Effects of Water Pollution on Diatom Communities of Roșia Montană Mining Area, Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
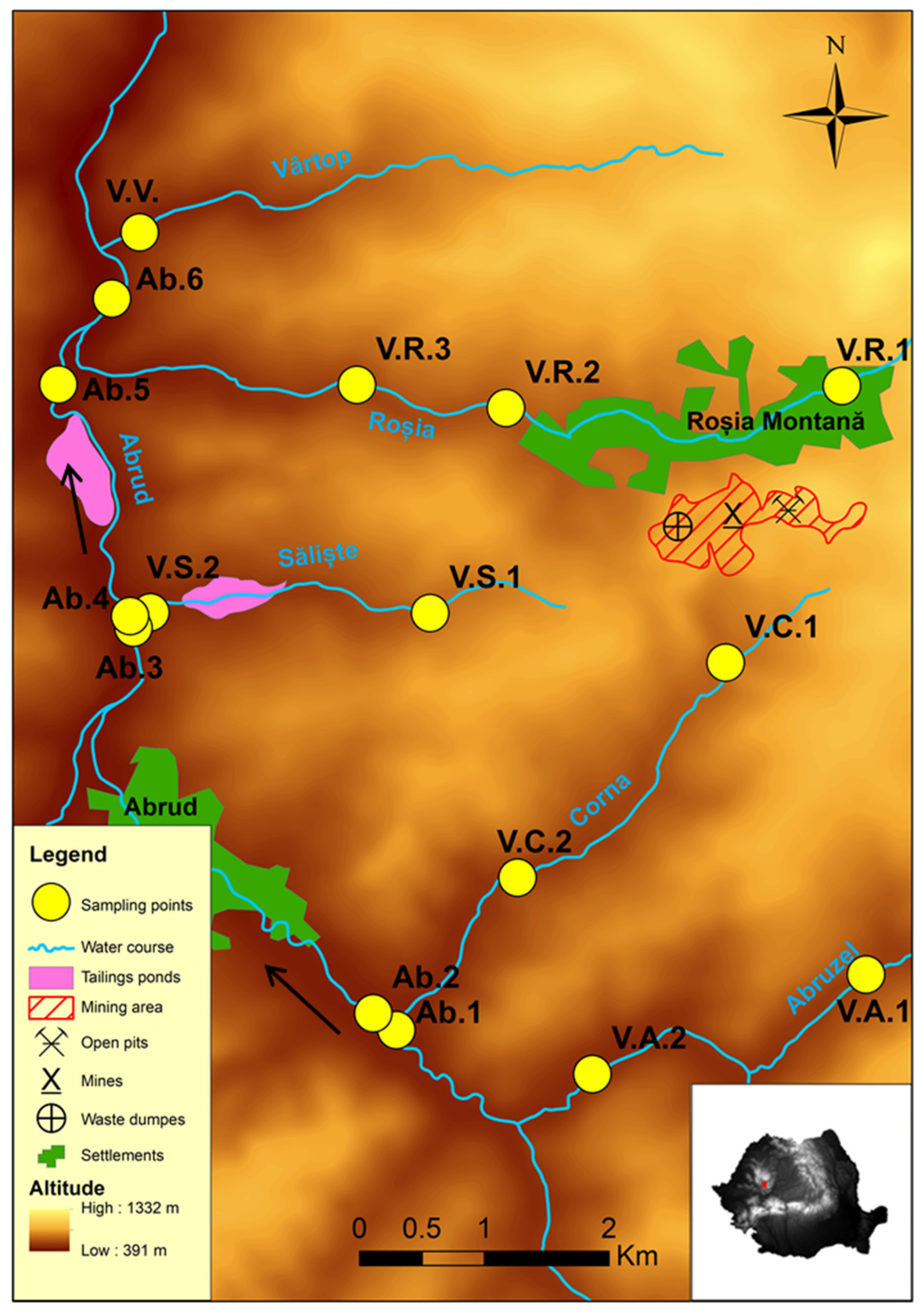
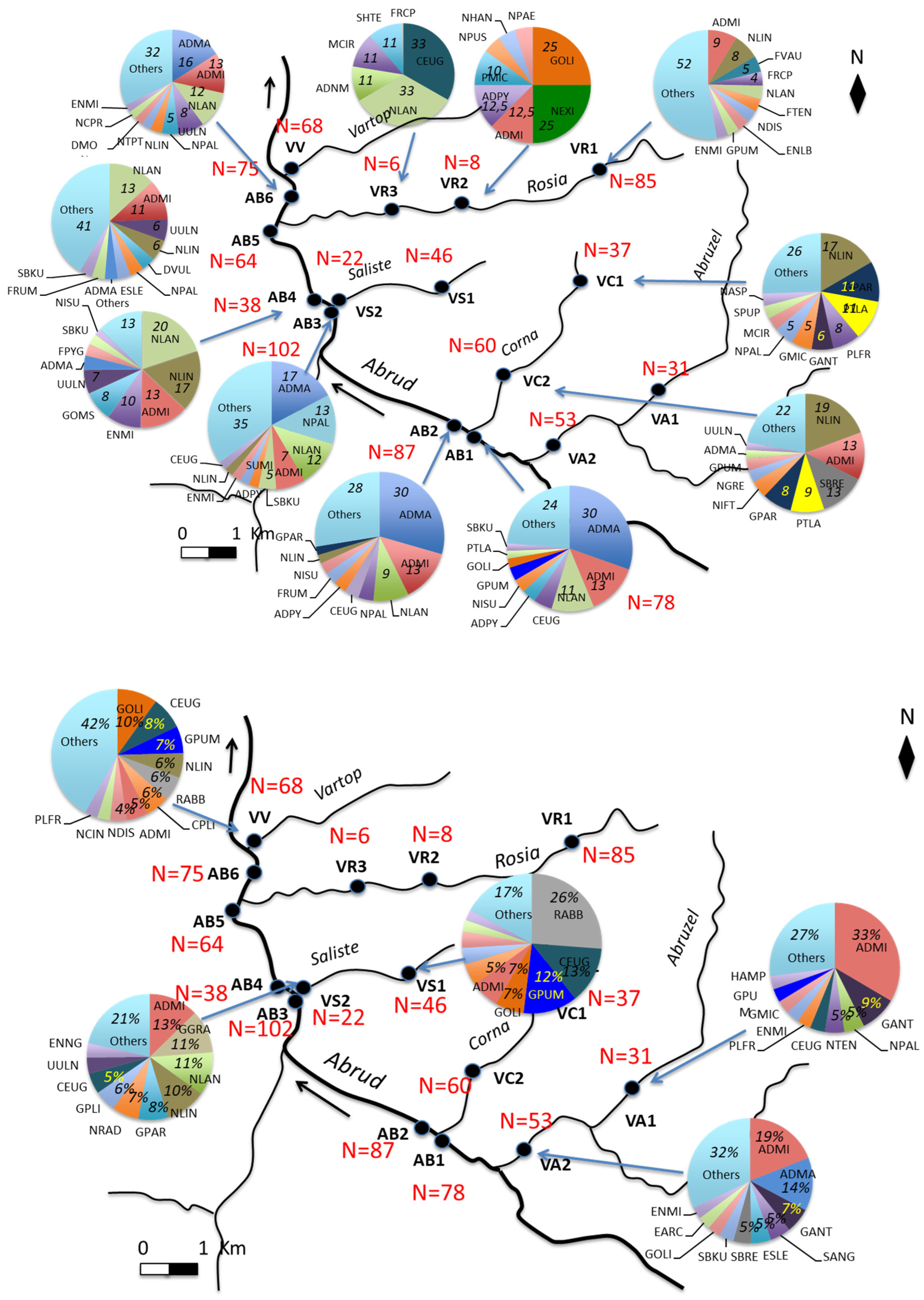
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental and Biological Data
Water Physicochemical and Heavy Metal Analyses
