Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
2.1.1. Adsorbents Preparation
2.1.2. XRD Characterization
2.1.3. SEM and EDX Analysis for ZR
2.1.4. Zero-Point Charge for Adsorbents
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.2.1. Experiments Development
2.2.2. Mathematical Models for Characterization the Equilibrium of Adsorption Processes
2.2.3. Mathematical Models for Characterization the Kinetic of Adsorption Processes
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
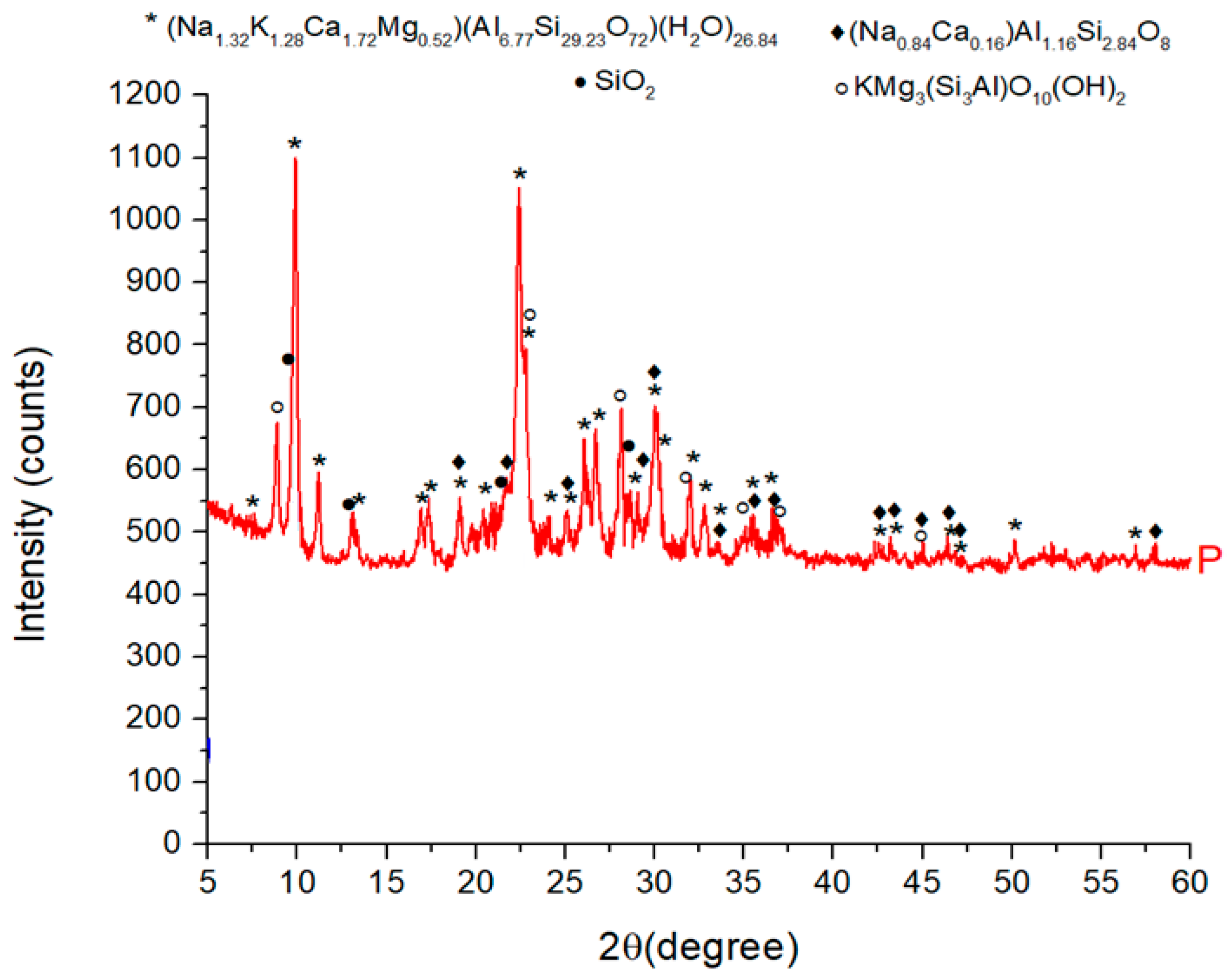
3.1.1. Mineralogical Structure of ZR, XRD Characterization
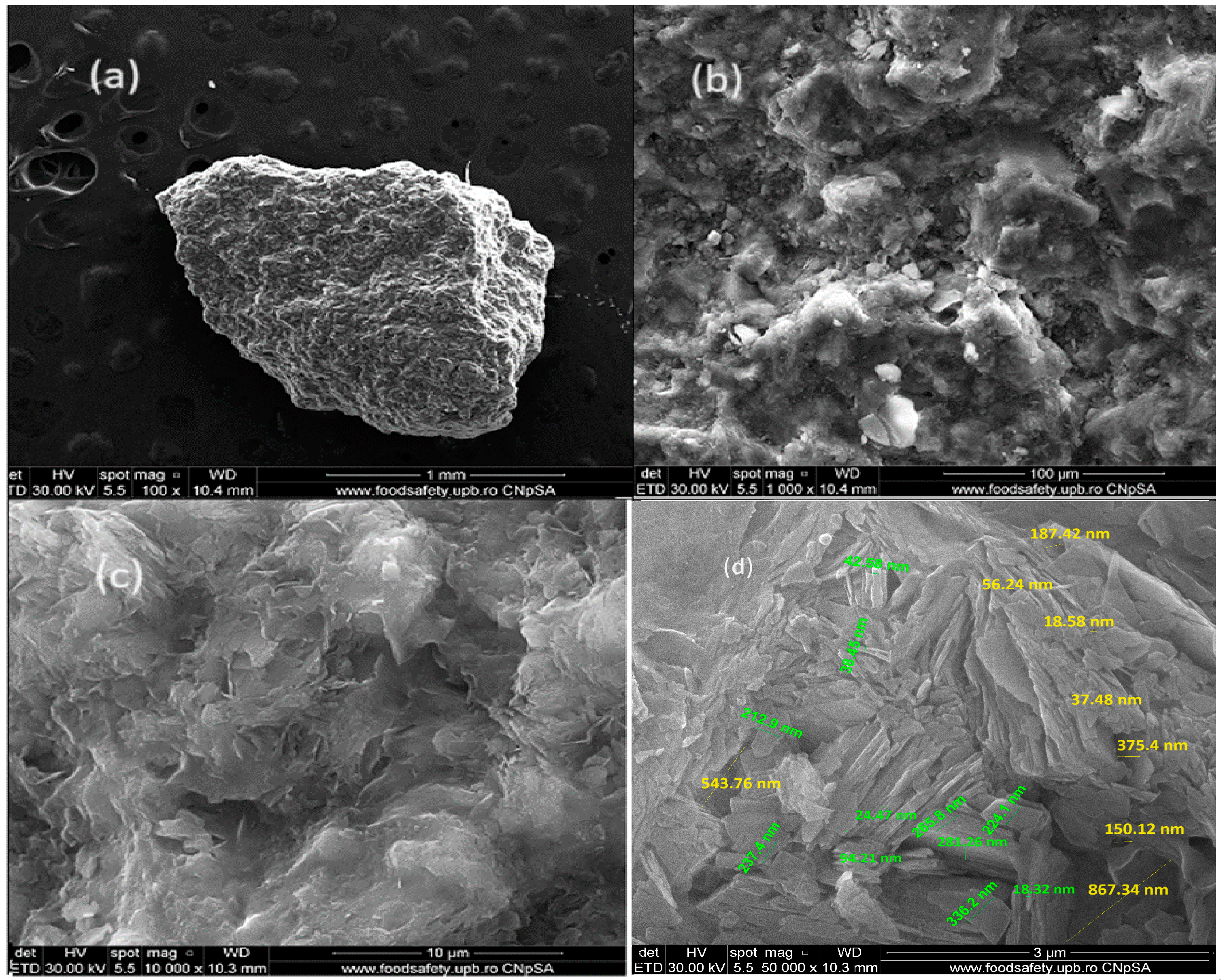
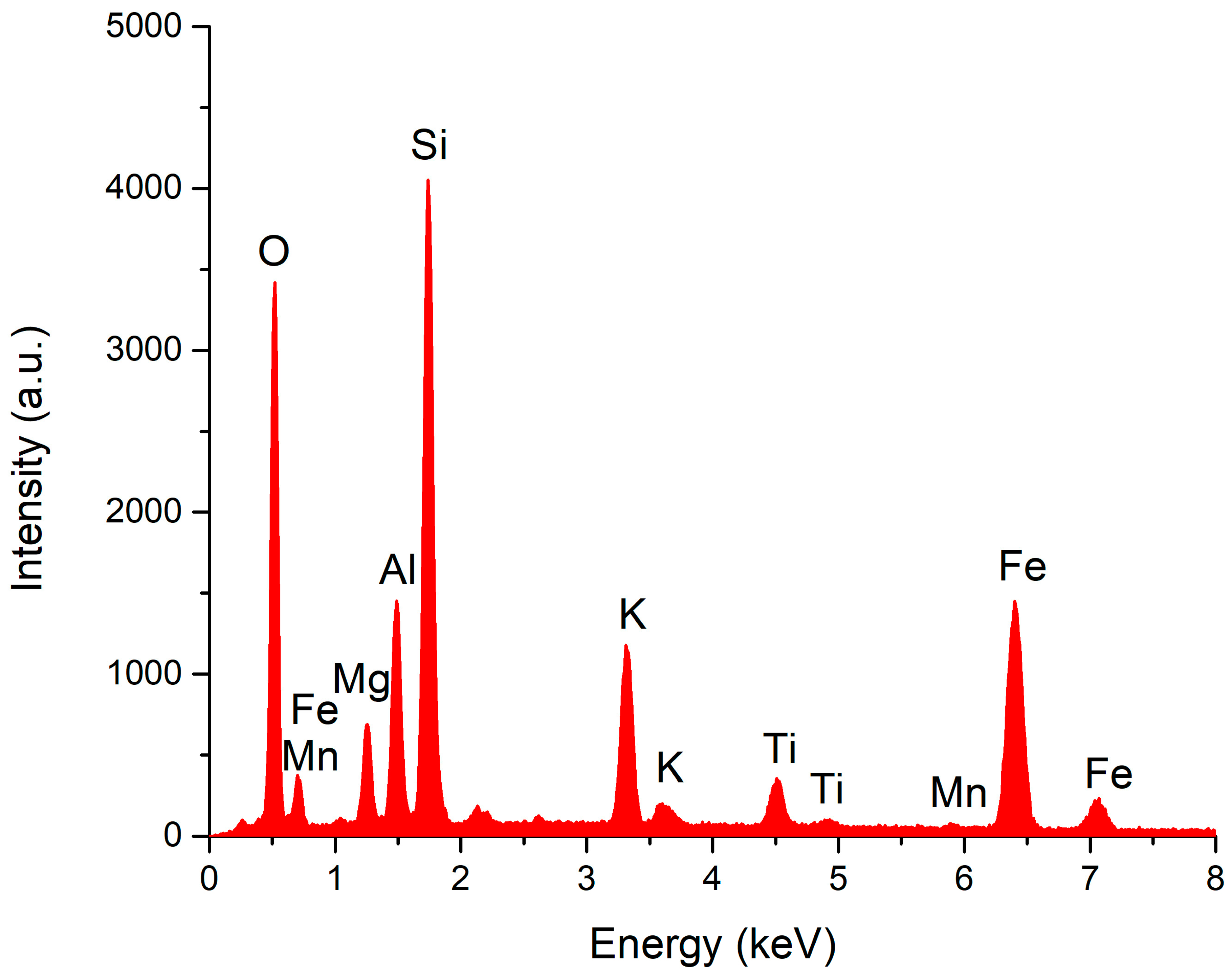
3.1.2. SEM and EDX Analysis for ZR
3.1.3. Zero-Point Charge, pHZPC, for Adsorbents
3.2. Adsorption Process
3.2.1. Equilibrium of Adsorption
Isotherm of Adsorption
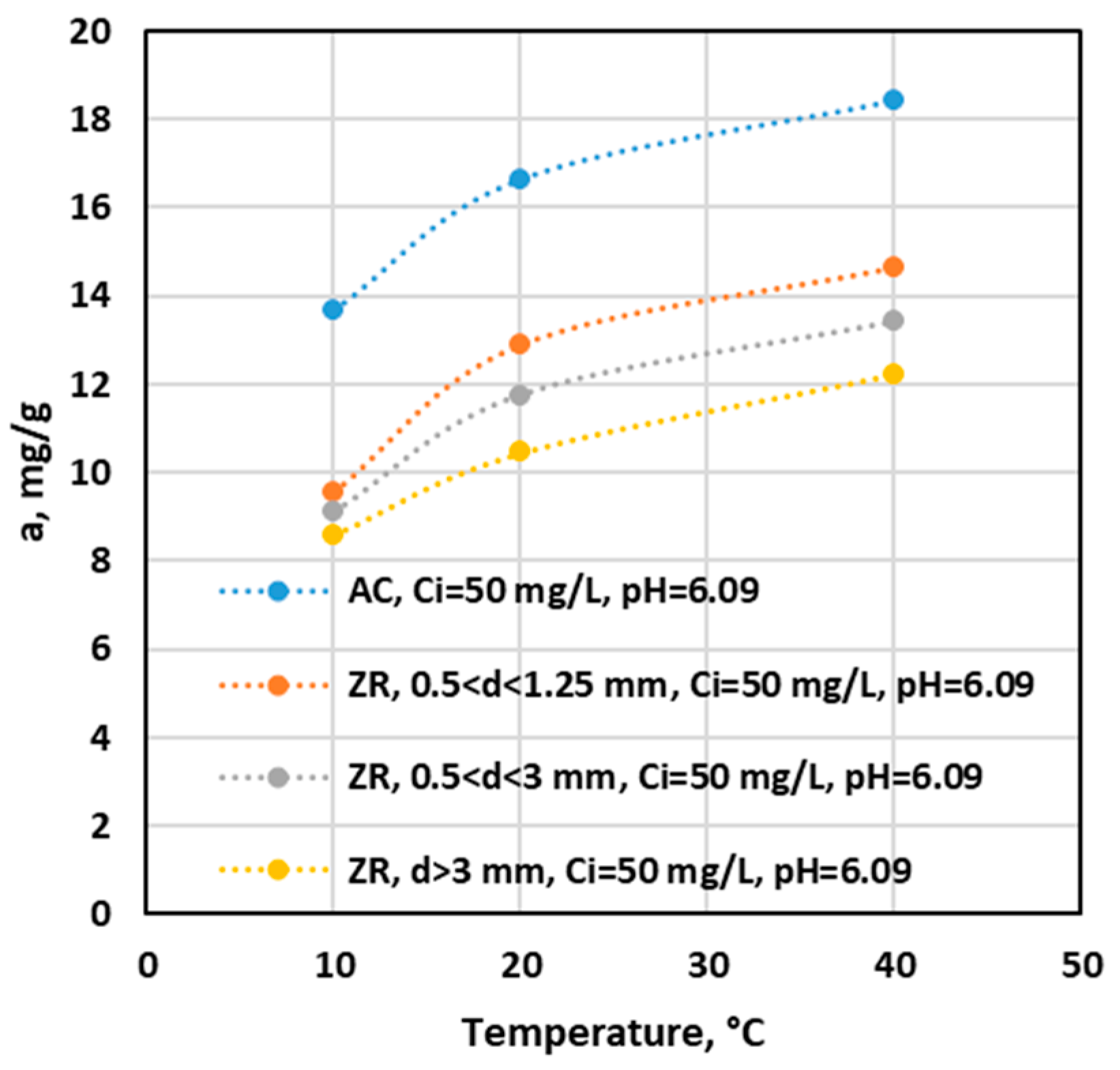
Influence of Temperature
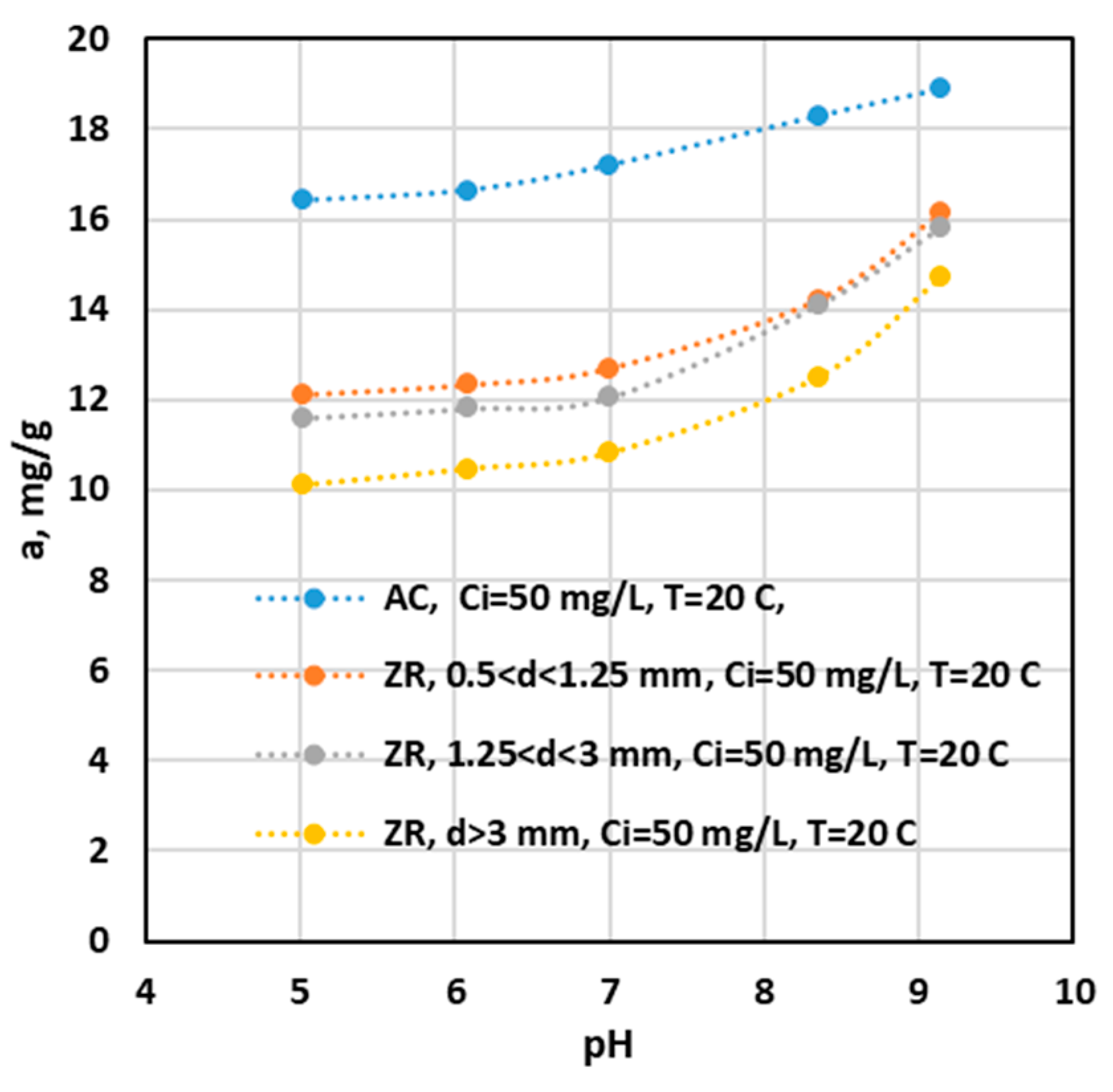
Influence of pH
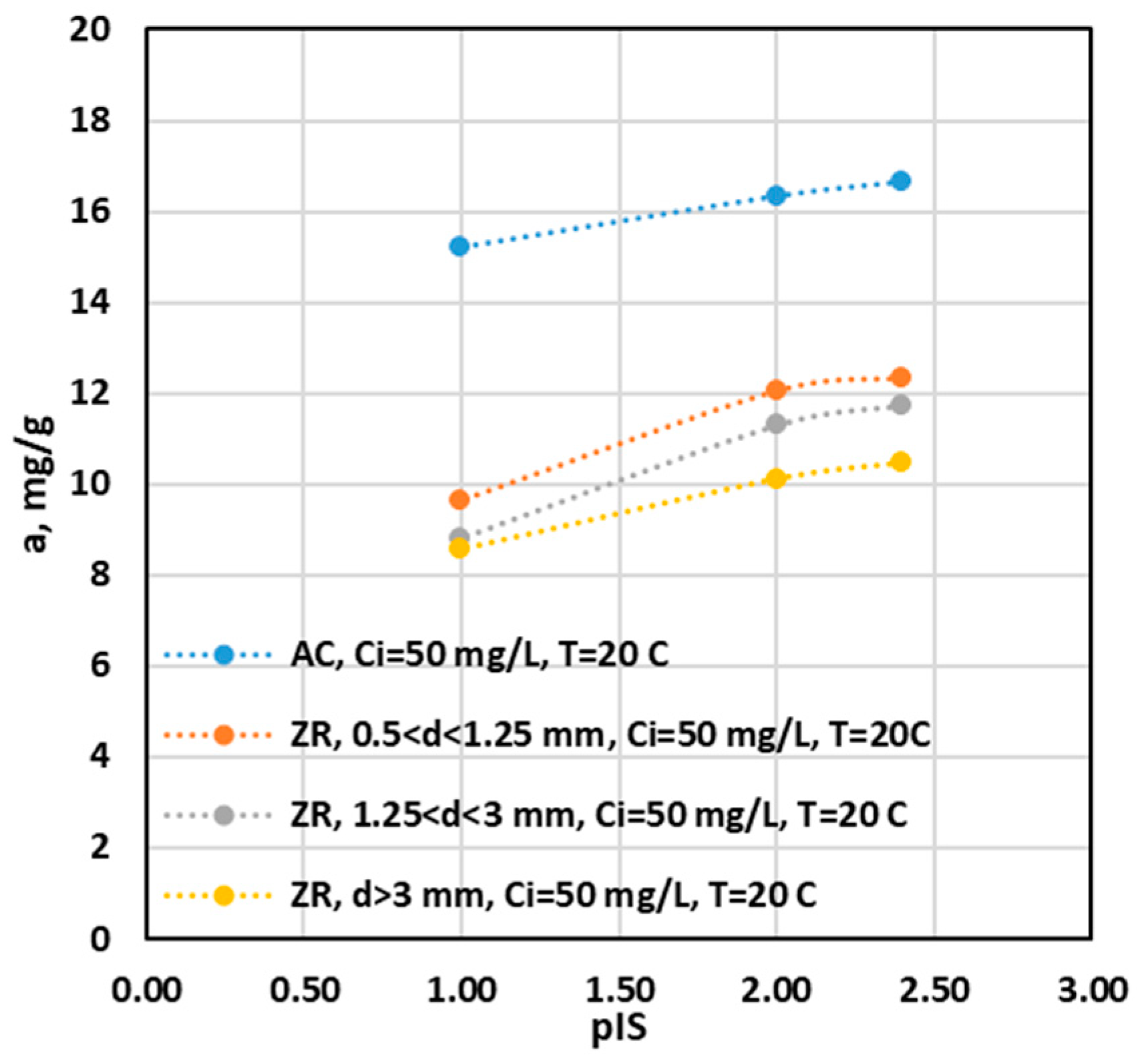
Influence of Ionic Strength
3.3. Kinetic of Adsorption
