Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
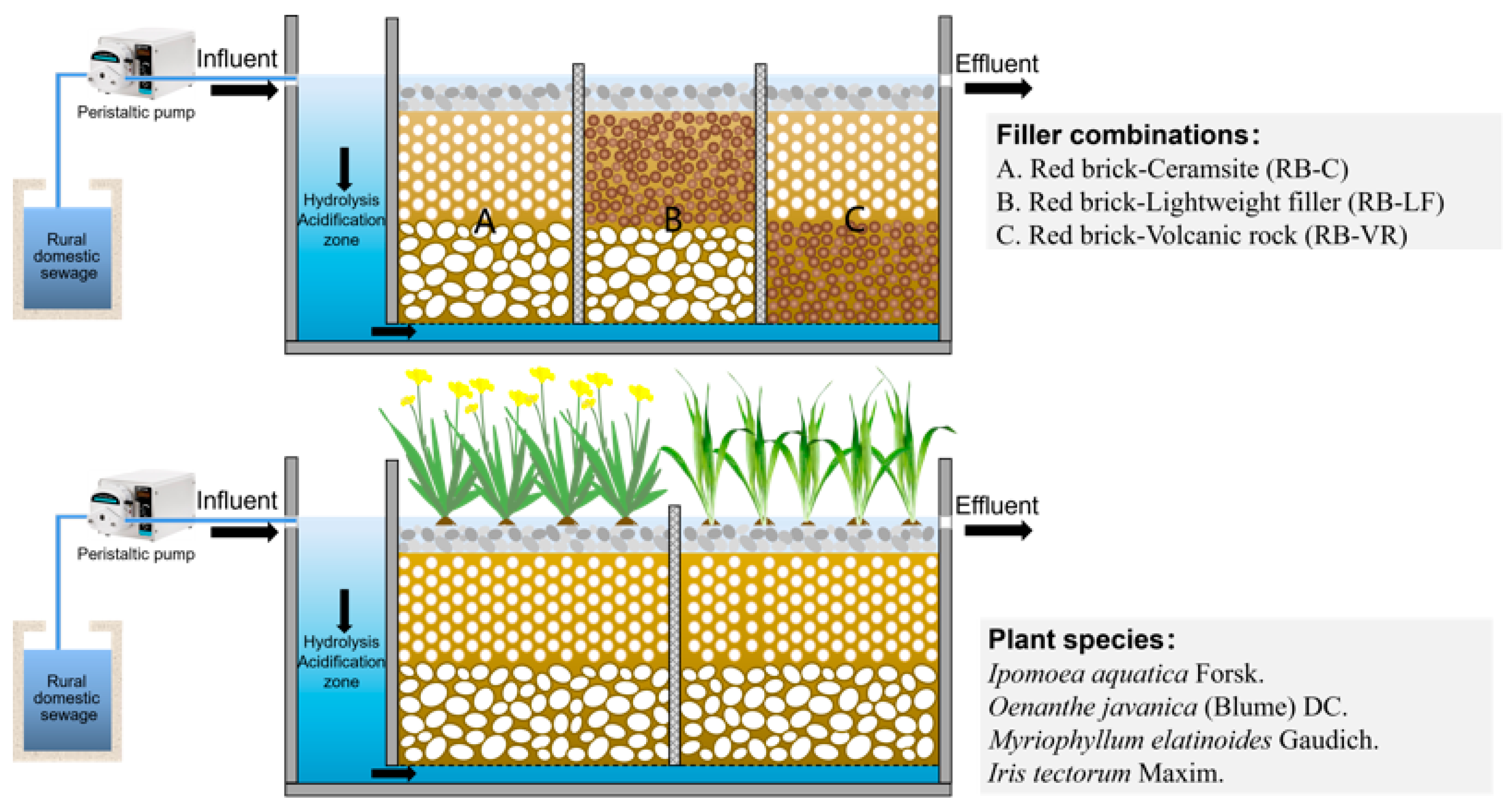
2.1. Lab-Scale Modular Constructed Wetland Setup
2.2. Wastewater Composition
2.3. Sampling and Data Analysis
2.3.1. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.3.2. Data Analysis
2.3.3. Water Quality Evaluation Method
- (1)
- Fuzzy relation matrix
- (2)
- Weight coefficient
- (3)
- Comprehensive evaluation model
3. Application Analysis of Engineering Cases
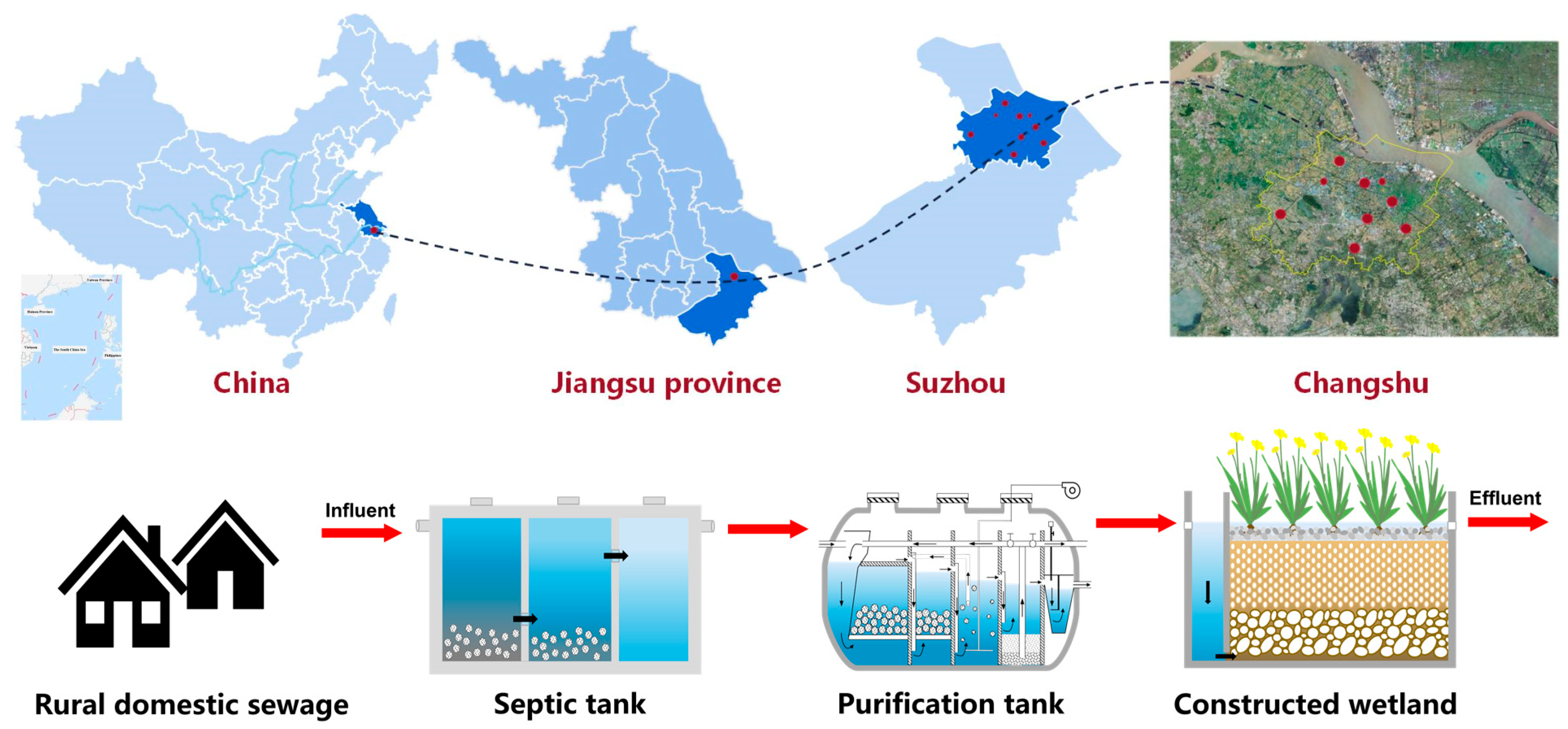
3.1. Project Description
3.2. Scale of Wastewater Treatment
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Filler Combinations on Pollutants Removal in MCWs
4.1.1. Nitrogen Removal
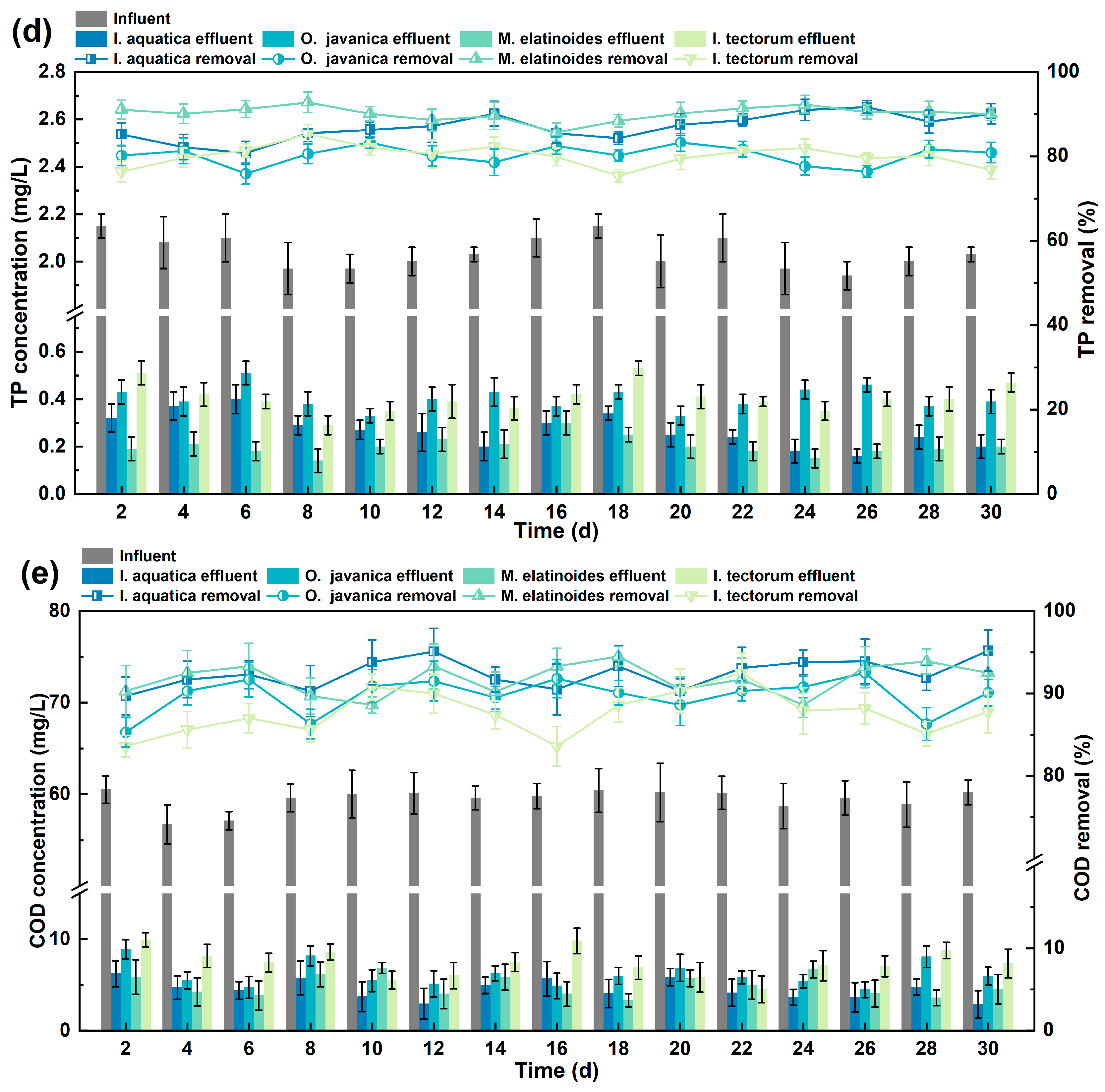
4.1.2. Phosphorus Removal
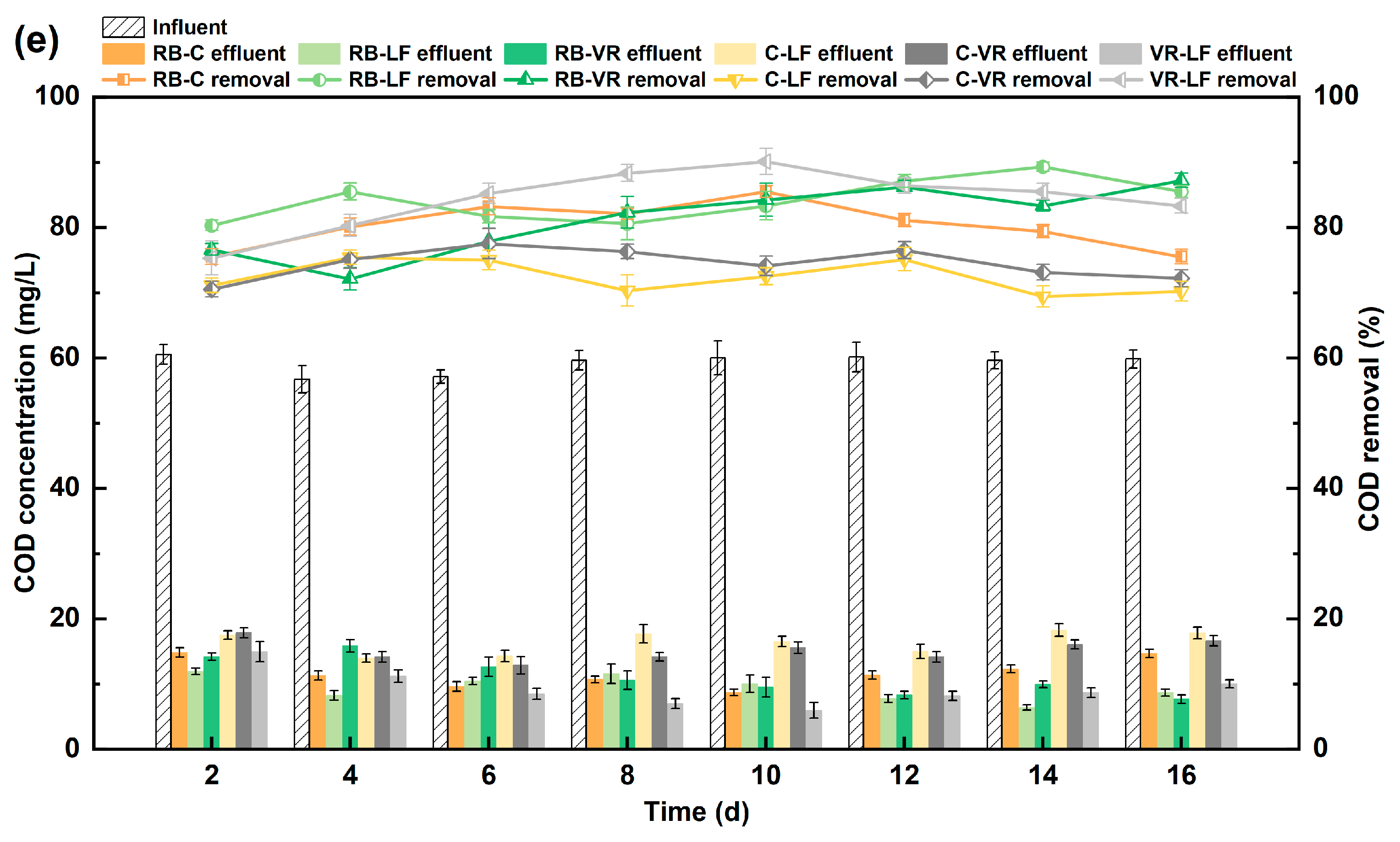
4.1.3. COD Removal
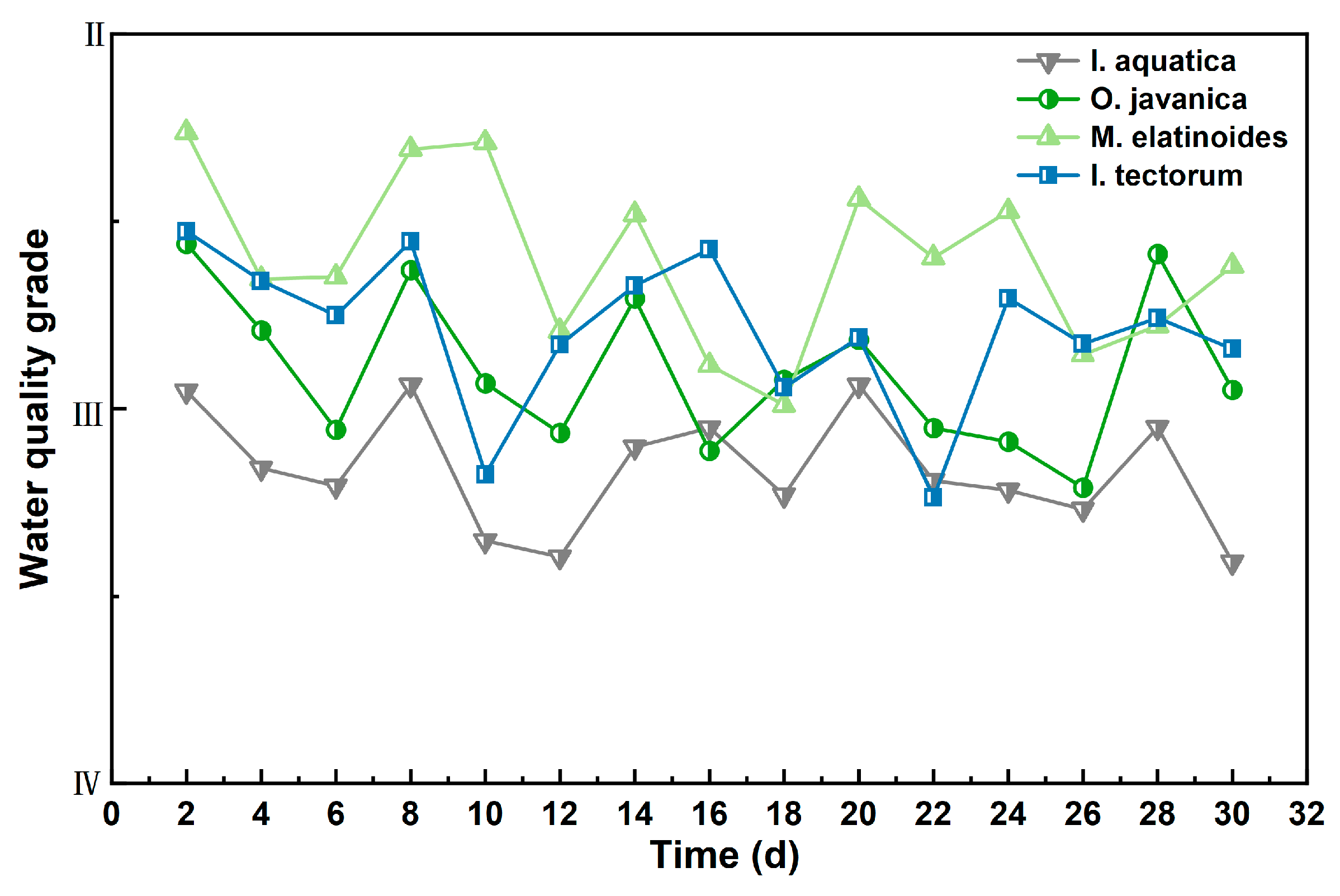
4.2. Long-Term Purification Effect of Plants on Rural Domestic Wastewater in MCWs
4.3. Evaluation of Water Quality Based on the Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method
4.4. Analysis of Influent and Effluent Water Quality in the Pilot Project
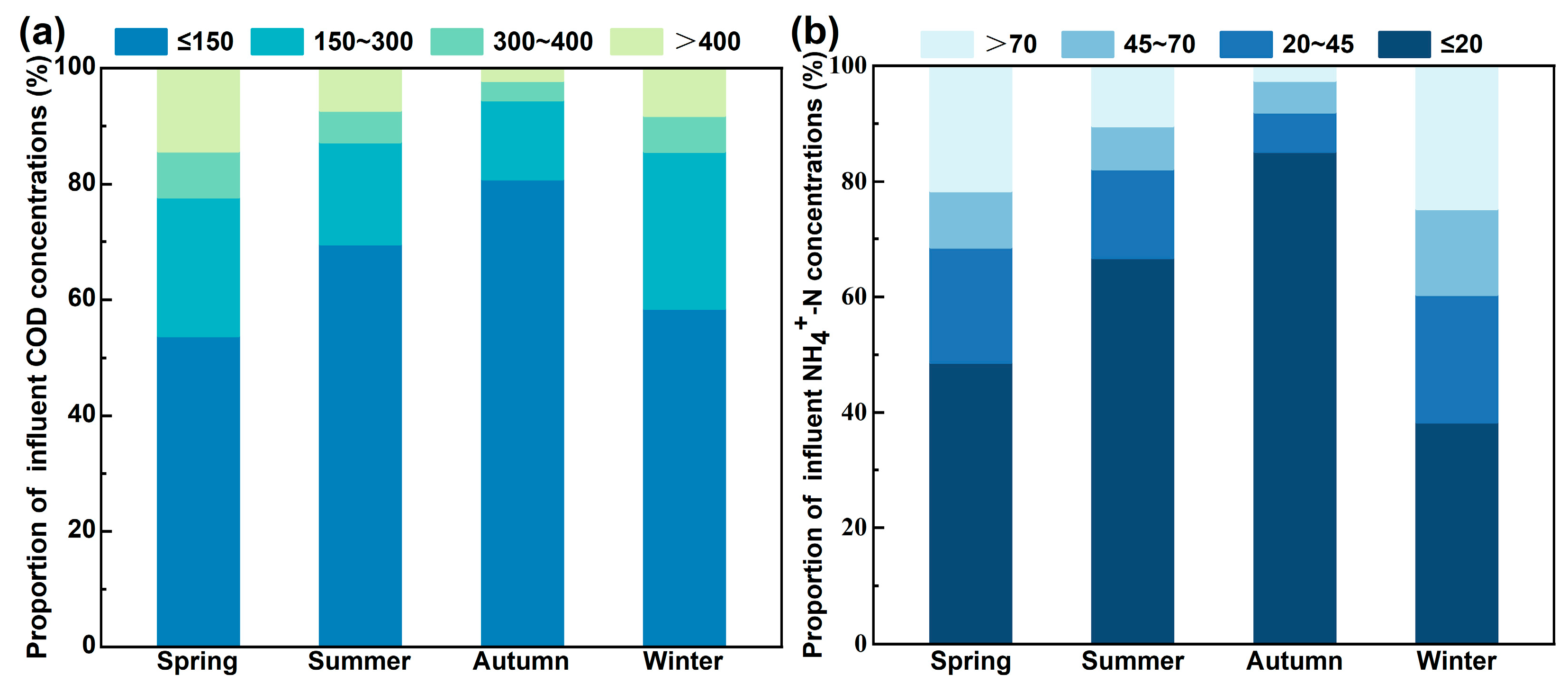
4.4.1. Analysis of Influent Water Quality
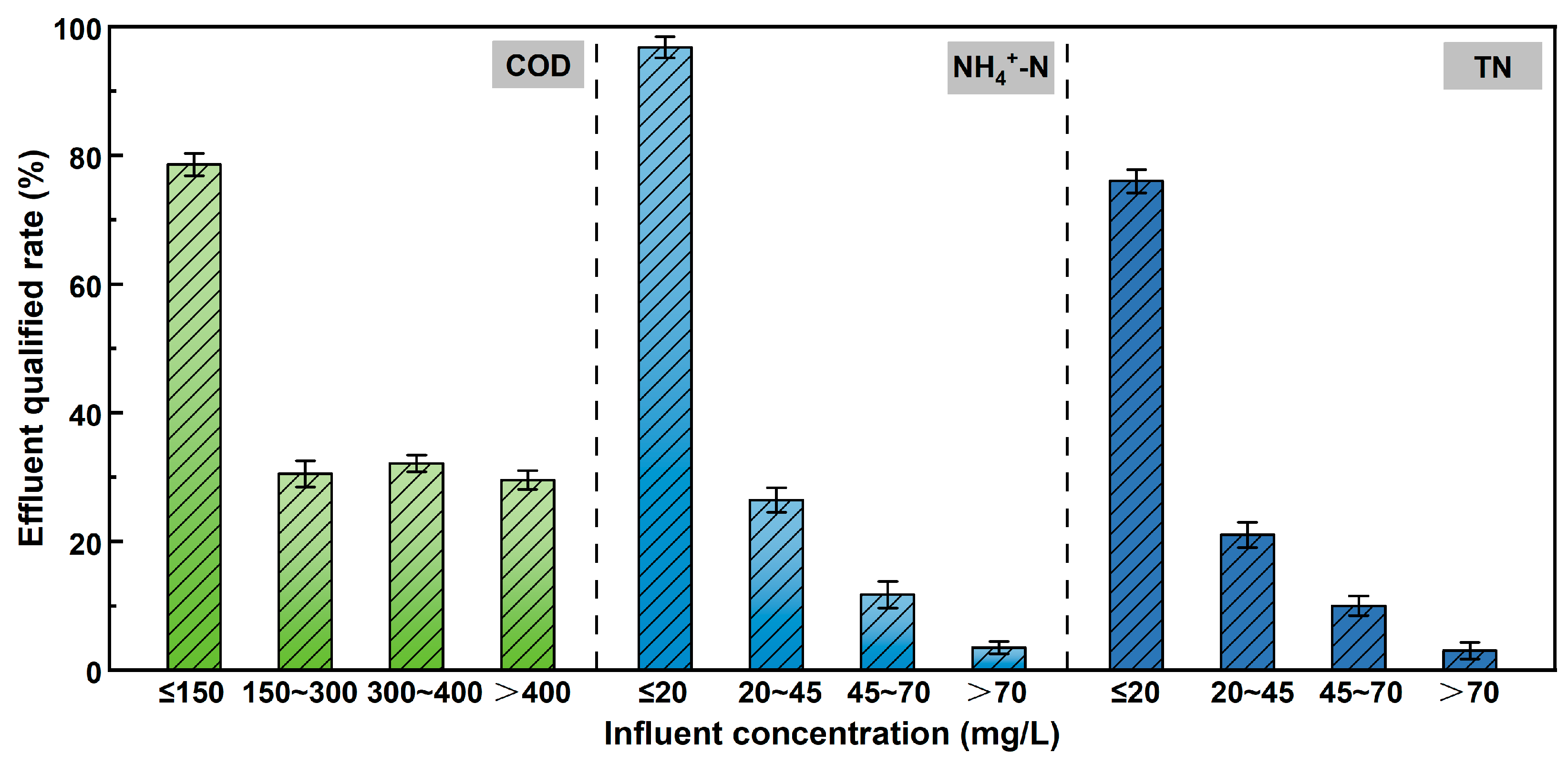
4.4.2. Analysis of Effluent Water Quality
4.5. Economic Analysis of the Pilot Project
4.5.1. Analysis of Investment in Equipment Construction
4.5.2. Analysis of Investment in Project Construction
4.5.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; He, J.; Lulu, C.; Dai, C.; Lijie, Z.; Xiahui, W. Utilization of rural domestic sewage as a resource: Progress, dilemmas, and future. J. Agric. Res. Environ. 2023, 40, 1255. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Feng, B.; Wang, P.; Guo, W.