Artificial Intelligence and the Transformation of Higher Education Institutions: A Systems Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology
2.2. Dimensions of AI Transformation in HEIs
2.2.1. Student Learning
2.2.2. Academic Integrity Problems
2.2.3. Faculty Research and Accelerated Scientific Discovery
2.2.4. Administration and Operations: Institutional Learning
2.2.5. AI Risks and Ethics in HEIs
2.3. Jobs for Graduating Students
3. Methods
3.1. Systems Approach and CLD
3.2. Development of a CLD
3.3. Steps We Followed to Develop Our CLD
4. CLD Model and Insights
4.1. Advances in AI Technology
4.2. Student Learning
4.3. Student Academic Integrity Problems
4.4. Faculty Research
4.5. HEI Administration and Operations
4.6. AI Risks
4.7. Job Placement
4.8. AI Transformation and HEI Success
4.9. Job Market Scenarios and HEI
4.10. Interventions
5. Discussion
5.1. Lessons for Academic Leadership
5.2. Limitations and Future Research Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Kshetri, N.; Hughes, L.; Slade, E.L.; Jeyaraj, A.; Kar, A.K.; Baabdullah, A.M.; Koohang, A.; Raghavan, V.; Ahuja, M.; et al. “So What If ChatGPT Wrote It?” Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Opportunities, Challenges and Implications of Generative Conversational AI for Research, Practice and Policy. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2023, 71, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, A.; Rock, D.; Brynjolfsson, E. How to Capitalize on Generative AI. Available online: https://hbr.org/2023/11/how-to-capitalize-on-generative-ai (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Ford, M. Rise of the Robots: Technology and the Threat of a Jobless Future; Basic Books: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- McKinsey Generative AI and the Future of Work in America. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/mgi/our-research/generative-ai-and-the-future-of-work-in-america (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Brynjolfsson, E.; McAfee, A. The Second Machine Age; W. W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer, T.; Fischer, C.; Alekseeva, A.; Chen, X.; Tate, T.; Warschauer, M.; Gerjets, P. ChatGPT in Education: Global Reactions to AI Innovations. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, B.A. Is Using ChatGPT Cheating, Plagiarism, Both, Neither, or Forward Thinking? Patterns 2023, 4, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell Group Russell Group Principles on the Use of Generative AI Tools in Education. Available online: https://russellgroup.ac.uk/news/new-principles-on-use-of-ai-in-education/ (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Lin, Z. Artificial Intelligence in Education: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 75264–75278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, H.; Burke, D. Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: The State of the Field. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawacki-Richter, O.; Marín, V.I.; Bond, M.; Gouverneur, F. Systematic Review of Research on Artificial Intelligence Applications in Higher Education—Where Are the Educators? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2019, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, I.; Wylie, R. Evolution and Revolution in Artificial Intelligence in Education. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2016, 26, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphosa, V.; Maphosa, M. Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Bibliometric Analysis and Topic Modeling Approach. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 2261730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahroun, Z.; Anane, C.; Ahmed, V.; Zacca, A. Transforming Education: A Comprehensive Review of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Educational Settings through Bibliometric and Content Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Siau, K.L. Artificial Intelligence Impacts on Higher Education. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Midwest Association for Information Systems Conference (MWAIS 2018), St. Louis, MO, USA, 17–18 May 2018; Volume 42, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, T.; Cobo, C.; Mariño, O.; Wheeler, S. Can Artificial Intelligence Transform Higher Education? Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2020, 17, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. The Economics of Generative Artificial Intelligence in the Academic Industry. Computer 2023, 56, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Xu, M.; Patros, P.; Wu, H.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, K.; Fuller, S.; Singh, M.; Arora, P.; Parlikad, A.K.; et al. Transformative Effects of ChatGPT on Modern Education: Emerging Era of AI Chatbots. Internet Things Cyber-Physical Syst. 2024, 4, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeralan, S.; Lee, L.A. Generative AI: Challenges to Higher Education. Sustain. Eng. Innov. 2023, 5, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempere, J.; Modugu, K.; Hesham, A.; Ramasamy, L.K. The Impact of ChatGPT on Higher Education. Front. Educ. 2023, 8, 1206936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; ISBN 007238915X. [Google Scholar]
