Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. General Concepts
2.1.1. Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption
2.1.2. Cultural Behavior
2.1.3. Developing Countries
2.2. Related Works
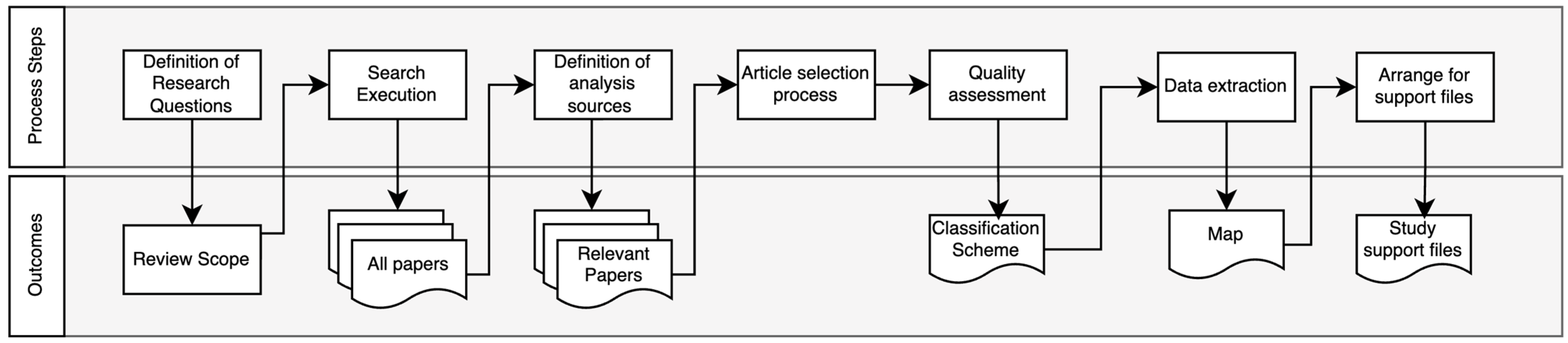
3. Methods
3.1. Definition of Research Questions
3.2. Conduct Search
3.3. Sources of Analysis
3.4. Article Selection Process
3.5. Quality Assessment
- QC1: The article articulates a specific research goal and provides a thorough contextual description;
- QC2: The article specifies the research methodology employed to meet the research goal;
