The Green Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Considering Cost, Carbon Emissions, and Customer Satisfaction under Time-of-Use Electricity Pricing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Multi-Objective GFJSP Model under the Time-of-Use Electricity Price
2.1.1. Problem Description
2.1.2. Explanation of Symbols
2.1.3. Modeling the Multi-Objective GFJSP Model
2.2. Model Solving Based on an Improved Genetic Algorithm
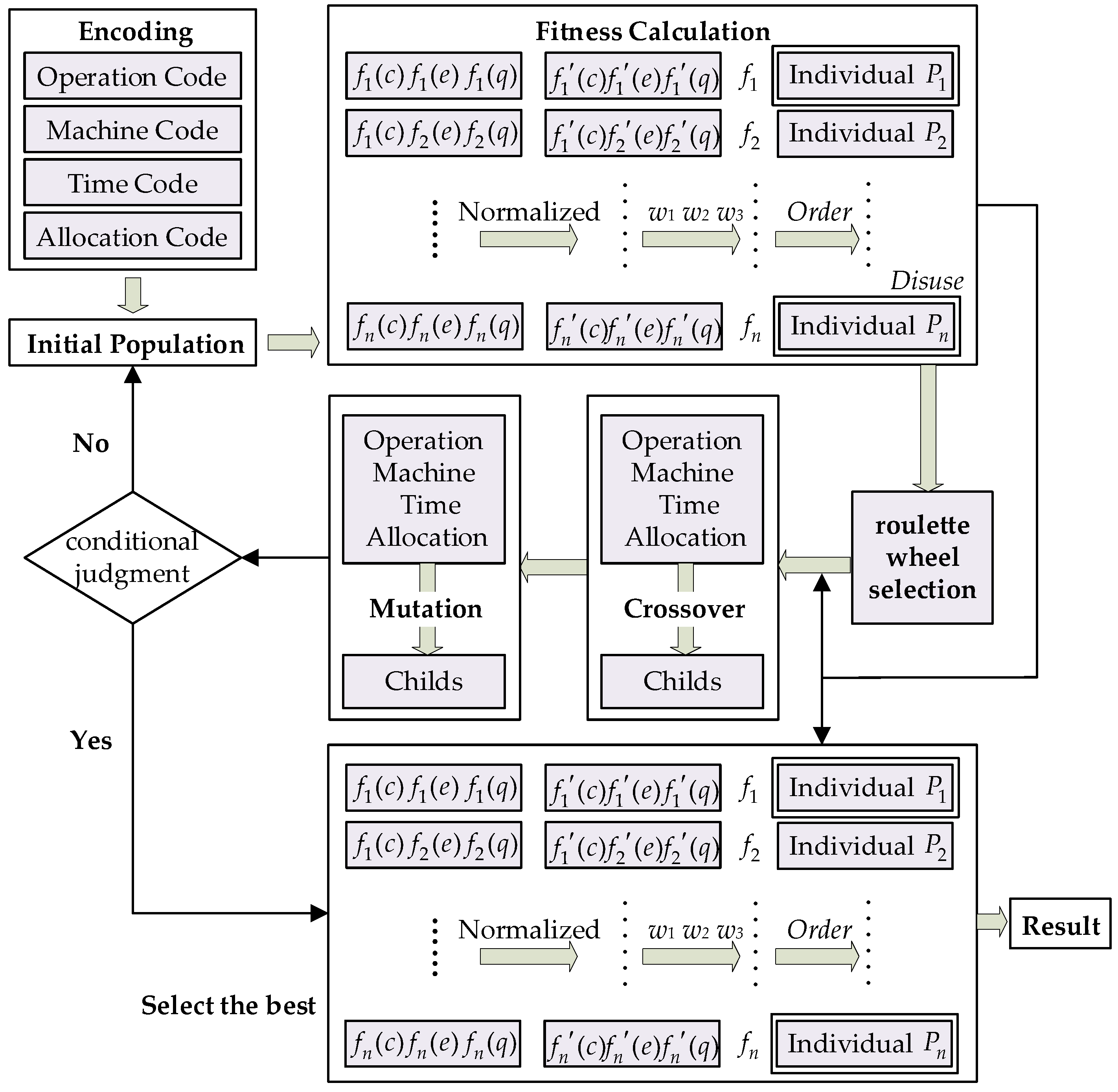
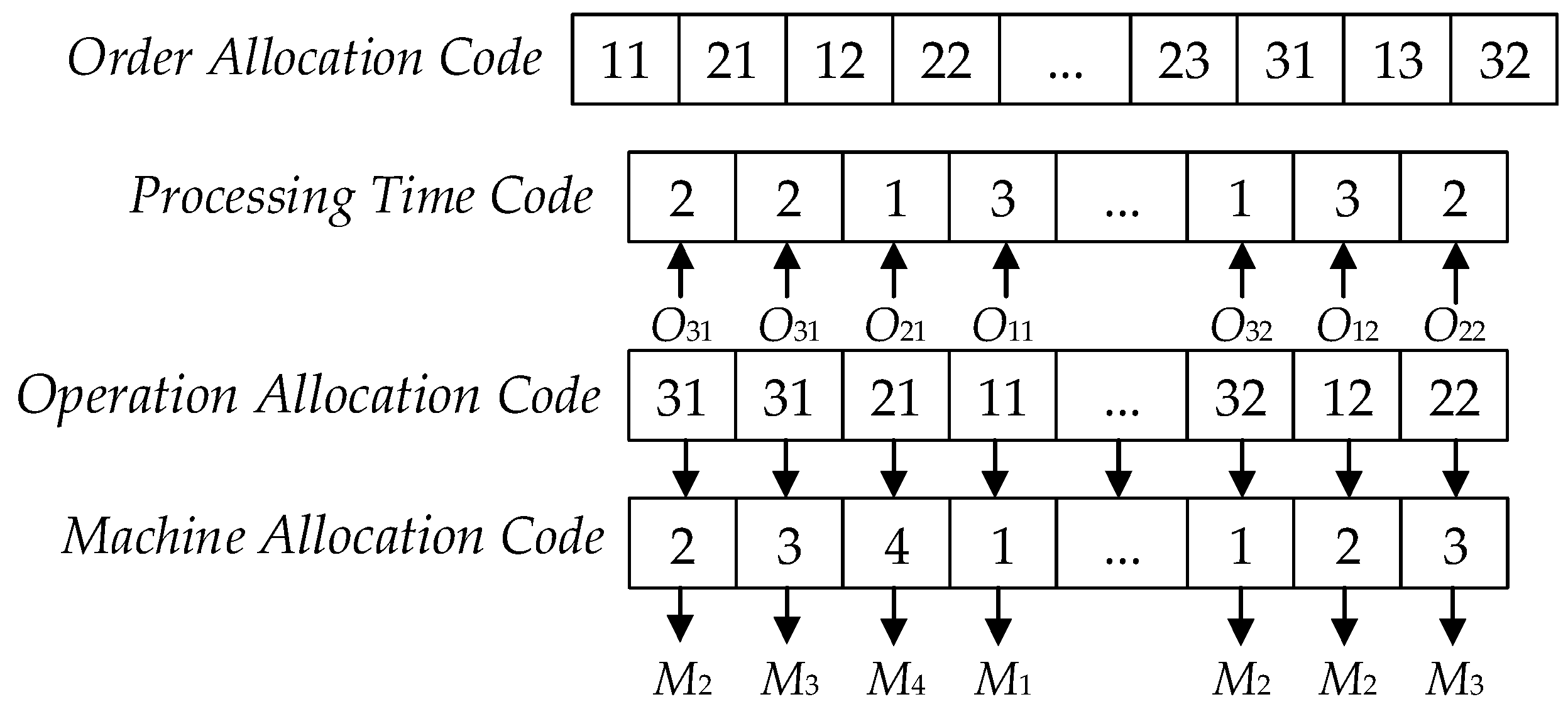
2.2.1. Chromosome Encoding
2.2.2. Initial Population
2.2.3. Fitness Calculation
2.2.4. Selection of Operations
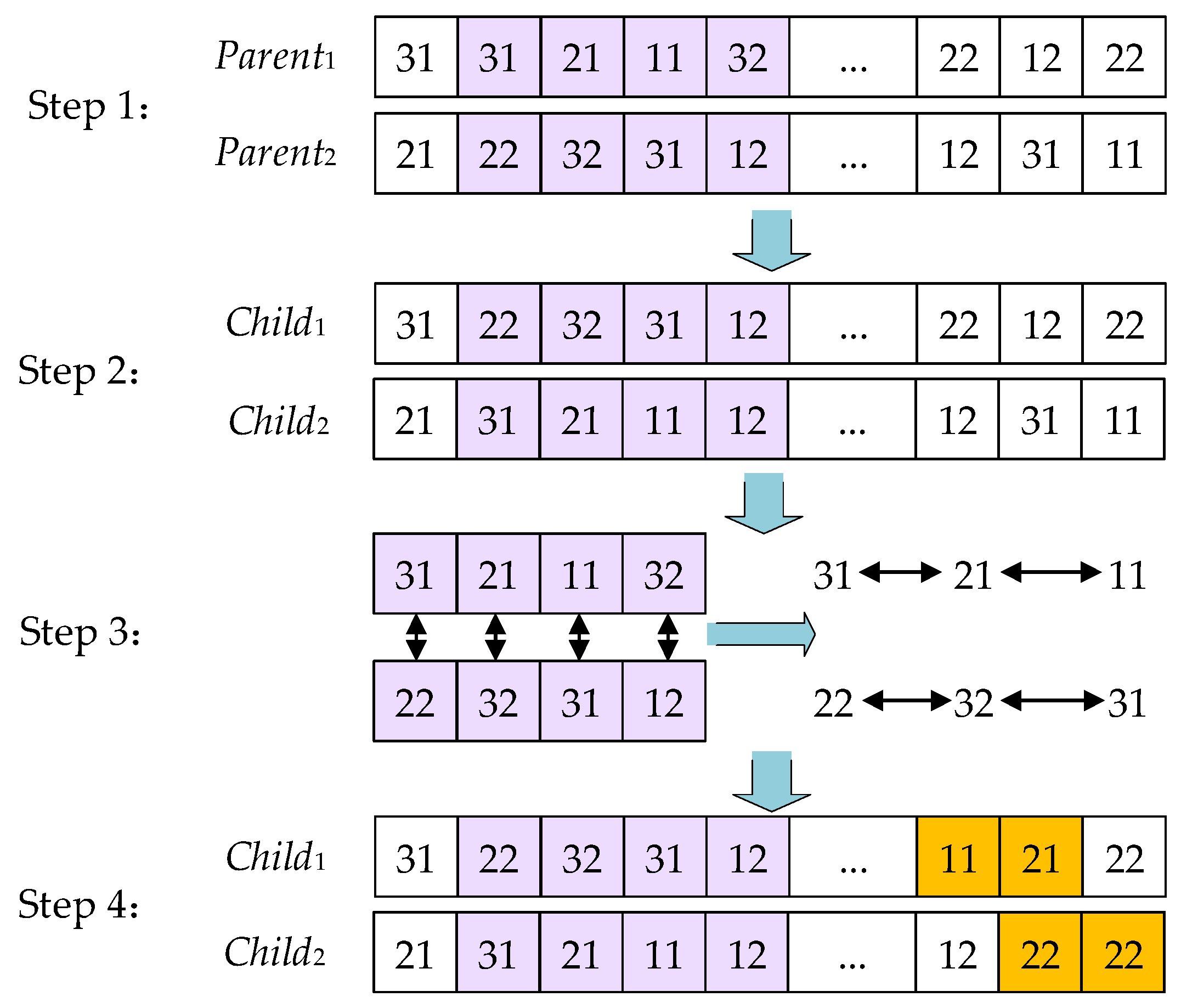
2.2.5. Crossover Operation
2.2.6. Mutation Operation
3. Case Study
3.1. Case Description
3.1.1. Description of the Flexible Job-Shop
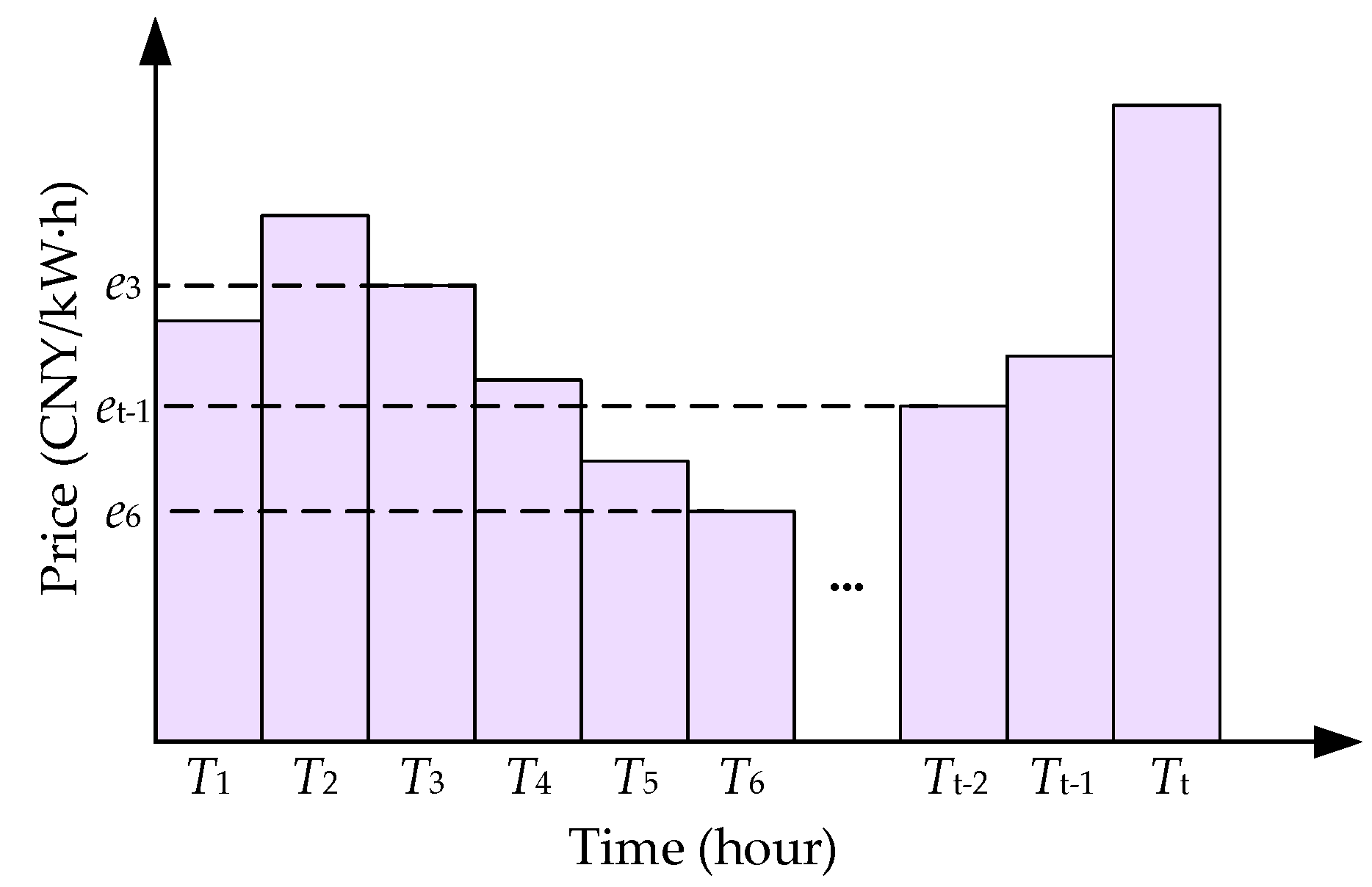
3.1.2. Description of the Time-of-Use Electricity Price
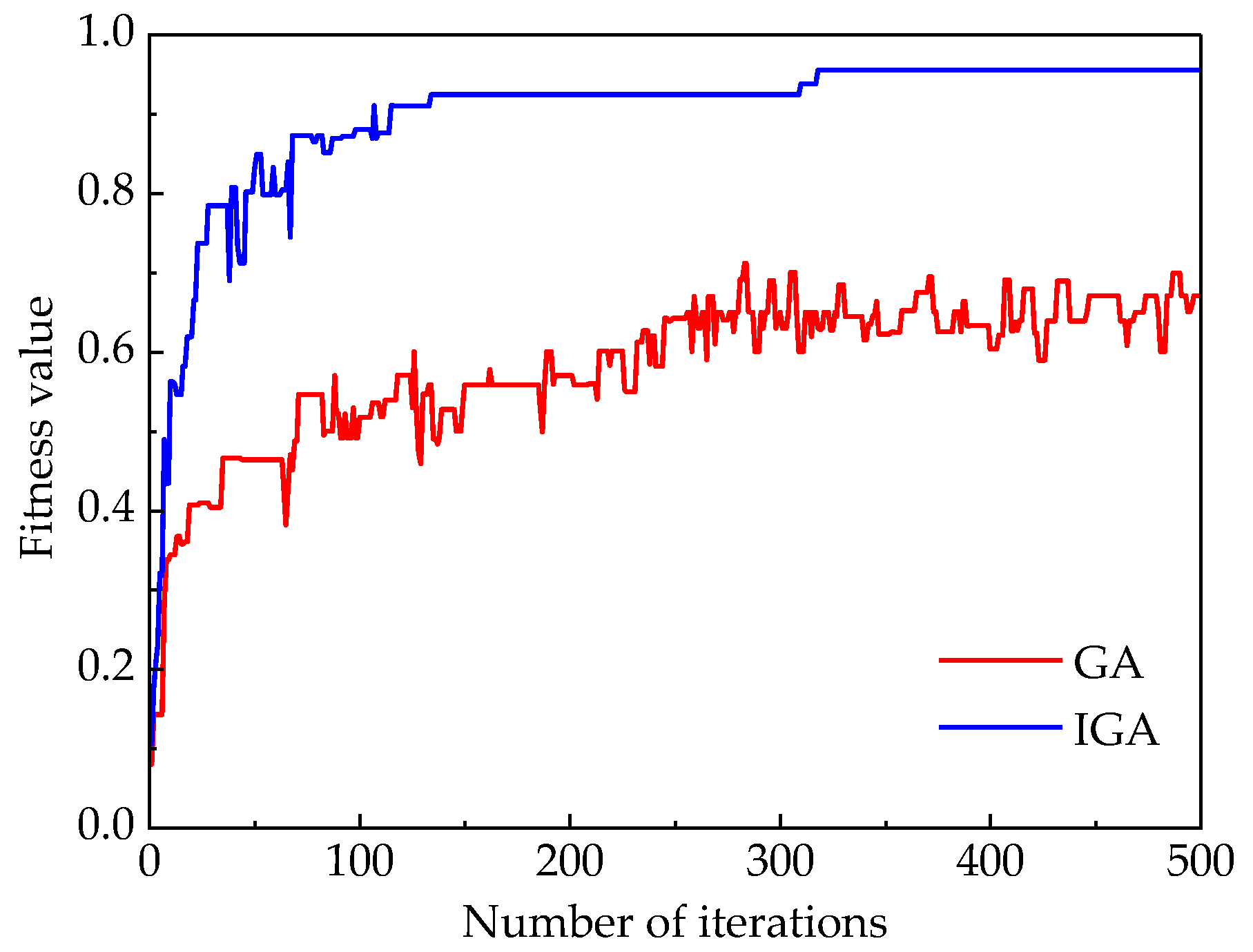
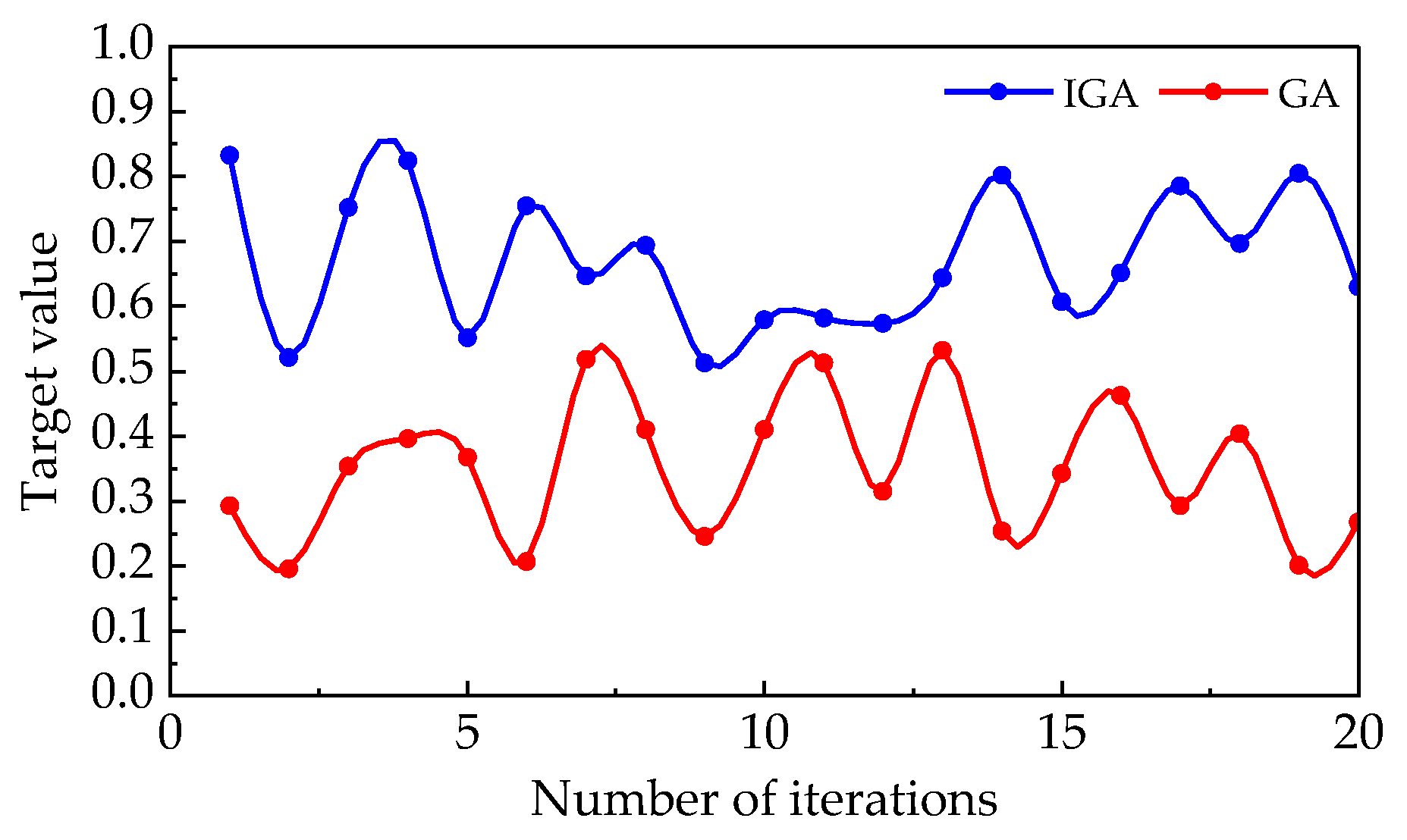
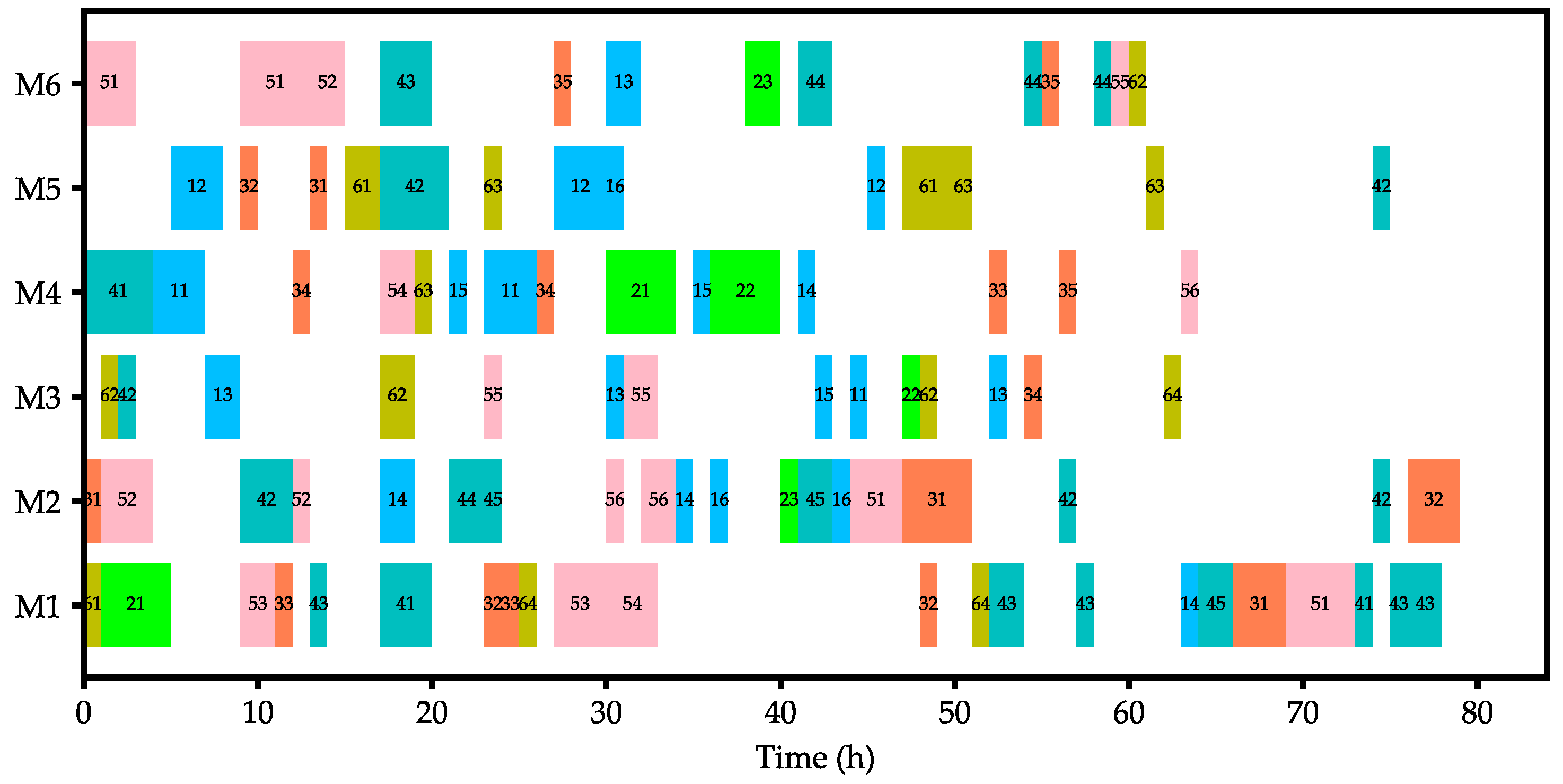
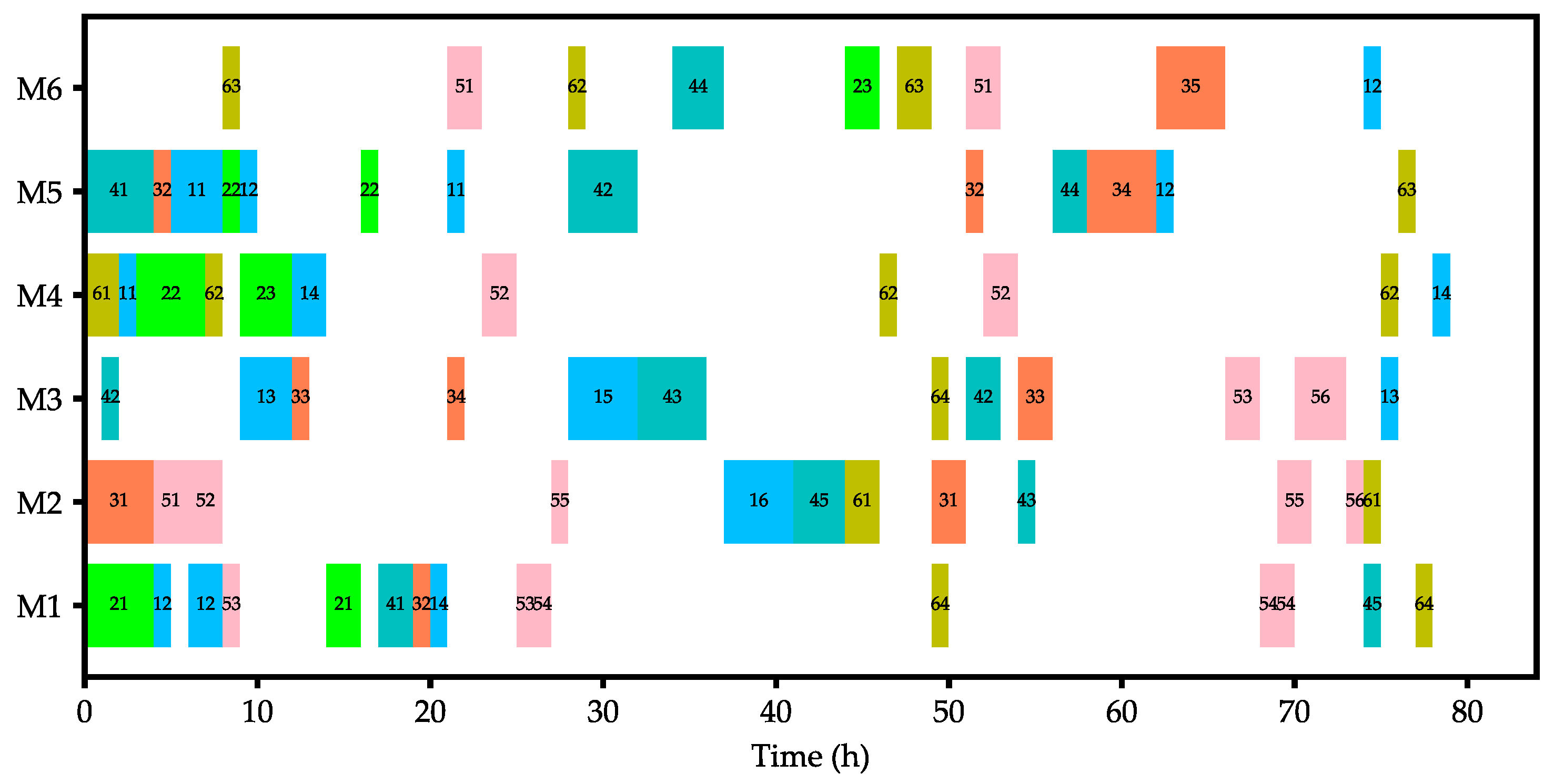
3.2. IGA Performance Analysis
3.2.1. Single-Objective Solution
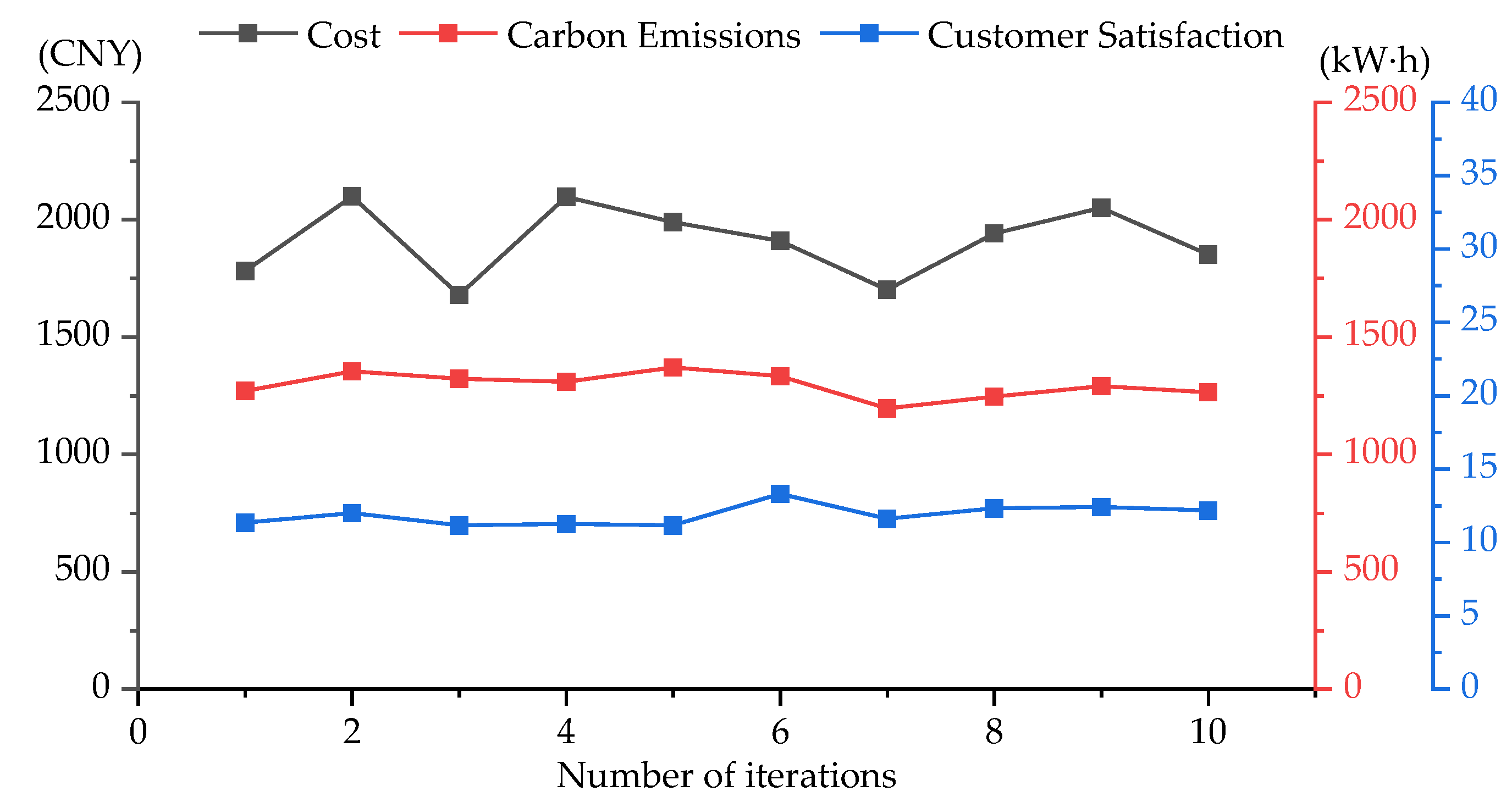
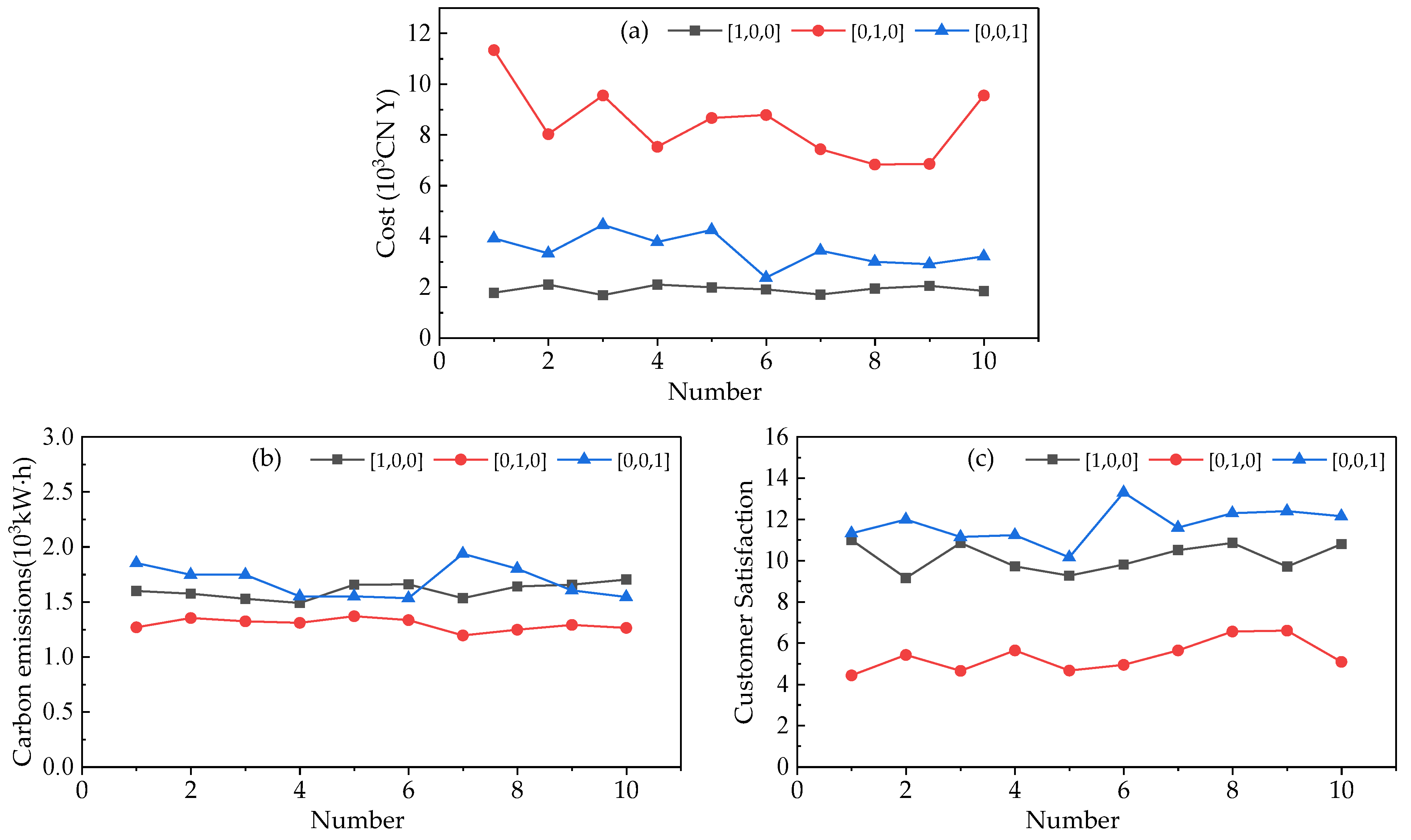
3.2.2. Multi-Objective Optimization
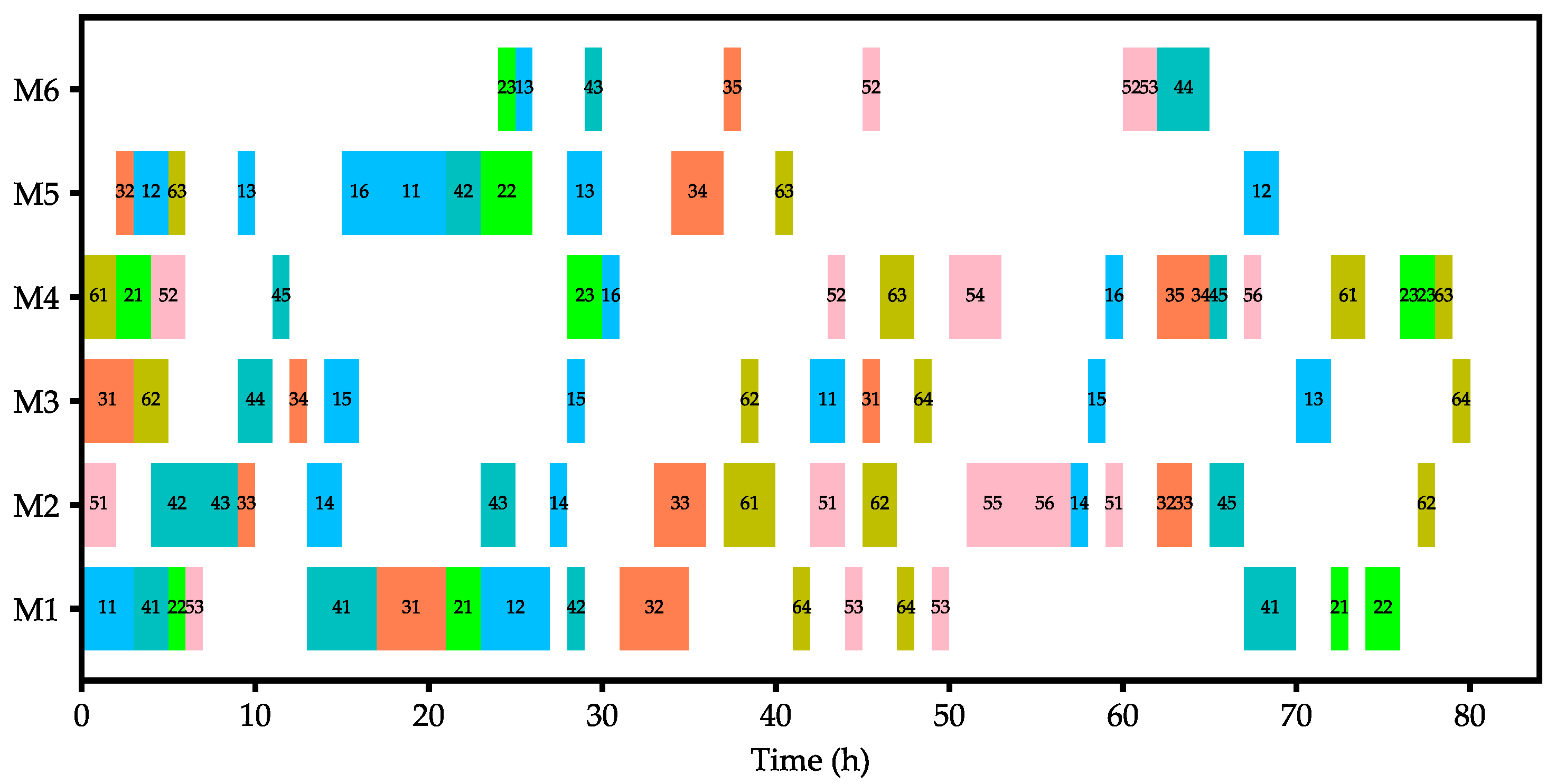
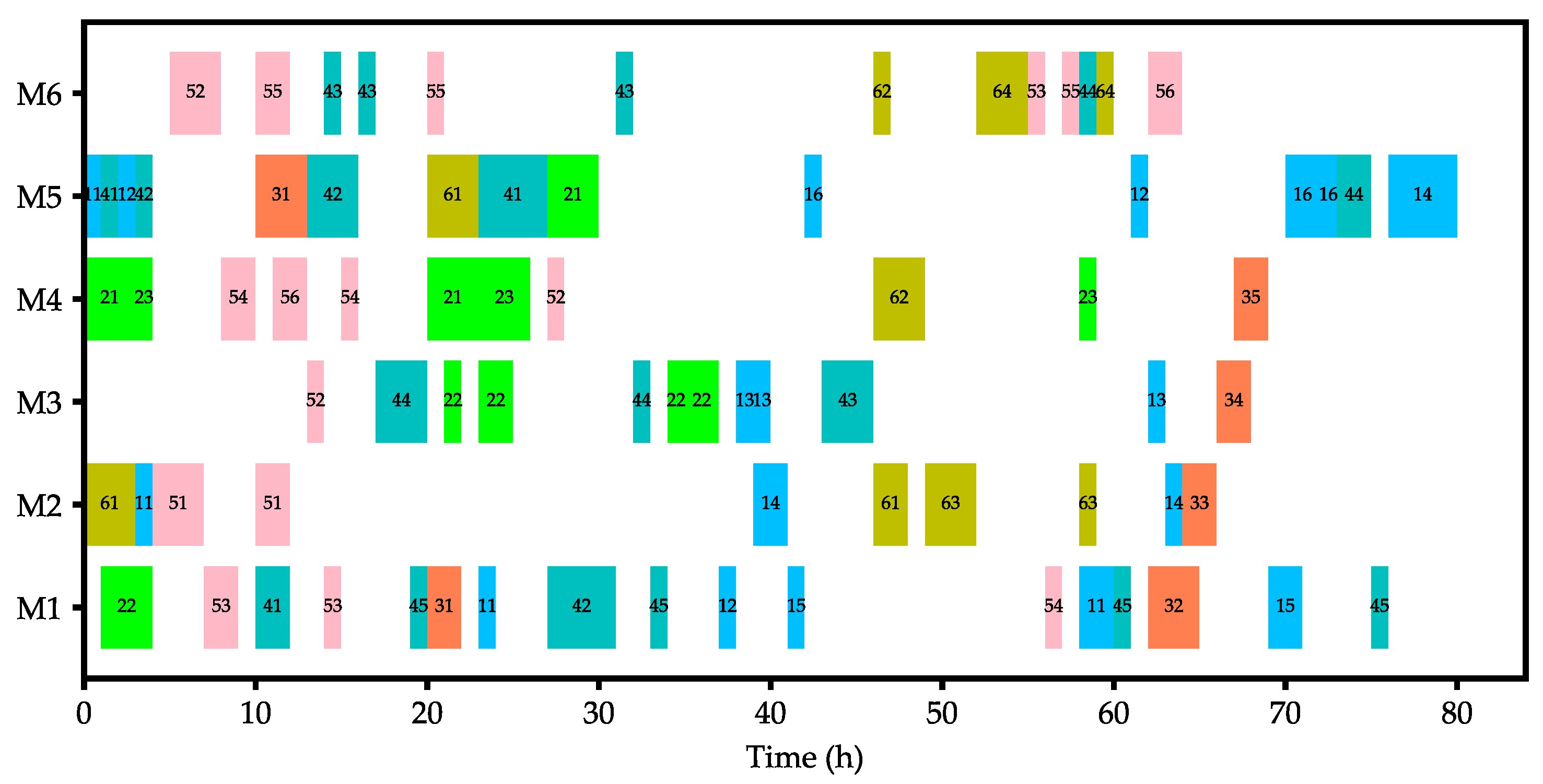
3.3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almusaed, A.; Yitmen, I.; Almssad, A. Reviewing and integrating aec practices into industry 6.0: Strategies for smart and sustainable future-built environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, B.; Li, S.; Wang, S. A self-learning genetic algorithm based on reinforcement learning for flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 149, 106778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, L.; Shi, Y. An effective genetic algorithm for the flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 3563–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baykasoglu, A. Linguistic-based meta-heuristic optimization model for flexible job shop scheduling. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2002, 40, 4523–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrich, C.R.; Armentano, V.A.; Laguna, M. Tardiness minimization in a flexible job shop: A tabu search approach. J. Intell. Manuf. 