Investigating the Impact of Streetscape and Land Surface Temperature on Cycling Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Land Surface Temperature Retrieval
2.3. Streetscape Measurements and Comparative Experimental Design
2.4. Exploring the Effects of Streetscapes and Land Surface Temperatures
2.4.1. Feature Importance Assessment Based on the Random Forest Algorithm
2.4.2. Interaction Effects Analysis Based on the GeoDetector Method
3. Results
3.1. Results of Land Surface Temperature Retrievals
3.2. Spatial Pattern of Street Landscape Measurement Results
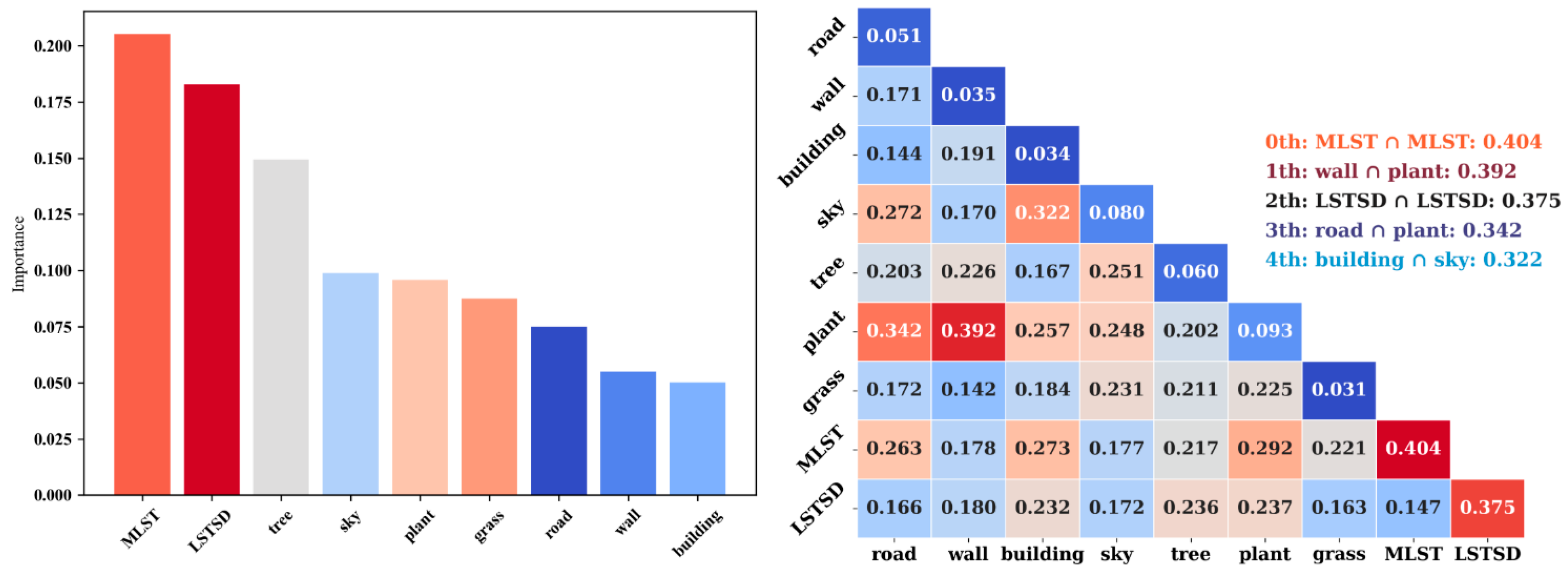
3.3. Effects of Streetscapes and Land Surface Temperatures on Cycling Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate Adaptation and Urban Planning Strategies Influence Cycling Behavior
4.2. Analysis of Urban Planning and Policy Guidance
4.3. Limitations and Future Avenues
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012.
