Eco-Environmental Assessment and Trend Analysis of the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
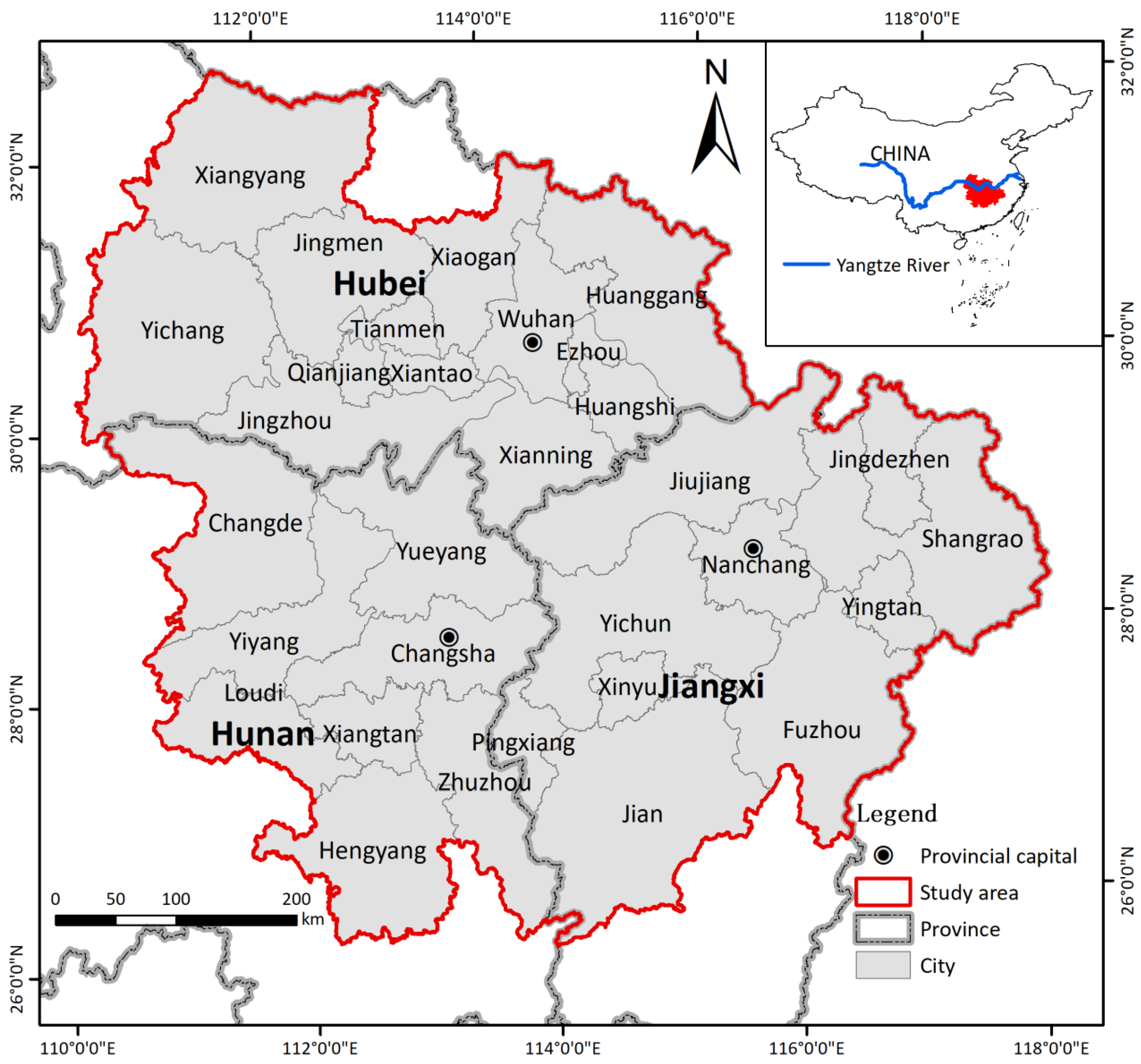
2.1. Study Area Profile
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
3. Methods
3.1. Modified RSEI
3.2. Trend Analysis
3.2.1. Theil–Sen Trend Analysis and Mann–Kendall Test
3.2.2. Hurst Exponent
4. Results
4.1. PCA
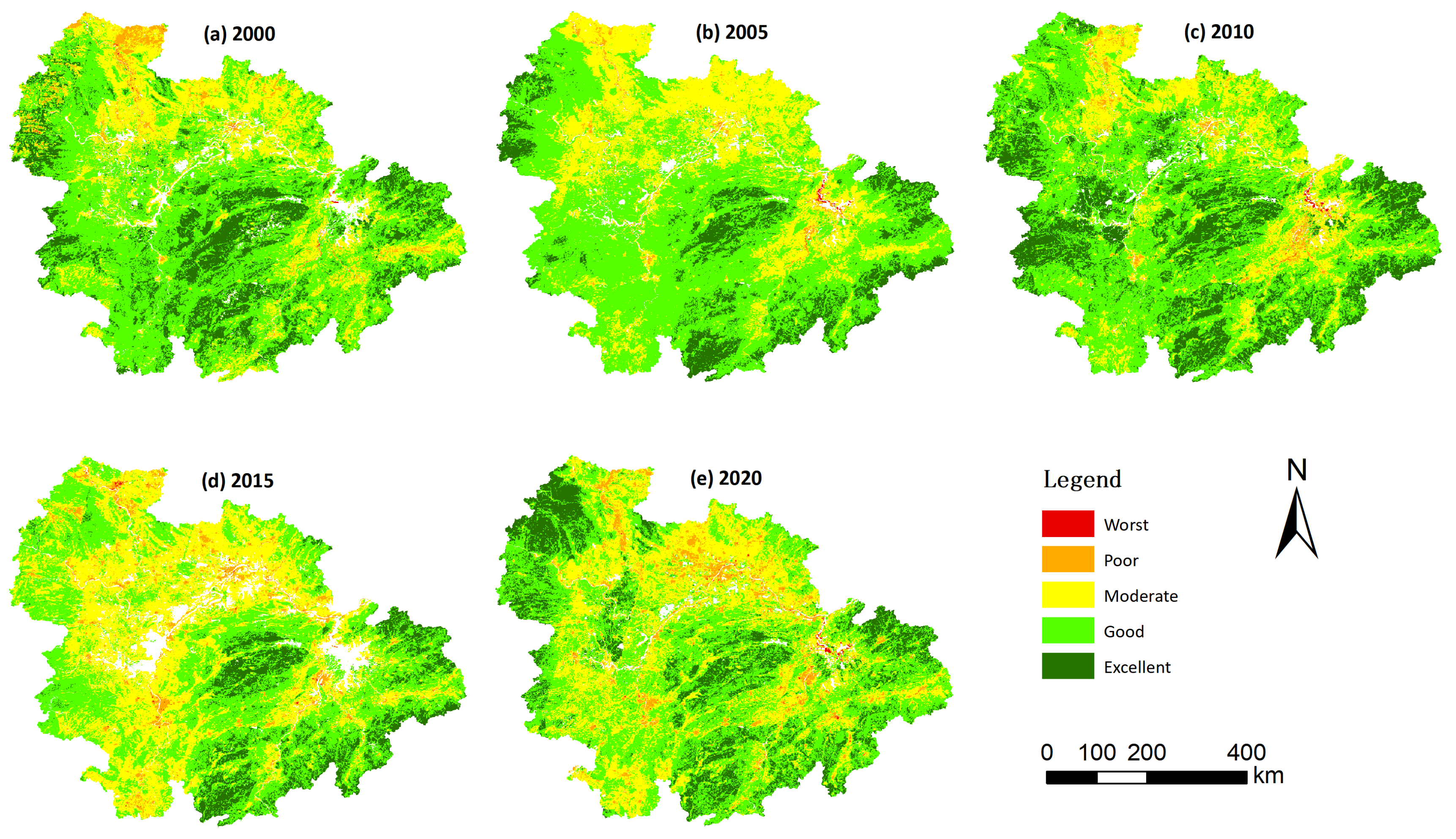
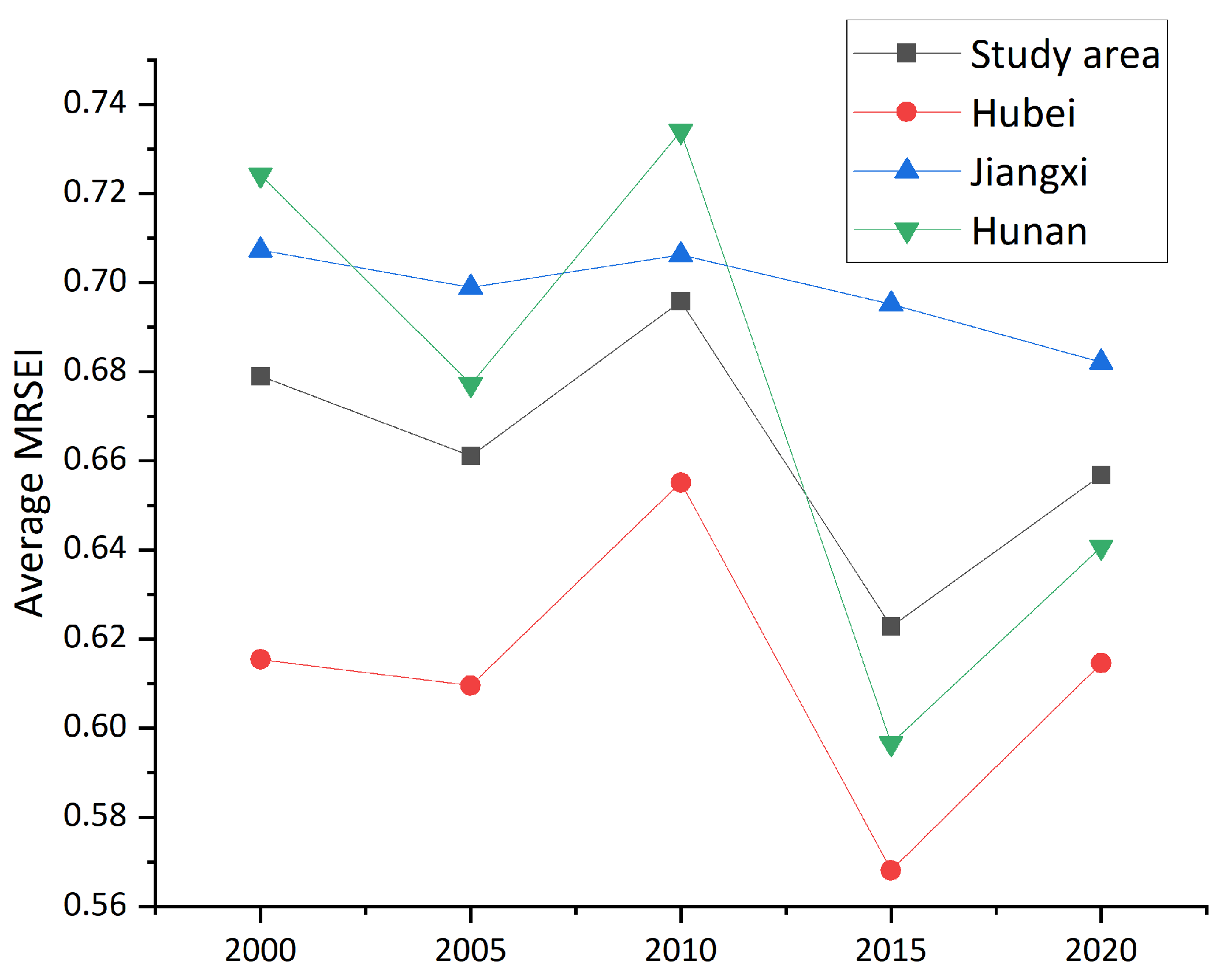
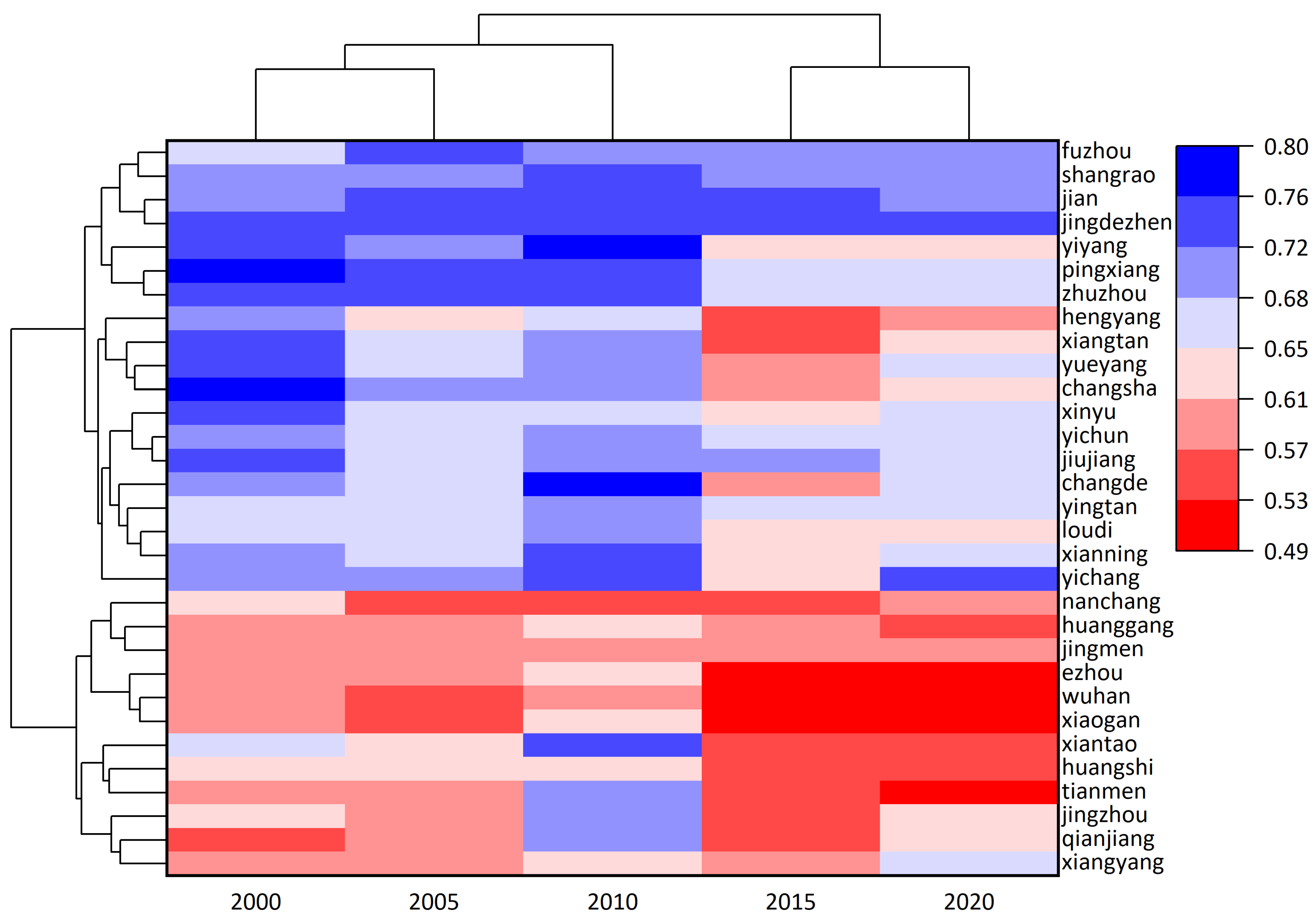
4.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Eco-Environmental Quality
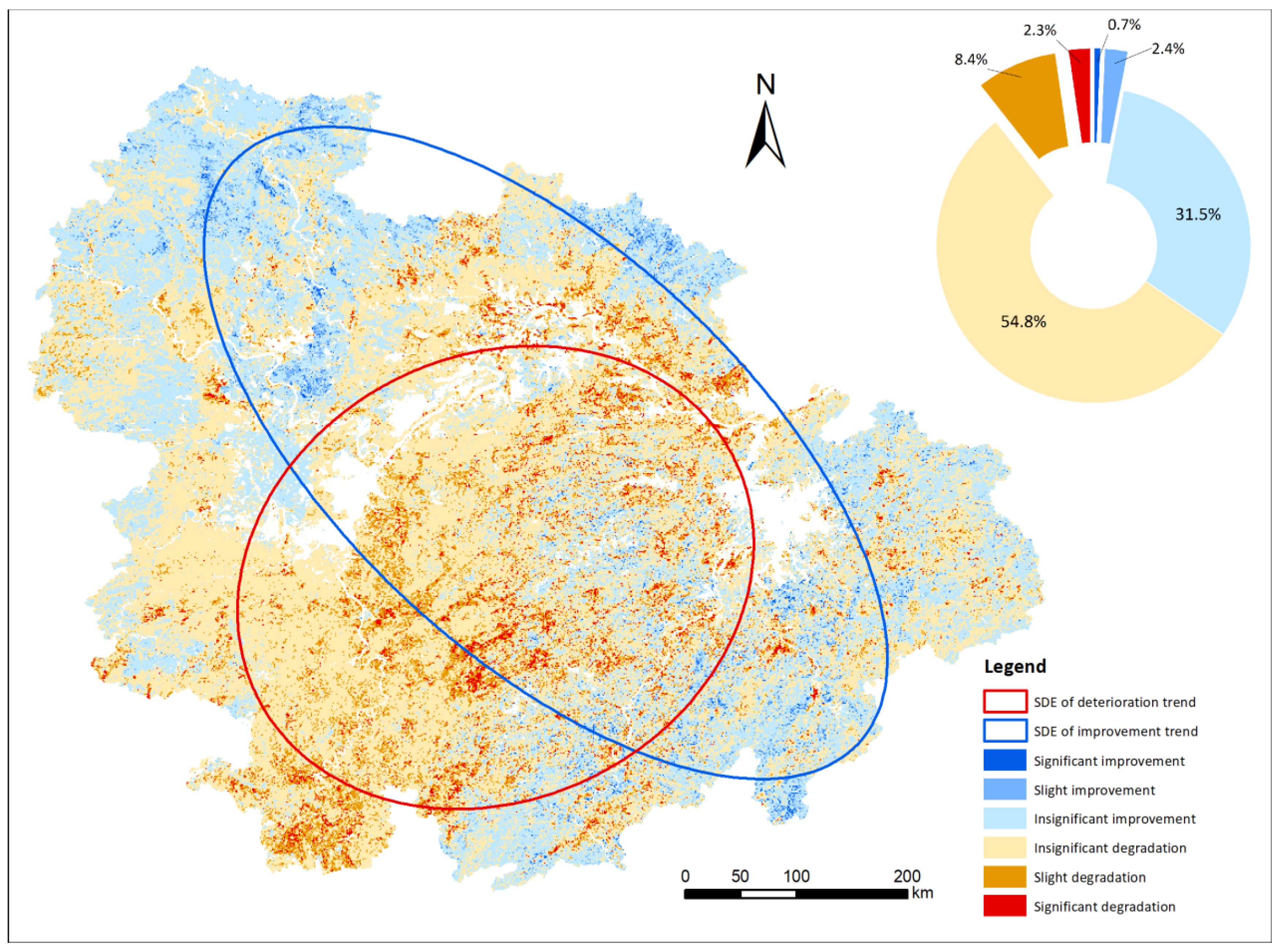
4.3. Trend and Sustainability Analysis
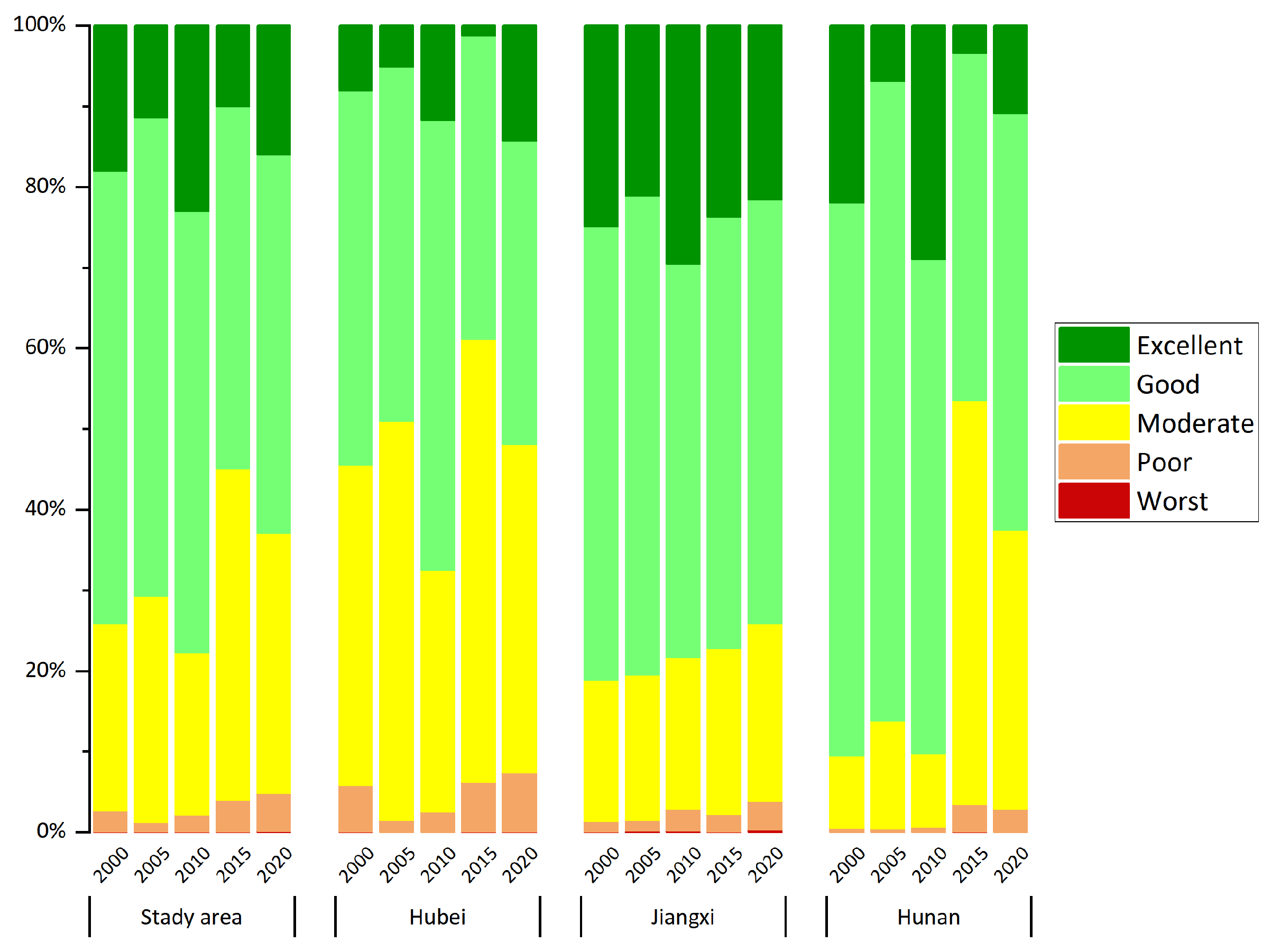
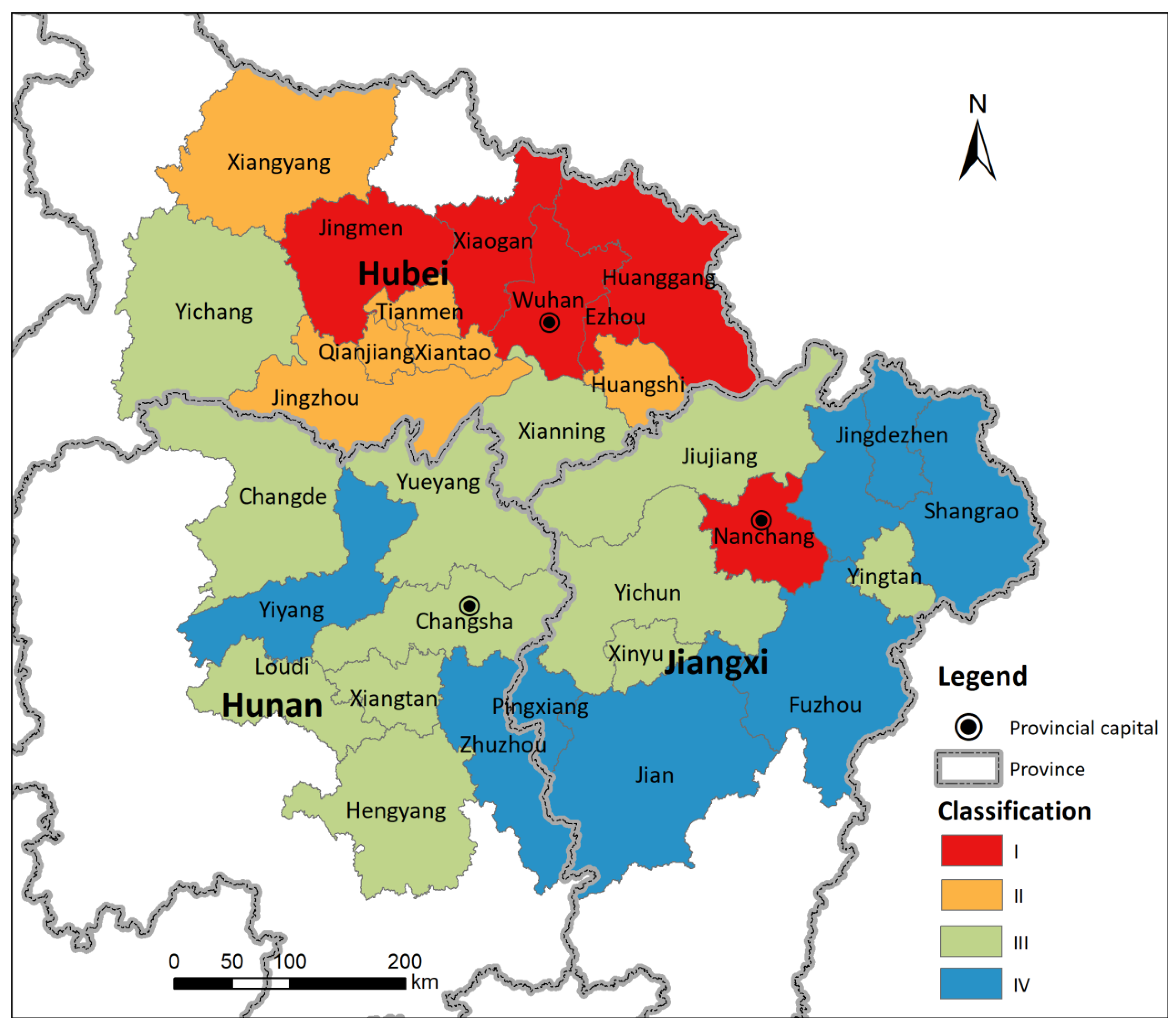
4.4. Comprehensive Eco-Environmental Assessment
5. Discussion
5.1. MRSEI Compared to Traditional RSEI
5.2. Factors Influencing Eco-Environmental Quality Changes
5.3. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The coupling curve between urbanization and the eco-environment: China’s urban agglomeration as a case study. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Fang, C.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Assessing sustainability of urbanization by a coordinated development index for an Urbanization-Resources-Environment complex system: A case study of Jing-Jin-Ji region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, T.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W.; Qin, C.; Song, C.; Gong, J.; Zhou, C. GIScience and remote sensing in natural resource and environmental research: Status quo and future perspectives. Geogr. Sustain. 