2004, 15, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.C.; Ho, N.B. Evolving dispatching rules using genetic programming for solving multi-objective flexible job-shop problems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2008, 54, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Chen, K.H.; Wu, J.J.; Chen, C.W. A study of the flexible job shop scheduling problem with parallel machines and reentrant process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 39, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, K.H. Flexible job shop scheduling with parallel machines using Genetic Algorithm and Grouping Genetic Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 10016–10021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shao, X.; Li, P.; Gao, L. An effective hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm for multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Sun, L.; Gen, M. A hybrid genetic and variable neighborhood descent algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 2892–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroozfard, H.; Wong, K.Y.; Wong, W.P. Minimizing total carbon footprint and total late work criterion in flexible job shop scheduling by using an improved multi-objective genetic algorithm. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 128, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loučanová, E.; Olšiaková, M.; Štofková, J. Ecological Innovation: Sustainable Development in Slovakia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhu, H.; Deng, G. Improved African buffalo optimization algorithm for the green flexible job shop scheduling problem considering energy consumption. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 38, 4573–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, X. A shuffled frog-leaping algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling with the consideration of energy consumption. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 3126–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouiri, M.; Bekrar, A.; Trentesaux, D. Towards energy efficient scheduling and rescheduling for dynamic flexible job shop problem. IFAC-PapersOnline 2018, 51, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shen, X.; Li, C. The flexible job-shop scheduling problem considering deterioration effect and energy consumption simultaneously. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gu, P.; Jiang, P. Low-carbon scheduling and estimating for a flexible job shop based on carbon footprint and carbon efficiency of multi-job processing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B-J. Eng. 2015, 229, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Lin, W. Low carbon flexible job shop scheduling problem considering worker learning