- QC3: The article employs a methodology that is both clear and suitable for this study’s objective;
- QC4: The article delivers findings relevant to digital transformation or the practical implementation of technology adoption.
3.6. Data Extraction
3.7. Study Support Files
4. Results
4.1. Context and Research Approach
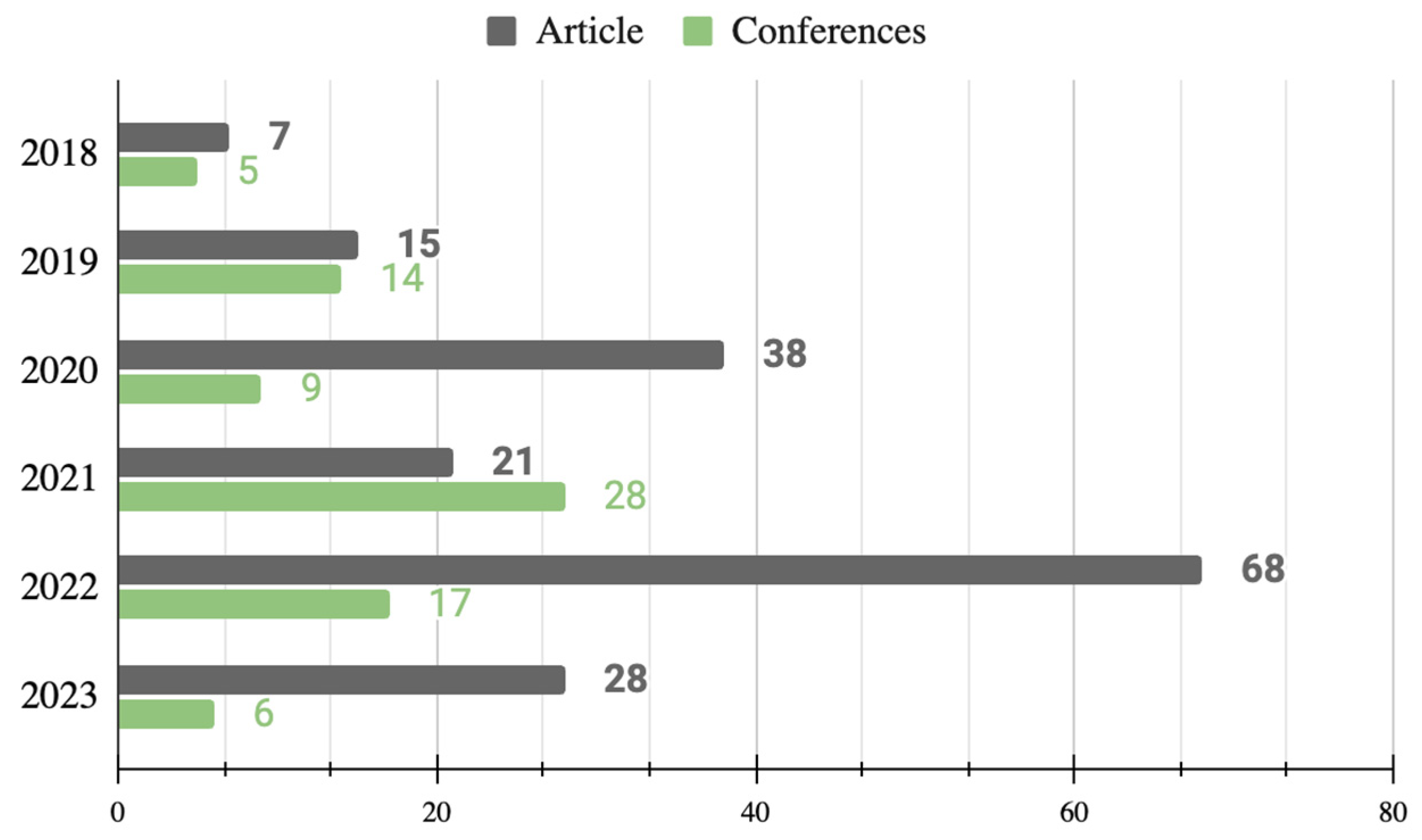
4.1.1. Publication Years
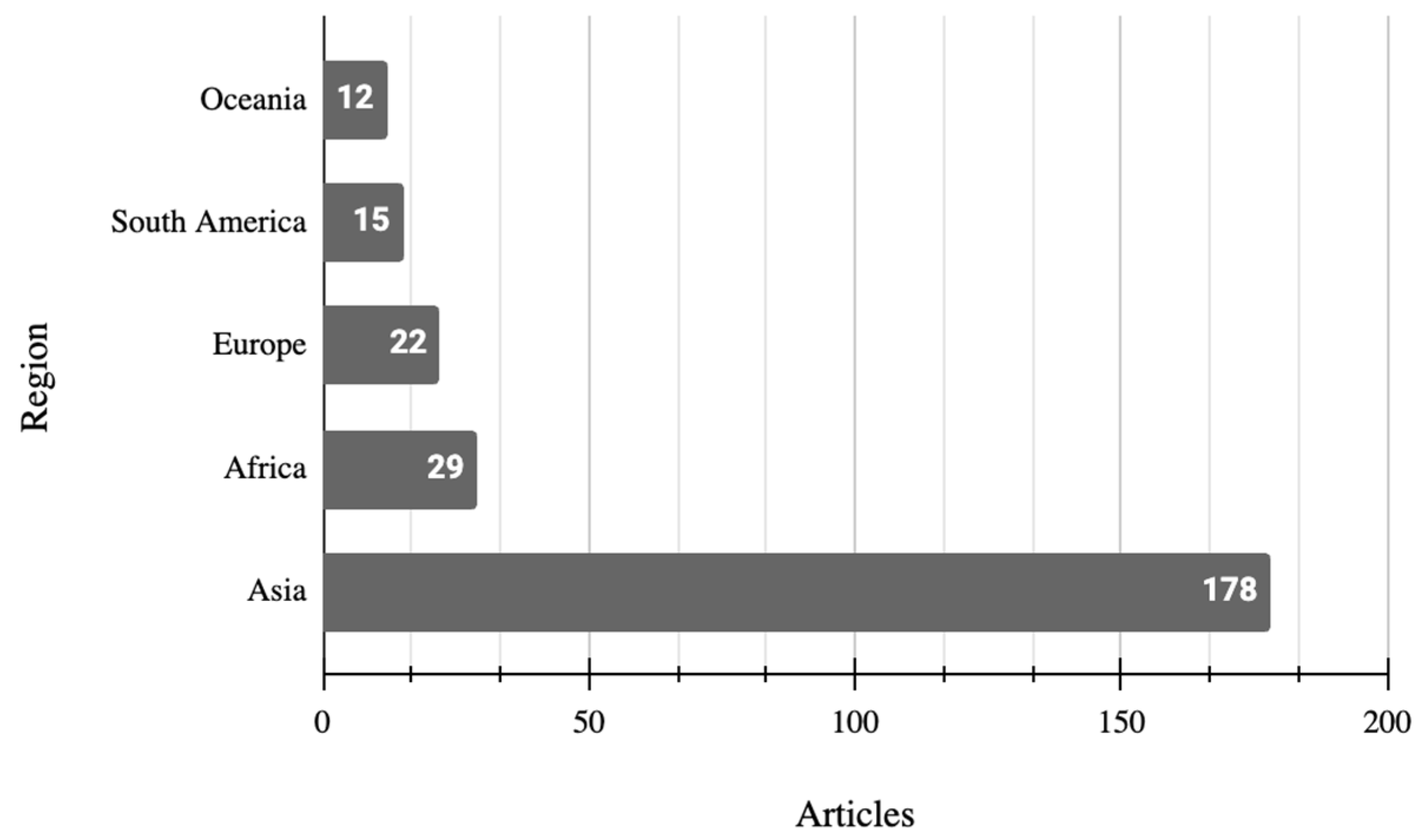
4.1.2. Data Sources
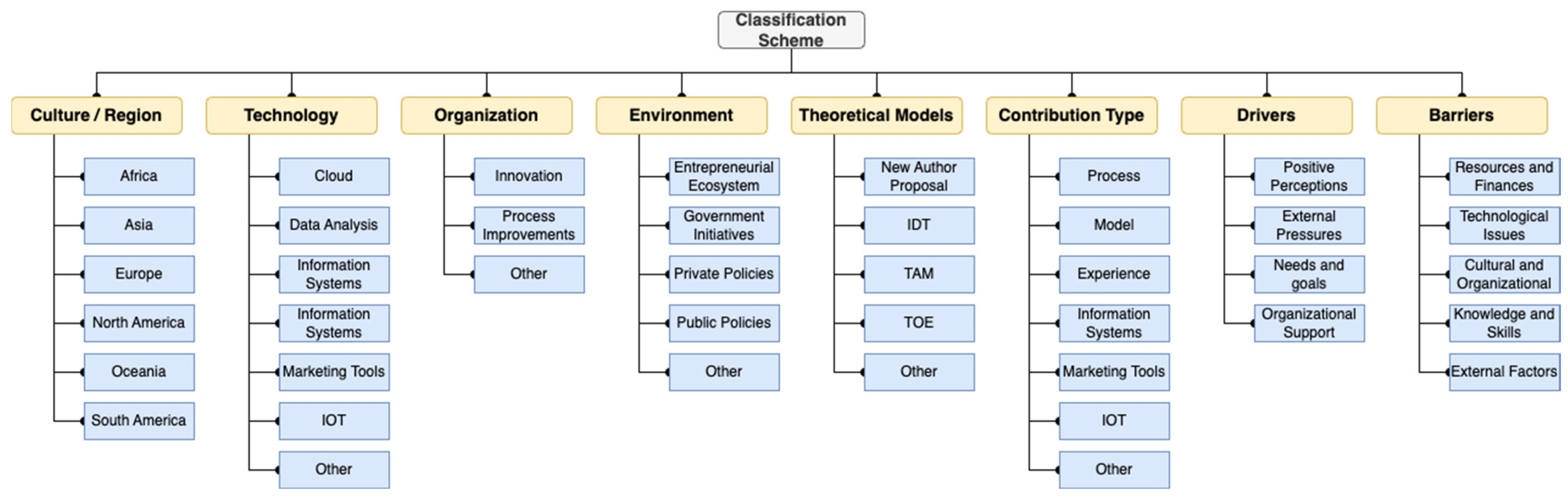
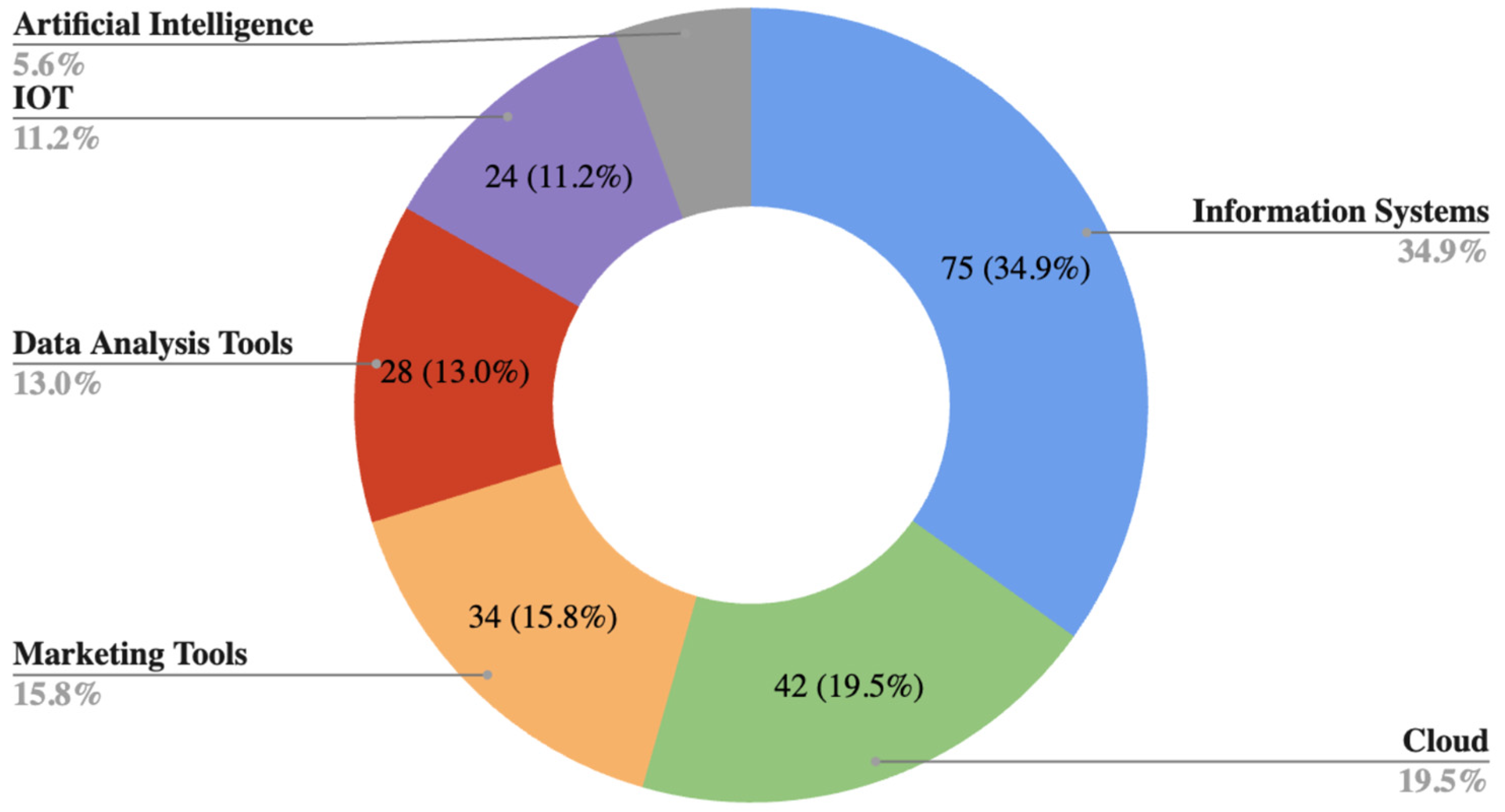
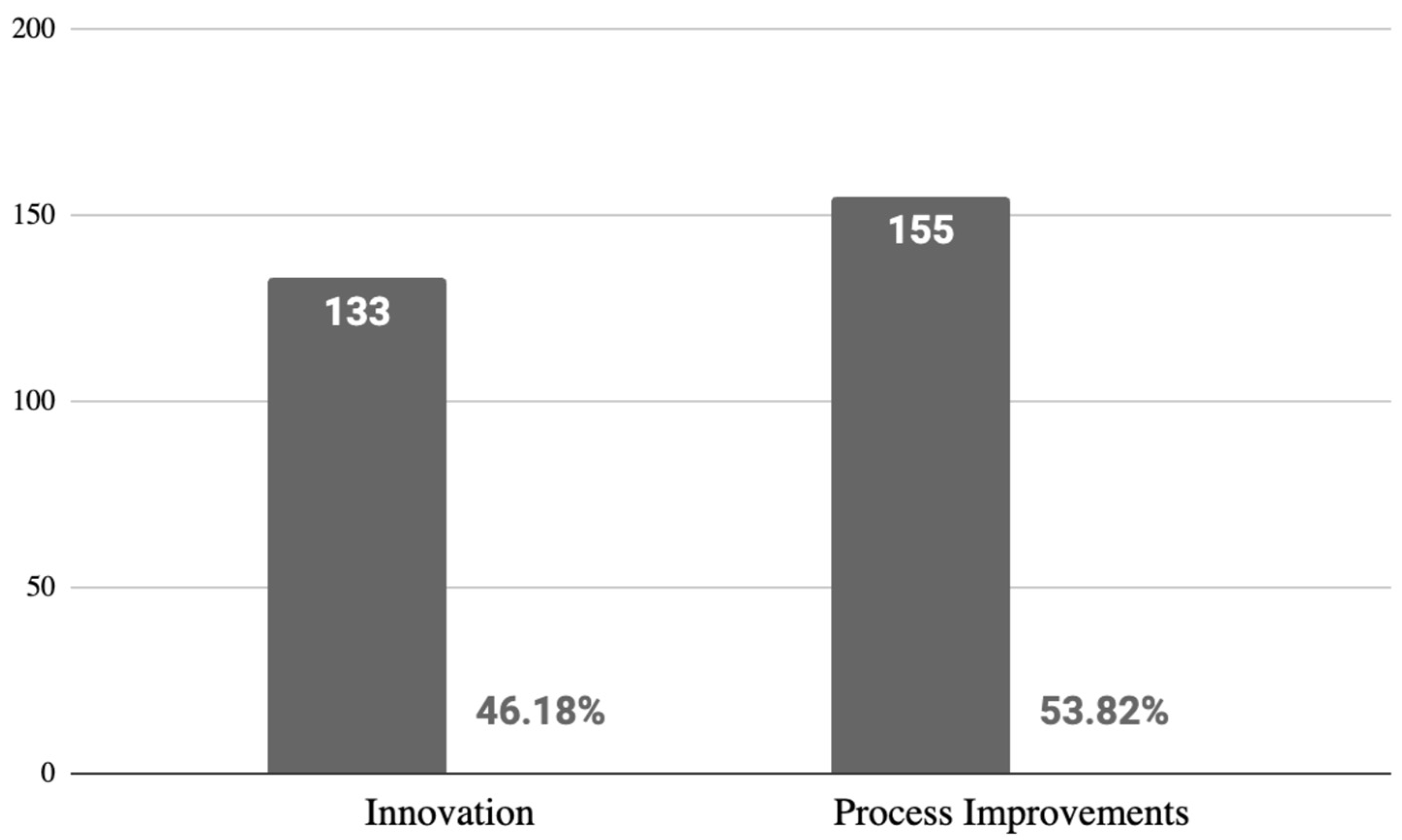
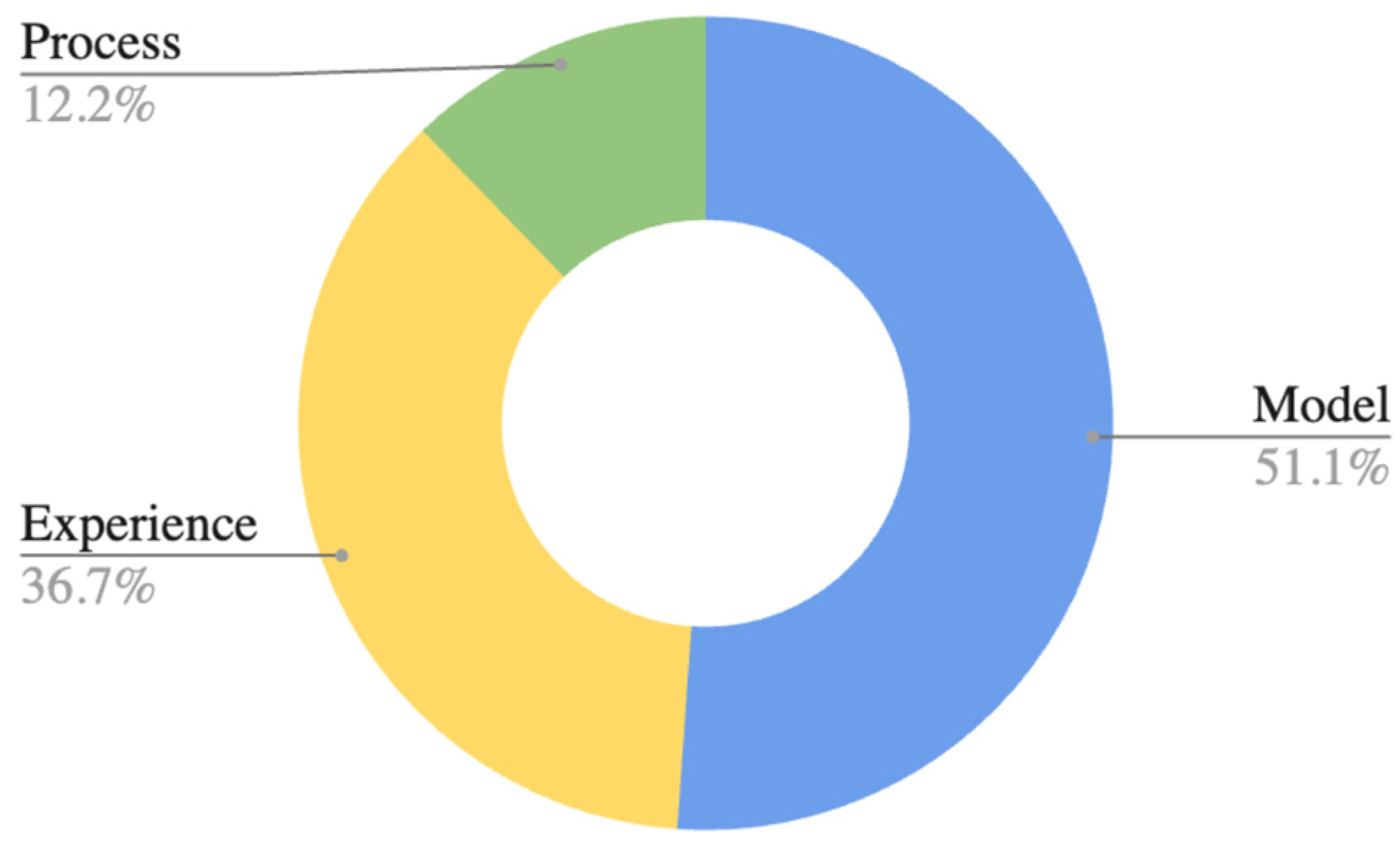
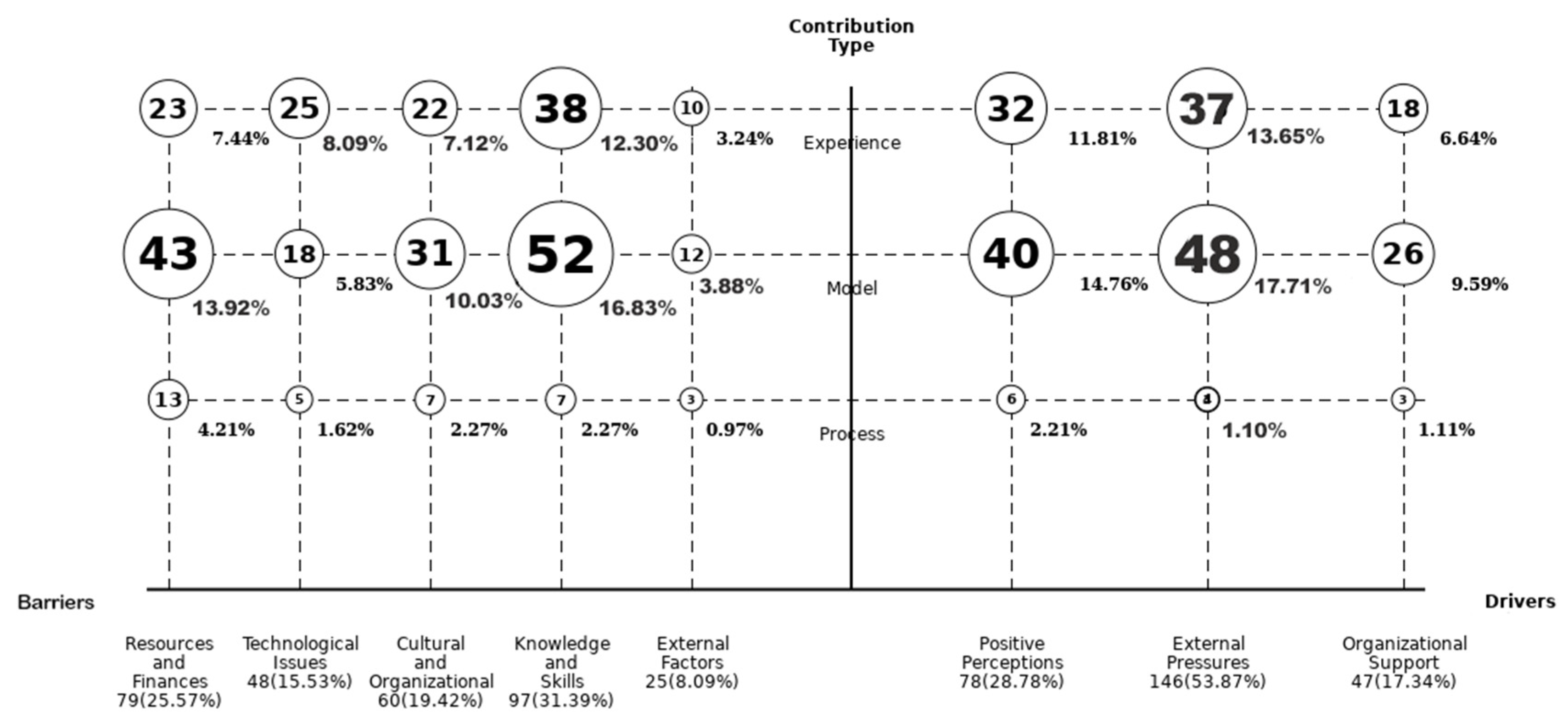
