Abstract
Electroplating sludge, a hazardous waste generated from the electroplating industry, contains significant quantities of heavy metals such as Cu, Cr, and Ni. Improper disposal of these metals poses severe environmental and health risks. This study proposes a comprehensive resource recovery process for Cu, Ni, and Cr from electroplating sludge, involving leaching, solvent extraction, stripping, and precipitation. The extraction efficiency of three extractants (P507, LIX984, and M5640) was evaluated, with M5640 demonstrating superior performance in Cu recovery (near 100%) at pH 3.0–4.0. Multi-stage extraction and stripping experiments further optimized metal recovery, achieving high efficiencies for Cu, Cr, and Ni. The recovered metals were precipitated as CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2, with wastewater discharge meeting environmental discharge standards. This study not only enriches the technical approaches for the selective recovery of high-value metals from electroplating sludge with complex components, but also closely aligns with the laws, regulations, and policies of the Chinese government regarding environmental governance. It serves as a driving force for promoting the construction of “waste-free cities” and the establishment of a closed-loop circular economy industrial chain.
1. Introduction
As a pillar industry of modern manufacturing, the electroplating industry plays an irreplaceable role in the fields of surface treatment, anti-corrosion, and decoration. However, due to its inherent production processes, the electroplating industry generates a large amount of hazardous waste [1]. Electroplating—a process involving the deposition of metal coatings—produces sludge enriched with heavy metals, referred to as electroplating sludge [2]. This sludge typically contains copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni), which, if improperly managed, can result in serious environmental pollution and health hazards [3]. With the rapid growth of the electroplating industry, the volume of sludge has surged, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatment and resource recovery. It is estimated that global electroplating sludge production exceeds 10 million tons annually, posing significant environmental risks and contributing to the loss of valuable resources—particularly Cu and Ni, which are widely used in lithium-ion batteries [4,5].
Due to its elevated heavy metal content, electroplating sludge is classified as hazardous waste, posing a leaching risk to the environment if not managed appropriately. Wang et al. reported that improper disposal may lead to heavy metal migration through the sludge–soil–crop–human pathway, contaminating groundwater and threatening human health [6]. Guo et al. emphasized its ecological risks, such as land occupation and secondary pollution, which can surpass those of electroplating wastewater [5]. The sludge’s high moisture content and complex composition create significant challenges, as traditional disposal methods—such as landfilling or solidification—frequently lead to gradual metal leaching and inefficient resource utilization [7,8].
Therefore, the treatment of electroplating sludge in terms of “reduction, resource utilization, and harmlessness” has received great attention from countries around the world. Various countries have successively introduced environmental regulations to provide a legal framework for the management of electroplating sludge, with a particular focus on core issues such as “wastewater discharge, hazardous waste control, and resource recovery”. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Electroplating Effluent Guidelines (2024) regulate facilities discharging into publicly owned treatment works to ensure compliance [9]. The Fact Sheet on Disposal Options for Electroplating Sludge further highlights recycling methods such as hydrometallurgical processing, promoting environmentally sound disposal strategies [10]. These regulations aim to minimize pollution, protect ecosystems, and foster sustainable industrial development.
In China, the government advocates the establishment of a full-chain management system featuring “source reduction—process control—end-of-pipe treatment” [11,12,13]. It has formulated laws and regulations such as the Law on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Wastes, the Law on the Comprehensive Utilization of Resources, the Circular Economy Promotion Law, the Cleaner Production Promotion Law, the Environmental Impact Assessment Law, and the Regulations on Ecological and Environmental Monitoring. These measures aim to promote the transformation of electroplating sludge from a “pollution source” to a “resource repository”.
In conclusion, the recovery and extraction of heavy metals from waste such as electroplating sludge can provide substantial economic and environmental benefits. As a result, it has become a research hotspot for scholars around the world. Hazardous waste treatment—particularly electroplating sludge—is subject to strict environmental regulations worldwide [14,15]. Due to the high concentrations of heavy metals, such sludge poses serious threats to ecosystems and human health if mishandled. Regulatory frameworks like the U.S. EPA’s Electroplating Effluent Guidelines provide standards for safe treatment and disposal [9]. In addition, legal standards outlined in the EPA Regulatory Exclusions and Alternative Standards ensure that recovered metals meet safety requirements for reuse, thus supporting a circular economy [16,17,18].
Traditional recovery techniques often involve complex procedures with limited efficiency in metal separation and purification. These methods also raise concerns about secondary pollution [19,20]. Therefore, the development of innovative technologies that enhance recovery efficiency while minimizing environmental impact is critical for resource conservation and sustainable development [21]. Such technologies reduce reliance on primary resources and mitigate the environmental hazards of waste disposal [21,22].
Commonly used recovery methods—such as precipitation, flotation, and pyrometallurgy—have been extensively applied but are limited by low efficiency, poor product purity, and environmental drawbacks [23]. For instance, precipitation often leads to co-precipitation of multiple metals, reducing separation efficiency [6]; flotation is hindered by the fine particle size of sludge; and pyrometallurgical methods require substantial energy and emit toxic gases, posing risks to both the environment and public health [24]. To overcome these issues, advanced methods such as solvent extraction, ion exchange, and membrane separation have been developed, offering enhanced selectivity and efficiency in metal recovery [25,26].
Among these, solvent extraction is particularly notable for its ability to selectively extract metals such as Cu from complex matrices. In the case of electroplating sludge, this method typically involves acid leaching followed by selective extraction using extractants like M5640, which has demonstrated high efficacy in Cu recovery [27]. This approach not only improves metal recovery rates but also promotes environmental sustainability through resource recycling. Furthermore, integrating solvent extraction with complementary methods can enhance both recovery efficiency and product purity, addressing the limitations of single techniques [28,29].
This study proposes a process integrating extraction, back-extraction, and stepwise precipitation to efficiently recover Cu, Ni, and Cr from electroplating sludge. This process not only improves the recovery of individual metals and the purity of the recovered products, but also simplifies the subsequent separation and purification steps and reduces the cost and complexity of industrial applications [30,31]. This process is based on electroplating sludge products from an actual electroplating metal plant in Fujian, China, and has the ability to guide industrial electroplating sludge treatment and disposal methods, promoting environmental protection, safe treatment and disposal of solid wastes, and resource utilization of secondary resources. Although solvent extraction has been widely studied and applied, existing technologies still face many challenges in treating electroplating sludge with complex composition. For example, traditional extraction methods often face the problem of co-extraction of metals, resulting in insufficient product purity [32,33]. The aim of this study is to develop an efficient, selective, and environmentally friendly resource recovery process for electroplating sludge by optimizing the conditions of the M5640 extractant. In addition, this study closely integrates with the existing environmental regulations in China to promote the reduction, harmlessness, and resourcefulness of electroplating sludge and to ensure that wastewater discharge complies with the stringent environmental standards, thus providing a practical and feasible path to the green transformation of the electroplating industry.
The objectives of this study are as follows: (1) to assess the extraction efficiencies of several extractants for Cu, Ni, and Cr from mixed electroplating sludge and determine the optimal extractant; (2) to investigate the optimal extraction conditions for each metal; (3) to integrate an industrial-scale recovery process involving solvent extraction, stripping, and precipitation; and (4) to evaluate the environmental implications of the proposed method in the context of hazardous waste and industrial wastewater treatment, as well as its relevance to existing environmental legislation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
All chemicals used in this study were of analytical grade and used without further purification. Two electroplating sludge samples, designated as sample XIN and sample CHENG, were obtained from electroplating factories in Fujian, China. The sample XIN was collected from an electroplating plant in Fujian, China, which specializes in nickel and chromium plating. Its high contents of Cu, Cr, and Ni originate from the specific metal salts, unique electroplating conditions, and particular wastewater treatment method. In contrast, the CHENG sample from a copper–nickel electroplating factory shows compositional differences due to alternative raw material suppliers and modified operating parameters. Prior to leaching, the samples were manually crushed into smaller fragments using a mortar and pestle.
Hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%), nitric acid (HNO3, 68%), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), kerosene, and sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%) were purchased from Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Anhydrous sodium carbonate (Na2CO3, AR), sodium phosphate (Na2PO4, AR), and the extractant M5640 (99.95%) were obtained from Aladdin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Extractants LIX984 and P507 were procured from Yien Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Standard solutions of Cu, Ni, Cr, Zn, and Fe ions were provided by Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Ultrapure water was used throughout all experiments. Vacuum filtration was performed using a 0.45 μm hydrophilic filter membrane (Tianjin Jinteng Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China). In all of the extraction, stripping, and precipitation experiments, we conducted three parallel tests to ensure data reliability and included error bars in the corresponding figures and tables.
2.2. Extractant Selection for Metal Recovery
The primary metal compositions of the sludge samples were determined using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF, 9800XP+; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Cu, Cr, Ni, Fe, and Zn were identified as the major metal components in both samples. A 15% H2SO4 solution (v/v) was used for leaching at 25 °C for 3 h, with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3 and stirring at 500 rpm using a magnetic stirrer (MSC; Joanlab Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China). After leaching, metal concentrations in the pregnant leach solution were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Optima 7000DV; PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA), and the residues were collected.
LIX984, P507, and M5640, commonly used for the extraction of associated metals, were selected to evaluate their performance in extracting metals from the sludge samples. The aqueous phase comprised the leach solution, while the organic phase consisted of 15% extractant in sulfonated kerosene. The sulfonated kerosene was prepared via a two-step process: kerosene and sulfuric acid were mixed in a 1:1 volume ratio and stirred for 30 min, followed by saponification with 6 M NaOH to achieve a 65% saponification rate.
Extraction was conducted using a water bath oscillator (SHA-B; Changzhou Ruyi Electric Appliance Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China) at 200 ± 2 rpm and 25 ± 0.5 °C for 60 min with an organic-to-aqueous (O/A) phase ratio of 1:1. The pH of the aqueous phase was adjusted to 2.0 to 4.0 to compare extraction efficiencies among the three extractants (Table 1). After centrifugation at 2000 rpm for 10 min, metal concentrations were measured by ICP-OES. Extraction efficiency was calculated using Equation (1).
where C0 (mg/L) and C1 (mg/L) represent the metal concentrations of the aqueous phase before and after extraction, respectively.
Extraction Efficiency (E) = (C0 − C1)/C0 × 100%

Table 1.
Influencing factor study conditions for metal extraction from electroplating sludge.
2.3. Optimization of Extraction Conditions
The aqueous phase used for extraction was the same pregnant leach solution obtained from sulfuric acid leaching. Metal concentrations (Cu, Cr, Ni, Fe, Zn) were determined via ICP-OES. The organic phase was prepared by dissolving the selected extractant in sulfonated kerosene.
The extraction efficiency was evaluated based on various influencing factors, including aqueous phase pH, extraction duration, and O/A ratio. The aqueous phase was adjusted to a final acidity of 1 M, and the remaining metal concentrations were measured by ICP-OES. The experimental conditions for influencing factors are summarized in Table 1.
When single-stage extraction did not yield satisfactory efficiency, multi-stage extraction was conducted. In such cases, the aqueous phase from the preceding stage was subjected to another extraction procedure under the same O/A ratio by adding a fresh organic phase. The overall extraction efficiency was calculated as the cumulative efficiency across all stages.
2.4. Stripping and Precipitation
Stripping (stripping) was performed using a vertical oscillator for 15 min with O/A ratios of 1:2, 1:5, and 1:10. The stripping agents included ultrapure water and diluted H2SO4 at concentrations of 0.1 M and 2 M. After adjusting the acidity to 1 M, metal concentrations in the aqueous phase were determined using ICP-OES. The stripping efficiency (S) was calculated based on mass balance (Equation (2)).
where S (%) represents the stripping efficiency; C0 is the metal concentration in the aqueous phase prior to extraction; C1 is the metal concentration in the aqueous phase after extraction; and C1′ is the metal concentration in the stripping liquid after stripping.
Metal precipitation was carried out following the extraction and stripping processes. Common sodium-based precipitants, including Na2CO3, Na2PO4, and NaOH, were used to recover Cu, Cr, and Ni, respectively. After precipitation, the residual metal concentrations in the solution were measured using ICP-OES to calculate the precipitation efficiency.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Extractant Selection for Metal Extraction from Electroplating Sludge
XRF analysis revealed that Cu, Cr, Ni, Fe, and Zn were the predominant metals in the electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG. Their exact concentrations were determined through sulfuric acid leaching, with the results summarized in Table 2. As shown, the overall metal contents were comparable between the two samples. Notably, the Cr content was higher in sample XIN (2.06%) than in CHENG (0.94%), whereas Cu, Ni, and Fe were slightly more concentrated in sample CHENG. Given the similar metal distributions, the selection of an appropriate extractant is crucial for the targeted recovery of Cu, Cr, and Ni.

Table 2.
Main metal contents in electroplating sludge samples.