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J. Revealing factors influencing spatial variation in the quantity and quality of rural domestic sewage discharge across China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Luo, H.; Zou, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, X.; Rousseau, D.P.; Li, J. Characteristics and removal of microplastics in rural domestic wastewater treatment facilities of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Xu, F.; Shi, J.; Song, X.; Yu, Q.; Liu, R.; Chen, L. Management of rural domestic wastewater in a city of Yangtze delta region: Performance and remaining challenges. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, D.; Bu, H.; Li, L.; Lu, S. A critical review of characteristics of domestic wastewater and key treatment techniques in Chinese villages. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhao, W.; Chen, D.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, X. Research progress on integrated treatment technologies of rural domestic sewage: A review. Water 2022, 14, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.R.; Ponce, P.; Yu, Z.; Golpîra, H.; Mathew, M. Environmental technology and wastewater treatment: Strategies to achieve environmental sustainability. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, P.R.; Shahid, M.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P.; Liu, D.; Varjani, S.; Zhang, T.C.; Surampalli, R.Y. Nutrient removal from domestic wastewater: A comprehensive review on conventional and advanced technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ding, J.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Pang, J.W.; Jiang, J.-P.; Jiang, J.-Q.; Li, Y.; Ren, N.-Q.; Yang, S.-S. Bibliometric overview of research progress, challenges, and prospects of rural domestic sewage: Treatment techniques, resource recovery, and ecological risk. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dzakpasu, M.; Wang, X.C. Nitrogen removal efficiency and mechanisms of an improved anaerobic-anoxic–oxic system for decentralized sewage treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 129976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinardell, S.; Astals, S.; Peces, M.; Cardete, M.; Fernández, I.