Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Impacts in Greek Viticultural Management Systems: An Integrated Life Cycle and Data Envelopment Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
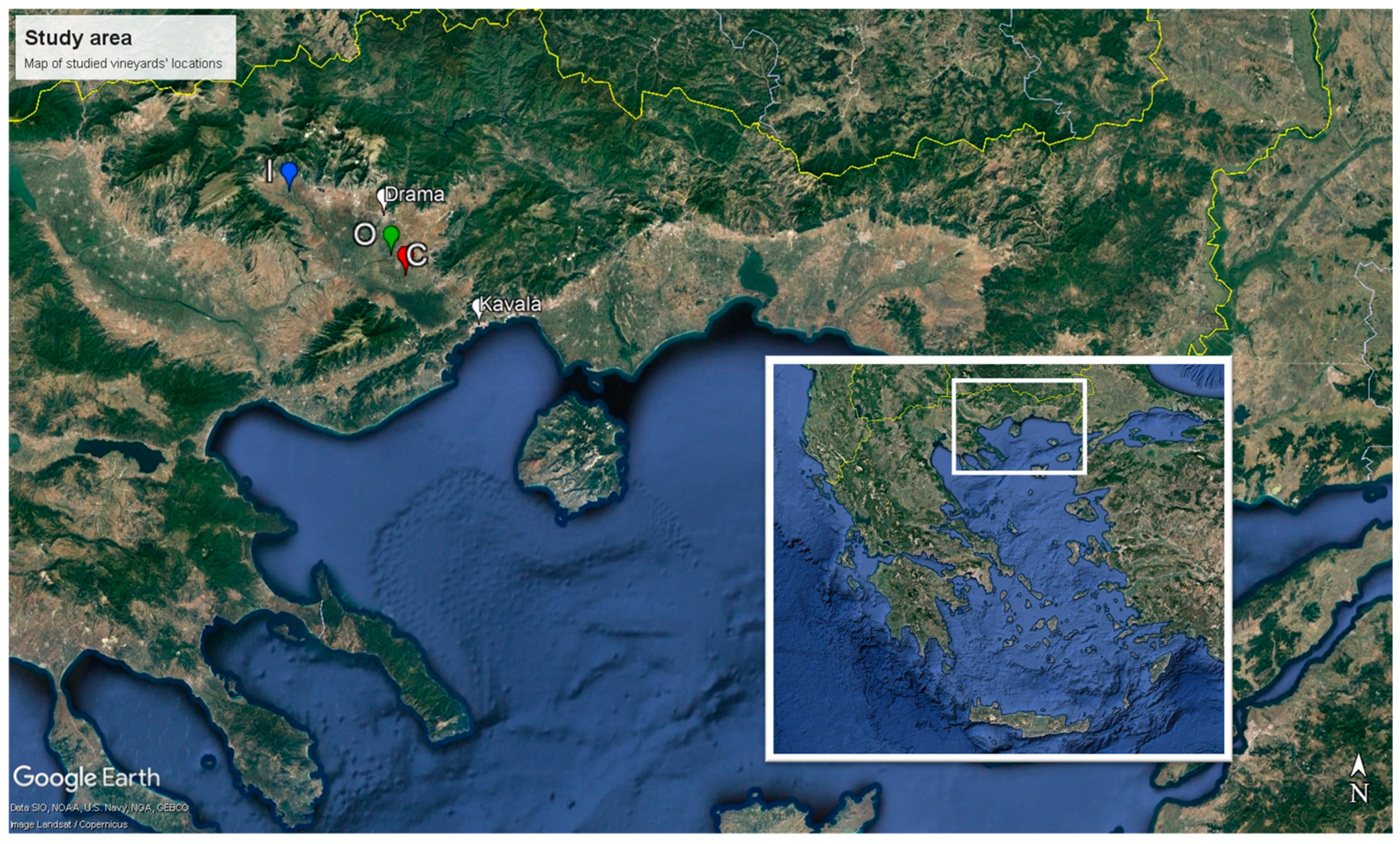
2.1. Case Study Area and Description of Management Systems
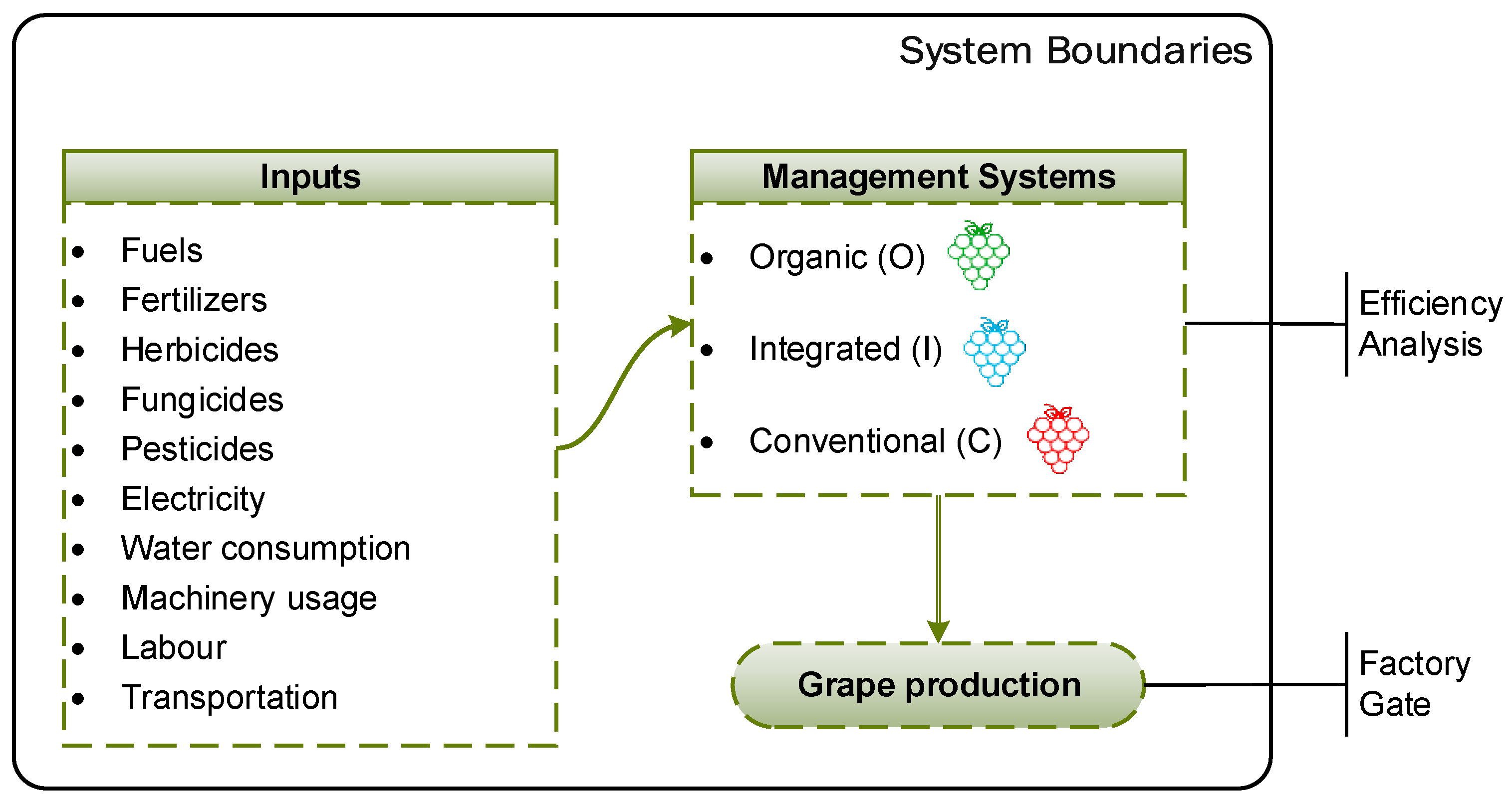
2.2. System Boundaries
2.3. Comprehensive Inventory Analysis
2.4. Economic and Environmental Assessment
2.5. Data Envelopment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Resource Inputs and Yield of the Selected Management Systems
3.2. Energy Demand and GHG Emissions
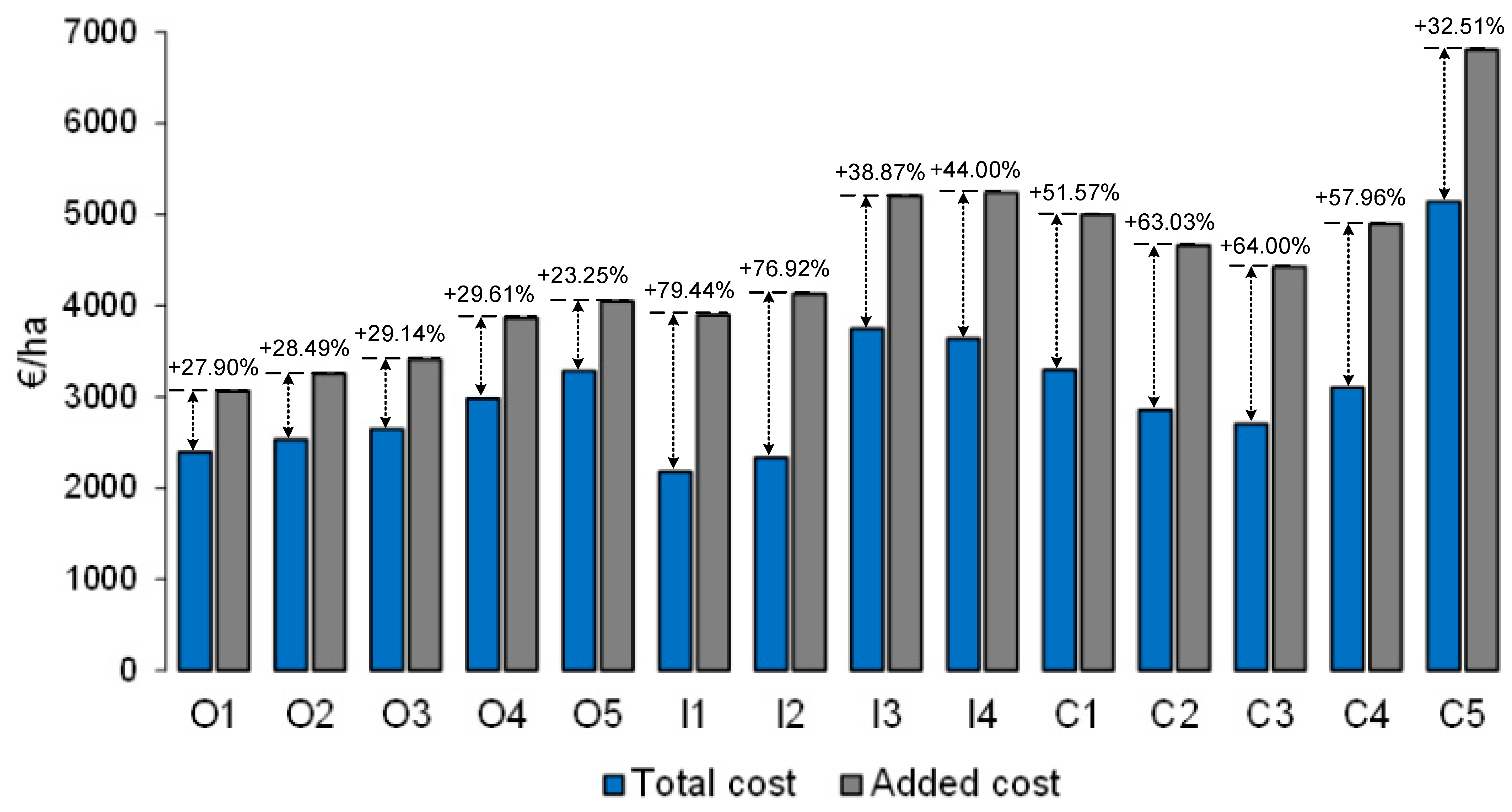
3.3. Economic Analysis and Shadow Prices
3.4. Efficiency Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karafolas, S. Wine Roads in Greece: A Cooperation for the Development of Local Tourism in Rural Areas. J. Rural Coop. 2007, 35, 71–90. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachos, V.A. A Macroeconomic Estimation of Wine Production in Greece. Wine Econ. Policy 2017, 6, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufos, G.C.; Mavromatis, T.; Koundouras, S.; Fyllas, N.M.; Theocharis, S.; Jones, G.V. Greek Wine Quality Assessment and Relationships with Climate: Trends, Future Projections and Uncertainties. Water 2022, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebaki, M.; Ioannides, D. Threats and Obstacles to Resilience: Insights from Greece’s Wine Tourism. In Tourism, Resilience, and Sustainability: Adapting to Social, Political and Economic Change; Routledge: Lnodon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiadis, F.; Alebaki, M. Mapping the Greek Wine Supply Chain: A Proposed Research Framework. Foods 2021, 10, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, S.; Detang-Dessendre, C. Reforming the Common Agricultural Policy (2023–2027): Multidisciplinary Views. Rev. Agric. Food Environ. Stud. 2023, 104, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Not Just Farmers’ Protests. Nat. Food 2024, 5, 93. [CrossRef]
- Ducman, A.A.; Diaconita, V.; Simonca, I.; Belciu, A.; Corbea, A.M.I. Government Oversight and Economic Impacts: Sustainability in the Vineyard and the Evolution of Wine Regulations, Trade and Production. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, J.; Collins, C.; Frisch, M.; Kauer, R. Organic and Biodynamic Viticulture Affect Biodiversity and Properties of Vine and Wine: A Systematic Quantitative Review. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2019, 70, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, G.; Athmann, M.; Fritz, J.; Kauer, R.; Stoll, M.; Schultz, H.R. Conversion to Organic and Biodynamic Viticultural Practices: Impact on Soil, Grapevine Development and Grape Quality. Oeno One 2019, 53, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Verdugo-Vásquez, N.; Díaz-Gálvez, I. Influence of Type of Management and Climatic Conditions on Productive Behavior, Oenological Potential, and Soil Characteristics of a ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ Vineyard. Agronomy 2019, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, C.; Wossink, A.; Giesen, G.; Vazzana, C.; Huirne, R. Evaluation of Sustainability of Organic, Integrated and Conventional Farming Systems: A Farm and Field-Scale Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 95, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, J.; Frisch, M.; Tittmann, S.; Stoll, M.; Kauer, R. Growth, Yield and Fruit Quality of Grapevines under Organic and Biodynamic Management. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ponti, T.; Rijk, B.; Van Ittersum, M.K. The Crop Yield Gap between Organic and Conventional Agriculture. Agric. Syst. 2012, 108, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschiero, M.; De Laurentiis, V.; Caldeira, C.; Sala, S. Comparison of Organic and Conventional Cropping Systems: A Systematic Review of Life Cycle Assessment Studies. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 102, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, H.S.; Kakar, R.; Kumar, N. Seema Impact of Organic and Conventional Farming Practices on Soil Quality: A Global Review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shennan, C.; Krupnik, T.J.; Baird, G.; Cohen, H.; Forbush, K.; Lovell, R.J.; Olimpi, E.M. Organic and Conventional Agriculture: A Useful Framing? Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2017, 42, 317–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Cruz, V.Y.V.; Tantriani; Cheng, W.; Tawaraya, K. Yield Gap between Organic and Conventional Farming Systems across Climate Types and Sub-Types: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Syst. 2023, 211, 103732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieno, I.; Simonetto, A.; Facciano, L.; Tonni, M.; Donna, P.; Valenti, L.; Gilioli, G. Comparing the Carbon Footprint of Conventional and Organic Vineyards in Northern Italy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merot, A.; Smits, N. Does Conversion to Organic Farming Impact Vineyards Yield? A Diachronic Study in Southeastern France. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the Yields of Organic and Conventional Agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.; Athmann, M.; Meissner, G.; Kauer, R.; Köpke, U. Quality Characterisation via Image Forming Methods Differentiates Grape Juice Produced from Integrated, Organic or Biodynamic Vineyards in the First Year after Conversion. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2017, 33, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.I.; Molari, G.; Seddaiu, G.; Toscano, A.; Bombino, G.; Ledda, L.; Milani, M.; Vittuari, M. Multidisciplinary and Innovative Methodologies for Sustainable Management in Agricultural Systems. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 1571–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Guidelines for the Measurement of Productivity and Efficiency in Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kyrgiakos, L.S.; Kleftodimos, G.; Vlontzos, G.; Pardalos, P.M. A Systematic Literature Review of Data Envelopment Analysis Implementation in Agriculture under the Prism of Sustainability. Oper. Res. 2023, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, A.; Olfati, M.; Pant, M.; Snasel, V. A Review on the 40 Years of Existence of Data Envelopment Analysis Models: Historic Development and Current Trends. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 5397–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gušavac, B.A.; Martić, M.; Popović, M.; Savić, G. Agricultural Route Efficiencies, Based on Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA). Acta Polytech. Hung. 2023, 20, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, D.