using a memetic algorithm. Optim. Eng. 2020, 21, 1691–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loučanová, E.; Nosáľová, M.; Olšiaková, M.; Štofková, Z.; Dumiter, F.C.; Nicoară, Ș.A.; Boiță, M. Innovation as a Tool for Sustainable Development in Small and Medium Size Enterprises in Slovakia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrouf, F.; Ordieres-Meré, J.; García-Sánchez, A.; Ortega-Mier, M. Optimizing the production scheduling of a single machine to minimize total energy consumption cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 67, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Uhan, N.A.; Zhao, F.; Sutherland, J.W. Scheduling on a single machine under time-of-use electricity tariffs. Ann. Oper. Res. 2016, 238, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, F.; Fang, K.; Sutherland, J.W. Energy-conscious flow shop scheduling under time-of-use electricity tariffs. CIRP Ann. 2014, 63, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, A.; Zeng, Y.; Lyu, K. An efficient greedy insertion heuristic for energy-conscious single machine scheduling problem under time-of-use electricity tariffs. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 129, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Ye, C.; Dai, Z.H.; Liu, L. Bi-objective re-entrant hybrid flow shop scheduling considering energy consumption cost under time-of-use electricity tariffs. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Buscher, U.; Shen, L. Multi-objective hybrid flow shop scheduling with variable discrete production speed levels and time-of-use energy prices. J. Bus. Econ. 2020, 90, 1315–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Hu, Y. Energy-efficient hybrid flow-shop scheduling under time-of-use and ladder electricity tariffs. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Fang, K.; Chu, F.; Chu, C. Scheduling on a two-machine permutation flow shop under time-of-use electricity tariffs. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 3173–3187. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Gao, L.; Peng, K.; Li, X.; Li, H. Review on flexible job shop scheduling. IET Collab. Intell. Manuf. 2019, 1, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.L.; Zhang, B.B.; Li, Y. A multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling model based on fuzzy theory and immune genetic algorithm. Int. J. Simul. Model. 2020, 19, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Gil, N.; Rosillo, R.; de la Fuente, D.; Pino, R. A discrete firefly algorithm for solving the flexible job-shop scheduling problem in a make-to-order manufacturing system. Cent. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 29, 1353–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. A hybrid biogeography-based optimization for the fuzzy flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 78, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, K.G.; Mishra, R.S.; Madan, A.K. A Dynamic Adaptive Firefly Algorithm for Flexible Job Shop Scheduling. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 31, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türkyılmaz, A.; Şenvar, Ö.; Ünal, İ.; Bulkan, S. A research survey: Heuristic approaches for solving multi objective flexible job shop problems. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1949–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabovati, H.; Haleh, H.; Vahdani, B. Multi-objective invasive weeds optimisation algorithm for solving simultaneous scheduling of machines and multi-mode automated guided vehicles. Eur. J. Ind. Eng. 2020, 14, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Peng, J. A hybrid differential evolution algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling with outsourcing operations and job priority constraints. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 201, 117182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, I.A.; Khan, A.A. A research survey: Review of flexible job shop scheduling techniques. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2016, 23, 551–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.K.; Butt, S.I.; Kousar, R.; Ahmad, R. Recent research trends in genetic algorithm based flexible job shop scheduling problems. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9270802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ge, J.; Liu, C.; He, R. Evaluating the energy consumption and air emissions of CO2-enhanced oil recovery in China: A partial life cycle assessment of extralow permeability reservoirs. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2020, 92, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, C. Application of grey wolf optimization for solving combinatorial problems: Job shop and flexible job shop scheduling cases. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 26231–26240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Tang, D. An improved hybrid particle swarm optimization for multi-objective flexible job-shop scheduling problem. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 2873–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tian, Z.; Liu, W.; Suo, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, X.; Li, Z. Energy-efficient scheduling of flexible job shops with complex processes: A case study for the aerospace industry complex components in China. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 27, 100293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, N.T.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Maroufkhani, P.; Asadi, S. Industry 4.0 applications for sustainable manufacturing: A systematic literature review and a roadmap to sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, M.; Fragapane, G.; Sgarbossa, F.; Kay, M. Digital facility layout planning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinast, A.; Doerner, K.F.; Rinderle-Ma, S. Biased random-key genetic algorithm for cobot assignment in an assembly/disassembly job shop scheduling problem. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 180, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerin, M.; Pham, D.T. A review of emerging industry 4.0 technologies in remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arviv, K.; Stern, H.; Edan, Y. Collaborative reinforcement learning for a two-robot job transfer flow-shop scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetto, M.; Peron, M.; Fragapane, G.; Sgarbossa, F. Digital assembly assistance system in Industry 4.0 era: A case study with projected augmented reality. In Advanced Manufacturing and Automation X 10; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 644–651. [Google Scholar]
| Objectives | Traditional Production Metrics | Energy Consumption or Carbon Emissions | Energy Consumption Cost | Customer Satisfaction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problem Type | |||||
| FJSP [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11] | YES | NO | NO | NO | |
| GFJSP [12,13,14,15,16,17,18] | YES | YES | NO | NO | |
| Simpler Systems [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27] | YES | YES | YES | NO | |
| GFJSP Under Time-of-Use (in this paper) | YES | YES | YES | YES | |
| Symbol | Explanation |
|---|---|
| i | Machine index . |
| j | Time index . |
| k | Workpiece index . |
| s | Operation index . |
| x | Actual delivery time (unit: days) . |
| y | Due delivery time (unit: days) . |
| c | Customer index . |
| Electricity price at time . | |
| Conversion coefficient between electrical energy consumption and carbon emissions. | |
| Energy consumption of machine processes operation of the workpiece in one hour. | |