The extraction behavior of Cu, Ni, Fe, and Zn using three extractants—P507, LIX984, and M5640—was evaluated as a function of pH [34,35]. Zn data were excluded due to its low content and poor extraction performance across all tested extractants. In the following experiments, although Zn extraction data were recorded, its minimal environmental relevance and negligible contribution to overall metal recovery warranted focused analysis on predominant metals (Cu, Cr, Ni). This selective presentation enhances clarity without compromising data integrity. The extraction experiments were conducted under uniform conditions: 25 °C, 1 h extraction time, organic-to-aqueous phase (O/A) ratio of 1:1, shaking at 200 rpm, and centrifugation at 2000 r/min for 5 min. Extraction efficiencies were calculated using Equation (1).
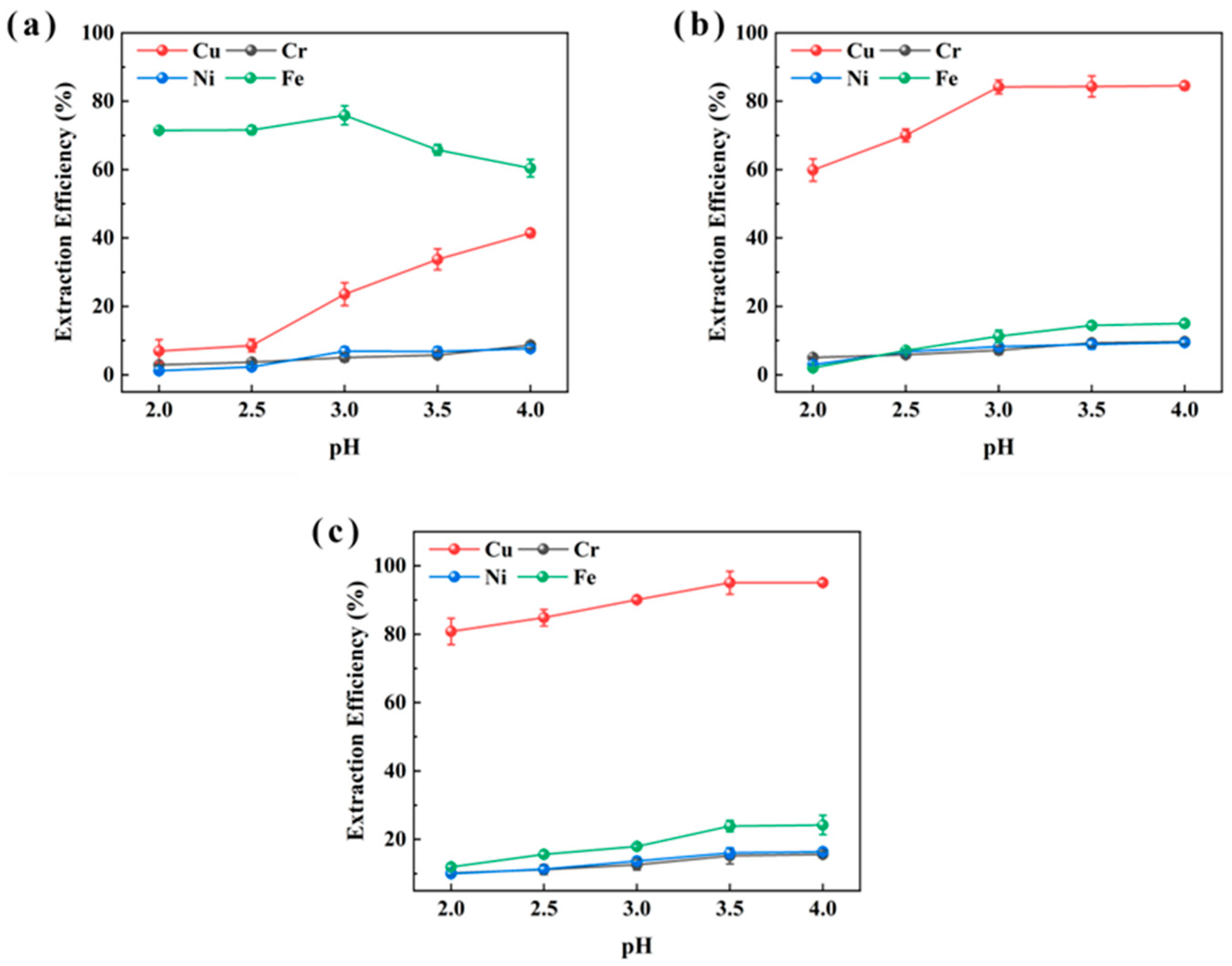
As illustrated in Figure 1, P507 demonstrated poor Cu extraction (maximum 41.4%) but relatively high Fe extraction (up to 75.9% at pH 3). LIX984 achieved up to 84.5% Cu extraction at pH 4. In contrast, M5640 provided nearly complete Cu extraction (approaching 100%) across the pH range 3.0–4.0, with minimal Fe co-extraction (10–25%), and the highest Cu recovery (95.1%) occurred at pH 4. For Cr and Ni, all three extractants displayed low extraction efficiencies (<16.0%). These results confirm that M5640 outperforms both P507 and LIX984 in Cu extraction. Given the relatively high Cu and low Fe content in the sludge, M5640 was identified as the most suitable extractant for efficient Cu recovery.
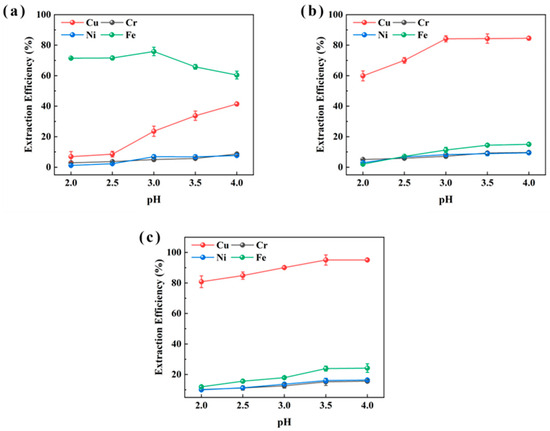
Figure 1.
pH effect of extraction aqueous phase on extraction efficiencies of Cu, Ni, Fe, and Cr from sample XIN using P507 (a), LIX984 (b), and M5640 (c) extractants for extractant selection.
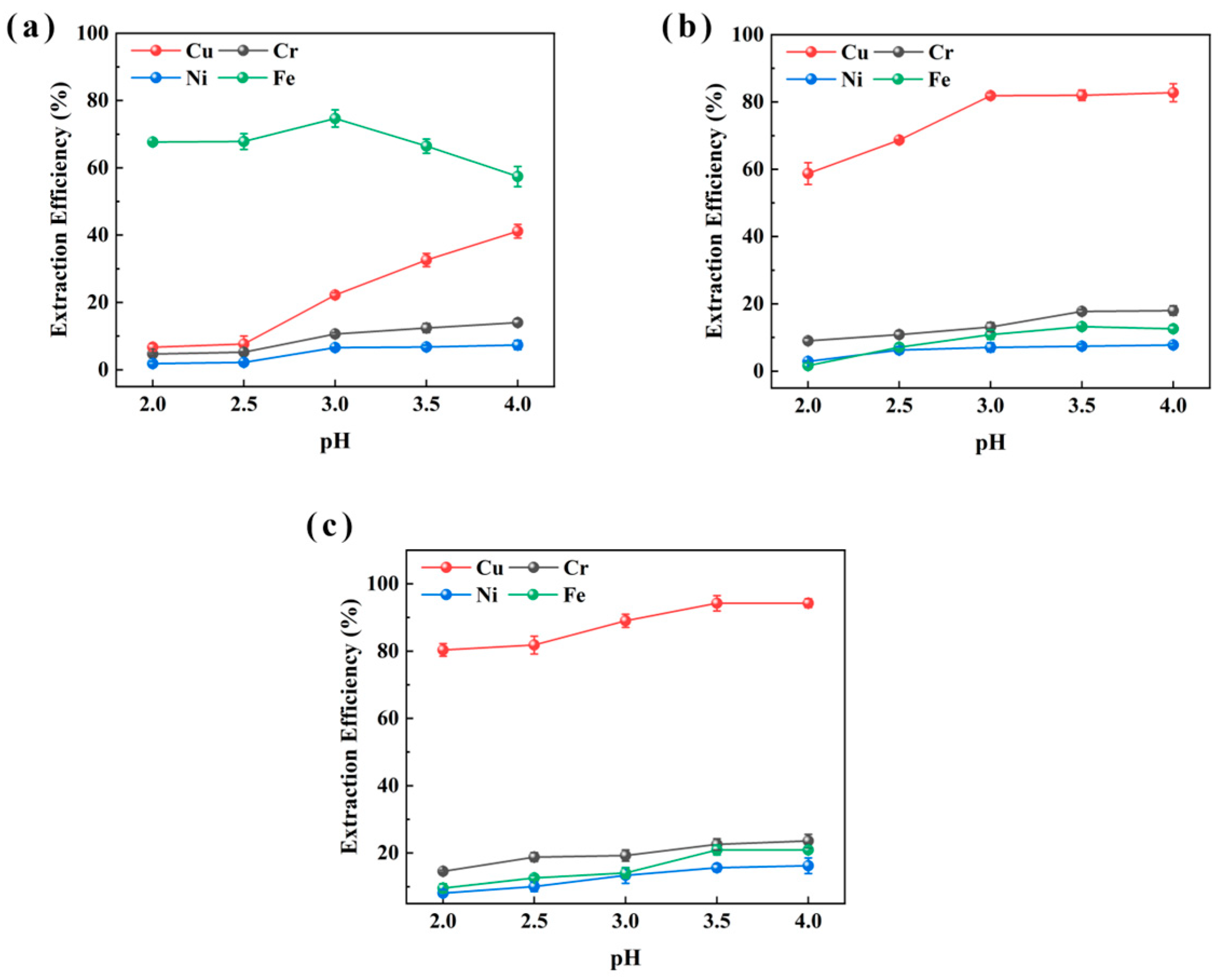
Figure 2 presents the extraction results for sample CHENG. Owing to the compositional similarity between the two sludge samples, similar extraction patterns were observed. Consistent with the results from sample XIN, P507 showed low Cu and high Fe extraction. LIX984 extracted 82.8% of Cu at pH 4 but also promoted Fe extraction. M5640 again yielded near-complete Cu extraction (up to 94.2%) within the pH range 3.0–4.0, while Fe extraction was restrained to around 20%. The extraction behaviors of Cr were observed compared to other metals (Cu, Ni, Fe) in both samples, because Cr exists predominantly as Cr (III) and Cr (VI) in electroplating sludge. These two species exhibit markedly different chemical properties and pH-dependent extraction behaviors. Under acidic conditions, Cr (VI) tends to reduce to Cr (III), whose aqueous stability and reactivity are strongly pH-dependent. This redox sensitivity may contribute to the observed fluctuations in Cr extraction efficiency across varying pH conditions [36]. Thus, M5640 demonstrated superior Cu extraction ability and was deemed the optimal extractant for both samples.
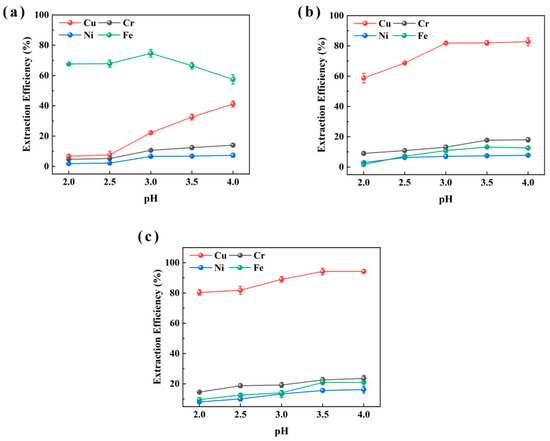
Figure 2.
pH effect of extraction aqueous phase on extraction efficiencies of Cu, Ni, Fe, and Cr from sample CHENG using P507 (a), LIX984 (b), and M5640 (c) extractants for extractant selection.
