Economic Structural Adjustment Promoting Sustainable Growth in Shanghai: A Two-Decade Study (2004–2023)
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How has Shanghai’s industrial structure evolved from 2004 to 2023, and what drivers underpin its transition toward a service-dominated economy?
- Which sectors (primary, secondary, and tertiary) have been most critical to sustaining GDP growth?
- What is the projected trajectory of Shanghai’s GDP under different forecasting models, and which approach offers the highest predictive accuracy for policy formulation?
2. Adopted Datasets and Prediction Models
2.1. Adopted Datasets
2.2. Prediction Models
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Shanghai’s Total GDP and Its Components
3.2. Future GDP Prediction of Shanghai
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDP | Gross Domestic Product |
| FDI | Foreign Direct Investment |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| WR | Wholesale and Retail |
| TSP | Transportation, Storage, and Postal |
| AF | Accommodation and Food |
| ISI | Information Transmission, Software, and Information Technology |
Appendix A
| Index | Total GDP | Primary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry | Secondary Industry | Tertiary Industry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industrial Development | Construction Industry | WR Trade | TSP Services | AF Services | ISI Services | Finance Industry | Real Estate Industry | |||||
| 2004 | 7450.27 | 96.71 | 3788.22 | 3565.34 | 3492.89 | 295.33 | 751.30 | 362.44 | 150.88 | 303.84 | 741.68 | 622.59 |
| 2005 | 9143.95 | 79.65 | 4475.92 | 4588.38 | 4155.23 | 320.69 | 833.95 | 581.27 | 168.31 | 359.21 | 689.87 | 670.23 |
| 2006 | 10,296.97 | 93.81 | 4929.20 | 5273.96 | 4456.04 | 473.16 | 919.43 | 683.61 | 194.08 | 421.31 | 799.37 | 824.10 |
| 2007 | 12,001.16 | 101.84 | 5677.50 | 6223.83 | 5295.9 | 381.60 | 1049.34 | 724.58 | 219.36 | 500.65 | 1195.72 | 1018.4 |
| 2008 | 13,698.15 | 111.80 | 6235.92 | 7350.43 | 5784.99 | 666.62 | 1266.37 | 769.64 | 244.26 | 591.42 | 1442.6 | 939.17 |
| 2009 | 14,900.93 | 113.82 | 5939.96 | 8847.15 | 5374.91 | 565.05 | 2183.86 | 642.13 | 238.36 | 599.26 | 1817.85 | 1220.92 |
| 2010 | 16,872.42 | 114.50 | 7139.96 | 9618.31 | 6456.78 | 524.37 | 2512.89 | 746.41 | 266.45 | 636.03 | 1931.73 | 1042.5 |
