Novel MPPT Controller Augmented with Neural Network for Use with Photovoltaic Systems Experiencing Rapid Solar Radiation Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. P&O Controller
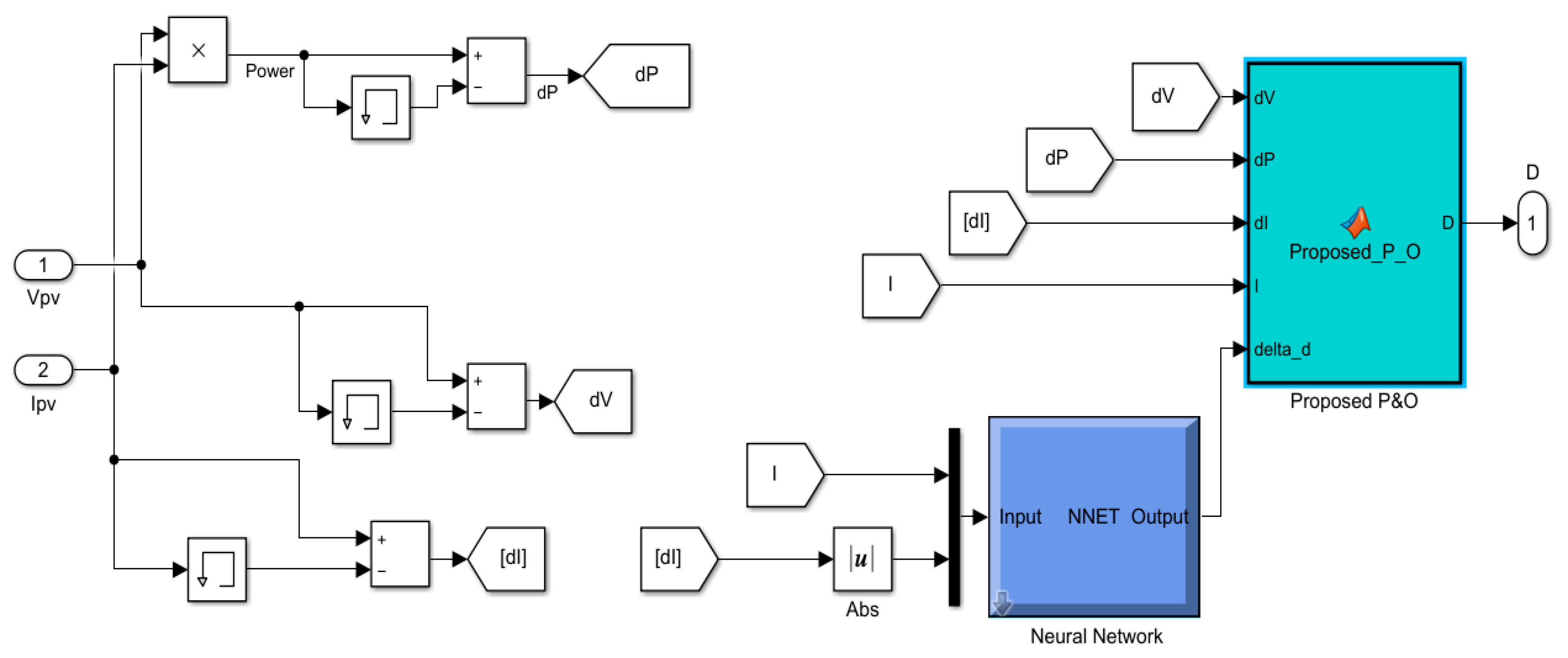
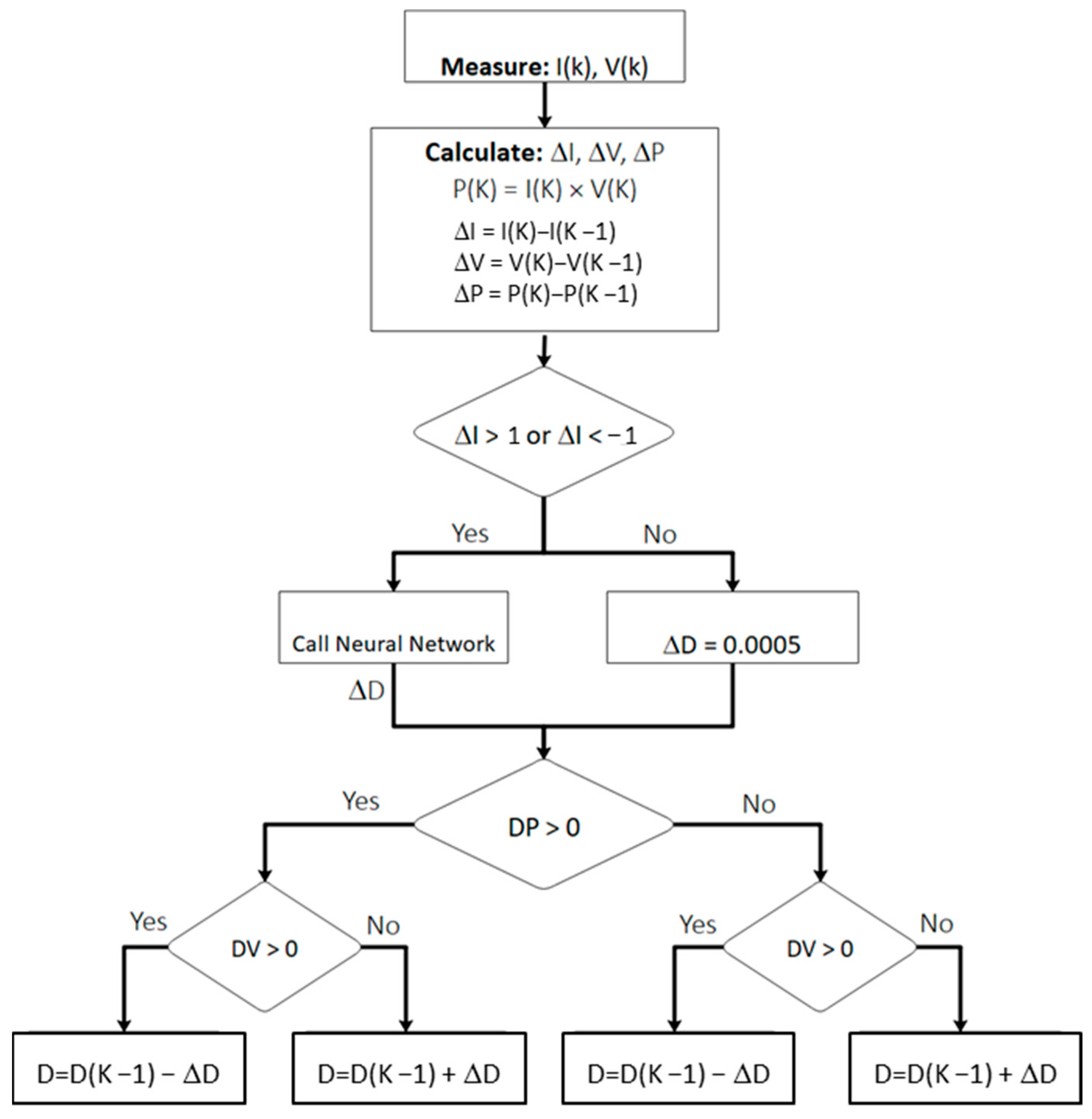