4.1.3. Type of Study and Contribution
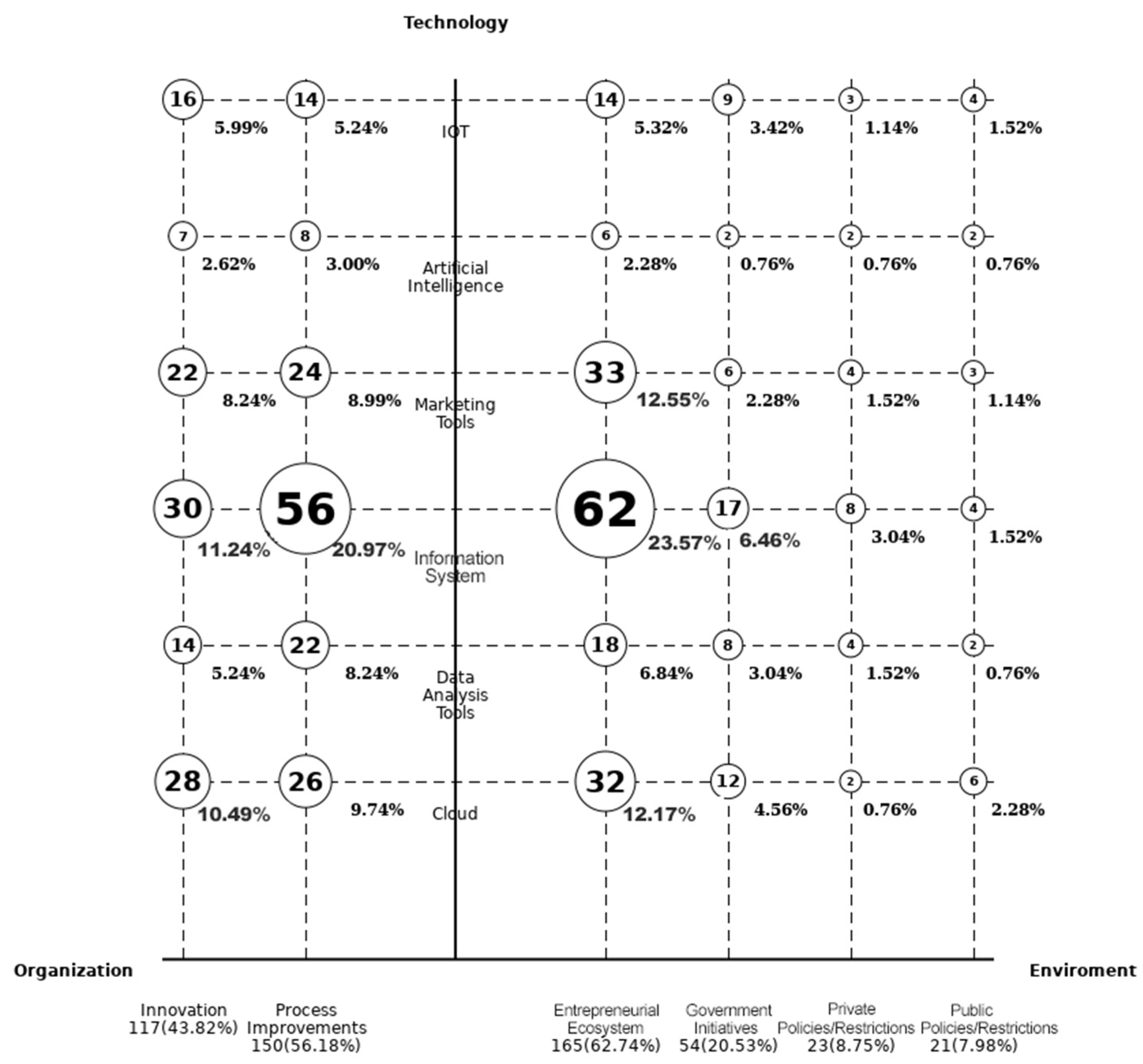
- Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: This refers to the network and conditions that facilitate entrepreneurship, including access to capital, mentorship, and a supportive community;
- Government Initiatives: These are programs or policies implemented by the government to encourage business activity, such as tax incentives, grants, or regulatory reforms;
- Private Policies: These consist of rules or guidelines set by private entities that influence their operations and the broader business environment, such as corporate governance standards or ethical sourcing requirements;