3.2. Effects of Extraction Conditions
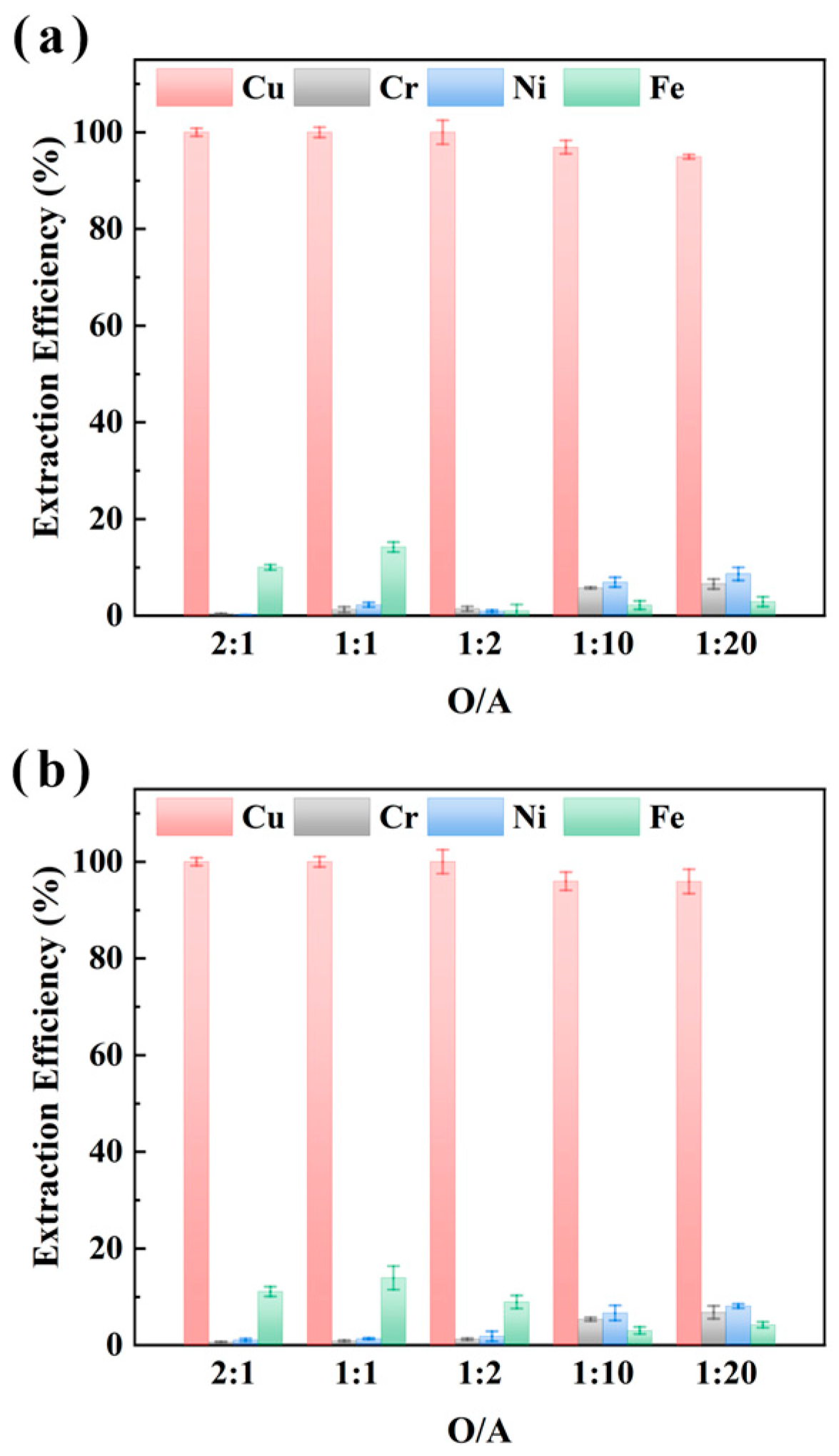
To clarify the selective recovery capability of M5640 for Cu in electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG under varying organic-to-aqueous phase ratios (O/A ratios), the impact of O/A ratios (2:1, 1:1, 1:2, 1:10, 1:20) on metal extraction efficiency (Cu, Ni, Fe, Cr) was investigated under conditions of 25 °C, 1 h extraction, and aqueous phase pH of 3.5 [37,38]. The results in Figure 3 demonstrate that Cu extraction efficiency remained near 100% across all O/A ratios for both samples, with no significant variation; Fe extraction was <15.0%, while Ni and Cr extraction remained low (<10%), showing no O/A ratio-dependent trends. These findings confirm that M5640 has robust selectivity and adaptability for Cu recovery, maintaining high efficiency over a wide O/A ratio range.
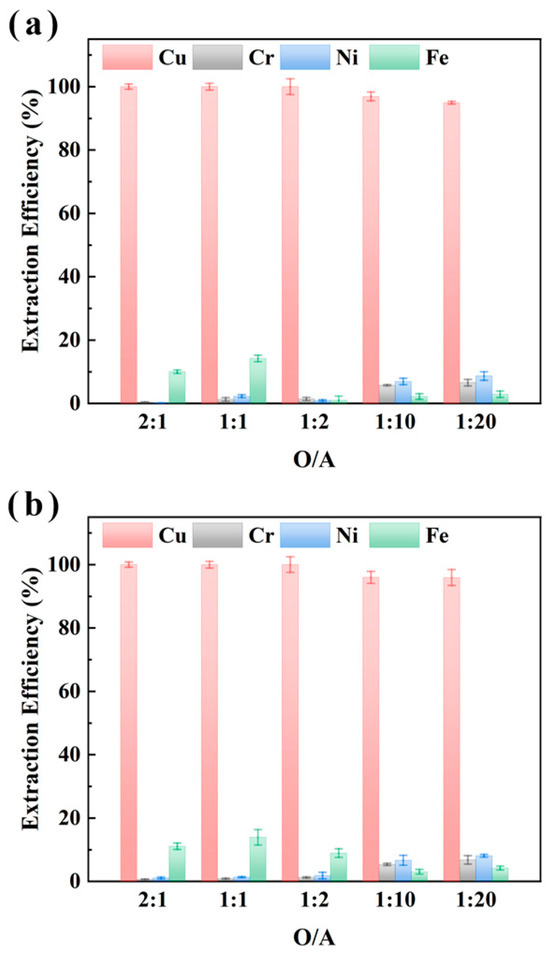
Figure 3.
O/A ratio (organic/aqueous phase volume ratio) effect on extraction efficiencies of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe from sample XIN (a) and CHENG (b) using M5640 extractant.
Further analysis indicates that while Cu extraction approached completeness (near 100%), the co-extraction of Fe (10–20%) and trace extraction of Ni/Cr (5–10%) might influence the purity of the recovered Cu. Additionally, the lack of significant efficiency differences across O/A ratios (2:1 to 1:20) suggests potential saturation of Cu extraction kinetics. Considering the cost of the extractant, it is more appropriate to choose an O/A ratio of 1:10; at this time, the extraction rate of M5640 for Cu in sample XIN and sample CHENG reached 96.9% and 96.0%, respectively. Moreover, the extraction efficiency of M5640 for the other three metals was less than 7%, which is conducive to the subsequent separation and purification of several metals. Although a 1:2 ratio yielded marginally higher extraction efficiency, the improvement was negligible compared to the significant increase in operational complexity and costs. Moreover, at a 1:2 O/A ratio, although Cu extraction was slightly higher, co-extraction of impurities increased, complicating downstream processing. Therefore, further experiments were conducted under a 1:10 O/A ratio.
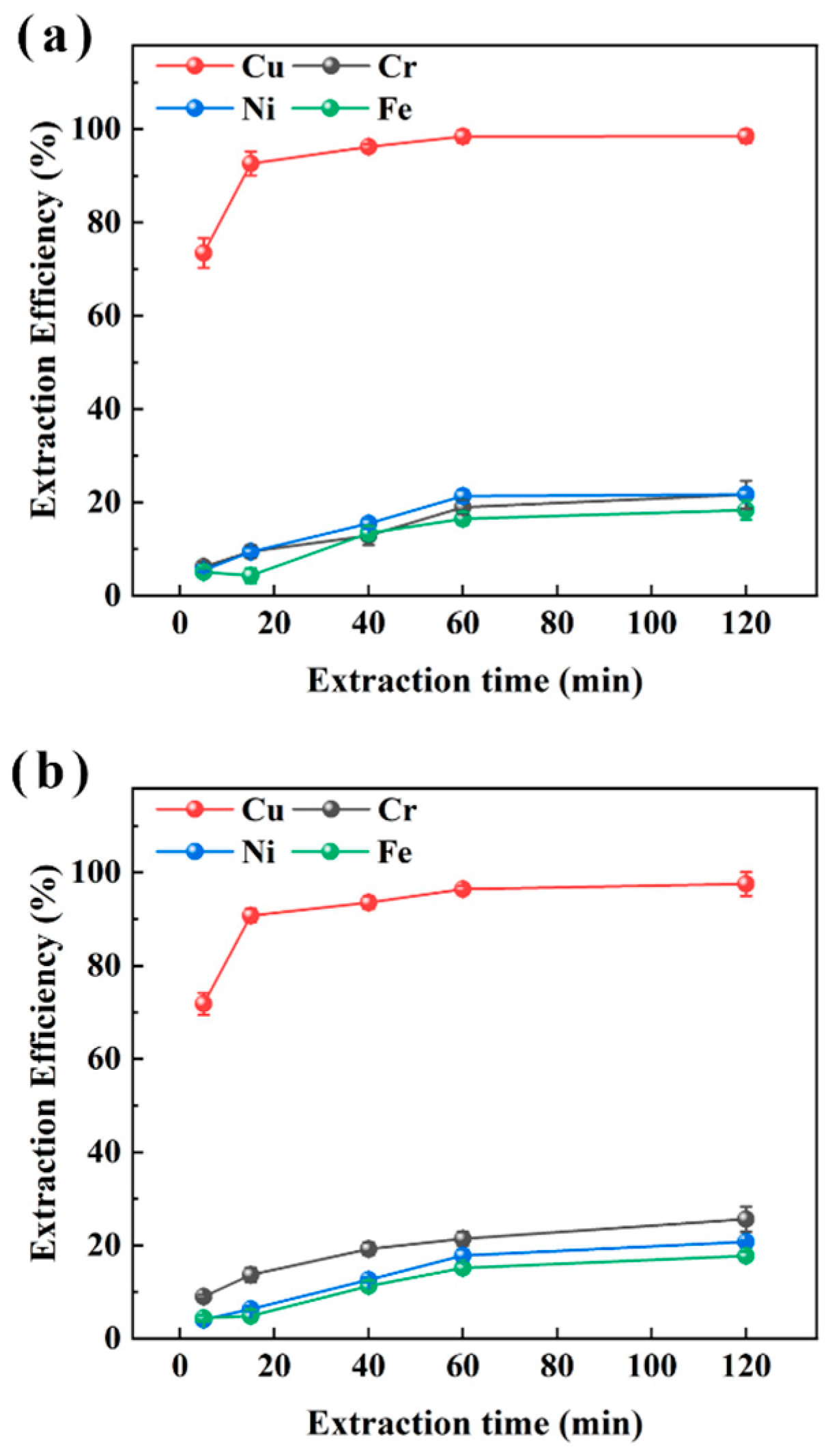
To investigate the extraction kinetics of M5640 in electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG, the impact of extraction time (5, 15, 40, 60, 120 min) on metal recovery efficiency (Cu, Ni, Fe, Cr) was systematically evaluated under conditions of 25 °C, an O/A ratio of 1:10, and an aqueous phase pH of 3.5, as shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 indicates that for sample XIN, Cu extraction efficiency increased significantly from 73.5% at 5 min to 98.5% at 120 min, while Fe extraction rose from 5.1% to 18.4%, with Ni and Cr remaining below 20%; sample CHENG showed a similar trend, with Cu extraction increasing from 71.8% to 97.5%, Fe from 4.4% to 17.7%, and Ni/Cr remaining below 25%. It can be also seen from Figure 4 that Cu extraction reached extraction equilibrium within 15 min, during which M5640 could extract 92.6% and 90.8% of the Cu in the samples XIN and CHENG, respectively, while the extraction efficiencies of Cr, Ni, and Fe were relatively low at this time, lower than 14.0%, 10.0%, and 5.0%, respectively. Therefore, it is proposed to use multi-stage extraction to recover Cu in order to improve the purity of the subsequent Cu products.

Figure 4.
Extraction efficiencies of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe with extraction time from sample XIN (a) and CHENG (b) using M5640 extractant for extraction time confirmation.