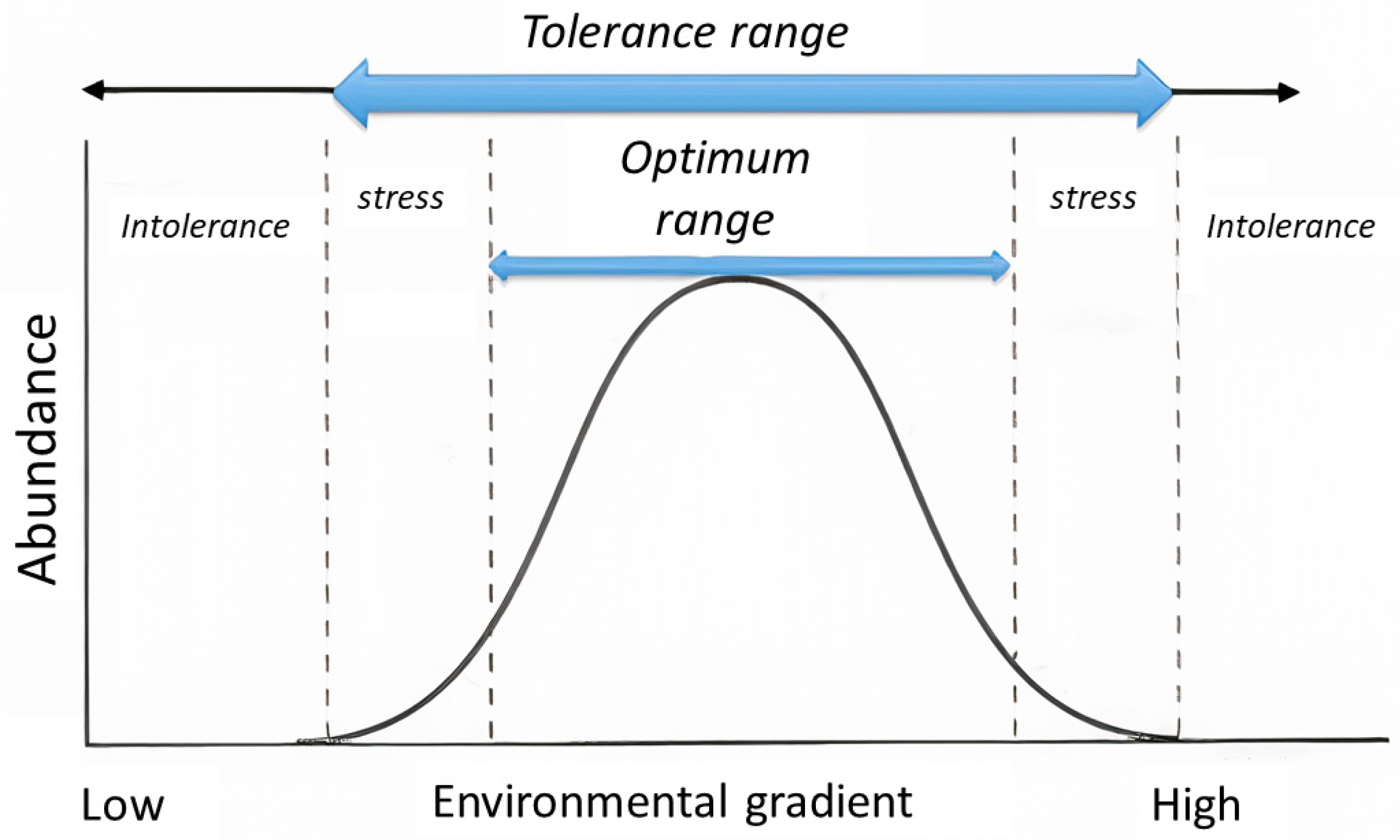
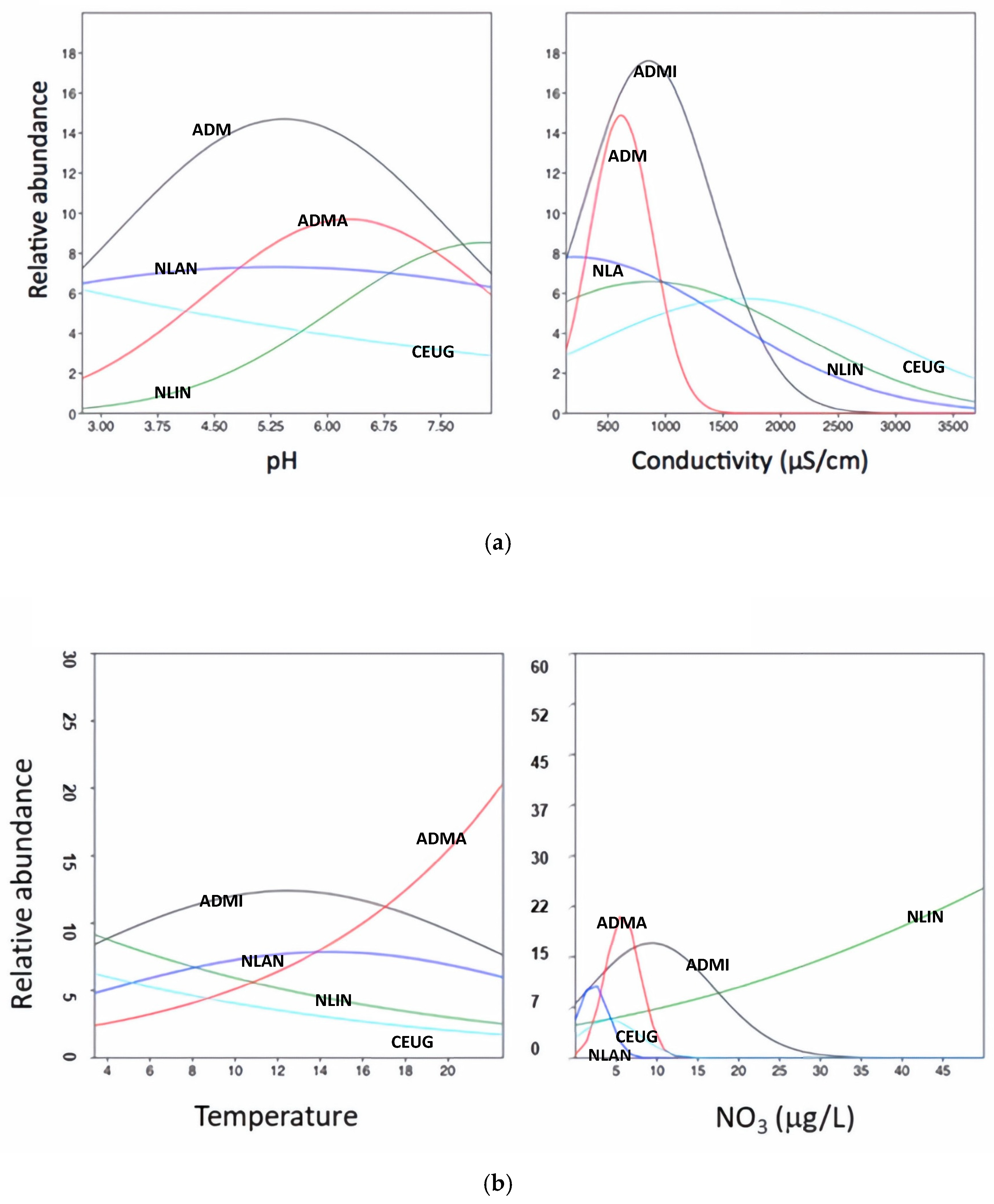
2.3. Ecological Profile
- (1)
- The selection of environmental variables: Based on their relevance in AMD contexts [23] and preliminary analyses, pH, electrical conductivity, temperature, and NO3− concentration were selected as the key environmental variables (corresponding to the X-axis in the conceptual response curves; cf. Figure 2).
- (2)
- Field survey: The diatom communities (bioindicators) were sampled concurrently with the in situ measurement of the selected environmental variables at each site. Two replicates were obtained from each sampling point.