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Dosta, J. Advances in anaerobic membrane bioreactor technology for municipal wastewater treatment: A 2020 updated review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2020, 130, 109936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.D.; Dias, E.H.O. Constructed wetlands applied in rural sanitation: A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 110016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghernaout, D.; Elboughdiri, N. Domestic Wastewater Treatment: Difficulties and Reasons, and Prospective Solutions-China as an Example. Open Access Libr. J. 2020, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mander, Ü. Recent research challenges in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changsong, C.; Mingsen, W.; Li, J.; Ye, T. Design of modular constructed wetland and its effect on rural domestic sewage treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 657, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Maniquiz, M.; Geronimo, F.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.; Kim, L. Development of a horizontal subsurface flow modular constructed wetland for urban runoff treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Núñez, A.E. Initial concept and embodiment to develop modular constructed wetland: A unique and promising solution to sustainability transitions in water management. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 450, 141912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, H.; Su, L.; Ma, J.; Li, H. Enhancement of nitrogen removal by a modular design of vertical flow constructed wetlands with a plant carbon source: Optimization of carbon dosage for nitrogen removal, practicability evaluation and strategy exploration for water quality control. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Tang, W.; Pei, Y. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Pei, L. Impacts of different media on constructed wetlands for rural household sewage treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, B.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Xia, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H. The use of constructed wetland for mitigating nitrogen and phosphorus from agricultural runoff: A review. Water. 2021, 13, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataki, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Vairale, M.G.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Gupta, D.K. Constructed wetland, an eco-technology for wastewater treatment: A review on types of wastewater treated and components of the technology (macrophyte, biolfilm and substrate). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Tan, X.; Yin, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z. Double-layer substrate of shale ceramsite and active alumina tidal flow constructed wetland enhanced nitrogen removal from decentralized domestic sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Ji, B.; García, Á.P.; Núñez, A.E. Developing a novel lightweight substrate for constructed treatment wetland: The idea and the reality. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Silva, L.; Bernardelli, J.K.B.; de Oliveira Souza, A.; Lafay, C.B.B.; Nagalli, A.; Passig, F.H.; Kreutz, C.; de Carvalho, K.Q. Biodegradation and sorption of nutrients and endocrine disruptors in a novel concrete-based substrate in vertical-flow constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, X.; Cao, S.; Liu, R. Research on the purification effect of major pollutants in water by modular constructed wetlands with different filler combinations. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 89, 2090–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Li, L.; Cheng, S. Study on the impact of hydraulic loading rate (HLR) on removal of nitrogen under low C/N condition by modular moving bed constructed wetland (MMB-CW) system. Environ. Technol. Innovation 2024, 34, 103579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Liang, H.; Gao, D. Insights into two stable mainstream deammonification process and different microbial community dynamics at ambient temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, F.; Tang, L.; He, S.; Zhou, W. Function of aquatic plants on nitrogen removal and greenhouse gas emission in enhanced denitrification constructed wetlands: Iris pseudacorus for example. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widayati, W.; Setyawan, S.A.A.; Kurniati, E.; Rachmansyah, A.; Anugroho, F. Performance of vertical subsurface flow constructed wetland (VSSFCW) with T. angustifolia and I. aquatica for BOD and COD removal from tofu wastewater. J. Biol. Res. 2023, 29, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Cui, Y.; Yang, C.; Wei, S.; Dong, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Ren, Z.; Wang, W. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation (FCE) and the principal component analysis (PCA) model simulation and its applications in water quality assessment of Nansi Lake Basin, China. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patyal, V.; Jaspal, D.; Khare, K. Materials in constructed wetlands for wastewater remediation: A review. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 2853–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Sheng, S.; Pan, F.; Chen, F.; Fu, J. Comprehensive evaluation of substrate materials for contaminants removal in constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Guo, Y.; Cai, Q.; Yang, P. Enhanced nitrogen removal by simultaneous nitrification-denitrification and further denitrification (SND-DN) in a moving bed and constructed wetland (MBCW) integrated bioreactor. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ling, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Cai, S.; Gao, B. Treatment of ammonium-nitrogen–contaminated groundwater by tidal flow constructed wetlands using different substrates: Evaluation of performance and microbial nitrogen removal pathways. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Li, D.; Kim, M.; Lee, I.; Kim, H.; Huang, C.-P. Process optimization for the synthesis of ceramsites in terms of mechanical strength and phosphate adsorption capacity. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi-yu, Z.; Zeng-jin, L.; Lai-sheng, L.; Na, L. Research on comprehensive evaluation model of rural domestic sewage treatment technology based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation and analytic hierarchy process method. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 452–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



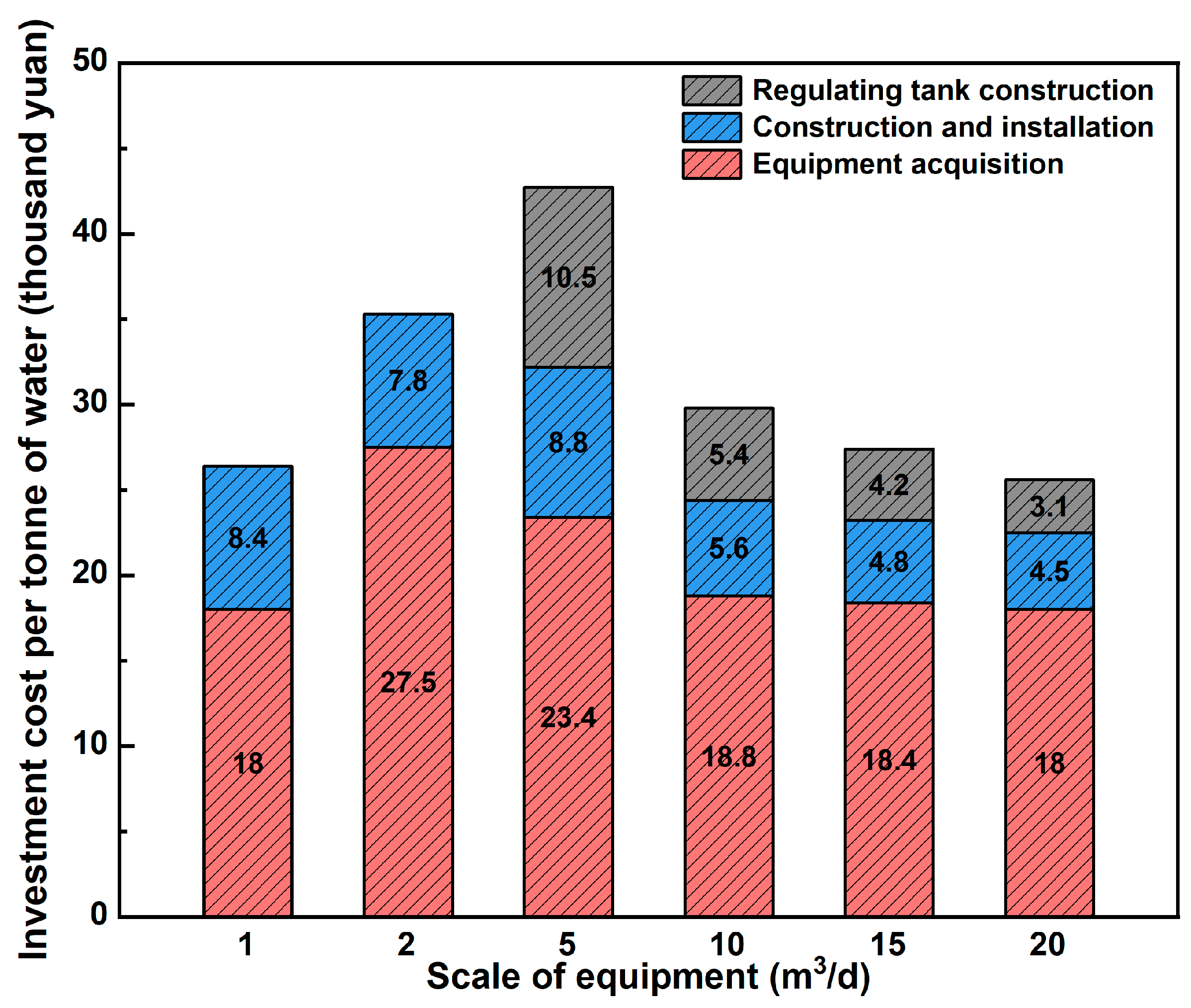
| Scale of Equipment (m3/day) | Quantity of Equipment | Total Scale of Equipment (m3/day) | Design Sewage Volume (m3/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1018 | 1018 | 772.04 |
| 2 | 29 | 58 | 66.66 |
| 5 | 89 | 445 | 462.18 |
| 10 | 68 | 680 | 607.21 |
| 15 | 33 | 495 | 268.66 |
| 20 | 19 | 380 | 364.81 |
| Aggregate | - | 3076 | 2541.6 |
| Plant Species | Time (d) | Pollution Factor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N | COD | TP | TN | ||
| I. aquatica | 2 | 0.0936 | 0.4756 | 0.1641 | 0.2668 |
| 4 | 0.0740 | 0.4173 | 0.1844 | 0.3242 | |
| 6 | 0.0894 | 0.4027 | 0.1923 | 0.3156 | |
| 8 | 0.1038 | 0.4773 | 0.1626 | 0.2563 | |
| 10 | 0.1467 | 0.3727 | 0.1974 | 0.2831 | |
| 12 | 0.1144 | 0.3430 | 0.2329 | 0.3096 | |
| 14 | 0.1214 | 0.4367 | 0.1792 | 0.2628 | |