| Idle energy consumption of machine in one hour. | |
| Profit (CNY/workpiece) of the workpiece . | |
| Penalty (CNY/workpiece) due to customer not delivering workpiece on time. | |
| The capacity of operation of machine machining workpiece . | |
| Customer orders quantity of workpiece with delivery date y. | |
| The importance level of customer has a range from 0 to 1; the larger the value, the higher the importance level. | |
| On day x, the inventory of finished workpiece . | |
| The quantity of the workpiece supplied to the customer on day x, including all overdue orders for delivery on day x. | |
| On day x, provide the customer with the quantity of overdue the workpiece , which should have been submitted on day y. | |
| On day x and time , the quantity of semi-finished workpieces in the operation of the workpiece . | |
| On day x, the output of the workpiece . | |
| The number of batch deliveries of the workpiece ordered by the Customer . | |
| For all overdue orders, the normalized value of the order quantity , equal to . | |
| For all overdue orders, the normalized value of the order overdue time , equal to . | |
| 0–1 variable. When the machine performs operation at time on day , then ; conversely, . | |
| 0–1 variable. When workpieces with the delivery date are provided to the customer on day , then ; conversely, . |
| Stamped Part | Operation | Optional Machine | Capacity | Energy Consumption (kW·h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J1 | O11 | M1/M3/M4/M5 | 25/28/34/38 | 8.8/13.5/9.2/12.7 |
| O12 | M1/M5/M6 | 27/33/32 | 11.0/12.9/5.1 | |
| O13 | M3/M5/M6 | 38/36/37 | 8.5/11.7/9.5 | |
| O14 | M1/M2/M4/M6 | 33/34/39/31 | 9.0/4.7/8.2/3.2 | |
| O15 | M2/M3/M4 | 36/33/36 | 7.4/5.8/11.7 | |
| O16 | M2/M3/M4/M5/M6 | 29/28/31/27/32 | 6.8/4.9/4.6/9.5/8.8 | |
| J2 | O21 | M1/M4/M5 | 35/28/38 | 5.3/11.8/7.3 |
| O22 | M1/M3/M4/M5 | 21/27/27/32 | 8.3/4.5/10.5/8.2 | |
| O23 | M2/M4/M6 | 38/29/34 | 11.7/6.4/8.1 | |
| J3 | O31 | M1/M2/M3/M5 | 36/41/27/24 | 9.6/10.1/2.8/12.2 |
| O32 | M1/M2/M5 | 28/36/33 | 8.1/13.3/12.4 | |
| O33 | M1/M2/M3/M4/M6 | 26/31/31/34/37 | 10.0/6.0/6.8/11.2/9.9 | |
| O34 | M3/M4/M5 | 25/23/32 | 4.2/5.8/10.7 | |
| O35 | M2/M4/M6 | 35/25/23 | 11.0/3.2/9.0 | |
| J4 | O41 | M1/M4/M5 | 41/34/33 | 11.6/13.5/7.5 |
| O42 | M1/M2/M3/M5 | 31/27/27/25 | 5.7/10.1/10.5/4 | |
| O43 | M1/M2/M3/M6 | 24/29/31/39 | 11.2/11.3/9.1/6.4 | |
| O44 | M2/M3/M5/M6 | 32/24/28/34 | 6.8/7.2/6.6/11.6 | |
| O45 | M1/M2/M4 | 39/32/32 | 7.6/5.9/9.5 | |
| J5 | O51 | M1/M2/M6 | 34/30/28 | 7.1/4.7/12.7 |
| O52 | M2/M3/M4/M6 | 26/29/26/29 | 4.2/4.5/4.5/7.9 | |