- (3)
- The calculation of ecological optima and tolerances: The ecological optimum (weighted average abundance) and tolerance for each species with respect to each selected environmental variable were calculated using weighted averaging (WA) methods [24]. The optimum [Zn] was calculated using the Zelinka–Marvan formula:
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality
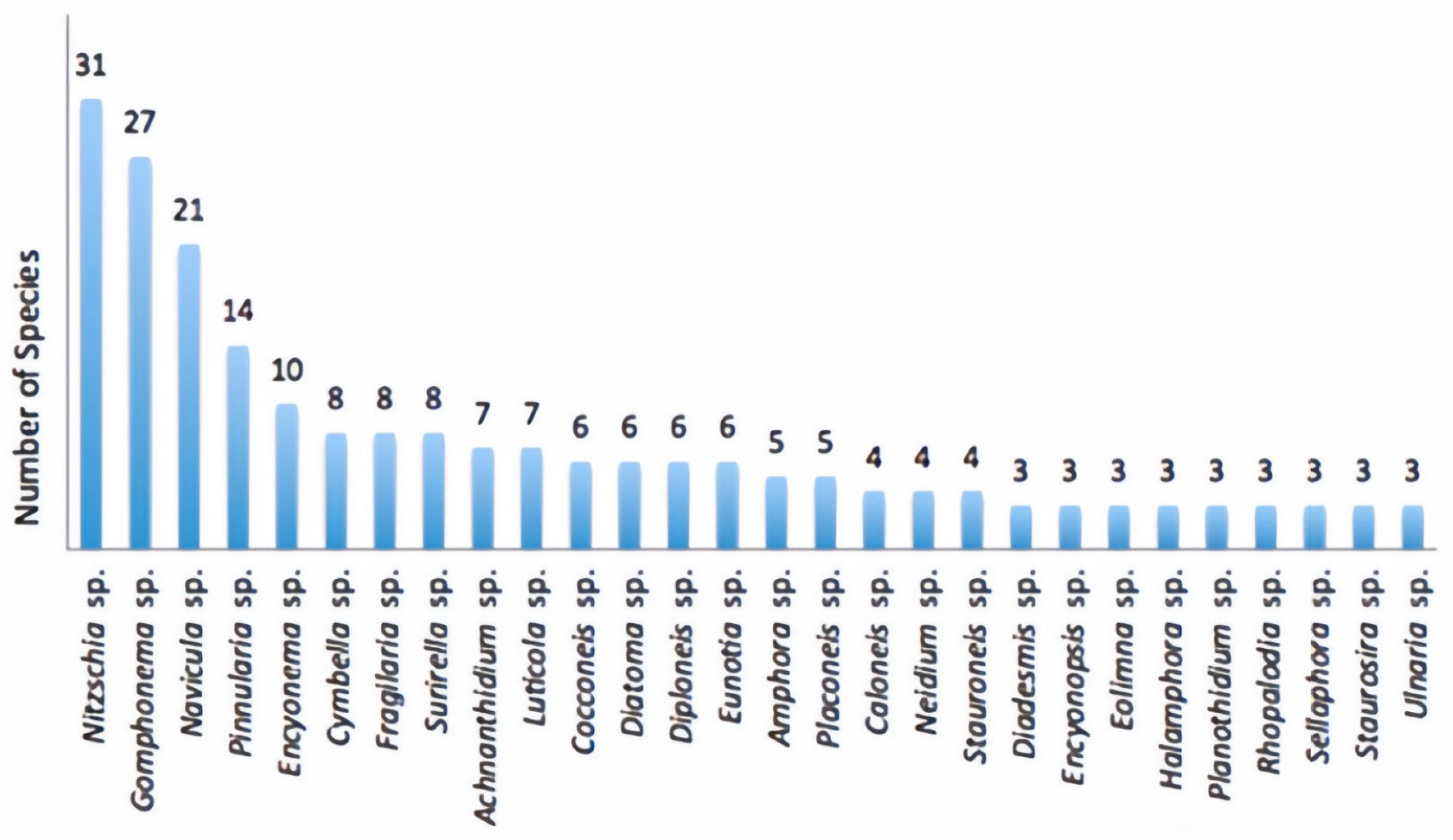
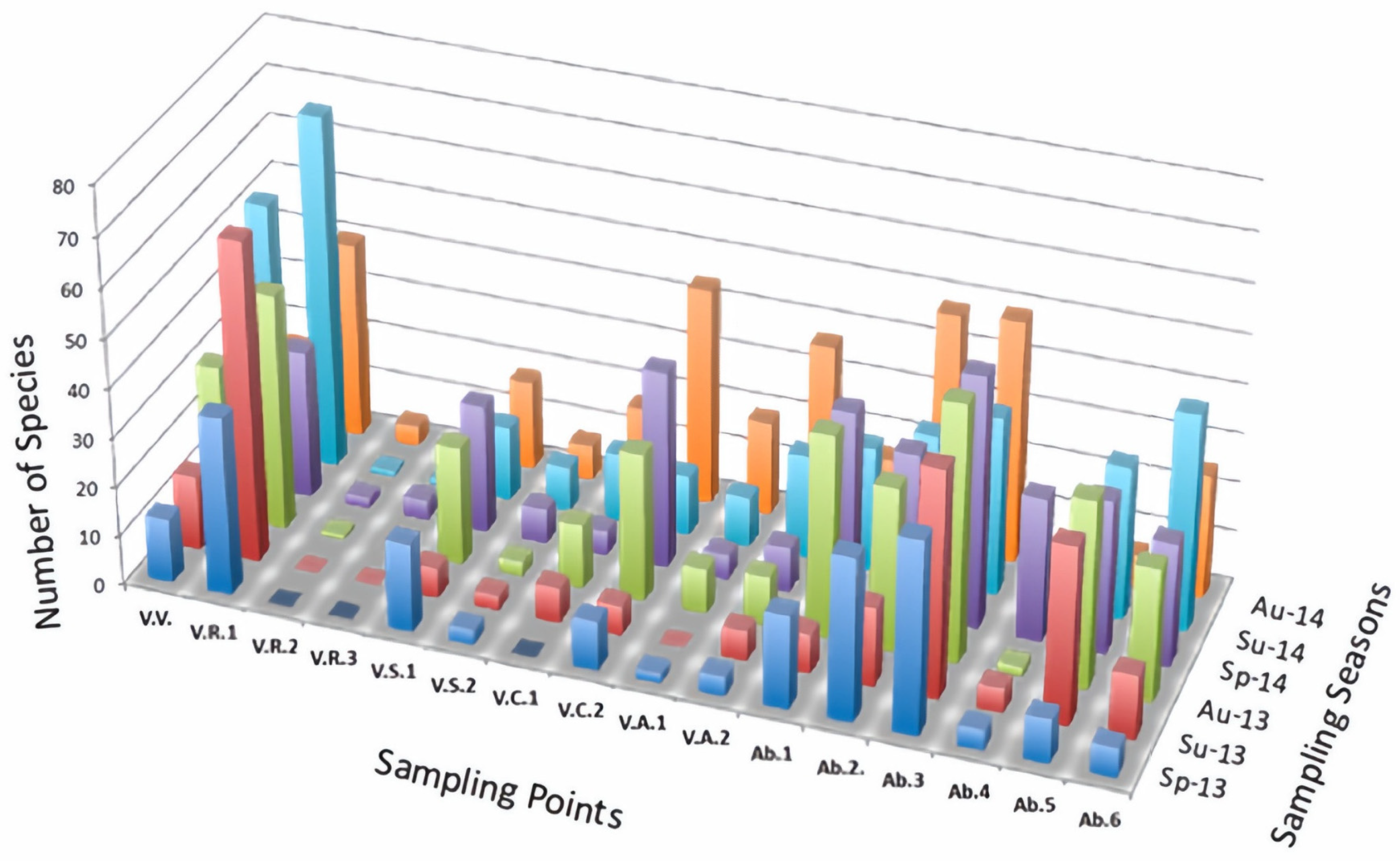
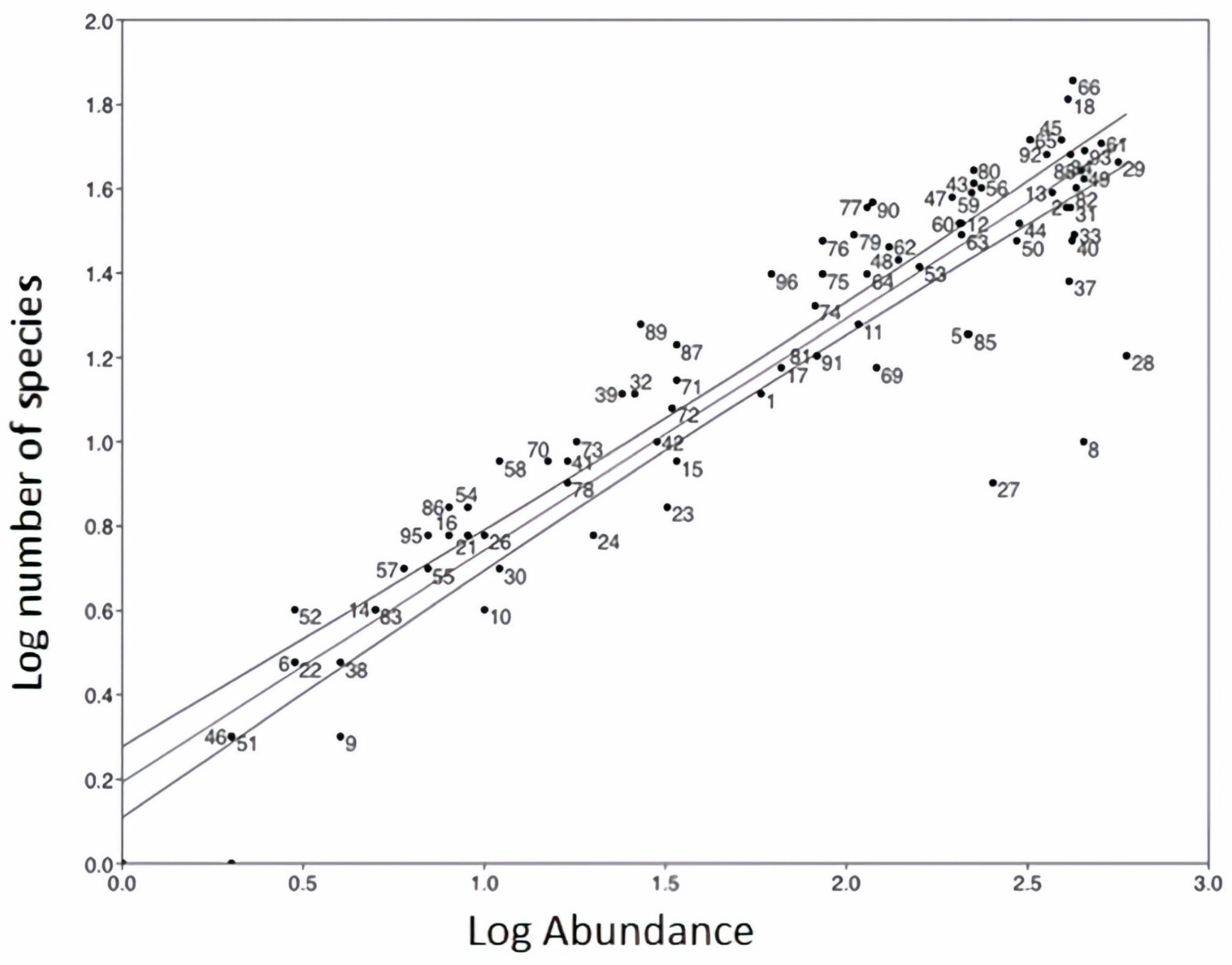
3.2. Diatom Flora Composition and Richness
3.3. Diatoms and Environmental Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. Water Quality and Diatom Community Patterns
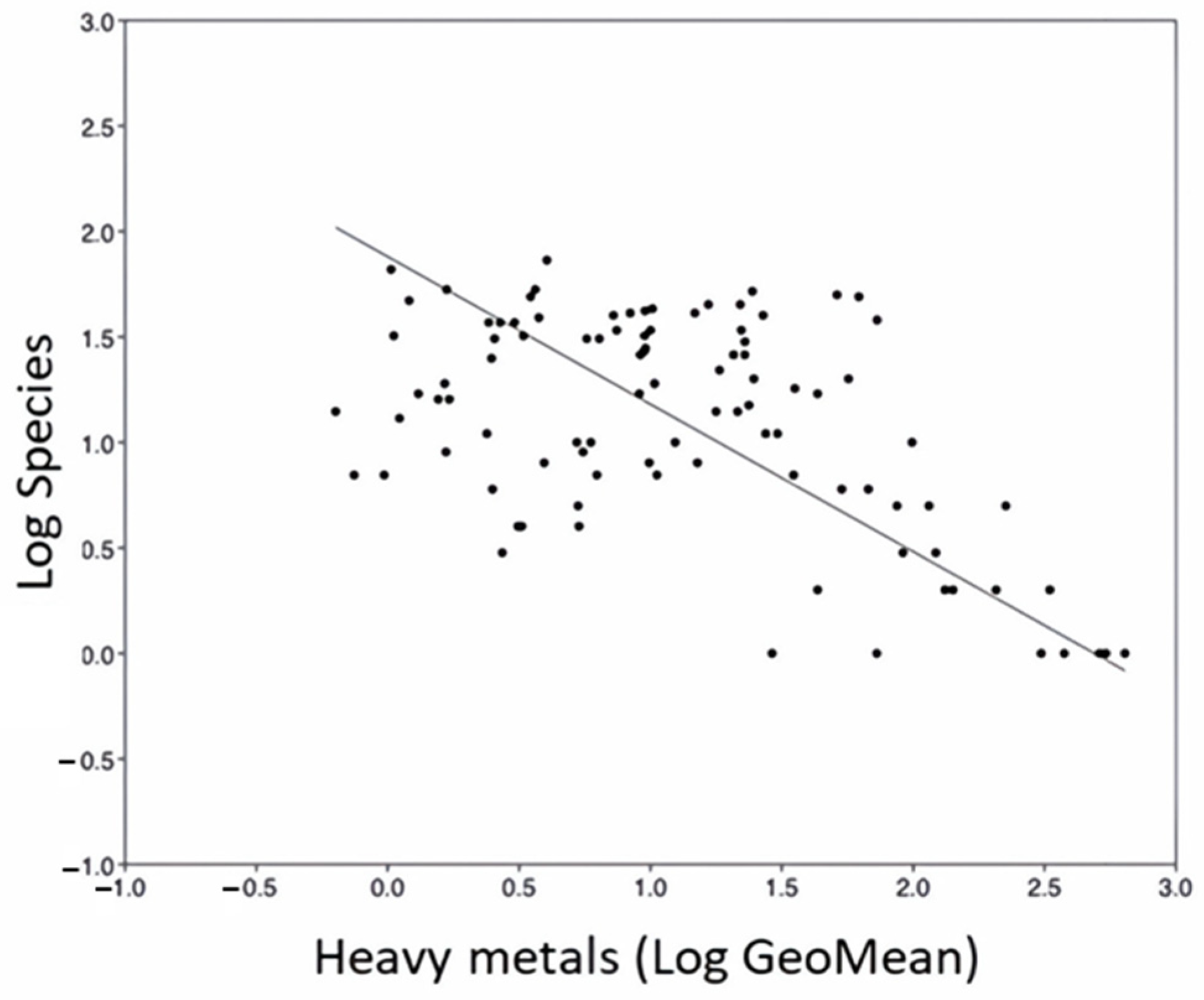
4.2. Influence of Heavy Metals and Acid Mine Drainage
4.3. Spatial Heterogeneity and Responses of Key Taxa
4.4. Contribution to Romanian Diatom Flora
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | Acid mine drainage |
| SEM | Scanning electronic microscopy |
| WQI | Water quality index |
| ADMI | Achnanthidium minutissimum |
| ADMA | Achnanthidium macrocephalum |
| NLAN | Navicula lanceolata |
| NLIN | Nitzschia linearis |
| CEUG | Cocconeis euglypta |
References
- Falkowski, P.G. The ocean’s invisible forest. Sci. Am. 2002, 287, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbrust, E.V. The life of diatoms in the world’s oceans. Nature 2009, 459, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciais, P.; Sabine, C.; Bala, G.; Bopp, L.; Brovkin, V.; Canadell, J.; Chhabra, A.; DeFries, R.; Galloway, J.; Heimann, M.; et al. Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 465–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoiston, A.S.; Ibarbalz, F.M.; Bittner, L.; Guidi, L.; Jahn, O.; Dutkiewicz, S.; Bowler, C. The evolution of diatoms and their biogeochemical functions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2017, 372, 20160397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prygiel, J.; Coste, M. Mise au point de l’indice Biologique Diatomée, an indice diatomique pratique applicable au réseau hydrographique français. Eau Ind. Nuis. 1998, 211, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Stoermer, E.F.; Smol, J.P. The Diatoms: Application for the Environmental and Earth Sciences; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G. Managing the ‘Monitoring Imperative’ in the Context of SDG Target 6.3 on Water Quality and Wastewater. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalapathy, R.; Karthikeyan, P. Application of diatom-based indices for monitoring environmental quality of riverine ecosystems: A review. In Environmental Management of River Basin Ecosystems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; Könönen, K. Comparative study of monitoring South-Finnish rivers and streams using macroinvertebrate and benthic diatom community structure. Aquat. Ecol. 2004, 38, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasselon, V.; Rimet, F.; Tapolczai, K.; Bouchez, A. Assessing ecological status with diatoms DNA metabarcoding: Scaling-up on a WFD monitoring network (Mayotte island, France). Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange-Bertalot, H.; Hofmann, G.; Werum, M.; Cantonati, M. Freshwater Benthic Diatoms of Central Europe: Over 800 Common Species Used in Ecological Assessment; Kelly, M.G., Ed.; Koeltz Botanical Books: Schmitten-Oberreifenberg, Germany, 2017; p. 942. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.G.; Chiriac, G.; Soare-Minea, A.; Hamchevici, C.; Birk, S. Defining ecological status of phytobenthos in very large rivers: A case study in practical implementation of the Water Framework Directive in Romania. Hydrobiologia 2019, 828, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.T.; Teixeira, P.; Almeida, S.F.P.; Ector, L.; Matos, J.X.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Impact of Acid Mine Drainage (AMD) on Water Quality, Stream Sediments and Periphytic Diatom Communities in the Surrounding Streams of Aljustrel Mining Area (Portugal). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 200, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, D.; Lewis, W., Jr.; McKnight, D. Effects of Stress from Mine Drainage on Diversity, Biomass, and Function of Primary Producers in Mountain Streams. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamțiu, I.; Al-Abed, S.; McKernan, J.; Baciu, C.; Gurzău, E.; Pogacean, O.; Bessler, S. Metal contamination in environmental media in residential areas around Romanian mining sites. Rev. Environ. Health 2017, 32, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baciu, C.; Goossens, M.; Reusen, I.; Tote, C.; Delalieux, S.; Raymaekers, D.; Dobrota, C.; Pop, C.; Varga, I.; Roba, C.; et al. Report on Roșia Montană Case Study Investigations, IMPACTMIN WP7.3 Project. 2012; 164p. Available online: https://impactmin.geonardo.com/downloads/impactmin_d73.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Papp, D.C.; Larkins, C.; Turunen, K.; Cociuba, I.; Baciu, C.; Cozma, A.; Lazăr, L.; Pop, I.C.; Roba, C.; Mänttäri, I.; et al. Geochemical and Isotope Methods for Assessing Contaminant Transport at Three Mine Sites: Kittilä Mine in Finland and Roșia Montană and Zlatna Mines in Romania; Report /ERA-MIN-SUSMIN-D5.1; 2018; 128p, Available online: https://tupa.gtk.fi/raportti/arkisto/89_2018.pdf (accessed on 27 February 2025).
