Teaching Innovation and Teaching–Learning Methods for Sustainable Tourism Development Education in the Bachelor of Tourism Degree
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Contextualization of the Research
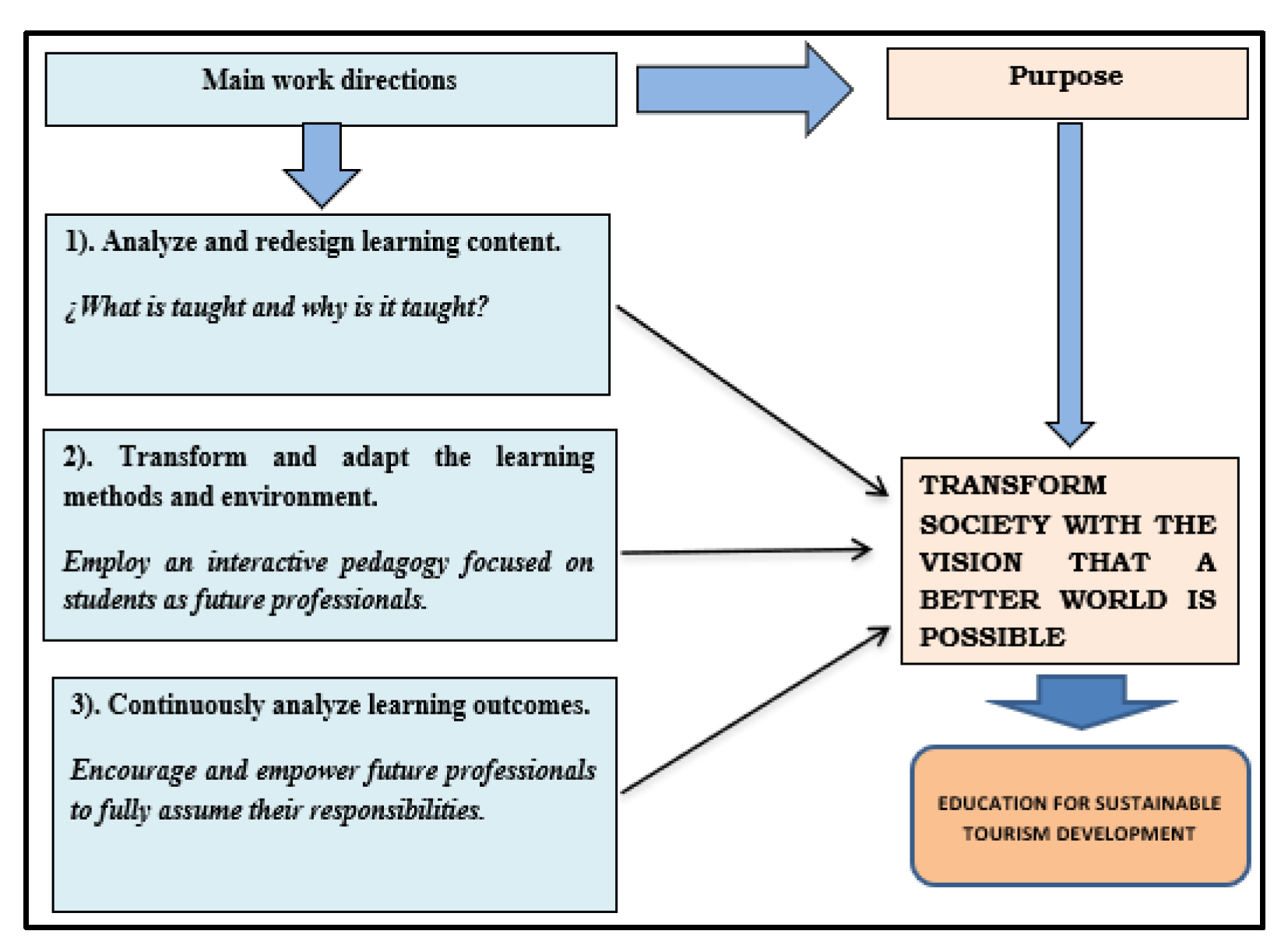
2.2. Experiences Achieved in the Materialization of Teaching Innovation Methods
- Expository master classes that allow the internalization of information and common teaching processes, which guarantee students’ knowledge of the training, methodologies and processes necessary to know, apply, intervene, propose and conclude direct interventions in their professional actions [59,60].