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Wu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; Jing, L.; Yu, P. Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the Southeastern Edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kankanamge, N.R.; Chow, C.; Welsh, D.T.; Li, T.; Teasdale, P.R. Removing ammonium from water and wastewater using cost-effective adsorbents: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, T.H.; Ștefan, D.S.; Pauna, G.; Ștefan, M. Study of the effectiveness of membrane aeration systems on the removal of ammonium ions from natural waters. U.P.B. Sci. Bull. Ser. B 2024, 86, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, G.; Luo, C.; Zhou, P. Groundwater nitrogen pollution and assessment of its health risks: A case study of a typical village in rural-urban continuum, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M. Application of Nanoporous Zeolites for the Removal of Ammonium from Wastewaters: A Review, Low-Dimensional and Nanostructured Materials and Devices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 477–504. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathy, R.; Karthikeyan, S.; Mandal, A.B.; Sekaran, G. Adsorption of Ammonium Ion by Coconut Shell-Activated, Carbon From Aqueous Solution: Kinetic, Isotherm, and Thermodynamic Studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Charan, S.S.; Pallavi, U.; Sreenivasulu, A.; Haripavan, N. The removal of ammonia from contaminated water by using various solid waste biosorbents. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, M.; Duta, A.; Teodosiu, C.; Draghici, C. Thermodynamic and kinetic study on ammonium removal from a synthetic water solution using ion exchange resin. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2014, 16, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Sadegh, H.; Yari, M.; Shahryari Ghoshekandi, R.; Maazinejad, B.; Chahardori, M. Removal of ammonium ions from wastewater: A short review in development of efficient methods. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2015, 1, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H. The mechanisms of ozonation for ammonia nitrogen removal: An indirect process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.; Hashemi, H.; Wu, H.; Glarborg, P. Study of Ammonia Oxidation with Ozone Addition. Appl. Energy Combust. Sci. 2023, 14, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; He, D.; Ma, J.; Waite, T.D. Active chlorine mediated ammonia oxidation revisited: Reaction mechanism, kinetic modelling and implications. Water Res. 2018, 145, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; He, C.; Yin, R.; Liu, J.; Qiu, T. Ultrasound-Enhanced Catalytic Ozonation Oxidation of Ammonia in Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Environ. Res. And. Public Health 2019, 16, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodalo, A.; Gomez, J.-L.; Gomez, E.; Leon Gerardo Tejera, M. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Reverse Osmosis Using Cellulose Acetate Membranes. Desalination 2005, 184, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Zhou, A.; Ye, F.; Xue, S.; Yue, X. Ammonia-nitrogen removal from water with gC3N4-rGO-TiO2 Z-scheme system via photocatalytic nitrification-denitrification process. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Shan, D.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Teng, Y. Distribution, genesis, and pollution risk of ammonium nitrogen in groundwater in an arid loess plain, northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potting, J.; Hekkert, M.; Worrell, E.; Hanemaaijer, A. Report Circular Economy: Measuring Innovation in the Product Chain, Policy Report January 2017; PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hungaro Arruda, E.; Brancalhão Melatto, R.A.P.; Levy, W.; Conti, D. Circular economy: A brief literature review (2015–2020). Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2021, 2, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Butterly, C.; Zhang, W.; Zheng He, J.; Chen, D. Adsorbent Materials For Ammonium and Ammonia Removal: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 283, 124611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Esmhosseini, M.; Khezri, S. Removal of Ammonium Ion from Aqueous Solutions Using Natural Zeolite: Kinetic, Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Studies. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 2905–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; Winnett, A.; Thompson, T.; Couperthwaite, S.J. Equilibrium Studies of Ammonium Exchange with Australian Natural Zeolites. J. Water Process. Eng. 2016, 9, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.N.; Swayze, G.A.; Gallagher, A.J.; King, T.V.; Calvin, W.M. The US Geological Survey, Digital Spectral Library, Version 1 (0.2 to 3.0 um); Geological Survey (US): Reston, VA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Directive EU 2020/2184 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (Recast) 2020, Drinking Water—Essential Quality Standards; europa.eu; Council of European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 Concerning Urban Waste-Water Treatment; Directive-91/271-EN-EUR-Lex; europa.eu; Council of European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1991.
