Abstract
In this paper, machine vision technology is used to recognize the coal flow on a conveyor belt and control the running speed of a motor according to the coal flow on the conveyor belt to achieve an energy-saving effect and provide technical support for the sustainable development of energy. In order to improve the accuracy of coal flow recognition, this paper proposes the color gain-enhanced multi-scale retina algorithm (AMSRCR) for image preprocessing. Based on the YOLOv8s-cls improved deep learning algorithm YOLO-CFS, the C2f-FasterNet module is designed to realize a lightweight network structure, and the three-dimensional weighted attention module, SimAm, is added to further improve the accuracy of the network without introducing additional parameters. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of the improved algorithm YOLO-CFS reaches 93.1%, which is 4.8% higher, and the detection frame rate reaches 32.68 frame/s, which is 5.9% higher. The number of parameters is reduced by 28.4%, and the number of floating-point operations is reduced by 33.3%. These data show that the YOLO-CFS algorithm has significantly improved the accuracy, lightness, and reasoning speed in the coal mine environment. Furthermore, it can satisfy the requirements of coal flow recognition, realize the energy-saving control of coal mine conveyor belts, and achieve the purpose of sustainable development of the coal mining industry.
1. Introduction
Energy consumption during coal mine production is a key issue for the sustainable development of the industry. In the production work process of coal mines, because of the differences in the storage capacity of coal seams, there are large fluctuations in the amount of coal coming out of the comprehensive mining face. The conveyor belt, as the main coal transfer tool, runs at a constant speed all day long after startup, often in a large marathon or even under the state of no load [1], resulting in a serious waste of energy [2]. It has been found that the energy consumption of a conveyor belt can be effectively reduced by constructing an energy-saving control strategy and adjusting the conveyor belt running speed in real time according to the conveyor belt coal flow [3]. A reduction in the reactive power consumption of the conveyor belt can change the energy waste situation in the coal mine production process and realize the sustainable development of energy.
Existing conveyor belt coal flow detection methods are mainly divided into two categories as follows: contact and non-contact. The electronic belt scale [4] is now a widely used contact dynamic coal flow detection method. However, the detection error of the electronic belt scale is large, and it is difficult to balance the sensitivity and detection accuracy. Non-contact detection methods such as nuclear scales and ultrasonic waves solve the problems of belt wear and the vibration of equipment that affect the accuracy of the contact type. However, nuclear scales require complex calibration, radioactive materials are damaging to the human body, and the equipment itself has the problem of radioactive source decay, so their scope of application has been limited [5]. The ultrasonic detection method determines the amount of coal by calculating the distance through the time difference between the emitted sound wave and the received sound wave and the speed of sound wave transmission, but it causes serious interference in the complex environment of coal mines [6].
In recent years, with the development of computer technology, non-contact detection technology based on visual detection and deep learning technology has begun to be widely used in coal mine production. Wang et al. [7] proposed a coal flow detection method based on binocular vision to obtain the volume of coal flow by three-dimensional modeling of the coal flow through binocular vision. However, the method cannot meet real-time demand in terms of speed and accuracy, and its practicality needs to be improved. Wen et al. [8] proposed reconstructing the centerline of laser stripes in two dimensions by binocular vision to obtain the cross-sectional area of coal flow and fit a three-dimensional stereo model to the continuous cross-section to obtain the coal flow information. However, this method requires complex equipment, relies on the stability of the dual camera installation, requires strict calibration of the camera, has poor robustness under the influence factors of vibration, smoke, and dust in the coal mine environment, and has a high cost. Article [9] used machine vision technology for the integrated detection of tears and deviation of belts. Mao et al. [10] used an improved yolov5 algorithm for foreign object identification of coal mine conveyor belts to ensure the safe operation of conveyor belts. Zhu et al. [11] utilized deep learning and extreme machine learning for the online detection of conveyor belts with deviation. Yang et al. [12] used infrared vision for conveyor belt longitudinal tear detection.
