Abstract
The results obtained reflect the determination of the possibility of the stability enhancement of the strength and thermal parameters of zirconium-containing ceramic materials via the addition of a stabilizing additive in the form of Y2O3. According to the data obtained, a connection between phase transformations caused by the addition of the stabilizing Y2O3 additive and an increase in strength characteristics, the growth of which is also due to the formation of the dispersion hardening effect during grain size reduction, was established. It was found that the formation of the stabilized Zr(Y)O2 phase results in thermal conductivity reduction, while the formation of the perovskite phase YZrO3 has a positive effect on the thermophysical parameters of ceramics. It was determined that the change in phase composition associated with the formation of the tetragonal Zr(Y)O2 phase at low dopant concentrations leads to an increase in strength characteristics, but a decrease in thermal conductivity, while the formation of the YZrO3 phase in the structure contributes to a growth not only in strength, but also thermophysical parameters.
1. Introduction
The expansion of the potential for using alternative energy sources to solve problems associated with the depletion of hydrocarbon reserves and environmental problems caused by their extraction is inextricably linked with the search for new technological solutions aimed at the energy extraction efficiency enhancement [1,2]. One of the most promising areas in alternative energy is increasing the burnup depth of nuclear fuel, as well as increasing the operating temperatures of the active zone, which will improve energy efficiency and reduce the concentration of spent nuclear fuel and its decay products in the form of minor actinides, the accumulation of which is one of the important problems in the nuclear fuel cycle due to their radioactivity and long decay times [3,4]. Also, these substances, together with nuclear fuel fission fragments during operation, are capable of having a negative impact on structural materials, and in the case of their disposal and long-term storage, require additional levels of protection from the radiation they emit, and also emit a large amount of heat, which can lead to thermal expansion, as well as the acceleration of thermally induced corrosion of protective materials used for storage. In this case, the considered concepts of transition to dispersed nuclear fuel, which are based on the placement of fissile nuclear material in inert matrices that must have high resistance to the radiation damage accumulation, as well as thermal effects associated with the release of heat and its removal as a result of the fission of nuclear fuel, are the most promising areas of development in nuclear energy, making it possible to expand the potential for the creation of new Gen IV generation reactors [5,6]. At the same time, much attention in this area of research is paid to the creation of new types of ceramic materials [7,8,9], high-entropy alloys [10,11,12] and composite ceramics [13,14,15], the interest in which is primarily due to the possibility of growth of the efficiency of nuclear fuel use by enhancement of the efficiency of production and burnup depth [16].
Interest in ZrO2 ceramics when considering their potential for use in nuclear applications, including the possibility of using them as structural materials, inert matrices for new generation fuel elements, and protective shielding materials, is primarily due to the combination of strength and thermophysical parameters [17,18]. However, possible polymorphic transformations caused by the structural features of these ceramics are one of the limiting factors that impose restrictions on the widespread use of ZrO2 ceramics in extreme conditions. The occurrence of polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-ZrO2 or t-ZrO2 → c-ZrO2 type are directly related to temperature effects, and as has been shown in several studies [19,20,21], these effects can also occur in the case of radiation damage accumulation, leading to polymorphic transformations and partial amorphization of the damaged layer. In this case, polymorphic transformations in ZrO2 ceramics can lead not only to a change in strength characteristics, but also to a change in thermophysical parameters, the variation of which in turn can lead to destabilization of damaged layers due to the formation of a local overheating effect in the structure, associated with the formation of structurally altered areas, whose density directly depends on the radiation damage degree [20].
One of the methods used to increase the resistance of ZrO2 ceramics not only to mechanical impacts arising during the operation of ceramics, but also to radiation damage, which determines the potential for their use in nuclear power, is the stabilization of ceramics with various dopants in the form of oxides (Y2O3, MgO, CeO2), the addition of which allows solving a number of issues related to polymorphic transformations, as well as increasing strength and thermal properties [22,23,24]. In this case, variation in the concentration of stabilizing additives, as a rule, leads to the possibility of reducing the temperature of polymorphic transformations, as well as compaction of ceramics due to structural changes. Also, variation in the concentration of stabilizing additives allows us to obtain composite ceramics that combine several phases with different properties, and as a result, allows us to combine several effects, including the dispersed hardening effect (associated with grain sizes) and interphase hardening, obtaining ceramics with higher density and low porosity [25,26].
As is known, one of the key features of ZrO2 is the polymorphic transformations that occur under thermal influence, which consist of the transformation of the monoclinic phase into a tetragonal one at temperatures above 1450 K and from tetragonal to cubic at temperatures of about 2600–2700 K. Moreover, these polymorphic transformations are usually accompanied by a change in the volume of ceramics, which leads to an alteration in their strength properties due to the metastability of the tetragonal phase and the instability of the high-temperature cubic phase, which can result in accelerated destruction processes in the case of prolonged exposure to high temperatures. One of the ways to maintain the stability of the phase composition of ZrO2 ceramics when used in extreme conditions is to stabilize their crystal structure during the manufacturing process by addition of stabilizing additives to the composition in the form of Y2O3, MgO, Al2O3, etc. The use of stabilizing additives allows acceleration of the processes of polymorphic transformations during the synthesis process, which results in sintering temperature reduction, and allows elevation of resistance to external influences due to substitution effects. The aim of the study is to establish the relationships between phase transformations in ZrO2 ceramics stabilized by Y2O3 and changes in strength and thermal parameters, the variation of which is caused by structural changes. The use of the stabilizing additive Y2O3 for the modification of ZrO2 ceramics is due to the possibility of initiating phase transformation processes, which are accompanied by a change in strength parameters due to the compaction of ceramics, which makes it possible to optimize the composition of ceramics for specific practical applications. The choice of Y2O3 as a stabilizing additive is primarily due to its high compatibility with zirconium dioxide, the combination of which allows for a significant reduction in the temperature of polymorphic transformations during the manufacturing process of ceramics, as well as an increase in the stability of the formed phase composition to subsequent thermal effects during operation. Also, due to its structural features, the substitution of zirconium by yttrium results in minimal distortions of the crystal lattice of the tetragonal phase due to the small difference in ionic radii (Y3+~0.9 Å, Zr4+~0.79 Å). At the same time, during the maintenance of electroneutrality, the substitution of zirconium by yttrium leads to the formation of oxygen vacancies, the formation of which leads to a decrease in the deformation elastic distortions of the tetragonal phase. Also, the preference towards a variable valence state of yttrium ions allows minimization of the contribution of electronic defects in the structure.