2021, 2, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadoni, G.L.; Cavalli, A.; Congedo, L.; Munafò, M. Analysis of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) multi-temporal series for the production of forest cartography. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, D.L.; Broadbent, E.N.; Crandall, R.M. Detecting vegetation recovery after fire in a fire-frequented habitat using normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI). Forests 2020, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijith, H.; Dodge-Wan, D. Applicability of MODIS land cover and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) for the assessment of spatial and temporal changes in strength of vegetation in tropical rainforest region of Borneo. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 18, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Volk, T.A.; Im, J. Forest and crop leaf area index estimation using remote sensing: Research trends and future directions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Chauhan, A.; Maurya, N.K. Evaluation of earth observation datasets for LST trends over India and its implication in global warming. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Gómez, R.; Flowers-Cano, R.S.; Medina-García, G. Sensitivity of the RDI and SPEI drought indices to different models for estimating evapotranspiration potential in semiarid regions. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2471–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.N.M.; Olatubara, C.; Ewemoje, T.; El-Hennawy, M.T.; Farouk, H. Inland wetland time-series digital change detection based on SAVI and NDWI indecies: Wadi El-Rayan lakes, Egypt. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 19, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Das, S.; Pattanayak, J.M.; Bera, B.; Shit, P.K. Assessment of ecological environment quality in Kolkata urban agglomeration, India. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 1137–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei Saleh, S.; Amoushahi, S.; Gholipour, M. Spatiotemporal ecological quality assessment of metropolitan cities: A case study of central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, T.; Zhen, N.; Niu, R. Monitoring the effects of open-pit mining on the eco-environment using a moving window-based remote sensing ecological index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15716–15728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L. Development of a large-scale remote sensing ecological index in arid areas and its application in the Aral Sea Basin. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Cheng, G.; Yang, J.; Ding, H.; He, S. Evaluation of Urban Ecological Environment Quality Based on Improved RSEI and Driving Factors Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Zhu, D.; Jia, K.; Plaza, A. RSEIFE: A new remote sensing ecological index for simulating the land surface eco-environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, Q. Examining the relationship between urbanization and the eco-environment using a coupling analysis: Case study of Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hou, K.