2.1. P&O Integrated with Neural Network
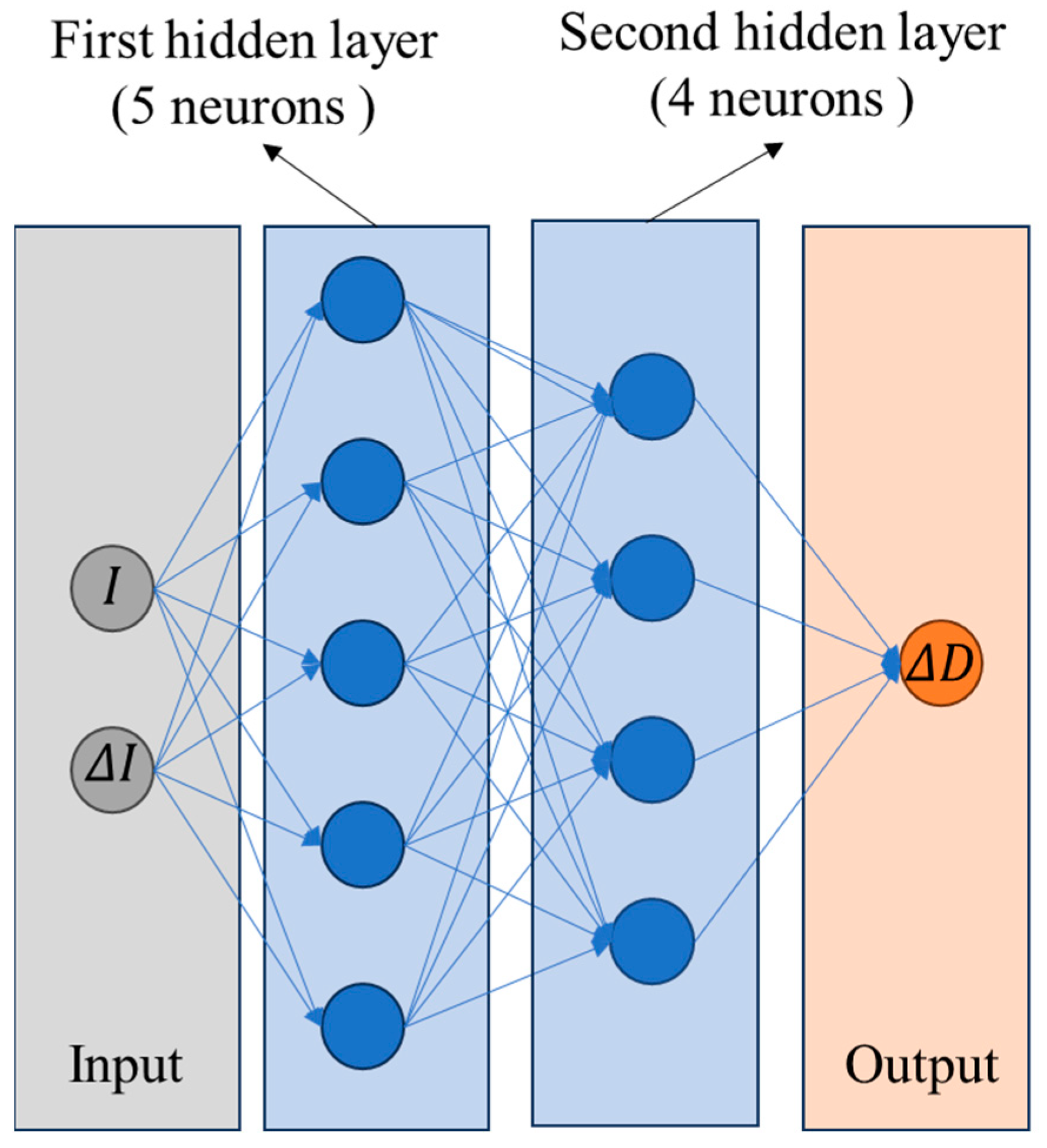
2.2. Neural Network (NN) Training
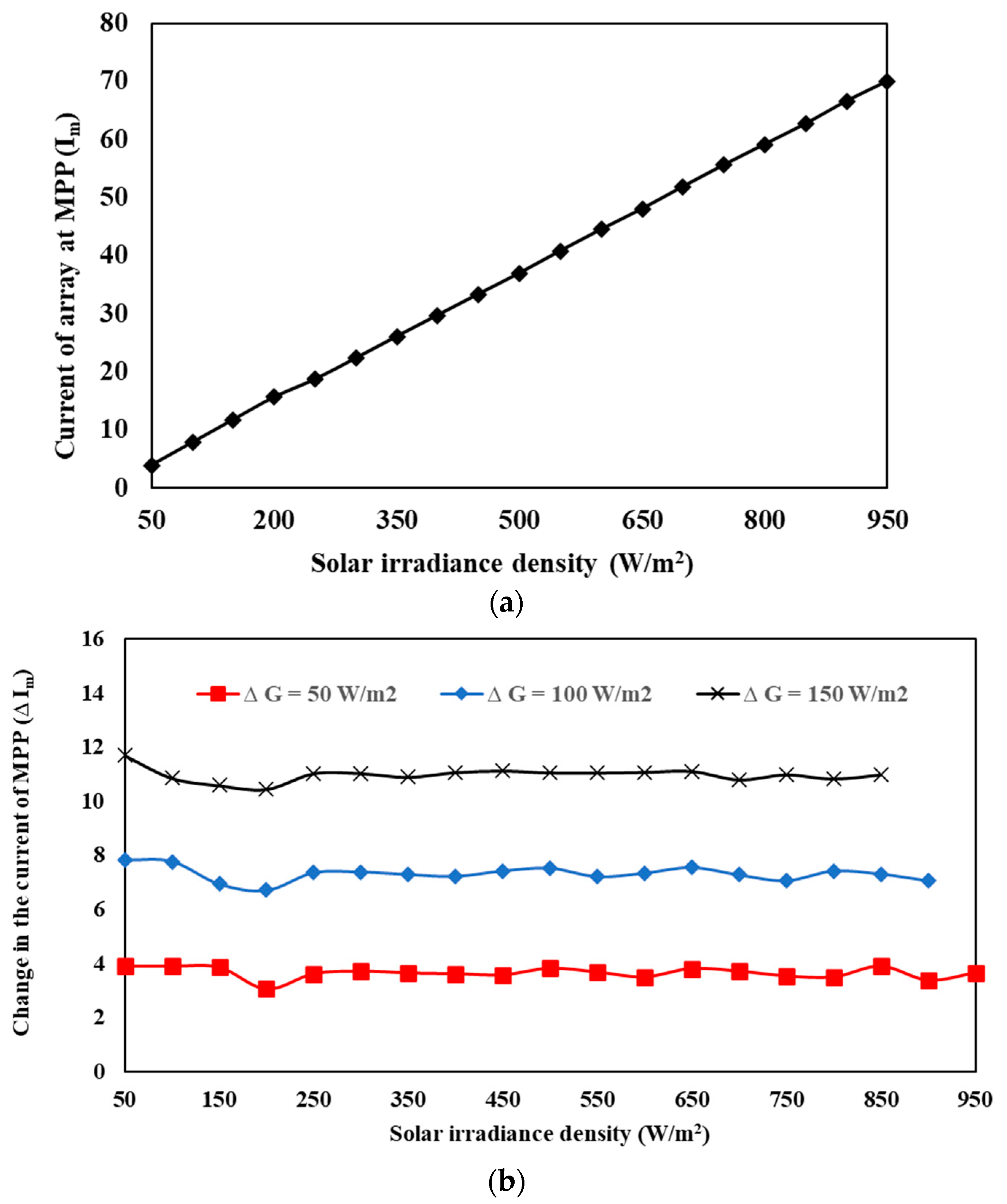
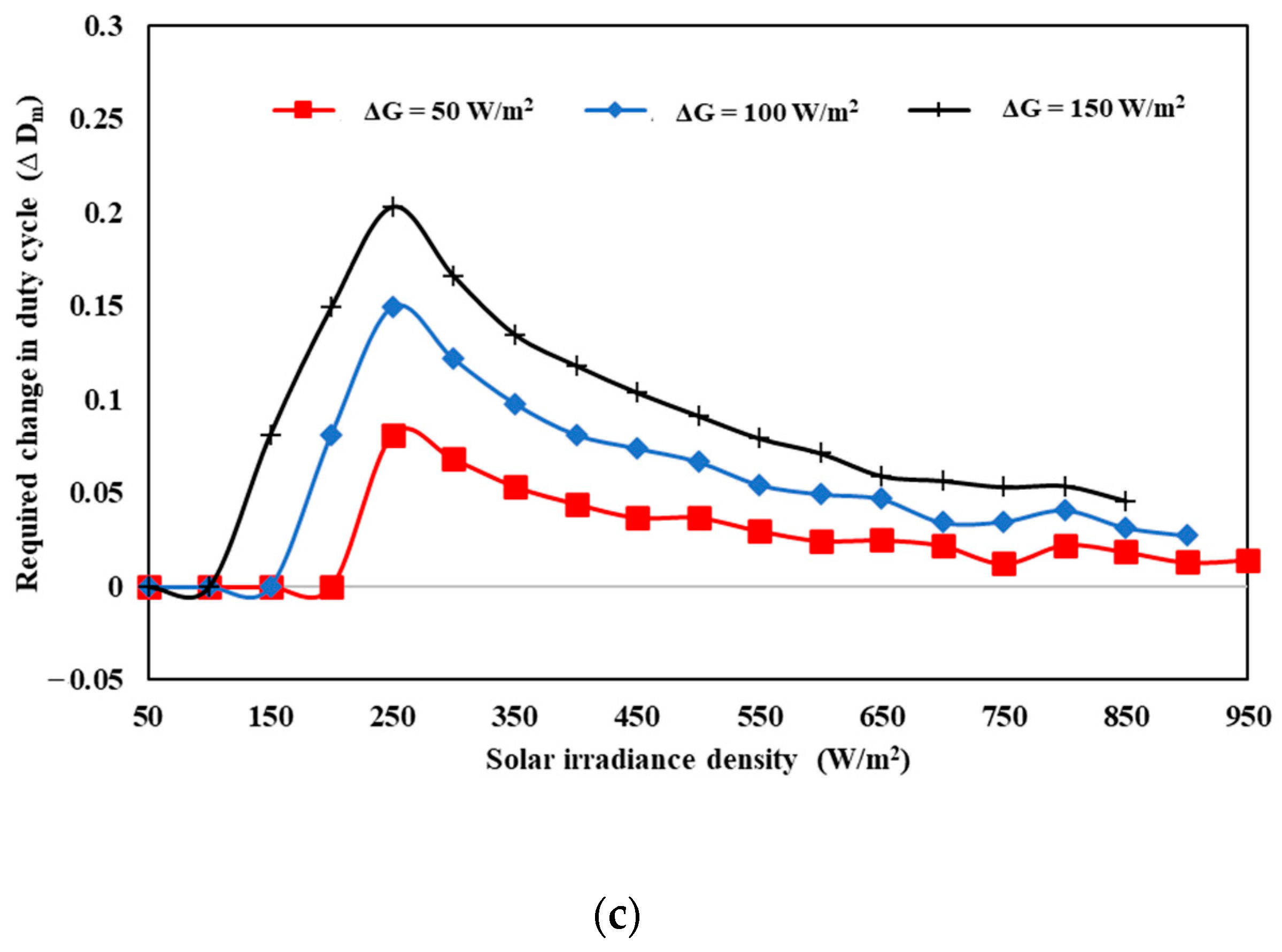
2.3. System Behavior
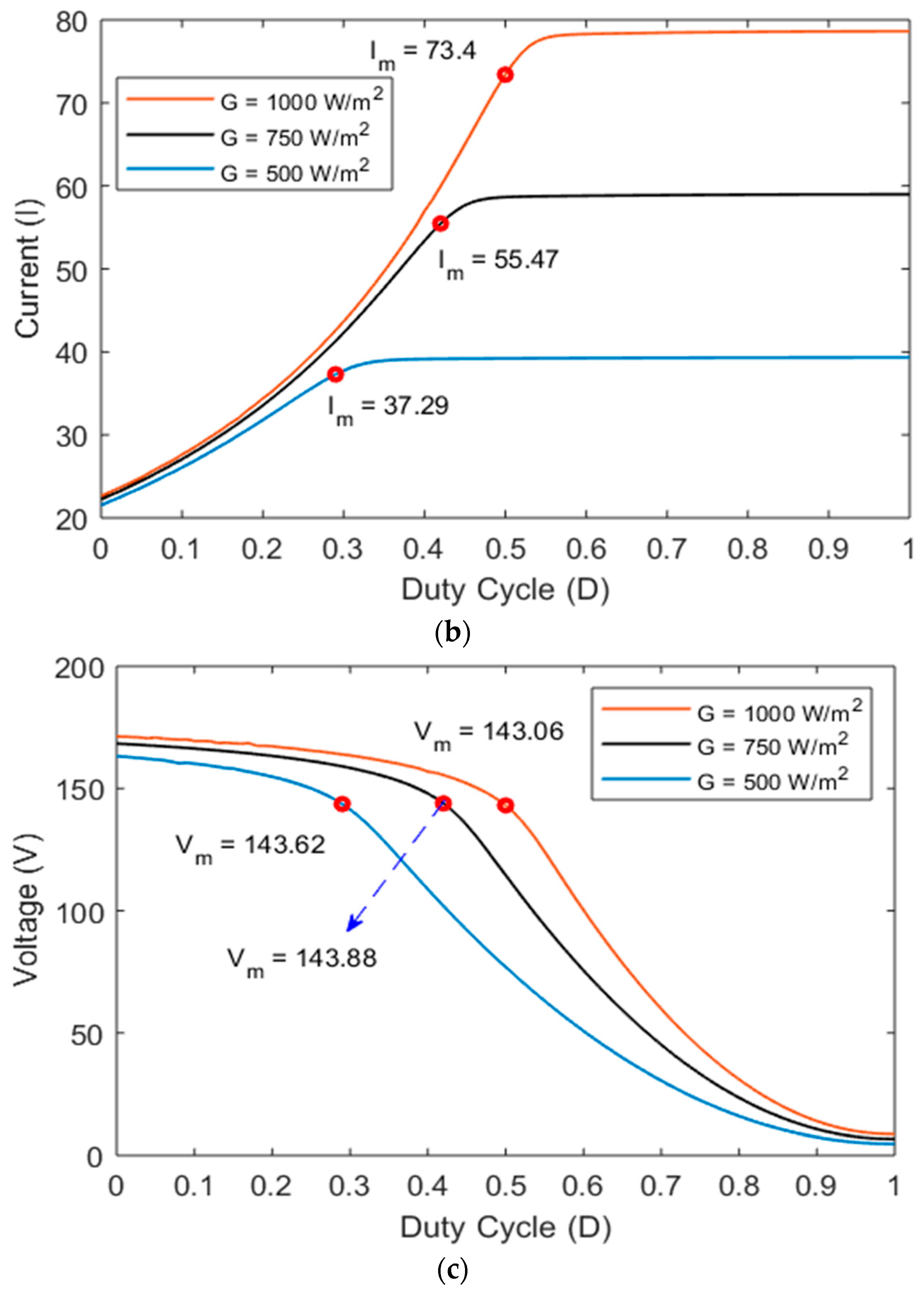