- Open, collaborative and integrated teaching (collaborative teaching model), which at professional and degree levels allows the student and teacher to integrate with the knowledge society, not only with the traditional methodologies that are applied, but also those that are practiced in the various contexts of action through the use of the various media of the information society and globalization [65,66].
- Open and collaborative teaching, as an essential element of education based on the development of soft and inclusive skills at professional and degree levels, allows insertion into innovation processes and sustainable endogenous local development of tourism and the generation of entrepreneurship through the practical application in the various contexts of action, in the use of the various media of the information society, knowledge management, innovation and globalization. Teachers change their role and reduce to a minimum their role as transmitters of information, which is achieved through the presentation and contextualization of topics, as well as the formulation of professional problems emphasizing important aspects or aspects that are difficult to understand, to allow students to easily access all kinds of information [67].
2.3. Research Methods, Techniques and Tools
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asencio, E.N.; García, E.J.; Redondo, S.R.; Ruano, B.T.; Fundamentos de la Investigación y la Innovación Educativa. UNIR Editorial, La Rioja, Spain: 2017. Available online: https://www.unir.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Investigacion_innovacion.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Harrington, D.; Kearney, A. The business school in transition: New opportunities in management development, knowledge transfer and knowledge creation. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2011, 35, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Karpov, A.O. Education for knowledge society: Learning and scientific innovation environment. J. Soc. Stud. Educ. Res. 2017, 8, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Stella, G.T. The Effects of Deductive, Inductive and a Combination of Both Types of Grammar Instruction in Pre-sessional Classes in Higher Education. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bedfordshire, London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiró, P.S.; Neutzling, D.M.; Lessa, B. Education for sustainability in higher education institutions: A multi-perspective proposal with a focus on management education. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azungah, T. Qualitative research: Deductive and inductive approaches to data analysis. Qual. Res. J. 2018, 18, 383–400. [Google Scholar]
- Yom, S. From methodology to practice: Inductive iteration in comparative research. Comp. Political Stud. 2015, 48, 616–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadewitz, N.; Jachna, T. Comparing inductive and deductive methodologies for design patterns identification and articulation. In Proceedings of the International Design Research Conference IADSR 2007 Emerging Trends in Design Research, Hong Kong, 12–15 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barrero-Barrero, D.; Baquero-Valdés, F. Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible: Un contrato social posmoderno para la justicia, el desarrollo y la seguridad. Rev. Científica Gen. José María Córdova 2020, 18, 113–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianet, G.C.; Georgina Marcia, S.S.; Liannet, S.S. La gestión de los procesos educativos universitarios enfocados a la educación ambiental. Mag. Las Cienc. Rev. Investig. E Innovación 2018, 3, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Huckle, J. Education for sustainability: Evaluating paths to the future. Aust. J. Environ. Educ. 1991, 7, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilbury, D. Environmental education for sustainability: Defining the new focus of environmental education in the 1990s. Environ. Educ. Res. 2006, 1, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, S. El Medio Ambiente en la Opinión Pública: Tendencias de Opinión. Demanda social. Análisis y Gestión de la Opinión Pública en Materia de Medio Ambiente. Comunicación Medioambiental en la Administración y en la Empresa. Ediciones Mundi-Prensa. 1997. Available online: https://books.google.es/books?hl=es&lr=&id=-Ab7syu2PRQC&oi=fnd&pg=PA31&dq=Calvo,+S.+(1997)&ots=Lu0E7ebDXT&sig=HIfUACspztsCbmX_t0U7UJ4eR70 (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Huckle, J.; Stephen, R. Sterling. Education for Sustainability. Earth Exploration. 1996. Available online: https://books.google.es/books?hl=es&lr=&id=dNsTFPRFAZ4C&oi=fnd&pg=PP9&dq=Sterling,+S.+(1996).+Good+Earth-keeping:+Education,+Training+%26+Awareness+for+the+Sustainable+Future,+Londres,+UNEP&ots=c7SjnqYUdx&sig=wz5zRQLDQCJbHcBb2fXKK9JVlbM (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Palmer, J. Environmental Education in the 21st Century: Theory, Practice, Progress and Promise; Routledge: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McNaughton, M.J. El drama educativo en la educación para el desarrollo sostenible: Ecopedagogía en acción. Pedagog. Cult. Y Soc. 2010, 18, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, J.; Liddy, M. The impact of development education and education for sustainable development interventions: A synthesis of the research. Environ. Educ. Res. 2018, 24, 1031–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeve-de Pauw, J.; Gericke, N.; Olson, D.; Berglund, T. The effectiveness of education for sustainable development. Sostenibilidad 2015, 7, 15693–15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ONU. Educación para el Desarrollo Sostenible. Hoja de Ruta. Repositorio UNESCO. Organización de las Naciones Unidas. 2020. Available online: http://es.unesco.org/open-access/terms-use-ccbysa-sp (accessed on 18 February 2024).