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Further Potentials in the Joint Implementation of Life Cycle Assessment and Data Envelopment Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5265–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaert, B.; Goossens, Y.; Geeraerd, A.; Mathijs, E.; Vranken, L. Calculating Environmental Cost Indicators of Apple Farm Practices Indicates Large Differences between Growers. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2017, 15, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bravo, P.; Chambers, V.E.; Noguera-Artiaga, L.; Sendra, E.; Chambers IV, E.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Consumer Understanding of Sustainability Concept in Agricultural Products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 89, 104136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Correia, T.; Ferraz-De-oliveira, I.; Helena Guimarães, M.; Sales-Baptista, E.; Pinto-Cruz, C.; Godinho, C.; Vieira Santos, R. Result-Based Payments as a Tool to Preserve the High Nature Value of Complex Silvo-Pastoral Systems: Progress toward Farm-Based Indicators. Ecol. Soc. 2022, 27, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, S.; Bijleveld, M.; de Graaff, L.; Schep, E.; Schroten, A.; Vergeer, R.; Ahdour, S. Environmental Prices Handbook EU28 Version—Methods and Numbers for Valuation of Environmental Impact; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn, S.M.; Korteland, M.H.; Markowska, A.Z.; Davidson, M.D.; De Jong, F.L.; Bles, M.; Sevenster, M.N. Shadow Prices Handbook: Valuation and Weighting of Emissions and Environmental Impacts; CE Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Karampatea, A.; Mamalis, S.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Skendi, A.; Kamenidou, I. Wine and Gastronomic Tourism in the Drama Region. Tour. Hosp. 2024, 5, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarou, C.; Tsartas, P.; Sarantakou, E. E-Storytelling and Wine Tourism Branding: Insights from the “Wine Roads of Northern Greece”. In Wine Tourism Destination Management and Marketing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Willer, H.; Organic Viticulture in Europe and the European Union. In EU Rules for Organic Wine Production. Background, Evaluation and Further Development. Available online: https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/25258/7/ifoameu_reg_wine_dossier_201307.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Romero, P.; Navarro, J.M.; Ordaz, P.B. Towards a Sustainable Viticulture: The Combination of Deficit Irrigation Strategies and Agroecological Practices in Mediterranean Vineyards. A Review and Update. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowder, D.W.; Reganold, J.P. Financial Competitiveness of Organic Agriculture on a Global Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7611–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.G. Viticultural and Vineyard Management Practices and Their Effects on Grape and Wine Quality. In Managing Wine Quality: Volume One: Viticulture and Wine Quality; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2021; ISBN 9780081020678. [Google Scholar]