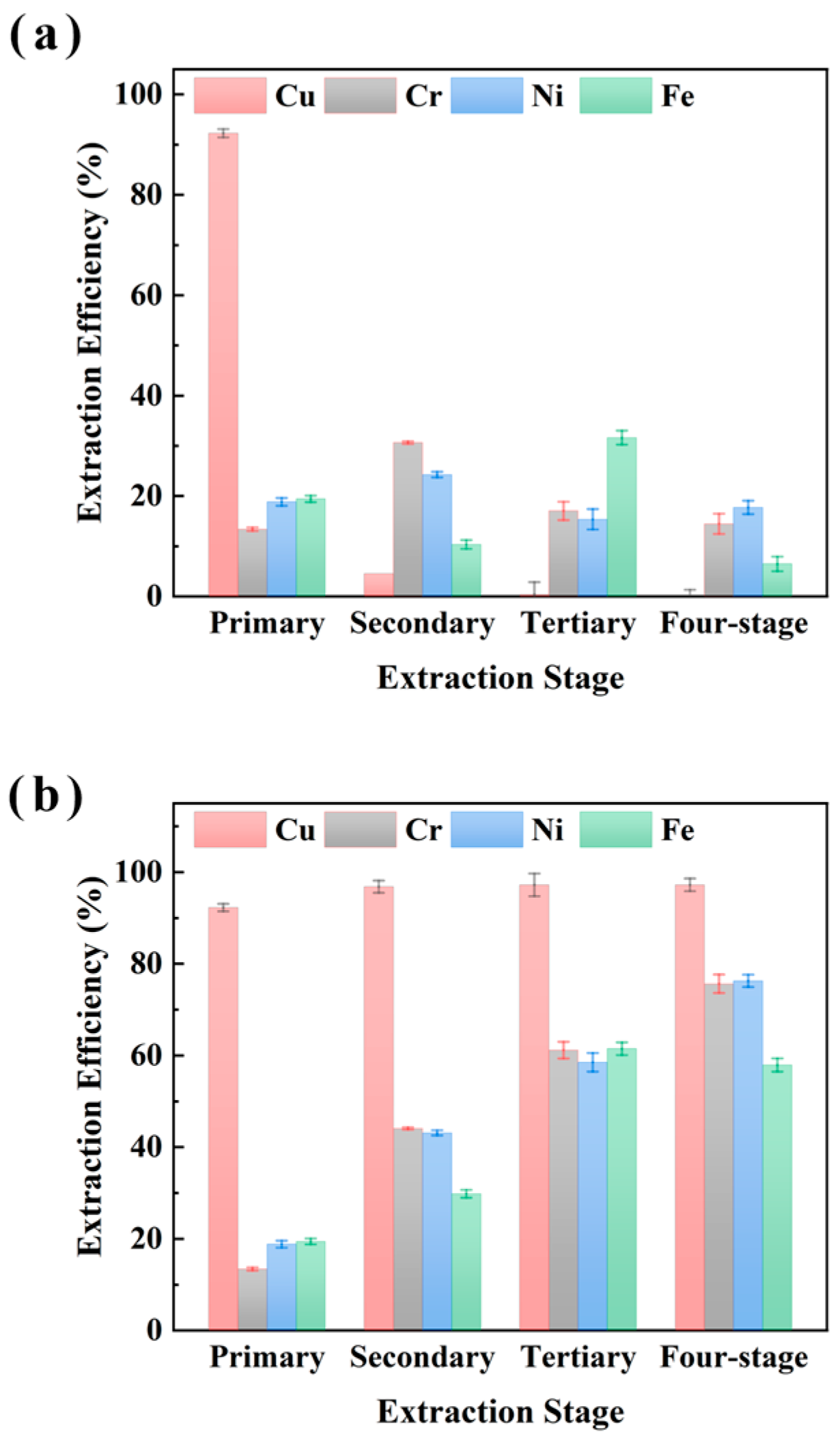
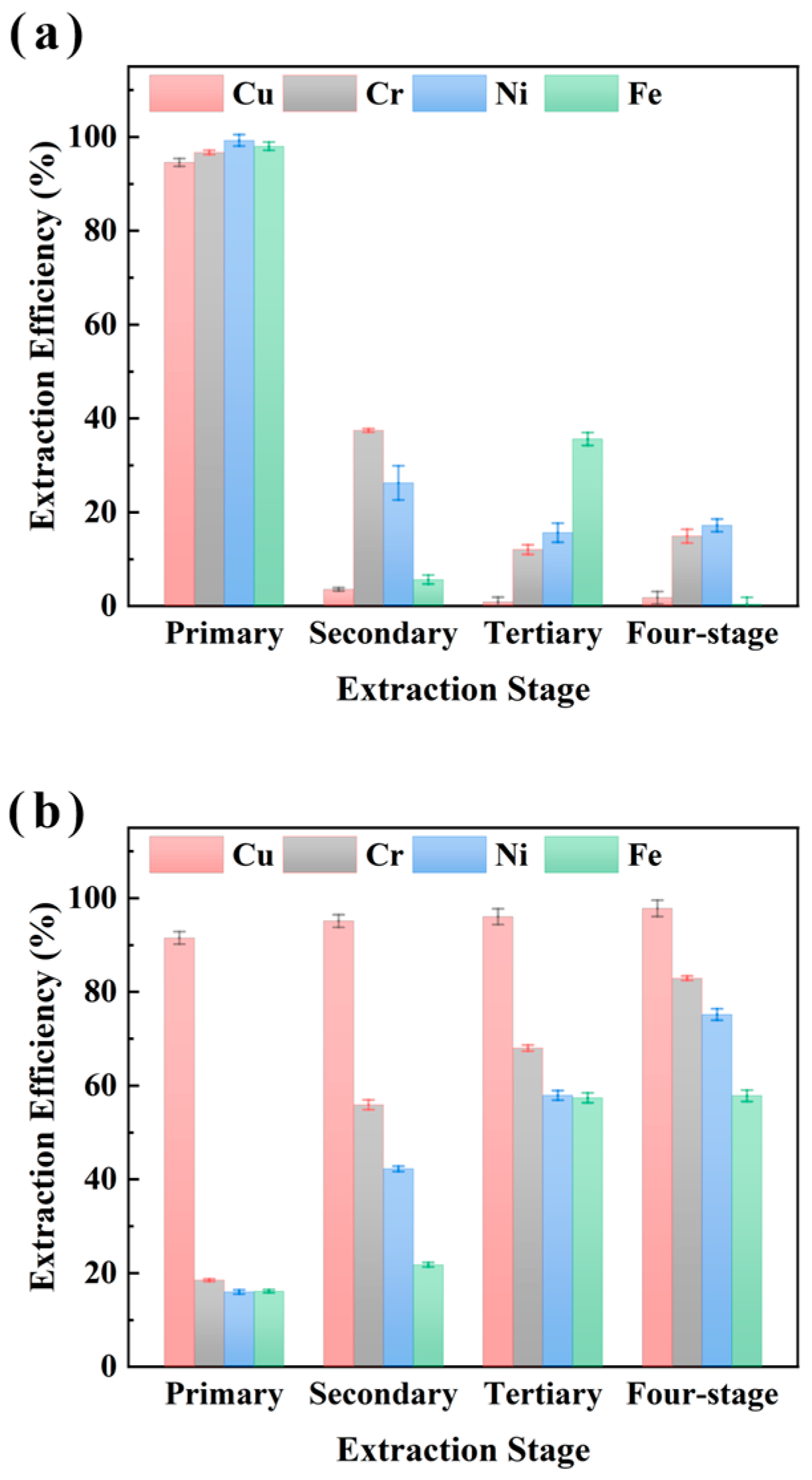
The impact of multi-stage extraction on the selectivity of M5640 for Cu recovery from electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG was evaluated and the results are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. The four-stage sequential extraction procedure was carried out under conditions of 25 °C, an O/A ratio of 1:10 (with fresh extractant added per stage), a 15 min extraction time, and an aqueous phase pH of 3.5. The extraction experiments shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6 are multi-stage, which builds upon single-stage extraction by successively using the aqueous phase from the previous extraction for the next cycle, with a fresh organic phase added each time. Both single-stage and cumulative efficiencies for metals were analyzed. Figure 5 shows that single-stage Cu extraction reached near 100% with no significant variation in subsequent stages. Meanwhile Fe, Ni, and Cr exhibited apparent single-stage efficiencies for four-stage extraction. Cumulative extraction revealed Cu efficiency plateauing at near 100% after the first stage, whereas Fe, Ni, and Cr accumulated to almost 70% by stage 4. These findings indicate that Cu extraction approaches saturation in a single stage, while Fe/Ni/Cr accumulation relies on multi-stage additive effects. The synchronized accumulation of Fe, Ni, and Cr (almost 70% at stage 4) suggests competitive extraction mechanisms.
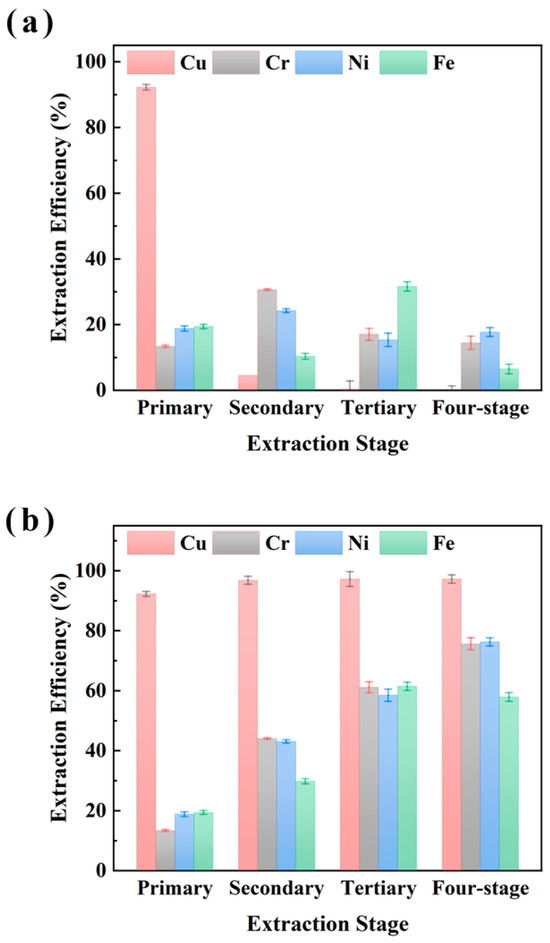
Figure 5.
Multi-stage extraction of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe from sample XIN using M5640 with single-stage extraction efficiency (a) and multi-stage cumulative extraction efficiency (b) for comprehensive study of extraction of Cu Cr, Ni, and Fe.
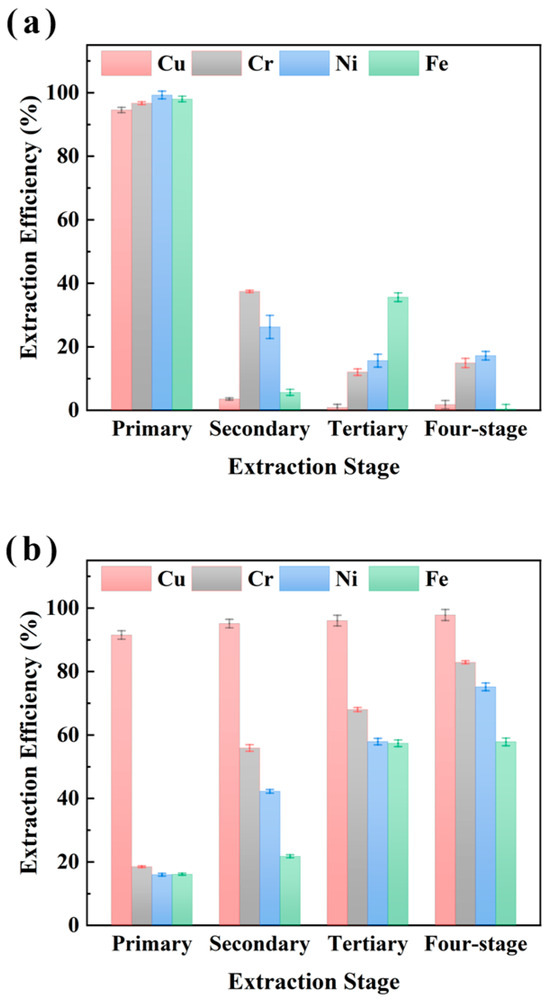
Figure 6.
Multi-stage extraction of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe from sample CHENG using M5640 with single-stage extraction efficiency (a) and multi-stage cumulative extraction efficiency (b) for comprehensive study of extraction of Cu Cr, Ni, and Fe.
Figure 6 shows a similar trend for multi-stage extraction from sample CHENG. The single-stage Cu extraction efficiency reached near 100% in the first stage with no significant change thereafter, while Fe, Ni, and Cr exhibited apparent extraction after four-stage extraction. Cumulative extraction revealed Cu efficiency plateauing at near 100% after the first stage, whereas Fe, Ni, and Cr accumulated to almost 70% by stage 4, indicating significant non-target metal co-extraction. However, under multi-stage extraction conditions, it was economically unfavorable to obtain better Cu separations under the condition of using more fresh extractants because the cumulative extraction efficiencies of Cu increased insignificantly, while the cumulative extraction efficiencies of Fe, Ni, and Cr increased significantly. Therefore, synthesizing the above experimental analyses, we believe that single-stage Cu extraction using the M5640 extractant is optimal, and synthesizing the experimental results shown in Figure 4, a single stage of 60 min is most favorable for the separation and recovery of Cu. The extraction experiments were conducted as follows: 25 °C, an O/A ratio of 1:10, 60 min extraction time, and an aqueous phase pH of of 3.5. Under these conditions, the extraction efficiencies of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe were 96.4%, 21.4%, 17.8%, and 15.2% respectively.