- Council of European Union. Interinstitutional File: 2022/0345(Cod, Proposal for A Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment 2022; Recast; Pdf, Europa.Eu; Council of European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lurie, I.I. Director of Analytical Chemistry; Technical Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 1970; pp. 250–252. [Google Scholar]
- Aziam, R.; Stefan, D.S.; Nouaa, S.; Chiban MAnd Bosomoiu, M. Adsorption of metal ions from single and binary aqueous systems on bio-nanocomposite, alginate-clay. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 362–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngenoa, E.C.; Shikukua, V.O.; Orataa, B.F.; Barazaa, L.D.; Kimosopa, S.J. Caffeine and Ciprofloxacin Adsorption from Water Onto Clinoptilolite: Linear Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamic and Mechanistic Studies. Shouth Afr. Chem. 2019, 72, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Kinetic Models: Physical Meanings, Applications, and Solving Methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dura, A.M.; Stefan, D.S.; Chiriac, F.L.; Trusca, R.; Nicoara, A.I.; Stefan, M. Clinoptilolite—A Sustainable Material for the Removal of Bisphenol A from Water. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norit Gac 830 W: Datasheet. Specification (Technical Standard). Carbon. Norit Gac 830 W: Datasheet | PDF | Specification. Available online: https://www.linkengineers.net/assets/pdf/GAC_830_W_Chemicals.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Bulushev, D.A.; Yuranov, I. Noble Metal Nanoparticles on Carbon Fibers. In Dekker Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 3195–3205. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280943506_Noble_Metal_Nanoparticles_on_Carbon_Fibers#fullTextFileContent (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Cotton, A. Research article Dissolution kinetics of clinoptilolite and heulandite in alkaline conditions. Biohorizons 2008, 1, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, M.T.; Latif, A.I. Ammonia Removal from Aqueous, Solution Using Organic Acid Modified Activated Carbon. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lin, F.; Pang, W.Q. Ammonium Exchange n Aqueous Solution Using Chinese Natural Clinoptilolite and Modified eolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Natural Iranian Zeolite in the Presence of organic Acids, Cations and Anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañón, E.; Ulmanu, M.; Fernández, Y.; Anger, I.; Castrillón, L. Removal of Ammonium from Aqueous Solutions with Volcanic Tuff. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.; Ramarao, B.V. Further Examination of the Relationship Between th Langmuir Kinetics and the Lagergren and the Second-Order Rate Models of Batch Adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsi, R.R.; Abou-El-Sherbini, K.S.; El-Dein, W.A.S.; Lotfy, H.R. R. Activated eco-waste of Posidonia oceanica rhizome as a potential adsorbent of methylene blue from saline water. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 2529–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherley, L.R.; Miladinovic, N.D. Comparison of the Ion Exchange Uptake of Ammonium Ion Onto New Zealand Clinoptilolite and Mordenite. Water Resour. 2004, 38, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Isotherm Model | Form Type | Mathematic Relations | Parameters Signification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | NL | —adsorption capacity, mg/g; Ce—equilibrium concentration, mg/L; L—maximum adsorption capacity, mg/g; KL—Langmuir constant, L/mg. | |
| L | |||
| Freundlich | NL | ae—adsorption capacity, mg/g; Ce—equilibrium concentration, mg/L; KF—Freundlich constant, mg/g; n—empirical constant related to heterogeneity of the adsorbent surface. | |
| L | |||
| Temkin | NL | T—temperature, K; R—universal gas constant, 8.314, J·mol−1K−1; bT—Temkin isotherm constant related to the heat of adsorption, J/mol; KT—equilibrium constant for the maximum binding energy, L/mg. | |
| L | |||
| Dubinin–Radushkevich. | NL | am—maximum adsorption capacity, mg/g; ε—Polanyi potential that can be calculated from Equation (10); Ce—equilibrium concentration, mg/L; KD—constant, (mol2 J–2). | |
| L | E= |