- Brunori, E.; Farina, R.; Biasi, R. Sustainable Viticulture: The Carbon-Sink Function of the Vineyard Agro-Ecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Wu, W. Soil and Crop Management Strategies to Ensure Higher Crop Productivity within Sustainable Environments. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziolas, E.; Karapatzak, E.; Kalathas, I.; Lytridis, C.; Mamalis, S.; Koundouras, S.; Pachidis, T.; Kaburlasos, V.G. Comparative Assessment of Environmental/Energy Performance under Conventional Labor and Collaborative Robot Scenarios in Greek Viticulture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziolas, E.; Karapatzak, E.; Kalathas, I.; Karampatea, A.; Grigoropoulos, A.; Bajoub, A.; Pachidis, T.; Kaburlasos, V.G. Assessing the Economic Performance of Multipurpose Collaborative Robots toward Skillful and Sustainable Viticultural Practices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biograce II. Harmonised Greenhouse Gas Calculations for Electricity, Heating and Cooling from Biomass, Calculation Rules 4a. 2021. Available online: https://biograce.net/biograce2/content/ghgcalculationtool_electricityheatingcooling/previousversions (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Cech, R.; Leisch, F.; Zaller, J.G. Pesticide Use and Associated Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Sugar Beet, Apples, and Viticulture in Austria from 2000 to 2019. Agriculture 2022, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsas, A.M.; Mamolos, A.P.; Tsatsarelis, C.A.; Nanos, G.D.; Kalburtji, K.L. Energy Budget in Organic and Conventional Olive Groves. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 122, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavargiris, S.E.; Mamolos, A.P.; Tsatsarelis, C.A.; Nikolaidou, A.E.; Kalburtji, K.L. Energy Resources’ Utilization in Organic and Conventional Vineyards: Energy Flow, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Biofuel Production. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrysh, V.; Kalinichenko, A.; Brzozowska, A.; Stebila, J. Life Cycle Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Agricultural Residue Feedstock for Bioenergy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Weekly Oil Bulletin—Price Developments—By Year (1994–2005) (for All EU Countries). Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/data-and-analysis/weekly-oil-bulletin_en (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Eurostat Electricity Price Statistics—Electricity Prices for Non-Household Consumers. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Electricity_price_statistics#Electricity_prices_for_non-household_consumers (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Soni, P.; Sinha, R.; Perret, S.R. Energy Use and Efficiency in Selected Rice-Based Cropping Systems of the Middle-Indo Gangetic Plains in India. Energy Rep. 2018, 4, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janulevičius, A.; Juostas, A.; Čipliene, A. Estimation of Carbon-Oxide Emissions of Tractors during Operation and Correlation with the Not-to-Exceed Zone. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 147, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.G.; Halberg, N.; Oudshoorn, F.W.; Petersen, B.M.; Dalgaard, R. Energy Inputs and GHG Emissions of Tillage Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 120, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantoam, E.J.; Romanelli, T.L.; Gimenez, L.M. Energy Demand and Greenhouse Gases Emissions in the Life Cycle of Tractors. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 151, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taxidis, E.T.; Menexes, G.C.; Mamolos, A.P.; Tsatsarelis, C.A.; Anagnostopoulos, C.D.; Kalburtji, K.L. Comparing Organic and Conventional Olive Groves Relative to Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Associated with the Cultivation of Two Varieties. Appl. Energy 2015, 149, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemtos, T.A.; Cavalaris, C.; Karamoutis, C.; Tagarakis, A.; Fountas, S. Energy Analysis of Three Energy Crops in Greece. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2013, 15, 52–66. [Google Scholar]
- Smart Freight Centre. Cefic Calculating GHG Transport and Logistics Emissions for the European Chemical Industry. Available online: https://cefic.org/app/uploads/2021/09/Calculating-GHG-transport-and-logistics-emissions-for-the-European-Chemical-Industry-Guidance.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Lynch, J.; Cain, M.; Pierrehumbert, R.; Allen, M. Demonstrating GWP: A Means of Reporting Warming-Equivalent Emissions That Captures the Contrasting Impacts of Short- A Nd Long-Lived Climate Pollutants. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 044023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute GHG Protocol Agricultural Guidance Interpreting the Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard for the Agricultural Sector. Available online: https://ghgprotocol.org/sites/default/files/standards/GHG%20Protocol%20Agricultural%20Guidance%20%28April%2026%29_0.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Strano, A.; Irene De Luca, A.; Falcone, G.; Iofrida, N.; Stillitano, T.; Gulisano, G. Economic and Environmental Sustainability Assessment of Wine Grape Production Scenarios in Southern Italy. Agric. Sci. 2013, 4, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, G.; De Luca, A.I.; Stillitano, T.; Strano, A.; Romeo, G.; Gulisano, G. Assessment of Environmental and Economic Impacts of Vine-Growing Combining Life Cycle Assessment, Life Cycle Costing and Multicriterial Analysis. Sustainability 2016, 8, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselli, L.; Casieri, A.; de Gennaro, B.C.; Sardaro, R.; Russo, G. Environmental and Economic Sustainability of Table Grape Production in Italy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Statistics Office CPM02—Consumer Price Index. Available online: https://data.cso.ie/ (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- European Union. The Polluter Pays Principle: Inconsistent Application across EU Environmental Policies and Actions; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/lists/ecadocuments/sr21_12/sr_polluter_pays_principle_en.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- ABC ABC Software Documentations. Available online: http://abcsoftware.org/software.aspx (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the Efficiency of Decision Making Units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Lu, L.Y.Y.; Lu, W.M.; Lin, B.J.Y. A Survey of DEA Applications. Omega 2013, 41, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.W.; Seiford, L.M.; Tone, K. Data Envelopment Analysis: A Comprehensive Text with Models, Applications, References and DEA-Solver Software, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; ISBN 0387452818. [Google Scholar]