At the same time, consideration of the possibility of using such elements as Al, Si, or Zn or their oxides as stabilizing additives to improve the thermophysical parameters was excluded due to the fact that the combination of zirconium dioxide with aluminum or silicon oxides leads to the formation of a structure of the “massive matrix with inclusions in the form of ZrO2 grains” type, which in turn does not allow growth of the strength properties due to the effect of dispersion hardening, and also does not allow the restraining of the processes of polymorphic transformations of ZrO2 at high temperatures.
The novelty of the research consists of the determination of the optimal compositions of ZrO2 ceramics with high strength characteristics, as well as thermophysical parameters that play a very important role in the determination of the applicability of these ceramics as structural materials for nuclear reactors, especially materials for inert matrices of dispersed nuclear fuel. Enhancement of stability against external influences (mechanical loads, pressure, aggressive environments, thermal expansion), as well as maintenance of the stability of the crystalline structure by prevention of the effects of polymorphic transformations during the operation of ceramics, is one of the key tasks, the solution of which will make it possible to obtain high-strength ceramics used as inert matrices for dispersed nuclear fuel, whose operation is accompanied by extreme conditions (high temperature and high doses of radiation).
2. Materials and Methods
The method of mechanochemical solid-phase synthesis was used for the synthesis of samples, including mixing ZrO2 powder with Y2O3, which is used as a stabilizing dopant. ZrO2 and Y2O3 powders were selected as the initial powders used for the synthesis of ceramics; their chemical purity was about 99.95%; the powders were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Mechanochemical grinding was carried out using a PULVERISETTE 6 planetary mill (Fritsch, Berlin, Germany). The process of stabilization of ZrO2 ceramics was carried out by adding Y2O3 to the composition in a molar ratio of 0.01 to 0.15 M.
The samples were ground at a grinding speed of 250 rpm for 30 min, after which the resulting powders were removed and subjected to thermal annealing in a muffle furnace. Annealing was carried out at a temperature of 1200 °C for 5 h at a heating rate of 20 °C/min. After annealing, the samples were cooled together with the furnace for 24 h until completely cooled. The choice of annealing temperature was determined by the possibilities of initiating phase transformation processes in zirconium dioxide associated with the transition from the monoclinic to the tetragonal phase, the formation of which occurs at a temperature above 1170 °C; however, these transformations can be caused by a change in the concentration of oxygen vacancies in the composition of ceramics, the concentration of which plays an important role in the processes of polymorphic transformations.
The study of morphological features was carried out using the scanning electron microscopy method implemented using a Phenom™ ProX microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). Images were acquired under the same imaging conditions and magnification scales to be able to assess changes in grain morphology associated with phase transformation processes when adding a stabilizing additive to the composition.
The study of phase transformations in ZrO2 ceramics with the addition of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 was carried out using X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. X-ray diffraction patterns were obtained on a D8 ADVANCE ECO diffractometer (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany). The diffraction patterns were obtained in the angular range of 2θ = 15–100°, with a step of 0.03° and a collection time of 1 sec per point. The total time for recording one diffraction pattern was about 1 h with the possibility of detailing the obtained diffraction patterns, as well as identifying impurity phases. Raman spectra were obtained using an Enspectr M532 Raman spectrometer (Spectr-M LLC, Chernogolovka, Russia).
The influence of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 on the change in strength properties was determined by measuring the values of hardness (indentation method) and bending strength (three-point bending methods). These methods were implemented using the Duroline M1 microhardness tester (Metkon, Bursa, Turkey) and the LFM-L 10kH single-column testing machine (Walter + Bai AG, Löningen, Switzerland).
Determination of thermophysical parameters (thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity) was carried out using a universal device KIT–800 (Teplofon, Moscow, Russia). Measurements were carried out in the mode of measuring the temperature difference on both sides of the sample using thermocouples and a special heater. The measurements were carried out on samples in the form of tablets with a diameter of 10 mm and a thickness of about 1 mm, placed on a heating element with a heating temperature recorded using a thermocouple. A thermocouple was also placed on the back side of the sample, allowing the temperature of the sample to be recorded from the back side. Based on the temperature difference measurements, the thermal conductivity coefficient was determined taking into account the size of the sample, its density and the type of material.
The optical characterization was performed using transmission and absorption spectra measurements obtained with SPECORD 200/210/250 PLUS spectrophotometer (Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany). The spectra were recorded in the wavelength range from 200 to 1000 nm, with a step of 1 nm.
Thermal shock tests were performed by simulating extreme situations, including rapid heating of samples to 1000 °C, holding at this temperature for 1 h, and then rapidly removing the samples into the air to create a large temperature gradient on the sample due to the temperature difference characteristic of thermal shock exposure. After a series of similar tests (10 consecutive tests), the values of hardness and bending strength were measured, which made it possible to determine the influence of such temperature effects on the change in the strength properties of ceramics.
All experimental work related to the determination of strength and thermal parameters was carried out in several parallels in order to eliminate errors and inaccuracies in measurements, as well as to determine the magnitude of measurement errors, the magnitude of which amounted to no more than 1–2% deviation from the measured values.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 1 shows SEM images of the original ZrO2 powder, reflecting its states in the original (not milled) state, after mechanochemical milling and after thermal sintering. These images reflect the effect of mechanochemical grinding and thermal annealing on the change in the morphological features of the powders under study, which serve as the basis for creating ceramics. In the initial state, ZrO2 powders are clusters of fairly large particles of varying sizes and shapes due to the manufacturing processes (see data in Figure 1a). Mechanochemical grinding results in grain fragmentation and the formation of smaller agglomerates that do not have a clearly defined shape, as well as a low degree of crystallinity due to the deformation impact of the grinding bodies during grinding. Thermal annealing of the samples leads to the initialization of transformation processes associated with the formation of ZrO2 grains having an elongated spherical shape, while the sizes of the formed grains are quite close, without any strong scatter, which indicates that the thermal annealing process leads to the formation of single-phase grains with a monoclinic crystal structure (according to the X-ray phase analysis data presented in Figure 2).