In the study of sustainability in coal mines, safety in mines has been a worldwide topic. Duda [13] proposed a strategy to reduce methane emissions by utilizing methane gas in the air and reducing the hazards of harmful gases such as methane in mines for miners. Sinha et al. [14] monitored the environmental changes in coal mines through a smart environmental detection system to protect miners’ safety. Kumar et al. [15] designed a Smart Helmet for Coal Mine Employees to improve the safety of employees by detecting and alerting them of potential risks. Karthika et al. [16] designed a safety jacket to carry out environmental detection in coal mines and to monitor the physical condition of miners to provide protection. These designs are worldwide contributions to smart coal mines, but they do not fundamentally address coal mine safety, whereas deep learning-based visual detection systems can reduce the time miners spend in risky environments by visually detecting coal mine environments and realizing remote control, which effectively reduces the occurrence of various types of personnel safety accidents.
Aiming at the real-time and accuracy problems of the existing detection methods, this paper proposes a visual detection method based on deep learning. Aiming at disturbing factors such as high dust and insufficient light in the coal mine environment, the image is preprocessed by the color gain-enhanced multi-scale retina algorithm (AMSRCR). In order to ensure system accuracy and real-time detection efficiency, the YOLO-CFS algorithm based on the YOLOv8-cls algorithm is proposed to improve the accuracy and inference speed of the algorithm by lightweighting the YOLOv8-cls algorithm, adding a lightweighting module, and further improving the accuracy of the algorithm by adding an attention mechanism.
2. Model Optimization and Improvement
2.1. Image Preprocessing
Compared with the normal lighting environment, coal mines have more disturbing factors such as harsh environment and dusty and insufficient light, causing the images captured by the image acquisition system to be of generally poor quality. The method of visual detection relies heavily on the quality of the image. The complexity of the coal mine environment, the gray color of the coal material, color changes in the conveyor belt, changes in ambient light, etc., will affect the detection effect and reduce detection accuracy, so it is of great practical significance to use image enhancement technology to preprocess captured images before deploying the coal flow detection system in the coal mine environment.
Image preprocessing is a key step in the identification of coal flow in a belt conveyor, which is related to whether the subsequent deep learning model can obtain accurate coal flow information. Thus, it is necessary to carry out noise reduction and enhancement processing on the original images collected to improve the robustness of the subsequent feature extraction and classification process.
The existing histogram equalization (HE) technique for image enhancement by boosting the contrast of an image is a standard image enhancement technique that can be used for unimodal images. There are currently a variety of variants of the basic HE, including Adaptive Histogram Equalization (AHE) [17] and Contrast-Limited Adaptive Libertarian Equalization (CLAHE) [18]. However, these methods have drawbacks in processing color images, and the processed color images do not behave naturally. To solve the problem of color image enhancement, the following three attributes are needed: the image can be dynamically compressed, the color information and illumination information are independent of each other, and the color information and illumination information can be reproduced.
Retinex theory suggests that the human eye’s perception of an object is mainly due to the reflective properties of the object itself. The perception of color, brightness, and other information stems from the information received by the human eye from the reflection of different lighting conditions, which is used in graphics enhancement to set the value of each pixel in the image as the product of the ambient illuminance information and the reflective component. After filtering the illumination information, the original reflective properties of the object are obtained.
where represents the coordinate position, S is the pixel information of the image acquired by the camera, R is the reflective component, and L is the illumination information that needs to be eliminated. The reflective component of the object is obtained after the operation. The color gain-enhanced multi-scale retinal algorithm (AMSRCR), a color constant algorithm used in this paper, is based on the Retinex algorithm, which adds a color recovery function for the problem of color distortion caused by the Retinex algorithm [19].
First, in order to realize the dynamic range compression of the image, a logarithmic operation is performed on Equation (2) to obtain the following equation:
The illumination information L is the key to recovering the reflection component R. Therefore, the problem reduces to solving for L. The Single-Scale Retina Algorithm (SSR) [20] utilizes Gaussian filtering and convolution of the original image S to obtain the illuminance component with the following equation:
where is the standard deviation of Gaussian filtering, which is the most important parameter in the calculation. The larger the value of , the better the smoothing effect of the image, and the smaller , the more image details are preserved. The use of Gaussian filtering can better highlight the details and contrast of the illumination component while reducing the impact of noise and making the processed image clearer and more natural.