| 2011 | 19,195.69 | 124.94 | 7959.69 | 11,111.06 | 7414.77 | 544.92 | 3040.99 | 913.60 | 279.34 | 763.86 | 2240.47 | 1019.68 |
| 2012 | 20,101.33 | 127.80 | 7912.77 | 12,060.76 | 7145.02 | 767.75 | 3291.93 | 895.31 | 298.40 | 918.83 | 2450.36 | 1085.96 |
| 2013 | 21,602.12 | 129.28 | 8027.77 | 13,445.07 | 7319.79 | 707.98 | 2831.23 | 1164.24 | 344.58 | 1036.32 | 3140.46 | 1462.44 |
| 2014 | 23,560.00 | 124.26 | 8164.79 | 15,271.89 | 7362.84 | 825.10 | 3809.31 | 1044.46 | 329.28 | 1211.83 | 3268.43 | 1530.96 |
| 2015 | 24,964.99 | 109.78 | 7940.69 | 16,914.52 | 7160.25 | 780.44 | 3826.42 | 1130.88 | 374.82 | 1374.51 | 4052.23 | 1696.02 |
| 2016 | 27,466.15 | 109.47 | 7994.34 | 19,362.34 | 7145.02 | 849.32 | 3809.31 | 1044.46 | 329.28 | 1618.58 | 4762.5 | 2124.78 |
| 2017 | 30,133.86 | 98.99 | 9251.40 | 20,783.47 | 8303.54 | 947.86 | 4393.36 | 1344.24 | 403.83 | 1952.14 | 5328.52 | 2571.38 |
| 2018 | 32,679.87 | 104.37 | 9732.54 | 22,842.92 | 8694.95 | 1071.75 | 4581.49 | 1533.36 | 421.46 | 2377.6 | 5781.63 | 1992.52 |
| 2019 | 38,155.32 | 103.88 | 10,299.16 | 27,752.28 | 9670.68 | 716.16 | 5023.23 | 1650.44 | 458.86 | 2830.11 | 6600.6 | 3300.72 |
| 2020 | 38,700.58 | 103.57 | 10,289.47 | 28,307.54 | 9656.51 | 719.64 | 4869.89 | 1474.82 | 369.14 | 2760.6 | 7166.26 | 3393.4 |
| 2021 | 43,214.85 | 99.97 | 11,449.32 | 31,665.56 | 10,738.8 | 798.49 | 5554.03 | 1843.46 | 399.31 | 3392.88 | 7973.25 | 3564.49 |
| 2022 | 44,652.80 | 96.95 | 11,458.43 | 33,097.42 | 10,794.54 | 743.57 | 5068.5 | 1914.53 | 330.45 | 3788.56 | 8626.31 | 3619.21 |
| 2023 | 47,218.66 | 96.09 | 11,612.97 | 35,509.6 | 10,846.16 | 882.25 | 5094.52 | 2331.48 | 408.66 | 4732.03 | 8646.86 | 3555.18 |
| 2024 | 53,926.71 | 99.70 | 11,637.57 | 42,189.44 | 10,910.88 | 893.45 | 6590.22 | 2003.02 | 513.18 | 6062.33 | 8072.73 | 5584.21 |
References
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X. Economic growth and industrial structure optimization in Shanghai. China Ind. Econ. 2017, 1, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Johnson, P. Industrial restructuring and environmental quality: Evidence from developed economies. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 93, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, J. The role of foreign direct investment in Shanghai’s economic growth. Int. Bus. Res. 2021, 14, 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. World Development Report 2023: Navigating Global Economic Challenges. 2023. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/publication/wdr2023 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Qiu, X. Quantification of the short-term impact of economic shock events on the gross domestic product of 31 provinces in China from 2005 to 2022. SN Bus. Econ. 2024, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Yi, H. A Two-Stage Evaluation of China’s New Energy Industrial Policy Package. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. An empirical analysis of economic structural transformation and air pollution prevention in Shanghai. Urban Dev. Stud. 2019, 26, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Research on the relationship between economic structural adjustment and air quality changes in Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangzhou. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 234–245. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wang, M. How Do Financial Development and Industrial Structure Affect Green Total Factor Energy Efficiency: Evidence from China. Energies 2024, 17, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rogelj, J.; Meinshausen, M.; Nakicenovic, N.; Schellnhuber, H.J. A roadmap for rapid decarbonization. Science 2017, 355, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/publications/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%20Development%20web.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Zhou, P.; Li, X. The effect of government policy on economic growth in Shanghai. Public Adm. Dev. 2023, 33, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, W.; Rockström, J.; Richardson, K.; Lenton, T.M.; Folke, C.; Liverman, D.; Summerhayes, C.P.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cornell, S.E.; Crucifix, M.; et al. Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8252–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of China. China’s 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives Through the Year 2035. 2021. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/ghwb/202103/t20210323_1270124.html (accessed on 1 January 2025). (In Chinese)