2.4. PV System Controller Design
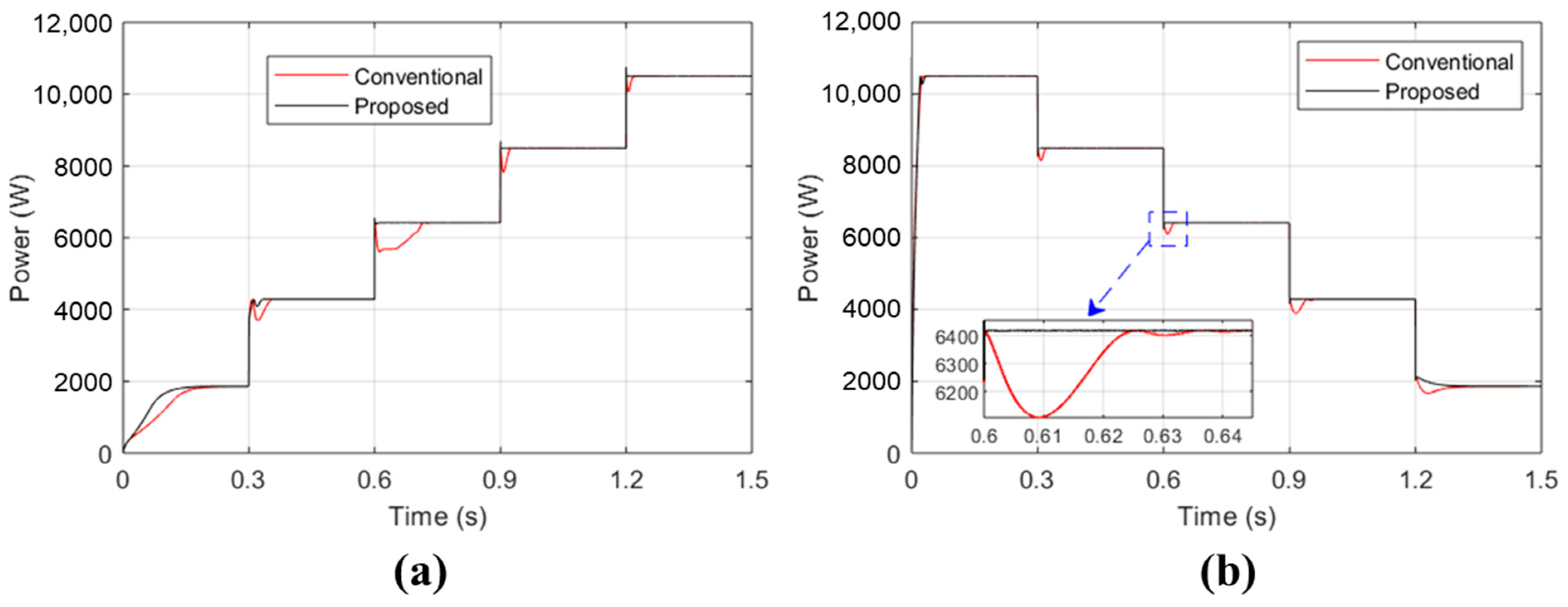
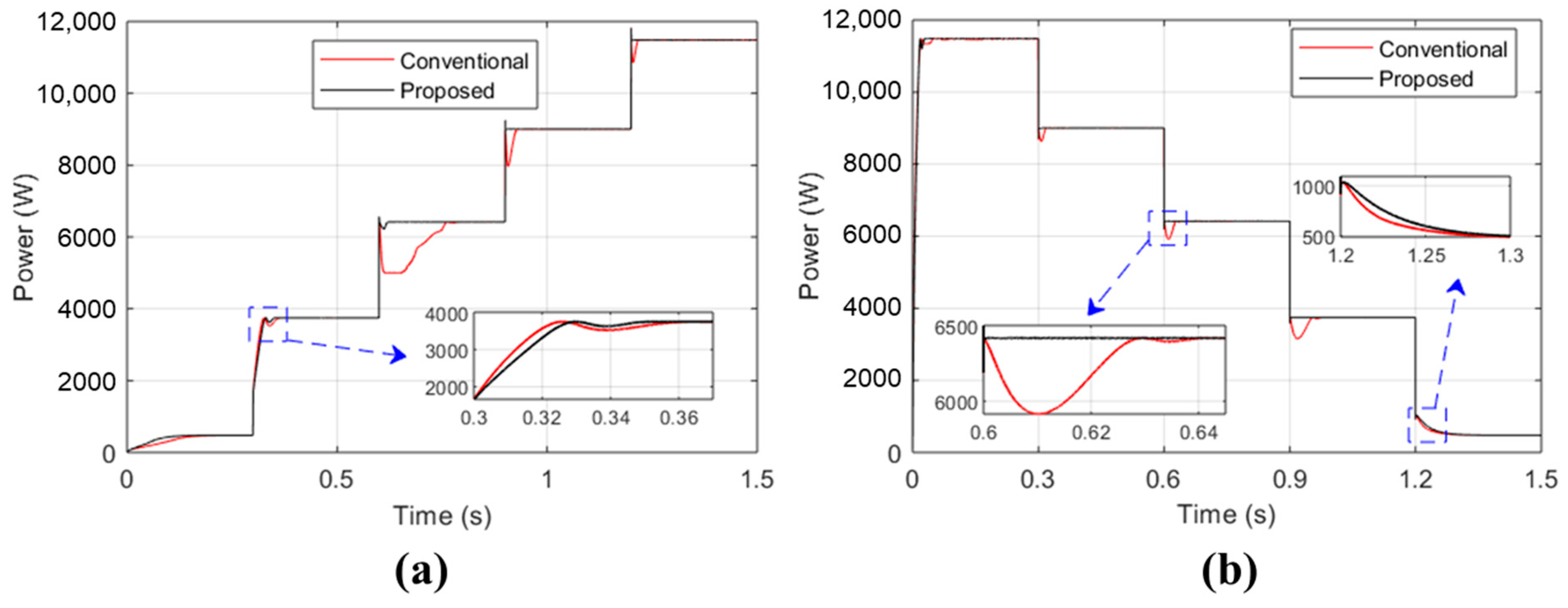
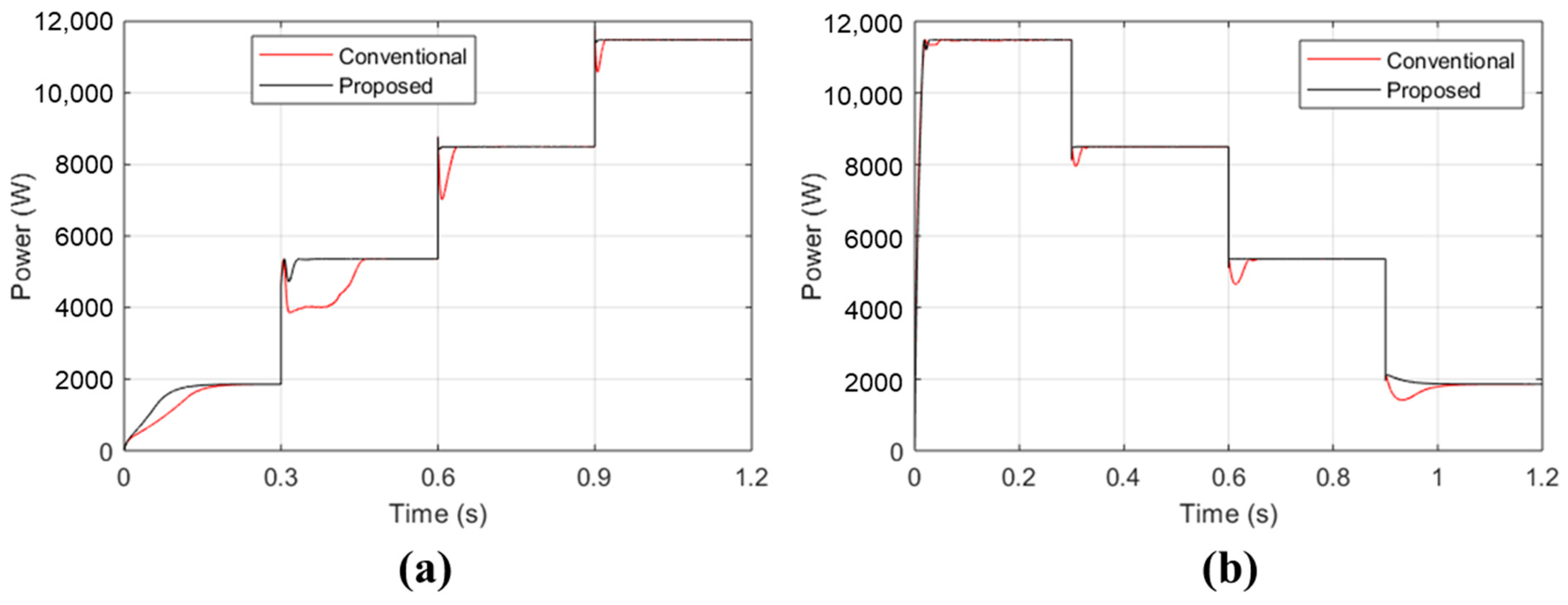
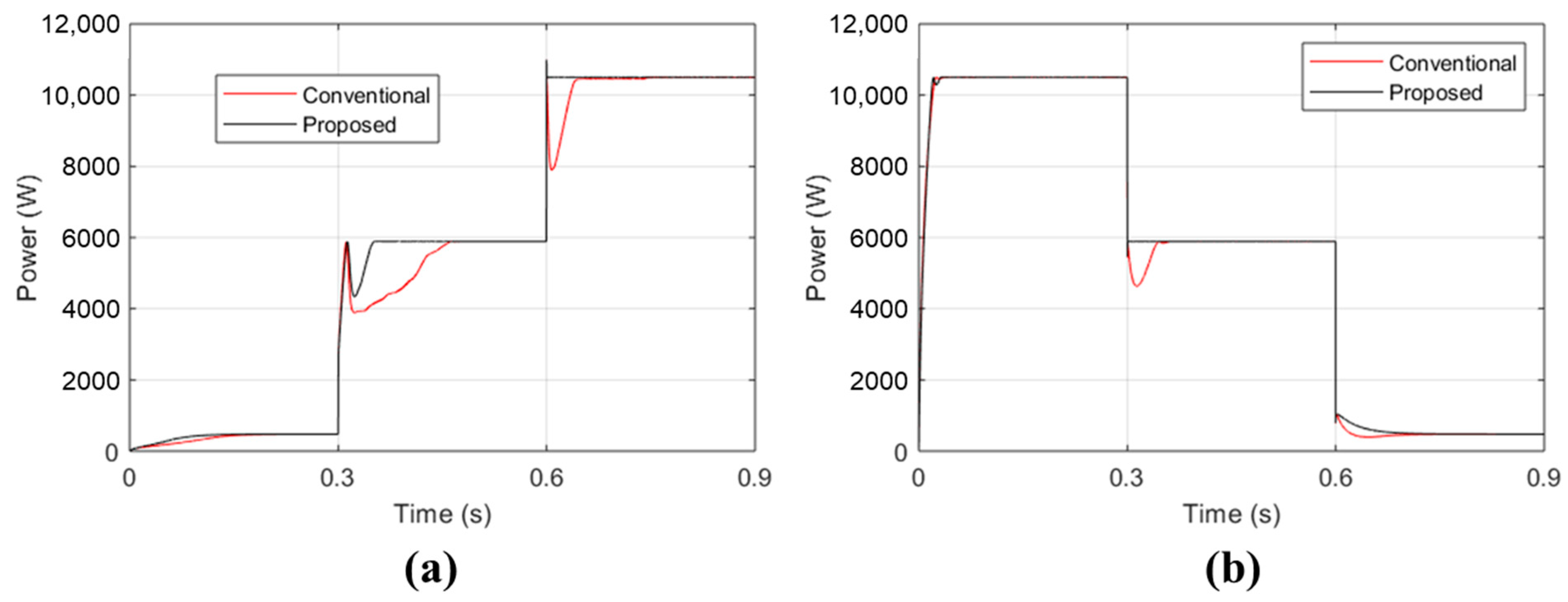
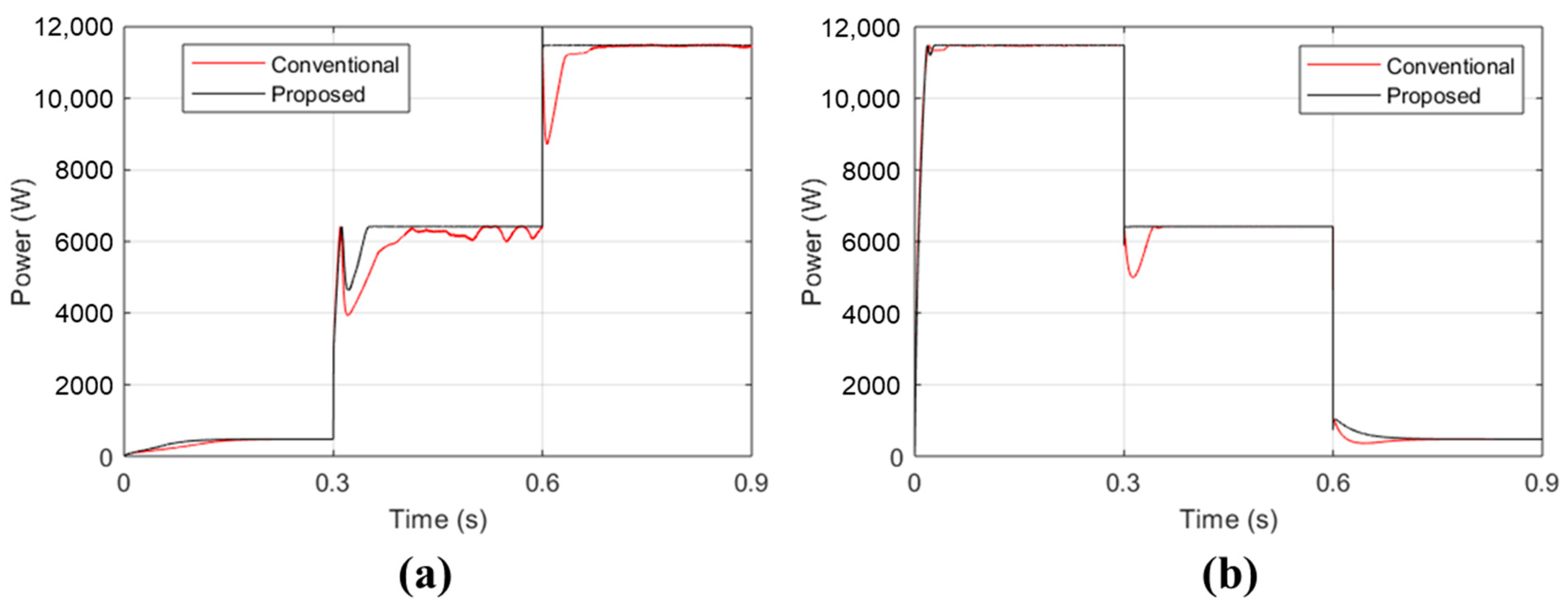
