Research on Composting of Garden Waste and Its Application in Cultivation Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Composting of Garden Waste
2.2.2. Substrate Application of Compost Products
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Different Treatments on the Composting Effect of Garden Waste
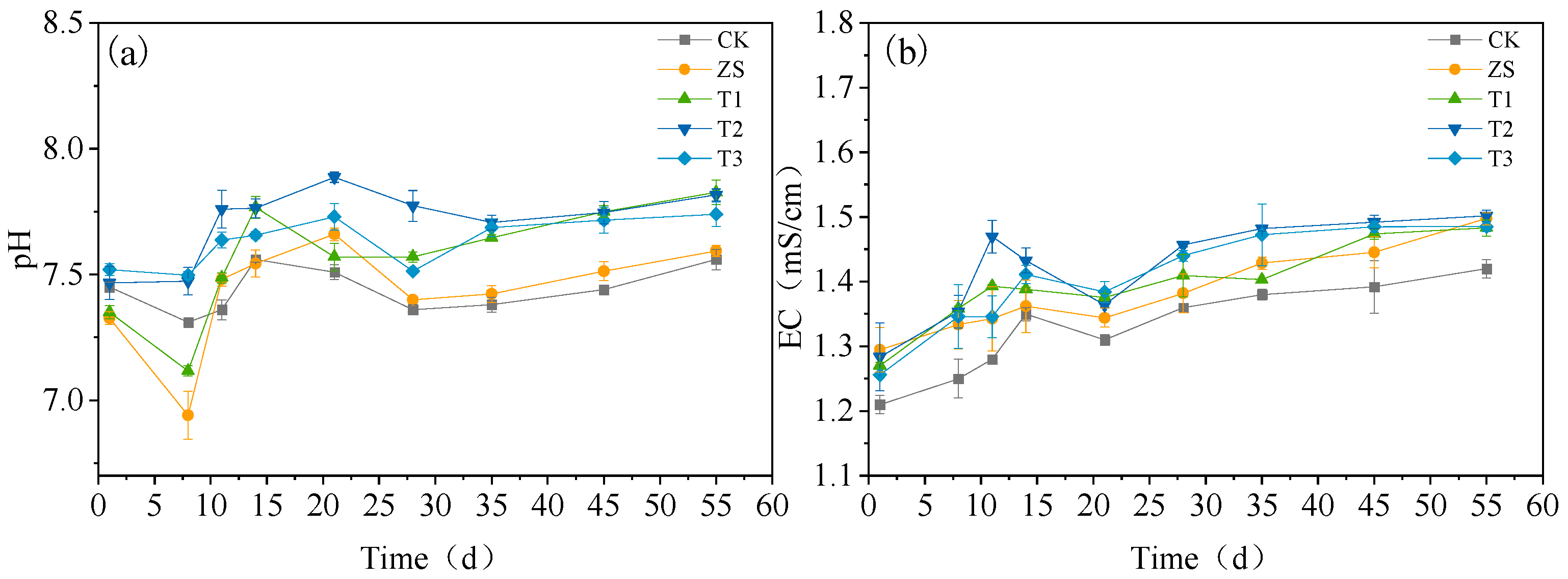
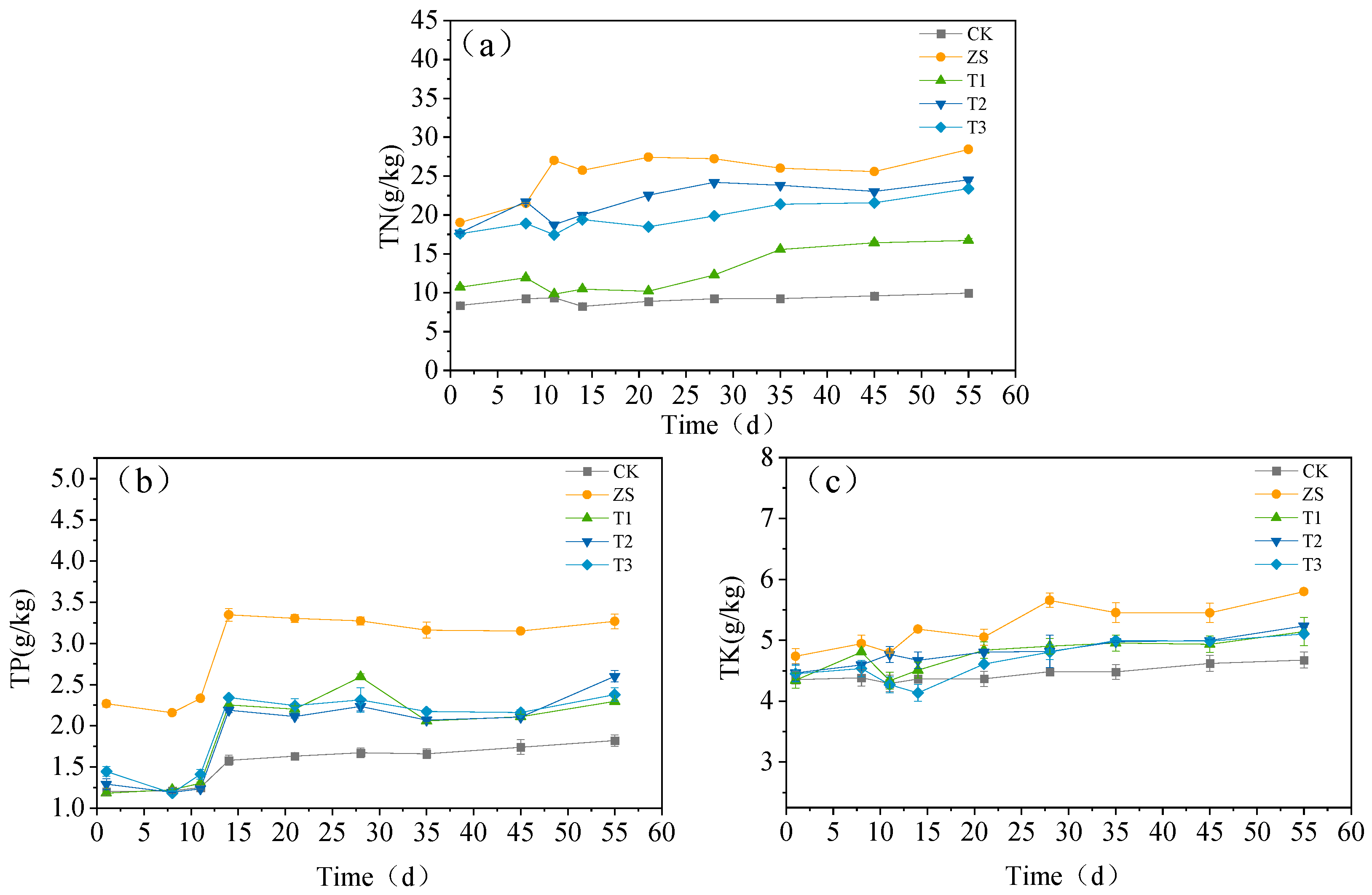
3.1.1. Effects on Physical and Chemical Properties
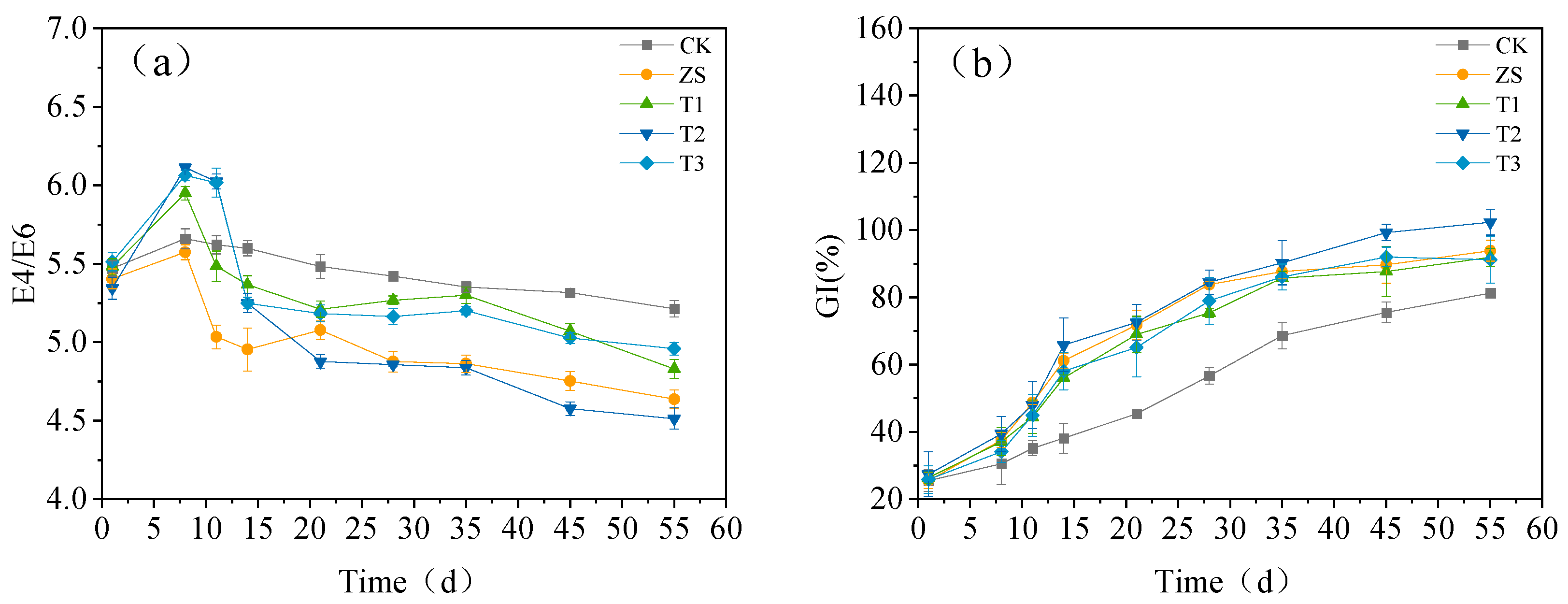
3.1.2. Impact on Spoilage Indicators
3.2. Effects of Different Ratios of Garden Waste and Other Horticultural Products on Lettuce Growth
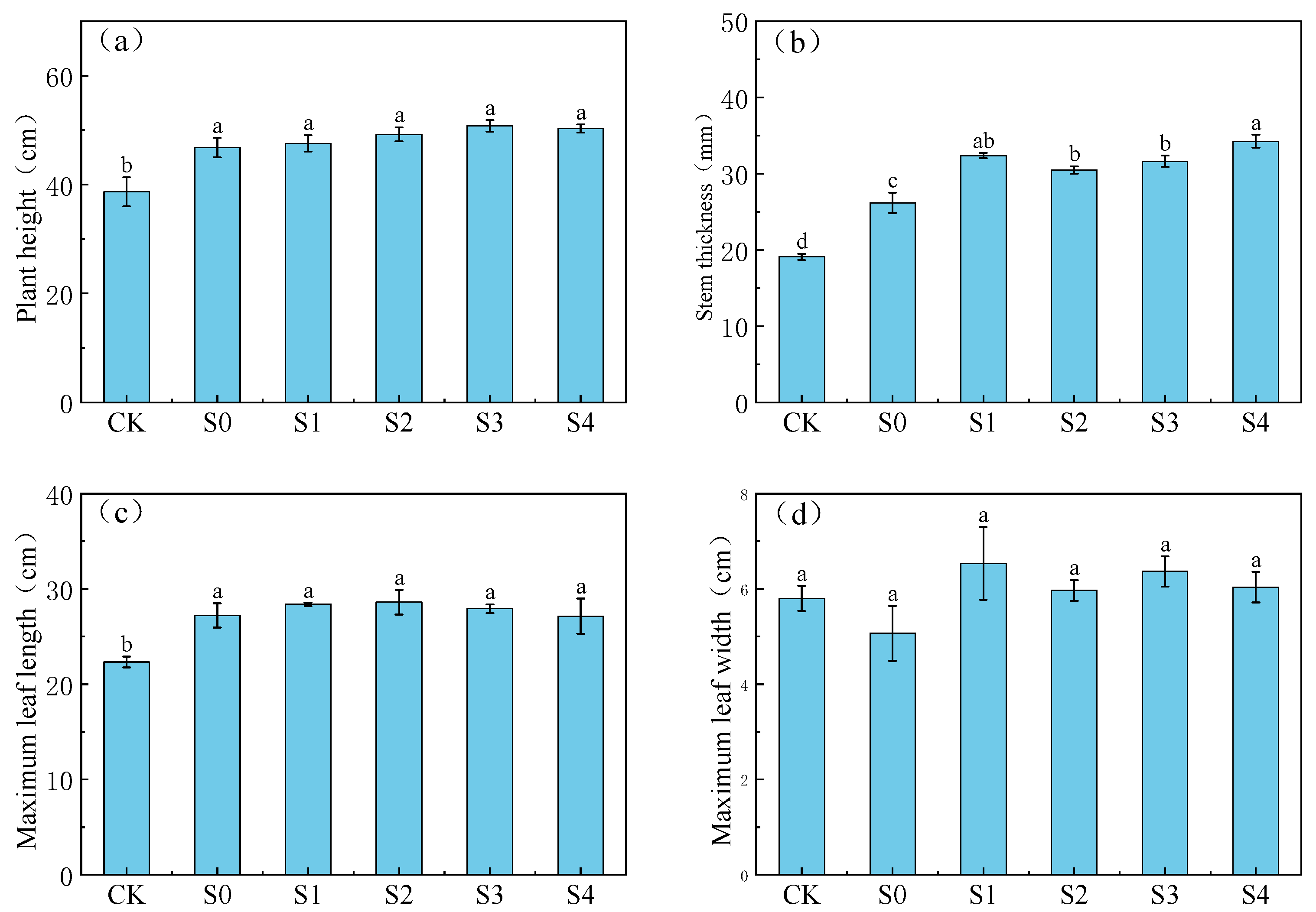
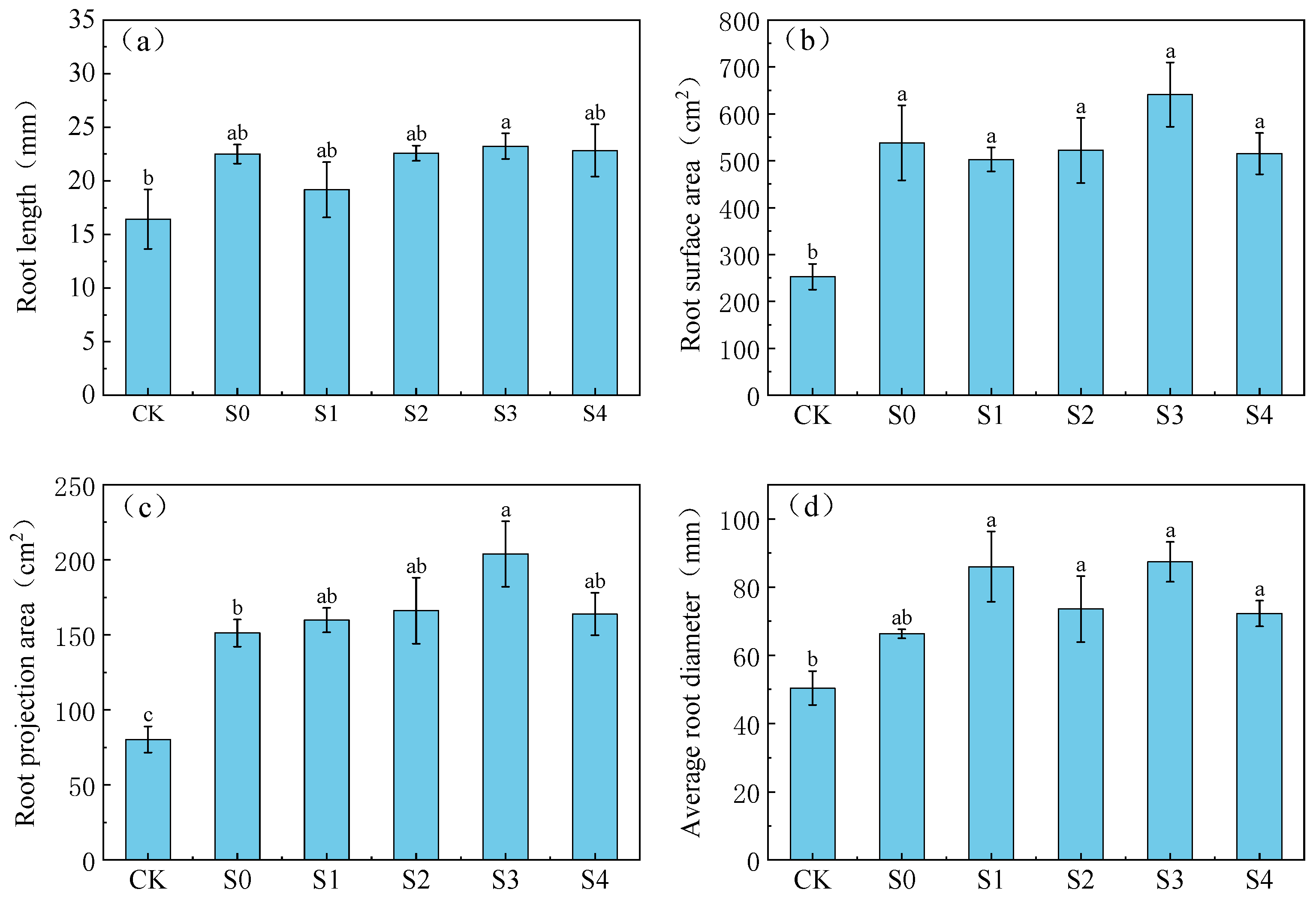
3.2.1. Effects of Different Treatments on the Growth Pattern of Lettuce
3.2.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Lettuce Quality Indexes
3.2.3. Comprehensive Evaluation of Lettuce Growth under Composted Garden Waste Product Composite Substrate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bustamante, M.A.; Ceglie, F.G.; Aly, A.; Mihreteab, H.T.; Ciaccia, C.; Tittarelli, F. Phosphorus availability from rock phosphate: Combined effect of green waste composting and sulfur addition. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, T.C.; Tong, L.; Guo, H.W.; Li, X.; Bai, B.J.; Chen, Y.; Nie, X.Q. Research Status of Generation and Management of Garden Waste in China: A case of Shanghai. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 766, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Monreal, C.; Barea, J.M.; Arriagada, C.; Borie, F.; Cornejo, P. Crop residue stabilization and application to agricultural and degraded soils: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 42, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattle, S.R.; Robinson, C.; Whatmuff, M. The character and distribution of physical contaminants found in soil previously treated with mixed waste organic outputs and garden waste compost. Waste Manag. 2020, 101, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, K.B.; Huang, Y.Z.; Wang, H.J. Re-utilization of Chinese medicinal herbal residues improved soil fertility and maintained maize yield under chemical fertilizer reduction. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.S.; Sun, B.; Deng, T.Y.; Lian, P.; Chen, J.H.; Peng, X.W. Safety and efficiency of sewage sludge and garden waste compost as a soil amendment based on the field application in woodland. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.J.; Tian, Y.; He, M.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Lyu, Q.; Xie, R.J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Deng, L.; Yi, S.L. Effects of Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer Application on Soil Properties, Citrus Growth Physiology, and Yield. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Palese, A.M.; Celano, G.; Zaccardelli, M. Effects of compost tea treatments on productivity of lettuce and kohlrabi systems under organic cropping management. Ital. J. Agron. 2014, 9, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, A.; Fernández, J.A.; Pascual, J.A.; Ros, M.; Egea-Gilabert, C. Application of Directly Brewed Compost Extract Improves Yield and Quality in Baby Leaf Lettuce Grown Hydroponically. Agronomy 2020, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hernández, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, R.; Plaza, J.; Morales-Corts, M.R. Compost tea as a sustainable alternative to promote plant growth and resistance against Rhizoctonia solani in potato plants. Sci. Hortic Amst. 2022, 300, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnchanawong, S.; Mongkontep, T.; Praphunsri, K. Effect of green waste pretreatment by sodium hydroxide and biomass fly ash on composting process. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 146, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Huang, Y.M.; Liu, H.J.; Xie, S.W.; Abbas, F. Impact of different nitrogen source on the compost quality and greenhouse gas emissions during composting of garden waste. Process. Saf. Environ. 2019, 124, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 525-2021; Agricultural Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Wang, X.Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.Q.; Sun, G.T.; Li, J.M. Greenhouse gas reduction and nitrogen conservation during manure composting by combining biochar with wood vinegar. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Xie, M.; Yu, X.; Feng, H.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T. A review of the definition, influencing factors, and mechanisms of rapid composting of organic waste. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Huang, S.; Zeng, Y.J.; Shao, H.; Zhang, J.; Groenigen, K.J. Liming increases yield and reduces grain cadmium concentration in rice paddies: A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulinas Masó, M.; Bonmatí Blasi, A. Evaluation of composting as a strategy for managing organic wastes from a municipal market in Nicaragua. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5120–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, M.K.; Duan, Y.M.; Awasthi, S.K.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Kim, S. Pandey, Ashok. Effect of biochar on emission, maturity and bacterial dynamics during sheep manure compositing. Renew Energy 2020, 152, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. Municipal solid waste management through vermicomposting employing exotic and local species of earthworms. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 90, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Karak, T.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Paul, R.K.; Das, T.; Saha, S.K. Evaluation of Composts from Agricultural Wastes with Fish Pond Sediment as Bulking Agent to Improve Compost Quality. CLEAN–Soil. Air Water 2013, 41, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Spaccini, R.; Piccolo, A.; Scala, F.; Bonanomi, G. Compost amendments enhance peat suppressiveness to Pythium ultimum, Rhizoctonia solani and Sclerotinia minor. Biol. Control 2011, 56, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Y.; Tian, W.H.; Jin, C.W. Nitrogen in plants: From nutrition to the modulation of abiotic stress adaptation. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, X.J.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.H. Ammonia volatilization as the major nitrogen loss pathway in dryland agro-ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Sivarajan, M.; Saravanapriya, S. Chemical changes during vermicomposting of sago industry solid wastes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.J.; Zhang, F.B.; Xu, P.Z.; Tang, S.H.; Xie, K.Z.; Huang, X.; Huang, Q.Y. Effects of sulphur and Thiobacillus thioparus on cow manure aerobic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6529–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Shutao, W.; Jin, Z.; Tong, X. Biochar influences the microbial community structure during tomato stalk composting with chicken manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, S.; Funamizu, N. Biodegradability of fecal nitrogen in composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3412–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.S.; Shen, Y.J.; Ding, J.T.; Cheng, H.S.; Zhou, H.B.; Ge, M.S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of biochar and volcanic rock addition on humification and microbial community during aerobic composting of cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.X.; Guo, S.W.; Han, Y.L.; Si, Y.K.; Li, P.P.; Li, F. Fulvic acid and fermentation agent optimize in situ composting by reducing antibiotic resistance genes abundances and altering succession of bacterial communities. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 191, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Huang, H.; Hao, Y.W.; Song, S.W.; Zhang, Y.T.; Su, W.; Liu, H.C. Nutritional quality, mineral and antioxidant content in lettuce affected by interaction of light intensity and nutrient solution concentration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.A.; Li, F.; Wenzel-Storjohann, A.; Sulieman, S.; Tasdemir, D.; Mühling, K.H. Comparative Metabolite Profile, Biological Activity and Overall Quality of Three Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.; Asteraceae) Cultivars in Response to Sulfur Nutrition. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 40199-2021; Technical Requirements for Resouree Recovery and Further Processing of Urban Garden Waste. State Administration for Market Regulation and National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2021.