Secondly, the Multi-scale Retinal Algorithm with Color Recovery (MSRCR) [21] adds a weighted superposition of Gaussian kernels at different scales on top of SSR, with an additional gain and offset value to focus on global information more comprehensively, while the gain and offset values achieve color recovery to solve the color distortion problem.
where G and b are the final gain and offset values, is the color recovery factor, and α and β denote the degree of controlled nonlinearity and gain constant, respectively. is the retinal algorithm for adding multiple scales, which is generally taken as N of 3, representing three scales, and is the weight of each scale. The three scale values are weighted to obtain the final retinal algorithm output.
Finally, the output of the MSRCR algorithm still has poor color restoration. The AMSRCR algorithm automatically selects the upper and lower cropping points according to the frequency of pixel appearances in the grayscale histogram and redistributes the cropped pixel points into so that the AMSRCR image is obtained. The process is automatically calculated to reduce human intervention, and the resulting image solves the color distortion problem and is complete with the three attributes of color image enhancement described above.
Experimentally verified, the AMSRCR algorithm can realize image defogging in coal mine environment and image enhancement in different lighting environment. Figure 1 shows a comparison of the actual running effect of image enhancement algorithms, which subjectively indicates that the effect of the AMSRCR algorithm is better than the other algorithms. The evaluation and comparison indexes were compared using objective parameters, and the results are shown in Table 1, where PSNR indicates the peak signal-to-noise ratio, SSIM indicates structural similarity, and RMSE indicates mean square error. The results of the comprehensive indexes of the AMSRCR algorithm are better than those of the other algorithms.
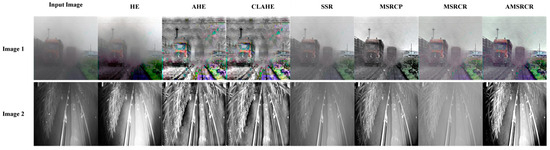
Figure 1.
Comparison of the effects of image preprocessing algorithms. Image 1 shows a picture of coal mine dust, and Image 2 shows a low-illumination picture of a mine conveyor belt.

Table 1.
Image preprocessing evaluation metrics results.
2.2. YOLOv8-cls Model Algorithm
YOLOv8, a major update from Ultralytics following YOLOv5, is a state-of-the-art (SOTA) model that builds on the success of the previous YOLO series and further improves on it by adding new features and modules to enhance the performance and flexibility of the network. The algorithm supports tasks such as image classification, target detection, instance segmentation, and target tracking. Similar to YOLOv5, the model includes several different size options N/S/M/L/X. The model parameters are gradually increased, where the larger the model, the higher the accuracy. The network structure consists of a backbone network, a feature extraction network, and a detection head section. Compared with YOLOv5, YOLOv8 adopts the C2f module in the backbone network instead of the C3 module of YOLOv5, which draws on the idea of multi-module stacking of YOLOv7 ELAN to improve the accuracy of feature extraction. The structure of the C2f module is simpler than the C3 module, so it can effectively reduce the complexity of the model and the amount of computation and improve the network model’s running speed. The C2f module contains a Split operation, which splits the channels of the feature map. The split feature map passes through the Bottleneck module and, finally, the feature map data at different scales are fused with features to form a structure similar to the residual connection, so that the network structure obtains richer information about the gradient flow, and the accuracy and speed of the model are effectively improved. The YOLOv8-cls model used in this paper is the model designed by YOLOv8 for image classification tasks, which mainly contains two parts, the backbone network and the detection head. Feature extraction is carried out in the backbone network, and the detection head of the classification and identification through the fully connected layer. The algorithm uses a cross-entropy loss function to measure the difference between the predicted and true values, which guides updating the model weights. The purpose of this paper is to carry out coal flow recognition of coal mine conveyor belts, taking into account the difficulty of hardware deployment, hardware cost, and algorithm accuracy. The YOLOv8s-cls model, which has a higher accuracy rate and a smaller model, is used as the base model to reduce the requirements for hardware equipment.