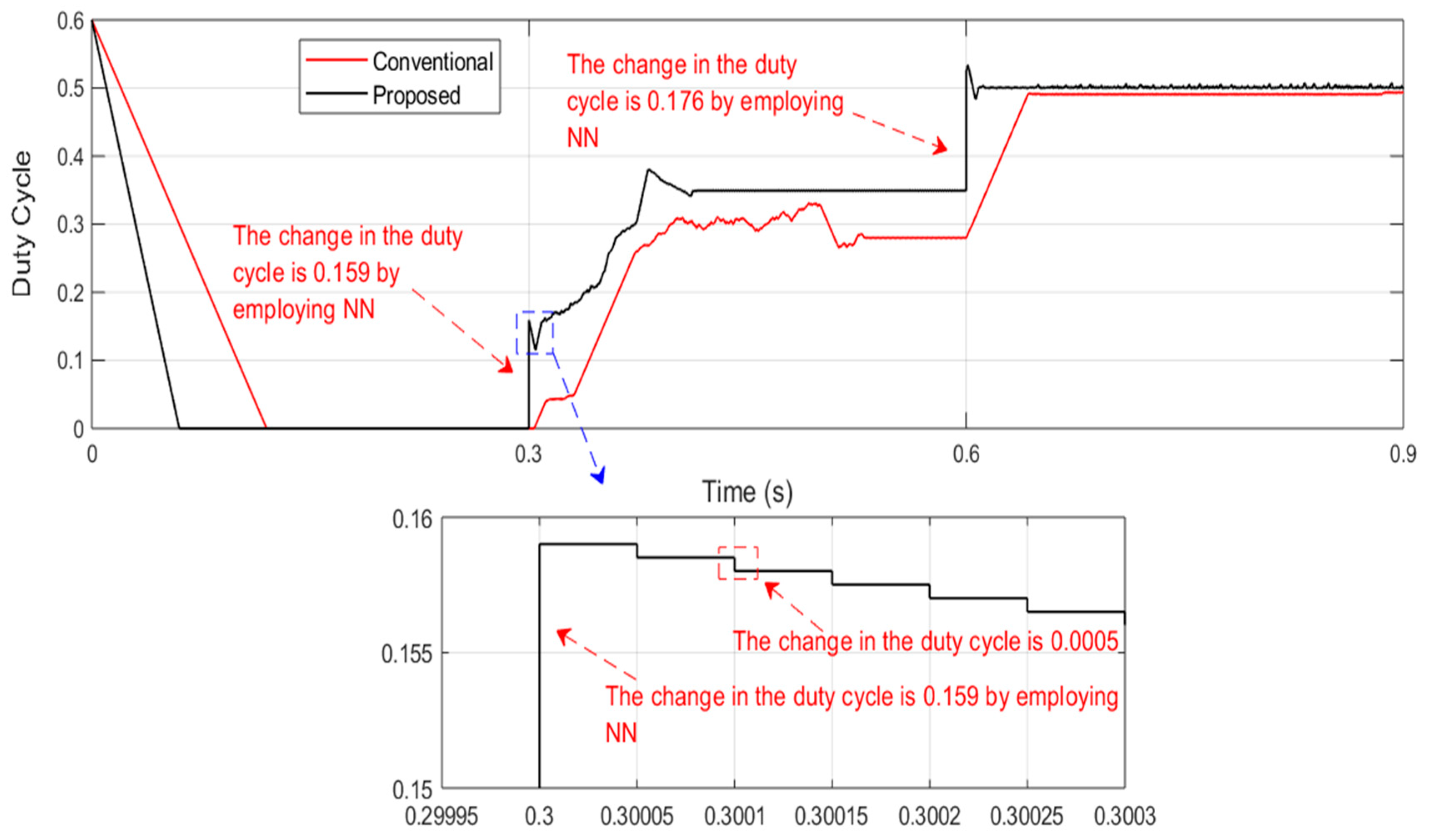
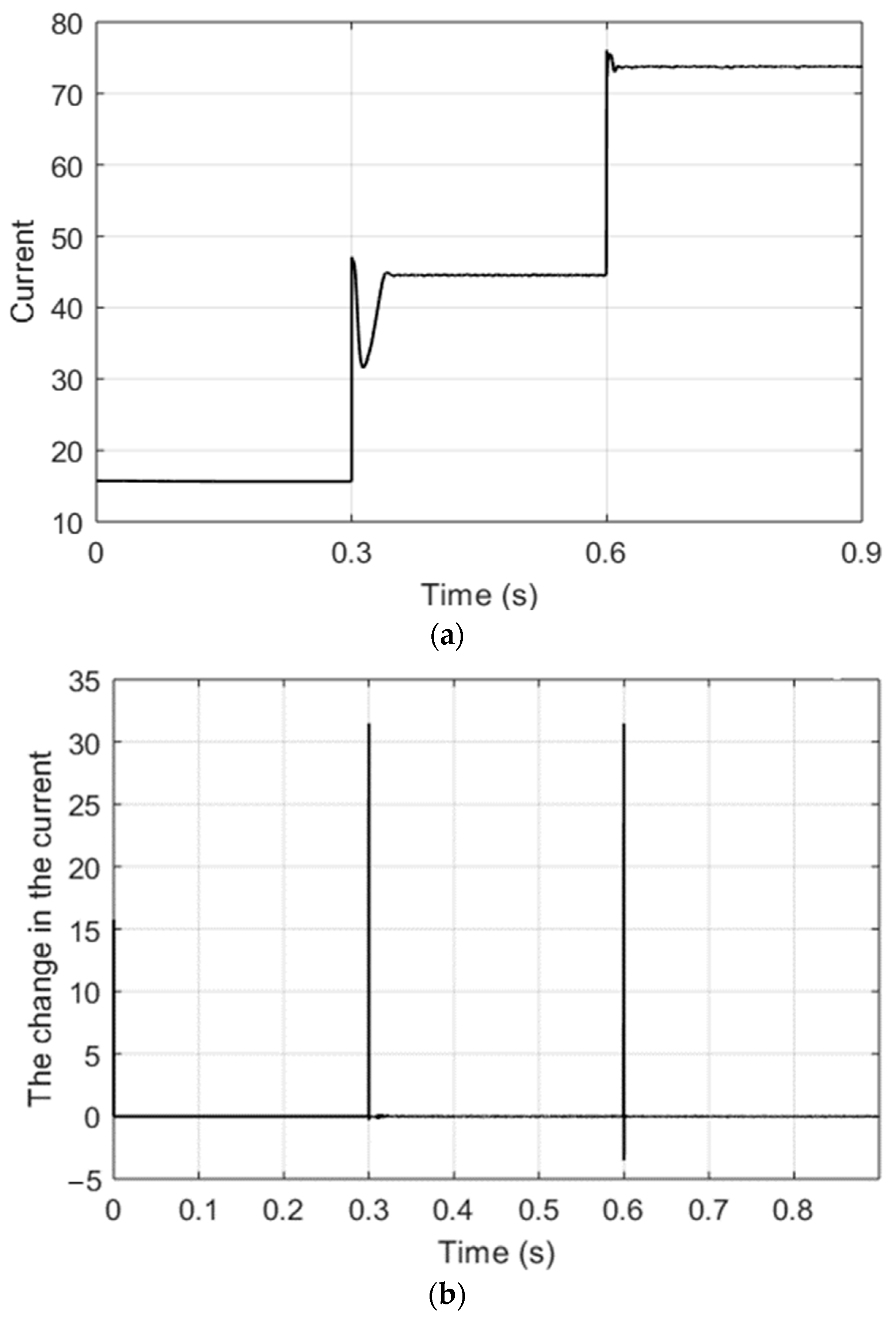
3. Result and Discussion
- Fast response. The proposed controller rapidly adjusts to variations in solar irradiance, ensuring it remains aligned with the MPP. This swift response prevents erroneous decisions regarding correct MPP tracking.
- Lower settling time. The proposed controller achieves steady-state conditions more quickly compared to the conventional P&O algorithm. The conventional P&O algorithm initially loses track of the MPP during sudden changes in solar irradiance and requires additional time to readjust back to the correct MPP track.
- Improved responsiveness. Compared to the traditional P&O controller, the proposed controller shows a faster response and better performance.