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. A conceptual framework for establishing the index system of ecological environment evaluation–A case study of the upper Hanjiang River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 107, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google earth engine cloud computing platform for remote sensing big data applications: A comprehensive review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, X.; Ma, X.; Tang, M. The spatial integration and coordinated industrial development of urban agglomerations in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Cities 2020, 104, 102801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.; Li, B.L.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. The development of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt: How to make it in a green way. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Qi, Q.; Wang, Y. An Ecological Quality Evaluation of Large-Scale Farms Based on an Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, A.; Hu, C.; You, L. Evaluation and Prediction of Ecological Restoration Effect of Beijing Wangping Coal Mine Based on Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Land 2023, 12, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, M.A.; de Leeuw, G.; Levy, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Air pollution scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and ranking of extremely polluted cities using long-term concentrations of aerosols and trace gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, Z.; Fatehi, P.; Darvishsefat, A. Vegetation dynamics trend using satellite time series imagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, U.; Yusuf, A.; Edet, C.; Oche, C.O.; Agbo, E. Trend analysis of temperature in Gombe state using Mann Kendall trend test. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Tabares, D.A.; Saa-Requejo, A.; Martín-Sotoca, J.J.; Tarquis, A.M. Multiscaling NDVI series analysis of rainfed cereal in Central Spain. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, T.; Jia, K.; Plaza, A. Coupling Analysis Between Ecological Environment Change and Urbanization Process in the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Urban Agglomeration, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Qi, K.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N. Research and analysis of ecological environment quality in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin between 2000 and 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanping, Z.; Pengbin, Z.; Tengfei, X.; Yuehua, J.; Lin, G.; Ranran, Y. Ecological environment changes in Yangtze River Economic Zone in recent 20 years. Geol. China 2021, 48, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y. Spatial-temporal evolution and motivation of ecological vulnerability based on RSEI and GEE in the Jianghan Plain from 2000 