Subsurface Drainage and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Affect Fertilizer Fate in Claypan Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Design
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.2.1. Gas Emission Measurements
2.2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2.3. Water Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
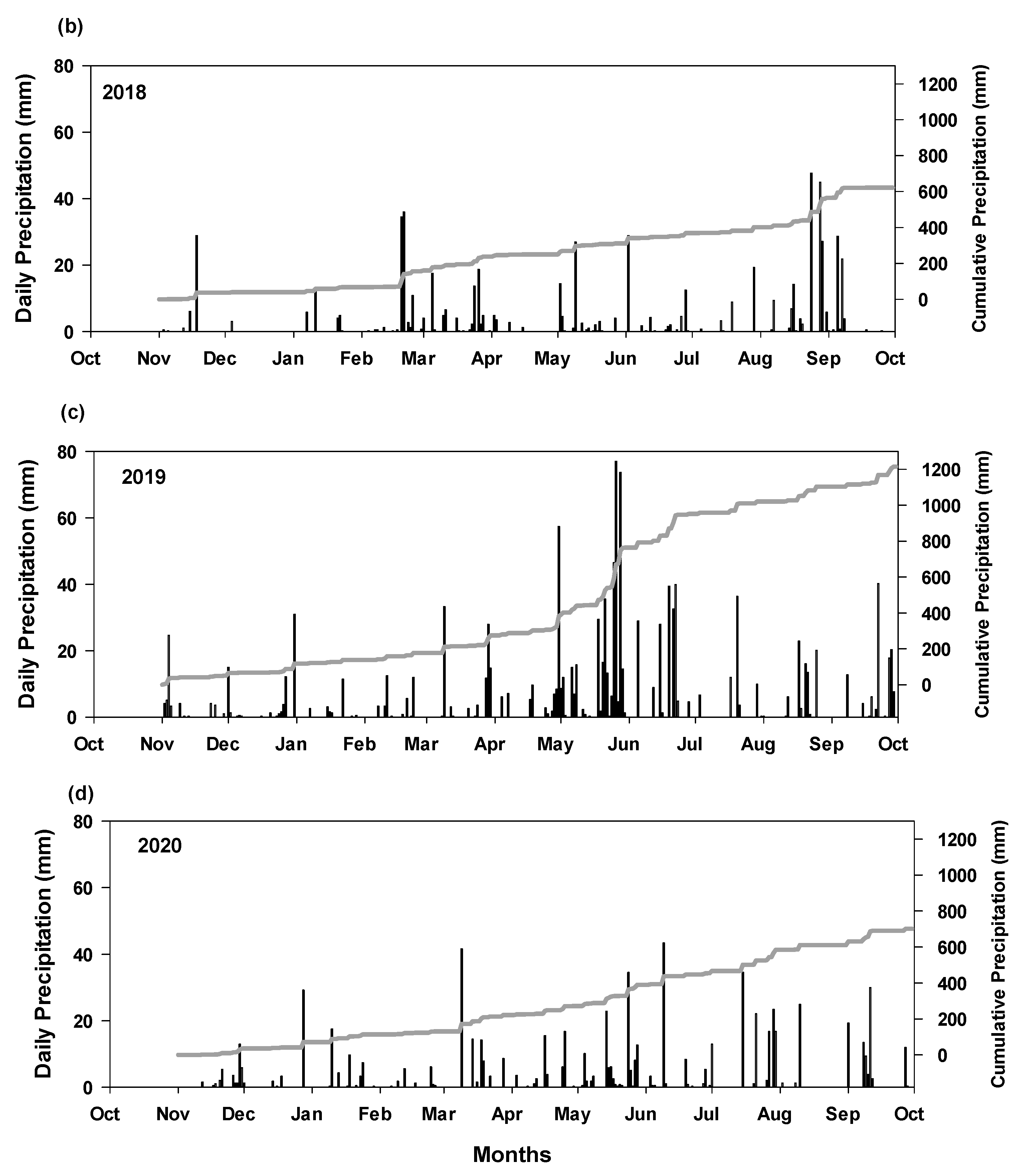
3.1. Weather
3.2. Nutrient Loss in Subsurface Drainage Water
3.2.1. Corn Season
3.2.2. Soybean Season
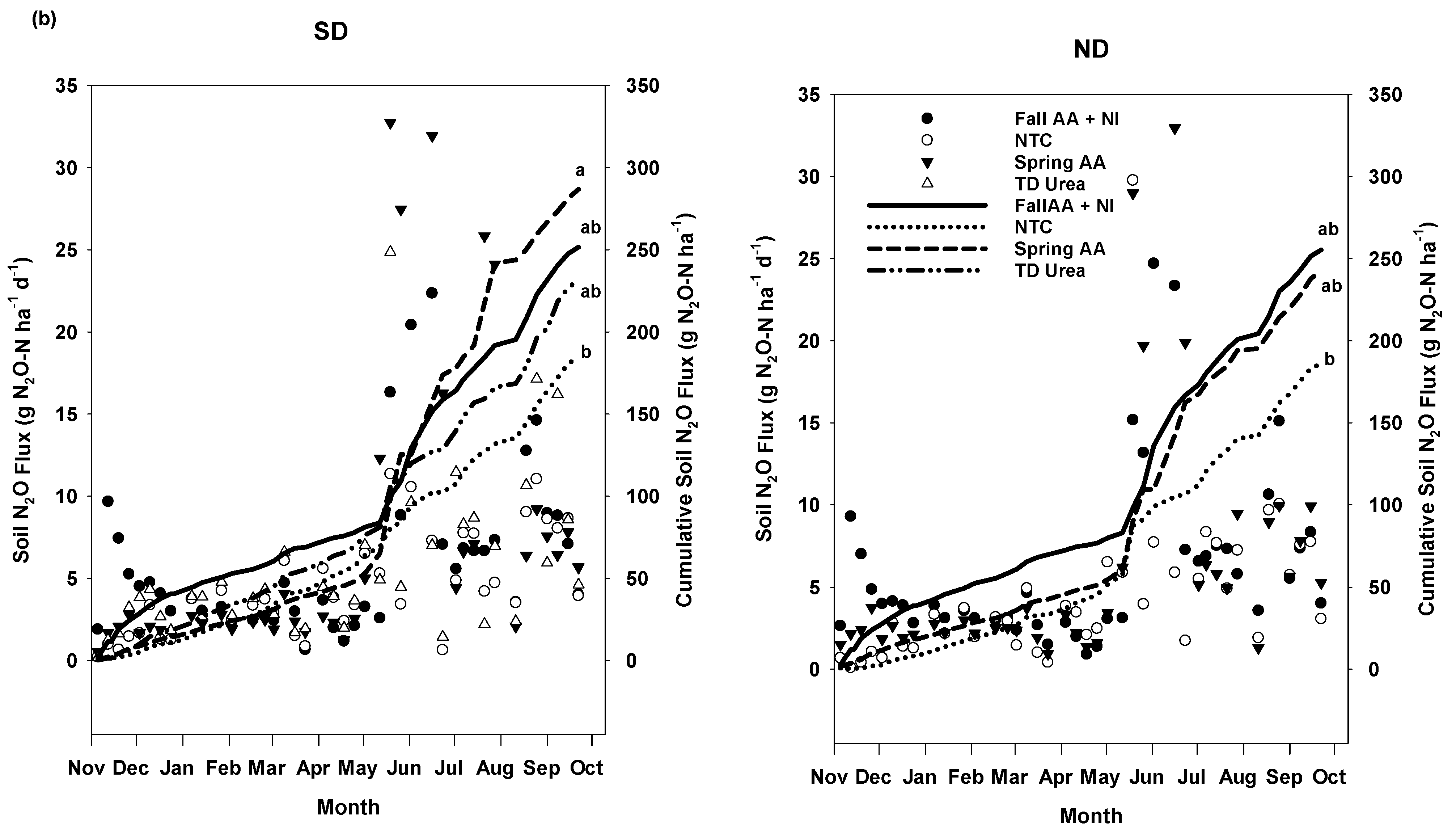
3.3. Soil Nitrous Oxide Flux and Cumulative Emissions
Corn Season
3.4. Soybean Season
3.5. Yield-Scaled N2O Loss
3.6. Ammonia Volatilization and Cumulative Losses
3.6.1. Corn Season
3.6.2. Soybean Season
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharratt, B.S.; Zandlo, J.; Spoden, G. Frequency of Precipitation across the Northern U.S. Corn Belt. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarecki, M.K.; Hatfield, J.L.; Barbour, W. Modeled Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn Fields in Iowa Based on County Level Data. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebilo, M.; Mayer, B.; Nicolardot, B.; Pinay, G.; Mariotti, A. Long-term fate of nitrate fertilizer in agricultural soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18185–18189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, C.; Reynolds, W.; Parkin, G.; Lauzon, J.; Saso, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, X.; Tan, C.; Liu, K.; Calder, W.; et al. Solute dynamics and the Ontario nitrogen index: II. Nitrate leaching. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 96, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.; Reynolds, W.D.; Calder, W.; Oloya, T.O.; Woodley, A.L. Combining Urease and Nitrification Inhibitors with Incorporation Reduces Ammonia and Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Increases Corn Yields. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodley, A.L.; Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Phillips, L.A.; Reynolds, D.W.; Calder, W.; Oloya, T.O. Ammonia volatilization, nitrous oxide emissions, and corn yields as influenced by nitrogen placement and enhanced efficiency fertilizers. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, D.S.; Davidson, E.A.; Smith, K.A.; Smith, P.; Melillo, J.M.; Dentener, F.; Crutzen, P.J. Global agriculture and nitrous oxide emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbak, I.; Millar, N.; Robertson, G.P. Global metaanalysis of the nonlinear response of soil nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions to fertilizer nitrogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9199–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moal, M.; Gascuel-Odoux, C.; Ménesguen, A.; Souchon, Y.; Étrillard, C.; Levain, A.; Moatar, F.; Pannard, A.; Souchu, P.; Lefebvre, A.; et al. Eutrophication: A new wine in an old bottle? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8657–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blann, K.L.; Anderson, J.L.; Sands, G.R.; Vondracek, B. Effects of Agricultural Drainage on Aquatic Ecosystems: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 909–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Brevé, M.A.; Gilliam, J.W. Hydrologic and water quality impacts of agricultural drainage∗. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flis, S. The 4Rs in crop nitrogen research. Crop. Soils 2017, 50, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, D.L.; Karlen, D.L.; Jaynes, D.B.; Kaspar, T.C.; Hatfield, J.L.; Colvin, T.S.; Cambardella, C.A. Nitrogen Management Strategies to Reduce Nitrate Leaching in Tile-Drained Midwestern Soils. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, L.E.; Harmel, R.D. 4R Water Quality Impacts: An Assessment and Synthesis of Forty Years of Drainage Nitrogen Losses. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1852–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, G.P.; Vitousek, P.M. Nitrogen in Agriculture: Balancing the Cost of an Essential Resource. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Adhikari, R.; Casey, P.; Muster, T.; Gill, H.; Adhikari, B. Enhanced efficiency fertilisers: A review of formulation and nutrient release patterns. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolt, J.D. A meta-evaluation of nitrapyrin agronomic and environmental effectiveness with emphasis on corn production in the Midwestern USA. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2004, 69, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittelkow, C.M.; Clover, M.W.; Hoeft, R.G.; Nafziger, E.D.; Warren, J.J.; Gonzini, L.C.; Greer, K.D. Tile Drainage Nitrate Losses and Corn Yield Response to Fall and Spring Nitrogen Management. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetsch, J.A.; Randall, G.W.; Fernández, F.G. Nitrate Loss in Subsurface Drainage from a Corn–Soybean Rotation as Affected by Nitrogen Rate and Nitrapyrin. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.; Chatterjee, A.; Awale, R.; McGranahan, D.A.; Daigh, A. Effect of Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers on Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Crop Yields: A Meta-analysis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Yan, X.; Xiong, Z. Mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from paddy soil under conventional and no-till practices using nitrification inhibitors during the winter wheat-growing season. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 49, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of effectiveness of enhanced-efficiency fertilizers as mitigation options for N2O and NO emissions from agricultural soils: Meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-G.; Saggar, S.; Roudier, P. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on soil ammonia emissions in nitrogen managed soils: A meta-analysis. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2012, 93, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Suter, H.; Mosier, A.R.; Chen, D. Using nitrification inhibitors to mitigate agricultural N2O emission: A double-edged sword? Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M. Fertilizer sources for irrigated corn. In Fertilizer Sources for Irrigated Corn; International Plant Nutrition Institute: Peachtree Corners, GA, USA, 2008; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Alluvione, F. Nitrogen Source Effects on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Irrigated No-Till Corn. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1554–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Alluvione, F. Tillage and Inorganic Nitrogen Source Effects on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Irrigated Cropping Systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, S.G.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Denmead, O. Ammonia Emission from Mineral Fertilizers and Fertilized Crops. Adv. Agron. 2004, 82, 557–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.A.; Scharf, P.C.; Bundy, L.G.; Tracy, P. Agricultural Management of Enhanced-Efficiency Fertilizers in the North-Central United States. Crop Manag. 2008, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Singh, G.; Kaur, G. Subsurface drainage and nitrogen management affects corn and soybean yield in claypan soils in upstate Missouri. Agron. J. 2023, 116, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Wikle, C.K.; Ferguson, R.; Singh, G. Nitrogen fertilizer and pronitridine rates for corn production in the Midwest U.S. Field Crop. Res. 2024, 306, 109200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA NRCS (Natural Resources Conservation Service). National Conservation Practice Standards; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: http://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/national/technical/?cid=NRCSDEV11_001020 (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Parkin, T.; Mosier, A.; Smith, J.; Venterea, R.; Johnson, J.; Reicosky, D.; Doyle, G.; McCarty, G.; Baker, J. USDA-ARS GRACEnet Chamber-Based Trace Gas Flux Measurement Protocol; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. Available online: http://www.ars.usda.gov/SP2UserFiles/person/31831/2003GRACEnetTraceGasProtocol.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2003).