- Katsamakas, E.; Pavlov, O.V. AI and Business Model Innovation: Leverage the AI Feedback Loops. J. Bus. Model. 2020, 8, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs THE 17 GOALS | Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Hughes, L.; Ismagilova, E.; Aarts, G.; Coombs, C.; Crick, T.; Duan, Y.; Dwivedi, R.; Edwards, J.; Eirug, A.; et al. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary Perspectives on Emerging Challenges, Opportunities, and Agenda for Research, Practice and Policy. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 2021, 57, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Edwards, J.S.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial Intelligence for Decision Making in the Era of Big Data—Evolution, Challenges and Research Agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 2019, 48, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Davenport, T.H.; Panteli, N. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Marketing: Applications, Opportunities, Challenges, and Research Agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 2023, 31, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerriegel, S.; Hartmann, J.; Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P. Generative AI. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2023, 66, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fui-Hoon Nah, F.; Zheng, R.; Cai, J.; Siau, K.; Chen, L. Generative AI and ChatGPT: Applications, Challenges, and AI-Human Collaboration. J. Inf. Technol. Case Appl. Res. 2023, 25, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 9780136042594. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar]
- Popenici, S.; Kerr, S. Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Teaching and Learning in Higher Education. Res. Pract. Technol. Enhanc. Learn. 2017, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quy, V.K.; Thanh, B.T.; Chehri, A.; Linh, D.M.; Tuan, D.A. AI and Digital Transformation in Higher Education: Vision and Approach of a Specific University in Vietnam. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, M.J. Letting Artificial Intelligence in Education Out of the Box: Educational Cobots and Smart Classrooms. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2016, 26, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Zou, D.; Xie, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, C. Two Decades of Artificial Intelligence in Education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2022, 25, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuban, C.; Moskal, P.; Parker, L.; Campbell, M.; Howlin, C.; Johnson, C. Adaptive Learning: A Stabilizing Influence across Disciplines and Universities. Online Learn. J. 2018, 22, 7–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Sivathanu, B.; Metri, B.; Kaushik, N. Students’ Adoption of AI-Based Teacher-Bots (T-Bots) for Learning in Higher Education. Inf. Technol. People 2023, 37, 328–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, S. Teacherbot: Interventions in Automated Teaching. Teach. High. Educ. 2015, 20, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, N.; Eynon, R.; Chiabaut, C.; Finkel, K.; Gillani, N.; Eynon, R.; Chiabaut, C.; Finkel, K. Unpacking the “Black Box” of AI in Education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2023, 26, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, K.; Singh, A.; Ganimian, A.J. Disrupting Education? Experimental Evidence on Technology-Aided Instruction in India. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 1426–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, A.; Lim, C.P. Reconceptualizing ChatGPT and Generative AI as a Student-Driven Innovation in Higher Education. Procedia CIRP 2023, 119, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollick, E.; Mollick, L. Assigning AI: Seven Approaches for Students, with Prompts. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extance, A. ChatGPT Enters the Classroom. Nature 2023, 623, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, S. Shaping the Future of Education: Exploring the Potential and Consequences of AI and ChatGPT in Educational Settings. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinka, K.; Peresíni, M.; Firc, A.; Hujnák, O.; Janus, F. On the Educational Impact of ChatGPT: Is Artificial Intelligence Ready to Obtain a University Degree? In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, Turku, Finland, 10–12 July 2023; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Mollick, E. The Homework Apocalypse. Available online: https://www.oneusefulthing.org/p/the-homework-apocalypse (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Pickering, E.; Schuller, C. Widespread Usage of Chegg for Academic Misconduct: Perspective from an Audit of Chegg Usage Within an Australian Engineering School. EdArXiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.; Kelly, A.; McLaughlan, P. ChatGPT in Higher Education: Considerations for Academic Integrity and Student Learning. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonevac, D.A. The Signaling Device. Acad. Quest. 2018, 31, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.A.; Moore, D.A.; Sharek, Z.S.; Gino, F. Inflated Applicants: Attribution Errors in Performance Evaluation by Professionals. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorbehbahani, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Aminazadeh, M. A Systematic Review of Research on Cheating in Online Exams from 2010 to 2021. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 8413–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, J. ChatGPT at Universities—The Least of Our Concerns. SSRN Electron. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathewson, T.G. AI Detection Tools Falsely Accuse International Students of Cheating. Available online: https://themarkup.org/machine-learning/2023/08/14/ai-detection-tools-falsely-accuse-international-students-of-cheating (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Michel-Villarreal, R.; Vilalta-Perdomo, E.; Salinas-Navarro, D.E.; Thierry-Aguilera, R.; Gerardou, F.S. Challenges and Opportunities of Generative AI for Higher Education as Explained by ChatGPT. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Noorden, R.; Perkel, J.M. AI and Science: What 1,600 Researchers Think. Nature 2023, 621, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Is AI Leading to a Reproducibility Crisis in Science? Nature 2023, 624, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dis, E.A.M.; Bollen, J.; Zuidema, W.; van Rooij, R.; Bockting, C.L. ChatGPT: Five Priorities for Research. Nature 2023, 614, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susarla, A.; Gopal, R.; Thatcher, J.B.; Sarker, S. The Janus Effect of Generative AI: Charting the Path for Responsible Conduct of Scholarly Activities in Information Systems. Inf. Syst. Res. 2023, 34, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockting, C.L.; van Dis, E.A.M.; van Rooij, R.; Zuidema, W.; Bollen, J. Living Guidelines for Generative AI—Why Scientists Must Oversee Its Use. Nature 2023, 622, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassabis, D. Using AI to Accelerate Scientific Discovery; Institute for Ethics in AI; Oxford University: Oxford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Fu, T.; Du, Y.; Gao, W.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z.; Chandak, P.; Liu, S.; Van Katwyk, P.; Deac, A.; et al. Scientific Discovery in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. Nature 2023, 620, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, H.H. ChatGPT Is Fun, but Not an Author. Science 2023, 379, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Veličković, P.; Buesing, L.; Blackwell, S.; Zheng, D.; Tomašev, N.; Tanburn, R.; Battaglia, P.; Blundell, C.; Juhász, A.; et al. Advancing Mathematics by Guiding Human Intuition with AI. Nature 2021, 600, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picciano, A.G. Planning for Online Education: A Systems Model. Online Learn. 2015, 19, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Picciano, A.G. Artificial Intelligence and the Academy’s Loss of Purpose. Online Learn. 2019, 23, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiba, D.; Fraboni, M.C. AI-Supported Academic Advising: Exploring ChatGPT’s Current State and Future Potential toward Student Empowerment. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, B. Big Data and Analytics in Higher Education: Opportunities and Challenges. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2015, 46, 904–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Yu, P.S.; Sun, L. A Comprehensive Survey of AI-Generated Content (AIGC): A History of Generative AI from GAN to ChatGPT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.04226. [Google Scholar]
- Chomsky, N. The False Promise of ChatGPT. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/08/opinion/noam-chomsky-chatgpt-ai.html (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Mitchell, M. How Do We Know How Smart AI Systems Are? Science 2023, 381, eadj5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floridi, L. AI as Agency without Intelligence: On ChatGPT, Large Language Models, and Other Generative Models. Philos. Technol. 2023, 36, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.S.; Hawn, A. Algorithmic Bias in Education. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 32, 1052–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S. The Dark Side of Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education. Serv. Ind. J. 2023, 43, 1055–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, P. Generative AI Meets Copyright. Science 2023, 381, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wired Millions of Workers Are Training AI Models for Pennies. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/millions-of-workers-are-training-ai-models-for-pennies/ (accessed on 9 December 2023).