- World Bank. The Changing Wealth of Nations 2021: Managing Assets for the Future. 2021. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10986/36400 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- World Economic Forum. The Future of Growth Report 2024; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Growth_Report_2024.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Holz, C.A. China’s economic growth 1978–2025: What we know today about China’s economic growth tomorrow. World Dev. 2008, 36, 1665–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2024. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H. The impact of high-tech industries on economic growth in Shanghai. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. (Sci.) 2022, 27, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Municipal Government. Shanghai’s 14th Five-Year Plan for Economic and Social Development and the Long-Range Objectives through the Year 2035; Shanghai Municipal Government: Shanghai, China, 2021. Available online: https://www.shanghai.gov.cn/2035nyjmbgy/# (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Shen, J.; Zhao, X. Innovation-driven development strategy and economic growth in Shanghai. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2019, 39, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S. A novel grey prediction model and its application in economic forecasting. Math. Comput. Model. 2012, 55, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.L. Control problems of grey systems. Syst. Control Lett. 1982, 1, 288–294. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. J. Time Ser. Anal. 2010, 31, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Li, M.; Gao, Z. Analysis of Economic Resilience Measurement and Influencing Factors under the Impact of the Epidemic. Stat. Decis. 2021, 37, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.R.; Majhi, R.; Kalli, R.; Managi, S.; Majhi, B. Impact of COVID-19 on GDP of major economies: Application of the artificial neural network forecaster. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 69, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Shen, T.; Ling, Y. The Impact and Countermeasures of the COVID-19 on Regional Economic Development: Summary of the 15th Symposium of “Chinese Regional Economists of 50 Forum”. Reg. Econ. Rev. 2020, 4, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sun, M.; Yang, W. Assessment of the Impact of COVID-19 Epidemic on China’s Economy: Empirical Analysis based on the GTAP Model. Stat. Decis. 