Comparative Study on the Catalytic Ozonation of Biotreated Landfill Leachate Using γ-Al2O3-Based Catalysts Loaded with Different Metals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Landfill Leachate Sample
2.2. Preparation of Catalysts
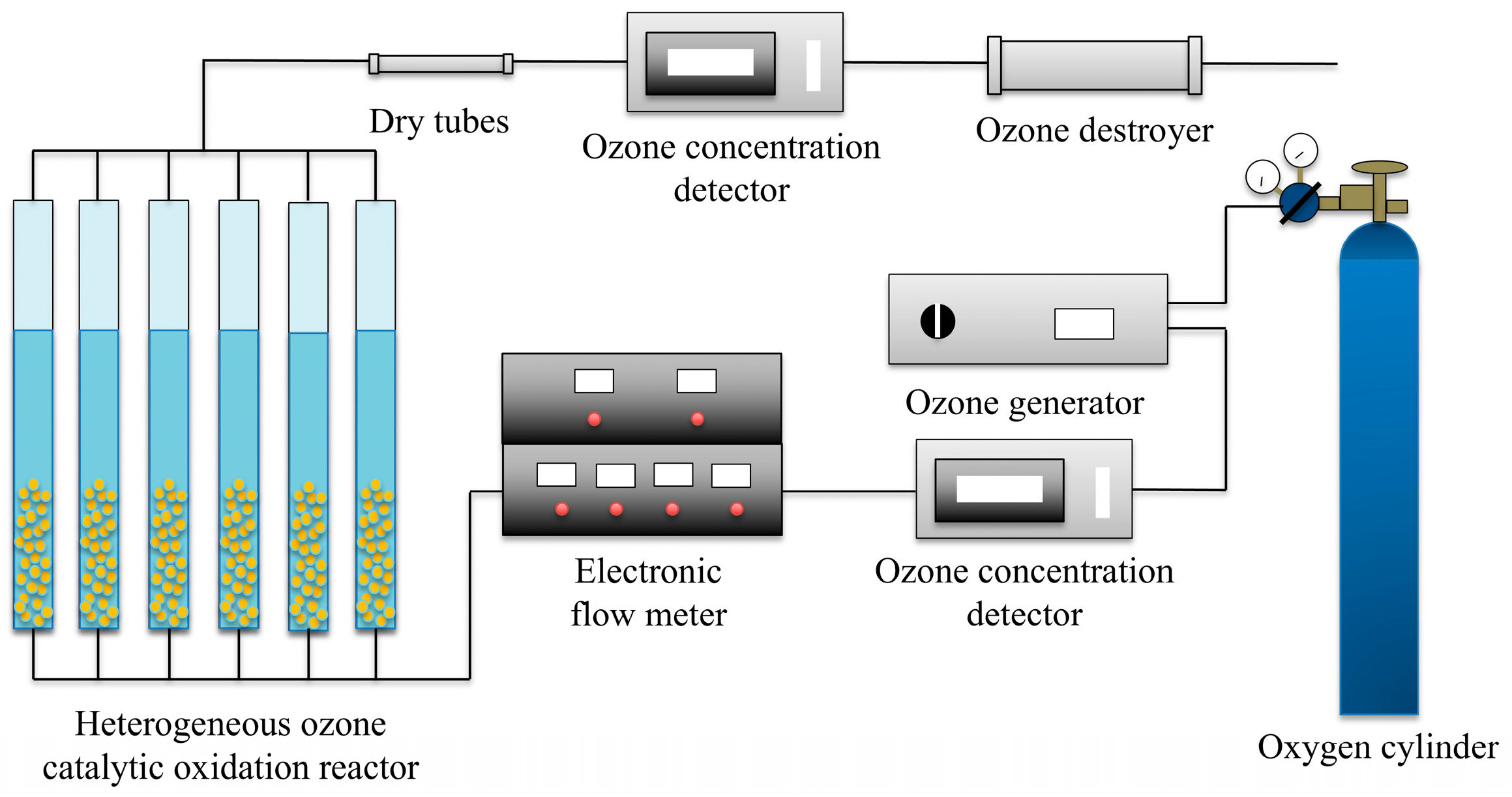
2.3. Ozonation and Catalytic Ozonation Procedure
2.4. Analytical Method
3. Result and Discussion
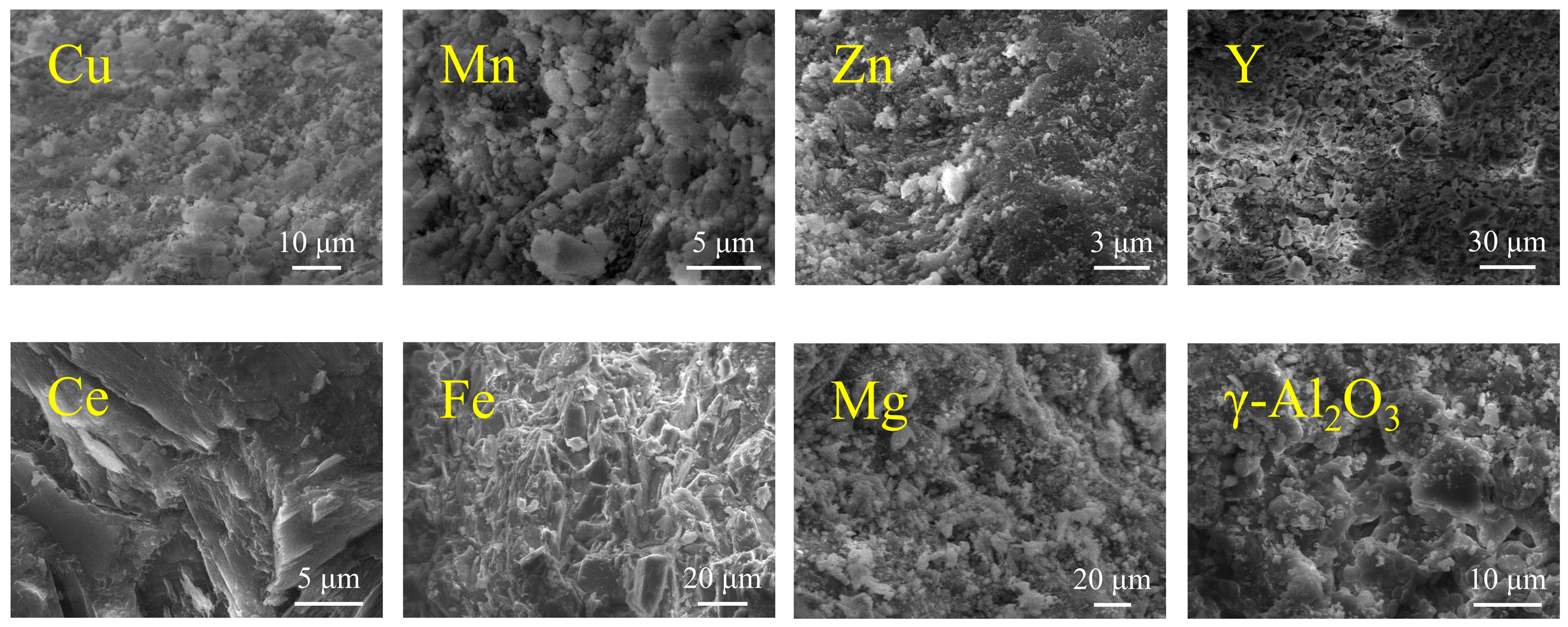
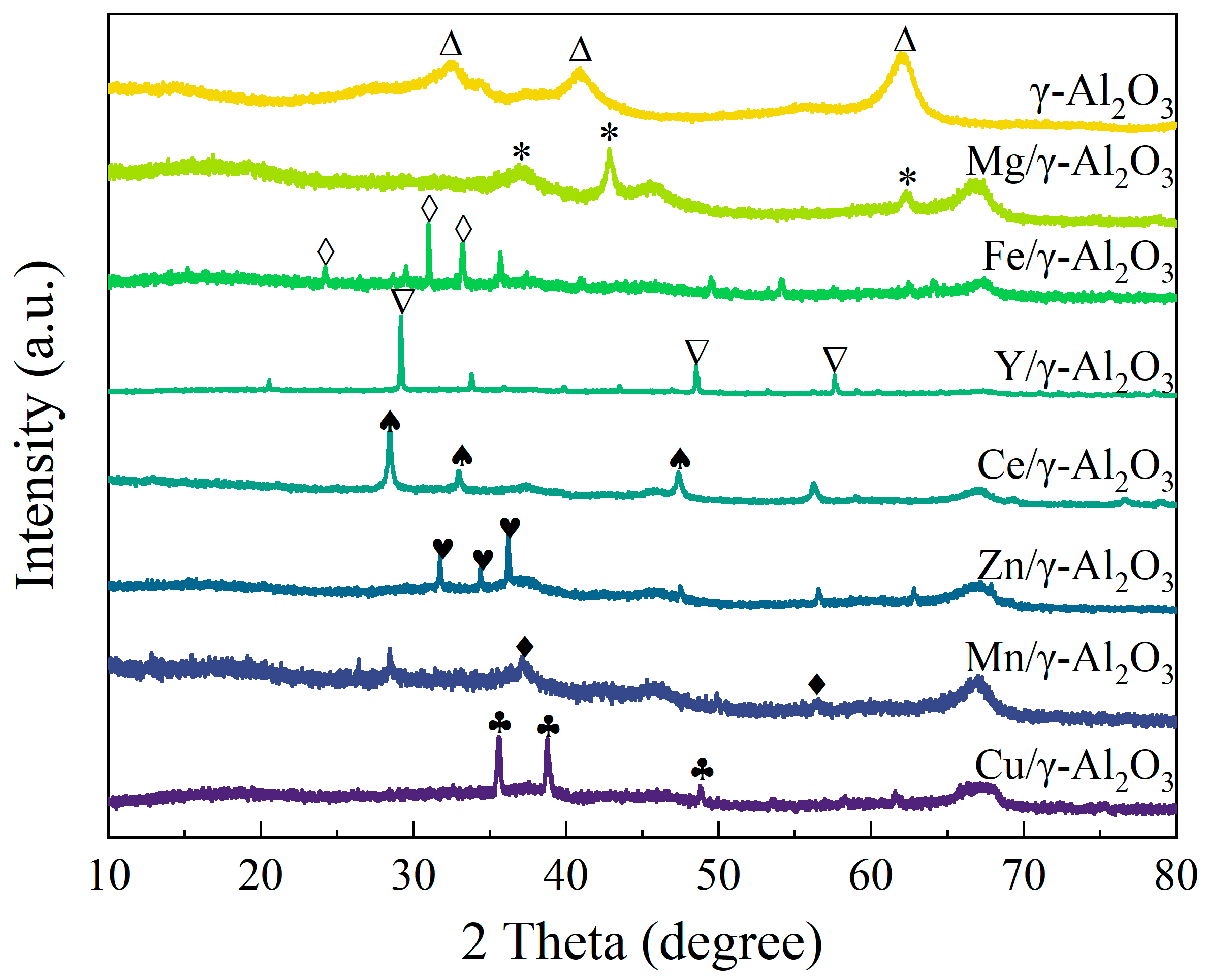
3.1. Characterization of Catalysts
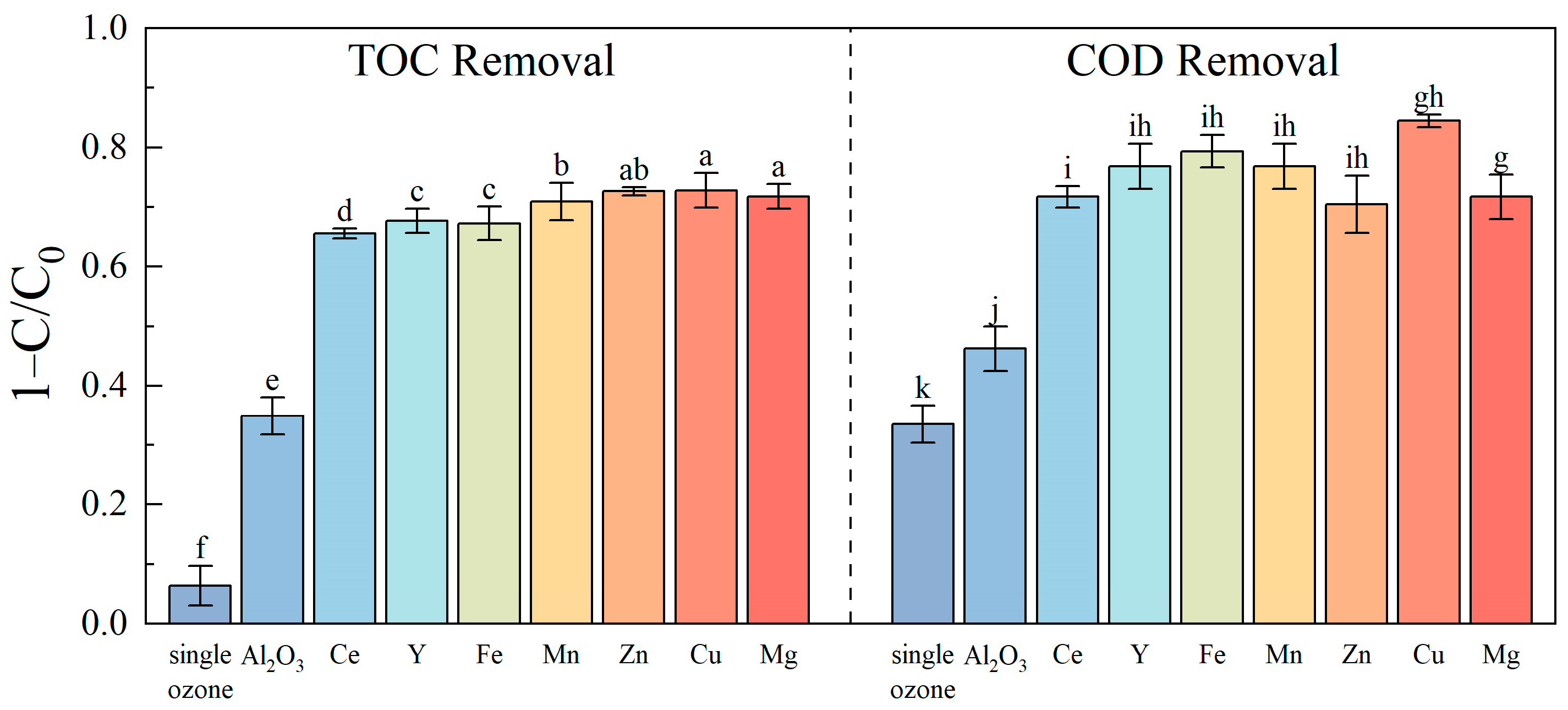
3.2. Catalytic Ozonation Efficiency of Different Catalysts
3.3. Catalytic Ozonation Characteristics of Different Catalysts
3.3.1. Water Quality Characteristics Based on UV–Vis
α210/254
α220/254
α254/204
α365/250
α400/300
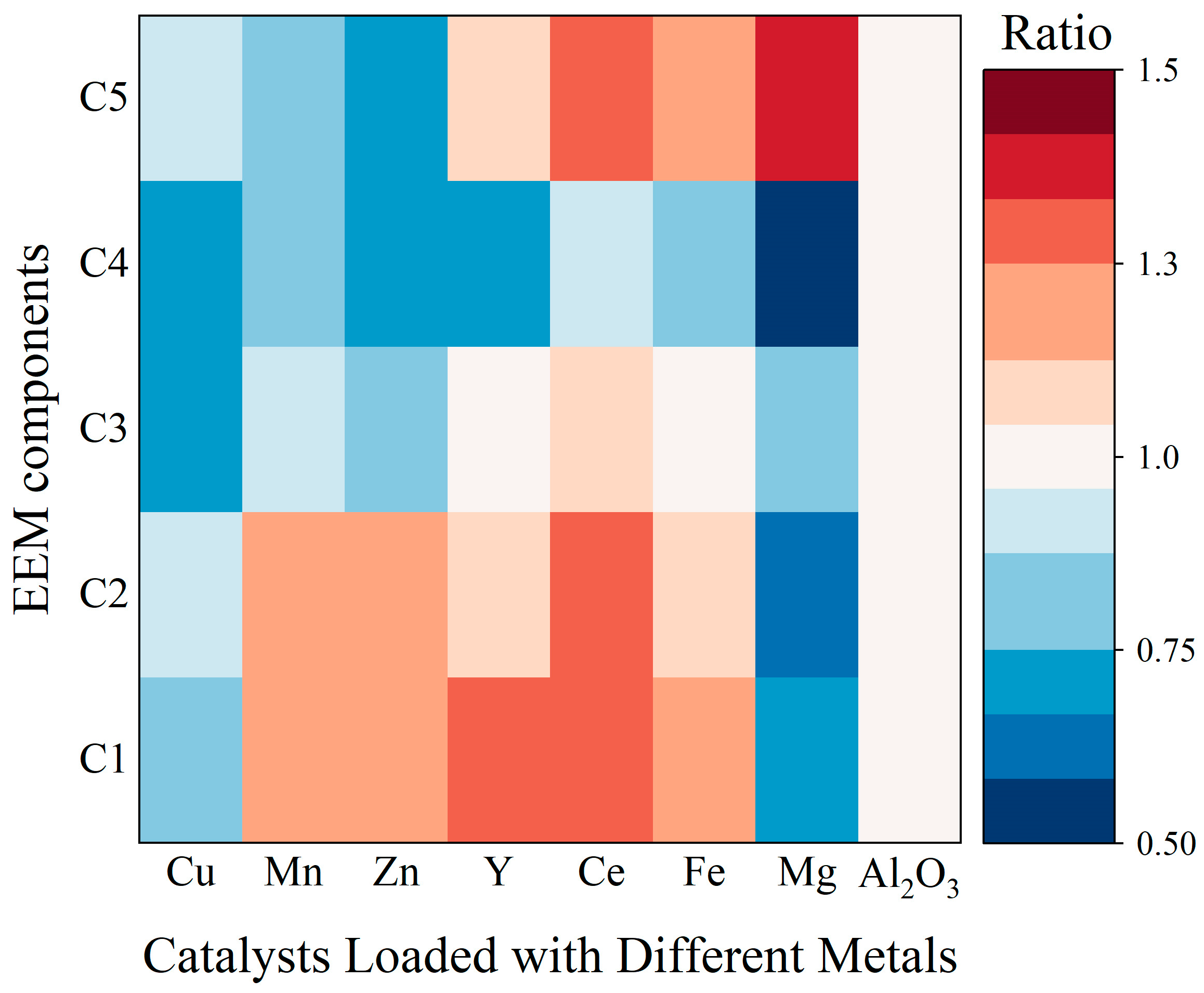
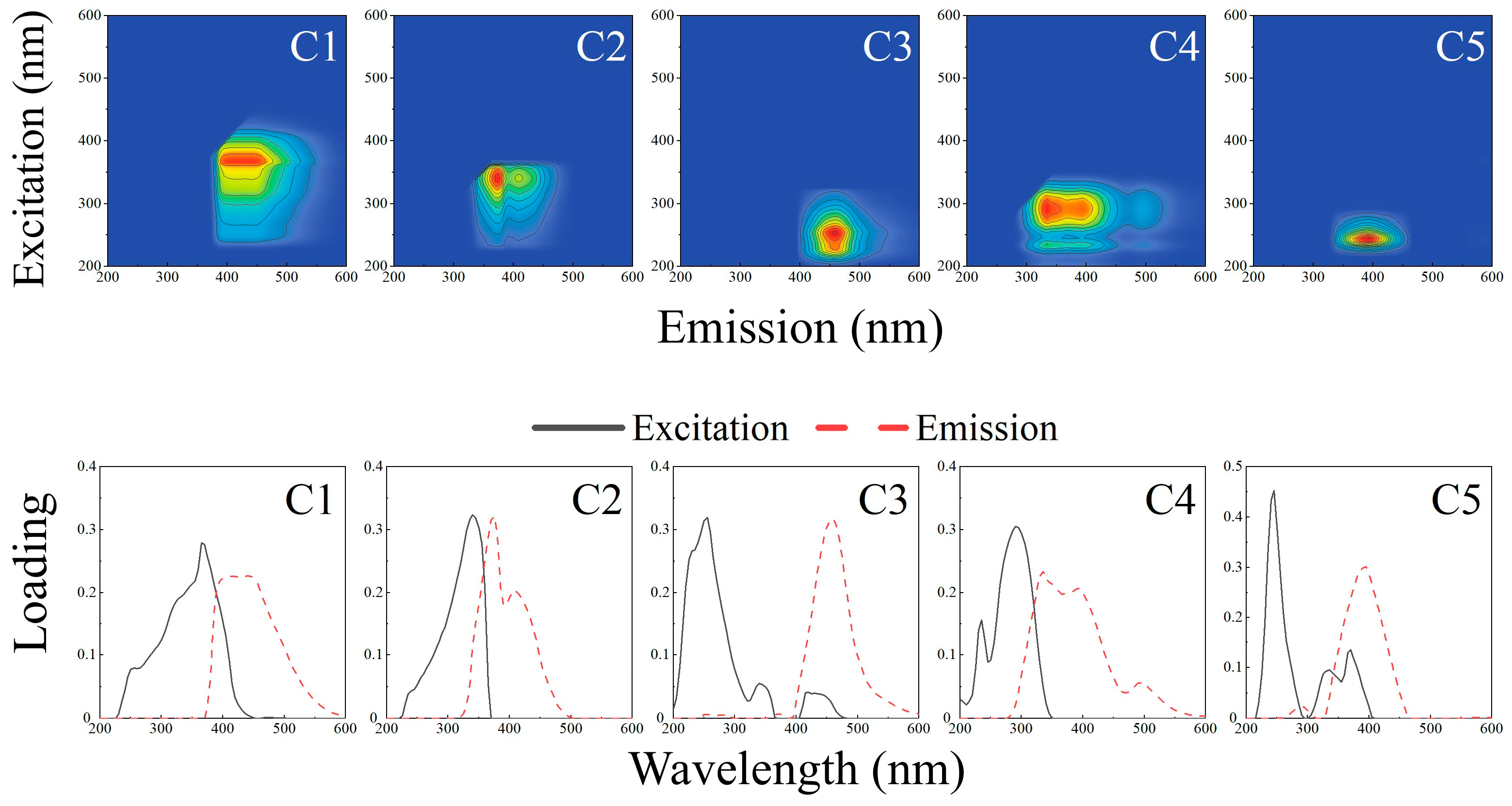
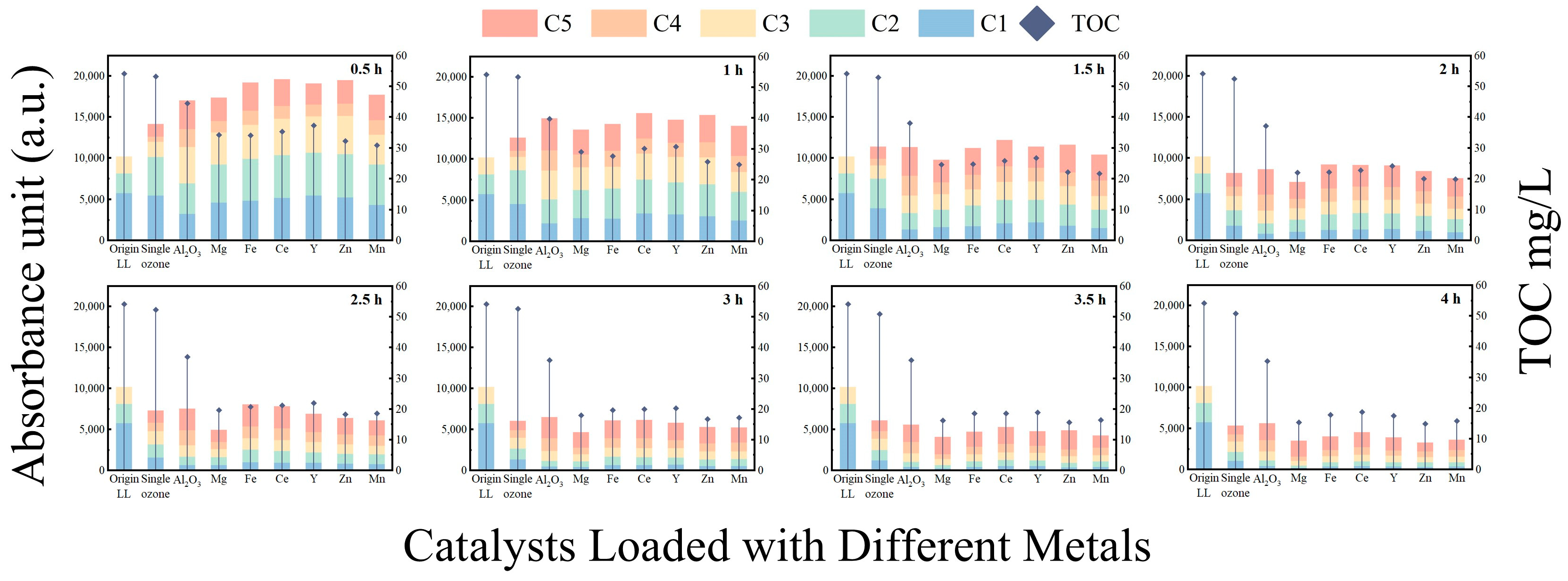
3.3.2. Degradation Characteristics of DOM Based on EEM
- (1)
- Cu/γ-Al2O3 outperformed γ-Al2O3 across all components (C1–C5);
- (2)
- Mn/γ-Al2O3 and Zn/γ-Al2O3 exhibited inferior C1/C2 removal but enhanced C3/C4/C5 degradation;
- (3)
- Y/γ-Al2O3, Ce/γ-Al2O3, and Fe/γ-Al2O3 improved C4 removal and maintained comparable C3 elimination, yet showed reduced efficacy for C1/C2/C5;
- (4)
- Mg/γ-Al2O3 surpassed the carrier in C1–C4 removal but underperformed in C5 elimination.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The γ-Al2O3 catalysts loaded with various metals significantly enhance the removal efficiency of organic pollutants in the biochemical effluent of landfill leachate. Among them, the Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalyst exhibits the best overall catalytic performance, achieving the highest removal rates of COD and TOC, making it the preferred catalyst for practical applications.
- (2)
- The removal efficiencies of different organic components in the biochemical effluent of landfill leachate vary among the catalysts loaded with different metals. The Mg/γ-Al2O3 catalyst demonstrates the best removal efficiency for aromatic compounds and non-polar substances, followed by the Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. In contrast, the Ce/γ-Al2O3 catalyst shows outstanding performance in degrading macromolecular substances.