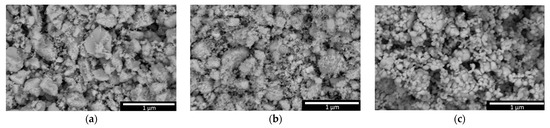
Figure 1.
SEM images of the studied ZrO2 powders: (a) in the initial state; (b) after mechanochemical grinding; (c) after thermal sintering.
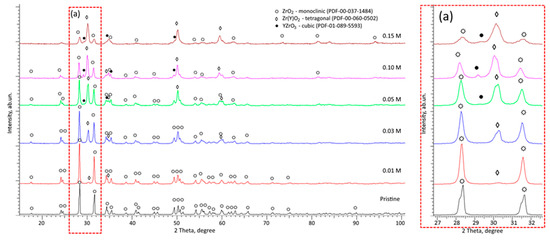
Figure 2.
Results of X-ray phase analysis of the studied ZrO2 ceramics with variations in the stabilizing additive Y2O3 (the inset (a) shows the details of the main changes in the reflections in the region of 2θ = 27–32°, reflecting the phase transformations).
Figure 2 shows X-ray diffraction patterns reflecting changes in the structure of ceramics associated with phase transformations upon addition of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3. The data are presented in the form of diffraction patterns, the changes in which are caused by the processes of phase transformations caused by the addition of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 in the composition during its variation. A diffraction pattern of ZrO2 ceramics without a stabilizing additive subjected to mechanochemical grinding and subsequent thermal annealing is shown as a comparative diffraction pattern. According to the presented data, the position of the observed reflections on the diffraction pattern of the original sample corresponds to the ZrO2 phase with a monoclinic type of crystal lattice (m-ZrO2, PDF-00-037-1484), and the shape of the diffraction lines indicates a sufficiently high degree of structural ordering caused by crystallization processes during thermal annealing. It should also be noted that the selected conditions of thermal annealing at a temperature of 1200 °C, as can be seen from the X-ray phase analysis data, do not lead to the initialization of the processes of phase polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-ZrO2 type, from which it can be concluded that the selected conditions of annealing in an oxygen-containing environment of samples subjected to mechanochemical milling lead to the stabilization of the crystal structure, while the processes of polymorphic transformations are not initiated. The addition of a stabilizing additive in the form of Y2O3 in small concentrations of 0.01–0.03 M to the composition of ZrO2 ceramics, according to the data presented in the X-ray diffraction pattern (see data in Figure 2), leads to the formation of low-intensity reflexes characteristic of the tetragonal phase of Zr(Y)O2, the appearance of which indicates phase polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type. Moreover, according to the data on the structural parameters presented in Table 1, an increase in the parameters of the crystal lattice of the tetragonal phase indicates a partial substitution of zirconium ions (Zr4+) by yttrium ions (Y3+), and an increase in the concentration of the stabilizing additive from 0.01 to 0.03 M leads to an increase in the intensity of diffraction reflections characterizing the presence of the tetragonal phase, which follows an increase in its weight contribution to the overall structure of the ceramics.

Table 1.
Data on the crystal lattice parameters of the observed phases in the composition of ZrO2 ceramics depending on the variation in the concentration of the Y2O3 stabilizing dopant.
It should also be noted that the observed shift of diffraction reflections for the monoclinic phase m-ZrO2 to the region of large angles (see inset in Figure 2), which characterizes the growth of interplanar distances, indicates the substitution of Zr4+ ions (0.84 Å) by Y3+ (0.90 Å), which results in the growth of oxygen vacancies (VO). The formation of additional oxygen vacancies in the structure leads to stabilization of the crystal structure, which results in the formation of the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2, as well as an increase in its weight contribution to the ceramics. At concentrations of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 in the ceramics starting from 0.05 M, in addition to a change in the intensity ratio of the monoclinic m-ZrO2 and tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2, the obtained diffraction patterns show the formation of diffraction reflections characteristic of the YZrO3 phase (PDF-01-089-5593) with a cubic type of crystal lattice, characteristic of perovskite structures. Crystallization of this phase in ZrO2 ceramics is associated with an excess of Y3+ ions, some of which cannot form the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2, but crystallize into the YZrO3 phase, which has a denser structure. At the same time, as can be seen from the presented X-ray diffraction patterns, in the case of high concentrations of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3, the process of polymorphic transformations of the type m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 is dominant in crystallization, and the content of the impurity phase of perovskite YZrO3 is insignificant. In this case, the formation of the t-Zr(Y)O2 and YZrO3 phases is caused not only by the effects of partial substitution, but also by the thermodynamic effects of polymorphic transformations m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2. In this case, the addition of yttrium oxide to the composition of ZrO2 ceramics leads to an increase in the number of oxygen vacancies due to dissociative substitution reactions of the type Y2O3→2YZr′ + VO ●● + 3OO×, which in turn affects the entropy due to the exothermic contribution of vacancies, leading to a decrease in the temperature at which polymorphic transformation reactions occur (in the case of unstabilized m-ZrO2, the polymorphic transformation into t-ZrO2 occurs at a temperature of 1450 K). Also, the reduction in grain size caused by mechanical grinding of samples, observed during the addition of Y2O3 to the composition, also contributes to a shift in thermodynamic equilibrium, which leads to an acceleration of the processes of polymorphic transformations.
As confirmation of the observed phase changes in the structure of ceramics depending on the variation in the dopant concentration, Figure 3 shows the results of Raman spectroscopy of the studied samples. The spectra of ZrO2 ceramics contain peaks characteristic of the monoclinic phase of zirconium oxide. For the original sample, without addition of a stabilizing additive, 15 peaks corresponding to m-ZrO2 were detected, including 178 (Ag), 190 (Ag), 221 (Bg), 306 (Ag), 333 (Bg), 347 (Ag), 382 (Bg), 450, 474 (Ag), 503 (Bg), 537 (Bg), 558 (Ag), 582, 615 (Bg) and 636 (Ag) cm−1 [27]. Furthermore, an additional peak was recorded at 756 cm−1, associated with defects in ZrO2 [28] caused by mechanochemical processing, as well as subsequent thermal annealing, which, as shown in Figure 1, causes changes in grain sizes and their formation. Also, the presence of this peak may be due to the presence of structural distortions associated with the presence of oxygen vacancies (VO) in the composition of ceramics.