- Coelli, T.J.; Prasada Rao, D.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Battese, G.E. An Introduction to Efficiency and Productivity Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; ISBN 0387242651. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi-Avval, S.H.; Rafiee, S.; Mohammadi, A. Optimization of Energy Consumption and Input Costs for Apple Production in Iran Using Data Envelopment Analysis. Energy 2011, 36, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Streimikiene, D.; Jusoh, A.; Khoshnoudi, M. A Comprehensive Review of Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) Approach in Energy Efficiency. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 1298–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banker, R.D.; Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W. Some Models for Estimating Technical and Scale Inefficiencies in Data Envelopment Analysis. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshroo, A.; Mulwa, R.; Emrouznejad, A.; Arabi, B. A Non-Parametric Data Envelopment Analysis Approach for Improving Energy Efficiency of Grape Production. Energy 2013, 63, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzębowski, S. Efficiency and Returns to Scale—A Concept of Using Deterministic Approach. Quant. Methods Econ. 2014, 15, 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R 2020.
- Rouault, A.; Beauchet, S.; Renaud-Gentie, C.; Jourjon, F. Life Cycle Assessment of Viticultural Technical Management Routes (TMRs): Comparison between an Organic and an Integrated Management Route. J. Int. Des Sci. De La Vigne Du Vin 2016, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxouzi, E.; Papanagiotou, E. Comparative Analysis of Organic and Conventional Farmers and Their Farming Systems. Where Does the Difference Lie? Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 16, 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- White, G.B. The Economics of Converting Conventionally Managed Vineyards to Organic Management Practices. In Proceedings of the Acta Horticulturae; International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), Leuven, Belgium, 1 August 1996; pp. 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Duan, C.B.; Jin, B.; Ali, A.S.; Han, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.Z.; Zhang, W.H.; Gu, Y.C. Recent Advances in the Natural Products-Based Lead Discovery for New Agrochemicals. Adv. Agrochem 2023, 2, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobey, J.A.; Smets, H. The Polluter-Pays Principle in the Context of Agriculture and the Environment. World Econ. 1996, 19, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognar, J.; Lam, L.; Forestier, O.; Finesso, A.; Bolscher, H.; Springer, K.; Nesbit, M.; Nadeu, E.; Hiller, N.; van Dijk, R.; et al. Pricing Agricultural Emissions and Rewarding Climate Action in the Agri-Food Value Chain; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Union Special Report 16/2021: Common Agricultural Policy and Climate: Half of EU Climate Spending but Farm Emissions Are Not Decreasing. Available online: https://www.eca.europa.eu/Lists/ECADocuments/SR21_16/SR_CAP-and-Climate_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2024).