- Public Policies: These involve regulations and laws established by governmental bodies that dictate how businesses must operate, covering aspects like labor laws, environmental regulations, and compliance requirements.
5. Discussion
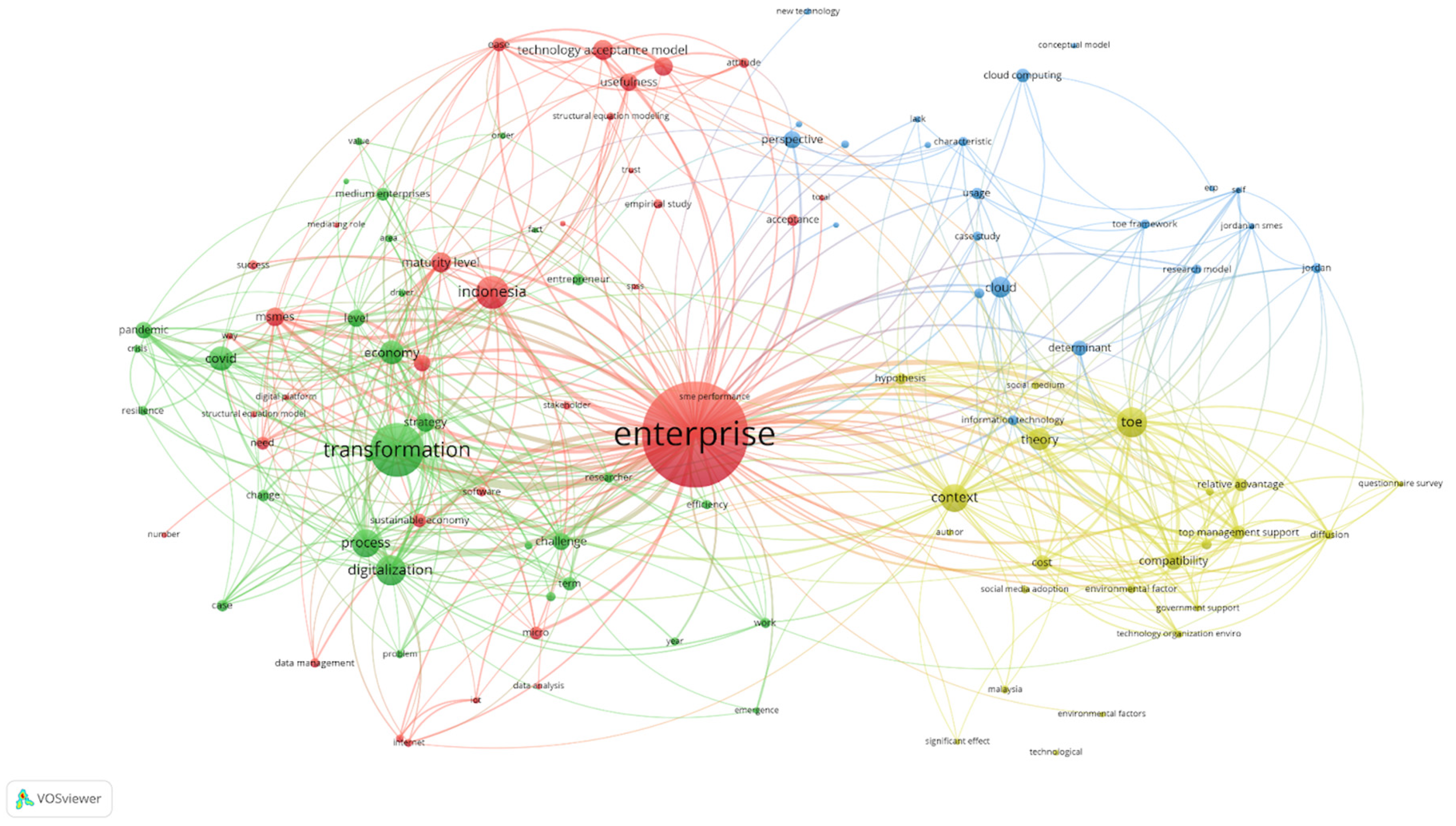
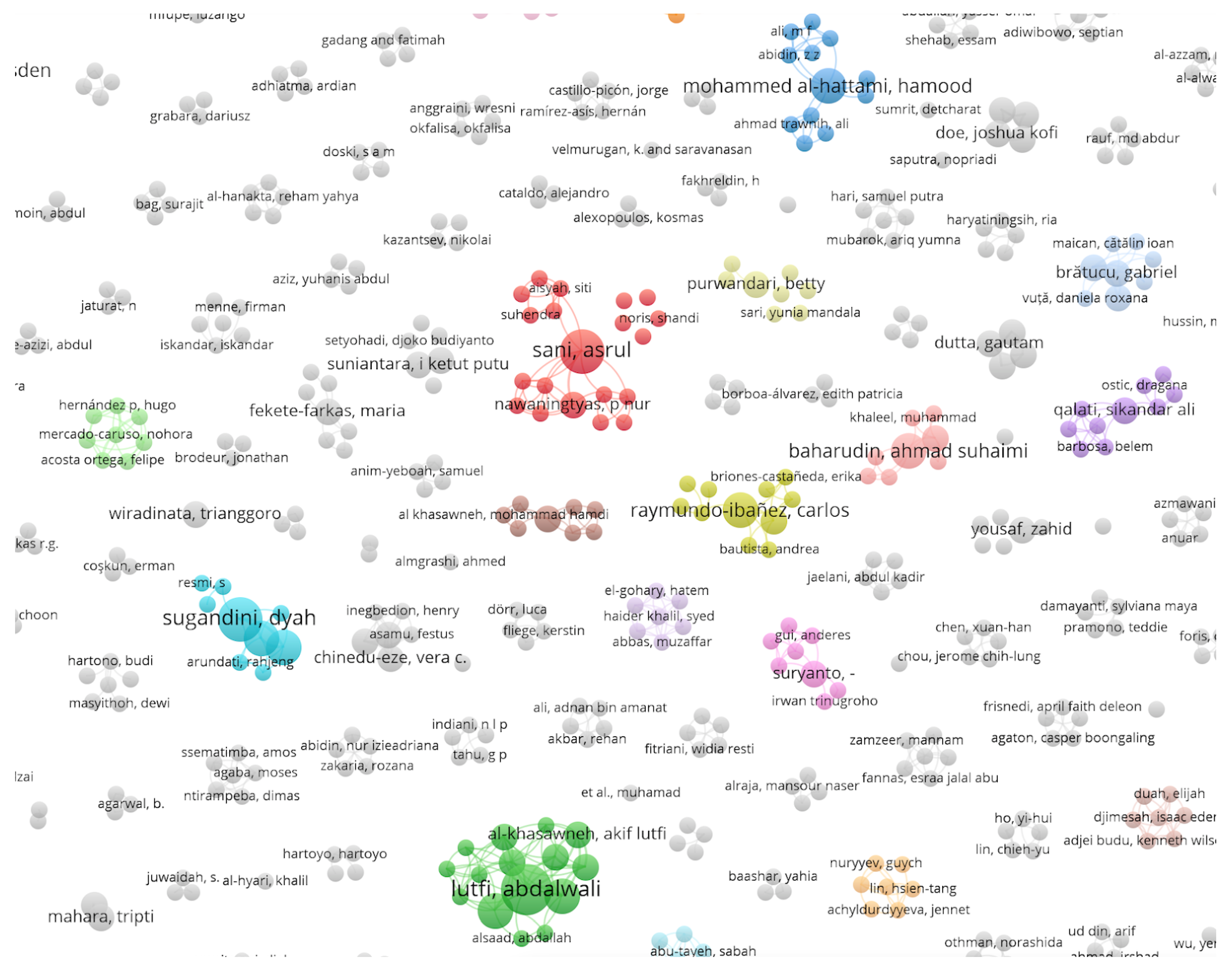
5.1. Bibliometric Analysis
5.2. Interpreting Answers to Research Questions
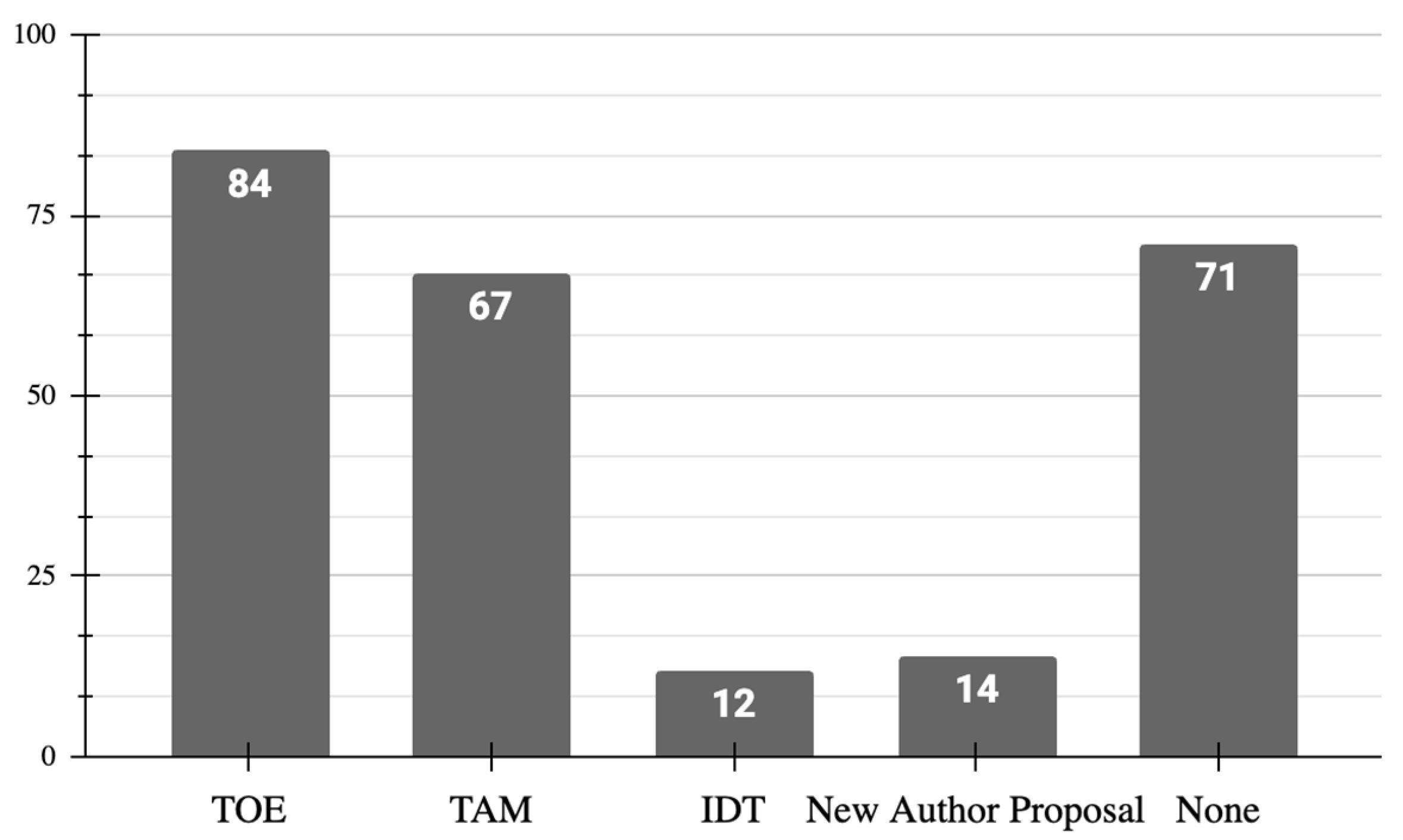
5.2.1. RQ1: What Are the Digital Transformation Models That Allow Evaluating Technological Adoption in Micro and Small Companies?