| Kinetic Model | Form Type | Mathematic Relations | Parameters Signification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first order | NL | am—adsorption capacity at equilibrium, mg/g; at—adsorption capacity at moment t, mg/g; k2—rate constant for the pseudo-first order kinetics model, (g·mg−1min−1); t—contact time t, min. | |
| L | |||
| `Pseudo-Second order | NL | am—adsorption capacity, mg/g; at—adsorption capacity at moment t, mg/g; k2—rate constant for the pseudo-second order kinetics model, g·mg−1min−1; t—contact time t, min. | |
| L | |||
| Elovich | NL | at -adsorption capacity at time t, mg/g; t—time, minute; α—initial adsorption rate, mg·g−1min−1; β—desorption constant, g·mg−1. | |
| L | |||
| Intra-particle diffusion | L | KID—intra-particle diffusion rate constant, mg−1·min1/2; cID—ammonium concentration, mg/L; at—adsorption capacity at moment t, mg/g; t—contact time, minutes. |
| No. | Compound | Crystallographic Formula | Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clinoptilolite Ca | (Na1.32K1.28Ca1.72Mg0.52)(Al6.77Si29.23O72)(H2O)26.84 | 81.0 |
| 2 | Phlogopite-1M | (KMg3Si3AlO10(OH)2) | 11.5 |
| 3 | Albite | (Na0.84Ca0.16)Al1.16Si2.84O8 | 5.4 |
| 4 | Quartz | SiO2 | 2.1 |
| Element | Weight % | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|
| O | 52.54 | 66.94 |
| Na | 0.39 | 0.35 |
| Mg | 0.52 | 0.44 |
| Al | 6.97 | 5.27 |
| Si | 32.81 | 23.81 |
| K | 2.52 | 1.32 |
| Ca | 2.32 | 1.18 |
| Fe | 1.92 | 0.7 |
| Model | Parameters | Adsorbents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC GAC | ZR 0.5 < d,1.25 mm | ZR 1.25 < d < 3 mm | ZR d > 3 mm | ||
| Langmuir | aL(mg/g) | 15.22 | 11.99 | 9.50 | 11.04 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.34 | 0.13 | |
| R2 | 0.990 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.970 | |
| Freundlich | 1/n | 0.251 | 0.632 | 0.630 | 0.757 |
| KF (mg/g) | 2.21 | 2.04 | 1.726 | 1.031 | |
| R2 | 0.899 | 0.917 | 0.936 | 0.948 | |
| Temkin | KT (L·mg–1) | 0.0027 | 0.01 | 0.0225 | 0.07 |
| bT (J·mol–1) | 8323.21 | 6328.9 | 5724.2 | 5644.1 | |
| R2 | 0.829 | 0.898 | 0.897 | 0.857 | |
| D-R | KD (mol2·J–1) | 1.43 | 1.42 | 1.43 | 0.3 |
| am (mg/g)) | 9.41 | 7.95 | 7.09 | 9.74 | |
| E (J·mol−1) | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 1.58 | |
| R2 | 0.825 | 0.854 | 0.845 | 0.812 | |
| Dimensionless Constant | Ammonium | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAC | ZR 0.5 < d < 1.25 mm | ZR 1.25 < d < 3 mm | ZR d > 3 mm | |
| RL | 0.5806 | 0.5373 | 0.5142 | 0.7346 |
| Kinetics Model | Parameters | Adsorbents | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC GAC | ZR 0.5 < d < 1.25 mm | ZR 1.25 < d < 3 mm | ZR d > 3 mm | ||
| Pseudo-first order model | am,exp (mg/g) | 16.64 | 12.20 | 9.876 | 8.26 |
| K1 (min−1) | 2.75 | 0.0051 | 0.04 | 0.034 | |
| am,cal (mg/g) | 12.97 | 7.84 | 7.042 | 6.59 | |
| R2 | 0.990 | 0.875 | 0.945 | 0.976 | |
| Pseudo-second order model | am,exp (mg/g) | 16.64 | 12.20 | 9.876 | 8.264 |
| K2 (g·mg−1min−1) | 0.018 | 0.056 | 0.043 | 0.036 | |
| am,cal (mg/g) | 14.1 | 12.24 | 9.794 | 8.21 | |
| R2 | 0.964 | 0.999 | 0.9985 | 0.995 | |
| Elovich model | am,exp (mg/g) | 16.64 | 12.20 | 9.876 | 8.264 |
| α | 0.0063 | 0.0026 | 0.018 | 0.018 | |
| β | 6.834 | 1.63 | 1.32 | 1.32 | |
| R2 | 0.984 | 0.941 | 0.951 | 0.951 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion | KInt (mg·g−1min−1/2) | 0.2384 | 1.21 | 0.97 | 0.74 |
| CI | 0.671 | 2.43 | 1.2 | 1.3 | |
| R2 | 0.943 | 0.790 | 0.895 | 0.947 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abed, T.H.; Stefan, D.S.; Berger, D.C.; Marinescu, N.C.; Stefan, M. Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7888. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187888
Abed TH, Stefan DS, Berger DC, Marinescu NC, Stefan M. Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):7888. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187888
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbed, Thaaer Hameed, Daniela Simina Stefan, Daniela Cristina Berger, Nicolaie Cicerone Marinescu, and Mircea Stefan. 2024. "Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 7888. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187888
APA StyleAbed, T. H., Stefan, D. S., Berger, D. C., Marinescu, N. C., & Stefan, M. (2024). Performance Evaluation of a Romanian Zeolite: A Sustainable Material for Removing Ammonium Ions from Water. Sustainability, 16(18), 7888. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187888