- Zuboff, S. The Age of Surveillance Capitalism: The Fight for a Human Future at the New Frontier of Power; PublicAffairs: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 1610395697. [Google Scholar]
- Popenici, S.; Rudolph, J.; Tan, S.; Tan, S. A Critical Perspective on Generative AI and Learning Futures. An Interview with Stefan Popenici. J. Appl. Learn. Teach. 2023, 6, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, M.; Ryan, J.; Ajjawi, R. Discourses of Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: A Critical Literature Review. High. Educ. 2023, 86, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, J.; Islam, M.A.; Ren, S. Making AI Less “Thirsty”: Uncovering and Addressing the Secret Water Footprint of AI Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03271. [Google Scholar]
- Bogina, V.; Hartman, A.; Kuflik, T.; Shulner-Tal, A. Educating Software and AI Stakeholders about Algorithmic Fairness, Accountability, Transparency and Ethics. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2022, 32, 808–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, E.; Sessler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; et al. ChatGPT for Good? On Opportunities and Challenges of Large Language Models for Education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, B.C.; Eke, D. The Ethics of ChatGPT—Exploring the Ethical Issues of an Emerging Technology. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2024, 74, 102700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Holmes, W. Guidance for Generative AI in Education and Research; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2023; ISBN 9789231006128. [Google Scholar]
- Simbeck, K. They Shall Be Fair, Transparent, and Robust: Auditing Learning Analytics Systems. AI Ethics 2023, 4, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Gans, J.S.; Goldfarb, A. Do We Want Less Automation? AI May Provide a Path to Decrease Inequality. Science 2023, 381, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. The Wrong Kind of AI? Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Labour Demand. Cambridge J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2020, 13, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Restrepo, P. The Race between Man and Machine: Implications of Technology for Growth, Factor Shares, and Employment. Am. Econ. Rev. 2018, 108, 1488–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCrory, F.; Westerman, G.; Alhammadi, Y.; Brynjolfsson, E. Racing with and against the Machine: Changes in Occupational Skill Composition in an Era of Rapid Technological Advance. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Information Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–17 December 2014; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Felten, E.W.; Raj, M.; Seamans, R. How Will Language Modelers like ChatGPT Affect Occupations and Industries? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.01157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloundou, T.; Manning, S.; Mishkin, P.; Rock, D. GPTs Are GPTs: An Early Look at the Labor Market Impact Potential of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.10130. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Kalliamvakou, E.; Cihon, P.; Demirer, M. The Impact of AI on Developer Productivity: Evidence from GitHub Copilot. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.06590. [Google Scholar]