- (3)
- The γ-Al2O3 catalysts loaded with metals exhibit significant catalytic effects on fluorescent substances in landfill leachate. The Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalyst achieves better removal efficiencies for components C1 through C5 compared to the γ-Al2O3 support alone, while the Mg/γ-Al2O3 catalyst shows the best specific removal effect on component C4.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, S.J.; Zhou, C.B.; Pan, J.J.; Yang, G.; Sun, C.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Chen, X.C.; Zhao, Z.L. Leachate from municipal solid waste landfills in a global perspective: Characteristics, influential factors and environmental risks. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 333, 130234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Heron, G. Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Guo, S.; Zeng, Z.; Cui, G.; Yang, Z. Optimization Research on Burner Arrangement of Landfill Leachate Concentrate Incinerator Based on “3T+E” Principle. Energies 2022, 15, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.N.; Sadaf, S.; Verma, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Kumari, S.; Polisetti, V.; Kallem, P.; Iqbal, J.; Banat, F. Old Landfill Leachate and Municipal Wastewater Co-Treatment by Sequencing Batch Reactor Combined with Coagulation–Flocculation Using Novel Flocculant. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Zhou, K.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Characterization and treatment of landfill leachate: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 16889–2024; Standard for Pollution Control on the Landfill Site of Municipal Solid Waste. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Kamal, A.; Makhatova, A.; Yergali, B.; Baidullayeva, A.; Satayeva, A.; Kim, J.