| O53 | M1/M3/M6 | 32/35/28 | 13.0/6.2/11.4 | |
| O54 | M1/M4/M5 | 34/28/31 | 14.9/6.4/13.3 | |
| O55 | M2/M3/M5/M6 | 26/34/38/27 | 11.0/14.0/11.3/8.8 | |
| O56 | M2/M3/M4/M5/M6 | 27/33/25/33/28 | 11.0/13.2/4.5/3.5/4.2 | |
| J6 | O61 | M1/M2/M4/M5 | 30/24/34/25 | 11.5/2.9/11.9/4.4 |
| O62 | M2/M3/M4/M6 | 28/26/35/26 | 11.5/7.8/6.5/7.4 | |
| O63 | M2/M4/M5/M6 | 28/27/34/31 | 5.6/9.0/8.6/4.9 | |
| O64 | M1/M3/M6 | 39/35/27 | 10.2/7.2/3.7 |
| Customer | Stamped Part | Quantity | Delivery Period (Days) | Delay Compensation (CNY) | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | J1 | 100 | 8 | 5 | 0.9 |
| J3 | 60 | 6 | 3 | ||
| J4 | 80 | 7 | 2 | ||
| J6 | 80 | 8 | 2 | ||
| H2 | J1 | 70 | 7 | 5 | 0.5 |
| J2 | 70 | 7 | 3 | ||
| J5 | 90 | 8 | 7 | ||
| H3 | J2 | 50 | 5 | 5 | 0.3 |
| J3 | 50 | 5 | 2 | ||
| H4 | J1 | 90 | 9 | 7 | 0.7 |
| J4 | 120 | 10 | 5 | ||
| J5 | 100 | 9 | 3 | ||
| H5 | J2 | 70 | 6 | 8 | 0.5 |
| J3 | 80 | 8 | 4 | ||
| J6 | 100 | 9 | 6 |
| Machine | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idle energy consumption (kW·h) | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.28 |
| Index | GA | IGA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Optimal solution | 1901.28 | 1700.94 |
| Worst solution | 2768.88 | 2098.96 | |
| Average deviation | 198.50 | 125.72 | |
| Energy Consumption | Optimal solution | 1218.10 | 1194.39 |
| Worst solution | 1780.93 | 1369.95 | |
| Average deviation | 136.27 | 42.31 | |
| Customer Satisfaction | Optimal solution | 12.40 | 13.30 |
| Worst solution | 9.48 | 11.15 | |
| Average deviation | 0.84 | 0.57 | |
| Algorithm | Target Mean | Optimal Solution | Worst Solution | Average Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 0.349 | 0.532 | 0.195 | 0.075 |
| IGA | 0.672 | 0.833 | 0.512 | 0.084 |
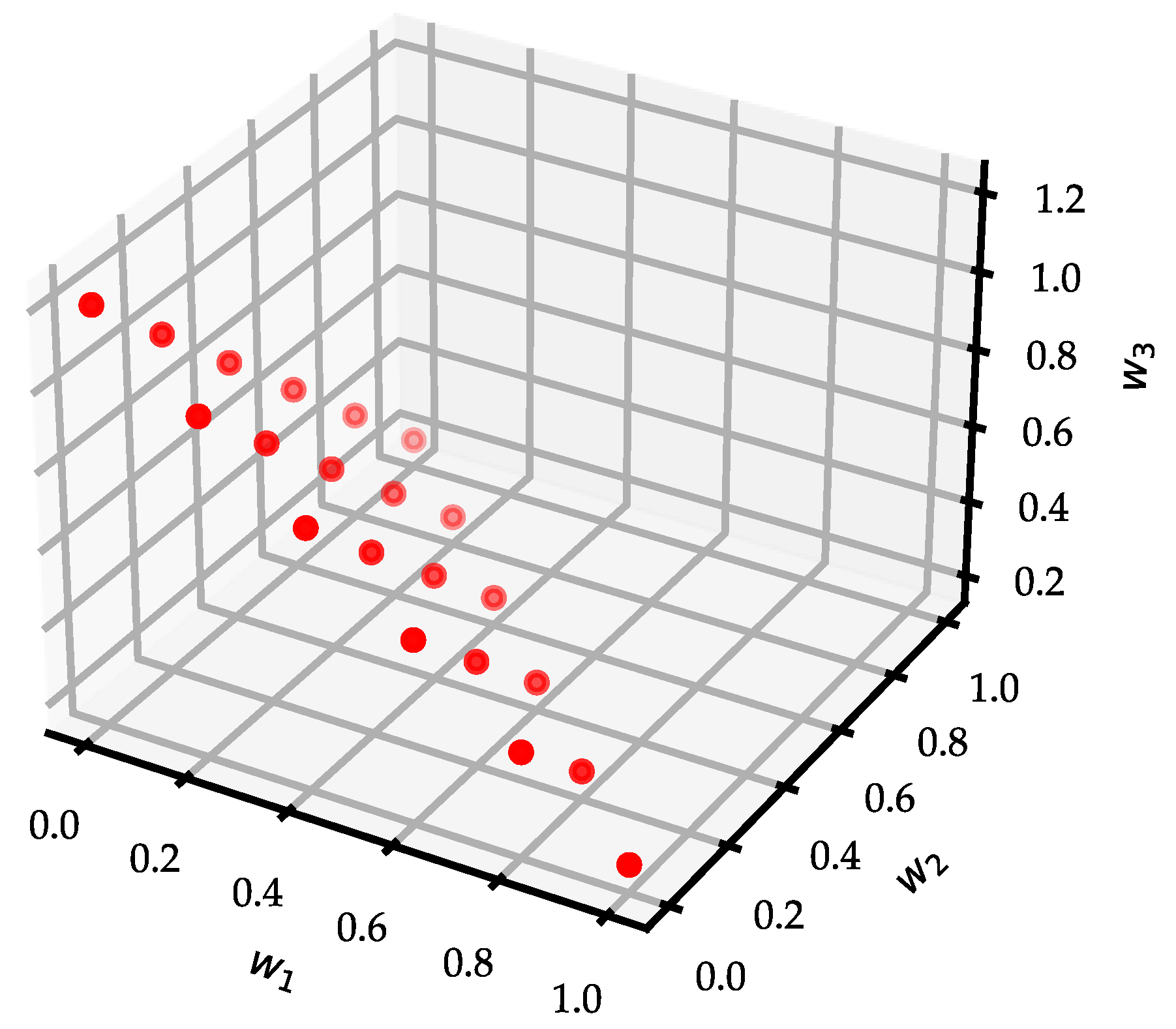
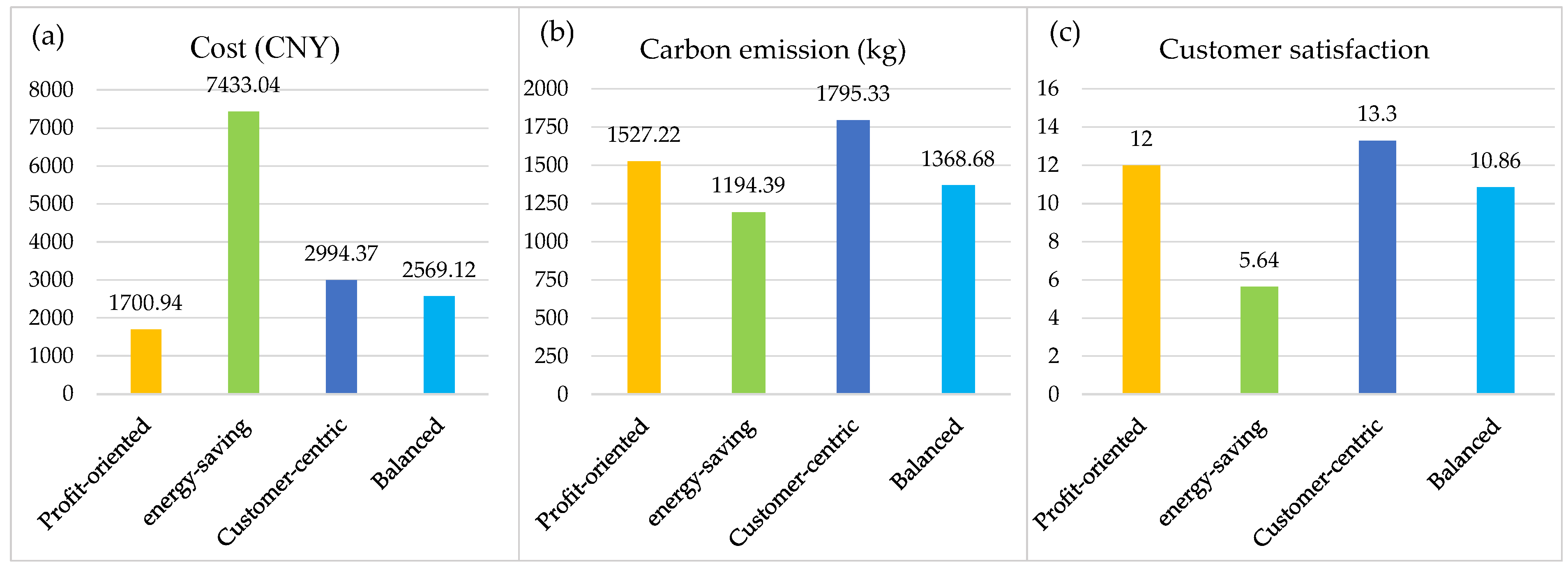
| NO. | W1 | W2 | W3 | Cost (CNY) | Carbon Emissions (kg) | Customer Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1700.94 | 1527.22 | 12.00 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7433.04 | 1194.39 | 5.64 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2994.37 | 1795.33 | 13.30 |
| 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0 | 1717.31 | 1458.62 | 12.16 |
| 5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0 | 2539.88 | 1457.78 | 11.38 |
| 6 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0 | 3364.86 | 1438.93 | 9.79 |
| 7 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0 | 3783.51 | 1413.73 | 8.57 |
