The Strategy of Continuous Commutation Failure Suppression by Combining Turn-off Angle Compensation and Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL
Abstract
1. Introduction
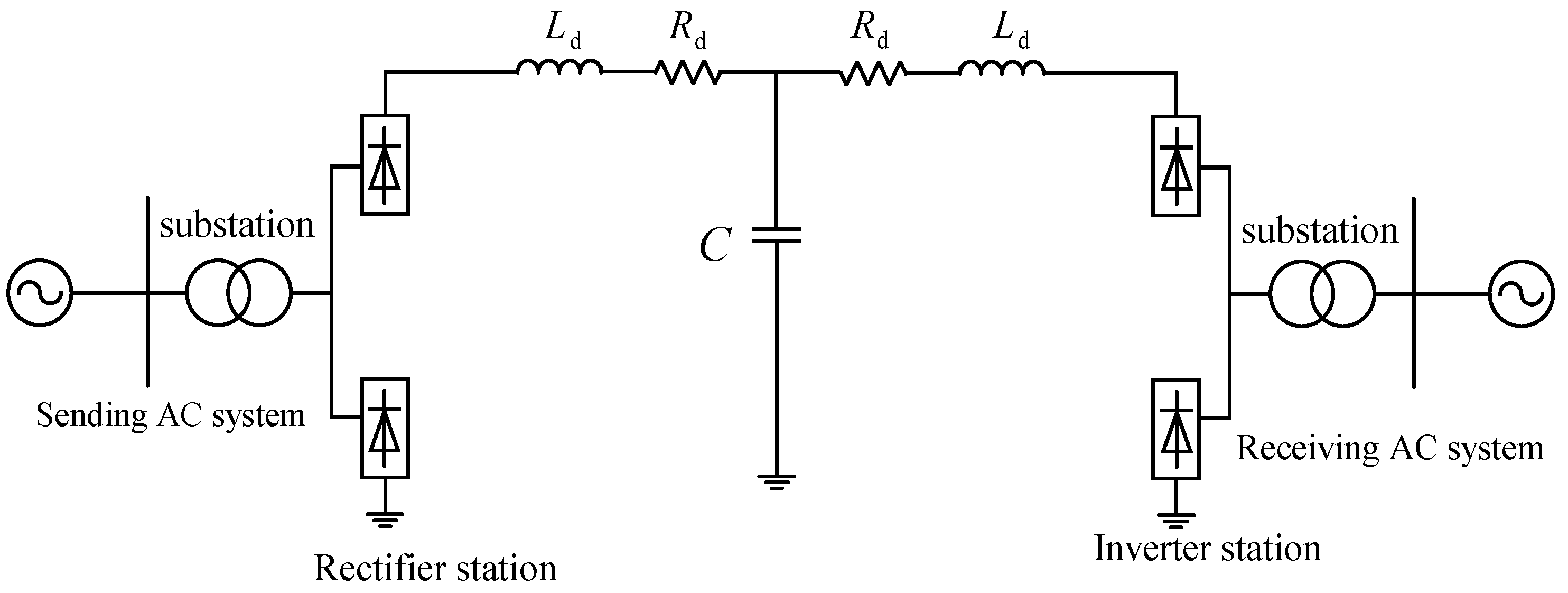
2. Mechanism Analysis of the LCC-HVDC Commutation Process
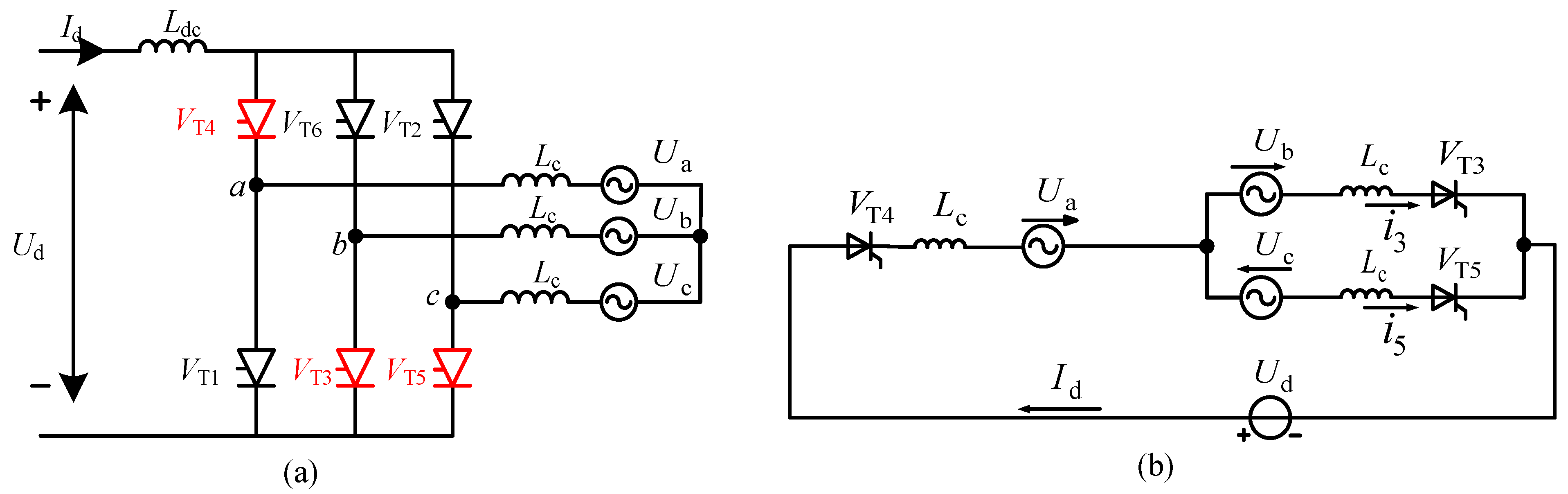
3. Analysis of LCC-HVDC Commutation Failure Mechanism
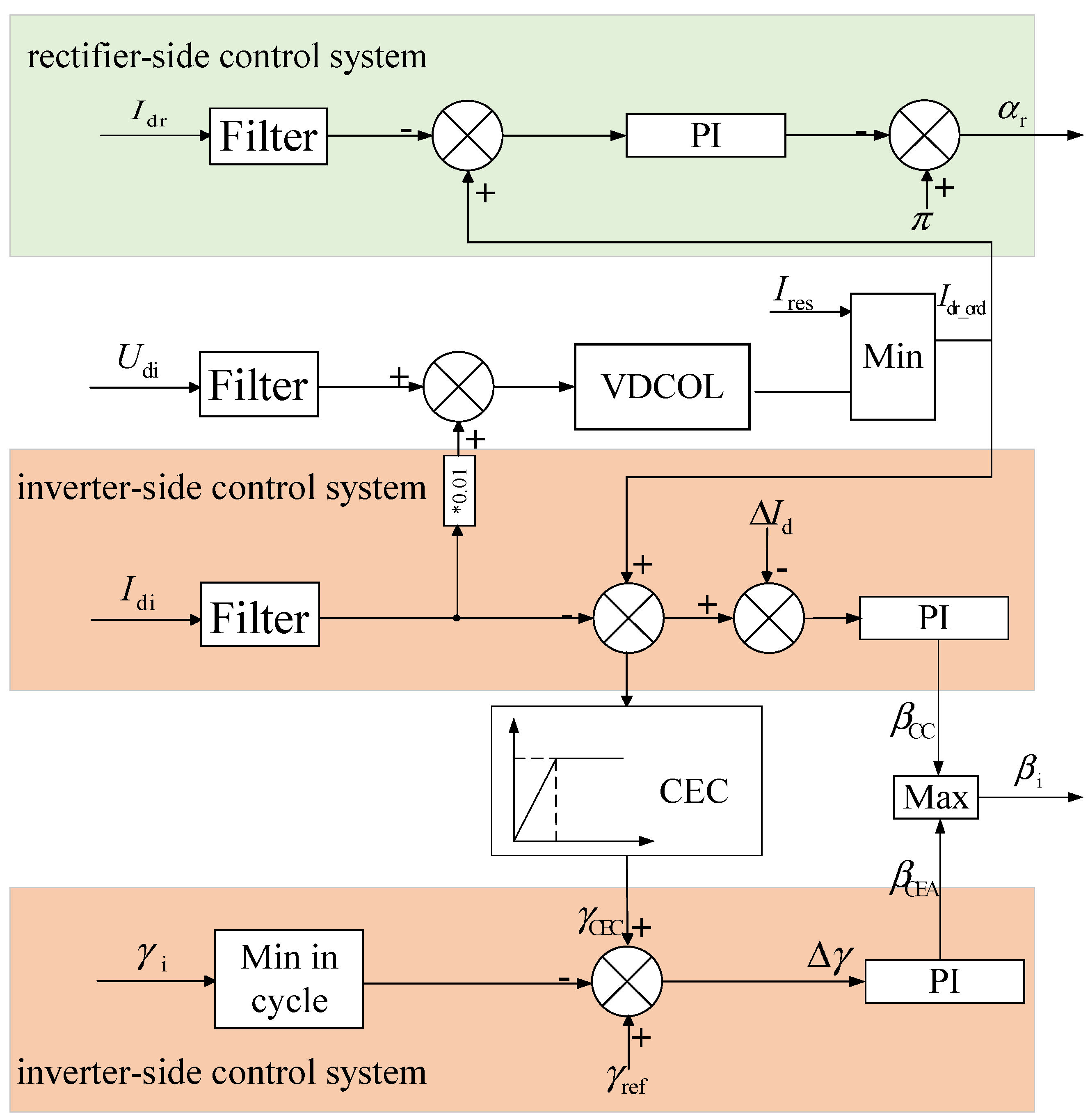
3.1. LCC-HVDC Control Structure Composition
3.2. LCC-HVDC Continuous Commutation Failure Mechanism
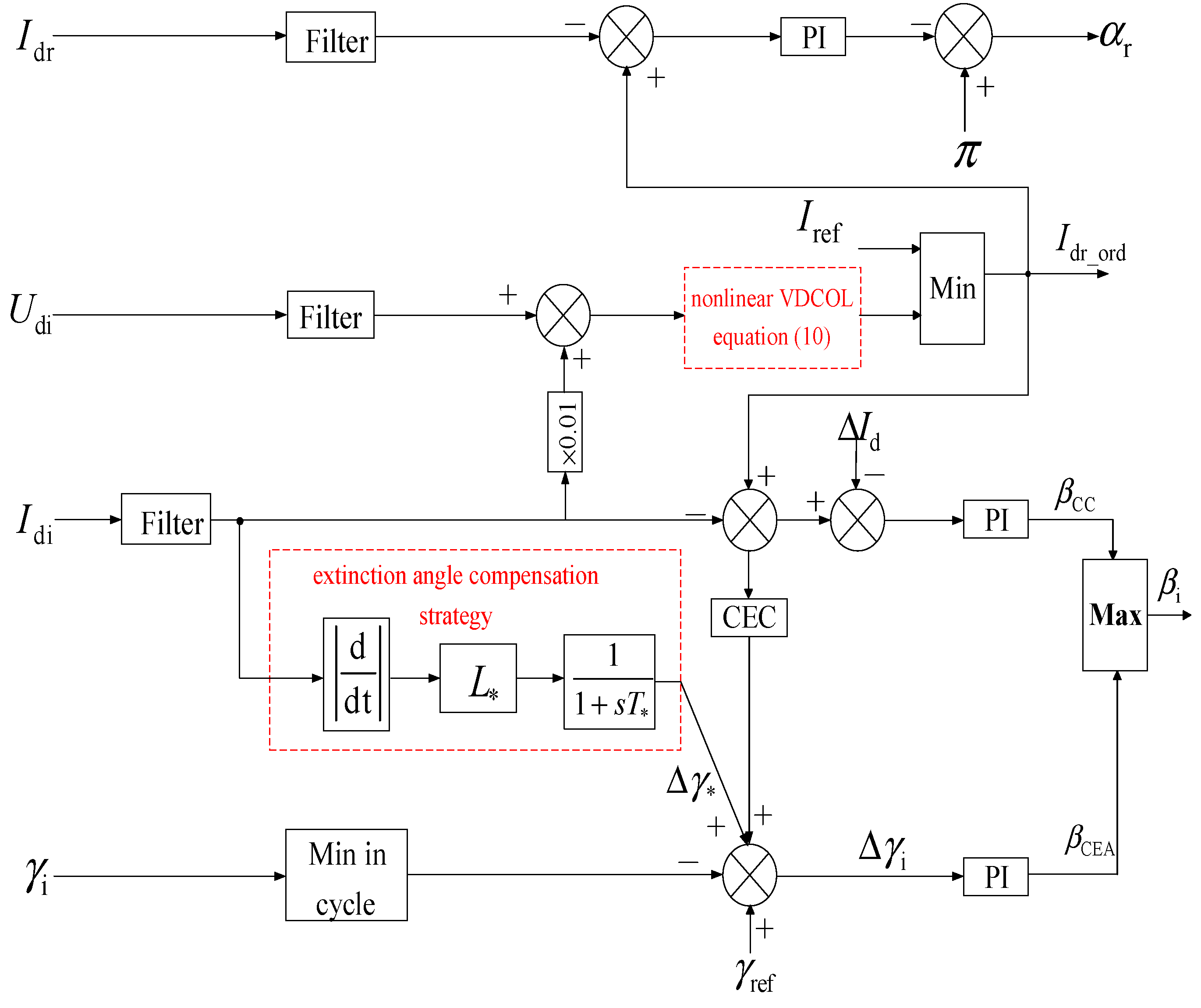
4. Joint Control Strategy to Suppress Continuous Commutation Failure of LCC-HVDC System
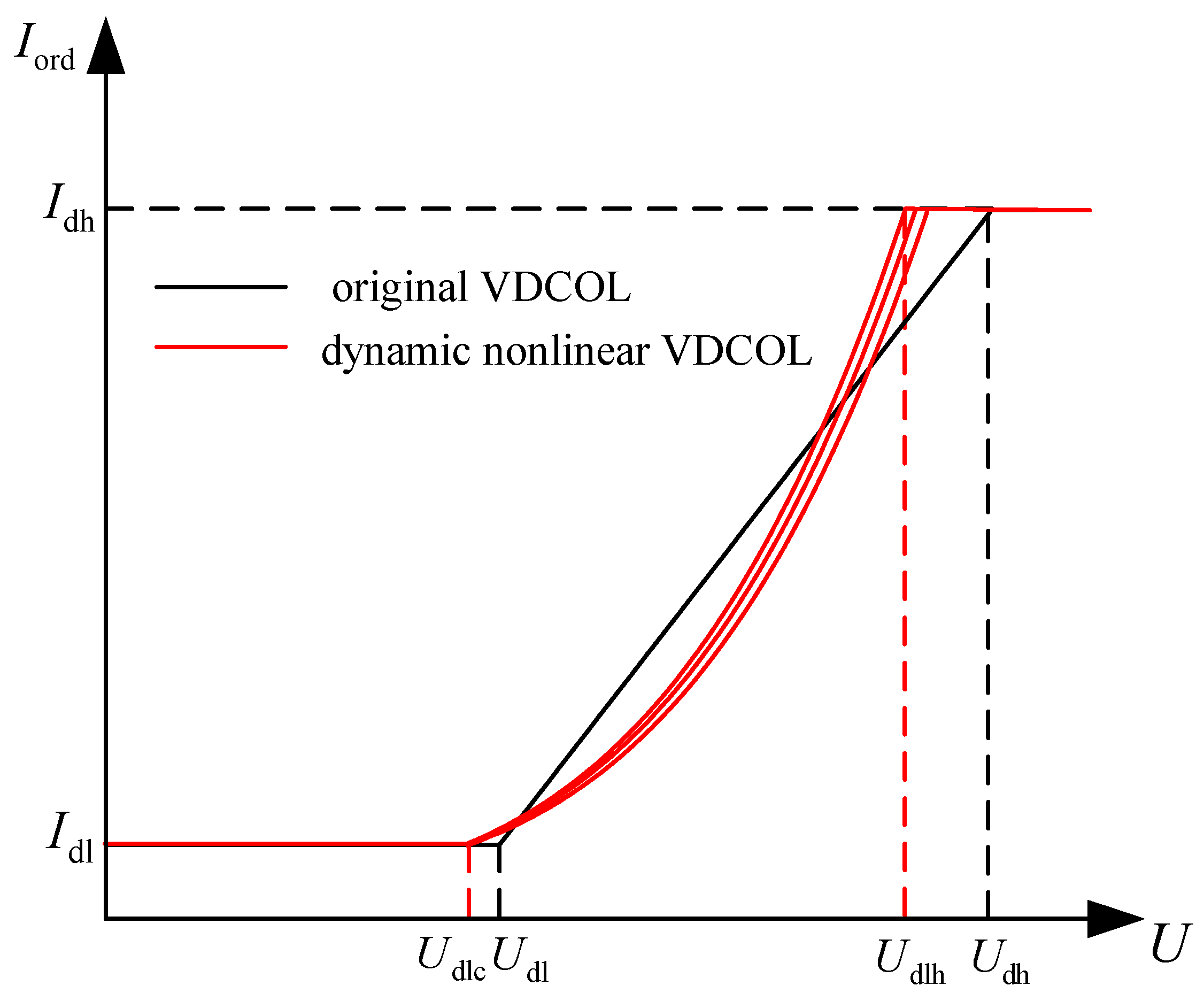
4.1. Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL Control Strategy
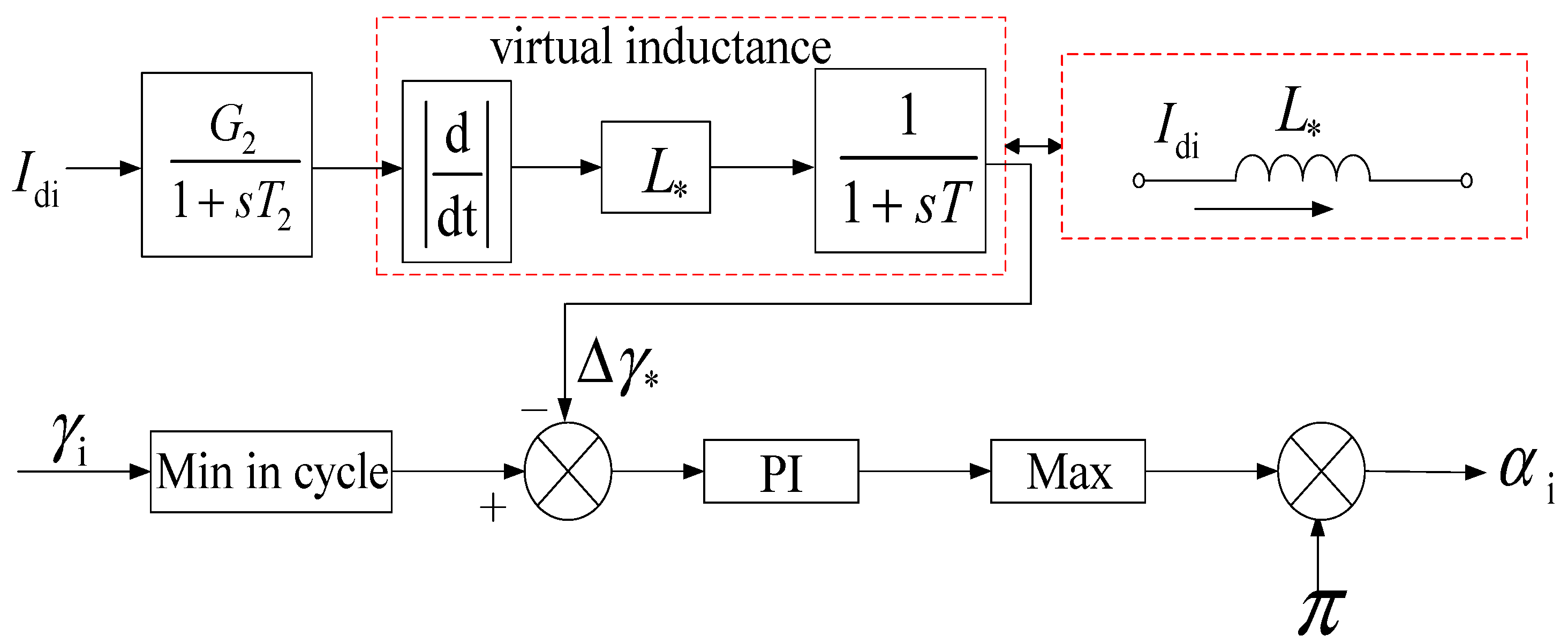
4.2. Shutdown Angle Compensation Control Strategy Based on Virtual Inductance
5. Simulation Results and Discussion
5.1. Determination of Virtual Inductance Parameters
5.2. Gain Coefficient G Is Determined
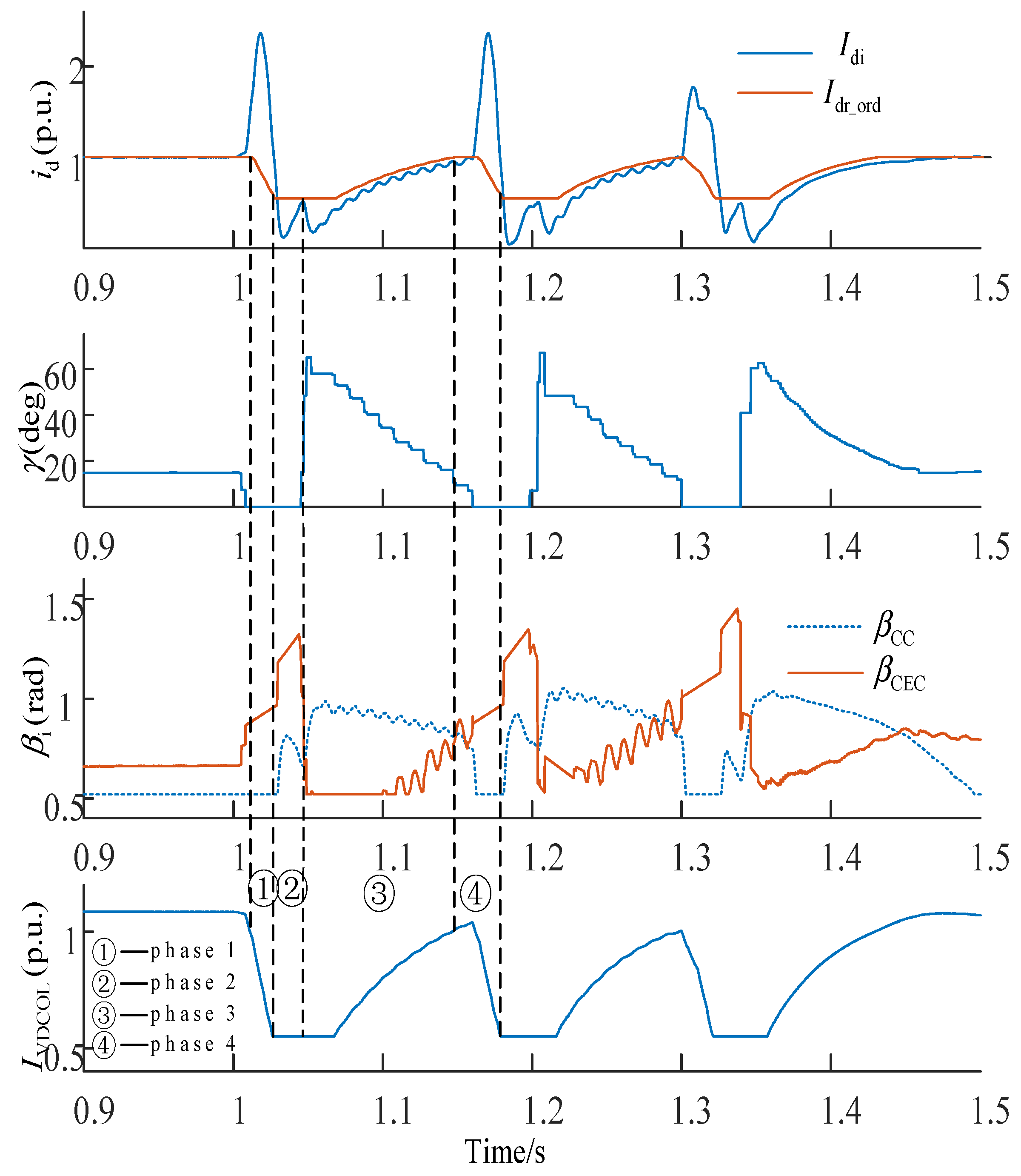
5.3. Simulation Analysis and Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Symbols | Parameter Name | Parameter Size |
|---|---|---|
| DC voltage | ||
| DC current | ||
| DC current on the rectifier side | ||
| DC current on the inverter side | ||
| DC voltage on the rectifier side | ||
| DC voltage on the inverter side | ||
| The triggering angle of the output is controlled by the rectifier siding current | ||
| DC current command value on the rectifier side | ||
| DC current reference angle | ||
| Current margin | ||
| Trigger lead angle of variable side | ||