- AghaKouchak, A.; Chiang, F.; Huning, L.S.; Love, C.A.; Mallakpour, I.; Mazdiyasni, O.; Moftakhari, H.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ragno, E.; Sadegh, M. Climate extremes and compound hazards in a warming world. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 48, 519–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aalst, M.K. The impacts of climate change on the risk of natural disasters. Disasters 2006, 30, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pl⊘ger, J. Urban planning and urban life: Problems and challenges. Plan. Pract. Res. 2006, 21, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, T.W.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L. Identifying risk factors of urban-rural conflict in urbanization: A case of China. Habitat Int. 2014, 44, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, H.S.; Butler, C.D. The interconnection between the built environment ecology and health. In Environmental Security and Environmental Management: The Role of Risk Assessment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Snep, R.P.H.; Clergeau, P. Biodiversity in cities, reconnecting humans with nature. In Sustainable Built Environments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pucher, J.; Dijkstra, L. Promoting safe walking and cycling to improve public health: Lessons from the Netherlands and Germany. Am. J. Public Health 2003, 93, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, A.; Ermagun, A.; Stathopoulos, A. Modelling determinants of walking and cycling adoption: A stage-of-change perspective. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2018, 58, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.J.; Johnson, N. Effects of physical activity upon the liver. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, J.C.; Suzuki, W.A. The effects of acute exercise on mood, cognition, neurophysiology, and neurochemical pathways: A review. Brain Plast. 2017, 2, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hötting, K.; Röder, B. Beneficial effects of physical exercise on neuroplasticity and cognition. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosie, M.P.; Sipos, M.; Britt, T.W. Maximizing Senior Leader Health and Wellbeing. 2023. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/trecms/pdf/AD1201134.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Mindell, J.S.; Cohen, J.M.; Watkins, S.; Tyler, N. Synergies between low-carbon and healthy transport policies. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Transport; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2011; Volume 164, pp. 127–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zuurbier, M.; Hoek, G.; Oldenwening, M.; Lenters, V.; Meliefste, K.; Van Den Hazel, P.; Brunekreef, B. Commuters’ exposure to particulate matter air pollution is affected by mode of transport, fuel type, and route. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Costa, P.D.; Abrantes, D.; Hora, J.; Felício, S.; Coimbra, M.; Dias, T.G. Identifying the determinants and understanding their effect on the perception of safety, security, and comfort by pedestrians and cyclists: A systematic review. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2022, 91, 136–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, M.; Mont, O.; Heiskanen, E. Nudging—A promising tool for sustainable consumption behaviour? J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, V.; Goodwin, P.; Witlox, F. Key research themes on travel behavior, lifestyle, and sustainable urban mobility. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. Urban and transport planning pathways to carbon neutral, liveable and healthy cities; A review of the current evidence. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, C.; Bichai, F.; Boisjoly, G. Synergy between green stormwater infrastructure and active mobility: A comprehensive literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryzek, M.; Adamska-Kmieć, D.; Klimach, A. Sustainable transport: An efficient transportation network—Case study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürçam, S. Paving the Way for Climate Resilience through Sustainable Urbanization: A Comparative Study. Lectio Soc. 2024, 8, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrath, M.; Kowarik, I.; Fischer, L.K. The influence of green streets on cycling behavior in European cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 190, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvennoinen, K.C. Influence of Urban Design in the Choice of Transportation Mode-Cycling for a People-Centred Urban Form. Master’s Thesis, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nijen, N.P. The Influence of Infrastructure and Land Use Allocation on the Route Choice of Cyclists. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Long, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y. Urban high-quality navigation path planning that integrates human emotion perception learning. Trans. GIS 2023, 27, 2297–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, J.; Othengrafen, F. Examining the Role of Innovative Streets in Enhancing Urban Mobility and Livability for Sustainable Urban Transition: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.D.; Ting, M.; Li, C.; Kornhuber, K.; Coffel, E.D.; Horton, R.M.; Raymond, C.; Singh, D. Recent increases in exposure to extreme humid-heat events disproportionately affect populated regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.C.; Macleod, T.; Both, A.; Hurley, J.; Butt, A.; Amati, M. A human-centred assessment framework to prioritise heat mitigation efforts for active travel at city scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilami, K.; Rudner, J.; Butt, A.; MacLeod, T.; Williams, G.; Romeijn, H.; Amati, M. Allowing users to benefit from tree shading: Using a smartphone app to allow adaptive route planning during extreme heat. Forests 2020, 11, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.M.; Shah, S.A.; Shukla, D.; Bentafat, E.; Bakiras, S. The role of ai, machine learning, and big data in digital twinning: A systematic literature review, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32030–32052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschka, S.; Patterson, J.; Nolet, C. Machine learning in python: Main developments and technology trends in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. Information 2020, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonlau, M.; Zou, R.Y. The random forest algorithm for statistical learning. Stata J. 2020, 20, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Parvin, F.; Ahmad, A. Retrieval of land surface temperature from Landsat 8 OLI and TIRS: A comparative analysis between radiative transfer equation-based method and split-window algorithm. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Guo, D. A refined pyramid scene parsing network for polarimetric SAR image semantic segmentation in agricultural areas. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4014805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Xu, H.; He, H.; Wei, Q.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, T. A Spatial Analysis of Urban Streets under Deep Learning Based on Street View Imagery: Quantifying Perceptual and Elemental Perceptual Relationships. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W. Landslide susceptibility mapping using hybrid random forest with GeoDetector and RFE for factor optimization. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Hipp, J.R.; Ki, D. Decoding urban landscapes: Google street view and measurement sensitivity. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 88, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Carstensen, T.A.; Nielsen, T.A.S.; Olafsson, A.S. Bicycle-friendly infrastructure planning in Beijing and Copenhagen-between adapting design solutions and learning local planning cultures. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addas, A. The importance of urban green spaces in the development of smart cities. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1206372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Guchhait, S.K. Urban green space in India: Perception of cultural ecosystem services and psychology of situatedness and connectedness. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, O.; Capon, A.; Berry, P.; Broderick, C.; de Dear, R.; Havenith, G.; Honda, Y.; Kovats, R.S.; Ma, W.; Malik, A.; et al. Reducing the health effects of hot weather and heat extremes: From personal cooling strategies to green cities. Lancet 2021, 398, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.; Friesenecker, M.; Kazepov, Y.; Brandl, J. How Context Matters: Challenges of Localizing Participatory Budgeting for Climate Change Adaptation in Vienna. Urban Plan. 2023, 8, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wei, Y.D. Assess the non-linear relationship between built environment and active travel around light-rail transit stations. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 151, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zheng, L.; Ding, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. Understanding dockless bike-sharing spatiotemporal travel patterns: Evidence from ten cities in China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 104, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesenheimer, J.S.; Sagioglou, C.; Kronbichler, A.; Gauckler, P.; Kolbinger, F.R. Why do people cycle (a lot)? A multivariate approach on mental health, personality traits and motivation as determinants for cycling ambition. J. Appl. Sport Psychol. 2023, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L. Urban heat islands and their effects on thermal comfort in the US: New York and New Jersey. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamolaei, R.; Azizi, M.M.; Aminzadeh, B.; O’donnell, J. A comprehensive review of outdoor thermal comfort in urban areas: Effective parameters and approaches. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 2204–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.T.; Zarghami, E. Investigating the effect of the physical layout of the architecture of high-rise buildings, residential complexes, and urban heat islands. Energy Built Environ. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, H.; Eon, C.; Breadsell, J.K. Improving City vitality through urban heat reduction with green infrastructure and design solutions: A systematic literature review. Buildings 2020, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Co-benefits and synergies between urban climate change mitigation and adaptation measures: A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J. New urban models for more sustainable, liveable and healthier cities post COVID 19; reducing air pollution, noise and heat island effects and increasing green space and physical activity. Environ. Int. 2021, 157, 106850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, P.; Baudry, S. Streets as new places to bring together both humans and plants: Examples from Paris and Montpellier (France). Soc. Cult. Geogr. 2014, 15, 871–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmohamadi, P.; Che-Ani, A.; Etessam, I.; Maulud, K.; Tawil, N. Healthy environment: The need to mitigate urban heat island effects on human health. Procedia Eng. 2011, 20, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelde, L.; Mendizabal, M.; Gutiérrez, L.; Artetxe, A.; Garbisu, C.; Feliu, E. Quantification of the environmental effectiveness of nature-based solutions for increasing the resilience of cities under climate change. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 67, 127433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, F.; Hashim, M. A brief review of land surface temperature retrieval methods from thermal satellite sensors. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2014, 22, 757–768. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, M.; Xu, H.; Huang, J. Investigating the Impact of Streetscape and Land Surface Temperature on Cycling Behavior. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051990
Qin M, Xu H, Huang J. Investigating the Impact of Streetscape and Land Surface Temperature on Cycling Behavior. Sustainability. 2024; 16(5):1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051990
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Minglu, Haibin Xu, and Jiantuan Huang. 2024. "Investigating the Impact of Streetscape and Land Surface Temperature on Cycling Behavior" Sustainability 16, no. 5: 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051990
APA StyleQin, M., Xu, H., & Huang, J. (2024). Investigating the Impact of Streetscape and Land Surface Temperature on Cycling Behavior. Sustainability, 16(5), 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051990