| Raw Materials | pH | TC g/kg | TN g/kg | C/N | TP g/kg | TK g/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garden waste | 7.45 | 412.91 | 8.42 | 49.04 | 1.60 | 4.31 |
| Balsam camphor waste | 6.96 | 432.37 | 9.21 | 46.95 | 2.42 | 4.67 |
| Experimental Treatment | Raw Materials | Adjusted C/N | Fungicide Addition |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Garden waste | / | / |
| XZ | Balsam camphor waste | 25:1 | 0.3% |
| T1 | Garden waste | 40:1 | 0.3% |
| T2 | Garden waste | 25:1 | 0.3% |
| T3 | Garden waste | 25:1 | 0.15% |
| Experimental Treatment | Substrates | Different Levels of Fertilization | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Fertilizer (g/pot) | Conventional Fertilization (N) (g/pot) | ||
| CK | Soil | / | 20 |
| S0 | Garden waste–charcoal–vermiculite = 45:45:10 | / | 20 |
| S1 | S0–earthworm manure = 1:9 | / | 20 |
| S2 | S0–earthworm manure = 2:8 | / | 20 |
| S3 | S0–earthworm manure = 3:7 | / | 20 |
| S4 | S0–earthworm manure = 4:6 | / | 20 |
| Treatment | Chlorophyll (mg/kgFW) | Soluble Protein Values (mg/gFW) | Vitamin C (mg/kgFW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.79 ± 0.02 b | 0.71 ± 0.02 cd | 71.4 ± 1.21 a |
| S1 | 0.81 ± 0.02 b | 0.85 ± 0.04 abc | 79.86 ± 7.82 a |
| S2 | 1.08 ± 0.12 a | 0.93 ± 0.10 a | 79.41 ± 10.88 a |
| S3 | 1.16 ± 0.06 a | 0.92 ± 0.02 ab | 89.72 ± 9.65 a |
| S4 | 1.14 ± 0.11 a | 0.64 ± 0.02 d | 68.02 ± 3.15 a |
| S5 | 0.99 ± 0.06 ab | 0.74 ± 0.08 bcd | 76.37 ± 1.79 a |
| Ingredient | Initial Eigenvalue | Contribution of Cumulative Variance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Contribution of Variance | ||
| 1 | 10.83 | 67.76 | 67.77 |
| 2 | 2.39 | 14.94 | 82.71 |
| 3 | 1.29 | 8.07 | 90.78 |
| 4 | 0.94 | 5.89 | 96.67 |
| 5 | 0.53 | 3.33 | 100.00 |
| Treatment | X1 | X2 | X3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | −0.81 | 0.53 | −0.37 |
| S0 | −0.34 | −1.70 | 0.50 |
| S1 | 0.35 | 1.19 | −0.21 |
| S2 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 1.77 |
| S3 | 1.10 | −0.15 | −0.89 |
| S4 | 0.26 | −0.37 | −0.80 |
| Treatment | U (X1) | U (X2) | U (X3) | D | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 6 |
| S0 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.43 | 5 |
| S1 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.26 | 0.74 | 3 |
| S2 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 2 |
| S3 | 1.00 | 0.54 | 0.00 | 0.84 | 1 |
| S4 | 0.71 | 0.46 | 0.03 | 0.61 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, X.; Wang, X.; Zheng, S.; Zhao, H.; Ju, J.; Wang, C. Research on Composting of Garden Waste and Its Application in Cultivation Substrates. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188216
Yao X, Wang X, Zheng S, Zhao H, Ju J, Wang C. Research on Composting of Garden Waste and Its Application in Cultivation Substrates. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):8216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188216
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Xu, Xin Wang, Shengyang Zheng, Haitao Zhao, Jing Ju, and Chenzhe Wang. 2024. "Research on Composting of Garden Waste and Its Application in Cultivation Substrates" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 8216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188216
APA StyleYao, X., Wang, X., Zheng, S., Zhao, H., Ju, J., & Wang, C. (2024). Research on Composting of Garden Waste and Its Application in Cultivation Substrates. Sustainability, 16(18), 8216. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188216