5.2.2. RQ2: What Are the Mechanisms for Assessing Cultural Behavior in Micro and Small Enterprises?
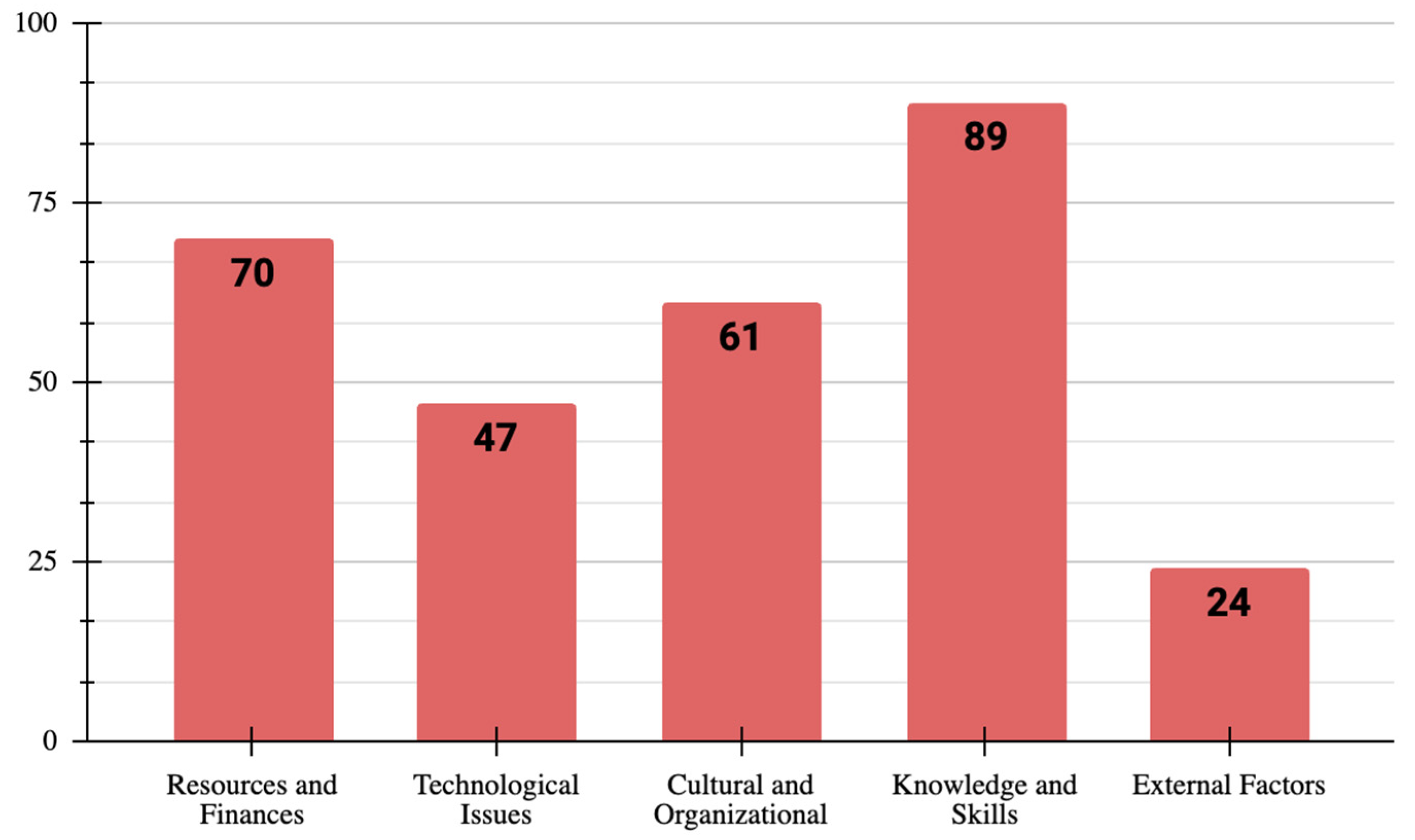
5.2.3. RQ3: What Are the Technological Barriers Affecting MSEs in Developing Countries?
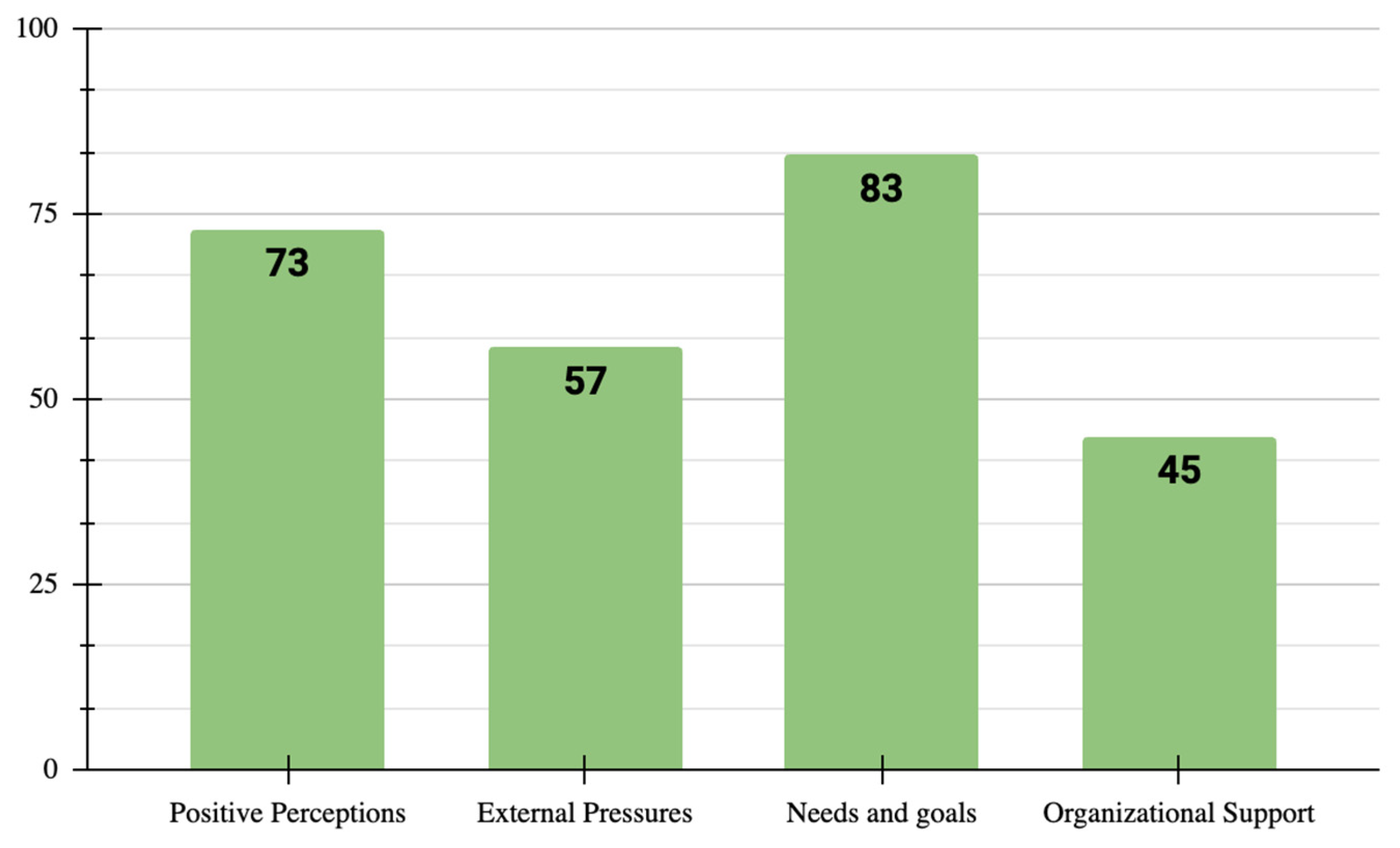
5.2.4. RQ4: What Are the Determining Factors and Drivers in the Digital Transformation Process for MSEs in Developing Countries?
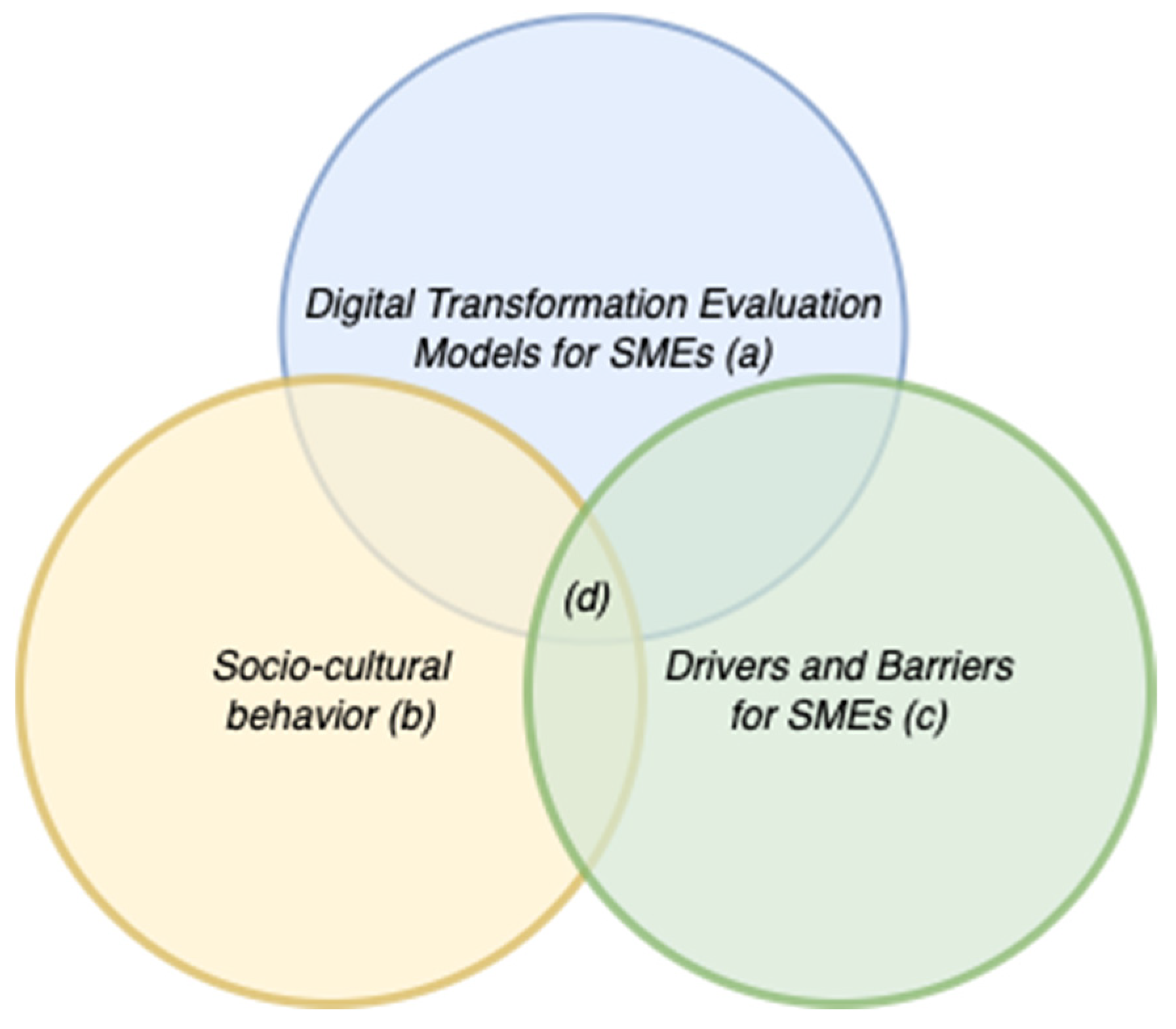
5.3. Orthogonal Discussion
5.4. Threats to Validity
- Study Search. To minimize search-related threats, we employed a predefined search string across major electronic databases. Prior to the actual search, a pilot search was conducted on each selected database to verify the accuracy and effectiveness of the search string.
- Study Selection Bias. We mitigated selection bias by using clearly defined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Additionally, several reviewers cross-checked all selected studies to ensure consistency. The inter-rater reliability, as measured by the Kappa coefficient, was 0.62, indicating substantial agreement among reviewers, thus significantly reducing the risk of discrepancies in study relevance.
- Data Extraction Bias. A systematic approach was used to ensure data extraction accuracy and reduce potential biases. Initially, one author developed a tool for distributing study results. Subsequently, five authors independently extracted data from an equal number of studies using a standardized form. Regular discussions between these authors helped to maintain consistency and mitigate data extraction bias.
Validity concerns the following:
- External Validity: External validity concerns the generalizability of the findings. The primary limitation is whether the studies adequately represent digital transformation initiatives in developing countries. This threat was addressed by selecting peer-reviewed studies and deliberately excluding the non-peer-reviewed (gray) literature to enhance the reliability and applicability of the findings.
- Conclusion Validity: This pertains to the reliability of drawing accurate conclusions from a study. Despite adhering to established best practices, it remains challenging to comprehensively encompass all relevant primary studies. We addressed this limitation by discussing our findings with industry professionals, enriching our interpretations and conclusions with practical insights.
- Construct Validity: Construct validity relates to the appropriateness of inferences from the operational measures to the theoretical constructs that they represent. A primary concern is the potential subjectivity of the results. To counteract this, three researchers independently executed critical phases of the systematic mapping study, subsequently convening to discuss and consolidate their findings into a consensus. This collaborative approach ensures that the conclusions drawn are robust and reflective of a collective agreement, thereby enhancing the construct validity of the study.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rozo-García, F. Revisión de las tecnologías presentes en la industria 4.0. Rev. UIS Ing. 2020, 19, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnafrah, I.; Mouselli, S.; Bogdanova, E. The Nexus between Digitisation and Knowledge-Based Economy in Low-Income Countries: The Case of Post-Conflict Syria. Int. J. Knowl.-Based Dev. 2020, 11, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ock, Y.-S.; Alnafrah, I.; Dagestani, A.A. What Aspects Explain the Relationship between Digital Transformation and Financial Performance of Firms? J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2023, 16, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pablos, P.O.; Zhang, X. Artificial Intelligence, Big Data, Blockchain and 5G for the Digital Transformation of the Healthcare Industry: A Movement toward More Resilient and Inclusive Societies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; ISBN 9780443215995. [Google Scholar]
- Stolterman, E.; Fors, A.C. Information Technology and the Good Life. In Information Systems Research: Relevant Theory and Informed Practice; Kaplan, B., Truex, D.P., Wastell, D., Wood-Harper, A.T., DeGross, J.I., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 687–692. ISBN 9781402080951. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, A.; Haenlein, M. Digital Transformation and Disruption: On Big Data, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence, and Other Things. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding Digital Transformation: A Review and a Research Agenda. In Managing Digital Transformation; Routledge: London, UK, 2021; pp. 13–66. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Dahms, H.F.; Welz, F.; Cattacin, S. Print Theories of Computer Societies. Introduction to the Digital Transformation of Social Theory. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 149, 119778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Salter, L.; McFarlane, D.; Schönfuß, B. Low-Cost (Shoestring) Digital Solution Areas for Enabling Digitalisation in Construction SMEs. Comput. Ind. 2023, 150, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinder, T.; Stenvall, J.; Koskimies, E.; Webb, H.; Janenova, S. Local Public Services and the Ethical Deployment of Artificial Intelligence. Gov. Inf. Q. 2023, 40, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Sharma, A.; Pan, B.; Quadri-Felitti, D. Information Asymmetry in the Innovation Adoption Decision of Tourism and Hospitality SMEs in Emerging Markets: A Mixed-Method Analysis. Tour. Manag. 2023, 99, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhao, S.; Shao, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B. Talking and Walking: Corporate Digital Transformation and Government Subsidies. Fin. Res. Lett. 2024, 64, 105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K. The Complementarity of Information Technology Infrastructure and E-Commerce Capability: A Resource-Based Assessment of Their Business Value. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2004, 21, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Arias-Aranda, D.; Benitez-Amado, J. Adoption of E-Commerce Applications in SMEs. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2011, 111, 1238–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdani, B.; Chevers, D.; Williams, D.A. SMEs’ Adoption of Enterprise Applications: A Technology-Organisation-Environment Model. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2013, 20, 735–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jesus, F.; Pinheiro, A.; Oliveira, T. Understanding CRM Adoption Stages: Empirical Analysis Building on the TOE Framework. Comput. Ind. 2019, 109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.; Martins, R.; Sarker, S.; Thomas, M.; Popovič, A. Understanding SaaS Adoption: The Moderating Impact of the Environment Context. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Guo, Y.; Barnes, S.J. Enterprise 2.0 Post-Adoption: Extending the Information System Continuance Model Based on the Technology-Organization-Environment Framework. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 67, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H. Organisational Factors Affecting Cloud Computing Adoption in Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Service Sector. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 121, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayer, A.; Talukder, M.S.; Bao, Y.; Hossain, M.N. Cloud Computing Adoption and Its Impact on SMEs’ Performance for Cloud Supported Operations: A Dual-Stage Analytical Approach. Technol. Soc. 2020, 60, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadegaridehkordi, E.; Nilashi, M.; Shuib, L.; Hairul Nizam Bin Md Nasir, M.; Asadi, S.; Samad, S.; Fatimah Awang, N. The Impact of Big Data on Firm Performance in Hotel Industry. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2020, 40, 100921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z.; Ahmad, N.; Abu Bakar, A.R. Reflections of Entrepreneurs of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Concerning the Adoption of Social Media and Its Impact on Performance Outcomes: Evidence from the UAE. Telemat. Inform. 2018, 35, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanda, S.; Brown, I. A Structuration Analysis of Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) Adoption of E-Commerce: The Case of Tanzania. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, S.S. Social Commerce Adoption Using TOE Framework: An Empirical Investigation of Saudi Arabian SMEs. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi Putra, P.O.; Santoso, H.B. Contextual Factors and Performance Impact of E-Business Use in Indonesian Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Heliyon 2020, 6, e03568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.D.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Lal, B.; Schwarz, A. Contemporary Trends and Issues in It Adoption and Diffusion Research. J. Inf. Technol. Impact 2009, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Imgrund, F.; Janiesch, C.; Winkelmann, A. Strategy Archetypes for Digital Transformation: Defining Meta Objectives Using Business Process Management. Inf. Manag. 2020, 57, 103262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekic, Z.; Koroteev, D. From Disruptively Digital to Proudly Analog: A Holistic Typology of Digital Transformation Strategies. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinan, P.J.; Parise, S.; Langowitz, N. Creating an Innovative Digital Project Team: Levers to Enable Digital Transformation. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergel, I.; Edelmann, N.; Haug, N. Defining Digital Transformation: Results from Expert Interviews. Gov. Inf. Q. 2019, 36, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.; Ahumada, D.; Hochstetter, J.; Paz, F. Relations on Cultural Behavior and Technology Adoption: A Chilean Perspective. In Proceedings of the Design, User Experience, and Usability: Design for Diversity, Well-Being, and Social Development; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, J.; Rusu, C.; Collazos, C.A. Experimental Validation of a Set of Cultural-Oriented Usability Heuristics: E-Commerce Websites Evaluation. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2017, 50, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, D.R.; Oliveira, T.; de Oliveira Santini, F. Drivers of Digital Transformation Adoption: A Weight and Meta-Analysis. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, C.; Hess, T.; Benlian, A. Digital Transformation Strategies. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2015, 57, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaridas-Nalda, F.; Clavel-San Emeterio, M.; Fernández-Ortiz, R.; Arias-Oliva, M. The Strategic Influence of School Principal Leadership in the Digital Transformation of Schools. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 112, 106481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Sivathanu, B.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Shopping Intention at AI-Powered Automated Retail Stores (AIPARS). J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 57, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, G.; Bagchi, K.; Maity, M. Exploring Factors Affecting Digital Piracy Using the Norm Activation and UTAUT Models: The Role of National Culture. J. Bus. Ethics 2016, 135, 517–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, L.; Jarvenpaa, S.L. Digital Action Repertoires and Transforming a Social Movement Organization. MIS Q. 2016, 40, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, G.; Paul, J.; Shrivastava, A. Hyper-Personalization, Co-Creation, Digital Clienteling and Transformation. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, G. The Technology Fallacy. Res. Technol. Manag. 2019, 62, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuukkanen, V.; Wolgsjö, E.; Rusu, L. Cultural Values in Digital Transformation in a Small Company. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 196, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, J.S.; Ding, A.W.; Li, S. From Cultural Entrepreneurship to Economic Entrepreneurship in Cultural Industries: The Role of Digital Serialization. J. Bus. Ventur. 2021, 36, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, M.A.; Counsell, S.; Swift, S. A Conceptual Model for the Process of IT Innovation Adoption in Organizations. J. Eng. Tech. Manag. 2012, 29, 358–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. Cultures and Organizations-Software of the Mind, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISBN 0071664181. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, G. Culture’s Consequences, 2nd ed.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjielias, E.; (Lola) Dada, O.; Discua Cruz, A.; Zekas, S.; Christofi, M.; Sakka, G. How Do Digital Innovation Teams Function? Understanding the Team Cognition-Process Nexus within the Context of Digital Transformation. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Qi Dong, J.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital Transformation: A Multidisciplinary Reflection and Research Agenda. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, A. Cross-Cultural User-Interface Design. Hum.-Comput. Interface Intern. (HCII) 2001, 2, 502–505. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Report. Chapter: Cultural Dimensions and Global Web Design—Experience Intelligent Design; Aaron Marcus and Associates, Inc: Emeryville, CA, USA. Available online: https://laofutze.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/ama_cultdim.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- World Economic Outlook Database April 2022--WEO Groups and Aggregates Information. Available online: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2022/01/weodata/groups.htm (accessed on 16 May 2024).