- Kalliamvakou, E. Research: Quantifying GitHub Copilot’s Impact on Developer Productivity and Happiness. Github Blog, 7 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Noy, S.; Zhang, W. Experimental Evidence on the Productivity Effects of Generative Artificial Intelligence. Science 2023, 381, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynjolfsson, E.; Li, D.; Raymond, L.R. Generative AI at Work. Available online: http://www.nber.org/papers/w31161 (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Dell’Acqua, F.; McFowland, E.; Mollick, E.R.; Lifshitz-Assaf, H.; Kellogg, K.; Rajendran, S.; Krayer, L.; Candelon, F.; Lakhani, K.R. Navigating the Jagged Technological Frontier: Field Experimental Evidence of the Effects of AI on Knowledge Worker Productivity and Quality; Working Paper 24-013; Harvard Business School: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, X.; Reshef, O.; Zhou, L. The Short-Term Effects of Generative Artificial Intelligence on Employment: Evidence from an Online Labor Market. SSRN Electron. J. 2023, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadows, D.H. Thinking in Systems; Chelsea Green Publishing: Hartford, VT, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781844077267. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, J.; Oliva, R. Maps and Models in System Dynamics: A Response to Coyle. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2001, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenborn, A.K.; Rahmandad, H.; Rick, J.; Hosseinichimeh, N. Depression as a Systemic Syndrome: Mapping the Feedback Loops of Major Depressive Disorder. Psychol. Med. 2016, 46, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbrook-Johnson, P.; Penn, A.S. Systems Mapping—How to Build and Use Causal Models of Systems; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 9783031018336. [Google Scholar]
- Amissah, M.; Gannon, T.; Monat, J. What Is Systems Thinking? Expert Perspectives from the WPI Systems Thinking Colloquium of 2 October 2019. Systems 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crielaard, L.; Quax, R.; Sawyer, A.D.M.; Vasconcelos, V.V.; Nicolaou, M.; Stronks, K.; Sloot, P.M.A. Using Network Analysis to Identify Leverage Points Based on Causal Loop Diagrams Leads to False Inference. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, P. The Fifth Discipline: The Art and Practice of the Learning Organization; Doubleday/Currency: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Casadesus-Masanell, R.; Ricart, J.E. From Strategy to Business Models and onto Tactics. Long Range Plann. 2010, 43, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, R.; Borghi, J.; Semwanga, A.R.; Binyaruka, P.; Singh, N.S.; Blanchet, K. How to Do (or Not to Do)…using Causal Loop Diagrams for Health System Research in Low and Middle-Income Settings. Health Policy Plan. 2022, 37, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yourkavitch, J.; Lich, K.H.; Flax, V.L.; Okello, E.S.; Kadzandira, J.; Katahoire, A.R.; Munthali, A.C.; Thomas, J.C. Interactions among Poverty, Gender, and Health Systems Affect Women’s Participation in Services to Prevent HIV Transmission from Mother to Child: A Causal Loop Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaveikaite, V.; Grundstrom, C.; Lourida, K.; Winter, S.; Priori, R.; Chouvarda, I.; Maglaveras, N. Developing a Strategic Understanding of Telehealth Service Adoption for COPD Care Management: A Causal Loop Analysis of Healthcare Professionals. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voulvoulis, N.; Giakoumis, T.; Hunt, C.; Kioupi, V.; Petrou, N.; Souliotis, I.; Vaghela, C.; binti Wan Rosely, W. Systems Thinking as a Paradigm Shift for Sustainability Transformation. Glob. Environ. Change 2022, 75, 102544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsamakas, E.; Pavlov, O.V. Artificial Intelligence Feedback Loops in Mobile Platform Business Models. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Networks 2022, 29, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kutzschenbach, M.; Schmid, A.; Schoenenberger, L. Using Feedback Systems Thinking to Explore Theories of Digital Business for Medtech Companies. In Business Information Systems and Technology 4.0; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 141, pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, O.; Salim, H.; Suprun, E.; Richards, R.; MacAskill, S.; Heilgeist, S.; Rutherford, S.; Stewart, R.A.; Beal, C.D. Developing a Preliminary Causal Loop Diagram for Understanding the Wicked Complexity of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Systems 2020, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams Esfandabadi, Z.; Ranjbari, M. Exploring Carsharing Diffusion Challenges through Systems Thinking and Causal Loop Diagrams. Systems 2023, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, P.L. System Dynamics and University Management. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1998, 14, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, L.M.; Borenstein, D. A System Dynamics Model for Long-Term Planning of the Undergraduate Education in Brazil. High. Educ. 2015, 69, 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, Y.; Diker, V.G. A Dynamic Simulation Game (UNIGAME) for Strategic University Management. Simul. Gaming 2000, 31, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyo, B.; Williams, D. Re-Conceptualisation of Higher Education Quality Management Problems Using Feedback Systems Thinking. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2009, 3, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, O.V.; Katsamakas, E. Will Colleges Survive the Storm of Declining Enrollments? A Computational Model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rissanen, M.; Savolainen, J.; Collan, M. Analyzing the Finnish University Funding System through System-Based Simulation. Policy Futur. Educ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, O.V.; Katsamakas, E. Tuition Too High? Blame Competition. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2023, 213, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faham, E.; Rezvanfar, A.; Movahed Mohammadi, S.H.; Rajabi Nohooji, M. Using System Dynamics to Develop Education for Sustainable Development in Higher Education with the Emphasis on the Sustainability Competencies of Students. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2017, 123, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhirasasna; Sahin A Multi-Methodology Approach to Creating a Causal Loop Diagram. Systems 2019, 7, 42. [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D.; Henderson, R.; Beinhocker, E.D.; Newman, L.I. Getting Big Too Fast: Strategic Dynamics with Increasing Returns and Bounded Rationality. Manag. Sci. 2007, 53, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Moyano, I.J.; Richardson, G.P. Best Practices in System Dynamics Modeling. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2013, 29, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsamakas, E.; Miliaresis, K.; Pavlov, O. V Digital Platforms for the Common Good: Social Innovation for Active Citizenship and ESG. Sustainability 2022, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angliss, K. An Alternative Approach to Measuring University Reputation. Corp. Reput. Rev. 2022, 25, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucciarelli, F.; Kaplan, A. Competition and Strategy in Higher Education: Managing Complexity and Uncertainty. Bus. Horiz. 2016, 59, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.R.; Musa, P. Structural Validation of Causal Loop Diagrams. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference of the System Dynamics Society, Atlanta, GA, USA, 23–27 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiu, A.; Wright, J. Data-enabled Learning, Network Effects, and Competitive Advantage. RAND J. Econ. 2023, 54, 638–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Zou, J.; Su, W.J.; Zhang, L. What Should Data Science Education Do with Large Language Models? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.02792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acemoglu, D.; Johnson, S. Power and Progress: Our Thousand-Year Struggle Over Technology and Prosperity; PublicAffairs: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Acemoglu, D.; Johnson, S. What’s Wrong with ChatGPT? Available online: https://www.project-syndicate.org/commentary/chatgpt-ai-big-tech-corporate-america-investing-in-eliminating-workers-by-daron-acemoglu-and-simon-johnson-2023-02 (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Giannini, S. Generative AI and the Future of Education. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000371316?posInSet=4&queryId=N-EXPLORE-f75771a0-8dfc-4471-9183-e25037d0705c (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Toma, A.; Senkaiahliyan, S.; Lawler, P.R.; Rubin, B.; Wang, B. Generative AI Could Revolutionize Health Care—But Not If Control Is Ceded to Big Tech. Nature 2023, 624, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.; Batzner, S.; Schoenholz, S.S.; Aykol, M.; Cheon, G.; Cubuk, E.D. Scaling Deep Learning for Materials Discovery. Nature 2023, 624, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, N.J.; Rendy, B.; Fei, Y.; Kumar, R.E.; He, T.; Milsted, D.; McDermott, M.J.; Gallant, M.; Cubuk, E.D.; Merchant, A.; et al. An Autonomous Laboratory for the Accelerated Synthesis of Novel Materials. Nature 2023, 624, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
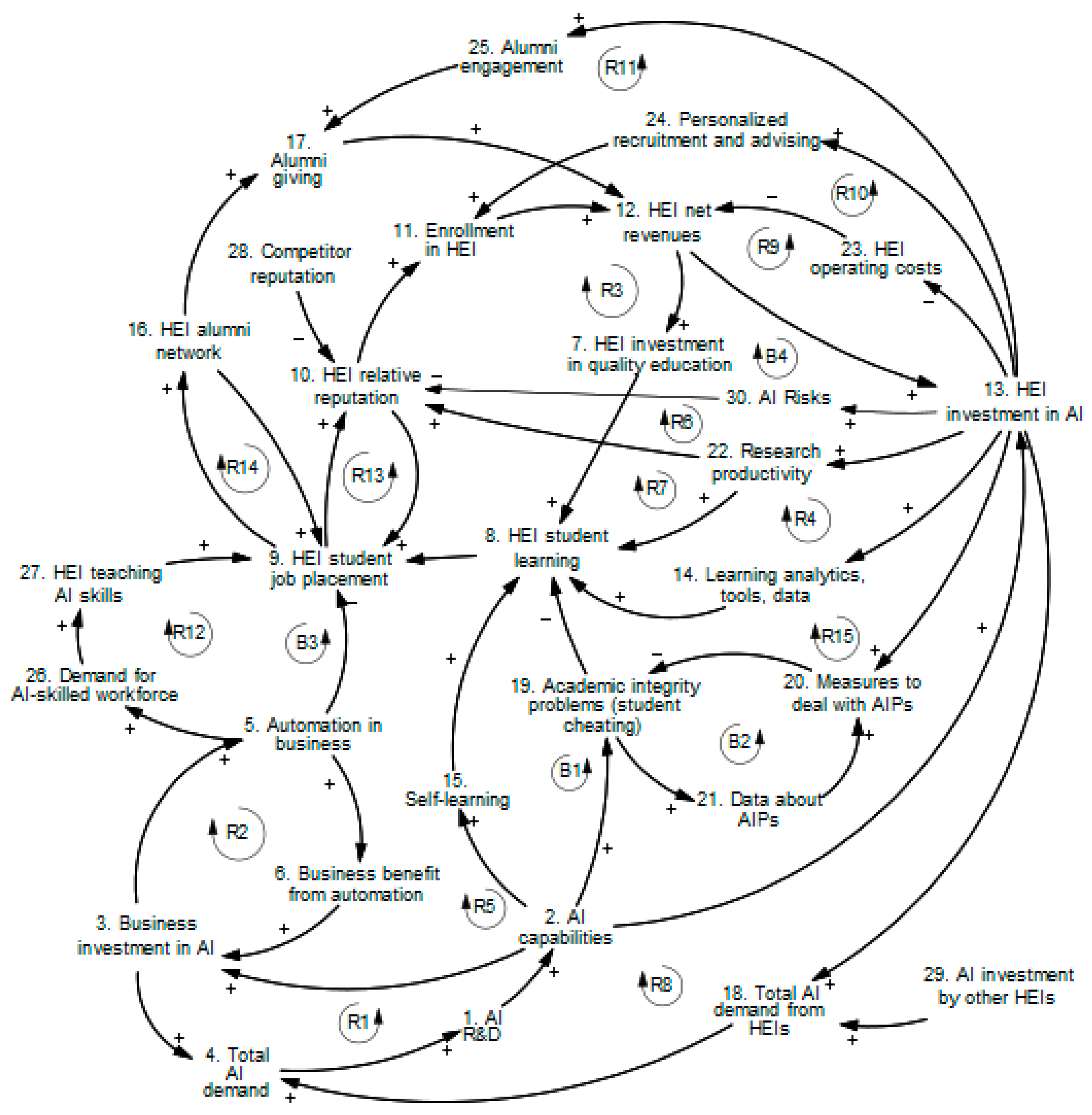
| # | Variable | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AI R&D | Total AI R&D leading to AI advances (2.1) |
| 2 | AI capabilities | Capabilities of AI resulting from AI advances (2.1) |
| 3 | Business investment in AI | Business sector investment in AI applications (2.1 and 2.3) |
| 4 | Total AI demand | Total demand for AI in the economy (2.3) |
| 5 | Automation in business | Level of business automation using AI (2.3) |
| 6 | Business benefit from automation | The value businesses gain from AI (2.3) |
| 7 | HEI investment in education | Level of HEI’s education investment (2.2) |
| 8 | HEI student learning | Student knowledge acquisition in HEI (2.2.1) |
| 9 | HEI student job placement | Successful HEI graduate employment (2.3) |
| 10 | HEI relative reputation | Overall HEI reputation (perceived quality) (2.2) |
| 11 | Enrollment in HEI | Total student enrollment in HEI (standard HEI metric) |
| 12 | HEI net revenues | HEI revenue minus the costs (standard HEI metric) |
| 13 | HEI investment in AI | HEI’s AI funding (2.2) |
| 14 | Learning analytics, tools, and data | Level of learning analytics use in HEI (2.2.1) |
| 15 | Self-learning | Independent learning by students (2.2.1) |
| 16 | HEI alumni network | Size of HEI’s alumni network (2.2.4) |
| 17 | Alumni giving | Level of alumni giving to HEI (2.2.4) |
| 18 | Total AI demand from HEIs | Total AI needs by colleges and universities (2.2) |
| 19 | Academic integrity problems (student cheating) | Violations of academic standards in HEI (2.2.2) |
| 20 | Measures to deal with AIPs | HEI efforts against academic misconduct (2.2.2) |
| 21 | Data about AIPs | Data about academic misconduct (2.2.2) |