- Valdiviezo, W.A. Ecoeficiencia: Nueva estrategia para la educación ambiental en instituciones educativas. Investig. Valdizana 2019, 13, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Barajas, L.N. Estudio de caso: Una estrategia para la enseñanza de la educación ambiental. Prax. Saber 2012, 3, 53–78. [Google Scholar]
- Huckle, J.; Wals, A.E.J. The UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development: Business as Usual in the End. In Neoliberalism and Environmental Education, 1st ed.; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2017; pp. 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Benayas, J.; Calvo, S. Educación para el desarrollo sostenible: Evaluación de retos y oportunidades del decenio 2005–2014. Rev. Iberoam. Educ. 2006, 40, 25–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallingre, N. Avances en la construcción del conocimiento del turismo: Pensando la disciplina del turismo desde una perspectiva integral. Estud. Y Perspect. Tur. 2011, 20, 149–170. [Google Scholar]
- Toker, U.; Gray, D.O. Innovation spaces: Workspace planning and innovation in US university research centers. Res. Policy 2008, 37, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rubiano, M.E.; Ortiz-Riaga, C.; Duque-Orozco, Y.V.; Plata-Pacheco, P.A. Fuentes de conocimiento e imágenes de la innovación en micro y pequeñas empresas de turismo: Agencias de viajes y hoteles en Bogotá y Pereira. Rev. Investig. Desarro. E Innovación 2017, 7, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chica Mera, J.C. La Importancia de Innovación en Las Actividades Turísticas de Recreación en Las Operadoras Turísticas del Puerto El Morro, de la Provincia del Guayas en el Año 2017. Bachelor’s Thesis, Tesis de Grado Bachelor in Tourism Administration, Repositorio de la Universidad Estatal de la Península de Santa Elena, Santa Elena, Ecuador, 2017. Available online: https://repositorio.upse.edu.ec/bitstream/46000/4126/1/UPSE-THT-2017-0005.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Pasaco, B.; Agudo, K. Análisis de la Innovación en las Mipymes Turísticas de la Ciudad de Cuenca en los Años 2011 y 2012. Thesis in Tourism Engineering. Universidad de Cuenca. Cuenca Ecuador. 2014. Available online: http://dspace.ucuenca.edu.ec/bitstream/123456789/5604/1/Tesis.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Morales, M.; León, A.; Adiós a los Mitos de la Innovación. Una Práctica Para innovar en América Latina. Ed. Innovare. 2013. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/-/es/Mario-Morales/dp/0989283208 (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- González, M.; León, C. Turismo Sostenible y Bienestar Social ¿cómo Innovar Esta Industria Global? Ed. Erasmus. Madrid. 2010. Available online: https://books.google.es/books?hl=es&lr=&id=EDAo6ThGYNUC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=Gonz%C3%A1lez,+M.%3B+Le%C3%B3n,+C.+Turismo+sostenible+y+bienestar+social+%C2%BFc%C3%B3mo+innovar+esta+industria+global%3F+Ed.+Erasmus.+Madrid.+2010&ots=wwPUvYMQ3g&sig=UQ7JSystuUWm5SkiwxvHYgDTPZs (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Picazo, P.; Moreno, S.; Difusión de la Investigación Científica en Turismo. El Caso de México. El Periplo Sustentable, Núm. 24, Enero-Junio. 2013, pp. 7–40. Available online: https://accedacris.ulpgc.es/bitstream/10553/22732/2/Difusi%C3%B3n_investigaci%C3%B3n_M%C3%A9xico.