The structure of the improved YOLO-CFS algorithm in this paper is shown in Figure 2. Firstly, the C2f module of the YOLOv8s-cls model is combined with the lightweight FasterNet to obtain the C2f-FasterNet module to replace the original C2f module, thus improving detection speed and accuracy. Secondly, the 3D weighted attention mechanism SimAM is added at the position of the third layer module (L3) of the model to obtain the channel and spatial features of the image, which effectively improves the accuracy rate.
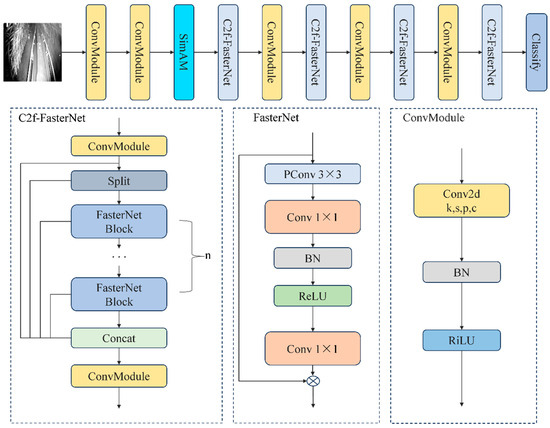
Figure 2.
Network structure diagram of YOLO-CFS.
2.3. C2f Module Improvement
The deep learning network structure performs convolutional operations. Because of the redundancy in different channels, for feature extraction, multi-channel convolutions are performed simultaneously, and these convolutions yield the same results. The feature maps of different channels have high similarity. The existing algorithms use operations such as filters to reduce the number of parameters and the number of floating-point operations, but these operations need to increase the width of the network in order to compensate for the decrease in accuracy, which increases the number of memory accesses to the network and reduces the network runtime speed. A truly effective model does not need to be run on expensive computing devices, so there is a need to design better cost-effective models of the network that reduce the complexity of the computation, the number of floating-point operands, and the running time. Chen et al. [23] proposed the FasterNet model. Their article suggested that previous models did not reduce the running time of the model when reducing the number of floating-point operands (FLOPs) because the computer needs to access the memory frequently, which consumes time. Therefore, a new partial convolution approach is needed to achieve reduced redundant computations and memory accesses.
As shown in Figure 2, the FasterNet model is composed of a PConv layer, followed by two Conv layers combined to behave as an inverted residual module. Normalization and activation layers are also indispensable for a high-performance network structure. However, in order to avoid overly restricting the diversity of features, resulting in a loss of performance, and increasing the network runtime, only batch normalization and ReLU activation functions are placed in the middle of the two Convs. Batch normalization has the feature of being able to be merged into the neighboring Conv layers to improve the inference speed. One of the PConv is a partial convolution operation, which can maintain high arithmetic by reducing floating-point operations. PConv exploits the redundancy in the feature mapping process by selecting by rule. Convolution is performed on some of the input channels, while the other channels remain unchanged, which reduces the number of redundant computations and memory accesses.
The C2f module of YOLOv8 first goes through the standard convolution, followed by the Split operation, then through several Bottleneck modules, and then concatenates all the outputs. The Bottleneck module increases the complexity of the network structure, resulting in a large amount of computation and a long running time. In order to deal with this problem, this paper proposed to combine it with the C2f-FasterNet module that combines with FasterNet, using the FasterNet module to replace the previous Bottleneck module. Compared with the original C2f module, it reduces the number of manipulated floating-point numbers and memory accesses, effectively improves accuracy, greatly reduces the running time of the model, and improves the inference speed of the model.
2.4. Introduction of the SimAm Attention Module
Because of the camera’s field of view, there will be a large amount of background interference information in the image captured by the camera. In the process of deep learning convolution, these background interferences will be superimposed to form a large amount of redundant information, which interferes with the acquisition of useful features. In order to inhibit background interference, this paper introduces the attention mechanism so that the algorithm focuses more on the acquisition of useful information. The use of the attention mechanism not only enhances the model’s ability to extract features but also makes the structure of the network more flexible. The attention mechanism is inspired by the attention mechanism of the human brain, which is one of the most important selection mechanisms that allows a person to prioritize information directly related to the target task. As shown in Figure 3, the mainstream attention mechanism is divided into a one-dimensional (1D) channel attention mechanism and a two-dimensional (2D) spatial attention mechanism, but in the human brain, spatial and channel attention coexist, and the two work together to realize visual processing and make information selection. Therefore, considering both spatial and channel dimensions simultaneously, it is inferred that the combination of the three-dimensional (3D) weighted channel attention mechanism and spatial attention mechanism is more suitable for the way the human brain works. Existing 3D weights attention mechanism modules, such as CBAM [24], estimate the spatial and channel weights separately and then combine the two together, which does not really generate 3D weights. Furthermore, the computation time of this two-step method is too long, which is not conducive to the real-time operation of the algorithm.