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Poulopoulos, S.G.; Arkhangelsky, E. Biological Treatment, Advanced Oxidation and Membrane Separation for Landfill Leachate Treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, P.; Koliyabandara, P.A.; Cooray, A.T.; Lam, S.S.; Athapattu, B.C.L.; Vithanage, M. Progress and prospects in mitigation of landfill leachate pollution: Risk, pollution potential, treatment and challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wen, P.; Li, Q. Degradation of refractory organic contaminants in membrane concentrates from landfill leachate by a combined coagulation-ozonation process. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Gao, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Sillanpää, M. Treatment of landfill leachate in the MBR and catalytic ozonation coupled system based on MnNi catalyst: Efficiency and bio/chemical mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 66, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Airoldi, M. Novel and Conventional Technologies for Landfill Leachates Treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Kumar, S.; Lokhandwala, S. Advanced oxidation processes for treatment of leachate from hazardous waste landfill: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, J. Advanced treatment of landfill leachate by catalytic ozonation with MnCeOx/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 46, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ma, P.; He, Z.; Mi, X. A Combined Catalytic Ozonation-MBR Approach to Remove Contaminants from the Mature Landfill Leachate in the Yellow River Basin. Toxics 2022, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HJ/T 399-2007; Water Quality—Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand—Quick Closed—Reflux Titrimetric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Xu, L.; He, Z.; Wei, X.; Shang, Y.; Shi, J.; Jin, X.; Bai, X.; Shi, X.; Jin, P. Facile-prepared Fe/Mn co-doped biochar is an efficient catalyst for mediating the degradation of aqueous ibuprofen via catalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Luo, P.R.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.P.