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Bowen, J.T. Managing a research career. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2005, 17, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jogaratnam, G.; Chon, K.; McCleary, K.; Mena, M.; Yoo, J. An Analysis of Institutional Contributors to Three Major Academic Tourism Journals: 1992–2001. Tour. Manag. 2005, 26, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ritchie, J.R.B. An Investigation of Academic Leadership in Tourism Research: 1985–2004. Tour. Manag. 2007, 28, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Phillips, W.J.; Canter, D.; Abbott, J. Hospitality and Tourism Research Rankings by Author, University, and Country using Six Major Journals: The First Decade of the New Millennium. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 2011, 35, 381–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullo Romero, E.d.C.; Salceso, J.P.C.; Herrera, S.R.G. Innovación y desarrollo turístico. Reflexiones y desafíos. Rev. Univ. Y Soc. 2019, 11, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Luque, T.; Adriana, M.; Pérez, I.R.; Aguilar, J.A.; Rozas, M.R. Aprendizaje cooperativo y habilidades sociales: Universidad Nacional Jorge Basadre Grohmann. Horiz. Cienc. 2021, 11, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Almiñana, D.; García, B.A. Algunas Experiencias de Aplicación del Aprendizaje Cooperativo y del Aprendizaje Basado en Proyectos. I Jornadas de Innovación Educativa. Escuela Politécnica Superior de Zamora. 2006. Available online: https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/9489 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Sánchez, G.I.; Claudia, M.; Concha, C.M.; Rojas, C.A. Hackathon social como metodología activo-participativa para el aprendizaje colaborativo e innovador en la formación universitaria. Inf. Tecnológica 2022, 33, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Ponce, L. El presupuesto de las universidades, ¿dinero bien gastado? Observatorio de gasto público de Ecuador. 2020. Available online: https://www.gastopublico.org/informes-del-observatorio/el-presupuesto-de-las-universidades-dinero-bien-gastado (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Consejo Universitario de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. Carrera de Turismo. Facultad de Ciencias Administrativas y Económicas. 2024. Available online: https://www.utm.edu.ec/carrera-de-turismo-modalidad-hibrida (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Siu, J.L.R. Las habilidades blandas como base del buen desempeño del docente universitario. Innova Res. J. 2020, 5, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, O.M.; Amar, R.M.; Triadú, J.X. Habilidades blandas: Necesarias para la formación integral del estudiante universitario. Rev. Científica ECOCIENCIA 2018, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noah, J.B.; Aziz, A.A. A Systematic review on soft skills development among university graduates. EDUCATUM J. Soc. Sci. 2020, 6, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, J.I.; Monereo, C. Introducción: La nueva cultura del aprendizaje universitario o por qué cambian nuestras formas de enseñar y aprender. In Psicología del Aprendizaje Universitario—Madrid: Ediciones Morata; Casalini: Fiesole, Italy, 2009; pp. 9–28. Available online: https://www.torrossa.com/en/resources/an/2953088 (accessed on 21 May 2024).