2020, 36, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zan, W. An empirical analysis of the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on China’s GDP. Hebei Enterp. 2022, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, Y. The impact of financial development on economic growth: Evidence from Shanghai. Financ. Econ. Res. 2018, 43, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J. The impact of changes in housing prices on China’s economy. Dean Fr. 2024, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Global Urban Economic Development Report. 2020. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Gu, X. Evolutionary Characteristics and Development Pathways of Shanghai’s Economy under the Dual Circulation Strategy. Mod. Bus. Trade Ind. 2022, 43, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. The Study of the Optimization of Industrial Structure and Population Size–Taking Shanghai as an Example. World J. Soc. Sci. 2014, 1, p72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Ma, L. A Study on the Impact of Population Age Structure Change on Economic Growth in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. The relationship between industrial structure and economic growth—Take Shanghai as an example. Foreign Econ. Relat. Trade 2021, 4, 75–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y. The influence of urbanization on economic growth: A case study of Shanghai. Urban Stud. 2020, 27, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development OECD. OECD Economic Outook, Volume 2022 Issue 2; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2023/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
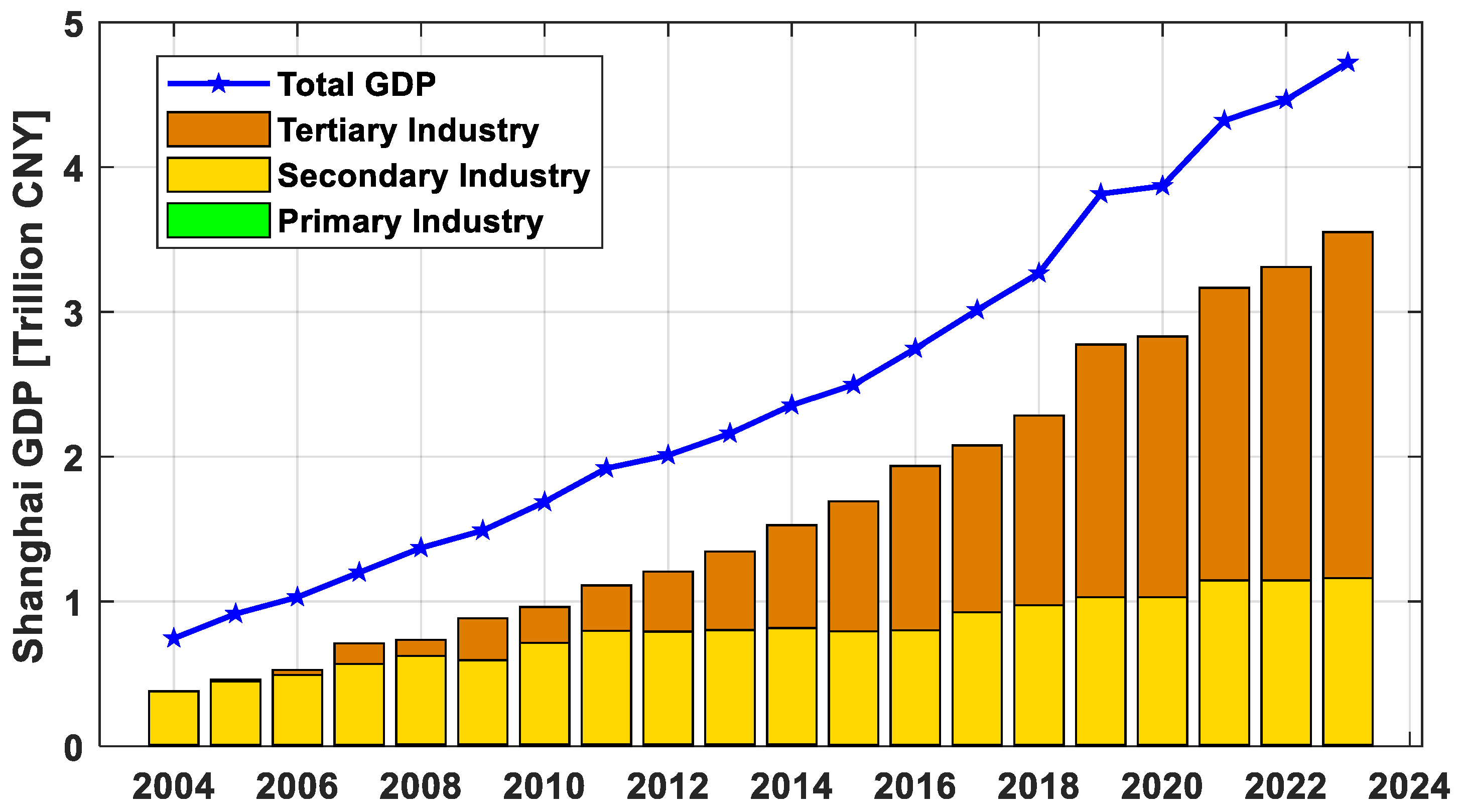
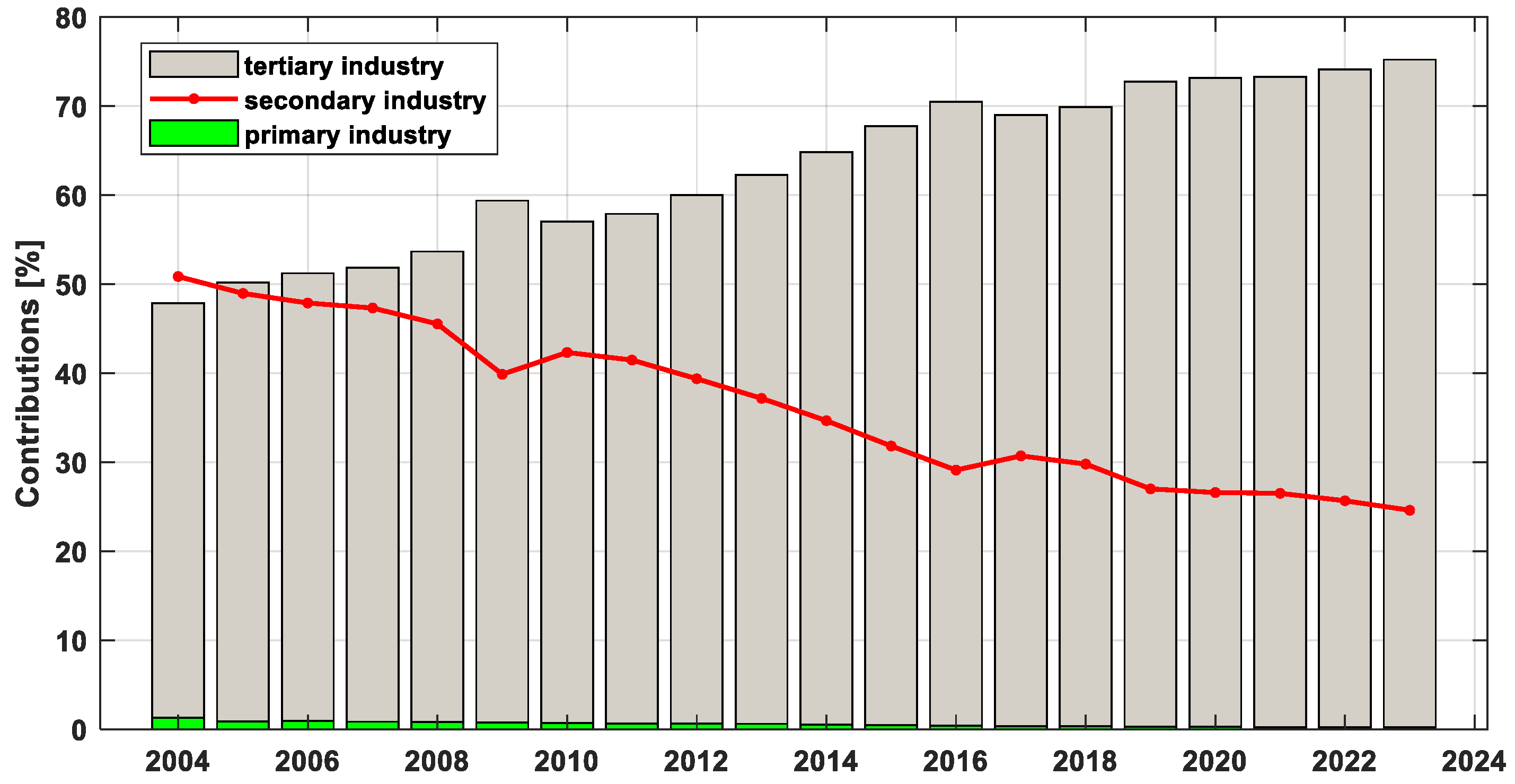
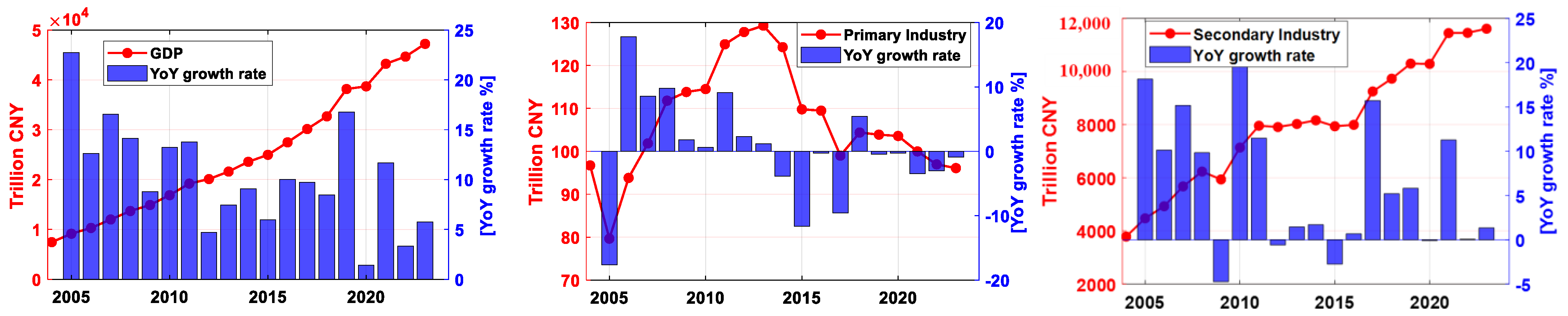
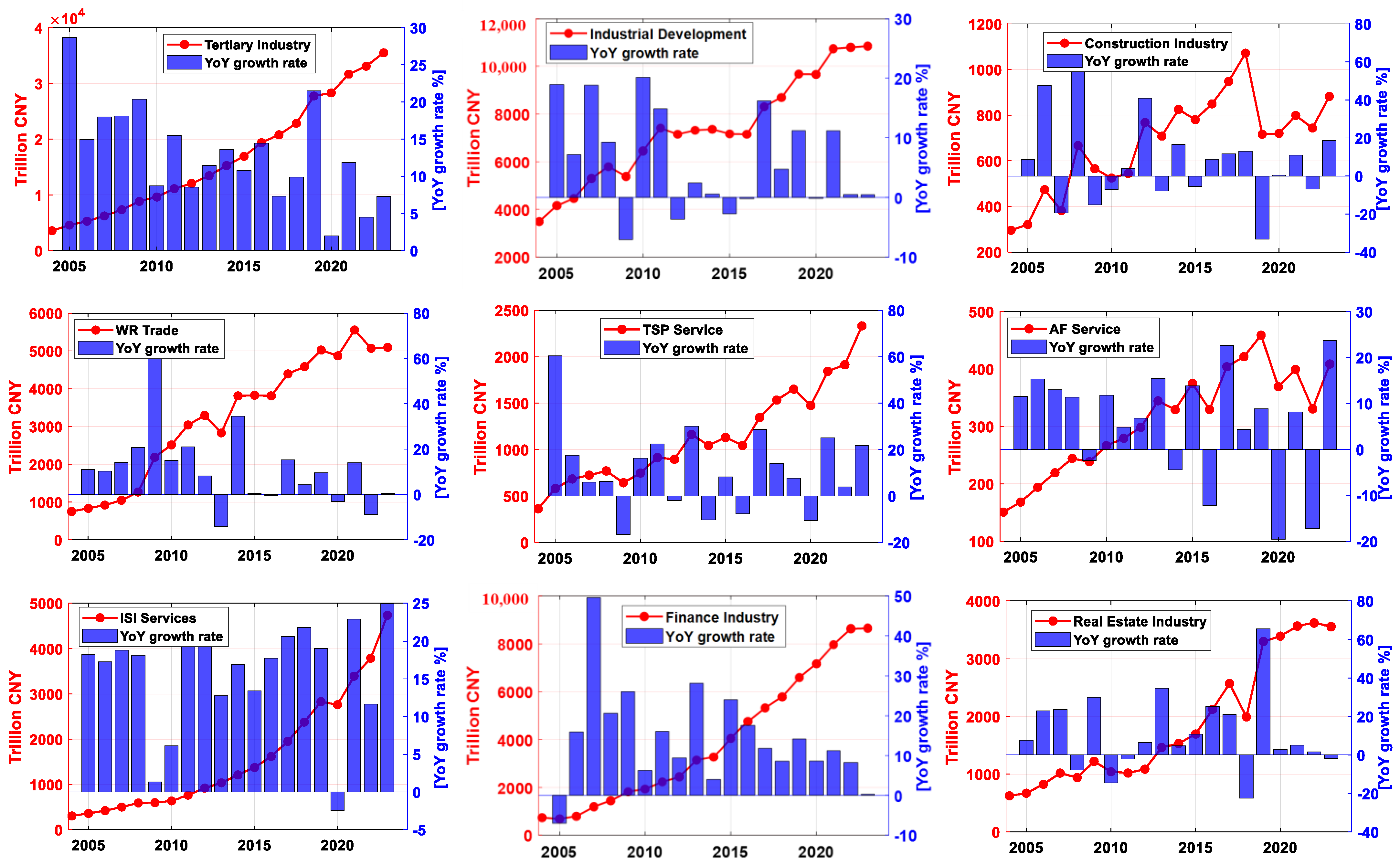
| Year | True GDP | GM(1,1) | SVM | ARIMA(1,1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction | Difference | Relative Error (%) | Prediction | Difference | Relative Error (%) | Prediction | Difference | Relative Error (%) | ||