| 16 | 0.1079 | 0.4525 | 0.1673 | 0.2723 | |
| 18 | 0.0815 | 0.3949 | 0.2098 | 0.3139 | |
| 20 | 0.0621 | 0.4773 | 0.1635 | 0.2972 | |
| 22 | 0.0928 | 0.4035 | 0.2042 | 0.2995 | |
| 24 | 0.0785 | 0.3955 | 0.2141 | 0.3120 | |
| 26 | 0.0992 | 0.3807 | 0.2032 | 0.3170 | |
| 28 | 0.0672 | 0.4446 | 0.1865 | 0.3017 | |
| 30 | 0.0763 | 0.3457 | 0.2429 | 0.3351 | |
| O. javanica | 2 | 0.0957 | 0.5840 | 0.0280 | 0.2923 |
| 4 | 0.1157 | 0.5079 | 0.0359 | 0.3404 | |
| 6 | 0.1248 | 0.4443 | 0.0474 | 0.3835 | |
| 8 | 0.1242 | 0.5763 | 0.0270 | 0.2725 | |
| 10 | 0.1530 | 0.4893 | 0.0295 | 0.3282 | |
| 12 | 0.1374 | 0.4528 | 0.0353 | 0.3746 | |
| 14 | 0.0936 | 0.5315 | 0.0369 | 0.3380 | |
| 16 | 0.1330 | 0.4359 | 0.0327 | 0.3984 | |
| 18 | 0.1396 | 0.4969 | 0.0354 | 0.3282 | |
| 20 | 0.1493 | 0.5353 | 0.0261 | 0.2894 | |
| 22 | 0.1608 | 0.4816 | 0.0317 | 0.3258 | |
| 24 | 0.1388 | 0.4540 | 0.0369 | 0.3703 | |
| 26 | 0.1318 | 0.4102 | 0.0420 | 0.4160 | |
| 28 | 0.0940 | 0.5695 | 0.0258 | 0.3107 | |
| 30 | 0.1364 | 0.4886 | 0.0318 | 0.3432 | |
| M. elatinoides | 2 | 0.0843 | 0.6228 | 0.0203 | 0.2727 |
| 4 | 0.1162 | 0.5140 | 0.0249 | 0.3449 | |
| 6 | 0.1092 | 0.5103 | 0.0246 | 0.3559 | |
| 8 | 0.1159 | 0.6150 | 0.0142 | 0.2549 | |
| 10 | 0.0883 | 0.6230 | 0.0178 | 0.2710 | |
| 12 | 0.0912 | 0.4834 | 0.0274 | 0.3980 | |
| 14 | 0.0939 | 0.5710 | 0.0206 | 0.3144 | |
| 16 | 0.1470 | 0.4662 | 0.0349 | 0.3518 | |
| 18 | 0.1063 | 0.4280 | 0.0321 | 0.4336 | |
| 20 | 0.0924 | 0.5795 | 0.0199 | 0.3083 | |
| 22 | 0.1356 | 0.5395 | 0.0195 | 0.3054 | |
| 24 | 0.1167 | 0.5847 | 0.0133 | 0.2854 | |
| 26 | 0.0923 | 0.4691 | 0.0213 | 0.4172 | |
| 28 | 0.1169 | 0.4767 | 0.0250 | 0.3814 | |
| 30 | 0.1125 | 0.5256 | 0.0236 | 0.3383 | |
| I. tectorum | 2 | 0.0874 | 0.5948 | 0.0304 | 0.2875 |
| 4 | 0.1120 | 0.5641 | 0.0292 | 0.2947 | |
| 6 | 0.1290 | 0.5458 | 0.0287 | 0.2965 | |
| 8 | 0.1158 | 0.5882 | 0.0198 | 0.2761 | |