3.3. Stripping and Precipitation for Metal Recovery from Electroplating Sludge Samples
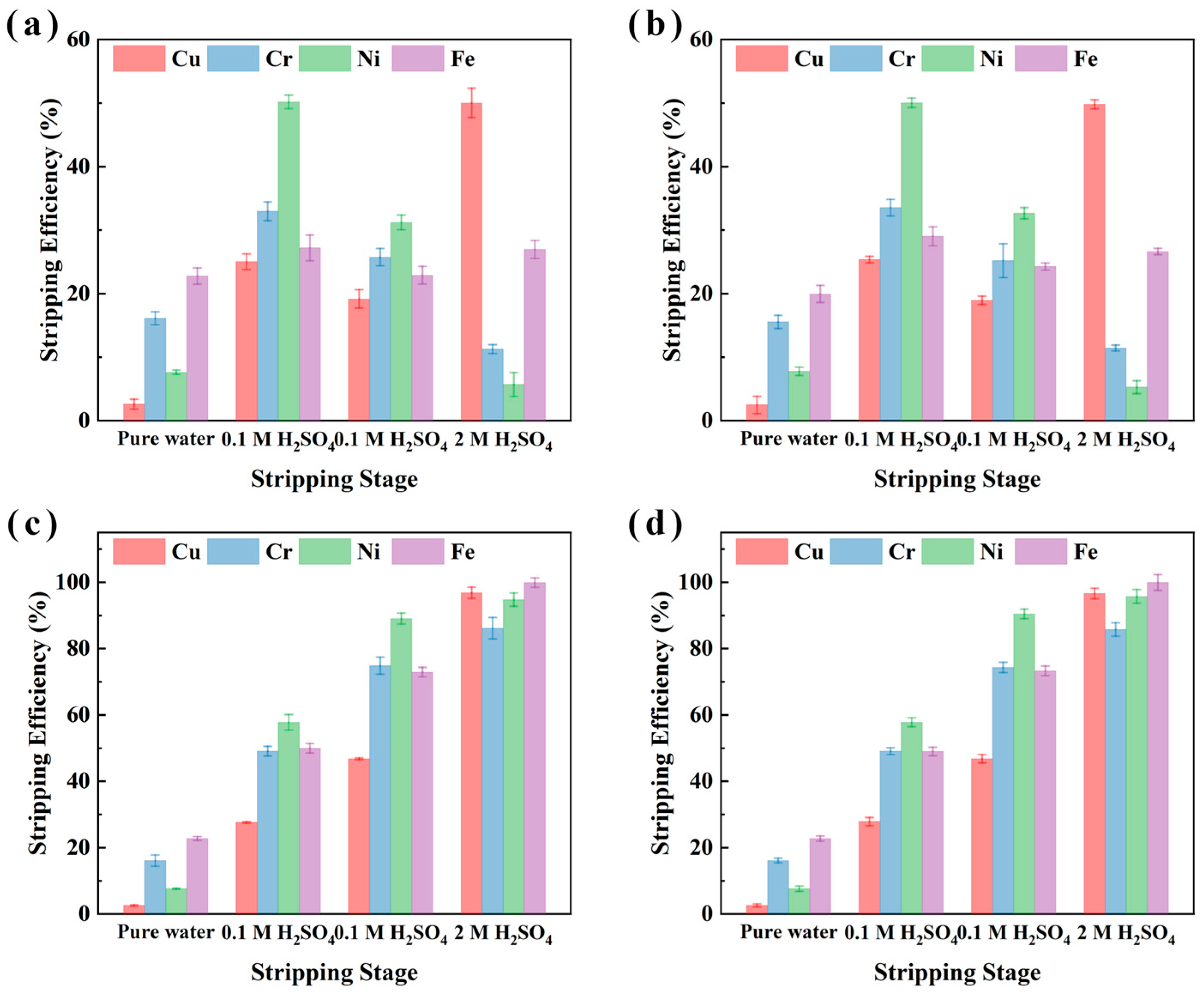
To optimize the stripping process of metals from the metal-loaded organic phase and to assess the effect of different stripping agents on metal recovery from electroplating sludge samples (XIN and CHENG), multi-stage stripping experiments were conducted. These experiments compared single-stage and multi-stage cumulative stripping efficiencies. Pure water, 0.1 M H2SO4, and 2 M H2SO4 were selected as the stripping agents under conditions of 25 °C, an O/A ratio of 1:10, and a 10 min stripping duration. The results, presented in Figure 7 indicate that the single-stage Cu stripping efficiency reached 49.8% for sample CHENG and 50% for sample XIN when using 2 M H2SO4, significantly higher than the efficiencies obtained with pure water (2.5% for sample CHENG and 2.6% for sample XIN) and 0.1 M H2SO4 (19.0% for sample XIN and 25.4% for sample CHENG). Additionally, 0.1 M H2SO4 was found to be effective for stripping Fe, Ni, and Cr, with stripping efficiencies for Ni, Cr, and Fe ranging from 31.2% to 50.2%, 25.2% to 33.5%, and 22.9% to 29.1%, respectively, for both samples.
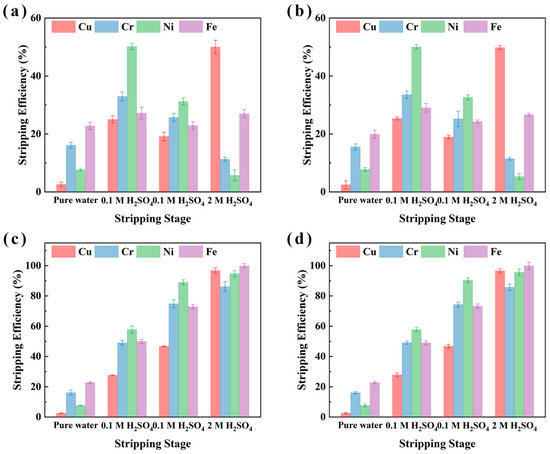
Figure 7.
Multi-stage stripping of the metal-loaded organic phase of M5640. Single-stage stripping of sample XIN (a); cumulative stripping of sample XIN (b); single-stage stripping of sample CHENG (c); cumulative stripping of sample CHENG (d).
When multi-stage cumulative stripping was employed, Cu stripping efficiency was enhanced to 96.6% for sample CHENG and 96.8% for sample XIN with 2 M H2SO4, while Fe, Ni, and Cr reached stripping efficiencies of 99.9%, 94.8–95.8%, and 85.8–86.2%, respectively. These findings suggest that the use of highly acidic 2 M H2SO4 selectively enhances Cu stripping. Given the substantial Cu recovery achieved during the extraction process, the direct use of 2 M H2SO4 for stripping can simplify operational procedures and improve overall recovery efficiency.
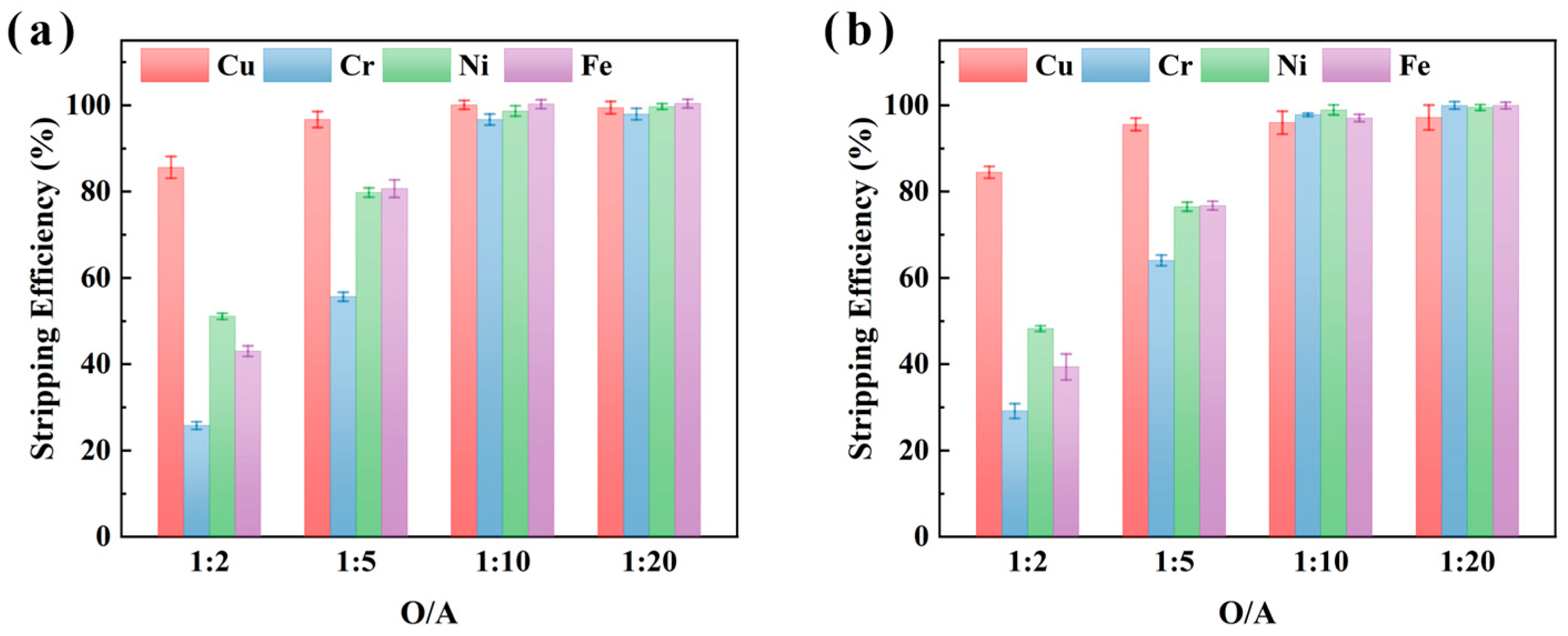
The effect of O/A ratio on the stripping efficiency of Cu, Cr, Ni, and Fe was further investigated using 2 M H2SO4 under conditions of 25 °C and 15 min stripping, as shown in Figure 8. The results demonstrate that Cu stripping efficiency increased significantly with higher O/A ratios, reaching 100.0% and 98.2% at an O/A ratio of 1:10 for samples XIN and CHENG, respectively. Furthermore, the stripping efficiencies of Cr increased to 98.0% and 100.0%, Fe to 100.0%, and Ni to 91.9% and 99.5% for XIN and CHENG at an O/A ratio of 1:20. These results suggest that higher O/A ratios facilitate near-complete recovery of Cu, Ni, Fe, and Cr, thus offering a cost-effective strategy for metal recovery from electroplating sludge. When the O/A ratio was 1:20, four metals in the metal-loaded organic phase could be efficiently back-extracted and recovered, and the wastewater discharge could meet the comprehensive sewage discharge standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB 8978-1996) [39].
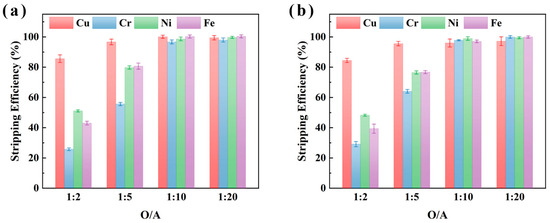
Figure 8.
The effect of the stripping O/A ratio (organic/aqueous phase volume ratio) on the stripping efficiencies of metals from the metal-loaded organic phase of M5640 using H2SO4 for samples XIN (a) and CHENG (b).