- Suárez-Escudero, J.C.; Posada-Jurado, M.C.; Bedoya-muñoz, L.J.; Urbina-Sánchez, A.J.; Ferreira-Morales, J.L.; Bohórquez-Gutiérrez, C.A. Enseñar y aprender anatomía: Modelos pedagógicos, historia, presente y tendencias. Acta Médica Colomb. 2020, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.J.; Martins, H. The future of soft skills development: A systematic review of the literature of the digital training practices for soft skills. J. E-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 2022, 18, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Álvarez, M.d.C.; Díaz, E.F.; Saiz, G.S. Planificación, colaboración, innovación: Tres claves para conseguir una buena práctica docente universitaria. REDU Rev. Docencia Univ. 2012, 10, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romillo, A.d.J.; Polaino, C.J. Aplicación del modelo de gestión pirámide del desarrollo universitario en la universidad de Otavalo, Ecuador. Form. Univ. 2019, 12, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, S.; Musau, R. Habilidades blandas: Qué son y cómo fomentarlas. In Bridging the Skills Gap. Educación y Formación Técnica y Profesional: Problemas, Preocupaciones y Perspectivas; Jayaram, S., Munge, W., Adamson, B., Sorrell, D., Jain, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 26, pp. 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, S.T.B.; Moreira-Cedeño, J.A.; Velásquez-Espinales, A.N.; Rodríguez-Gámez, M. Autoevaluación, Coevaluación y Heteroevaluación como enfoque innovador en la práctica pedagógica y su efecto en el proceso de enseñanza-aprendizaje. Polo Del Conoc. Rev. Científico-Prof. 2021, 6, 828–845. [Google Scholar]
- Morales Páez, M.; García-Galván, R. Colaboración tecnocientífica academia-empresa. Un análisis de la percepción de profesores-investigadores. Econ. Teoría Y Práctica 2020, 52, 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.Q.; Galárraga, F.M.; Duque, D.A.S. Reflexiones Acerca Del Desarrollo Del Turismo: Caso de estudio observatorio de turismo para la Provincia de Pichincha. An. Bras. Estud. Turísticos, 2018; 8, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasing Sánchez, L.P.; Peña, V.M.V.; Herrera, S.R.G. La práctica pre profesional en el currículum de la carrera Turismo. Conrado 2018, 14, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Marín, H.C.; Velasco, R.E.; Medina, C.A.B.; Vargas, M.V.R.; Ríos, M.G.G.; Fuentes, N.N.M.; del Corral Villaroel, V.H. Evaluación del currículo ofertado por la Universidad Estatal Amazónica para la carrera de Ingeniería en Turismo. Rev. Educ. 2018, 42, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, C.Y.; Robinson, H.S. La sustentabilidad en el currículo del profesional de turismo en la Universidad Politécnica Estatal del Carchi UPEC. Tierra Infin. 2019, 5, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitseva, N.A.; Larionova, A.A.; Skrobotova, O.V.; Trufanova, S.N.; Dashkova, E.V. The Business Integration Mechanism and the Training System for the Tourism Industry. Int. Electron. J. Math. Educ. 2016, 11, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Pelegrín Entenza, N.; Llupart, M.R.N.; Báster, L.E.L.; Llaver, L.R.M. Perspectiva del currículo de la licenciatura en turismo de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. Encuentros. Rev. Cienc. Humanas Teoría Soc. Y Pensam. Crítico. 2023, 19, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronchoni, H.; Izquierdo, C.; Anguera, M.T. Interacción participativa en las clases magistrales: Fundamentación y construcción de un instrumento de observación. Publicaciones 2018, 48, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.D. “Enseñanza Expositiva en Grupos Pequeños: Capacitar a Líderes de Grupos Pequeños Sobre Cómo Desarrollar y Enseñar Lecciones Expositivas”. Ph.D. Thesis, Liberty University, Lynchburg, VA, USA, 2022; p. 3697. Available online: https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4756&context=doctoral (accessed on 17 May 2024).