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1191532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tong, Y.; Tang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y. Identifying Spatiotemporal Interactions between Urbanization and Eco-Environment in the Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Lv, J.; He, L.; Ma, K.; Hu, Q.; Liu, X. Spatial and temporal evolution of air pollution and verification of the environmental Kuznets curve in the Yangtze River Basin during 1980—2019. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 56, 2265157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y. Eco-environmental quality assessment in China’s 35 major cities based on remote sensing ecological index. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51295–51311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xi, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, C. Comprehensive evaluation and spatial-temporal changes of eco-environmental quality based on MODIS in Tibet during 2006–2016. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, R.A.; Nassikas, A.A. Global and regional fluxes of carbon from land use and land cover change 1850–2015. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2017, 31, 456–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.; Shabbir, R.; Ahmad, S.S.; Malik, A.H.; Aziz, N.; Butt, A.; Erum, S. Dynamics of land use and land cover change (LULCC) using geospatial techniques: A case study of Islamabad Pakistan. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Pei, F.; Xu, X. A new global land-use and land-cover change product at a 1-km resolution for 2010 to 2100 based on human–environment interactions. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1040–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, A.K.; Ping, O.W. The influence of land-use/land-cover changes on land surface temperature: A case study of Kuala Lumpur metropolitan city. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 51, 1049–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittnik, S.; Semmler, W.; Haider, A. Climate disaster risks—Empirics and a multi-phase dynamic model. Econometrics 2020, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandalinas, S.I.; Fritschi, F.B.; Mittler, R. Global warming, climate change, and environmental pollution: Recipe for a multifactorial stress combination disaster. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, H. Spatial temporal patterns and driving factors of industrial pollution and structures in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; She, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, M. Spatio-temporal evolution and driving factors of eco-environmental quality based on RSEI in Chang-Zhu-Tan metropolitan circle, central China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| β | Z | Change Trends |
|---|---|---|
| β > 0 | 2.58 > |Z| ≥ 1.96 | Significant improvement |
| 1.96 > |Z| ≥ 1.65 | Slight improvement | |
| |Z| < 1.65 | Insignificant improvement | |
| β < 0 | |Z| < 1.65 | Insignificant degradation |
| 1.96 > |Z| ≥ 1.65 | Slight degradation | |
| 2.58 > |Z| ≥ 1.96 | Significant degradation |