| 2022 | 44,652.80 | 46,426.99 | 1774.19 | 3.97 | 47,660.15 | 3007.35 | 6.73 | 45,938.23 | 1285.43 | 2.88 |
| 2023 | 47,218.66 | 49,833.09 | 2614.43 | 5.54 | 52,105.81 | 4887.15 | 10.35 | 48,661.61 | 1442.95 | 3.06 |
| Evaluation index | Mean absolute error | — | 2194.31 | 4.76 | — | 3947.25 | 8.54 | — | 1364.19 | 2.97 |
| Index | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction | True GDP | Relative Error (%) | Prediction | Prediction | ||
| 0 | Total GDP | 53,770.10 | 53,926.71 | 0.29 | 56,135.72 | 60,321.54 |
| 1 | Primary | 96.0374 | 99.70 | 3.67 | 96.0329 | 96.0326 |
| 2 | Secondary | 11,859.19 | 11,637.57 | 1.90 | 12,095.03 | 12,320.91 |
| 3 | Tertiary | 41,848.53 | 42,189.84 | 0.81 | 44,001.65 | 46,154.06 |
| 2-1 | Industrial development | 11,068.78 | 10,910.88 | 1.45 | 11,281.50 | 11,484.76 |
| 2-2 | Construction industry | 833.85 | 893.45 | 6.70 | 840.27 | 839.42 |
| 3-1 | WR Trade | 6678.13 | 6590.22 | 1.33 | 6598.42 | 6670.82 |
| 3-2 | TSP Services | 2219.06 | 2003.02 | 10.78 | 2317.36 | 2231.41 |
| 3-3 | AF Services | 453.84 | 513.18 | 11.56 | 513.58 | 453.84 |
| 3-4 | ISI Services | 5335.24 | 6062.33 | 11.99 | 5938.45 | 6541.66 |
| 3-5 | Finance Industry | 9043.56 | 8072.73 | 12.03 | 9436.03 | 9824.32 |
| 3-6 | Real Estate Industry | 5595.71 | 5584.21 | 0.20 | 5589.85 | 5592.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F. Economic Structural Adjustment Promoting Sustainable Growth in Shanghai: A Two-Decade Study (2004–2023). Sustainability 2025, 17, 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104318
Wang D, Zhou Y, Wang F. Economic Structural Adjustment Promoting Sustainable Growth in Shanghai: A Two-Decade Study (2004–2023). Sustainability. 2025; 17(10):4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104318
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Danjun, Yunqi Zhou, and Fengwei Wang. 2025. "Economic Structural Adjustment Promoting Sustainable Growth in Shanghai: A Two-Decade Study (2004–2023)" Sustainability 17, no. 10: 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104318
APA StyleWang, D., Zhou, Y., & Wang, F. (2025). Economic Structural Adjustment Promoting Sustainable Growth in Shanghai: A Two-Decade Study (2004–2023). Sustainability, 17(10), 4318. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17104318