- Fernández, M.J.M.; Vivar, D.M. Modelos didácticos y Estrategias de enseñanza en el Espacio Europeo de Educación Superior. Tend. Pedagógicas 2010, 15, 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, E.S. An instructional model for teaching learning strategies. Focus Except. Child. 1991, 23, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, M.T.; Trujillo, A.D.; de Justo Moscardo, E. Un nuevo modelo didáctico para el aprendizaje activo de Estructuras. Jorn. Sobre Innovación Docente En Arquit. JIDA 2017, 5, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Carrasco, C.J.; Molina, J.O.; Martínez, P.M. Enseñar Ciencias Sociales con Métodos Activos de Aprendizaje. Ediciones Octaedro SL. 2018. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10201/137730 (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Roselli, N.D. El aprendizaje colaborativo: Bases teóricas y estrategias aplicables en la enseñanza universitaria. Rev. Propósitos Y Represent. 2016, 4, 219–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez Gutiérrez, E.J. Modelos socioconstructivistas y colaborativos en el uso de las TIC en la formación inicial del profesorado. Rev. Educ. 2012, 358, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M. Aprendizaje basado en proyectos colaborativos. Una experiencia en educación superior. Laurus 2008, 14, 158–180. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza Freire, E.E. El aprendizaje basado en problemas, un reto a la enseñanza superior. Conrado 2021, 17, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Oblitas De Las Casas, K.M. Modelo Didáctico Basado en el Trabajo Colaborativo Para Mejorar el Aprendizaje del Pensamiento lógico en Estudiantes del Nivel Superior. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Cesar Vallejo Chiclayo Perú, Trujillo, Peru, 2020. Available online: https://repositorio.ucv.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.12692/40972/Oblitas_DLCKM.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Grover, R. Multi-disciplinary and inter-disciplinary research. J. Mark.-Focus. Manag. 1996, 1, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, A. Multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary research. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2021, 49, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sampieri, R.; Fernández-Collado, C.; Baptista-Lucio, P. Metodología de la Investigación, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Available online: https://apiperiodico.jalisco.gob.mx/api/sites/periodicooficial.jalisco.gob.mx/files/metodologia_de_la_investigacion_-_roberto_hernandez_sampieri.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Dahl, P. Hypothetico-Deductive Method. Music and Knowledge: A Performer’s Perspective. Brill 2017, 51–61. [CrossRef]
- Moisey, R.N.; McCool, S.F. Sustainable Tourism in the 21st Century: Lessons from the Past, Challenges to Address. Tourism, Recreation and Sustainability: Linking Culture and the Environment; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; pp. 283–291. Available online: https://books.google.es/books?hl=es&lr=&id=huoLBvVw0gkC&oi=fnd&pg=PA283&dq=Sustainable+tourism+for+the+21st+century&ots=Q2236W4rWz&sig=C-ud6iupn4rliPlS7dwnUvMFyJU (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Farid, H.; Hakimian, F.; Nair, V.; Nair, P.K.; Ismail, N. Trend of research on sustainable tourism and climate change in 21st century. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2016, 8, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, M.T.; Portell, M.; Salvador, S.C.M.; Sanduvete-Chaves, S. Indirect observation in everyday contexts: Concepts and methodological guidelines within a mixed methods framework. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 254638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, J.L.L. Research experiences in the application of the Historical-logical research method and the. Analysis of Content qualitative technique in educational research. Dilemas Contemp. Educ. Política Y Valore Año 2017, 1, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Iannone, P.; Nardi, E. On the pedagogical insight of mathematicians: Interaction and ‘transition from the concrete to the abstract’. J. Math. Behav. 2005, 24, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, P. A systemic approach to professional development: Learning as practice. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2002, 18, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.L.; Well, A.D.; Lorch, R.F., Jr. Research Design and Statistical Analysis; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassine, J.; Amyot, D. A questionnaire-based survey methodology for systematically validating goal-oriented models. Requir. Eng. 2016, 21, 285–308. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consejo Universitario de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. Reglamento de Régimen Académico de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. 