Has Climate Change Affected the Occurrence of Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Rainfall Events in Poland?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Heat Waves
2.2.2. Heavy Precipitation Events
2.2.3. Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Precipitation Events
2.2.4. Case Study Characteristics
3. Results
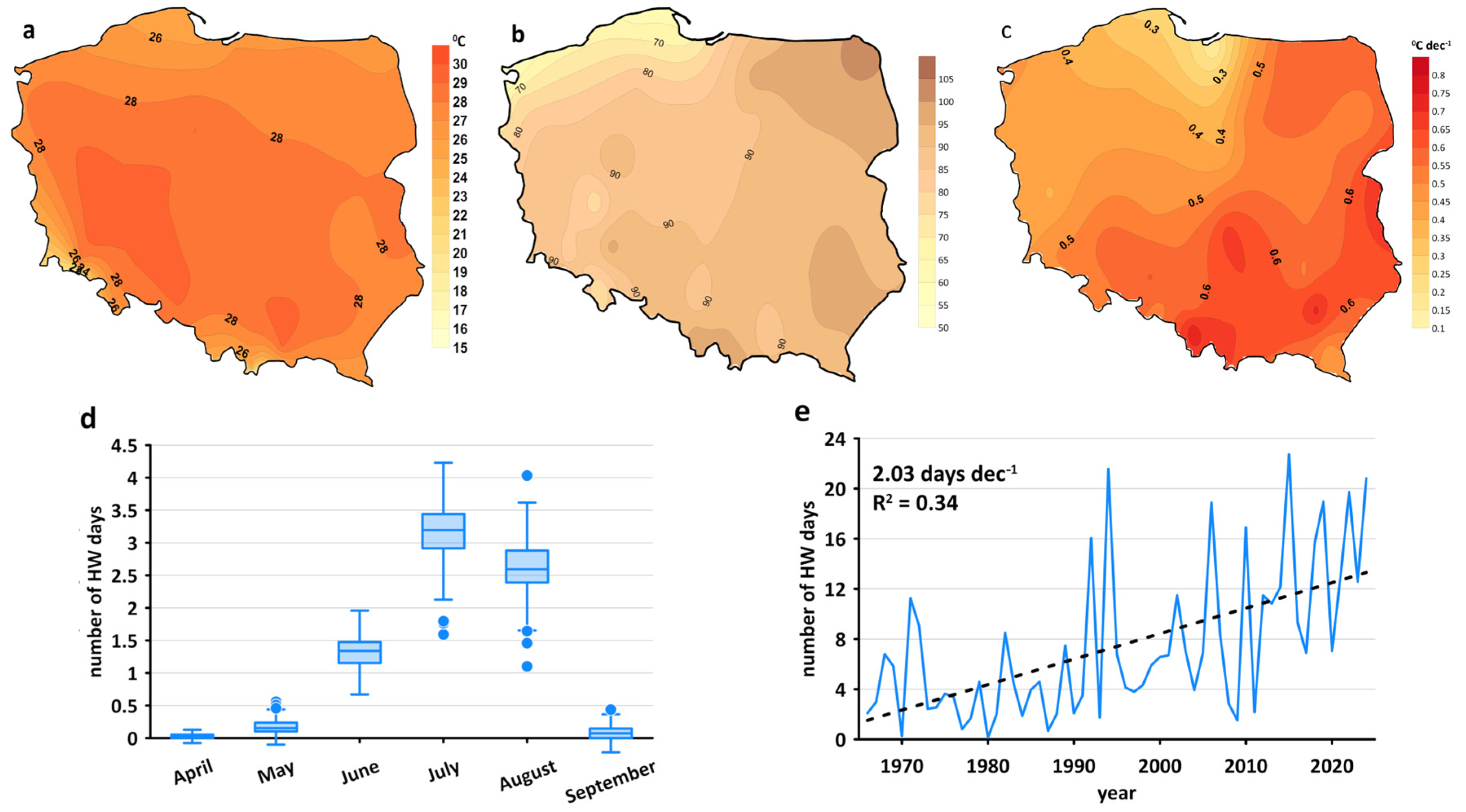
3.1. Heat Wave Characteristics
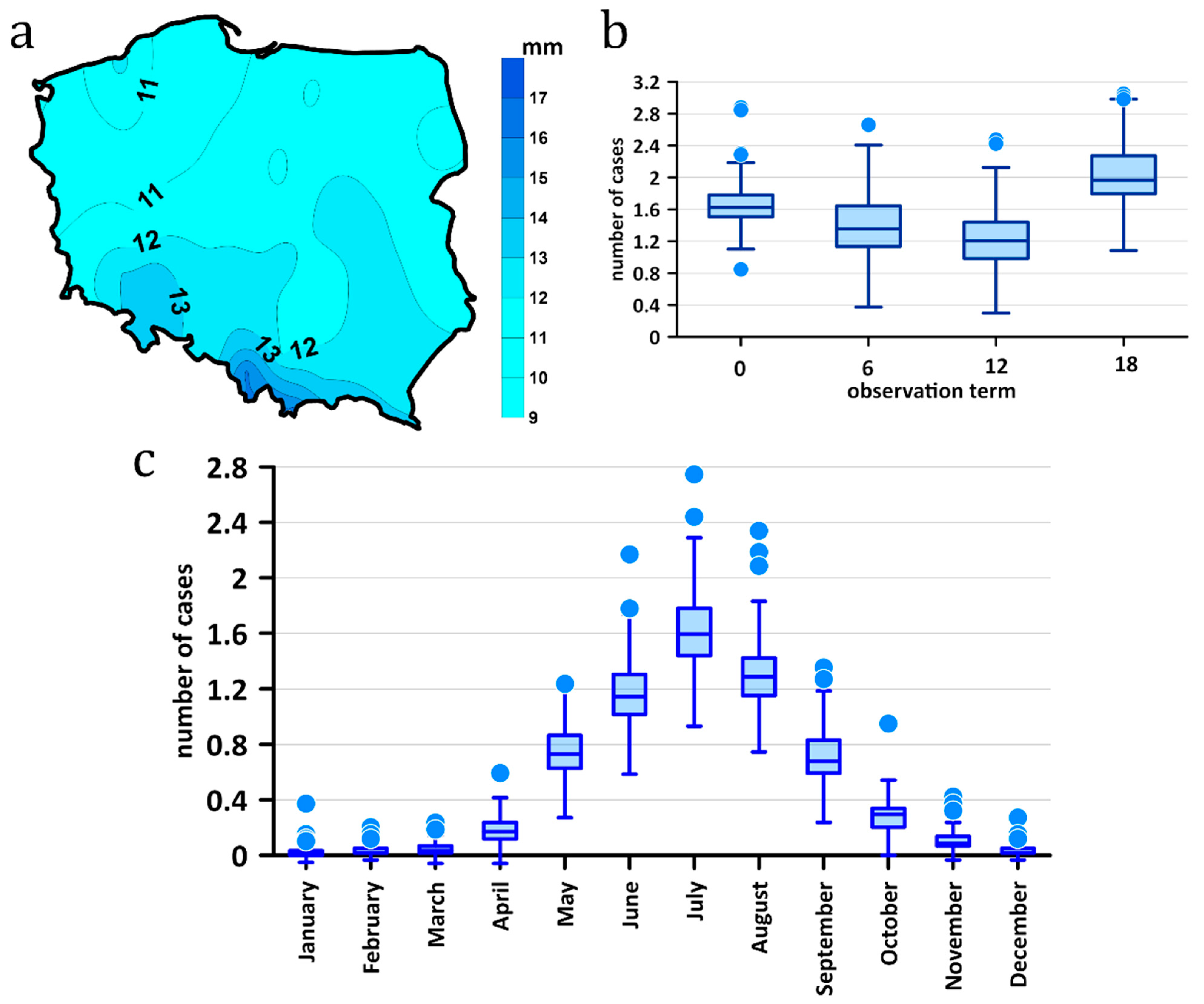
3.2. Heavy Precipitation Characteristic
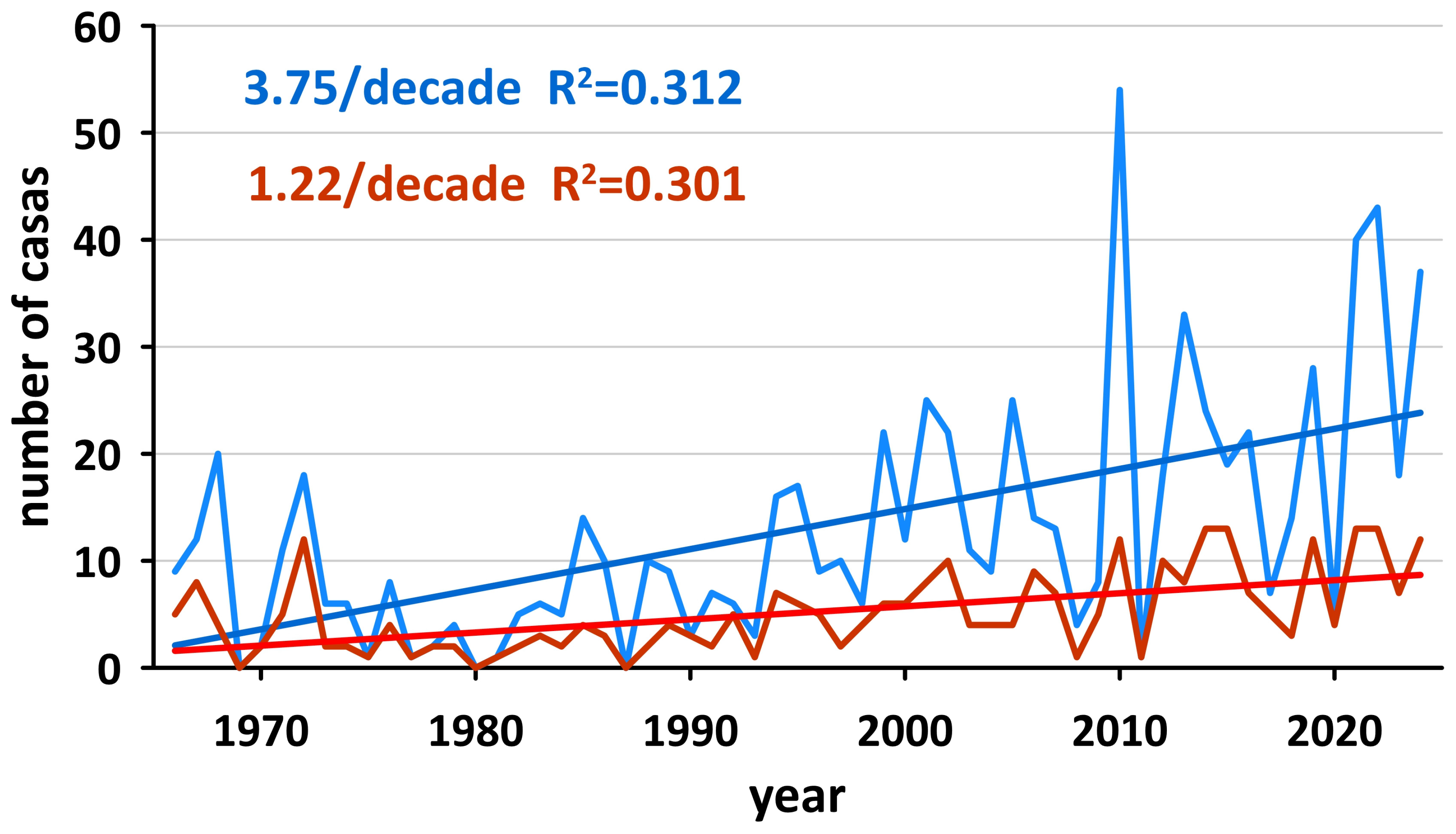
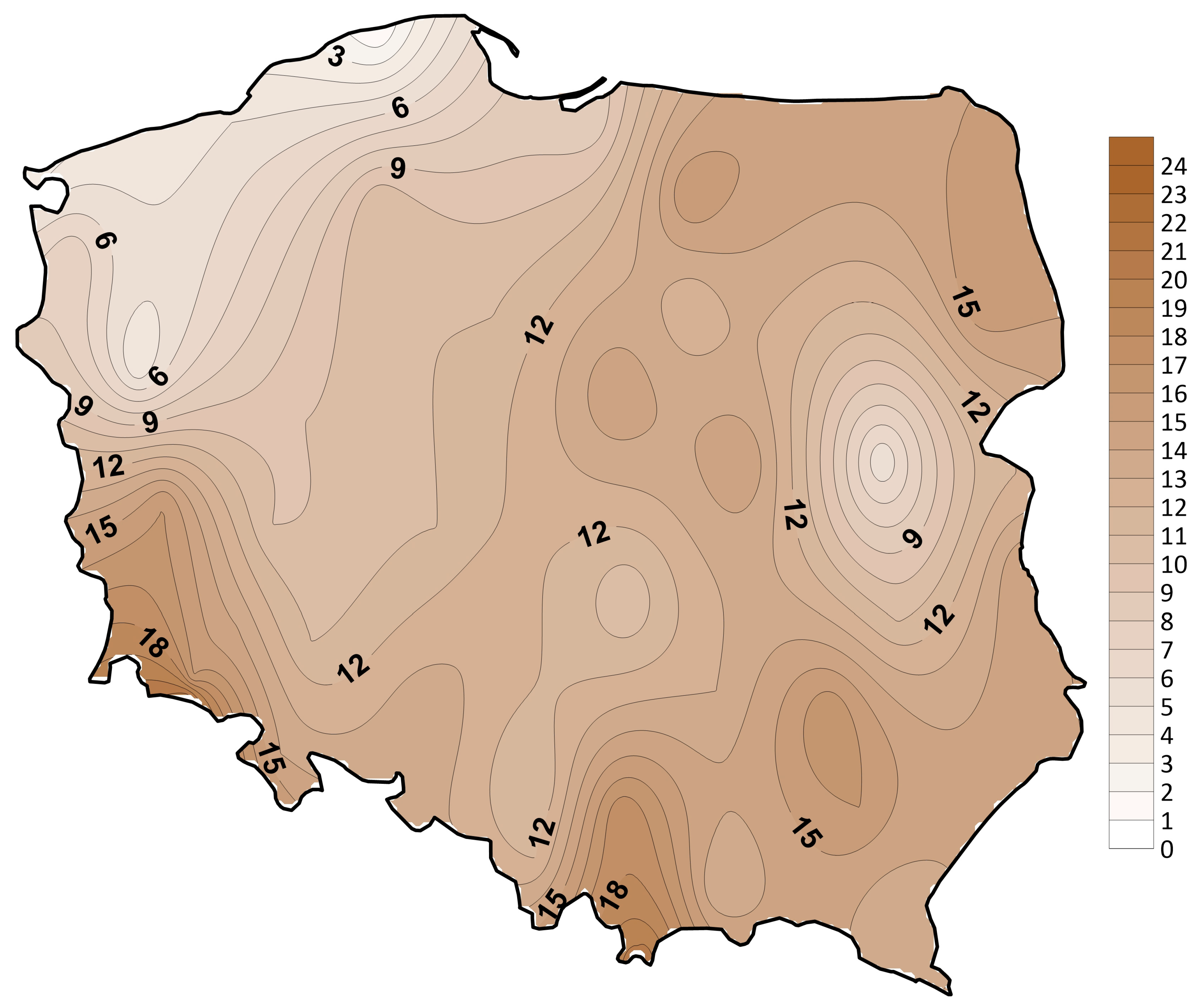
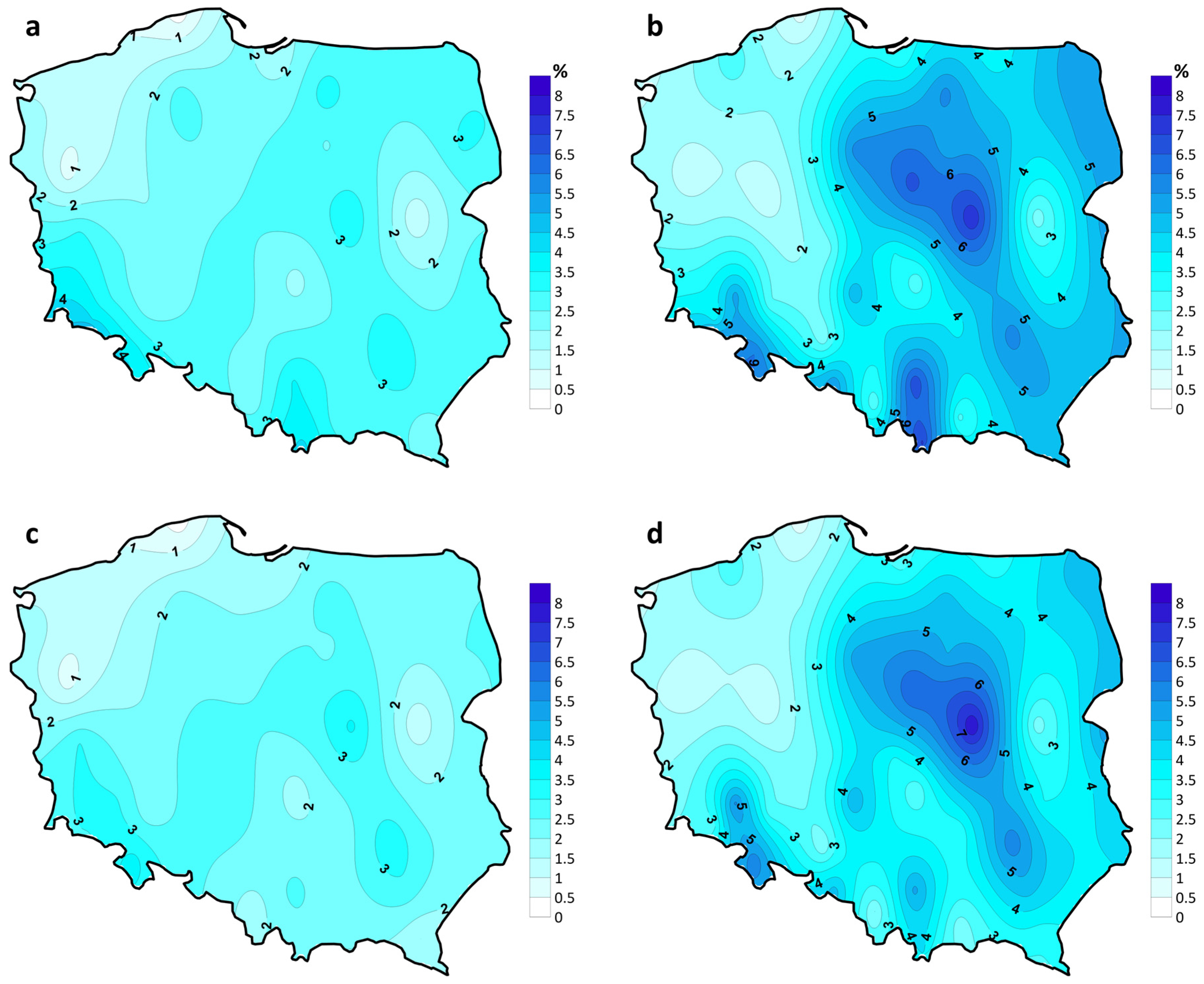
3.3. Compound HWHP Characteristics
3.4. Case Study
3.4.1. HWHP Event on 8 July 2001
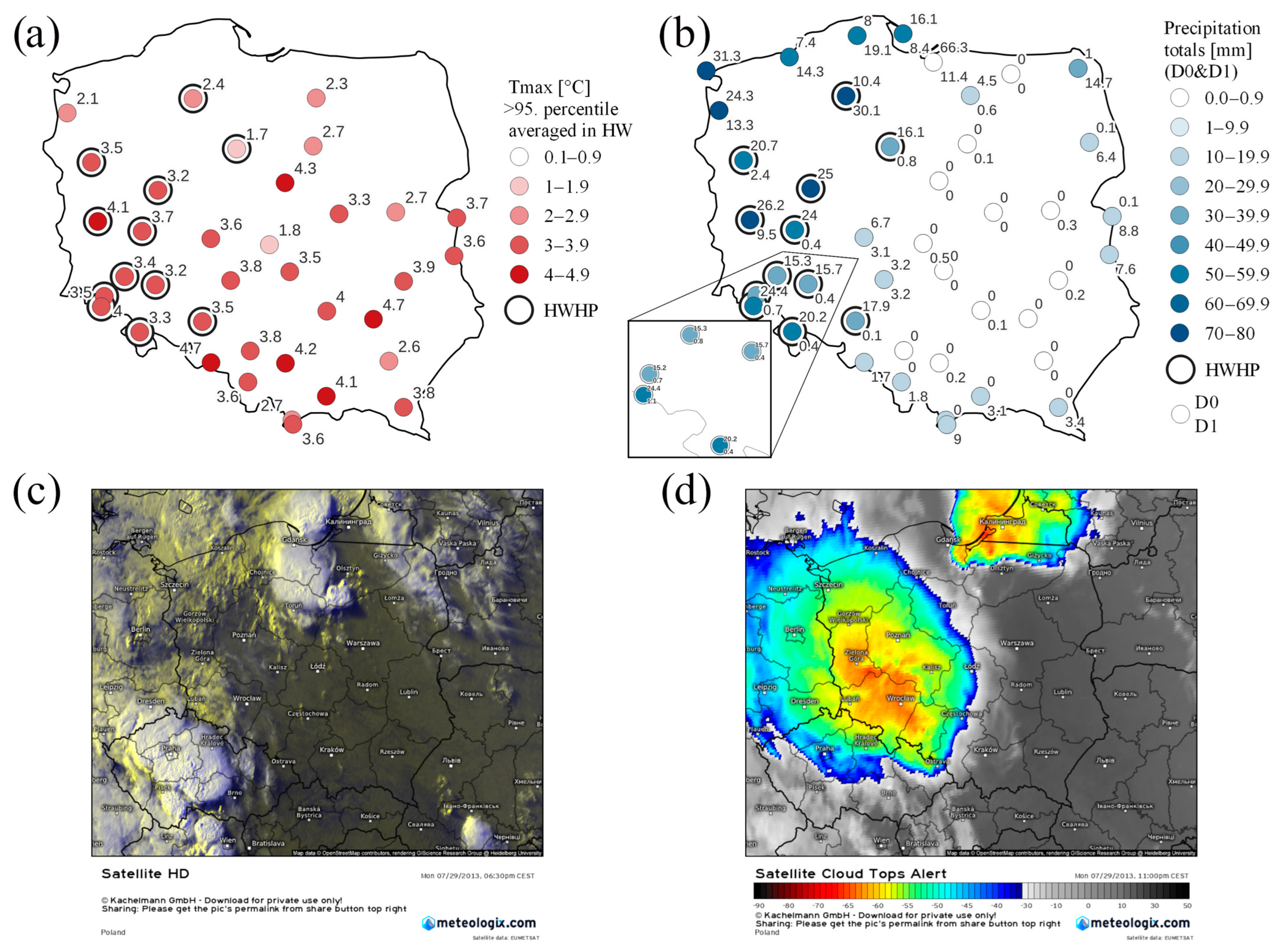
3.4.2. HWHP Event on 29 July 2013
3.4.3. HWHP Event on 10 August 2018
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, D.; Kotova, L.; Teichmann, C.; Sobolowski, S.P.; Vautard, R.; Donnelly, C.; Koutroulis, A.G.; Grillakis, M.G.; Tsanis, I.K.; Damm, A.; et al. Climate Impacts in Europe Under +1.5 °C Global Warming. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Karoly, D.J. Climate Extremes in Europe at 1.5 and 2 Degrees of Global Warming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 114031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Nicholls, N.; Easterling, D.; Goodess, C.M.; Kanae, S.; Kossin, J.; Luo, Y.; Marengo, J.; McInnes, K.; Rahimi, M.; et al. Changes in Climate Extremes and Their Impacts on the Natural Physical Environment. In Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Field, C.B., Barros, V., Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Dokken, D.J., Ebi, K.L., Mastrandrea, M.D., Mach, K.J., Plattner, G.-K., Allen, S.K., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 109–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zscheischler, J.; Martius, O.; Westra, S.; Bevacqua, E.; Raymond, C.; Horton, R.M.; van den Hurk, B.; AghaKouchak, A.; Jézéquel, A.; Mahecha, M.D.; et al. A Typology of Compound Weather and Climate Events. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazdiyasni, O.; AghaKouchak, A. Substantial Increase in Concurrent Droughts and Heatwaves in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11484–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mujumdar, P. Increasing Frequency and Spatial Extent of Concurrent Meteorological Droughts and Heatwaves in India. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciais, P.; Reichstein, M.; Viovy, N.; Granier, A.; Ogée, J.; Allard, V.; Aubinet, M.; Buchmann, N.; Bernhofer, C.; Carrara, A.; et al. Europe-Wide Reduction in Primary Productivity Caused by the Heat and Drought in 2003. Nature 2005, 437, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, K.P.; Mishra, A.K. How Unusual Is the 2022 European Compound Drought and Heatwave Event? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibig, J.; Jȩdruszkiewicz, J. Warm and Dry Compound Events in Poland. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating Soil Moisture–Climate Interactions in a Changing Climate: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.G.; Gentine, P.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Teuling, A.J. Land–Atmospheric Feedbacks During Droughts and Heatwaves: State of the Science and Current Challenges. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1436, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Slater, L.; Gu, L.; Liao, Z.; Guo, S.; Gentine, P. Global Increases in Lethal Compound Heat Stress: Hydrological Drought Hazards Under Climate Change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.; White, C.J.; Fowler, H.J.; Westra, S. Temporally Compounding Heatwave–Heavy Rainfall Events in Australia. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.; Fowler, H.J.; Westra, S.; Ali, H.; Peleg, N.; White, C.J. Compound Extreme Hourly Rainfall Preconditioned by Heatwaves Most Likely in the Mid-Latitudes. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 40, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Wang, S. Higher Probability of Occurrence of Hotter and Shorter Heat Waves Followed by Heavy Rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenderink, G.; van Meijgaard, E. Increase in Hourly Precipitation Extremes Beyond Expectations from Temperature Changes. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, P.; Moseley, C.; Haerter, J.O. Strong Increase in Convective Precipitation in Response to Higher Temperatures. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Lewis, E.; Pritchard, D. Consistent Large-Scale Response of Hourly Extreme Precipitation to Temperature Variation Over Land. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibig, J.; Piotrowski, P. Impact of the Air Temperature and Atmospheric Circulation on Extreme Precipitation in Poland. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4533–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Villarini, G. Deadly Compound Heat Stress-Flooding Hazard Across the Central United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barendrecht, M.H.; Matanó, A.; Mendoza, H.; Weesie, R.; Rohse, M.; Koehler, J.; de Ruiter, M.; Garcia, M.; Mazzoleni, M.; Aerts, J.C.J.H.; et al. Exploring Drought-to-flood Interactions and Dynamics: A Global Case Review. Wires Water 2024, 11, e1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibig, J. Hot Days and Heat Waves in Poland in the Period 1951–2019 and the Circulation Factors Favoring the Most Extreme of Them. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibig, J. Heat Waves in Poland in the Period 1951–2015: Trends, Patterns and Driving Factors. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. 