- Nadoveza Jelić, O.; Šimurina, J. Evaluating Sectoral Effects of Agricultural Nitrogen Pollution Reduction Policy in Croatia within a CGE Framework. Agric. Food Econ. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauerhofer, V.; Hubacek, K.; Coleby, A. From Polluter Pays to Provider Gets: Distribution of Rights and Costs under Payments for Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandya, A. Accounting for the Hidden Costs of Agrifood Systems in Data-Scarce Contexts; No. 23-12; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; ISBN 2521-1838. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Calculation, Elasticity and Regional Differences of Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Shadow Prices. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Investment Bank. EIB Group Climate Bank Roadmap 2021–2025; European Investment Bank: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Casson, A.; Ortuani, B.; Giovenzana, V.; Brancadoro, L.; Corsi, S.; Gharsallah, O.; Guidetti, R.; Facchi, A. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Assess Environmental and Economic Impact of Conventional and Innovative Vineyards Management Systems in Northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niles, M.T.; Garrett, R.D.; Walsh, D. Ecological and Economic Benefits of Integrating Sheep into Viticulture Production. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirezaee, M.R.; Howland, M.; Van De Panne, C. Sampling Size and Efficiency Bias in Data Envelopment Analysis. J. Appl. Math. Decis. Sci. 1998, 2, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zervopoulos, P. Dealing with Small Samples and Dimensionality Issues in Data Envelopment Analysis. IDEAS Work. Pap. Ser. RePEc 2012, 39226. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/39226/ (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Sokol, O.; Frýd, L. DEA Efficiency in Agriculture: Measurement Unit Issues. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 86, 101497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, R.G.; Allen, R.; Camanho, A.S.; Podinovski, V.V.; Sarrico, C.S.; Shale, E.A. Pitfalls and Protocols in DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 132, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, E.; Rossi, E.S.; Zabala, J.Á.; Fosci, L.; Sorrentino, A. Are Citizens Willing to Pay for the Ecosystem Services Supported by Common Agricultural Policy? A Non-Market Valuation by Choice Experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Inputs | Unit | Energy Content | Unit | GHGs | Unit | Cost | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ν | MJ/kg | 48.99 | gCO2eq/kg | 4524.41 | EUR/kg | 0.44–3.5 | [44] |
| Ρ | MJ/kg | 15.23 | gCO2eq/kg | 541.67 | EUR/kg | 0.49–2.5 | [44] |
| Κ | MJ/kg | 9.68 | gCO2eq/kg | 416.67 | EUR/kg | 0.33–3.5 | [44] |
| Pesticides | MJ/kg | 268.4 | gCO2eq/kg | 12,003.33 | EUR/kg | 10 | [44] |
| Fungicides | MJ/kg | 99.00 | gCO2eq/kg | 3900.00 | EUR/kg | 3.86–117.4 | [45,46] |
| Herbicides | MJ/kg | 418.00 | gCO2eq/kg | 9100.00 | EUR/kg | 3.47–8 | [45,47] |
| Lubricants | MJ/kg | 53.28 | gCO2eq/kg | 947.00 | EUR/L | 6 | [44] |
| Diesel | MJ/kg | 56.80 | gCO2eq/MJ | 95.10 | EUR/L | 1.602 | [44,48,49] |
| Petrol | MJ/kg | 60.20 | gCO2eq/MJ | 93.30 | EUR/L | 1.852 | [44,48,49] |
| Electricity | MJ/MJ | 2.73 | gCO2eq/MJ | 243.49 | EUR/kWh | 0.1941 | [44,50] |
| Tractor | MJ/h | 16.42 | gCO2eq/h | 9800 | EUR/h | 5.22–11.65 | [51,52] |
| Human | MJ/h | 1.80 | gCO2eq | - | EUR/h | 4.5–7.3 | [51] |
| Machinery | MJ/h | 0.10–35.05 | gCO2eq/h | 0.10–190 | EUR/h | 0.32–4.45 | [53,54,55] |
| Irrigation system | MJ/ha | 373.7 | gCO2eq | - | EUR/h | 0.05 | [56] |
| Use of diesel | MJ | - | gCO2eq/MJ | 0.9 | EUR | - | [44] |
| Supplies | MJ/t·km | 0.87 | gCO2eq/t·km | 71 | EUR | - | [44,57] |
| Biomass | MJ/t·km | 0.81 | gCO2eq/t·km | 71 | EUR | - | [44,57] |
| Type | Land (ha) | Yield (t/ha) | Human Labour (h/ha) | Residues (t/ha) | Diesel (L/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 7.20 | 5.05 | 215 | 1.5 | 165.00 |
| O2 | 7.50 | 4.65 | 230 | 1.4 | 172.00 |
| O3 | 6.00 | 6.11 | 225 | 1.7 | 185.00 |
| O4 | 5.00 | 6.17 | 250 | 1.7 | 210.00 |
| O5 | 2.40 | 5.33 | 425 | 1.5 | 142.00 |
| I1 | 2.50 | 5.73 | 200 | 1.4 | 130.00 |
| I2 | 3.00 | 5.23 | 208 | 1.4 | 145.00 |
| I3 | 2.90 | 8.53 | 450 | 3.9 | 255.00 |
| I4 | 1.90 | 8.02 | 447 | 4.2 | 255.00 |
| C1 | 11.00 | 9.07 | 240 | 3.2 | 165.00 |
| C2 | 9.50 | 10.1 | 270 | 3.5 | 180.00 |
| C3 | 8.00 | 10.3 | 240 | 3.0 | 165.00 |
| C4 | 7.00 | 9.90 | 270 | 3.2 | 180.00 |
| C5 | 5.90 | 8.48 | 372 | 2.9 | 250.00 |
| Type | Unit | Land | Raw Materials | Energy | Labor | Machinery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | EUR/ha | 300.00 | 154.00 | 343.74 | 1245.05 | 257.51 |
| O2 | EUR/ha | 300.00 | 196.85 | 368.93 | 1312.55 | 257.51 |
| O3 | EUR/ha | 300.00 | 168.60 | 423.53 | 1356.35 | 296.62 |