2021. Available online: https://www.utm.edu.ec/la-universidad/nuestra-universidad/reglamentos?download=1977:reglamento-de-regimen-academico-de-la-universidad-tecnica-de-manabi&start=60 (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Consejo Universitario de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. Reglamento de Evaluación Integral al Desempeño del Personal Académico de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. 2018. Available online: https://www.utm.edu.ec/la-universidad/nuestra-universidad/reglamentos?download=14:reglamento-de-evaluacion-integral-al-desempeno-del-personal-academico (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Bisquerra Alzina, R.; Escoda, N.P. Les escales de Likert poden augmentar en sensibilitat? Rev. D’innovació I Recer. En Educ. 2015, 8, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergel, M.; Vega, O.; Bustos, V.J. Modelo de quíntuple hélice en la generación de ejes estratégicos durante y postpandemia 2020. Rev. Boletín Redipe 2022, 9, 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Barth, T.D.; Campbell, D. The Quintuple Helix innovation model: Global warming as a challenge and driver for innovation. J. Innov. Entrep. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Vergara, M. La teoría de las N-hélices en los tiempos de hoy. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2020, 15, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ciro Romero, D.L. Evaluación de Las Intenciones Ambientales de LOS estudiantes de la Universidad Nacional de Colombia-Sede Bogotá. Tesis de Maestría, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá, Colombia, 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.unal.edu.co/handle/unal/80188 (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Kilroy, D.A. Problem based learning. Emerg. Med. J. 2004, 21, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.; Jonassen, D.H.; Liu, R. Problem-based learning. In Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology; Routledge: London, UK, 2008; pp. 485–506. [Google Scholar]
- Dooley, K.E. Hacia un modelo holístico para la difusión de tecnologías educativas: Una revisión integradora de los estudios de innovación educativa. Rev. Tecnol. Y Soc. Educ. 1999, 2, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera-Esparza, Z.A.; Mosquera-Esparza, M.E.; Suárez-Monzón, N. Estrategias para la mejora de la gestión de la innovación didáctica en los docentes de la Unidad Educativa “Los Andes”. Rev. Metrop. Cienc. Apl. 2023, 6, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Juárez-Ibarra, Gerónimo. El rol del docente ante un ambiente innovador de aprendizaje en escuelas y facultades de negocios. El caso de la: Facultad de Administración y Contaduría. Fuentes 2018, 878, 56–65.
- Orihuela Gallardo, F.; Casanova, C.C.S. Una experiencia de innovación docente: El debate académico en Administración de Empresas. Rev. Estud. Socioeducativos 2020, 8, 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Molina Ruiz, E. Creación y desarrollo de comunidades de aprendizaje: Hacia la mejora educativa. Rev. Educ. 2005, 337, 235–250. [Google Scholar]

| Level | Integrative Subject | Significant Elements Resulting from the Research |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Introduction to the Tourism System | Argue from theoretical, methodological and epistemological assumptions the relationship that exists between the components that are part of the tourism system for the establishment of cause-effect relationships. |
| 2nd | Tourist Geography of Ecuador | Compare differences and similarities of the regions and tourist destinations of Ecuador, emphasizing geographical location, resources and attractions. |
| 3rd | Tourist Modalities I | Diagnose the processes and sub-processes of tourism exploitation related to accommodation, apartments and restaurants based on case studies linked to the community in the tourism modalities studied. |
| 4th | Regional and Ecuadorian Cuisine | Apply basic techniques and preparations in food preparation in regional and Ecuadorian cuisine. |
| 5th | Tourist Modalities II | Diagnose, from the case study linked to the community, the tourism modalities II that are studied, the processes and sub-processes of tourist operation related to recreation, tourist entertainment and bar service. |
| 6th | Quality Management in Tourism | Apply the standards, tools and techniques used in quality management in tourism companies and their statistical foundations. |
| 7th | Integrated Management of Tourist Destinations | Apply the main tools and good practices on the integrated strategic planning and management of sustainable tourist destinations. |
| 8th | Sustainable Tourism Ventures | Design and execute sustainable tourism ventures in the areas of social and community tourism. |
| Teaching Work Procedures | ||
|---|---|---|
| Types of Procedure | Activities | Instruments |
| Panels. | Network meetings. | Study of tourist communities. |
| Round tables. | Problem-based learning. | Presentation and evaluation of tourist services and products. |
| Debates. | Interinstitutional scientific meetings. | Checklists and process audits. |
| Forums. | Pre-professional guided scientific visits. | Verification of standards and procedure manuals. |
| Seminars. | Link with the community. | Inventories of resources and tourist attractions. |