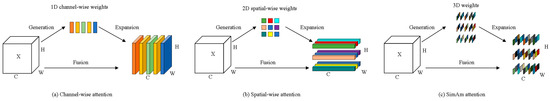
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of different attention structures. H represents the spatial pixel height, W represents the spatial pixel width, and C represents the number of channels.
The SimAM attention mechanism module is a lightweight, plug-and-play 3D weighted attention module designed by yang et al. [25] to simulate the working mechanism of the human brain. The module generates the weights as an energy function and then derives a closed solution of this energy function to form a closed loop. No additional parameters are introduced for the network structure, so no major changes to the original architecture are required to further improve the performance of the network structure in the task. By modeling the human brain, each neuron is assigned a weight. The truly active neurons of the human brain experience spatial inhibition with the surrounding neurons. Based on this principle, neurons with high priority are searched for, and an energy function is defined for each neuron . The principle is given in Equation (8) below.
where and represent the mean and variance, respectively, of the neurons in the channel except for t. t represents the target neuron on a channel, represents the other neurons, i is indexed in the spatial dimension, and represents the total number of neurons on that channel. Equation (8) shows that the smaller is, the more distinct this neuron is from the surrounding neurons. E is a combination of energy functions for all spatial and channel dimensions on which feature refinement is performed, and the value of E is constrained by a sigmoid function.
where represents the input features.
In this paper, through comparative experiments, the accuracy of the whole algorithm is significantly improved by adding this module before the C2f-FasterNet module of YOLOv8s-cls, which is the L3 module position.
2.5. Algorithmic Visual Analysis
When training a deep learning network model, it is difficult to show the feature map information of the detection target intuitively. So, in order to explore the specific working principle of the model and show the interpretability of deep learning, this paper adopts Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping [26] (Grad-CAM) to generate the heat map and, through the calculation of the feature map’s gradient information and an in-depth understanding of the model’s attention distribution in the detection process, intuitively show the algorithm’s attention to the target features. Figure 4 shows the visualization results of the YOLO-CFS algorithm in detecting the dataset used in this paper. In this figure, the attention of the algorithm to the coal flow region on the conveyor belt can be intuitively seen, proving the feasibility of the algorithm.
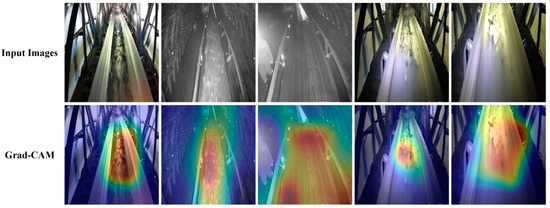
Figure 4.
Grad-CAM visualization results. Input images from conveyor belt dataset, Grad-CAM for visualization results.
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Experimental Environment Configuration and Dataset Creation
The configuration of the experimental environment in this paper is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Experimental platform configuration.
The source of the dataset used in this paper is the actual images taken from real coal mine conveyor belt scenes, as well as sampling frames from the coal mine conveyor belt production and operation monitoring video. A total of 3008 images were obtained in different scenes and categorized into four categories according to the amount of coal flow as follows: null, little, middle, and full load. Selecting the production and operation monitoring videos of different conveyor belts in several coal mines as the source of the dataset can more adequately cover a variety of actual production environments and, at the same time, ensure the balance of the dataset to avoid overfitting. It is guaranteed that the sample data covering the current situation of the actual production environment ensures the generalizability of the model algorithm, which is conducive to deploying the algorithm’s reasoning in actual production. The dataset is divided into a training set and a test set according to the ratio of 8 to 2 so that the model has sufficient data for learning and evaluation at all stages to ensure the accuracy of the algorithm.