| 22 | Research productivity | Scholarly output by HEI faculty (2.2.3) |
| 23 | HEI operating costs | HEI’s operational expenses (standard HEI metric) |
| 24 | Personalized recruitment and advising | AI supported student recruitment and help (2.2.4) |
| 25 | Alumni engagement | HEI engagement with alumni network (2.2.4) |
| 26 | Demand for AI-skilled workforce | Business need for AI-skilled employees (2.3) |
| 27 | HEI teaching AI skills | Quality of AI-related education in HEI (2.2.1) |
| 28 | Competitor reputation | Reputation of HEI competitors (2.2) |
| 29 | AI investment by other HEIs | AI funding by other colleges and universities (2.2) |
| 30 | AI risks | Bias, security, and other AI risks (2.2.5) |
| Name | Variables | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | Business investment drives AI R&D and AI advances |
| R2 | 3, 5, 6 | Benefits from automation drive business investment in AI |
| R3 | 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 | HEI creates value (and revenues) through quality education |
| R4 | 13, 14, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 | HEI invests in AI to improve learning |
| R5 | 2, 15, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 4, 1 | AI facilitates students’ self-learning |
| R6 | 22, 10, 11, 12, 13 | AI can support research productivity and HEI reputation |
| R7 | 22, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 | AI supports research that contributes to student learning |
| R8 | 2, 13, 18, 4, 1 | Advances in AI motivate the HEI to invest more in AI |
| R9 | 23, 12, 13 | HEI uses AI to lower operating costs |
| R10 | 24, 11, 12, 13 | AI supports admissions and student advising |
| R11 | 13, 25, 17, 12 | HEI uses AI to support alumni engagement and giving |
| R12 | 26, 27, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 4, 1, 2, 3, 5 | HEI teaches AI skills as a response to business demand for an AI-skilled workforce |
| R13 | 9, 10 | HEI’s reputation and job placement reinforce each other |
| R14 | 9, 16 | The size of the alumni network helps job placement, which grows the alumni network |
| R15 | 20, 19, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 | HEI benefits from measures to deal with academic integrity problems (AIPs) |
| B1 | 2, 19, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 4, 1 | AI advances lead to more AIPs which hurts HEI |
| B2 | 19, 21, 20 | HEI’s efforts to deal with AIPs |
| B3 | 5, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 18, 4, 1, 2, 3 | The job-substitution effect of AI hurts HEI job placement |
| B4 | 30, 10, 11, 12, 13 | AI risks can harm the HEI’s reputation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsamakas, E.; Pavlov, O.V.; Saklad, R. Artificial Intelligence and the Transformation of Higher Education Institutions: A Systems Approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16146118
Katsamakas E, Pavlov OV, Saklad R. Artificial Intelligence and the Transformation of Higher Education Institutions: A Systems Approach. Sustainability. 2024; 16(14):6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16146118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsamakas, Evangelos, Oleg V. Pavlov, and Ryan Saklad. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence and the Transformation of Higher Education Institutions: A Systems Approach" Sustainability 16, no. 14: 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16146118
APA StyleKatsamakas, E., Pavlov, O. V., & Saklad, R. (2024). Artificial Intelligence and the Transformation of Higher Education Institutions: A Systems Approach. Sustainability, 16(14), 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16146118