| Discussion groups. | Video filming. | Degree projects. |
| Conversations. | Competencies and display of skills of various operational processes. | Visits to museums and work centers, tourist routes and guided tours of cultural and natural heritage. |
| Conferences. | Practical classes to develop skills. | Process monitoring. |
| Virtual tutorials. | Experimentation projects. | Presentation of papers. |
| Case studies. | Community linkage projects. | Participatory diagnoses. |
| Meetings with clients, familiarization groups, FAM and travel agents. | Evaluation of satisfaction rates. | Monitoring and feedback in destinations, hotels and restaurants in tourist sites. |
| Application of survey systems and feedback systems. | Website design and monitoring. | Study of tourist image in social networks. |
| Market study and research. | Application of integrated project management tools. | Presentation of tourism projects. |
| Creation of ventures. | Application of SWOT matrix and other hotel management tools. | Evaluation of tourism sustainability indicators. |
| Practical application in different tourism modalities with emphasis on sustainable tourism. | Study of good international practices in sustainable tourism. | Poster presentation. |
| Items | Sample | La | OK (4 Points) | I Have No Opinion (3 Points) | In Disagreement (2 Points) | Strongly Disagree (1 Point) | Total Points | Arithmetic Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 102 | 85 | 15 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 489 | 4.79 |
| 2 | 102 | 78 | 10 | 2 | 8 | 4 | 454 | 4.45 |
| 3 | 102 | 4 | 13 | 7 | 20 | 58 | 191 | 1.87 |
| 4 | 102 | 84 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 476 | 4.66 |
| 5 | 102 | 79 | 15 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 469 | 4.59 |
| 6 | 102 | 80 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 467 | 4.57 |
| 7 | 102 | 75 | 16 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 459 | 4.50 |
| 8 | 102 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 88 | 125 | 1.22 |
| 9 | 102 | 86 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 483 | 4.73 |
| 10 | 102 | 83 | 15 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 482 | 4.72 |
| 11 | 102 | 84 | 14 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 482 | 4.72 |
| 12 | 102 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 83 | 132 | 1.29 |
| 13 | 102 | 81 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 466 | 4.56 |
| 14 | 102 | 88 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 486 | 4.76 |
| 15 | 102 | 80 | 11 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 466 | 4.56 |
| Items | Elderly Punctuation | Minor Punctuation | Average of the Scores of the 5 Items |
|---|---|---|---|
| Items 1 to 5 (Learning in contact with the teacher) | 4.79 | 1.87 | 4.07 |
| Items 6 to 10 (Autonomous learning) | 4.73 | 1.22 | 3.94 |
| Items 11 to 15 (Experimental practical learning) | 4.76 | 1.29 | 3.97 |
| Evaluated Competencies | Evaluated Periods | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2021– February 2022 | May 2022– September 2022 | October 2022– February 2023 | May 2023– September 2023 | October 2023– January 2024 | |
| Mastery of the contents of the subject. | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.3 | 4.5 |
| Teaching methodologies used. | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 4.8 |
| Use of new information and communication techniques. | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Exercise of tutoring and evaluation of learning. | 3.9 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4.8 | 5.0 |
| Ethical attitudes and interpersonal relationships. | 4.3 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelegrín Entenza, N.; Naranjo Llupart, M.R.; Ruiz Cedeño, S.d.M.; Vázquez Pérez, A. Teaching Innovation and Teaching–Learning Methods for Sustainable Tourism Development Education in the Bachelor of Tourism Degree. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8115. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188115
Pelegrín Entenza N, Naranjo Llupart MR, Ruiz Cedeño SdM, Vázquez Pérez A. Teaching Innovation and Teaching–Learning Methods for Sustainable Tourism Development Education in the Bachelor of Tourism Degree. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):8115. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188115
Chicago/Turabian StylePelegrín Entenza, Norberto, María Rosa Naranjo Llupart, Sebastiana del Monserrate Ruiz Cedeño, and Antonio Vázquez Pérez. 2024. "Teaching Innovation and Teaching–Learning Methods for Sustainable Tourism Development Education in the Bachelor of Tourism Degree" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 8115. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188115
APA StylePelegrín Entenza, N., Naranjo Llupart, M. R., Ruiz Cedeño, S. d. M., & Vázquez Pérez, A. (2024). Teaching Innovation and Teaching–Learning Methods for Sustainable Tourism Development Education in the Bachelor of Tourism Degree. Sustainability, 16(18), 8115. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188115