In order to improve the robustness of the system in the coal mine environment, during the model training process, the online image enhancement module of YOLOv8 is enabled to enhance the training dataset, including the active addition of image noise, MixUp, panning, inversion, etc., to increase the diversity of the dataset and to effectively improve the model’s generalization ability.
In this paper, in the model training phase, the number of training epochs is set to 200, the initial learning rate is set to 0.01, the batch size is set to 16, the optimizer is selected as automatic, the use of dropout regularization is set to 0.3, and MixUp image enhancement is set to 0.2.
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
In this paper, coal flow is categorized into 4 classes, which belong to the multi-classification task, and accuracy (Acc), model parameters (Params), floating-point operands (FLOPs), and detection frames per second (FPS) are used as the evaluation metrics for the performance test. Acc is calculated as follows:
where TP is the correctly predicted positive sample, TN is the correctly predicted negative sample, FP is the incorrectly predicted positive sample, and FN is the incorrectly predicted negative sample.
4. Results and Discussion
In order to verify the practical effect of the algorithm proposed in this paper for coal flow recognition of conveyor belts in a coal mine environment, the following experiments are designed for comparison. Firstly, the mainstream feature extraction module is selected to replace the C2f module of YOLOv8; secondly, different attention mechanisms are added to the original model and then ablation experiments of different modules are carried out to compare the effects of different modules on the performance of the model; and, finally, different network models are selected for comparison. A comprehensive comparison of the effectiveness of the network model is carried out from various aspects such as the accuracy of the model, the speed of reasoning, and the complexity of the model.
4.1. Feature Extraction Modules Comparison Experiment
In the process of coal flow recognition, the conveyor belt runs faster. To realize real-time detection of coal flow, the detection speed of the algorithm is required to be higher, and, at the same time, to adapt to the coal mine environment, the hardware deployment is required to be as low as possible. Thus, it is necessary to improve the detection speed of the algorithm, as well as reduce the difficulty of deploying the algorithm, while ensuring accuracy. In this paper, the experimental results of different feature extraction modules are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Experimental comparison of feature extraction modules.
Table 3 shows that the lightweight C2f-FasterNet module reduces the number of parameters and floating-point operations of the model. It also increases the detection speed by 14.23% over the original model while increasing the accuracy by 3.8%. The final algorithm of this paper, which was further improved, has a 1% increase in accuracy, although the detection speed is reduced, which effectively improves the detection effect of the model. C2f-ghost [27], which is also lightweight, improves detection accuracy only to a limited extent, although the model complexity is greatly reduced. The C2f-DynamicConv [28] and C3-FasterNet modules improve the accuracy and detection frame rate compared with the original model, although the effect is relatively insignificant, and the model is too complex to be deployed on hardware. The model accuracy curve during training is shown in Figure 5.
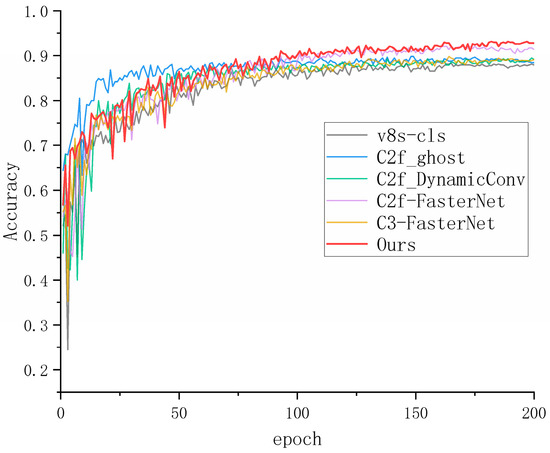
Figure 5.
Accuracy curves of different modules.
4.2. Attention Module Comparison Experiment
The effect is verified by adding different attention mechanisms at the same location, and the results are shown in Table 4. Table 4 shows that detection accuracy is improved by adding attention mechanisms and, at the same time, the detection speed of the model is affected. Among them, CPCA [29] and CBAM increased the number of parameters and floating-point operations, but the accuracy rate was slightly increased. MLCA [30] increased the accuracy rate by only 0.1% instead of decreasing the detection speed.