- Nash, P.R.; Motavalli, P.P.; Nelson, K.A. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Claypan Soils Due to Nitrogen Fertilizer Source and Tillage/Fertilizer Placement Practices. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, B.R.; Norman, R.J.; Wilson, C.E.; Slaton, N.A. Ammonia Volatilization and Nitrogen Uptake for Conventional and Conservation Tilled Dry-Seeded, Delayed-Flood Rice. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, M.; Sun, Y. Methods for plant analysis. In A Guide for Conducting Plant Analysis in Missouri; University of Missouri-Columbia: Columbia, MO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, M.V.; Thomas, D.J.D. The Structure of Silicon Oxide Films. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 1967, 22, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D. Cation-exchange capacity. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Amer Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1965; Volume 9, pp. 891–901. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1485982 (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Ball, D.F. Loss-on-ignition as an estimate of organic matter and organic carbon in non-calcareous soils. J. Soil Sci. 1964, 15, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.J.; Mi, H.; Yesiller, N. experimental analysis of desiccation crack propagation in clay liners. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, G.W.; Mulla, D.J. Nitrate Nitrogen in Surface Waters as Influenced by Climatic Conditions and Agricultural Practices. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, L.L.; Walsh, L.M.; Keeney, D.R. Effectiveness of Nitrapyrin in Controlling Nitrification of Fall and Spring-Applied Anhydrous Ammonia. Agron. J. 1978, 70, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, G.W.; Vetsch, J.A.; Huffman, J.R. Nitrate Losses in Subsurface Drainage from a Corn–Soybean Rotation as Affected by Time of Nitrogen Application and Use of Nitrapyrin. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H. Drainage Water Management Practices Affect Water Quality, Soil Properties, and Crop Production. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Tal, A. The effects of nitrogen form on interactions with potassium. In Nitrogen and Potassium Interactions; International Potash Institute: Zug, Switzerland, 2011; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes, D.; Colvin, T.; Karlen, D.; Cambardella, C.; Meek, D. Nitrate Loss in Subsurface Drainage as Affected by Nitrogen Fertilizer Rate. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, P.A.; Helmers, M.J.; Baker, J.L.; Melvin, S.W.; Lemke, D.W. Nitrogen Application Rate Effect on Nitrate-Nitrogen Concentration and Loss in Subsurface Drainage for a Corn-Soybean Rotation. Trans. ASABE 2008, 51, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, D.S.; Mitchell, A.M. The effects of drying and re-flooding on the sediment and soil nutrient dynamics of lowland river–floodplain systems: A synthesis. Regul. Rivers Res. Manag. Int. J. Devoted River Res. Manag. 2000, 16, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Reynolds, W.D.; Yang, X.M.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Welacky, T.W.; Calder, W.; Grant, C.A. Nitrogen Source, Application Time, and Tillage Effects on Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Corn Grain Yields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Reule, C.A. Nitrogen, Tillage, and Crop Rotation Effects on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Irrigated Cropping Systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Hatfield, J.L. Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizers: Effect on Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Iowa. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, F.; Deng, A.; Feng, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, W. Integrated assessment of the impact of enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizer on N2O emission and crop yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.; Hatfield, J. Influence of nitrapyrin on N2O losses from soil receiving fall-applied anhydrous ammonia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 136, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.-Y.; Ma, B.L.; Liang, B.C. Quantification of seasonal soil nitrogen mineralization for corn production in eastern Canada. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2007, 81, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venterea, R.T.; Maharjan, B.; Dolan, M.S. Fertilizer Source and Tillage Effects on Yield-Scaled Nitrous Oxide Emissions in a Corn Cropping System. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Recous, S.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; De Notaris, C.; Rittl, T.F.; Topp, C.F.; Petersen, S.O.; Hansen, S.; Bleken, M.A.; Rees, R.M.; et al. A review and me-ta-analysis of mitigation measures for nitrous oxide emissions from crop residues. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kanani, T.; MacKenzie, A.F.; Barthakur, N.N. Soil Water and Ammonia Volatilization Relationships with Surface-Applied Nitrogen Fertilizer Solutions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ruijter, F.; Huijsmans, J.; Rutgers, B. Ammonia volatilization from crop residues and frozen green manure crops. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3362–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Tremblay, N.; Deen, W.; Morrison, M.J.; Mclaughlin, N.B.; Gregorich, E.G.; Stewart, G. Nitrous oxide fluxes from corn fields: On-farm assessment of the amount and timing of nitrogen fertilizer. Glob. Change Biol. 2009, 16, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinuma, R.; Balster, N.J.; Norman, J.M. An Improved Model of Nitrogen Release for Surface-applied Controlled-release Fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamper, J.D. Evaluation of Method of Placement, Timing, and Rate of Application for Anhydrous Ammonia in No-till Corn Production. Doctoral Dissertation, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, E.E.; Edwards, T.M.; Givens, C.E.; Kolpin, D.W.; Hladik, M.L. Widespread Use of the Nitrification Inhibitor Nitrapyrin: Assessing Benefits and Costs to Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Environmental Health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fertilizer | Year | NO3-N | TP | TK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| --------------mg L−1------------- | ||||
| NTC | 8.9 b | 1 ab | 4.5 c | |
| TD urea | 9.1 b | 1.1 a | 4.3 a | |
| Fall AA + NI | 14.6 a | 1.1 a | 3.7 bc | |
| Spring AA | 13.8 a | 0.9 b | 2.5 ab | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | 0.0374 | 0.0001 | |
| 2018 | 13.2 a | 0.3 a | 6.3 a | |
| 2020 | 10 b | 1.7 b | 1.2 b | |
| p-value | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |
| NTC | 2018 | 9 bc | 0.3 c | 7.8 c |
| TD urea | 2018 | 10.4 bc | 0.4 b | 7.2 a |
| Fall AA + NI | 2018 | 17.6 a | 0.4 b | 6.2 a |
| Spring AA | 2018 | 15.8 a | 0.3 c | 3.8 b |
| NTC | 2020 | 8.8 bc | 1.8 a | 1.2 d |
| TD urea | 2020 | 7.8 c | 1.8 a | 1.3 d |
| Fall AA + NI | 2020 | 11.6 b | 1.8 a | 1.2 d |
| Spring AA | 2020 | 11.7 b | 1.5 a | 1.2 d |
| p-value | 0.026 | 0.0954 | 0.0007 | |
| Treatment † | Fertilizer ‡ | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -----------g N2O-N mg−1----------- | ||||
| SD | NTC | 47.7 bc | 56.6 bc | 43.2 b |
| TD urea | 43.3 c | 79.4 abc | 27.1 c | |
| Fall AA + NI | 68.7 ab | 52.9 c | 21.8 c | |
| Spring AA | 68.8 ab | 70.6 abc | 25.2 c | |
| ND | NTC | 50.7 bc | 83.9 ab | 68.9 a |
| Fall AA + NI | 60.7 abc | 63.4 abc | 28.6 c | |
| Spring AA | 80.1 a | 85.3 a | 22.5 c | |
| p-value | 0.0797 | 0.1439 | 0.0002 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A. Subsurface Drainage and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Affect Fertilizer Fate in Claypan Soils. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156477
Kaur H, Nelson KA. Subsurface Drainage and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Affect Fertilizer Fate in Claypan Soils. Sustainability. 2024; 16(15):6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156477
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaur, Harpreet, and Kelly A. Nelson. 2024. "Subsurface Drainage and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Affect Fertilizer Fate in Claypan Soils" Sustainability 16, no. 15: 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156477
APA StyleKaur, H., & Nelson, K. A. (2024). Subsurface Drainage and Nitrogen Fertilizer Management Affect Fertilizer Fate in Claypan Soils. Sustainability, 16(15), 6477. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156477