| Turn-off angle compensation for current deviation control | ||
| Compensating resistance | ||
| Turn-off angle measurement | ||
| The triggering advance angle of the output is controlled by the inverter side setting the current | ||
| the triggering advance angle of the output is controlled by the fixed turn-off angle. | ||
| Upper and lower limits of DC voltage | ||
| Upper and lower limits of DC current | ||
| The start-up voltage of the VDCOL control link | ||
| Conventional VDCOL output current command value | ||
| Failure factor | ||
| The effective value of the phase voltage of the AC system on the inverter side | ||
| Phase voltage rating | 187.79 kV | |
| New upper and lower limits for voltages | ||
| Commutation voltage change factor | ||
| Minimum cutoff angle | 7.2° | |
| Virtual inductors | 0.006 | |
| Turn-off angle compensation | ||
| Line inductance | 0.5968 H | |
| Line resistance | 2.5 Ω | |
| Line capacitance | 26 μF | |
| Ground inductance | ||
| Fault level | ||
| RMS voltage of the AC bus on the inverter side | 215.05 kV | |
| Rated active power | 1000 MW |
| Main Parameters of the AC System | |||||
| AC System Voltage/kV | Rated Voltage/kV | Reactive Power Compensation Capacity/Mvar | Fundamental Impedance/Ω | SCR | |
| Rectifier side | 382.9 | 345 | 626 | 47.7∠84° | 2.5 |
| Inverter side | 215.1 | 230 | 626 | 21.2∠75° | 2.5 |
| Converter Transformer Parameters | |||||
| Ratio/kV | capacity/MVA | Short-Circuit Impedance/p.u. | |||
| Rectifier side | 345/213 | 591 | 0.18 | ||
| Inverter side | 230/209 | 603 | 0.18 | ||
| Main Parameters of the DC Line | |||