- O’Sullivan, S. Economics: Principles in Action (Texas Edition), 2nd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780130634597. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, D.L.; Meira, L.H.; Costa, C.S.; Pitombo, C.S. An Overview of the Impacts of Ridesourcing in Developing Countries: Main Topics and Questions for Future Research. Lat. Am. Transp. Stud. 2024, 2, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talla Fokam, D.N.D.; Kamga, B.F.; Nchofoung, T.N. Information and Communication Technologies and Employment in Developing Countries: Effects and Transmission Channels. Telecomm. Policy 2023, 47, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Abdelli, M.E.A.; Mogaji, E. Do Digital Technologies Influence the Relationship between the COVID-19 Crisis and SMEs’ Resilience in Developing Countries? J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, P.I.; Sensuse, D.I. Exploring the Influence Factor of Social Media Adoption to SMEs Performance: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference of Computer and Informatics Engineering (IC2IE), Depok, Indonesia, 14–15 September 2021; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Alhamami, A.A.; Hashim, N.A.; Hamid, R.A.; Hamid, S.N.A. The Adoption of Social Media by Small and Medium Enterprise: A Systematic Literature Review. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 24, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, K.; Nurul, C.A.; Subaeki, B.; Pitara, S.; Kaffah, F.M.; Rahman, A.B.A. E-Readiness Model to Measure Implementation Information and Communication Technology on Cooperatives in Indonesian: A Systematic Literature. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Wireless and Telematics (ICWT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 21–22 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alsibhawi, I.A.A.; Yahaya, J.B.; Mohamed, H.B. Business Intelligence Adoption for Small and Medium Enterprises: Conceptual Framework. NATO Adv. Sci. Inst. Ser. E Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Technology Adoption Models: A Critical Review for SMEs in Odisha. Available online: https://iaeme.com/MasterAdmin/Journal_uploads/IJMET/VOLUME_9_ISSUE_4/IJMET_09_04_042.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2024).
- Ahmad, M.; Siraj, S. A Systematic Review and Analysis of Determinants Impacting Adoption and Assimilation of E-Commerce in Small and Medium Enterprises. Int. J. Electron. Bus. 2018, 14, 326–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhim, R.; Wulandari, P.; Mayasari, I. Small Medium Enterprises Technology Acceptance Model: A Conceptual Review. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2018, 19, 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Ammeran, M.Y.; Noor, S.; Yusof, M. Digital Transformation of Malaysian Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Review and Research Direction. In Proceedings of the Innovation of Businesses, and Digitalization during COVID-19 Pandemic; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 255–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ragazou, K.; Passas, I.; Sklavos, G. Investigating the Strategic Role of Digital Transformation Path of SMEs in the Era of COVID-19: A Bibliometric Analysis Using R. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2022, 14, 11295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, E.P.; Sumartias, S.; Priyatna, S.; Rahmat, A. A Review on Digitalization of CSR during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia: Opportunities and Challenges. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenbach, S.; de Kock, I.H.; Grobler, J. Data Science for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises: A Structured Literature Review. S. Afr. J. Ind. Eng. 2022, 33, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratana, L.S.; Zakaria, R.; Munikanan, V.; Aminudin, E.; Shamsuddin, S.M.; Yahya, M.A.; Sam, A.R.M.; Wahi, N.; Gara, J.; Sahamir, S.R. SME Contractor Multi-Criteria Business Model on Adaptation of Construction Industry Revolution 4.0 in Malaysia—A Review on Business Models and Adaptation Challenges. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 97, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Vilkas, M.; Grybauskas, A.; Amran, A. Drivers and Barriers of Industry 4.0 Technology Adoption among Manufacturing SMEs: A Systematic Review and Transformation Roadmap. Int. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 1029–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viloria-Núñez, C.; Vázquez, F.J.; Fernández-Márquez, C.M. A Review of the Digital Transformation Maturity Models for SMEs in Search of a Self-Assessment. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE ANDESCON, Barranquilla, Colombia, 16–19 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.R.; Akhter, F.; Sultana, M.M. SMEs in Covid-19 Crisis and Combating Strategies: A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) and A Case from Emerging Economy. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2022, 9, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, V.; Santoso, I.; Mustaniroh, S.A. Development Strategy of SMEs in the New Normal Era of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Literature Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 733, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokundun, M.; Ogbari, M.E.; Falola, H.; Ibidunni, A.S. Leveraging 5G Network for Digital Innovation in Small and Medium Enterprises: A Conceptual Review. J. Innov. Entrep. 2022, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Falahat, M. The Impact of Digitalization and Resources on Gaining Competitive Advantage in International Markets: Mediating Role of Marketing, Innovation and Learning Capabilities. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, G.A.; Alves Junior, P.N.; Costa Melo, I. Digitalization as an Enabler to SMEs Implementing Lean-Green? A Systematic Review through the Topic Modelling Approach. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2022, 14, 14089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangarso, A.; Sisilia, K.; Setyorini, R.; Peranginangin, Y.; Awirya, A.A. The Long Path to Achieving Green Economy Performance for Micro Small Medium Enterprise. J. Innov. Entrep. 2022, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for Conducting Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering: An Update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781405150149. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.A.; Charters, S. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; EBSE Technical Report EBSE-2007-01; Keele University: Newcastle, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gwet, K. Inter-Rater Reliability: Dependency on Trait Prevalence and Marginal Homogeneity. Stat. Methods Inter-Rater Reliab. Assess. Ser. 2002, 2, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Tornatzky, L.G.; Fleischer, M.; Chakrabarti, A.K. The Processes of Technological Innovation; Lexington Books: Lexington, MI, USA, 1990; ISBN 9780669203486. [Google Scholar]
- Frantzi, K.; Ananiadou, S.; Mima, H. Automatic Recognition of Multi-Word Terms: The C-value/NC-Value Method. Int. J. Digit. Libr. 2000, 3, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, R.; Day, J. Determinant Factors of E-Commerce Adoption by SMEs in Developing Country: Evidence from Indonesia. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, H. Factors Affecting E-Marketing Adoption and Implementation in Tourism Firms: An Empirical Investigation of Egyptian Small Tourism Organisations. Tour. Manag. 2012, 33, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-S.; Tao, Y.-H. Understanding Business-Level Innovation Technology Adoption. Technovation 2009, 29, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M.; Singhal, A.; Quinlan, M.M. Diffusion of Innovations. In An Integrated Approach to Communication Theory and Research; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahway, MJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Molla, A.; Licker, P.S. eCommerce Adoption in Developing Countries: A Model and Instrument. Inf. Manag. 2005, 42, 877–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özşahin, M.; Çallı, B.A.; Coşkun, E. ICT Adoption Scale Development for SMEs. Sustain. Sci. Pract. Policy 2022, 14, 14897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniasari, F.; Gunawan, D.; Utomo, P. Factors Influencing Small Medium Enterprise’s Behavior in Adopting E-Fulfillment Services. Int. J. Prof. Bus. Rev. 2022, 7, e0550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, S.C.; Chinedu-Eze, V.C.; Oluyemi, B.A.; Inegbedion, H.; Nwanji, T.; Asamu, F. Mobile Marketing Technology Adoption in Service SMEs: A Multi-Perspective Framework. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2019, 10, 569–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bvuma, S.; Marnewick, C. An Information and Communication Technology Adoption Framework for Small, Medium and Micro-Enterprises Operating in Townships South Africa. South. Afr. J. Entrep. Small Bus. Manag. 2020, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiaei, A.; Ab. Rahim, N.Z. A Multifaceted Framework for Adoption of Cloud Computing in Malaysian SMEs. J. Sci. Technol. Policy Manag. 2019, 10, 708–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramantoko, G.; Fatimah, L.V.; Pratiwi, S.C.; Kinasih, K. Measuring Digital Capability Maturity: Case of Small-Medium Kampong-Digital Companies in Bandung. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2018, 26, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Khin, S.; Hung Kee, D.M. Identifying the Driving and Moderating Factors of Malaysian SMEs’ Readiness for Industry 4.0. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 35, 761–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, Ł.; Cyplik, P. The Concept of Building a Digital Transformation Model for Enterprises from the SME Sector. Logforum 2020, 16, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahama, F.; Dahlan, H.M. Accounting Information System Adoption Model for Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Northern Ghana. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 25–26 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jayashree, S.; Reza, M.N.H.; Malarvizhi, C.A.N.; Gunasekaran, A.; Rauf, M.A. Testing an Adoption Model for Industry 4.0 and Sustainability: A Malaysian Scenario. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 31, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Mahara, T. Factors Affecting E-Commerce Adoption by Handicraft SMEs of India. JECO 2019, 17, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creating a Market for eHealth Entrepreneurs. In European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreneurship; Academic Conferences International Limited: Kalamata, Greece, 2019.