| Year | PC1 | Contribution (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDVI | WET | NDBSI | LST | AOD | ||
| 2000 | 0.690 | 0.239 | −0.660 | −0.106 | −0.138 | 86.20 |
| 2005 | 0.697 | 0.240 | −0.437 | −0.071 | −0.510 | 76.67 |
| 2010 | 0.740 | 0.240 | −0.588 | −0.075 | −0.207 | 80.95 |
| 2015 | 0.520 | 0.193 | −0.659 | −0.310 | −0.401 | 77.82 |
| 2020 | 0.715 | 0.262 | −0.639 | −0.034 | −0.101 | 88.06 |
| H | Persistence Type | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0.25 | Strong anti-persistence | 2.4% |
| 0.25–0.5 | Weak anti-persistence | 16.2% |
| 0.5–0.75 | Weak persistence | 51.8% |
| 0.75–1 | Strong persistence | 29.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Wei, S.; Wu, Y. Eco-Environmental Assessment and Trend Analysis of the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188118
Zhu X, Wei S, Wu Y. Eco-Environmental Assessment and Trend Analysis of the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):8118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188118
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiang, Siyu Wei, and Yijin Wu. 2024. "Eco-Environmental Assessment and Trend Analysis of the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 8118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188118
APA StyleZhu, X., Wei, S., & Wu, Y. (2024). Eco-Environmental Assessment and Trend Analysis of the Yangtze River Middle Reaches Megalopolis Based on a Modified Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sustainability, 16(18), 8118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188118