4. Future Work and Design Challenges
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ANFIS | Adaptive network-based fuzzy |
| Duty cycle | |
| The duty cycle of the maximum power point | |
| Solar radiation | |
| Genetic algorithm | |
| GMPP | Global maximum power point |
| Current | |
| Current at the maximum power point | |
| MPP | Maximum power point |
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| NN | Neural network |
| P | Power |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| P&O | Perturb and observation |
| T | Cell temperature |
| Ta | Ambient temperature |
| V | Voltage |
| Vm | Voltage at the maximum power point |
| VMPP | Voltage at the maximum power point |
References
- Ahmed, J.; Salam, Z. An improved perturb and observe (P&O) maximum power point tracking(MPPT) algorithm for higher efficiency. Appl. Energy 2015, 150, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukriz, A.; Haddadi, M.; Messalti, S. Simulation and experimental design of a new advanced variable stepsize Incremental Conductance MPPT algorithm for PV systems. ISA Trans. 2016, 62, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salama, M.; El-Mohandesa, M.-T.; Goda, M. An improved perturb-and-observe based MPPT method for PV systems undervarying irradiation levels. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killi, M.; Samanta, S. Modified Perturb and Observe MPPT Algorithm for Drift Avoidance in Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrag, A.; Messalti, S. Variable step size modified P&O MPPT algorithm using GA-based hybrid of fl ine/online PID controller. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Luo, Y.-F. A comparative study on maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic generation systems operating under fast changing environments. Sol. Energy 2015, 119, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Azar, A.T. Adaptive fractional tracking control of robotic manipulator using fixed-time method. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Azar, A.T.; Tounsi, M.; Ibraheem, I.K. Adaptive Control Design for Euler–Lagrange Systems Using Fixed-Time Fractional Integral Sliding Mode Scheme. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Azar, A.T.; Tounsi, M.; Anjum, Z. Trajectory Tracking Control of Euler–Lagrange Systems Using a Fractional Fixed-Time Method. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, H.; Jiang, L.; Xiao, W.; Du, Y.; Zhao, C. An Improved MPPT Method for PV System With Fast-Converging Speed and Zero Oscillation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 5051–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metry, M.; Shadmand, M.B.; Balog, R.S.; Abu-Rub, H. MPPT of Photovoltaic Systems Using Sensorless Current-Based Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathabadi, H. Novel fast dynamic MPPT (maximum power point tracking) technique with the capability of very high accurate power tracking. Energy 2016, 94, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Subudhi, B.; Member, S.; Ray, P.K. A New MPPT Design Using Grey Wolf Optimization Technique for Photovoltaic System Under Partial Shading Conditions. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Subudhi, B.; Member, S.; Ray, P.K. A Grey Wolf-Assisted Perturb & Observe MPPT Algorithm for a PV System. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundareswaran, K.; Vignesh, V.; Palani, S. Application of a combined particle swarm optimization and perturb and observe method for MPPT in PV systems under partial shading conditions. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Fathy, A.; Abdelaziz, A.Y. A comparison of di ff erent global MPPT techniques based on meta-heuristic algorithms for photovoltaic system subjected to partial shading conditions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.S.; Mukherjee, V. Metaheuristic based comparative MPPT methods for photovoltaic technology under partial shading condition. Energy 2020, 212, 118592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.F.; Mansoor, M.; Zhan, K.; Ling, Q. High-efficiency swarm intelligent maximum power point tracking control techniques for varying temperature and irradiance. Energy 2021, 228, 120602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenciaga, F.; Inthamoussou, F.A. A novel PV-MPPT method based on a second order sliding mode gradient observer. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 176, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihal, A.; Krim, F.; Laib, A.; Talbi, B.; Afghoul, H. An improved MPPT scheme employing adaptive integral derivative sliding mode control for photovoltaic systems under fast irradiation changes. ISA Trans. 2019, 87, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulaksız, A.A.; Akkaya, R. A genetic algorithm optimized ANN-based MPPT algorithm for a stand-alone PV system with induction motor drive. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 2366–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrouche, B.; Belhamel, M.; Guessoum, A. Artificial intelligence based P&O MPPT method for photovoltaic systems. In Revue des Energies Renouvelables ICRESD-07 Tlemcen. 2007, pp. 11–16. Available online: https://www.cder.dz/download/ICRESD07_3.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Messalti, S.; Harrag, A.G. A New Neural Networks MPPT controller for PV Systems. In Proceedings of the IREC2015 The Sixth International Renewable Energy Congress, Sousse, Tunisia, 24–26 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendib, B.; Krim, F.; Belmili, H.; Almi, M.F.; Boulouma, S. Advanced Fuzzy MPPT Controller for a stand-alone PV system. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, G. An improved step-up converter with a developed real-time fuzzy-based MPPT controller for PV-based residential applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2019, 29, e12140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, A.M.O.; Omar, F.A.; Kulaksiz, A.A. Design of a Fuzzy Logic-based MPPT Controller for a PV System Employing Design of a Fuzzy Logic-based MPPT Controller for a PV System Employing Sensorless Control of MRAS-based PMSM. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2020, 18, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.U.; Abbassi, R.; Jerbi, H.; Mehmood, K.; Tahir, M.F.; Cheema, K.M.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Ali, F.; Khan, I.A. A novel algorithm for MPPT of an isolated PV system using push pull converter with fuzzy logic controller. Energies 2020, 13, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Taghipour, M.; Gharehpetian, G.B.; Abedi, M. Optimized Fuzzy Controller for MPPT of Grid-connected PV Systems in Rapidly Changing Atmospheric Conditions. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, D.; Genc, N. Dynamic behaviour analysis of ANFIS based MPPT controller for standalone photovoltaic systems. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2020, 10, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, U.; Kircay, A.; Borekci, S. PV system fuzzy logic MPPT method and PI control as a charge controller. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.; El Telbany, M.; Zekry, A. Reconfigurable generic FPGA implementation of fuzzy logic controller for MPPT of PV systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messai, A.; Mellit, A.; Massi, P.A.; Guessoum, A.; Mekki, H. FPGA-based implementation of a fuzzy controller (MPPT) for photovoltaic module. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbes, C.; Cheikh, S.M.A.; Obeidi, T.; Zerguerras, A. Genetic algorithms optimized fuzzy logic control for the maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic system. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messai, A.; Mellit, A.; Guessoum, A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Maximum power point tracking using a GA optimized fuzzy logic controller and its FPGA implementation. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenounou, O.; Dahhou, B.; Chabour, F. Adaptive fuzzy controller based MPPT for photovoltaic systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 78, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nabulsi, A.; Dhaouadi, R. Efficiency optimization of a dsp-based standalone PV system using fuzzy logic and dual-MPPT control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.S.; Neelakantan, P.; Yoong, H.P.; Teo, K.T.K. Optimatization of fuzzy based maximum power point tracking in PV system for rapidly changing solar irradiance. Trans. Sol. Energy Plan. 2011, 2, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.C.; Peng, B.R.; Liu, Y.H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Huang, J.W. Optimization of a fuzzy-logic-control-based MPPT algorithm using the particle Swarm optimization technique. Energies 2015, 8, 5338–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Lini, K. Fuzzy logic controller-based MPPT for hybrid photo-voltaic/wind/fuel cell power system. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 6331–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, P.; Rizwan, M. Development of Fuzzy Logic based MPPT controller for PV system at varying meteorological parameters. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE International Conference Electronics, Energy, Environment, Communication, Computer, Control: (E3-C3), INDICON, New Delhi, India, 17–20 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjai, T.; Rahmani, L.; Mekhilef, S.; Gaubert, J.P. Implementation of a modified incremental conductance MPPT algorithm with direct control based on a fuzzy duty cycle change estimator using dSPACE. Sol. Energy 2014, 110, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.K.; Wei, Y.C.; Chen, B.C. A study on the fuzzy-logic-based solar power MPPT algorithms using different fuzzy input variables. Algorithms 2015, 8, 100–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, M.; Pourfarzad, H.; Nemati, M. Design of a fuzzy current-sensor less maximum power point tracking algorithm for photovoltaic systems. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2021, 14, 3724–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajdadian, S.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Optimization of fuzzy-based MPPT controller via metaheuristic techniques for stand-alone PV systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 25457–25472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, S.; Altin, N.; Sefa, I. Fuzzy logic based MPPT controller for high conversion ratio quadratic boost converter. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17748–17759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Radzi, M.A.M.; Soh, A.C.; Rahim, N.A. Development of adaptive perturb and observe-fuzzy control maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic boost dc-dc converter. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2014, 8, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, Z.Z. An asymmetrical fuzzy-logic-control-based MPPT algorithm for photovoltaic systems. Energies 2014, 7, 2177–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L. A novel beta parameter based fuzzy-logic controller for photovoltaic MPPT application. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajmi, B.N.; Ahmed, K.H.; Finney, S.J.; Williams, B.W. Fuzzy-Logic-Control Approach of a Modified Hill-Climbing Method for Maximum Power Point in Microgrid Standalone Photovoltaic System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, M.; Razaz, M.; Seifossadat, S.G.; Mortazavi, S.S. A new MPPT scheme based on a novel fuzzy approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1147–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrojerdi, F.; Taheri, S.; Cretu, A.M. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based MPPT controller for photovoltaic arrays. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 12–14 October 2016; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouachi, A.; Kamel, R.M.; Nagasaka, K. A novel multi-model neuro-fuzzy-based MPPT for three-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system. Sol. Energy 2010, 84, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essefi, R.M.; Souissi, M.; Abdallah, H.H. Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Using Neural Networks for Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems. Int. J. Mod. Nonlinear Theory Appl. 2014, 2, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assahout, S.; Elaissaoui, H.; El Ougli, A.; Tidha, B.; Zrouri, H. A Neural Network and Fuzzy Logic based MPPT Algorithm for Photovoltaic Pumping System. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2018, 9, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendib, B.; Krim, F.; Belmili, H.; Almi, M.F.; Bolouma, S. An intelligent MPPT approach based on neural-network voltage estimator and fuzzy controller, applied to a stand-alone PV system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Istanbul, Turkey, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, R. DSP implementation of a PV system with GA-MLP-NN based MPPT controller supplying BLDC motor drive. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M. Improving Efficiency of Photovoltaic System by Using Neural Network MPPT and Predictive Control of Converter. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2019, 6, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Bouselham, L.; Hajji, M.; Hajji, B.; Bouali, H. A new MPPT-based ANN for photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions. Energy Procedia 2017, 111, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A.M. Electrical Power and Energy Systems MPPT control design and performance improvements of a PV generator powered DC motor-pump system based on artificial neural networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 43, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazi, M.; Barradi, Y. The MPPT Control ofPV System by Using Neural Networks Based on Newton Raphson Method. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference (IRSEC), Ouarzazate, Morocco, 17–19 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Issaadi, S.; Issaadi, W.; Khireddine, A. New intelligent control strategy by robust neural network algorithm for real time detection of an optimized maximum power tracking control in photovoltaic systems. Energy 2019, 187, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekired, F.; Mellit, A.; Kalogirou, S.A.; Larbes, C. Intelligent maximum power point trackers for photovoltaic applications using FPGA chip: A comparative study. Sol. Energy 2014, 101, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dounis, A.I.; Kofinas, P.; Papadakis, G.; Alafodimos, C. A direct adaptive neural control for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic system. Sol. Energy 2015, 115, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.N.; Mahmoud, K.; Lehtonen, M. Promising MPPT Methods Combining Metaheuristic, Fuzzy-Logic and ANN Techniques for Grid-Connected Photovoltaic. Sensors 2021, 21, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafaruddin; Karatepe, E.; Hiyama, T. Artificial neural network-polar coordinated fuzzy controller based maximum power point tracking control under partially shaded conditions. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2009, 3, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punitha, K.; Devaraj, D.; Sakthivel, S. Artificial neural network based modified incremental conductance algorithm for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic system under partial shading conditions. Energy 2013, 62, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Tseng, C.; Hong, G.; Lin, S. A Novel MPPT Control Design for PV Modules Using Neural Network Compensator. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Hangzhou, China, 28–31 May 2012; pp. 1742–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Sheraz, M.; Abido, M.A. An Efficient MPPT controller Using Differential Evolution and Neural Network. In Proceedings of the EEE International Conference on Power and Energy, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 2–5 December 2012; pp. 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.D.; Shine, V.J.; Janamala, V. Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Optimizing MPPT Control for Standalone Solar PV System. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Mysuru, India, 27–29 November 2014; pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayat, A. Short Circuit Current Based ANN MPPT For Battery Charging. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Electronics Symposium (IES), Surabaya, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2019; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, M.N. Hybrid Maximum Power Point Tracking Using Artificial Neural Network-Incremental Conduction with Short Circuit Current of Solar Panel. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Electronics Symposium (IES), Surabaya, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2019; pp. 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zečević, Ž.; Rolevski, M. Neural Network Approach to MPPT Control and Irradiance Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, H.A. High performance PV system based on artificial neural network MPPT with PI controller for direct current water pump applications. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2019, 10, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, A.; Sharadga, H.; Hajimirza, S. Design of optimal power point tracking controller using forecasted photovoltaic power and demand. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 1820–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Fuzzy Logic | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Inputs | Output | Notes |
| [24,25,26,27] | |||
| [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35] | In [29], the fuzzy is ANFIS-based. In [33] and [34], fuzzy logic is optimized by using GA. In [35] the controller is adaptive. | ||
| [36] | |||
| [37] | (Size of perturbed voltage) | ||
| [38] | , | ∆V (Size of perturbed voltage) | Particle swarm optimization algorithm optimized fuzzy logic. |
| [39] | |||
| [40] | |||
| [41] | |||
| [42] | ∆E= E(K) − E (K − 1) | ||
| [43] | Where: | current sensorless | |
| [44,45,46,47] | ) variations | , or changes in the reference voltage ∆V | |
| [48] | C is a function of cell number, cell temperature, and PV module type | ||
| [49] | ) | ||
| [50] | |||
| [51] | ANFIS-based | ||
| Neural Network | |||
| Reference | Inputs | Output | Notes |
| [23] | 1 or −1 (increase or decrease of the duty cycle) | ||
| [21,52,53,54] | In [21], NN configuration is optimized using GA. In [52], three trained NNs. NN is selected based on the weather conditions (cloudy, normal, sunny, etc.) | ||
| [55] | Fuzzy is used to find . | ||
| [56] | |||
| [57] | |||
| [58] | under partial shading conditions | ||
| [59] | |||
| [60,61] | |||
| [62,63,64] | | In [62], a comparison between NN, ANFIS, Fuzzy, and Fuzzy optimized by use of GA was conducted. | |
| [65] | are the average of incoming irradiance levels on a group of modules | under partially shaded conditions | |
| [66] | |||
| [67] | The perturb size for PI controller | ||
| [68] | |||
| [69] | |||
| [70,71] | Short-circuit current | ||
| [72] | is estimated using different NN with as inputs. | ||
| [73] | |||
| Parameter | Parameter Information |
|---|---|
| Type | feed-forward backpropagation |
| Number of hidden layers | 2 |
| Number of neurons in the first and second layer | 5, 4 |
| The inputs | ) |
| The output | ) |
| Case | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 75 | 5.89 | 0 | 409 − 75 = 334 | = 24.49 | = 0.2105 |
| 2 | 409 | 30.38 | 0.2105 | 619 − 409 = 210 | = 14.06 | = 0.124 |
| 3 | 619 | 44.44 | 0.3345 | - | - | - |
| Parameter | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Array | |
| Series-connected modules per string | 5 |
| Parallel strings | 10 |
| Module Data | |
| Module | Aleo solar A18.210 |
| Maximum power | 210.16 W |
| Open circuit voltage VOC | 35.7 V |
| Voltage at the maximum power point Vmp | 28.4 V |
| Current at the maximum power point Imp | 7.4 A |
| Short-circuit current ISC | 7.85 A |
| Number of cells per module | 60 |
| Temperature coefficient of Voc | −0.34 |
| Temperature coefficient of Isc | 0.041006 |
| Boost Converter Parameters | |
| L | 400 µH |
| C | 50 µF |
| PMW adjusting frequency | 10 kHz |
| The change in duty cycle ΔD | 0.0005 |
| The maximum duty cycle Dmax | 0.65 |
| The minimum duty cycle Dmin | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dawahdeh, A.; Sharadga, H.; Kumar, S. Novel MPPT Controller Augmented with Neural Network for Use with Photovoltaic Systems Experiencing Rapid Solar Radiation Changes. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031021
Dawahdeh A, Sharadga H, Kumar S. Novel MPPT Controller Augmented with Neural Network for Use with Photovoltaic Systems Experiencing Rapid Solar Radiation Changes. Sustainability. 2024; 16(3):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031021
Chicago/Turabian StyleDawahdeh, Ahmad, Hussein Sharadga, and Sunil Kumar. 2024. "Novel MPPT Controller Augmented with Neural Network for Use with Photovoltaic Systems Experiencing Rapid Solar Radiation Changes" Sustainability 16, no. 3: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031021
APA StyleDawahdeh, A., Sharadga, H., & Kumar, S. (2024). Novel MPPT Controller Augmented with Neural Network for Use with Photovoltaic Systems Experiencing Rapid Solar Radiation Changes. Sustainability, 16(3), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16031021