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.Y.; Liu, X.N.; Pan, Z.C.; et al. Regulating surface acid-base properties of Mn-Mg/Al2O3 for the enhanced catalytic ozonation of oxytetracycline hydrochloride degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, F. Nano ferrites (AFe2O4, A = Zn, Co, Mn, Cu) as efficient catalysts for catalytic ozonation of toluene. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5116–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.T.; De Buyck, P.J.; Zhang, R.; Manhaeghe, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.C.; Zhao, Y.L.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Enhanced removal of refractory humic- and fulvic-like organics from biotreated landfill leachate by ozonation in packed bubble columns. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.N.; Sun, Y.J.; Fu, Y.X.; Gong, Z.G.; Liu, K.Q. Simultaneous degradation of refractory organics, antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes from landfill leachate concentrate by GAC/O3. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 135016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.F.; Lu, K.C.; Yin, M.X.; Yan, N.; Sai, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.Y. Single-atom cobalt enables efficient catalytic ozonation for advanced wastewater treatment: Mechanisms and application. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Dacquin, J.-P.; Royer, S.; Zhang, H. Mechanism and kinetics of catalytic ozonation for elimination of organic compounds with spinel-type CuAl2O4 and its precursor. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, R. On the structure of γ-Al2O3. J. Catal. 2020, 392, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C. The catalytic oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons over supported metal oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 91, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Enhancement Mechanism of Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation by Cordierite-Supported Copper for the Degradation of Nitrobenzene in Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshani, B.; McMaster, I.; Rezaei, E.; Soltan, J. Catalytic ozonation of benzotriazole over alumina supported transition metal oxide catalysts in water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.; Amy, G.; Park, H.