- Handayani, S.F.; Er, M. Antecedent and Business Process Management Non-Technical Capabilities in Social Media Implementation for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises: A Conceptual Model. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 161, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leso, B.H.; Cortimiglia, M.N.; Ghezzi, A. The Contribution of Organizational Culture, Structure, and Leadership Factors in the Digital Transformation of SMEs: A Mixed-Methods Approach. Cogn. Technol. Work 2023, 25, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okfalisa, O.; Anggraini, W.; Nawanir, G.; Saktioto, S.; Wong, K.Y. Measuring the Effects of Different Factors Influencing on the Readiness of SMEs towards Digitalization: A Multiple Perspectives Design of Decision Support System. Decis. Sci. Lett. 2021, 10, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulas, D. Digital Transformation Process and SMEs. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, D.T.; Talero-Sarmiento, L.H.; Ortiz, J.D.; Guerrero, C.D. Technology Readiness for IoT Adoption in Colombian SMEs. In Proceedings of the 2021 16th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Chaves, Portugal, 23–26 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, C.; Samikon, S.A.; Kharuddin, A.F.; Nuvriasari, A.; Pratama, H. The Impact of Online Business Marketing on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Performance (SMEs). Gen. Manag. 2022, 23, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Kofi, D.J.; de Wetering Rogier, V.; Honyenuga, B.; Versendaal, J. Extended Contextual Validation of Stakeholder Approach to Firm Technology Adoption: Moderating and Mediating Relationships in an Innovation Eco-System. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2022, 17, 506–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qalati, S.A.; Ostic, D.; Sulaiman, M.A.B.A.; Gopang, A.A.; Khan, A. Social Media and SMEs’ Performance in Developing Countries: Effects of Technological-Organizational-Environmental Factors on the Adoption of Social Media. Sage Open 2022, 12, 21582440221094594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Khan, M.R. Identification of Roles and Factors Influencing the Adoption of ICTs in the SMEs of Pakistan by Using an Extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). Innov. Dev. 2024, 14, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawati, E.; Kohar, U.H.A.; Meiji, N.H.P.; Handayati, P.; Ilies, D.C. Digital Transformation for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises to Develop Sustainable Community-Based Marine Tourism. Afr. J. Hosp. Tour. Leis. 2022, 11, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Ascúa, R.A. Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing SMEs of Argentina and Brazil. J. Int. Counc. Small Bus. 2021, 2, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumrit, D. What Are the Obstacles Hindering Digital Transformation for Small and Medium Enterprise Freight Logistics Service Providers? An Interpretive Structural Modeling Approach. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 2021, 9, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, H.; Wee, S.Y.; Rina, R.; Ikram, B.R. A Model of the E-Wallet Adoption in Small and Medium Enterprises (sme) Indonesia. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2020, 98, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar]
- Rozak, H.A.; Adhiatma, A.; Fachrunnisa, O.; Rahayu, T. Social Media Engagement, Organizational Agility and Digitalization Strategic Plan to Improve SMEs’ Performance. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, Z.; Hee, O.C. Affiliate Marketing in SMEs: The Moderating Effect of Developmental Culture. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2021, 29, 1249–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.; Villareal, A.; Aguirre, A.; Collazos, C.A.; Rusu, C.; Quiñones, D.; Virginica, R. Website Transformation of a Latin American Airline: Effects of Cultural Aspects and User Experience on Business Performance. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2019, 17, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N | Objective | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Adoption of Digital Technologies and Social Networks: Includes studies investigating how the adoption of social networks and digital technologies influences the performances of SMEs. This covers the influence of social networks on business performance, the current and future direction of social network marketing, and the adoption of social media in SMEs. | [55,56] |
| 2 | E-readiness and ICT Implementation: This includes works that develop models to measure ICT implementation in organizations, such as the e-readiness model for cooperatives, and the adoption of business intelligence systems based on theories such as TAM and UTAUT. | [57,58,59,60,61] |
| 3 | Digital Transformation in Response to External Challenges: This association considers papers highlighting the importance of digital transformation in response to COVID-19, assessing how SMEs adapt their strategies and operations through digitization and how the pandemic has influenced Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) digitization. | [62,63,64] |
| 4 | Impact of Industrial Revolution 4.0 and Digitization: This section focuses on studies examining the impact of Industrial Revolution 4.0 and digitization on SMEs, including adaptation strategies, the role of digitization in Lean–Green practices, and the challenges and opportunities involved in implementing data science. | [65,66,67] |
| 5 | Digital Maturity Assessment and Improvement: This section includes analyses that seek to develop self-assessment models to measure the digital maturity of SMEs and provide a framework for the adoption of 5G technology to foster digital innovation. | [68] |
| 6 | Responses to the COVID-19 Crisis and Strategies for Development: This topic brings together research on the impacts of the COVID-19 crisis on SMEs, offering strategies to combat challenges and improve resilience. | [69,70] |
| 7 | Competitive Advantages and Access to International Markets: This chapter examines how digitization and other determinants can contribute to SMEs’ competitive advantages in international markets, including the role of digitization in the adoption and uptake of e-commerce. | [71,72] |
| 8 | Sustainability and the Green Economy: This topic focuses on studies that provide frameworks on how MSMEs can achieve green economic performance through green economy readiness and digitization. | [73,74] |
| ID | Item | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| RQ1 | (a) What are the digital transformation models that allow for evaluating technological adoption in micro and small companies? | To identify general technology adoption models. |
| RQ2 | (b) What are the mechanisms for assessing cultural behavior in micro and small enterprises? | To identify formal models of cultural behavior and sociocultural impacts on digital transformation. |
| RQ3 | (c) What are the technological barriers affecting MSEs in developing countries? | To identify technology gaps and barriers. |
| RQ4 | (c) What are the determining factors and drivers in the digital transformation process for MSEs in developing countries? | To identify drivers of the digital transformation process. |
| Criteria | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Population | micro enterprise, small enterprise, medium-sized enterprise |
| Intervention | technology adoption model, digital transformation |
| Comparison | n/a |
| Outcome | process, initiatives, proposals, products, software, model |
| Context | academy, industry |
| Keyword | Synonyms |
|---|---|
| digital transformation | digital disruption, digital innovation, digital modernization, digitalization |
| model | approach, practice, procedure, protocol, technique, framework, initiative, method, process, product, proposal, software |
| small enterprise | SME, SMEs, medium enterprise, micro enterprise |
| technology adoption model | TAM, TOE, technology acceptance, technology adaptation, Tornatzky |
| Research Chain |
|---|
| (“small enterprise” OR “SME” OR “SMEs” OR “medium enterprise” OR “micro enterprise”) AND (“digital transformation” OR “Digital disruption” OR “Digital innovation” OR “Digital modernization” OR “digitalization” OR “technology adoption model” OR “TAM” OR “TOE” OR “Technology acceptance” OR “Technology adaptation” OR “Tornatzky”) AND (“model” OR “Approach” OR “Practice” OR “Procedure” OR “Protocol” OR “Technique” OR “framework” OR “initiative” OR “method” OR “process” OR “product” OR “proposal” OR “software”) |
| Source | Link |
|---|---|
| ACM Digital Library | http://portal.acm.org (accessed on 1 December 2023) |
| IEEE Digital Library | http://ieeexplore.ieee.org (accessed on 1 December 2023) |
| ISI Web of Science | http://www.isiknowledge.com (accessed on 1 December 2023) |
| Scopus | http://www.scopus.com (accessed on 1 December 2023) |
| Wiley | https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com (accessed on 1 December 2023) |
| Criteria | Scenarios |
|---|---|