2017, 6, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, M.; Tomczyk, A.M. Impact of Atmospheric Circulation on the Occurrence of Very Strong and Extreme Cold Stress in Poland. Quaest. Geogr. 2022, 41, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.M.; Bednorz, E.; Półrolniczak, M.; Kolendowicz, L. Strong Heat and Cold Waves in Poland in Relation with the Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1909–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łupikasza, E. Seasonal Patterns and Consistency of Extreme Precipitation Trends in Europe, December 1950 to February 2008. Clim. Res. 2017, 72, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Łupikasza, E.; Małarzewski, Ł. Precipitation Change. In Climate Change in Poland: Past, Present, Future; Falarz, M., Ed.; Springer Climate: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 349–373. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, S.E.; Alexander, L.V. On the Measurement of Heat Waves. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4500–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchcik, M. Defining Heat Wave—Different Approaches. Geogr. Pol. 2006, 79, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kossowska-Cezak, U. Heat Waves and Heat Periods—Distinguishing Methods and Results of Application. Pr. Geogr. 2010, 123, 143–149. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Krzyżewska, A. The Review of the Methods Defining Heat Waves and Frost Waves. Przegląd Geofiz. 2014, 59, 157–173. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Abaurrea, J.; Asín, J.; Cebrián, A.C.; Centelles, A. Modeling and forecasting extreme heat events in the central Ebro Valley, a continental Mediterranean area. Glob. Planet. Change 2007, 57, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Jia, B.; Liu, L.; Tang, Z.; Chen, J. Amplified Temperature Sensitivity of Extreme Precipitation Events Following Heat Stress. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report, Summary for Policymakers. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Core Writing Team; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Sauter, C.; Catto, J.L.; Fowler, H.J.; Westra, S.; White, C.J. Compounding Heatwave-Extreme Rainfall Events Driven by Fronts, High Moisture, and Atmospheric Instability. JGR Atmos. 2023, 128, e2023JD038761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Months | Number of Days |
|---|---|
| May | 6 |
| June | 59 |
| July | 136 |
| August | 91 |
| September | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wibig, J.; Jędruszkiewicz, J. Has Climate Change Affected the Occurrence of Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Rainfall Events in Poland? Sustainability 2025, 17, 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104447
Wibig J, Jędruszkiewicz J. Has Climate Change Affected the Occurrence of Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Rainfall Events in Poland? Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104447
Chicago/Turabian StyleWibig, Joanna, and Joanna Jędruszkiewicz. 2025. "Has Climate Change Affected the Occurrence of Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Rainfall Events in Poland?" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104447
APA StyleWibig, J., & Jędruszkiewicz, J. (2025). Has Climate Change Affected the Occurrence of Compound Heat Wave and Heavy Rainfall Events in Poland? Sustainability, 17(10), 4447. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104447