Table 4.
Experimental comparison of attention modules.
These results are not in line with the original intention of the attention mechanism to improve detection accuracy. SimAm increased the accuracy rate by 0.8% based on the slight decrease in the detection speed, and the accuracy rate was improved most obviously. This algorithm combines the advantages of the FasterNet network and SimAm to significantly improve the accuracy while increasing the detection speed and reducing the number of floating-point operations of the model. The accuracy curve of the model with added attention mechanism is shown in Figure 6.
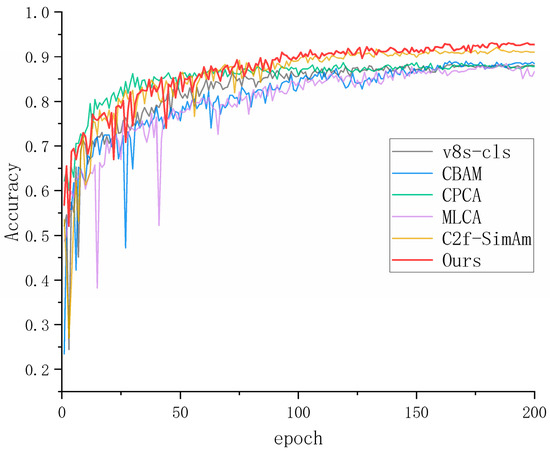
Figure 6.
Accuracy curves of different attention modules.
4.3. Ablation Comparison Experiment
In order to verify the effect of different improvements on the model performance, ablation experiments are set up to continue the comparative analysis, and the results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Experimental comparison of ablation modules.
c2f-FasterNet improves the accuracy by 3.8% over the original model, and the number of floating-point operations is reduced to 8.4G, while the detection speed is improved by 14.23%. Meanwhile, in order to verify the effect of the position of the attention mechanism addition on model performance, we added the attention mechanism in the position of the 10th module (L10), 9th module (L9), and 3rd module (L3). The experimental results show that the accuracy rate improved by 0.4%, 0.3%, and 1%, respectively, and the detection speed decreased by 9.5%, 10.2%, and 7.3%, respectively. The results demonstrated that adding the SimAm attention mechanism at the third module position, i.e., before all C2f-FasterNet modules, gives the best performance. Finally, it was verified that adding the attention mechanism only at the L3 position without adding C2f-FasterNet modules showed a 0.8% improvement in accuracy over the original v8-cls, proving the effectiveness of the SimAm attention mechanism. The comparison curves of the ablation experiments are shown in Figure 7.
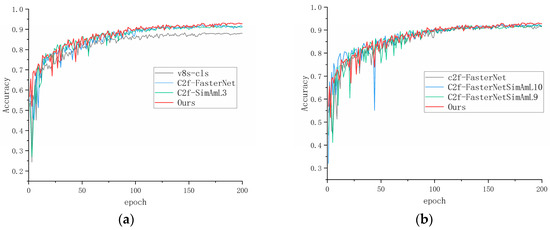
Figure 7.
Accuracy curves of ablation: (a) ablation experiments of different modules and (b) ablation experiments of attention at different layers.
4.4. Mainstream Model Comparison Experiment
Table 6 validates the effectiveness of this algorithm by comparing the mainstream deep learning algorithms.

Table 6.
Experimental comparison of mainstream models.
YOLOv5 is the predecessor of v8, with similar accuracy, but the number of parameters and floating-point operations of v8 is greatly reduced, and the detection speed is improved. The detection speeds of EfficientFormerV2 and ResNet5 are lower than that of v8-cls. In addition, the number of model parameters in ResNet50 is much higher than in the algorithm in this paper, and the arithmetic is complicated, which is not favorable for deployment on limited hardware resources. GoogLeNet [31] has an advantage in accuracy compared with the original v8-cls model, but the number of parameters is relatively large. Inception-ResNet [32] is the V4 version of Inception, which is the core part of GoogLeNet, and it is also combined with the ResNet model, which significantly improves the accuracy compared with the GoogLeNet algorithm. However, at the same time, the number of parameters and floating-point operations are greatly increased. In contrast, the YOLO-CFS algorithm proposed in this paper is more advantageous in the coal mining environment. The graph of the comparison experiment is shown in Figure 8.