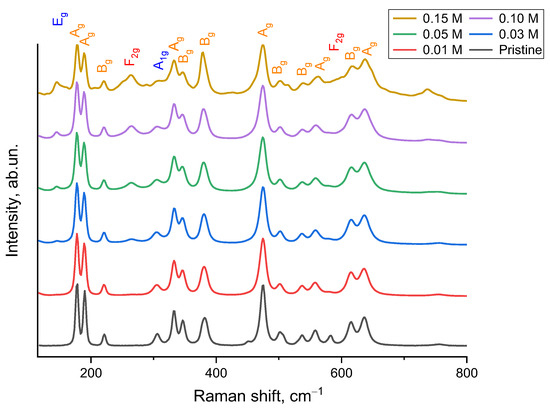
Figure 3.
Results of Raman spectroscopy of the studied ZrO2 ceramics depending on the change in the concentration of the stabilizing additive Y2O3.
Addition of 0.01 M Y2O3 leads to the disappearance of the modes at 450 and 580 cm−1, which indicates a change in the defect structure, as well as the initialization of phase transformations in the samples associated with the stabilization of the crystal lattice. At a concentration of 0.03 Y2O3, peaks at 146 and 265 cm−1 appear in the spectra, corresponding to the tetragonal phase of Zr(Y)O2, while the broadened shape of the spectral lines, as well as their positions, indicate cationic substitution, confirming the results of X-ray phase analysis (see data in Figure 2) [29]. With a further increase in the Y2O3 concentration, an increase in the intensity of the modes characteristic of the tetragonal phase of Zr(Y)O2 is observed, which is in good agreement with the X-ray phase analysis data. At a content of 0.05–0.15 M Y2O3, in addition to the increase in intensity, additional low-intensity peaks appear at 206, 252, 288, 423 and 513 cm−1, the formation of which is due to the formation of the perovskite phase of YZrO3 with a cubic type of crystal lattice in the composition of the ceramics.
Based on the method of estimation of the weight contributions of each phase in the composition of ceramics, including determining the intensity and area values of diffraction peaks (in the case of X-ray phase analysis) and spectral modes (in the case of Raman spectroscopy), phase diagrams were constructed that reflect the change in the phase ratio in the composition of ceramics with variations in the concentration of the stabilizing additive Y2O3. The results are shown in Figure 4a,b. The calculation of inclusions of the phases formed in the composition of ceramics in the case of addition of Y2O3 to them was performed using the standard method of estimation of weight contributions. This method includes determination of the areas of all reflections characteristic of the established main and impurity phases with subsequent calculation of their contribution to the diffraction pattern or Raman spectrum. This method allows quite accurate determination of the change in phase composition in samples in the case of the formation of impurity inclusions, the content of which exceeds 0.1 wt.%.
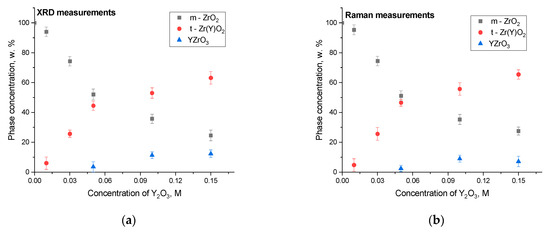
Figure 4.
Assessment results of the phase composition of the studied ZrO2 ceramics depending on the variation in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3: (a) data obtained using the X-ray diffraction method; (b) data obtained using the Raman spectroscopy method.
The overall view of the obtained dependences of the change in the weight contributions of various phases indicates that the addition of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 in small quantities (0.01–0.05 M) leads to the formation of a small proportion of the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2, the weight contribution of which increases as the concentration of the stabilizing dopant in the composition of the ceramics grows. At a concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 in the composition, the observed formation of a contribution of the perovskite phase t-Zr(Y)O2 indicates an excess of yttrium ions in the composition of the ceramics, which leads to the formation of this phase, the content of which does not exceed 10–15% in the case of high concentrations of the dopant (0.1–0.15 M).
The obtained results indicate the dynamics of phase transformations, which have a direct relationship between changes in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 in the composition, and phase polymorphic transformations that occur during thermal sintering. At the same time, the general appearance of the presented dependencies indicates that the selected synthesis conditions make it possible to obtain two- and three-phase ceramics with different phase ratios in the composition, which can be used to increase the resistance of ceramics to external influences, including thermal effects during heat resistance tests, and also to contribute to an increase in resistance to radiation-induced destruction processes in the case of testing this type of ceramics as structural materials.
The analysis of the ratio of weight contributions determined using the two methods, as can be seen from the data presented in Figure 4, has good agreement, from which one can conclude about the possibilities of using not only the X-ray diffraction method to clarify the phase composition, but also, in certain cases, to use the Raman spectroscopy method.
Figure 5 reveals the results of the change in the grain morphology of the studied ZrO2 ceramics depending on the variation in the concentration of Y2O3 in the composition after thermal sintering at a temperature of 1200 °C. The SEM image data reflect the change in the shape of the grains and their agglomeration associated with phase transformations that occur during thermal sintering with different variations in the stabilizing additive concentration.
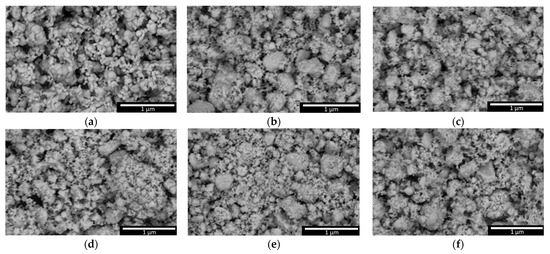
Figure 5.
Results of morphological features of the studied ZrO2 ceramics with the addition of the stabilizing additive Y2O3: (a) pristine; (b) 0.01 M; (c) 0.03 M; (d) 0.05 M; (e) 0.10 M; (f) 0.15 M.