| O4 | EUR/ha | 300.00 | 252.45 | 474.28 | 1503.55 | 330.80 |
| O5 | EUR/ha | 150.00 | 136.08 | 346.21 | 2335.97 | 254.85 |
| I1 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 420.80 | 300.72 | 848.25 | 335.41 |
| I2 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 465.70 | 326.36 | 910.25 | 362.78 |
| I3 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 525.00 | 764.99 | 1264.25 | 493.65 |
| I4 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 175.00 | 735.88 | 1572.00 | 455.30 |
| C1 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 418.00 | 578.87 | 1378.00 | 626.08 |
| C2 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 485.00 | 384.74 | 1267.25 | 453.05 |
| C3 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 431.50 | 368.72 | 1177.25 | 453.05 |
| C4 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 485.00 | 433.47 | 1410.25 | 504.74 |
| C5 | EUR/ha | 200.00 | 500.36 | 604.86 | 1878.00 | 455.30 |
| Type | Unit | Profit | Sales | Shadow Prices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | EUR/ha | 2143.79 | 3289.31 | 668.34 |
| O2 | EUR/ha | 1741.33 | 3025.12 | 721.93 |
| O3 | EUR/ha | 2623.89 | 4016.94 | 770.26 |
| O4 | EUR/ha | 2615.21 | 4348.72 | 883.31 |
| O5 | EUR/ha | 2235.68 | 4268.79 | 763.40 |
| I1 | EUR/ha | 2362.92 | 4016.12 | 1726.38 |
| I2 | EUR/ha | 2376.74 | 4189.85 | 1794.55 |
| I3 | EUR/ha | 2751.78 | 5979.67 | 1456.97 |
| I4 | EUR/ha | 2902.94 | 6021.12 | 1600.81 |
| C1 | EUR/ha | 3123.04 | 5899.21 | 1699.77 |
| C2 | EUR/ha | 3213.39 | 5551.45 | 1801.32 |
| C3 | EUR/ha | 2968.82 | 5147.36 | 1727.09 |
| C4 | EUR/ha | 3354.55 | 5936.03 | 1797.54 |
| C5 | EUR/ha | 3857.95 | 8476.47 | 1670.29 |
| Type | CRS Model | VRS Model | NIRS Model | Scale Efficiency | Returns to Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.98 | IRS |
| O2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| O3 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.98 | IRS |
| O4 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.97 | IRS |
| O5 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.93 | 0.93 | IRS |
| I1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| I2 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.00 | SE |
| I3 | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.90 | IRS |
| I4 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.84 | IRS |
| C1 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.94 | DRS |
| C2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| C3 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | DRS |
| C4 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| C5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| Type | CRS Model | VRS Model | NIRS Model | Scale Efficiency | Returns to Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 1.00 | SE |
| O2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| O3 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
| O4 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.96 | IRS |
| O5 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.96 | IRS |
| I1 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.55 | IRS |
| I2 | 0.47 | 0.82 | 0.47 | 0.57 | IRS |
| I3 | 0.75 | 0.99 | 0.75 | 0.76 | IRS |
| I4 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.66 | 0.66 | IRS |
| C1 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.76 | DRS |
| C2 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.84 | DRS |
| C3 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.98 | DRS |
| C4 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.99 | IRS |
| C5 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | SE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tziolas, E.; Karampatea, A.; Karapatzak, E.; Banias, G.F. Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Impacts in Greek Viticultural Management Systems: An Integrated Life Cycle and Data Envelopment Approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209043
Tziolas E, Karampatea A, Karapatzak E, Banias GF. Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Impacts in Greek Viticultural Management Systems: An Integrated Life Cycle and Data Envelopment Approach. Sustainability. 2024; 16(20):9043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209043
Chicago/Turabian StyleTziolas, Emmanouil, Aikaterini Karampatea, Eleftherios Karapatzak, and George F. Banias. 2024. "Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Impacts in Greek Viticultural Management Systems: An Integrated Life Cycle and Data Envelopment Approach" Sustainability 16, no. 20: 9043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209043
APA StyleTziolas, E., Karampatea, A., Karapatzak, E., & Banias, G. F. (2024). Balancing Efficiency and Environmental Impacts in Greek Viticultural Management Systems: An Integrated Life Cycle and Data Envelopment Approach. Sustainability, 16(20), 9043. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16209043