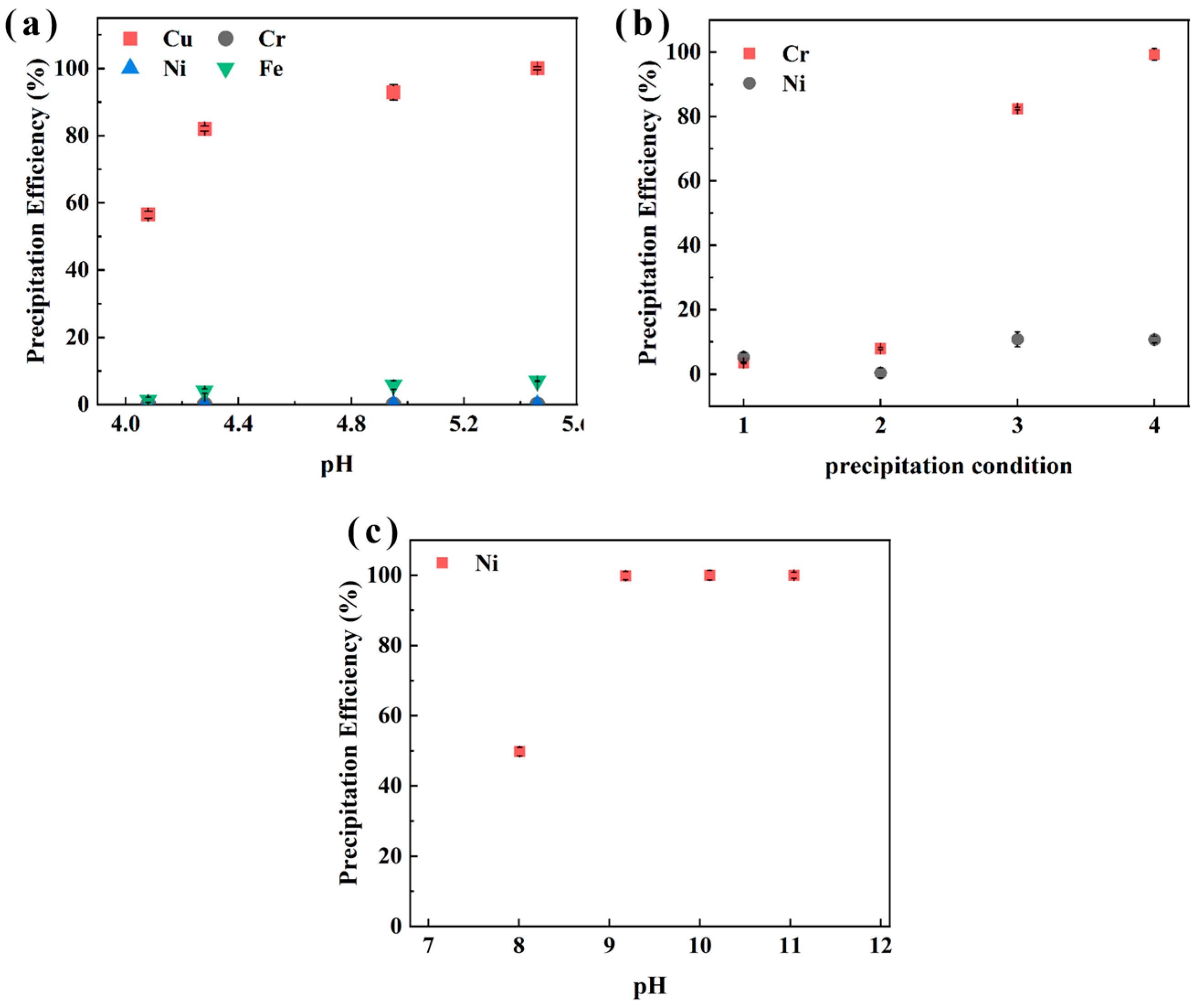
To sequentially recover Cu, Cr, and Ni, a water bath precipitation method (45 °C, 45 min) using Na2CO3, Na3PO4, and NaOH as precipitants to evaluate pH-dependent precipitation efficiency was applied [40]. The results in Figure 9 for sample XIN show that Cu precipitation efficiency reached 56.5%, 82.1%, and 100% at pH 4.1, 4.3, and 6.0, respectively. The conditions for Cr precipitation were 25 °C, 60 min, pH 3.0, and M(PO43−/Cr3+) = 0.75 for label 1; 90 °C, 60 min, pH 2.0, and M(PO43−/Cr3+) = 0.75 for label 2; 90 °C, 60 min, pH 2.0, and M(PO43−/Cr3+) = 1.2 for label 3; 90 °C, 60 min, pH 2.8, and M(PO43−/Cr3+) = 1.2 for label 4. Figure 9b illustrates that a higher Na3PO4 concentration M(PO43−/Cr3+) = 1.2 and higher pH (2.8) can promote the precipitation of Cr, reaching an efficiency of 99.3%, while only 2.4% of Ni was precipitated. Ni precipitation was conducted after, and 99.9% of Ni was recovered at pH 9.2. These findings demonstrate pH-controlled selective precipitation for Cu, Cr, and Ni.
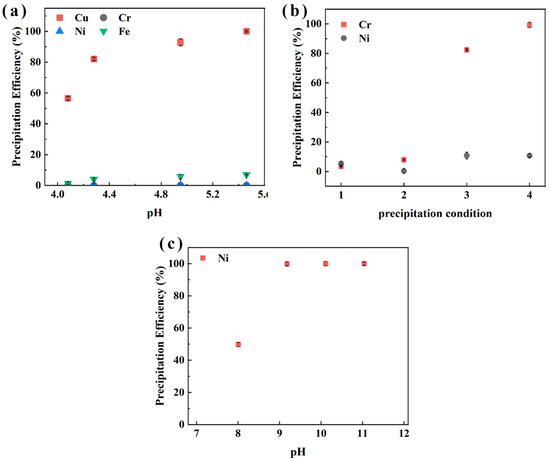
Figure 9.
The effect of pH on the precipitation efficiency of Cu (a), Cr (b), and Ni (c) in sample XIN from the aqueous phase after stripping.
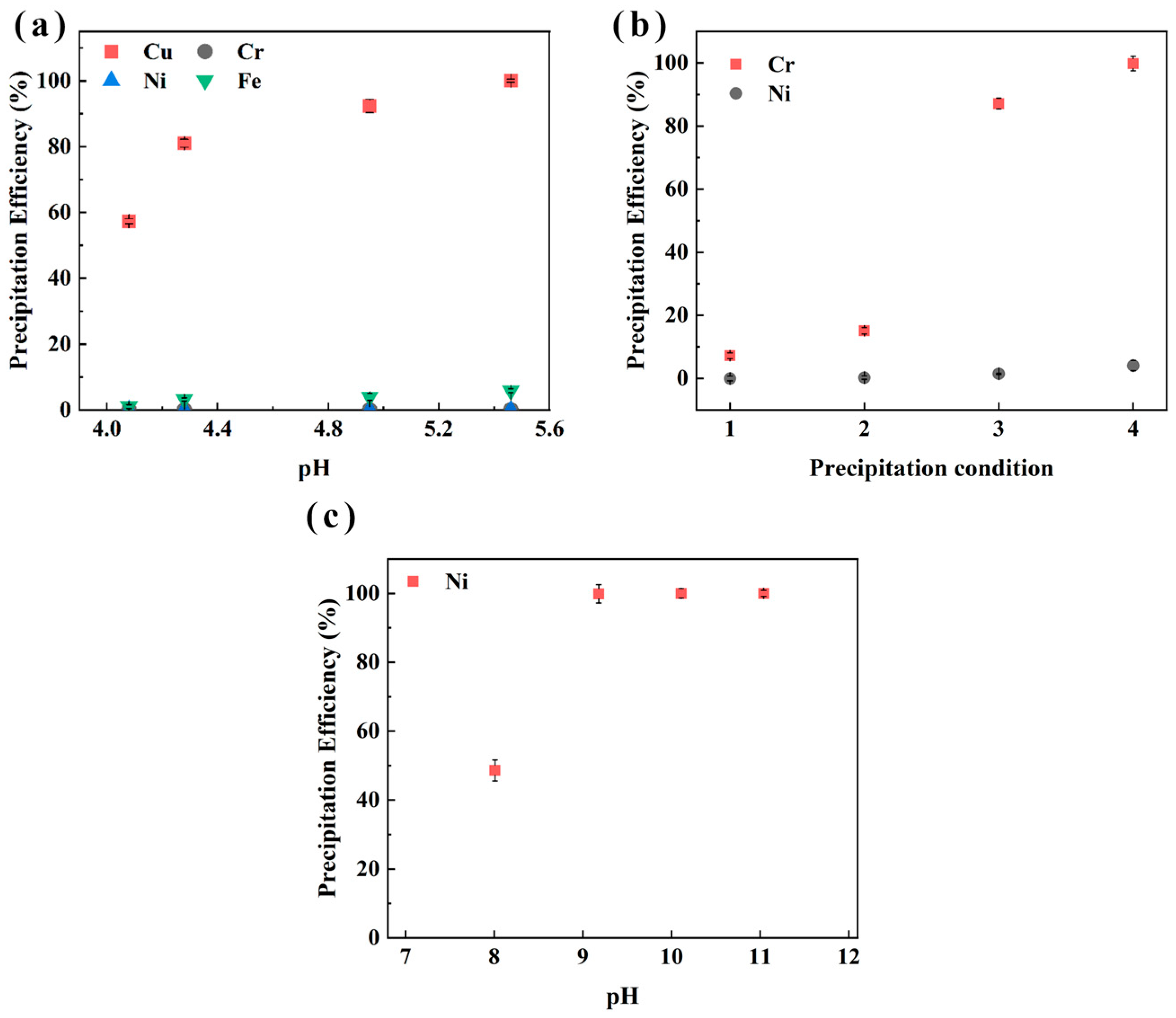
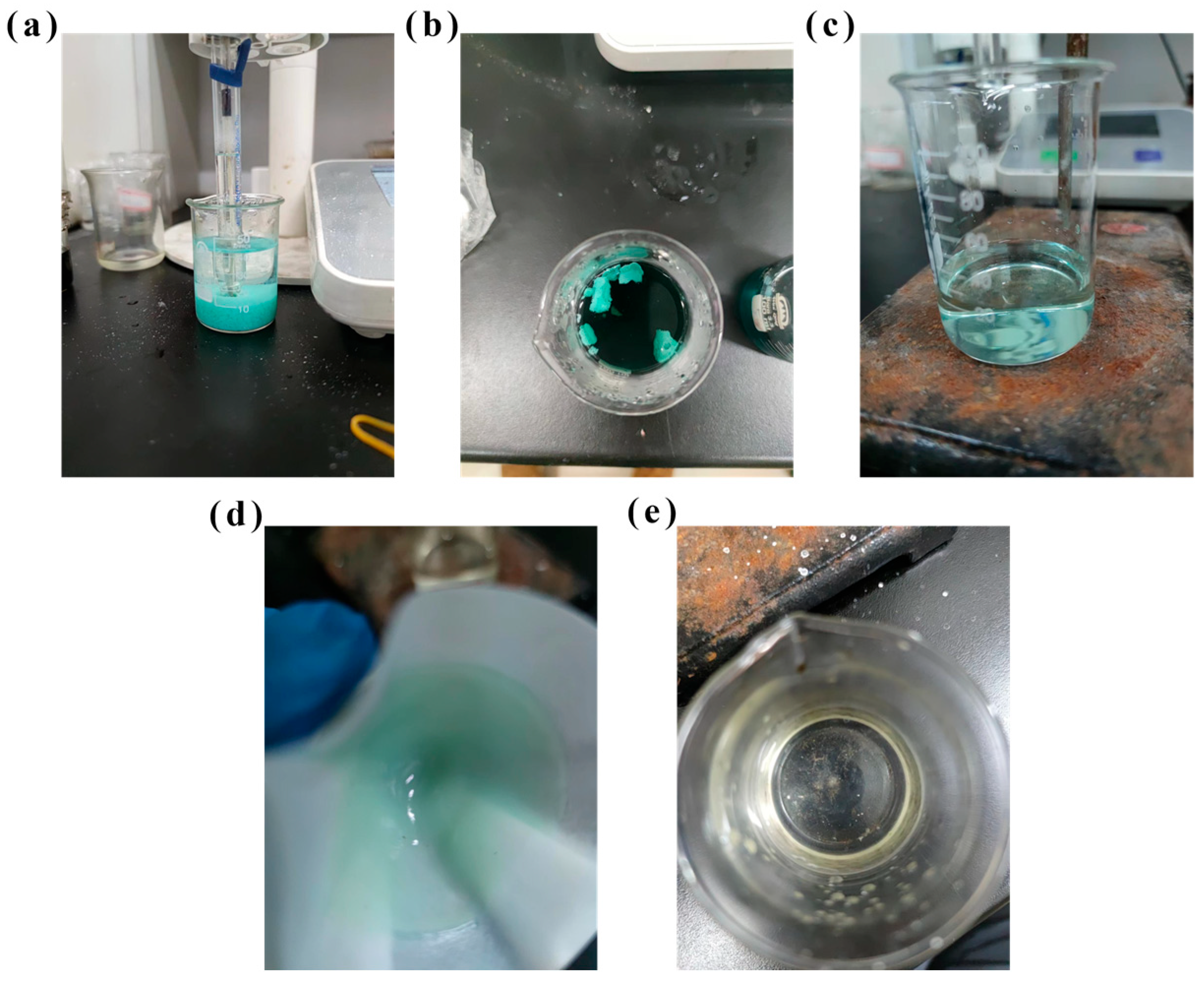
The sequential precipitation for metals from sample CHENG is shown in Figure 10. The results are similar to those in Figure 9. The precipitation efficiency of Cu increased with the increased pH. Moreover, 100.0% of Cu was recycled at pH 6.0. The optimal Cr precipitation condition was 90 °C, 60 min, pH 2.8, and M (PO43−/Cr3+) = 1.2, and 99.8% of Cr was recovered. After Cu and Cr precipitation, 99.9% of Ni was recovered as a Ni(OH)2 product. Pictures of the metal precipitation process are shown in Figure 11. CuCO3 precipitation was blue-green, while CrPO4 was light green, and Ni ions were predominant in the solution after precipitation of Cu and Cr. When the light blue-green Ni(OH)2 was precipitated, the solution became clear (Figure 11e), which indicates that the major metals (i.e., Cu, Cr, Ni) in the electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG were recovered. Stoichiometric analysis of the precipitation reaction (Cu2+ + CO32− → CuCO3) indicated that at pH 6.0, the molar ratio of Cu2+ to CO32− closely matched the theoretical 1:1 ratio, supporting the formation of CuCO3. ICP-OES analysis of the residual solution post-precipitation detected no Cu2+ (below the detection limit of 0.1 mg/L), confirming near-complete precipitation and high purity of the CuCO3 product. The stoichiometric ratio of PO43− to Cr3+ was maintained at 1.2 to ensure complete precipitation, and ICP-OES analysis of the residual solution showed Cr3+ concentrations below 0.2 mg/L, indicating high precipitation efficiency and minimal contamination by other metals (e.g., Ni2+ at 2.4%). ICP-OES confirmed negligible Ni2+ in the residual solution (<0.1 mg/L), and the molar ratio of OH− to Ni2+ during precipitation aligned with the theoretical 2:1 ratio for Ni(OH)2 formation. To further validate the quality of the recovered products, the precipitates were filtered, washed with ultrapure water, and dried at 60 °C for 24 h. The dried CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products were subjected to dissolution tests in diluted H2SO4 (0.1 M), followed by ICP-OES analysis to assess purity. The results show that CuCO3 contained <0.5% Ni and <0.2% Cr, CrPO4 contained <0.3% Cu and <0.4% Ni, and Ni(OH)2 contained <0.2% Cu and <0.1% Cr, indicating high selectivity and minimal cross-contamination. After stepwise precipitation, Cu, Cr and Ni were not detected in the solution, and the concentration of Fe was only 0.59 mg/L, which met the comprehensive sewage discharge standard of the People’s Republic of China (GB 8978-1996) [39]. This avoids secondary contamination in the resource recovery process from the electroplating sludge.