As can be seen from the data presented, in the case of thermal annealing of ZrO2 ceramics without addition of a stabilizing dopant, the grain morphology is represented by agglomerates of large spherical particles. The addition of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 leads to the formation of two types of particles: large spherical particles and a finely dispersed fraction surrounding large agglomerates. Such changes in grain shape, in particular the formation of a finely dispersed fraction, are associated with phase changes caused by the addition of the stabilizing Y2O3 dopant to the composition of ceramics. It should be noted that an elevation in the concentration of the Y2O3 dopant leads to an increase in the proportion of the finely dispersed fraction in the composition of ceramics. Comparing the results of X-ray phase analysis (data on the weight contributions of the established phases) and the ratio of large and fine fractions in the composition of ceramics, it can be concluded that the formation of the fine fraction is associated with phase polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type, arising due to a change in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant in the composition of ceramics. The observed growth in the fine fraction in the composition of ceramics with an increase in the concentration of the stabilizing Y2O3 dopant leads to the fact that larger agglomerates are completely covered with small grains, thereby creating the effect of “large core—fine shell” filling the intergranular space, and also creating a large number of grain boundaries that have a positive effect on hardening.
Figure 6 illustrates a block diagram reflecting the relationship between changes in the morphological features and phase composition of ZrO2 ceramics when a stabilizing additive Y2O3 is added to the composition, a change in the concentration of which leads to the initialization of phase transformation processes caused by transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type, as well as the formation of the perovskite phase YZrO3. According to the general analysis of the observed changes in the phase composition caused by phase polymorphic transformations with a change in the concentration of the Y2O3 dopant, it can be concluded that transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type are associated with the formation of a finely dispersed fraction covering larger grains of the monoclinic phase ZrO2. In this case, as a result of the increase in the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2 with the subsequent formation of the perovskite phase YZrO3 in the composition, the proportion of finely dispersed fraction in the composition of ceramics increases, which in turn can lead to the occurrence of the effect of dispersion hardening associated with a change in grain size, as well as filling the interpore space with finely dispersed fractions, which in turn leads to the compaction of ceramics and an increase in strength properties.
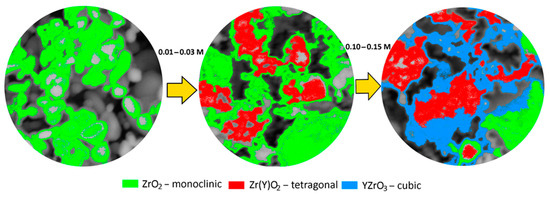
Figure 6.
Scheme of phase transformations in ZrO2 ceramics with the addition of the stabilizing additive Y2O3.
A similar size effect, characterized by the fact that during phase polymorphic transformations, a change in grain sizes is observed associated with the transformations of zirconium dioxide, was established in the work [30], in which the authors established the formation of a cubic phase in the form of a finely dispersed fraction, agglomerating near large grains of the monoclinic phase during the hydrothermal synthesis of ZrO2 ceramics (see the data presented in Figure 7). A similar effect is observed in the case of both mechanochemical synthesis with subsequent thermal annealing, from which it can be concluded that polymorphic phase transformations in ZrO2 ceramics cause dimensional changes associated with the fact that the formation of new phases occurs due to the crushing of large grains of the monoclinic phase into smaller grains of the tetragonal or cubic phase. Moreover, this effect is observed for all synthesis methods that involve the thermal action procedure. Such disintegration of large particles into smaller ones can be caused not only by the processes of the need to maintain electroneutrality, the change of which is associated with cation substitution and the formation of oxygen vacancies, but also by maintaining an energy balance, in which the formation of a new phase is energetically favorable during the coagulation of small grains, which leads to their nucleation and subsequent release from the large fraction.

Figure 7.
(a) TEM image of synthesized ZrO2 particles (data presented based on the results of work [30]); (b) detailing of ZrO2 particles with differences in phase composition highlighted.
Figure 8a reveals the results of the assessment of strength characteristics, reflecting the influence of the phase transformation variation on the change in hardness and bending strength. According to the presented data, in the case of the initial ceramic sample, the hardness value is about 940 HV, and the bending strength value is about 170 MPa. The addition of a low concentration of a stabilizing dopant (0.01–0.03 M) leads to a slight increase in strength characteristics, which is about 3–5% (see data in Figure 9), from which we can conclude that the initialization of polymorphic transformation processes in ceramics, caused by the addition of stabilizing dopants, leads to the hardening of ceramics. It should also be noted that the hardening effect can be explained by two factors: the size factor associated with the appearance of a finely dispersed fraction in the ceramics during the initialization of polymorphic transformation processes, as well as phase transformation, characterized by higher strength indicators of the tetragonal phase. An elevation in the weight contribution of the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2 leads to an increase in the strength characteristics, which indicates a positive effect of the variation in the phase composition of ceramics on hardening, which is associated with both a change in the phase composition due to polymorphic transformations and size effects that cause hardening due to compaction and the creation of additional grain boundaries that prevent the propagation of microcracks under external loads. A growth in the resistance of ceramics due to structural features indicates that this effect can be used to obtain high-strength ceramics due to stabilization processes when stabilizing dopants are added to the composition.
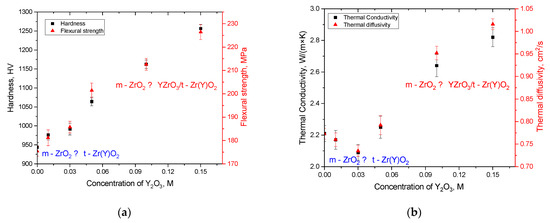
Figure 8.
(a) Results of alterations in the values of hardness and flexural strength of ceramics depending on the concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3; (b) results of alterations in the values of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of ceramics depending on the concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3.
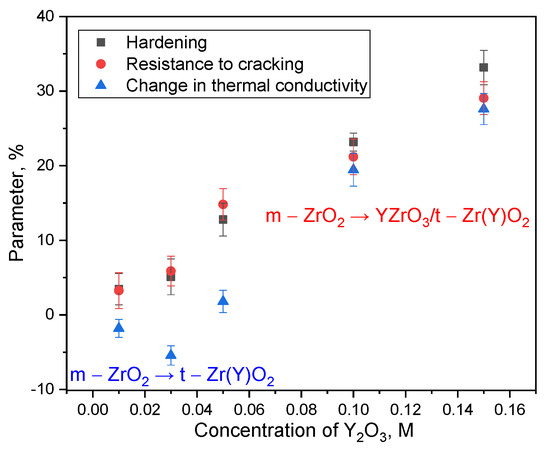
Figure 9.