-R.; Song, M. Characterizing algogenic organic matter (AOM) and evaluating associated NF membrane fouling. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshin, G.V.; Li, C.-W.; Benjamin, M.M. Monitoring the properties of natural organic matter through UV spectroscopy: A consistent theory. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yi, J.; Chen, L.; Lan, T.; Dai, J. Pretreatment of printing and dyeing wastewater by Fe/C micro-electrolysis combined with H2O2 process. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2017, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juboori, R.A.; Yusaf, T.; Pittaway, P.A. Exploring the correlations between common UV measurements and chemical fractionation for natural waters. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16324–16335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Williams, M.A.; Schlautman, M.A. Evaluating spectroscopic and chromatographic techniques to resolve dissolved organic matter via end member mixing analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuravuori, J.; Pihlaja, K. Molecular size distribution and spectroscopic properties of aquatic humic substances. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artinger, R.; Buckau, G.; Geyer, S.; Fritz, P.; Wolf, M.; Kim, J.I. Characterization of groundwater humic substances: Influence of sedimentary organic carbon. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Dai, M.; Qian, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; et al. Fluorescent dissolved organic matter facilitates the phytoavailability of copper in the coastal wetlands influenced by artificial topography. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 147855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Andrade, J.A.; Diaz, E.; Iglesias Vega, D.; Hain, E.; Rose, M.R.; Blaney, L. Spatiotemporal analysis of fluorescent dissolved organic matter to identify the impacts of failing sewer infrastructure in urban streams. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainard, P.G.; Guéguen, C.; McDonald, N.; Williams, W.J. Photobleaching of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in Beaufort Sea and North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Mar. Chem. 2015, 177, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Cory, R.M.; Nishioka, J.; Kuma, K.; Tanoue, E.; Jaffé, R. Fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter in the deep waters of the Okhotsk Sea and the northwestern North Pacific Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, M.; Kojima, T.; Tanabe, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Kudoh, S.; Maie, N.; Fujitake, N. Origin, distributions, and environmental significance of ubiquitous humic-like fluorophores in Antarctic lakes and streams. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Gudasz, C.; Guillemette, F.; Hensgens, G.; Ye, L.; Karlsson, J. Systematic microbial production of optically active dissolved organic matter in subarctic lake water. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osburn, C.L.; Oviedo-Vargas, D.; Barnett, E.; Dierick, D.; Oberbauer, S.F.; Genereux, D.P. Regional Groundwater and Storms Are Hydrologic Controls on the Quality and Export of Dissolved Organic Matter in Two Tropical Rainforest Streams, Costa Rica. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2018, 123, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Clauson, K.; Zhou, M.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, Y. Hillslopes in Headwaters of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau as Hotspots for Subsurface Dissolved Organic Carbon Processing During Permafrost Thaw. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2021, 126, e2020JG006222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Talbot, J.; Arsenault, J.; Martinez-Cruz, K.; Sepulveda-Jauregui, A.; Hoyos-Santillan, J.; Lapierre, J.