Figure 10.
Effect of pH on precipitation efficiency of Cu (a), Cr (b), and Ni (c) in sample CHENG from aqueous phase after stripping.

Figure 11.
Pictures of Cu precipitation (a), Cr precipitation (b), solution after Cr precipitation (c), Ni precipitation (d), and solution after Ni precipitation (e).
Although Cu, Ni, and Cr were almost completely recovered from the metal-loaded organic phase, the aqueous phase after Cu extraction still contained substantial amounts of Ni and Cr. Based on the experimental conditions and results from Figure 9 and Figure 10, further precipitation of Cr and Ni from the aqueous phase was conducted, and the results are presented in Table 3. Stepwise precipitation successfully recovered 99.9% and 96.8% of Cr and Ni from sample XIN, respectively, and 99.7% and 97.4% from sample CHENG. Li et al. investigated the recovery of heavy metals from electroplating sludge using an ultrasonically enhanced two-stage acid leaching method [1]. Their reported efficiencies were 85.2% for Cu, 82.1% for Ni, and 78.5% for Cr. Our method significantly outperforms this approach, achieving Cu (96.4–98.6% vs. 85.2%), Ni (96.8–97.8% vs. 82.1%), and Cr (96.8–97.1% vs. 78.5%) recoveries that are 11.2–13.4%, 14.7–15.7%, and 18.3–18.6% higher, respectively. This enhancement is likely due to the selective extraction capabilities of M5640 and optimized process conditions, which minimize the co-extraction of impurities and improve metal separation efficiency compared to the acid leaching technique. These findings indicate that the recovery method employed in this study can efficiently and selectively recover Cu, Ni, and Cr from electroplating sludge, producing CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products. CuCO3 serves as an important chemical raw material, widely used in pigments and catalysts. CrPO4, as a stable chromium compound, finds applications in pigment preparation for ceramics and glass industries. Ni(OH)2 is a key raw material for producing nickel metal and nickel-based alloys, with extensive applications in batteries, electroplating, and magnetic materials. These high-value-added products play significant roles in their respective industrial fields, demonstrating broad application prospects for the resource utilization of electroplating sludge [41,42,43].

Table 3.
Precipitation conditions and results for Cr and Ni from sample XIN and CHENG.
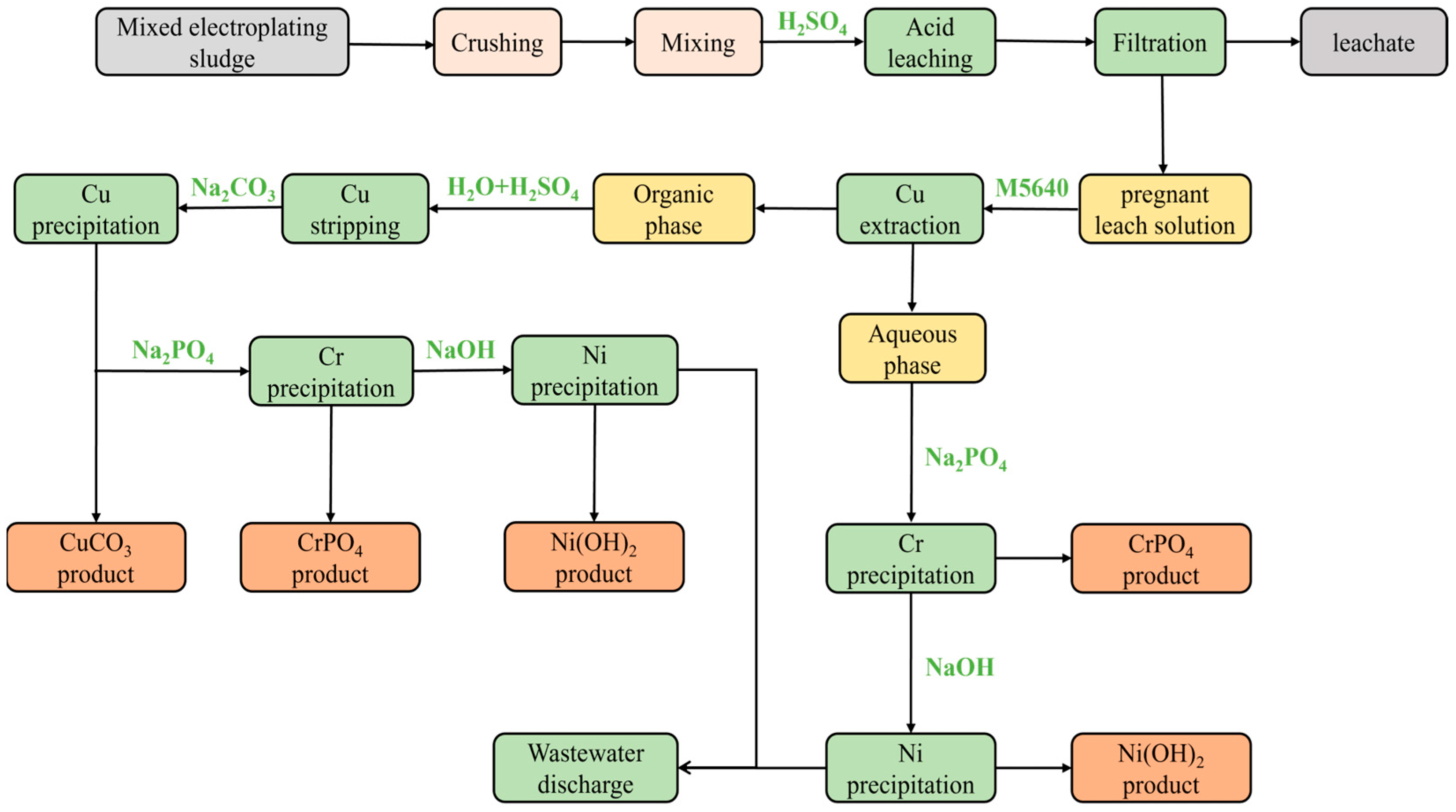
Building on previous studies, we propose a comprehensive method for recovering Cu, Ni, and Cr from electroplating sludge samples to produce CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products, as illustrated in the flowchart in Figure 12. Initially, electroplating sludge samples are crushed, mixed, and subjected to H2SO4 leaching, followed by filtration to obtain the leachate. The pregnant leach solution is then extracted with M5640 to recover most of the Cu, leaving an aqueous solution containing mainly Cr and Ni. After Cu extraction, CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products are obtained through H2SO4 stripping and sequential precipitation. The aqueous phase remaining after Cu extraction undergoes stepwise precipitation of Cr and Ni to yield CrPO4 and Ni(OH)2 products. The entire process, involving leaching, extraction, stripping, and precipitation, effectively recovers Cu, Cr, and Ni from electroplating sludge and ensures that the wastewater meets the comprehensive sewage discharge standards of the People’s Republic of China (GB 8978-1996) [39]. The recovery process also complies with Chinese environmental regulations including the Law on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Wastes and the Cleaner Production Promotion Law. To ensure the environmental sustainability of the proposed recovery process, the management of leaching residues generated during H2SO4 leaching can be addressed through a combination of stabilization/solidification and resource utilization strategies. Stabilization/solidification, using cement-based binders (20% cement, 5% fly ash), can be employed to immobilize residual heavy metals, reducing their leachability to comply with China’s Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes (GB 5085.3-2007) [44]. The stabilized residues should be tested for incorporation into non-load-bearing bricks. Moreover, the heavy metal concentrations in the leachate should be confirmed through leaching tests to ensure the concentrations are below regulatory limits, enabling safe resource utilization.

Figure 12.
Flowchart of recovery technique for recovering Cu, Ni, and Cr from electroplating sludge samples to produce CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products.
To further evaluate the sustainability of this treatment process, the energy consumption, reagent cost, and consumption were calculated. The sustainability of the proposed metal recovery process is underscored by its energy efficiency, as detailed in Table 4. The total energy consumption for treating 1 ton of electroplating sludge is estimated at 18 kWh, encompassing leaching (9 kWh), extraction (2.475 kWh), stripping (2.475 kWh), and precipitation (3.15 kWh). This figure is significantly lower than that of conventional pyrometallurgical methods, as pyrometallurgical methods are often considered more energy-intensive than other recovery processes such as hydrometallurgy [24]. Our process operates at ambient temperature and pressure, minimizing energy demands. For instance, the leaching stage, which accounts for 50% of the total energy use, employs a modest 1.1 kW stirrer over 9 h, aligning with energy-efficient hydrometallurgical approaches reported by Zhang and Xu [24]. This reduction in energy consumption not only lowers operational costs but also aligns with China’s Cleaner Production Promotion Law, emphasizing resource efficiency and environmental protection.

Table 4.
Energy consumption for treatment unit in metal recovery process from electroplating sludge.
Economic viability is a critical aspect of the proposed recovery process. The reagent price and consumption of the metal recovery process from electroplating sludge in this study are shown in Table 5. The total reagent cost for processing 1 ton of electroplating sludge is calculated at USD 276.44, with major contributions from the M5640 extractant (107 USD) and kerosene (39.68 USD). These costs are offset by the market value of the recovered products: CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2. For sample XIN, the recovered metals yield a revenue of USD 392.8, while sample CHENG generates USD 446.5, based on current market prices [23]. This results in net profits of 116.36 USD/t and 170.06 USD/t, respectively, demonstrating economic feasibility. Compared to traditional methods, where reagent costs often exceed recovery value due to lower selectivity [23], our process leverages the high efficiency of M5640 and stepwise precipitation, consistent with findings by Krishnan et al. (2021) [23], who reported similar economic benefits in metal recovery from industrial wastes.

Table 5.
Reagent price and consumption of metal recovery process from electroplating sludge.
The mass balance for Cu, Ni, and Cr recovery through a process including extraction, stripping, and precipitation from electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG was also calculated and is shown in Table 6. For each stage, the metal concentrations in the aqueous and organic phases were measured using ICP-OES, and the masses were calculated based on the volumes of the phases and the solid-to-liquid ratios. The recovered metals were quantified as CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 precipitates, with their masses determined based on precipitation efficiencies, as reported in Figure 9 and Figure 10. The efficiency of the recovery process is evidenced by the mass balance of Cu, Ni, and Cr, as presented in Table 6. For sample XIN, the overall recovery efficiencies are 96.4% for Cu, 97.8% for Ni, and 97.1% for Cr, while sample CHENG achieves 98.6%, 96.8%, and 96.8%, respectively. These high recovery rates are achieved through a multi-unit process of leaching, extraction, stripping, and precipitation. For instance, Cu extraction with M5640 reaches 98.4% in sample XIN, followed by 100% precipitation as CuCO3, reflecting the process’s selectivity and completeness. Similarly, Ni and Cr are recovered at near-quantitative levels via stepwise precipitation, with efficiencies surpassing those of conventional methods (e.g., 85–90% in pyrometallurgy) [1]. These results outperform the recovery rates reported by Li et al. (2010) [1] for electroplating sludge, where acid leaching alone yielded lower efficiencies due to co-extraction challenges. This shows that the electroplating sludge treatment method proposed in this paper is highly efficient.

Table 6.
The mass balance for Cu, Ni, and Cr recovery through a process including extraction, stripping, and precipitation from electroplating sludge samples XIN and CHENG.
3.4. Evaluation of the Environmental Relevance to Existing Environmental Legislation
Due to the highly complex composition of electroplating sludge, it poses significant risks to human health and the surrounding environment, and its disposal is often subject to strict legal supervision [45]. From a legal perspective, the Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Environmental Pollution by Solid Wastes clearly requires that hazardous waste should be “reduced in quantity, recycled, and made harmless”, strengthens the main responsibilities of enterprises, and stipulates the criminal liabilities for illegal disposal [46]. The government has also formulated national standards for electroplating sludge, namely “Classification of Treatment and Disposal of Electroplating Sludge” (GB/T 38066-2019) [47] and “Methods for Reduction Treatment of Electroplating Sludge” (GB/T 39301-2020) [48]. It requires enterprises involved in the disposal to refine the technical routes, select solidification and stabilization, metal recovery, or co-disposal processes according to the composition of the sludge, and set the pollutant emission limits [49]. At the same time, guided by the concept of a circular economy and drawing on the “waste hierarchy” concept of the EU Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC), the Chinese government encourages the transformation of electroplating sludge into secondary resources [50]. Through the Law on the Comprehensive Utilization of Resources, it encourages enterprises to use the recovered products for new energy materials, such as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries [13,51].