| Rated voltage/kv | 500 | Inductance/H | 0.6 |
| Rated power/MW | 1000 | Resistance/Ω 26 | 26 |
| Rated current/kA | 2 | Capacitance/μF | 2.5 |
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, J. Analysis of Asymmetric Fault Commutation Failure in HVDC System Considering Instantaneous Variation of DC Current. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitali, J.; Dhinakaran, S.; Mohamad, A.A. Energy storage systems: A review. Energy Storage Sav. 2022, 1, 166–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Z.; Niu, C.; Wang, Z.B. An Extinction Angle Dynamic Compensation Control Method for Suppressing Continuous Commutation Failure. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 7621–7630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Yao, W.; Ai, X.; Li, D.; Wen, J.; Li, C. Comprehensive Review of Commutation Failure in HVDC Transmission Systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 205, 107768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, L.R.; Yang, C.X.; Li, C.H.; Wen, J.Y. Review of Commutation Failure on HVDC Transmission System Under Background of Multi-infeed Structure. Power Syst. Technol. 2022, 46, 834–850. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.-P.; Yang, C. Elimination of Commutation Failures of LCC HVDC System with Controllable Capacitors. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 31, 3289–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Mechanism Analysis and Prevention Methods of Commutation Failure in LCC-HVDC Transmission System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 8th International Conference on Advanced Power System Automation and Protection (APAP), Xi’an, China, 21–24 October 2019; pp. 