Results of comparative analysis of changes in hardening parameters (increase in hardness and resistance to cracking) and thermal conductivity depending on the concentration of the stabilizing additive and phase transformations.
Figure 8b demonstrates the assessment results of the alterations in the thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity values, reflecting the effect of changing the concentration of stabilizing dopants on the thermophysical parameters, which are one of the key parameters of ceramics that determine their use as heat-dissipating materials. According to the data presented, the formation of a finely dispersed t-Zr(Y)O2 phase in the structure of ceramics in small concentrations leads to an insignificant decrease in the thermophysical parameters. This reduction is due to the effect of lower thermal conductivity of the tetragonal phase, as well as size effects associated with the large difference between the grain sizes of the monoclinic phase, which is dominant in the composition of ceramics, and the tetragonal phase, represented by fine grains. In this case, the difference in grain sizes, which creates a hardening effect, can contribute to a negative effect that reduces thermal conductivity. It should also be noted that small values of thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity can be affected by the concentration of oxygen vacancies, the presence of which is due to the effects of phase transformations and partial substitution of zirconium ions by cerium ions, accompanied by the appearance of oxygen vacancies. An increase in the contribution of the tetragonal phase t-Zr(Y)O2 in the composition of ceramics, as well as the formation of inclusions in the form of the perovskite phase YZrO3, leads to an increase in thermal conductivity, which can be caused by both the effects of structural ordering associated with changes in the phase composition of ceramics, and size factors that expressed a decrease in the spread in grain sizes and the dominance of the finely dispersed fraction in the samples. The presence of the perovskite phase YZrO3, which has higher thermal conductivity, also contributes to the change in thermophysical parameters, which leads to a positive effect not only in hardening of ceramics, but also in increasing thermal conductivity, which eliminates the effect of local overheating. In this case, the growth of thermophysical parameters with an increase in the contribution of the perovskite YZrO3 phase in the composition of ceramics is due to the higher thermal conductivity of this phase compared to the monoclinic phase ZrO2 and t-Zr(Y)O2, the displacement of which leads to an increase in the heat transfer rate. Thus, by variation in the composition of ceramics, it is possible to control not only the strength characteristics, but also the thermophysical parameters, which play an important role in determining the applicability potential of ceramics.
Figure 9 illustrates the results of a comparative analysis of changes in the parameters of ceramic hardening and changes in the thermophysical characteristics associated with changes in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant in the composition of the samples. The general trend presented indicates positive growth dynamics of strength and thermophysical parameters, reflecting the direct influence of the phase composition on the properties of ceramics. The most noticeable effects of changes in thermophysical and strength parameters are observed in the case when the composition of ceramics is represented by a mixture of three phases: monoclinic phase ZrO2, tetragonal phase with partially substituted zirconium ions Zr(Y)O2 and inclusions of perovskite phase YZrO3, the share of which in the composition of ceramics varies from 5 to 10–12% in the composition, which is about 1/10 of the total phase composition, taking into account that this phase in the composition of ceramics is distributed isotropically throughout the volume. It is evident that the formation of the Zr(Y)O2 phase in the case of low concentrations of the stabilizing dopant leads to a decrease in thermal conductivity, while a change in strength parameters indicates an increase in resistance to external mechanical influences.
Figure 10 reveals the assessment results of changes in the optical UV transmission and absorption spectra, reflecting the influence of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 on the transmittance of ceramics, as well as the concentration of vacancy defects, the presence of which is indicated by the absorption peak in the region of 200–300 nm (see data in Figure 10b). The general appearance of the transmission spectra indicates that stabilization of the crystalline structure of ceramics by adding the Y2O3 dopant leads to an increase in the transmittance of ceramics, the change in which is primarily due to changes in the phase composition, as well as size effects. Stabilization of the crystal structure leads to a decrease in the concentration of defective inclusions in the ceramics, which in turn has a positive effect on the optical properties. Analysis of the absorption spectra revealed the presence of an absorption band in the region of 200–300 nm, described by the presence of oxygen vacancies in the structure, the density of which can have a negative effect on both the optical properties and the thermal parameters. In this case, the observed decrease in the intensity of the spectral line characterizing the presence of oxygen vacancies allows us to conclude that the stabilization of the crystal structure due to polymorphic transformations leads to a decrease in the density of oxygen vacancies; however, the observed processes of polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type are accompanied by the substitution of Zr⁴⁺ for Y3+. As a result, oxygen vacancies are formed, from which we can conclude that only a large part of the oxygen vacancies is retained in the structure. The formation of the perovskite phase YZrO3 leads to a slight decrease in the concentration of oxygen vacancies in the composition of ceramics, but their density remains quite high (at least half of the density for unstabilized ceramics).
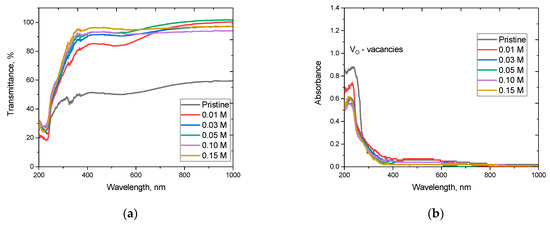
Figure 10.
Results of measurements of optical properties of ZrO2 ceramics: (a) results of changes in transmission spectra; (b) results of changes in absorption spectra.
One of the key parameters reflecting the stability of ceramics against external influences is the preservation of their strength characteristics for resistance to sudden temperature changes arising as a result of critical emergency situations capable of destabilizing the system. As a rule, sudden temperature changes are accompanied by rapid heating of samples and rapid cooling, which leads to destabilization of the crystal structure caused by a sharp change in the temperature of the oscillation of the crystal lattice, and the interaction of the heated surface of the samples with oxygen, which can lead to oxidation or penetration of oxygen into the near-surface layer of ceramics. The combination of these factors can contribute to the degradation of strength properties due to a decrease in hardness and bending strength. Figure 11a shows the results of a comparative analysis of the values of hardness and bending strength in the initial state and after 10 cycles of rapid heating and cooling, simulating the effect of thermal shock on ceramics. The general appearance of the presented dependencies indicates a negative impact of thermal heating and rapid cooling by removing samples into the air. At the same time, the change in the phase composition of ceramics due to an increase in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant in the composition leads to a decrease in the difference in the values of hardness and bending strength before and after testing, which in turn indicates that these changes caused by the stabilizing dopant and polymorphic transformations lead to an increase not only in strength characteristics, but also to an increase in resistance to external influences.