| 8 | 0.8 | 0 | 0.2 | 2932.89 | 1815.34 | 11.23 |
| 9 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 3063.99 | 1501.21 | 10.66 |
| 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 3337.77 | 1497.38 | 10.10 |
| 11 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 4220.00 | 1411.80 | 9.09 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 4664.30 | 1266.92 | 9.02 |
| 13 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.4 | 2273.49 | 1580.20 | 12.34 |
| 14 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 2914.33 | 1573.12 | 12.05 |
| 15 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 3037.02 | 1479.72 | 10.67 |
| 16 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 3277.49 | 1336.47 | 10.20 |
| 17 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.6 | 2635.45 | 1787.86 | 10.63 |
| 18 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 2975.39 | 1581.01 | 12.17 |
| 19 | 0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 5160.20 | 1496.64 | 10.74 |
| 20 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.8 | 2946.03 | 1675.49 | 11.78 |
| 21 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 2791.81 | 1511.50 | 11.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Li, A.; Cai, W.; Liu, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, L. The Green Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Considering Cost, Carbon Emissions, and Customer Satisfaction under Time-of-Use Electricity Pricing. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062443
Jia S, Yang Y, Li S, Wang S, Li A, Cai W, Liu Y, Hao J, Hu L. The Green Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Considering Cost, Carbon Emissions, and Customer Satisfaction under Time-of-Use Electricity Pricing. Sustainability. 2024; 16(6):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062443
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Shun, Yang Yang, Shuyu Li, Shang Wang, Anbang Li, Wei Cai, Yang Liu, Jian Hao, and Luoke Hu. 2024. "The Green Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Considering Cost, Carbon Emissions, and Customer Satisfaction under Time-of-Use Electricity Pricing" Sustainability 16, no. 6: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062443
APA StyleJia, S., Yang, Y., Li, S., Wang, S., Li, A., Cai, W., Liu, Y., Hao, J., & Hu, L. (2024). The Green Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Considering Cost, Carbon Emissions, and Customer Satisfaction under Time-of-Use Electricity Pricing. Sustainability, 16(6), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062443