- Azzali, E.; Marescotti, P.; Frau, F.; Dinelli, E.; Carbone, C.; Capitani, G.; Lucchetti, G. Mineralogical and chemical variations of ochreous precipitates from acid sulphate waters (asw) at the Roşia Montană gold mine (Romania). Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3567–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13946; Water Quality—Guidance Standard for the Routine Sampling and Pretreatment of Benthic Diatoms from Rivers and Lakes. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Hofmann, G.; Werum, M.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Diatomeen im Süßwasser-Benthos von Mitteleuropa. Bestimmungsflora Kieselalgen für die ökologische Praxis. Über 700 der häufigsten Arten und ihre Ökologie; Koeltz Scientific Books: Königstein, Germany, 2013; 908p. [Google Scholar]
- Nasirian, M. A new water quality index for environmental contamination contributed by mineral processing: A case study of amang (tin tailing) processing activity. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 7, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A water quality index-do we dare? Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Olenici, A.; Blanco, S.; Borrego-Ramos, M.; Momeu, L.; Baciu, C. Exploring the effects of acid mine drainage on diatom teratology using geometric morphometry. Ecotoxicology 2017, 26, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, M.; Marvan, P. Zur Präzisierung der biologischen klassifikation der Reinheit flieβender Gewässer. Arch. Fur Hydrobiol. 1961, 57, 389–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelford, V.E. Animal Communities in Temperate America: As Illustrated in the Chicago Region: A Study in Animal Ecology; No. 5; Geographic Society of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 1913. [Google Scholar]
- Lecointe, C.; Coste, M.; Prygiel, J. “Omnidia”: Software for taxonomy, calculation of diatom indices and inventories management. Hydrobiologia 1993, 269, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, M.B.; García-Ruíz, R.; Viñegla, B.; Carreira, J.A. Microbiological rates and enzyme activities as indicators of functionality in soils affected by the Aznalcóllar toxic spill. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.; Looman, C.W. Weighted averaging, logistic regression and the Gaussian response model. Vegetatiot 1986, 65, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustedt, F. Systematische und okologische Untersuchungen über die Diatomeenflora von Java, Bali und Sumatra. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1938, 15, 131–177. [Google Scholar]
- McFarland, B.; Hill, B.; Willingham, W. Abnormal fragilaria spp. (Bacillariophyceae) in streams impacted by mine drainage. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1997, 12, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsher, S.; Verb, R.; Vis, M. Analysis of acid mine drainage impacted streams using a periphyton index. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2004, 19, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Monoylov, K. Diatom Deformities from an Acid Mine Drainage Site at Friendship Hills National Historical Site, Pennsylvania. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2007, 22, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallanzasca, I.; Boutry, S.; Laviale, M.; Quinton, E.; Morin, S. Development of a collaborative web platform documenting the diversity and extent of diatom deformities. Bot. Lett. 2024, 171, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenici, A.; Blanco, S.; Borrego-Ramos, M.; Jiménez-Gómez, F.; Guerrero, F.; Momeu, L.; Baciu, C. A new diatom teratology driven by metal pollution in a temperate river (Roșia Montanǎ, Romania). Ann. Bot. 2019, 9, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkwitz, G.R.; Marsson, M. Okologie der pflanzlichen Saprobien. Berrichten Dtsch. Bot. Ges. 1908, 26, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, R. A proposed biological measure of stream conditions, based on a survey of the Conestoga Basin, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. USA 1949, 101, 277–341. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, C. Étude des Effets de la Pollution Métallique (Cd/Zn) sur la Structure des Communautés de Diatomées Périphytiques des Cours d’eau: Approches Expérimentales In Situ et en Laboratoire. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Bordeaux-I, Bordeaux, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, C.; Feurtet-Mazel, A.; Coste, M.; Boudou, A. Effects of cadmium stress on periphytic diatom communities in indoor artificial streams. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; McGowan, S.; Yang, X. Diatom response to heavy metal pollution and nutrient enrichment in an urban lake: Evidence from paleolimnology. Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2014, 50, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurozzi, D.; Cesarini, G.; Scalici, M. Diatoms as bioindicators for health assessments of ephemeral freshwater ecosystems: A comprehensive review. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Paturzo, M.; Sardo, A.; Orefice, I.; Yu, Q.; Rubano, A.; Paparo, D. Toxic Effect of Metal Doping on Diatoms as Probed by Broadband Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. Molecules 2022, 27, 5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Dubey, R.S. Lead toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanità di Toppi, L.; Gabbrielli, R. Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1999, 41, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yruela, I. Copper in plants: Acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2005, 32, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.; Willingham, W.; Parrish, L.; McFarland, B. Periphyton community responses to elevated metal concentrations in a Rocky Mountain stream. Hydrobiologia 2000, 428, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.T.; Alexander, A.C.; Almeida, S.F.P.; Ferreira da Silva, E.; Culp, J.M. Benthic diatom communities in streams from zinc mining areas in continental (Canada) and Mediterranean climates (Portugal). Water Qual. Res. J. 2013, 48, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servida, D.; Comero, S.; Dal Santo, M.; Capitani, L.; Grieco, G.; Marescotti, P.; Porro, S.; Forray, F.L.; Gal, A.; Szakacs, A. Waste rock dump investigation at Roşia Montană gold mine (Romania): A geostatistical approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, G.; Brewer, P.A.; Macklin, M.G.; Serban, M.; Balteanu, D.; Driga, B. Heavy metal contamination in the Arieş River catchment, western Romania: Implications for development of the Roșia Montană gold deposit. J. Geochem. Explor. 2005, 86, 26–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșia Montană Gold Corporation. Report on Environmetal Impact Assessment Study; Roșia Montană Gold Corporation: Bucharest, Romania, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sabater, S. Diatom communities as indicators of environmental stress in the Guadiamar River, S-W. Spain, following a major mine tailings spill. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-H.; Luo, B.; Zhou, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-H. Generalized solutions for advection–dispersion transport equations subject to time- and space-dependent internal and boundary sources. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 178, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cărăuş, I. Algae of Romania. A Distributional Checklist of Actual Algae, 3rd ed.; University of Bacău: Bacău, Romania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Momeu, L.; Peterfi, L.S.; Blaga, L. Planktonic algal communities occurring in the wetlands of the Cefa Nature Park (Crișana, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. Cefa Nat. Park 2012, 13, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Butiuc-Keul, A.; Momeu, L.; Craciunas, C.; Dobrota, C.; Cuna, S.; Balas, G. Physico-chemical and biological studies on water from Arieş River (Romania). J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florescu, H.M.; Cîmpean, M.; Momeu, L.; Leonte, L.; Bodea, D.; Battes, K.P. Ecological analyses on benthic diatom and invertebrate communities. Stud. Univ. Babeș-Bolyai Biol. 2015, 1, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Szigyarto, I.L.; Bakos, A. Diatoms and water quality of the Zetea and sourrounding river courses (Harghita County, Romania). Contrib. Bot. 2015, 50, 151–164. [Google Scholar]
- Buczko, K. Guide to diatoms in mountain lakes in the retezat mountains, South Carpathians, Romania. Stud. Bot. Hung. 2016, 47, 9–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szigyarto, I.L.; Buczkó, K.; Rákossy, I.; May, Z.; Urak, I.; Zsigmond, A.R. Contrasting diatom diversity in lentic and lotic habitats of Romanian peat bogs and the relation to environmental variables. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2017, 189, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidoni, D.G.; Nicorescu, V.; Negrea, S.; Stoica, C.; Pahomi, A.; Nita-Lazar, M. Diatoms. A viable tool for quantifying surface water pollution. Rom. J. Ecol. Environ. Chem. 2023, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeu, L.; Péterfi, L.Ş. Evaluarea calităţii apei din bazinul de drenaj al râului Arieş folosind diatomeele epilitice ca bioindicatori. Contrib. Bot. 2007, XLII, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Momeu, L.; Péterfi, L.Ş. Assesment of the ecological state of rivers based on benthic algae especially diatoms. Stud. Univ. Babeș-Bolyai Biol. 2009, 54, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Szekely-Andorko, J.; Momeu, L.; Péterfi, L.Ș. Structure of the benthic diatom communities from Arieș river catchment area (Transylvania, Romania). Contrib. Bot. 2011, XLVI, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Battes, K.P.; Cîmpean, M.; Momeu, L.; Avram, A.; Battes, K.W.; Stoica, I.V. Multiple impact assessment and water quality based on diatom, benthic invertebrate and fish communities in the Arieș River catchment area (Transylvania, Romania). Stud. Univ. Babeș-Bolyai Biol. 2018, 63, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sites | WQI Range | Quality |
|---|---|---|
| V.A.1 | 30–40 | Bad |
| V.A.2 | 40–50 | Moderate |
| V.C.1 | 30–40 | Bad |
| V.C.2 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| V.S.1 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| V.S.2 | 40–50 | Moderate |
| V.R.1 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| V.R.2 | 20–30 | Very bad |
| V.R.3 | 20–30 | Very bad |
| V.V. | 50–60 | Moderate |
| Ab.1 | 40–50 | Moderate |
| Ab.2 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| Ab.3 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| Ab.4 | 40–50 | Moderate |
| Ab.5 | 50–60 | Moderate |
| Ab.6 | 40–50 | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olenici, A.; Blanco, S.; Jiménez-Gómez, F.; Borrego-Ramos, M.; Baciu, C. Effects of Water Pollution on Diatom Communities of Roșia Montană Mining Area, Romania. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104592
Olenici A, Blanco S, Jiménez-Gómez F, Borrego-Ramos M, Baciu C. Effects of Water Pollution on Diatom Communities of Roșia Montană Mining Area, Romania. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104592
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlenici, Adriana, Saúl Blanco, Francisco Jiménez-Gómez, María Borrego-Ramos, and Călin Baciu. 2025. "Effects of Water Pollution on Diatom Communities of Roșia Montană Mining Area, Romania" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104592
APA StyleOlenici, A., Blanco, S., Jiménez-Gómez, F., Borrego-Ramos, M., & Baciu, C. (2025). Effects of Water Pollution on Diatom Communities of Roșia Montană Mining Area, Romania. Sustainability, 17(10), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104592