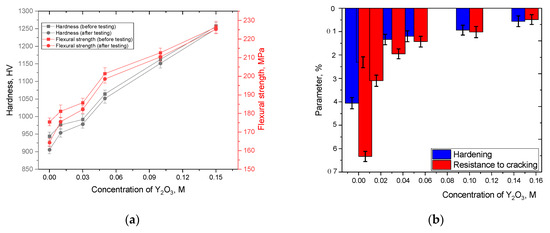
Figure 11.
Results of tests of the studied ZrO2 ceramics for heat resistance: (a) results of comparative analysis of hardness and bending strength values before and after 10 cycles of thermal exposure; (b) comparative diagram of changes in strength parameters of ceramics after 10 cycles of thermal exposure.
The evaluation results of the values of the reduction in strength parameters after heat resistance tests are presented in Figure 11b. The crack resistance parameters were calculated by comparison of the bending strength values for the samples in the initial state and after thermal shock tests, which made it possible to determine the effect of changes in the phase composition of ceramics on the crack resistance during ceramic degradation. The data were obtained by comparing the values of hardness and bending strength in the initial state and after the tests, the percentage value shows how much the strength characteristics have decreased depending on the phase composition of the ceramics. As can be seen from the data presented, the dominance in the structure of the ceramics of the t-Zr(Y)O2 phase with inclusions in the form of the perovskite phase YZrO3 and the monoclinic phase m-Zr(Y)O2, with partially substituted zirconium yttrium (see the data on the structural parameters of the crystal lattice in Table 1), leads to the highest resistance of the ceramics to thermal effects and the destruction processes associated with them. Moreover, in comparison with non-stabilized ZrO2 ceramics, for which the reduction in hardness is about 4%, and reduction in bending strength is about 6.5%, the stabilization of Y2O3 ceramics at dopant concentrations of 0.1–0.15 M leads to a 4–5-fold reduction in softening and an increase in resistance to external thermal influences. It should be noted that the change in the phase composition of ceramics due to the formation of inclusions in the form of t-Zr(Y)O2 and YZrO3, which is also accompanied by a change in grain size, leads to a growth in resistance to external influences. In this case, the observed hardening effects (increase in hardness and bending strength), as well as an increase in resistance to softening processes caused by thermal shock exposure, indicate a positive effect of phase changes. The observed hardening effects in this case can be explained by the effects of dispersion hardening associated with an increase in the proportion of finely dispersed fractions in the samples, creating a large number of grain boundaries that prevent the propagation of cracks under external influences, and also enhanced resistance to oxidation processes under thermal influences.
Table 2 demonstrates the results of a comparative analysis of the strength characteristics of the studied ceramics with a number of works obtained by other authors, reflecting the possibilities of modification of ZrO2 ceramics and the role of modification in hardening and enhancement of stability to external influences.

Table 2.
Results of comparative analysis.
4. Conclusions
The paper presents the assessment results of the influence of variations in the concentration of the stabilizing dopant Y2O3 on the change in the strength and thermophysical parameters of ZrO2 ceramics caused by phase polymorphic transformations, as well as size effects.
Using X-ray phase analysis and Raman spectroscopy methods, phase transitions associated with a change in the concentration of a stabilizing additive in the form of Y2O3 were established, a change in the composition concentration of which leads to the initialization of polymorphic transformations of the m-ZrO2 → t-Zr(Y)O2 type at low concentrations, and the formation of a perovskite phase YZrO3 with a cubic crystal lattice type in the case of a dopant concentration of more than 0.05 M in the composition.
An assessment of the morphological features showed that an increase in the proportion of t-Zr(Y)O2 and YZrO3 in the composition of ceramics leads to growth in the fine fraction, the presence of which in turn ensures hardening and increased stability to external mechanical and thermal influences.
According to the assessment of changes in the strength parameters of ceramics depending on the concentration of the stabilizing dopant in the composition in the case of heat resistance tests, it was found that the presence of three phases in the composition of ceramics leads to an increase in resistance to thermally stimulated destruction processes, which consists of less than a 1% reduction in strength parameters for modified ceramics.