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, K.J.; Ren, Z.; Jing, Y. Research on commutation failure in HVDC transmission system Part1: Commutation failure factors analysis. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2003, 23, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Ou, K.J.; Jing, Y. Research on commutation failure in HVDC transmission system part 2: Measures against commutation failure. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2003, 23, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Li, X.N.; Yu, J.; Li, T.; Lu, P.; Yin, Y. A method based on the detection of the sin-cos components mitigates commutation failure in HVDC. Pros. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2005, 25, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.Z.Y.; Cai, W.Y.; Tan, Z.P.; Chen, Z.S.; Cai, Z.X. Improvement of HVDC CFPREV based on a three-phase simultaneity sampling values algorithm. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2020, 48, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tamai, S.; Naitoh, H.; Ishiguro, F.; Sato, M.; Yamaji, K.; Honjo, N. Fast and predictive HVDC extinction angle control. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, Y.; Lan, T. Sending End AC Faults Can Cause Commutation Failure in LCC-HVDC Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2020, 35, 2554–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, F.; Yin, C. Impact of voltage restoration of commutation bus on rectifier side on commutation of inverters. Power Syst. Technol. 2020, 44, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wei, X.; Xu, W. Power Component Fault Detection Method and Improved Current Order Limiter Control for Commutation Failure Mitigation in HVDC. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2015, 30, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, G.; Sun, Y. Direct-current predictive control strategy for inhibiting commutation failure in HVDC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2014, 29, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gole, A.M.; Meisingset, M. Capacitor commutated converters for long-cable HVDC transmission. Power Eng. J. 2002, 16, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gole, A.M.; Zhao, C. Analysis of dual-infeed HVDC with LCC-HVDC and VSC-HVDC. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 27, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, Q. A dynamic series voltage compensator for the mitigation of LCC-HVDC commutation failure. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 36, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wen, J.; Geng, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Luo, Z.; Tan, M. Study on HVDC commutation failure and voltage compensated variable slope VDCOL control. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Beijing, China, 20–22 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Saha, T.K.; Eghbal, M. Master self-tuning VDCOL function for hybrid multi-terminal HVDC connecting renewable resources to a large power system. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 11, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Wang, J.-J.; Li, Z.-L.; Fu, C. VDCOL parameters setting influenced by reactive power characteristics of HVDC system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Smart Grid and Clean Energy Technologies (ICSGCE), Chengdu, China, 19–22 October 2016; pp. 364–370. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Overview on VDCOL control strategy for improving DC system recovery characteristics. East China Electr. Power Syst. 2016, 42, 826–832. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Design of variable slope VDCOL controller based on fuzzy control. Power Syst. Technol. 2015, 39, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Qin, L. The Influence of VDCOL Parameters on the Recovery Characteristic after Commutation Failures of HVDC Links Fed into Weak AC Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Power and Energy Technology (ICPET), Beijing, China, 29–31 July 2022; pp. 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Zheng, B.W.; Wang, T.; Qiao, X. Mechanism analysis and mitigation measures for continuous commutation failure during the restoration of LCC-HVDC. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 3163–3172. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Hong, L.R.; Zhou, X.; Xia, H.T.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, X. A suppression method based on nonlinear VDCOL to mitigate the continuous commutation failure. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2019, 47, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Lin, S.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Li, X.; He, Z. Mechanism analysis of continuous commutation failure caused by improper interaction of controllers. Power Syst. Technol. 2019, 43, 3562–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Tong, K.; Ning, L.R.; Xuan, J.; Guo, C.; Zhao, C. A Method Mitigating Continuous Commutation Failure for Double-Infeed HVDC System Based on Virtual Inductor. Power Syst. Technol. 2017, 41, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.Y.; Li, C.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, Q. A DC Current Limitation Control Method Based on Virtual Resistance to Mitigate the Continuous Commutation Failure for Conventional HVDC. Proc. CSEE 2016, 36, 4930–4937+5117. [Google Scholar]
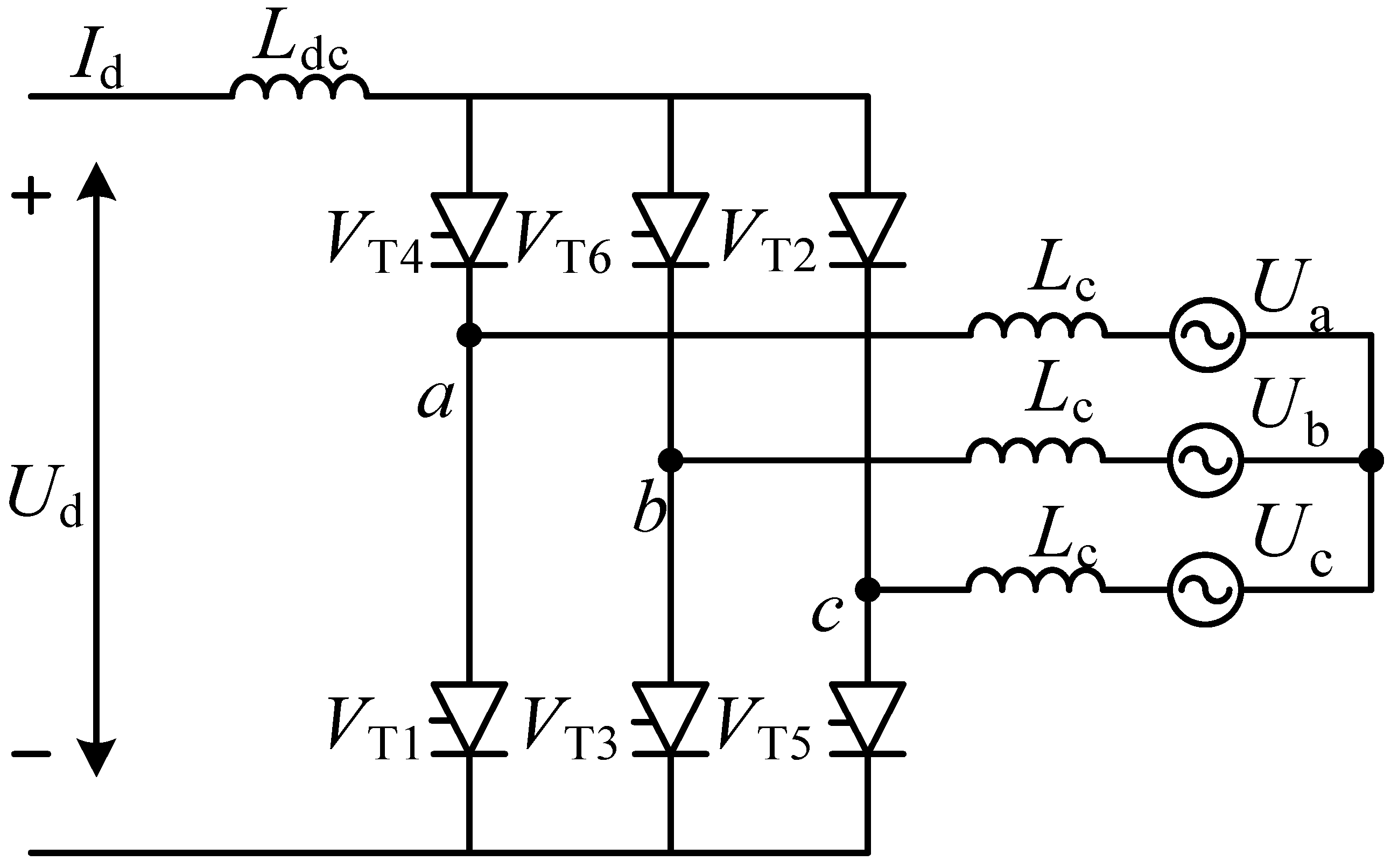
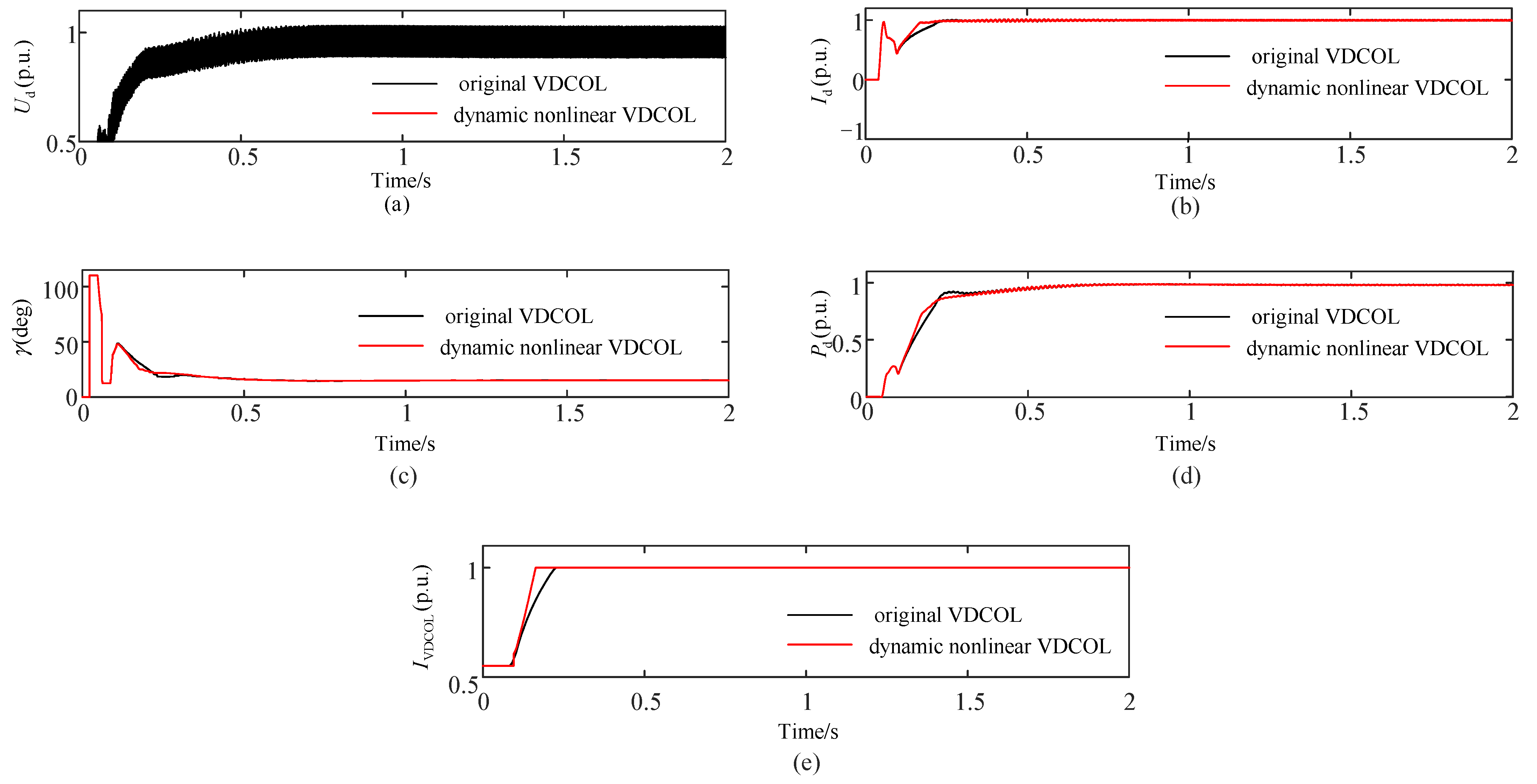
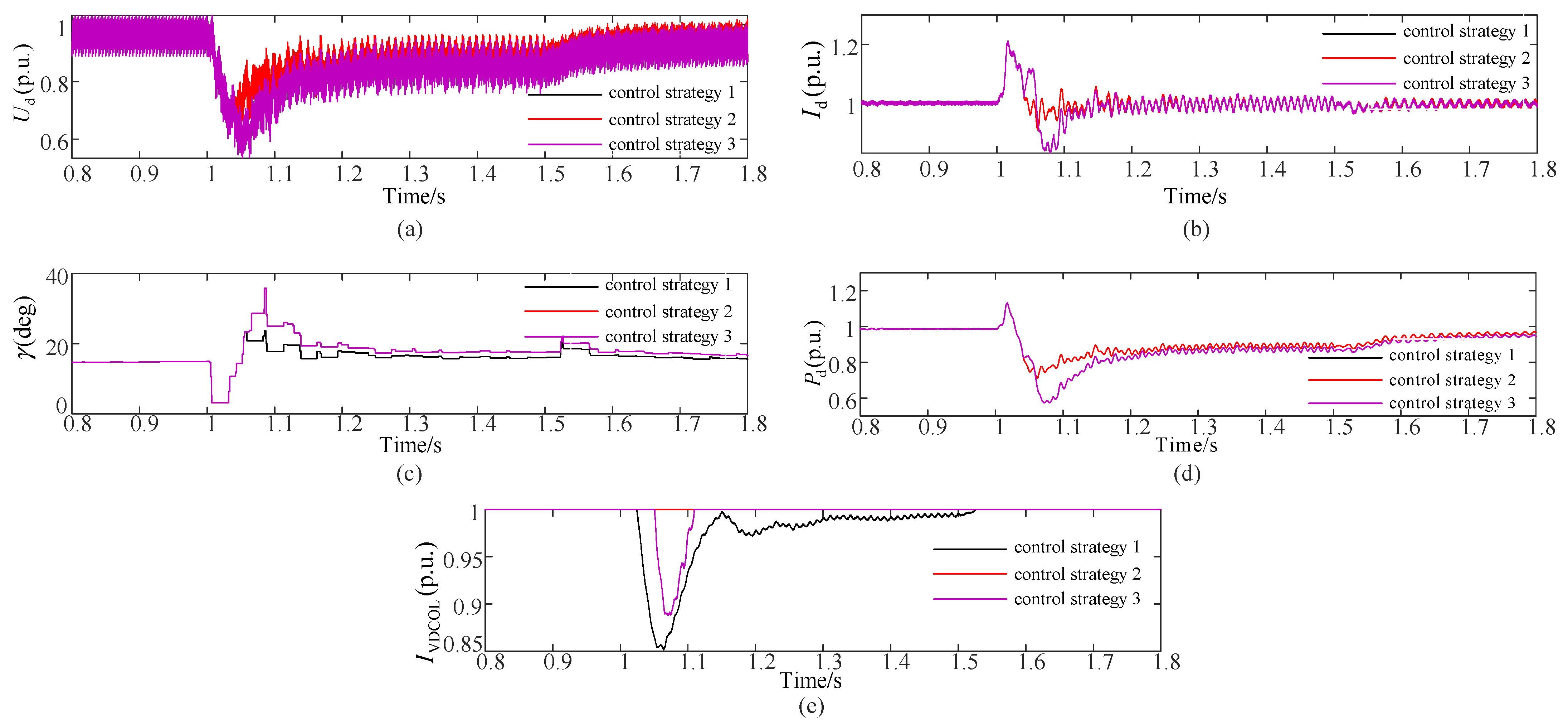
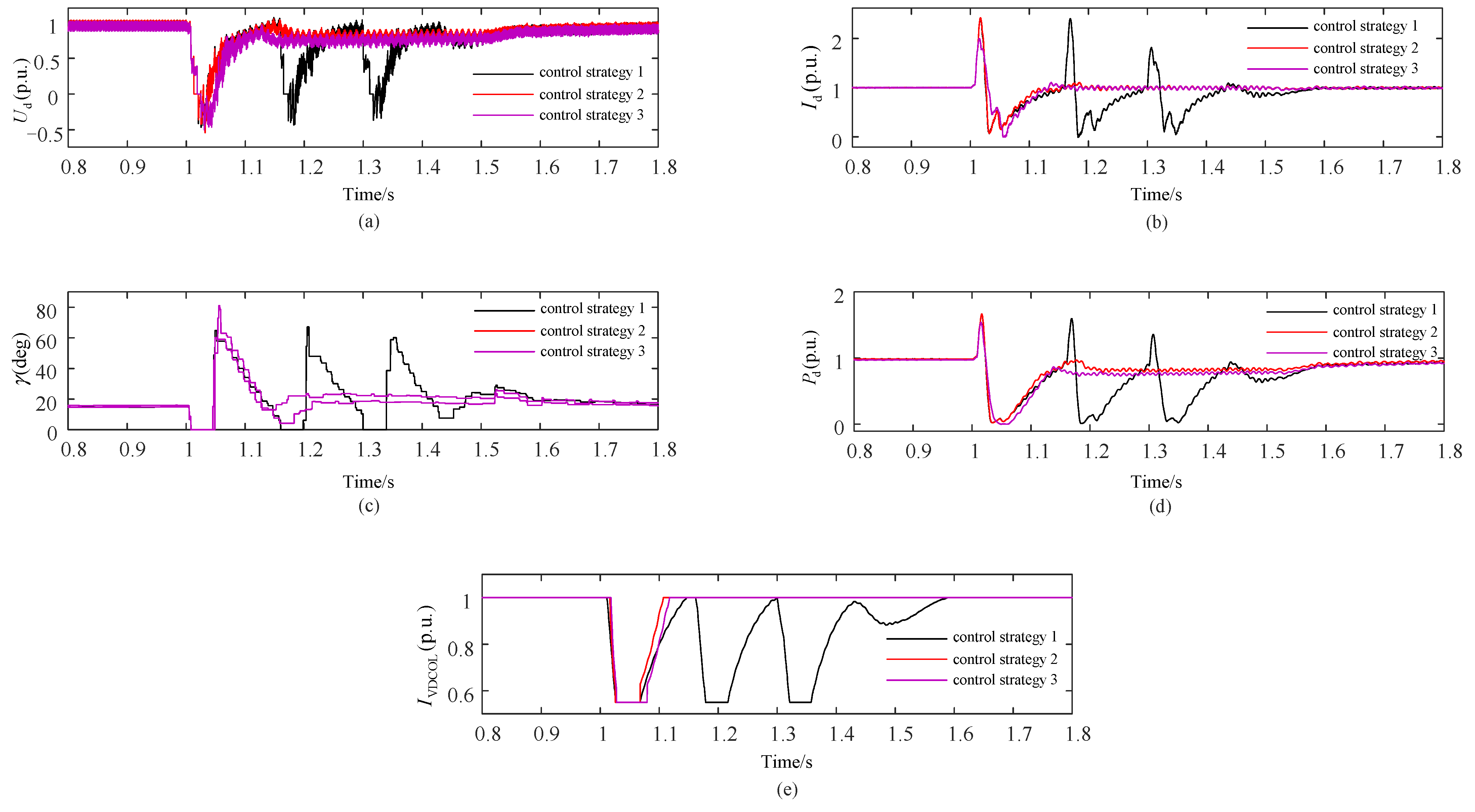
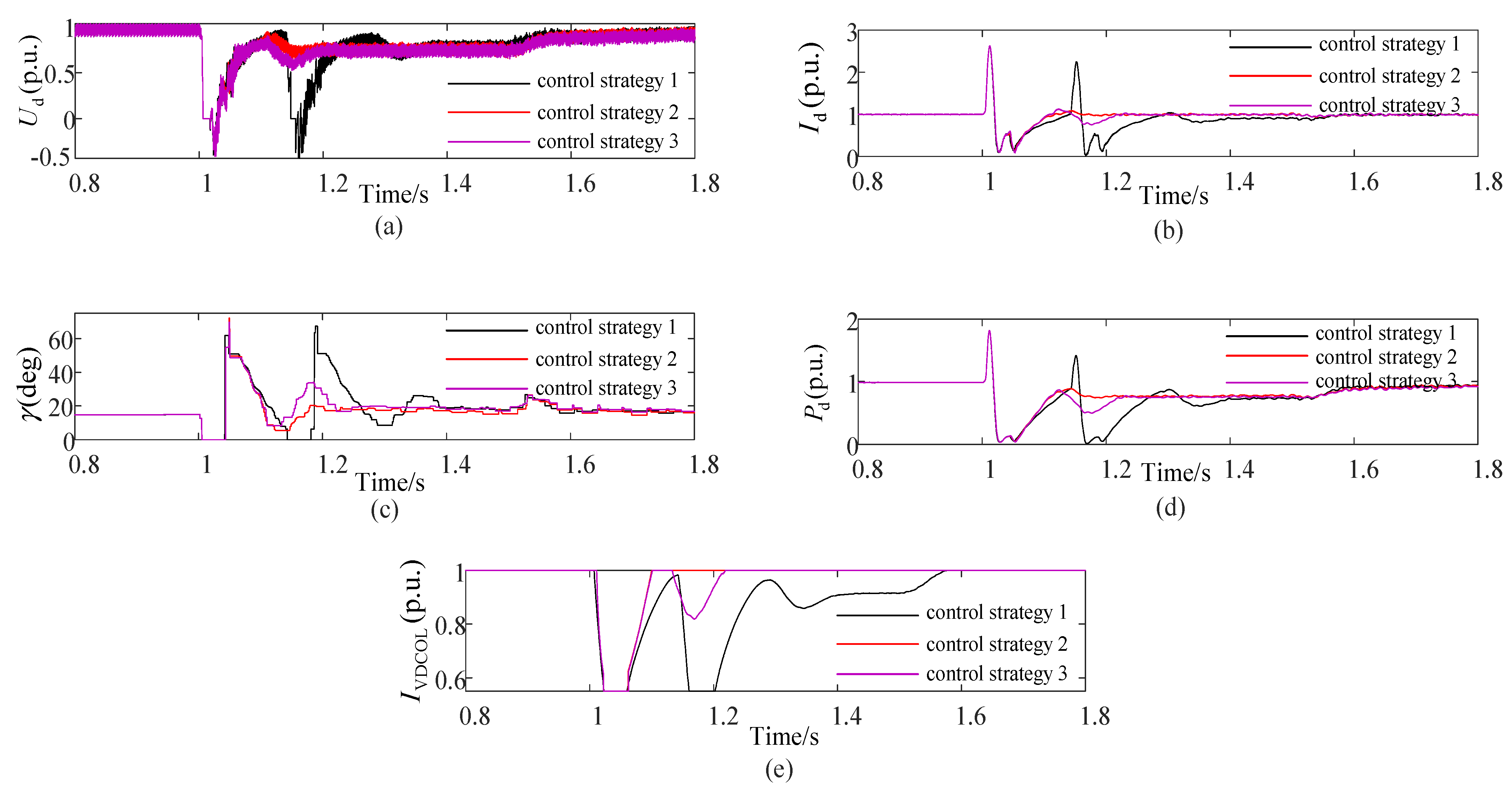
| Coefficient L*/p.u. | Number of Commutation Failures | Failure Recovery Time/s |
|---|---|---|
| 0.002 | 2 | 0.581 |
| 0.004 | 2 | 0.582 |
| 0.006 | 1 | 0.571 |
| 0.008 | 1 | 0.583 |
| 0.009 | 1 | 0.573 |
| 0.01 | 1 | 0.584 |
| Coefficient G Value | Number of Commutation Failures | Failure Recovery Time/s |
|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 3 | 0.735 |
| 0.06 | 2 | 0.586 |
| 0.08 | 2 | 0.584 |
| 0.1 | 2 | 0.596 |
| 0.12 | 2 | 0.609 |
| 0.14 | 1 | 0.608 |
| 0.16 | 2 | 0.620 |
| 0.18 | 2 | 0.633 |
| 0.2 | 1 | 0.582 |
| 0.22 | 1 | 0.614 |
| Fault Level/% | Single-Phase Fault | Three-Phase Fault | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Strategy 1 | Control Strategy 2 | Control Strategy 3 | Control Strategy 1 | Control Strategy 2 | Control Strategy 3 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 25 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 30 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 35 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 40 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 45 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| 50 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Jin, G. The Strategy of Continuous Commutation Failure Suppression by Combining Turn-off Angle Compensation and Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052145
Liu H, Jin G. The Strategy of Continuous Commutation Failure Suppression by Combining Turn-off Angle Compensation and Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL. Sustainability. 2024; 16(5):2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052145
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hewei, and Guobin Jin. 2024. "The Strategy of Continuous Commutation Failure Suppression by Combining Turn-off Angle Compensation and Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL" Sustainability 16, no. 5: 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052145
APA StyleLiu, H., & Jin, G. (2024). The Strategy of Continuous Commutation Failure Suppression by Combining Turn-off Angle Compensation and Dynamic Nonlinear VDCOL. Sustainability, 16(5), 2145. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16052145