-F. Linking Dissolved Organic Matter to CO2 and CH4 Concentrations in Canadian and Chilean Peatland Pools. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2023, 37, e2023GB007715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S. Tracing the production and degradation of autochthonous fractions of dissolved organic matter by fluorescence analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yang, M.; Cui, F. Three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy and fractions of dissolved organic matter change in landfill leachate by biological treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Gupta, A.; Novak, J.T.; Goldsmith, C.D.; Driskill, N. Characterization and treatment of organic constituents in landfill leachates that influence the UV disinfection in the publicly owned treatment works (POTWs). J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258–259, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, A.; Shi, Y.; Yue, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Cui, D. An innovative approach for landfill leachate treatment based on selective adsorption of humic acids with carbon nitride. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, J.; Song, G.; Tan, Y. Ozonation reactivity characteristics of dissolved organic matter in secondary petrochemical wastewater by single ozone, ozone/H2O2, and ozone/catalyst. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, P.; Lambert, N.; Degrève, J.; Liers, S.; Luyten, J. Comparison of Different Oxidation Methods for Recalcitrance Removal of Landfill Leachate. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2011, 33, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; He, C.; Gu, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, Q. Molecular-level insights into the transformation mechanism for refractory organics in landfill leachate when using a combined semi-aerobic aged refuse biofilter and chemical oxidation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | pH | TOC | DOC | COD | NH3-N | UV254 | UV365 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 7.15–7.25 | 106–110 | 100–103 | 300–330 | 24.5–26.2 | 1.613–1.615 | 0.380–0.382 |