| Inclusion Criteria | cultural behavior, developing countries, developing enterprises, digital transformation, technology adoption model |
| Exclusion Criteria | congress ranking, literature review, non-article or non-conference, non-technology-related, short paper/position paper/poster, software-only approach, year, developed countries, full/big enterprise, inaccessible |
| Data Extraction Form | sociocultural objective, technology, organization, environment, cultural behavior model, application context, technology adoption method |
| Stage | Filter Element | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Search | Metadata |
|
| Filter 1 | Title |
|
| Filter 2 | Type of Article |
|
| Filter 3 | Title and abstract |
|
| Filter 4 | Title and abstract |
|
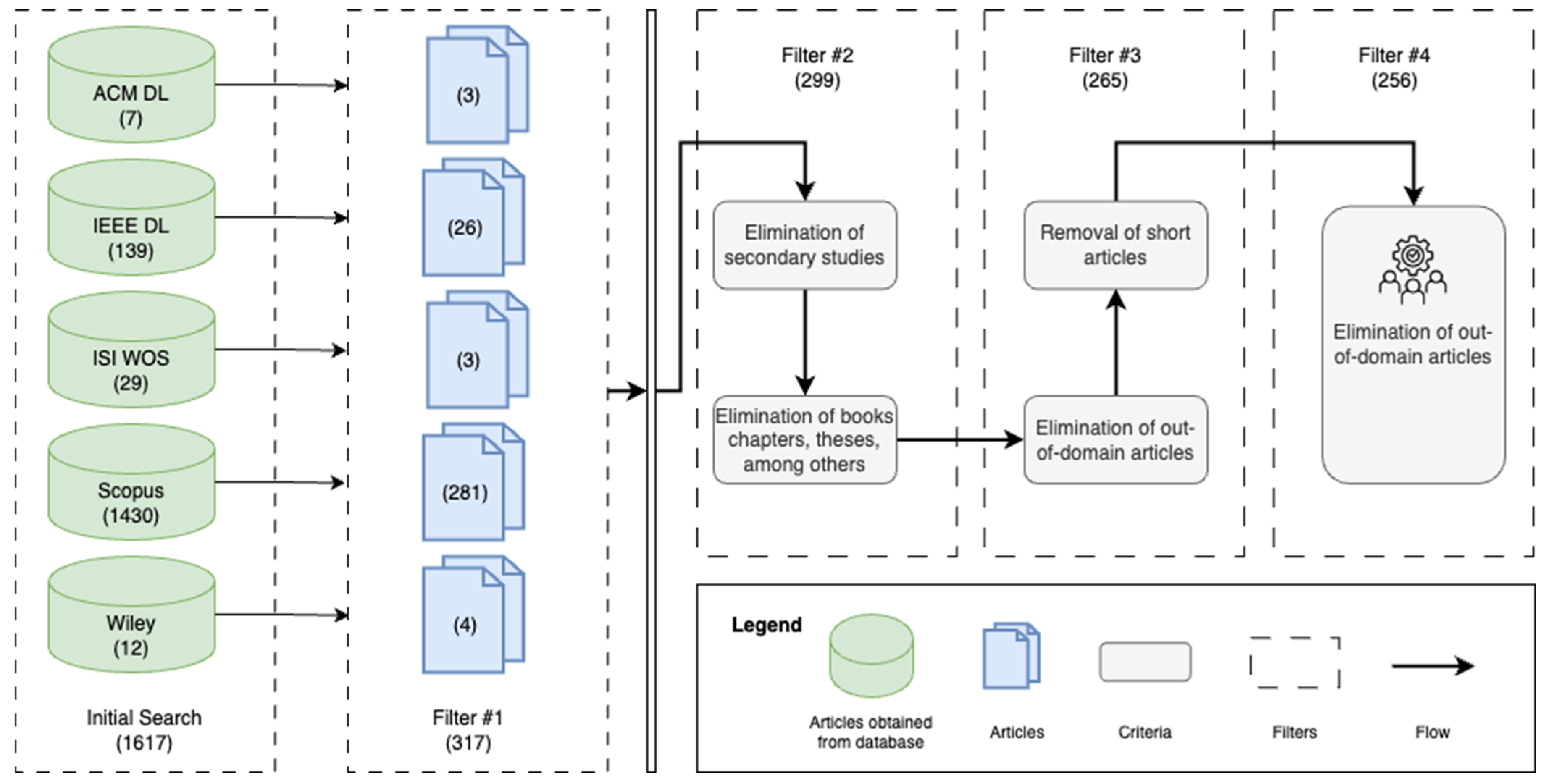
| Data Source | Initial Search | Filter 1 | Filter 2 | Filter 3 | Filter 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACM DL | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| IEEE DL | 139 | 26 | 26 | 24 | 17 |
| ISI WOS | 29 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| SCOPUS | 1430 | 281 | 264 | 237 | 236 |
| WILEY | 12 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 1617 | 317 | 299 | 265 | 256 |
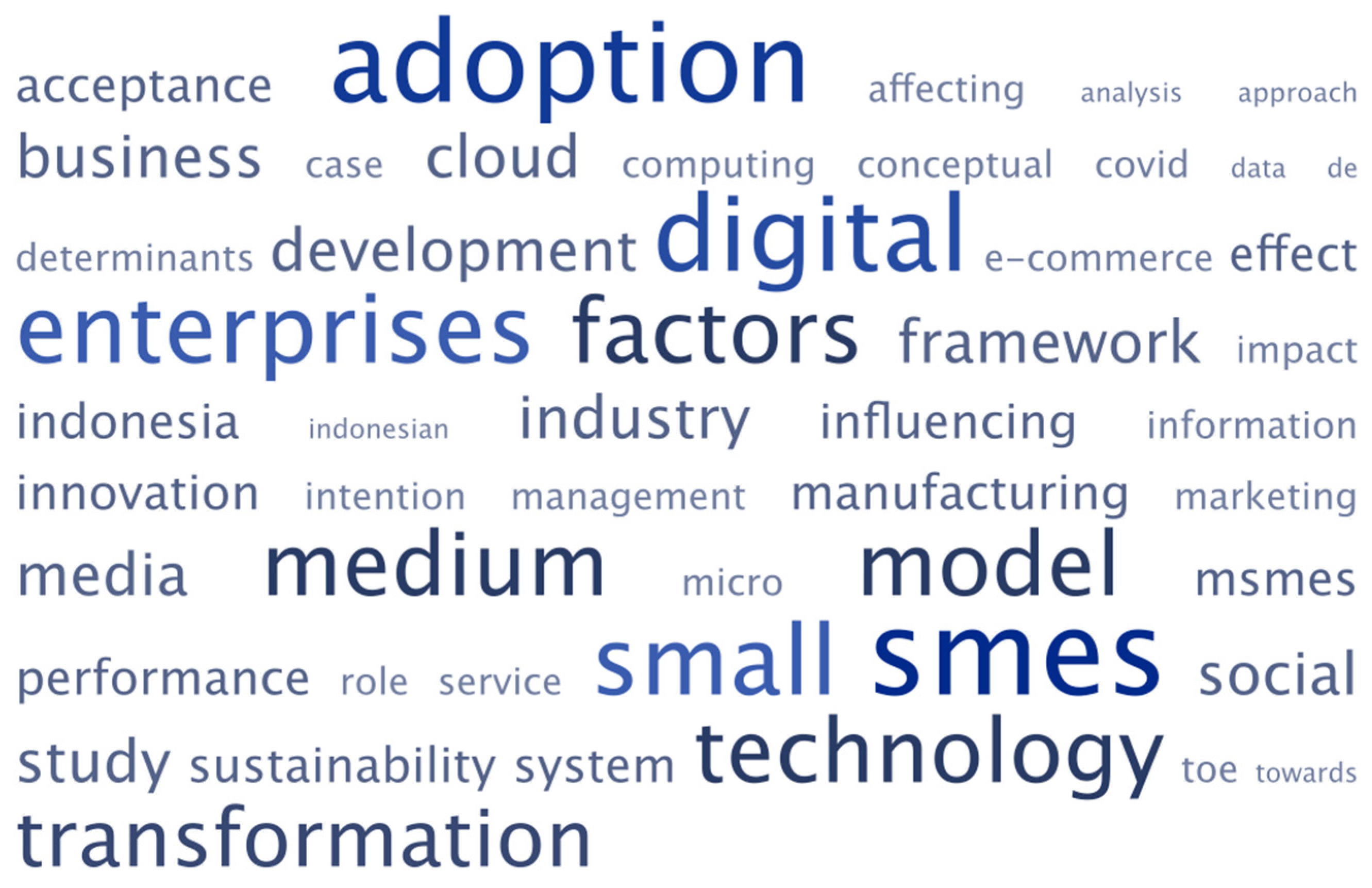
| Rank | Term | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | digital transformation | 145.6 |
| 2 | medium enterprise | 93.6 |
| 3 | social medium | 89.8 |
| 4 | technology acceptance model | 80.8 |
| 5 | medium-sized enterprise | 54.0 |
| 6 | cloud computing | 52.7 |
| 7 | structural equation | 51.2 |
| 8 | technology acceptance | 50.5 |
| 9 | top management support | 49.1 |
| 10 | acceptance model | 40.2 |
| 11 | structural equation modeling | 37.9 |
| 12 | business model | 37.6 |
| 13 | digital technology | 36.7 |
| 14 | technology adoption | 35.9 |
| 15 | top management | 31 |
| 16 | information technology | 30.9 |
| 17 | social commerce | 24.8 |
| 18 | adoption model | 24.6 |
| 19 | competitive advantage | 24 |
| 20 | digital innovation | 22.3 |
| 21 | TOE framework | 22 |
| 22 | competitive pressure, research model | 21 |
| 23 | government support | 20 |
| 24 | social medium adoption | 19.8 |
| 25 | supply chain | 19.7 |
| 26 | management support | 19 |
| 27 | social medium marketing, ICT adoption | 18.7 |
| 28 | literature review | 17.6 |
| 29 | structural equation model | 17.1 |
| 30 | behavioral intention | 17 |
| 31 | cloud ERP | 16.8 |
| 32 | information system | 16.5 |
| 33 | SME performance | 16 |
| 34 | conceptual framework, environmental factor | 15 |
| 35 | big datum | 14.8 |
| 36 | digital marketing | 14.6 |
| 37 | cloud ERP adoption | 14.2 |
| 38 | SME owner, practical implication | 14 |
| 39 | ERP adoption | 13.8 |
| 40 | financial inclusion | 13.6 |
| Article | Ref. |
|---|---|
| ICT Adoption Scale Development For SMEs | [87] |
| Factors Influencing Small Medium Enterprises Behavior In Adopting E-Fulfillment Services | [88] |
| Mobile Marketing Technology Adoption In Service SMEs: A Multi-Perspective Framework | [89] |
| An Information And Communication Technology Adoption Framework For Small, Medium And Micro Enterprises Operating In Townships South Africa | [90] |
| A Multifaceted Framework For Adoption Of Cloud Computing In Malaysian SMEs | [91] |
| Measuring Digital Capability Maturity: Case Of Small-Medium Kampong-Digital Companies In Bandung | [92] |
| Identifying The Driving And Moderating Factors Of Malaysian SMEs’ Readiness For Industry 4.0 | [93] |
| The Concept Of Building A Digital Transformation Model For Enterprises From The SME Sector | [94] |
| Accounting Information System Adoption Model For Small And Medium-Sized Enterprises In Northern Ghana | [95] |
| Testing An Adoption Model For Industry 4.0 And Sustainability: A Malaysian Scenario | [96] |
| Factors Affecting E-Commerce Adoption By Handicraft SMEs Of India | [97] |
| Creating A Market For E-Health Entrepreneurs | [98] |
| Antecedent And Business Process Management Non-Technical Capabilities In Social Media Implementation For Micro, Small And Medium Enterprises: A Conceptual Model | [99] |
| Article Title | Author’s Keywords | Behavioral Model/ Construct Correlation | Cultural Behavior Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| [100] The contribution of organizational culture, structure, and leadership factors in the digital transformation of SMEs: a mixed-methods approach | digital transformation; organizational culture; organizational structure; leadership; small and medium enterprises; mixed methods; business model | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [101] Measuring the effects of different factors influencing on the readiness of SMEs towards digitalization: A multiple perspectives design of decision support system | small–medium enterprises; performance measurement; decision support system;, digitalization readiness; fuzzy analytical hierarchy process | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [102] Digital Transformation Process and SMEs | digital transformation; SMEs; e-commerce, enterprise 4.0.; big data; cloud computing; 3D printing | No | Yes—Organizational |
| [103] Technology readiness for IoT adoption in Colombian SMEs | digital transformation; IoT adoption; IoT readiness; SMEs; technology readiness; TOE framework | No | Yes—Organizational |
| [104] The Impact of Online Business Marketing on Small and Medium-Sized Enterprise Performance (SMEs) | online business marketing; competitiveness; SMEs; performance; implementation | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [105] Extended contextual validation of stakeholder approach to firm technology adoption/moderating and mediating relationships in an innovation eco-system | F-tam; innovation; stakeholder ecosystem; SMEs | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [106] Social Media and SMEs’ Performance in Developing Countries Effects of Technological-Organizational-Environmental Factors on the Adoption of Social Media | TOE framework; SME performance; social media adoption; developing countries | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [107] Identification of roles and factors influencing the adoption of ICTs in the SMEs of Pakistan by using an extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) | SME growth, entrepreneurial behavior; innovation development; information and communication technology factors; technology acceptance model; emerging economies | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [108] Digital Transformation for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises to Develop Sustainable Community-Based Marine Tourism | CBT; youth; MSMEs; marine tourism | No | Yes—Organizational |
| [109] Industry 4.0 in manufacturing SMEs of Argentina and Brazil | SMEs; industrial organization; technology | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [110] What are the obstacles hindering digital transformation for small and medium enterprise freight logistics service providers? An interpretive structural modeling approach | digital transformation; interpretive structural modeling; logistics service providers; matrix impact of cross-multiplication applied to classification; small–medium enterprises | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [111] A Model Of The E-Wallet Adoption In Small And Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Indonesia | e-wallet; small and medium enterprises (SMEs); technology acceptance model (TAM); diffusion of innovations (DOI); technology–organization–environment (TOE); Guanxi | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [112] Social Media Engagement, Organizational Agility and Digitalization Strategic Plan to Improve SMEs Performance | digital skill; ICT utilization; media engagement; organizational agility; small–medium enterprise (SME) performance | Yes | Yes—Organizational |
| [113] Affiliate Marketing in SMEs: The Moderating Effect of Developmental Culture | affiliate marketing; developmental culture; SMEs; technology adoption models | Yes | Yes—Author’s approach |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Arancibia, J.; Hochstetter-Diez, J.; Bustamante-Mora, A.; Sepúlveda-Cuevas, S.; Albayay, I.; Arango-López, J. Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145946
Díaz-Arancibia J, Hochstetter-Diez J, Bustamante-Mora A, Sepúlveda-Cuevas S, Albayay I, Arango-López J. Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries. Sustainability. 2024; 16(14):5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145946
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Arancibia, Jaime, Jorge Hochstetter-Diez, Ana Bustamante-Mora, Samuel Sepúlveda-Cuevas, Isidora Albayay, and Jeferson Arango-López. 2024. "Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries" Sustainability 16, no. 14: 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145946
APA StyleDíaz-Arancibia, J., Hochstetter-Diez, J., Bustamante-Mora, A., Sepúlveda-Cuevas, S., Albayay, I., & Arango-López, J. (2024). Navigating Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption: A Literature Review from Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Developing Countries. Sustainability, 16(14), 5946. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16145946