The obtained results can be further used to develop the technology of industrial production and to scale up the technology of manufacture of ceramics and ceramic powder used as structural materials for the creation of inert matrices of dispersed nuclear fuel. In the future, research will continue in the field of study of the resistance of synthesized ceramics to radiation damage, as well as the possibility of containing it due to phase changes associated with the addition of stabilizing dopants to the composition of ceramics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: I.E.K., A.L.K., M.B., P.B., A.T. and A.I.P.; methodology, I.E.K., A.L.K., M.B., P.B., A.T. and A.I.P.; formal analysis, I.E.K., A.L.K., M.B., P.B., A.T. and A.I.P.; investigation, I.E.K., A.L.K., M.B., P.B., A.T. and A.I.P.; resources, I.E.K., A.L.K., M.B., P.B., A.T. and A.I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, review, and editing, I.E.K. and A.L.K.; visualization, I.E.K. and A.L.K.; supervision, I.E.K. and A.L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out within the framework of program-targeted funding (program No. BR21882237 «Development and research of advanced composite materials for energy and the fuel cycle») with the support of the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Durdovic, M.; Turcanu, C.; Sala, R.; Geysmans, R.; López-Asensio, S.; Gonçalves, L. The outlooks of nuclear energy in society: Unraveling public attitudes in the context of climate and energy security challenges. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 174, 105286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal-Pereira, J.; Esteban, M.; Araújo, K. Exposure of future nuclear energy infrastructure to climate change hazards: A review assessment. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 53, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Razi, U.; Usman, M.; Sarwar, S.; Talan, A.; Mundi, H.S. Role of nuclear energy, geothermal energy, agriculture, and urbanization in environmental stewardship. Gondwana Res. 2024, 125, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrela, P.; Stanek, W.; Simla, T. Sustainability assessment of hydrogen production based on nuclear energy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 49, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evarts, J.S.; Chong, S.; Oshiro, J.M.; Riley, B.J.; Asmussen, R.M.; McCloy, J.S. Ceramic–metal (cermet) composites: A review of key properties and synthesis methods focused on nuclear waste immobilization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 6003–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, S.; Xiang, X.; Zhao, S. Irradiation performance of high entropy ceramics: A comprehensive comparison with conventional ceramics and high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 143, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Kabiev, M.B.; Shlimas, D.I.; Uglov, V.V. Study of the effect of the formation of two-phase ceramics based on neodymium zirconate due to doping with MgO and Y2O5 on the stability of strength and thermophysical parameters under irradiation. Eurasian Phys. Tech. J. 2024, 21, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyrzhanov, K.K.; Tinishbaeva, K.; Uglov, V.V. Investigation of the effect of exposure to heavy Xe22+ ions on the mechanical properties of carbide ceramics. Eurasian Phys. Tech. J. 2020, 17, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhu, J.; Ye, S.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; He, J. Novel high-entropy perovskite titanate: A potential thermal protective material with improved thermophysical properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2025, 45, 116878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Guo, Y.; Su, Y.; Siow, K.S.; Chen, C. Unveiling the damage evolution of SAC305 during fatigue by entropy generation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 244, 108087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Su, T.; Lu, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Chang, C. An insight into dynamic properties of SAC305 lead-free solder under high strain rates and high temperatures. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2023, 175, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubich, V.; Fasol, Y.; Cherneta, O.; Yershina, A.K.; Sakipov, N.Z. Resistance of heat-resistant yttrium-containing sealing coatings to mechanical fracture when forming cutting PATHS. Eurasian Phys. Tech. J. 2024, 21, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Jacques, D.; Shen, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Heating-induced transformations in calcium silicate hydrate (CSH): In-situ investigations of composition, structure, and morphology. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 190, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Hou, W.; Shi, X.; Han, D.; Feng, T.; Fu, Q. The effect of Hf6Ta2O17 self-sintering on the cyclic ablation and mechanical performances of C/Hf-Ta-Si-C composites with a PyC-SiC bilayer interphase. Compos. Part B Eng. 2025, 294, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmuldin, M.K.; Skakov, K.; Baklanov, V.V.; Gradoboyev, A.V.; Akaev, A.S. Heat-resistant composite coating with a fluidized bed of the under-reactor melt trap of a light-water nuclear reactor. Eurasian Phys. Tech. J. 2021, 18, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Kang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Irradiation response of MgO-(Nd1-xYx)2(Zr1-xCex)2O7 composite ceramics for inert matrix fuel under helium ions and xenon ions. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1020, 179481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.; Montazerian, M.; Deng, B.; Sly, J.J.; Mauro, J.C. Zirconia-containing glass-ceramics: From nucleating agent to primary crystalline phase. Int. J. Ceram. Eng. Sci. 2024, 6, e10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chauhan, V.; Gupta, D.; Upadhyay, S.; Ram, J.; Kumar, S. Advancement of high–k ZrO2 for potential applications: A review. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2021, 59, 811–826. [Google Scholar]
- Ghyngazov, S.A.; Boltueva, V.A.; O’Connell, J.H.; Vershinina, T.N.; Kirilkin, N.S.; Rymzhanov, R.A.; Surzhikov, A.P. Swift heavy ion induced phase transformations in partially stabilized ZrO2. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 192, 109917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alin, M.; Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Uglov, V.V. Study of the mechanisms of the t-ZrO2→ c-ZrO2 type polymorphic transformations in ceramics as a result of irradiation with heavy Xe22+ ions. Solid State Sci. 2022, 123, 106791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskiy, A.L.; Konuhova, M.; Borgekov, D.B.; Popov, A.I. Study of irradiation temperature effect on radiation-induced polymorphic transformation mechanisms in ZrO2 ceramics. Opt. Mater. 2024, 156, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovskiy, A.; Borgekov, D.B.; Zdorovets, M.V.; Kadyrzhanov, K.K.; Shlimas, D.I. Study of radiation-induced damage processes in CeZrO4–YZrO3 ceramics caused by Helium irradiation. Materials 2022, 16, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Zhou, G.; Shimai, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. ZrO2-doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics via slip casting and vacuum sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 2139–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, J.; Feng, M.; Zhang, L. Investigation of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties of ZrO2-doped Y2O3 transparent ceramics fabricated by HIP. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, T.S.; Laval, J.Y.; Nguyen-van-Huong, C.; Dubon, A. Effect of ZrO2 doping on structure and superconductingproperties of sintered DyBaCuO ceramics. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2001, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, X.; Luo, K.; Wang, C.; Song, S.; Zhou, W. Effects of liquid phases on densification of TiO2-doped Al2O3–ZrO2 composite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 3989–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakfali, J.; Chaabene, S.B.; Akkari, R.; Dappozze, F.; Berhault, G.; Guillard, C.; Zina, M.S. High photocatalytic activity of aerogel tetragonal and monoclinic ZrO2 samples. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 430, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Hong, M.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Cai, G.; Yin, R.; Ren, F. Different Radiation Tolerances of Ultrafine-Grained Zirconia–Magnesia Composite Ceramics with Different Grain Sizes. Materials 2019, 12, 2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materano, M.; Reinig, P.; Kersch, A.; Popov, M.; Deluca, M.; Mikolajick, T.; Schroeder, U. Raman Spectroscopy as a Key Method to Distinguish the Ferroelectric Orthorhombic Phase in Thin ZrO2-Based Films. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL) Rapid Res. Lett. 2022, 16, 2100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garanin, Y.; Shakirzyanov, R.; Borgekov, D.; Kozlovskiy, A.; Volodina, N.; Shlimas, D.; Zdorovets, M. Study of morphology, phase composition, optical properties, and thermal stability of hydrothermal zirconium dioxide synthesized at low temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Yuan, L.; Liu, T.; Sun, Q.; Jin, E.; Tian, C.; Yu, J. Enhanced ionic conductivity and thermal shock resistance of MgO stabilized ZrO2 doped with Y2O3. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19835–19842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