For the recovery process of metals in the electroplating sludge samples, the leaching process was regulated in the experiment so that the heavy metal leaching efficiency complied with the requirements for reduction in China’s Law on Prevention and Control of Solid Waste Pollution of the Environment. This process effectively reduces the total amount of heavy metals in the electroplating sludge, which reduces the difficulty and risk for subsequent treatment. After several rounds of extraction, counter-extraction, and precipitation experiments, Cu, Cr, and Ni were almost completely recovered. This meets the requirements of the Circular Economy Promotion Law on improving the efficiency of resource utilization, realizes the transformation of heavy metals from waste to resources, and reduces the dependence on primary metal resources. Additionally, the concentration of Fe in the final wastewater was only 0.59 mg/L, which is far lower than the limit value of the primary standard (Fe ≤ 1.0 mg/L) in the Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB 8978-1996). Meanwhile, other heavy metals such as Cu, Cr, Ni, etc., were not detected, indicating that this process effectively controls wastewater discharge and avoids secondary pollution while recovering resources. Moreover, the technical pathway for the construction of a “waste-free city” proposed in this study is highly compatible with the concept of “waste hierarchy” in the EU Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC). By prioritizing the use of source reduction and resource recovery strategies, the amount of electroplating sludge generated is minimized and converted into valuable resources.
To meet the above requirements, this study proposes an innovative technology for the resource utilization of electroplating sludge, achieving policy objectives such as a “reduction of hazardous waste, compliance of wastewater discharge, and high-value recovery of metals”, and constructing a trinity solution integrating “environmental risk control, resource recycling, and regulatory compliance assurance”. This technical solution not only meets the strict requirements of domestic and international environmental regulations for pollutant control and resource utilization but also provides an innovative path for the electroplating industry to achieve green manufacturing and a circular economy through the synergy of economic and environmental benefits.
4. Conclusions
This study presents a comprehensive and efficient method for recovering Cu, Cr, and Ni from electroplating sludge through a multi-unit process involving leaching, solvent extraction, stripping, and precipitation. The results demonstrate that the extractant M5640 achieves near-complete Cu extraction (96.4%) under optimized conditions (pH 3.5, 60 min extraction, O/A ratio 1:10), with minimal co-extraction of Fe, Ni, and Cr. The stripping process using 2 M H2SO4 and sequential precipitation yield high-purity CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2 products, with recovery efficiencies exceeding 99% for Cu and Ni and 99.7–99.9% for Cr. The final wastewater meets China’s stringent environmental discharge standards, ensuring no secondary contamination. Beyond its technical efficacy, this method offers significant practical implications for the electroplating industry and environmental management.
The process is economically feasible, with a total reagent cost of USD 276.44 per ton of sludge treated. The recovered products—CuCO3, CrPO4, and Ni(OH)2—generate revenues of USD 392.8 (sample XIN) and USD 446.5 (sample CHENG) per ton, resulting in net profits of USD 116.36 and USD 170.06, respectively. This cost-effectiveness, coupled with the process’s adaptability to industrial-scale operations, positions it as a viable solution for large-scale implementation. The low energy consumption of 18 kWh/t, compared to conventional pyrometallurgical methods, further reduces operational costs and enhances the process’s appeal for industrial adoption, particularly in regions with high energy costs or stringent carbon emission regulations.
By transforming hazardous waste into valuable secondary resources, this process reduces reliance on primary metal extraction, aligning with global sustainability goals and China’s Circular Economy Promotion Law. The recovery of high-value metals like Cu and Ni, essential for lithium-ion batteries and other green technologies, supports the development of a closed-loop industrial chain. The process’s compliance with environmental regulations, such as China’s Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standard, ensures that it meets legal requirements for pollutant control while promoting the “waste-free city” initiative. This dual focus on resource recovery and environmental protection provides a replicable model for other industries facing similar waste management challenges.
The adaptability of the process to different sludge compositions—demonstrated by the successful treatment of two distinct samples (XIN and CHENG)—suggests its potential for application to other types of industrial sludge, such as those from mining or metallurgical operations. This versatility enhances its industrial relevance and scalability. Future research will focus on scaling up the process, optimizing it for diverse waste streams, and integrating it with emerging technologies to further improve efficiency and reduce costs. These advancements will solidify the process’s role in advancing sustainable industrial practices and resource conservation.
In summary, this study not only advances the technical approaches for selective metal recovery from complex electroplating sludge but also provides a practical, economically viable, and environmentally sustainable solution for industrial application. By bridging technology with environmental regulation, our method offers a pathway toward green transformation in the electroplating industry, supporting both economic growth and ecological protection.
Author Contributions
J.M.: conceptualization, formal analysis, visualization, writing—original draft preparation; Z.X.: conceptualization, resources, formal analysis, methodology, visualization, supervision, methodology, writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by funds from the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX24_0342) and the Major Project of the Late-stage Funding for Philosophy and Social Sciences by the Ministry of Education (23HQ10286009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the XRF analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, C.; Xie, F.; Ma, Y.; Cai, T.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, G. Multiple heavy metals extraction and recovery from hazardous electroplating sludge waste via ultrasonically enhanced two-stage acid leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhikuan, W.; Xia, X.; Yongqi, C.; Tao, Q. Recovery of heavy metals from electroplating sludge and stainless steel pickle waste liquid by ammonia leaching method. J. Environ. Sci. 1999, 11, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, I.; Kuo, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chang-Chien, G. Electroplating sludge metal recovering with vitrification using mineral powder additive. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 58, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Pandey, B. Bio-processing of solid wastes and secondary resources for metal extraction—A review. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. Approaches for the Treatment and Resource Utilization of Electroplating Sludge. Materials 2024, 17, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Approaches for electroplating sludge treatment and disposal technology: Reduction, pretreatment and reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 349, 119535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruqi, M.; Siddiqui, F.; Hassan, S. Optimization of microwave treatment for dewaterability enhancement of electroplating sludge. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, P.; Chen, L.; Tang, Q. Utilization of Electroplating Sludge as Subgrade Backfill Materials: Mechanical and Environmental Risk Evaluation. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 4891418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electroplating Effluent Guidelines. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/eg/electroplating-effluent-guidelines (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Fact Sheet on Disposal Options for Electroplating Sludge. Available online: https://p2infohouse.org/ref/11/10471.htm (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Bi, G.; Song, W.; Zhou, P.; Liang, L. Does environmental regulation affect energy efficiency in China’s thermal power generation? Empirical evidence from a slacks-based DEA model. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. Impact of energy conservation policies on the green productivity in China’s manufacturing sector: Evidence from a three-stage DEA model. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Oh, W. Determinants of innovation in energy intensive industry and implications for energy policy. Energy Policy 2015, 81, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, J.; Hill, J.; Morgan, J.; Wilkinson, J. Recycling of sewage sludge to grassland: A review of the legislation to control of the localization and accumulation of potential toxic metals in grazing systems. Grass Forage Sci. 2003, 58, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitiu, M.; Marcus, M.; Vlad, M.; Balaceanu, C. Stability of Ceramic Glazes Obtained by Valorification of Anorganic Pigments Extracted from Electroplating Sludge. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulatory Exclusions and Alternative Standards for the Recycling of Materials, Solid Wastes and Hazardous Wastes. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw/regulatory-exclusions-and-alternative-standards-recycling-materials-solid-wastes-and-hazardous (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Luo, J.; Zhao, C.; Huang, W.; Wang, F.; Fang, F.; Su, L.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y. A holistic valorization of treasured waste activated sludge for directional high-valued products recovery: Routes, key technologies and challenges. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiess, S.; Kucera, J.; Vaculovic, T.; Birklbauer, L.; Habermaier, C.; Conde, A.; Mandl, M.; Haberbauer, M. Zinc recovery from bioleachate using a microbial electrolysis cell and comparison with selective precipitation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1238853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piferi, R.; Kline, K.; Younger, J.; Lawler, K. An alternative approach for achieving cardiovascular baseline: Viewing an aquatic video. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 37, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Zhen, J. In Separation Status of Discarded or Obsolete TNT/RDX/Al Explosive based on Material Properties. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1046, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Stuckman, M.; Means, N.; Lopano, C.; Hakala, J. Determination of transition metal ions in fossil fuel associated wastewaters using chelation ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1668, 462924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Ma, L.; Xi, X. “Complexation-precipitation” metal separation method system and its application in secondary resources. Rare Met. 2014, 33, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Zulkapli, N.; Kamyab, H.; Taib, S.; Din, M.; Abd Majid, Z.; Chaiprapat, S.; Kenzo, I.; Ichikawa, Y.; Nasrullah, M.; et al. Current technologies for recovery of metals from industrial wastes: An overview. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. A review of current progress of recycling technologies for metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Cattrall, R.; Kolev, S. Recent trends in extraction and transport of metal ions using polymer inclusion membranes (PIMs). J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Bruening, M. Ion separations with membranes. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 2831–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkiran, N.; Tanaydin, M. Recovery of Cu(II) by Acorga M5640 After Leaching of Malachite Ore in Perchloric Acid Solutions. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Sun, G.X.; Dang, Q.Y.; Zhao, X.P. The Extraction Behavior of Cu2+ with N,N,N′,N′-Tetrabutyl-3-Oxy-Glutaramide from Hydrochloric Acid. Adv. Environ. Technol. 2013, 726–731, 2795–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Separation and recovery of copper from waste printed circuit boards leach solution using solvent extraction with Acorga M5640 as extractant. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Liang, X. Separating Nickel-Copper Involves Performing Sulfuric acid Leaching of Electroplating Sludge to Obtain Sulfuric Acid Leachate, Adjusting pH Value of Sulfuric Acid-leaching Solution, Sequentially Performing Lix984 Extraction Agent Extraction, Washing, Back-Extracting to Obtain Copper Sulfate Solution. Chinese Patent CN116751982-A, 15 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Xin, L.; Zheng, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Kaung, H.; Yang, W.; Qin, W.; Jadambaa, T.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hydrometallurgy recycling of heavy metals from electroplating sludge: Recent development and challenge. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2025, 214, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Selective extraction of chromium from chromium-bearing electroplating sludge by pressure oxidation alkaline leaching. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 191, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, Z. Understanding and controlling the key phase transformation for selective extracting Ni and Cu from Cr-containing electroplating sludge. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J. Recent developments in the separation of nickel and cobalt from sulfate-solutions by solvent-extraction. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1983, 83, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Itabashi, O.; Suzuki, T.; Inoue, K. Hydrometallurgical process for recovery of metal values from spent lithium-ion secondary batteries. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 47, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.; de Mello, N.; Duarte, M.; Montenegro, M.; Araújo, A.; Neto, B.; da Silva, V. Extraction and recovery of chromium from electroplating sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deep, A.; Kumar, P.; Carvalho, J. Recovery of copper from zinc leaching liquor using ACORGA M5640. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Reis, M.; Ismael, M.; Carvalho, J. Extraction of Cu(II) with Acorga M5640 using hollow fibre liquid membrane. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. National Environmental Protection Agency of China; National Bureau of Technical Supervision of China: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 1–23.
- Li, Q.; Gadd, G. Biosynthesis of copper carbonate nanoparticles by ureolytic fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7397–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Luo, J.; Han, W.; Li, M. Formation and evolution of new α grain boundary and its influence on globularization of α lamellae in TC17 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 848, 156141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, J.; Tian, J.; Liu, B.; Yan, S. MOF-derived Fe2O3@MoS2: An efficient electrocatalyst for ammonia synthesis under mild conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyenkeadi, V.; Aboelazayem, O.; Saha, B. Systematic multivariate optimisation of butylene carbonate synthesis via CO2 utilisation using graphene-inorganic nanocomposite catalysts. Catal. Today 2020, 346, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5085.3-2007; Identification Standards for Hazardous Wastes-Identification for Extraction Toxicity. China National Environmental Protection Administration; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 1–8.
- Fang, Z.; Kong, X.; Sensoy, A.; Cui, X.; Cheng, F. Government’s awareness of Environmental protection and corporate green innovation: A natural experiment from the new environmental protection law in China. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 70, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, A.; Wu, Y. Environmental regulation and green innovation: Evidence from China’s new environmental protection law. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 38066-2019; Classification of Treatment and Disposal of Electroplating Sludge. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 39301-2020; Methods for Reduction Treatment of Electroplating Sludge. Chinese Standard: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Xie, R.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J. Different Types of Environmental Regulations and Heterogeneous Influence on “Green” Productivity: Evidence from China. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Xiang, Q. Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: Based on an extended CDM model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, D. Does command-and-control regulation promote green innovation performance? Evidence from China’s industrial enterprises. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).