Impact of Environmental Degradation on the Transition to Clean Energy: New Evidence from Sultanate of Oman. Energies 2025, 18, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikru, M.G.; Kilinc-Ata, N.; Belaïd, F. Climate policy stringency and trade in energy transition minerals: An analysis of response patterns. Resour. Policy 2024, 96, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, W.U.; Nadeem, M.; Saltik, O.; Degirmen, S.; Jalil, F. Investing in knowledge assets: A novel approach for measuring national intellectual capital index in emerging economies. J. Intellect. Cap. 2024, 25, 535–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, M.A.; Riaz, T.; Shafiq, U.S.; Abbas, M.A. Exploring the Effects of Economic Policy Uncertainty, FDI, and Energy Use, on Environmental Quality in BRICS. J. Soc. Sci. Arch. 2024, 2, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Rahman, M.P. Digitalization and financial development contribution to the green energy transition in Malaysia: Findings from the BARDL approach. Nat. Resour. Forum. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Barut, A.; Citil, M. Do military expenditures have an impact on the adoption of renewable energy in OECD nations? Evidence from a panel cointegration test approach. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2024, 18, 1745–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, S. How technological progress affects the carbon emission efficiency? Evidence from national panel quantile regression. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Khan, N.; Omri, A. Environmental policy stringency, ICT, and technological innovation for achieving sustainable development: Assessing the importance of governance and infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Development Indicators. 2023. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- UNIDO. Industrial Development Report 2022: The Future of Industrialization in a Post-Pandemic World; United Nations Industrial Development Organization: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://unido.org (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- UNCTAD. World Investment Report 2023: Investing in Sustainable Energy for All; United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://unctad.org (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Chu, L.K. Determinants of ecological footprint in OECD countries: Do environmental-related technologies reduce environmental degradation? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23779–23793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazhar, M.; Majeed, M.T.; Hussain, Z. Remittance inflows, technological innovations, financial development, and ecological footprint: A global analysis using PSQR approach. Pak. J. Commer. Soc. Sci. 2022, 16, 424–451. [Google Scholar]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Fikru, M.G. A Framework for Evaluating EV Battery Mineral Sourcing Challenges. Sustain. Futures 2025, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K. Environmental policy stringency, technological change, and emissions inventory in 20 OECD countries. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Khan, N.; Baloch, M.A.; Saud, S.; Fatima, T. The effect of ICT on CO2 emissions in emerging economies: Does the level of income matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22850–22860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Meng, F.; Baloch, M.A. The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO2 emissions: An empirical analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30708–30719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N. The asymmetric impact of economic growth, energy consumption, population, and R&D on carbon emission in Turkey: Evidence from ARDL and non-linear ARDL. In Handbook of Research on Sustainable Development Goals, Climate Change, and Digitalization; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 200–215. [Google Scholar]
- Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Gokmenoglu, K.K.; Taspinar, N.; Cantos-Cantos, J.M. An approach to the pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses in MINT countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23010–23026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, M.; Caglar, A.E. Testing pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses for Turkey: A new perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32933–32943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 60, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Lean, H.H.; Shabbir, M.S. Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Pakistan: Cointegration and Granger causality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisswani, K.M.; Zaitouni, M. Does FDI affect environmental degradation? Examining pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses using ARDL modeling. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2023, 28, 1406–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.F.; Tan, B.W. The impact of energy consumption, income, and foreign direct investment on carbon dioxide emissions in Vietnam. Energy 2015, 79, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Ajaz, T. Natural resources management and technological innovation under EKC framework: A glimmer of hope for sustainable environment in newly industrialized countries. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Doan, T.Q.; Nguyen, H.N. Does foreign direct investment improve environmental sustainability in developing countries? The role of absorptive capacity and environmental regulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33092–33108. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.F.; Tan, B.W.; Ozturk, I. Foreign direct investment, energy consumption, and carbon emissions: New evidence from the ASEAN-5 countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 4692–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, K. FDI and environmental sustainability: Evidence from South Asia using a nonlinear ARDL approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45579–45596. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, Y. Foreign direct investment, technological innovation, and environmental performance: Evidence from emerging markets. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 398, 136586. [Google Scholar]
- Grossman, G.M.; Krueger, A.B. Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. Work. Pap. 1991, 3914, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayotou, T. Empirical Tests and Policy Analysis of Environmental Degradation at Different Stages of Economic Development; International Labor Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi, T.; Managi, S. Decomposition of the environmental Kuznets curve: Scale, technique, and composition effects. Environ. Econ. Policy Stud. 2010, 11, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Dolmatov, I. The Russian Federation’s renewable energy development determinants: Evidence from empirical research. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2023, 17, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Mitra, S.K. The environmental Kuznets curve for carbon dioxide in India and China: Growth and pollution at crossroads. J. Policy Model. 2017, 39, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narcisse, M.; Zhang, S.; Shahid, M.S.; Shehzad, K. Investigating the N-shaped EKC in China: An imperious role of energy use and health expenditures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1149507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Sun, R.; Jiang, H.; Zeng, X. CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: What roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutascu, M. Beyond the EKC: Economic development and environmental degradation in the US. Ecol. Econ. 2025, 232, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, A.; Bhattacharya, M.; Afshan, S.; Shahbaz, M. Disaggregated renewable energy sources in mitigating CO2 emissions: New evidence from the USA using quantile regressions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 57582–57601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sultana, N.; Velayutham, E. Renewable energy, energy intensity, and carbon reduction: Experience of large emerging economies. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lei, Y. The impacts of renewable energy and technological innovation on environment-energy-growth nexus: New evidence from a panel quantile regression. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alola, A.A.; Ozkan, O.; Usman, O. Role of non-renewable energy efficiency and renewable energy in driving environmental sustainability in India: Evidence from the load capacity factor hypothesis. Energies 2023, 16, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Ozkan, O. Investigating the influence of socioeconomic conditions, renewable energy and eco-innovation on environmental degradation in the United States: A wavelet quantile-based analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Alam, M.M.; Ozturk, I.; Alvarado, R.; Murshed, M.; Işık, C.; Ma, H. Globalization and renewable energy use: How are they contributing to an upsurge in CO2 emissions? A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 9699–9712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadorsky, P. Financial development and energy consumption in Central and Eastern European frontier economies. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J. The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: An empirical analysis in China. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihombo, S.; Ahmed, Z.; Chen, S.; Adebayo, T.S.; Kirikkaleli, D. Linking financial development, economic growth, and ecological footprint: What is the role of technological innovation? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 61235–61245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Jahanger, A.; Ali, M. Remittance inflows affect the ecological footprint in BICS countries: Do technological innovation and financial development matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23482–23500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, N.; Usman, M.; Ozturk, I.; Sharif, A. Harnessing the synergistic impacts of environmental innovations, financial development, green growth, and ecological footprint through the lens of SDG policies for countries exhibiting high ecological footprints. Energy Policy 2024, 184, 113863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamazian, A.; Rao, B.B. Do economic, financial, and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evidence from transitional economies. Energy Econ. 2010, 32, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, J.A.; Asif, M. Does financial development improve environmental quality in Turkey? An application of endogenous structural breaks based cointegration approach. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2018, 29, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OWD. Our World in Data. 2025. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/explorers (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- WDI. World Bank Indicators. 2025. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- IMF. International Monetary Fund. 2024. Available online: https://data.imf.org/?sk=f8032e80-b36c-43b1-ac26-493c5b1cd33b&sid=1481126573525, (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G., Jr. Regression quantiles. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc-Ata, N.; Kaya, E.; Barut, A. Exploring the Influence of Democracy, Rule of Law, and Societal Well-being on Climate Action in OECD Nations. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, J.; Ma, S.; Chen, X.; Cui, S.; Xiang, L. The emission-inequality nexus: Empirical evidence from a wavelet-based quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 871846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, O.; Popescu, I.A.; Destek, M.A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. Time-quantile impact of foreign direct investment, financial development, and financial globalization on green growth in BRICS economies. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, D.A.; Fuller, W.A. Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1979, 74, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P.C.; Perron, P. Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 1998, 75, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, K.; Xu, D.; Ali, H.; Ali, I.; Khan, I.; Khan, M.M.; Cheng, J. Asymmetric impact of energy consumption and economic growth on ecological footprint: Using asymmetric and nonlinear approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Razi, U.; Quddoos, M.U.; Adebayo, T.S. Do green innovation and financial globalization contribute to the ecological sustainability and energy transition in the United Kingdom? Policy insights from a bootstrap rolling window approach. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broock, W.A.; Scheinkman, J.A.; Dechert, W.D.; LeBaron, B. A test for independence based on the correlation dimension. Econom. Rev. 1996, 15, 197–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Su, J.; Du, Y. Impact of global value chain and technological innovation on China’s industrial greenhouse gas emissions and trend prediction. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 13347–13358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeagha, M.C.; Ngepah, N. The asymmetric effect of technological innovation on CO2 emissions in South Africa: New evidence from the QARDL approach. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 985719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J. A new look at the FDI–income–energy–environment nexus: Dynamic panel data analysis of ASEAN. Energy Policy 2016, 91, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, F.; Ertugrul, H.M.; Cetin, M. The impact of foreign direct investment on environmental quality: A bounds testing and causality analysis for Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wei, H.; Xiang, J.; Xu, Z.; Akram, R. The impacts of FDI inflows on carbon emissions: Economic development and regulatory quality as moderators. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 9, 820596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Meng, T.; Kharuddin, S.; Ashhari, Z.M.; Zhou, J. The impact of renewable energy consumption, green technology innovation, and FDI on carbon emission intensity: Evidence from developed and developing countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, R. Rethinking the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis across 214 countries: The impacts of 12 economic, institutional, technological, resource, and social factors. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H. Influence of green investment on China’s sustainable development. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Bukhari, A.A.A.; Bukhari, W.A.A.; Ahmad, S.; Hayat, N. Why fossil fuels stifle green economic growth? An environmental management perspective in assessing the spatial spillover impact of energy consumption in South Asia. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadeyan, O.J.; Muthivhi, J.; Linganiso, L.Z.; Deenadayalu, N. Decoupling economic growth from carbon emissions: A transition toward low-carbon energy systems—A critical review. Clean Technol. 2024, 6, 1076–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Koengkan, M. Assessing the advancement of new renewable energy sources in Latin American and Caribbean countries. Energy 2021, 237, 121611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Chishti, M.Z.; Onwe, J.C.; Awan, A. How far renewable energy and globalization are useful to mitigate the environment in Mexico? Application of QARDL and spectral causality analysis. Renew. Energy 2022, 201, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Xinbang, C. The impact of financial development on CO2 emissions: New evidence from developed and emerging countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31453–31466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakher, H.A.; Nathaniel, S.P.; Ahmed, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Moradhasel, N. The environmental repercussions of financial development and green energy in BRICS economies: From the perspective of new composite indices. Energy Environ. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, H.M.; Rafique, M.Z.; Nadeem, A.M. Impact of financial development on CO2 emissions: A comparative analysis of developing countries (D8) and developed countries (G8). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12461–12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).