| 10 | 0.1629 | 0.4520 | 0.0289 | 0.3562 | |
| 12 | 0.1159 | 0.5058 | 0.0327 | 0.3456 | |
| 14 | 0.0996 | 0.5479 | 0.0262 | 0.3263 | |
| 16 | 0.1044 | 0.5922 | 0.0255 | 0.2780 | |
| 18 | 0.1429 | 0.5093 | 0.0391 | 0.3087 | |
| 20 | 0.1301 | 0.5138 | 0.0361 | 0.3199 | |
| 22 | 0.1591 | 0.4179 | 0.0366 | 0.3865 | |
| 24 | 0.1198 | 0.5445 | 0.0272 | 0.3086 | |
| 26 | 0.1306 | 0.5265 | 0.0298 | 0.3131 | |
| 28 | 0.1264 | 0.5592 | 0.0252 | 0.2892 | |
| 30 | 0.1260 | 0.5249 | 0.0337 | 0.3154 | |
| Town/District | Quantity of Equipment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 m3/day | 2 m3/day | 5 m3/day | 10 m3/day | 15 m3/day | 20 m3/day | |
| Bixi district | 71 | - | 1 | 8 | 2 | 1 |
| Changfu district | 21 | - | 3 | 2 | - | - |
| Dongbang town | 68 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Guli town | 59 | - | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Haiyu town | 61 | - | 2 | 2 | - | 2 |
| Meili town | 86 | 3 | 12 | 14 | 2 | 1 |
| Shajiabang town | 11 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Shanghu town | 180 | 3 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 2 |
| Zhitang town | 190 | 4 | 12 | 8 | 3 | 1 |
| Aggregate | 747 | 10 | 44 | 47 | 11 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Han, R.; Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; He, B. Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104427
Zhao X, Yang J, Han R, Luo H, Chen L, Liu M, He B. Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104427
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaolin, Jing Yang, Rubin Han, Hui Luo, Limin Chen, Meng Liu, and Baojie He. 2025. "Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104427
APA StyleZhao, X., Yang, J., Han, R., Luo, H., Chen, L., Liu, M., & He, B. (2025). Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application. Sustainability, 17(10), 4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104427