| Support | Active Components | Particle Size (mm) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3 | Cu, Mn, Zn, Y, Ce, Fe, Mg | 3–5 | 0.41–0.45 | 5.88–7.56 | 151.44–236.73 |
| Parameter | Cu | Mn | Zn | Y | Ce | Fe | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kobs | 4.54 | 3.81 | 5.24 | 5.00 | 5.35 | 3.98 | 3.08 |
| Qe | 0.85 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.85 |
| AOP Process | Initial COD Concentration (mg/L) | COD Removal (%) | Ozone Dosing (g O3/g COD) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalytic ozonation | 314 | 84% | 0.64 | This work |
| Lava rock-packed bubble column | 400–430 | 46% | 0.60 | [19] |
| MnCeOx/γ-Al2O3 catalytic ozonation | 1062 | 82% | 0.43 | [13] |
| GAC/O3 | 1628–1732 | 56% | 1.42 | [20] |
| Co0.25-NC@Al2O3 catalytic ozonation | 110 | 65% | 4.36 | [21] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Fu, L.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, H.; Wu, C. Comparative Study on the Catalytic Ozonation of Biotreated Landfill Leachate Using γ-Al2O3-Based Catalysts Loaded with Different Metals. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104376
Li J, Fu L, Yu Y, Yuan Y, Xi H, Wu C. Comparative Study on the Catalytic Ozonation of Biotreated Landfill Leachate Using γ-Al2O3-Based Catalysts Loaded with Different Metals. Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104376
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiancheng, Liya Fu, Yin Yu, Yue Yuan, Hongbo Xi, and Changyong Wu. 2025. "Comparative Study on the Catalytic Ozonation of Biotreated Landfill Leachate Using γ-Al2O3-Based Catalysts Loaded with Different Metals" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104376
APA StyleLi, J., Fu, L., Yu, Y., Yuan, Y., Xi, H., & Wu, C. (2025). Comparative Study on the Catalytic Ozonation of Biotreated Landfill Leachate Using γ-Al2O3-Based Catalysts Loaded with Different Metals. Sustainability, 17(10), 4376. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104376