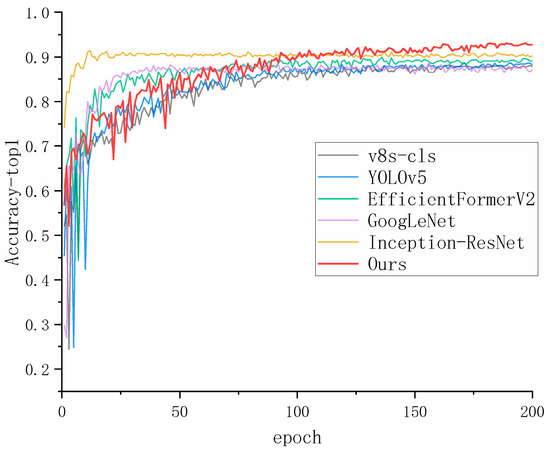
Figure 8.
Accuracy curves of mainstream models.
5. Conclusions
In order to reduce the energy consumption of coal mines and improve the energy utilization rate of coal conveyor belts, the running speed of conveyor belts is intelligently controlled by coal flow. In this paper, visual detection is used for coal flow recognition, and an improved deep learning algorithm, YOLO-CFS, is proposed. To address the problem of dust and uneven light in the environment of coal mines, the AMSRCR algorithm is proposed to perform image preprocessing to obtain a coal flow image that is favorable for recognition. Aiming at the problems of large computation, slow detection time, and insufficient accuracy of deep learning networks, the C2f-FasterNet module is proposed, which reduces the number of floating-point operations of the network, improves the detection frame rate, increases the detection accuracy, and improves the real-time detection of the algorithm. In order to further improve the model’s attention to the key features and improve the detection accuracy, the SimAm attention mechanism is proposed to improve the weight of the key areas of feature extraction so that the accuracy rate is improved.
The experimental results show that the detection accuracy of the YOLO-CFS algorithm is improved by 4.8%, the number of parameters is reduced by 28.4%, the number of floating-point operations is reduced by 33.3%, and the detection frame rate is improved by 5.9%. This proves that the algorithm is effective and real-time-ready and provides a technological guarantee for energy saving and emission reduction in coal mines.
In subsequent work, a series of model deployments will be carried out. By adjusting the model structure, such as removing the batch normalization of the model to make the model more lightweight, the model will be converted into the ONNX and TensorRT format suitable framework for hardware deployment. Finally, the model will be deployed on NVIDIA’s Jetson Orin NX to realize energy-saving control through joint control with a lower computer. In the model deployment stage, in order to cope with the fissure of the mine passage [33] and the explosion-proof requirements of the coal mine, the existing electrical equipment needs to be modified for intrinsically safe design, while the stability and robustness of the equipment in the coal mine environment need to be verified by more experiments.
Through this study, it was found that deep learning algorithms have a high value for use in coal mine production. Thus, deep learning and machine vision can be considered to be used for coal gangue sorting in coal mines to realize dynamic gangue sorting, to reduce the cost of coal sorting, to save resources, and to ensure the sustainability of resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.X. and Z.S.; methodology, Z.X.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.X. and Z.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62201199).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data and materials are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank everyone who helped with this study for their insightful remarks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, G.; Ye, L. Design and Research of Belt Conveyor Energy-saving Control System Based on Coal Flow Recognition. Coal Mine Mach. 2023, 44, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, H. Research of energy saving control system with frequency conversion speed regulation for belt conveyor. Ind. Mine Autom. 2013, 39, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Miao, C.; Li, X. Research on the Energy-Saving Control Strategy of a Belt Conveyor with Variable Belt Speed Based on the Material Flow Rate. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, D. Technical status and development trend of belt weigher. Weigh. Instrum. 2012, 41, 1–4+10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. On-Line Monitoring System for Mine Nuclear Belt Weighing. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mihuţ, N.M. Designing a System for Measuring the Flow of Material Transported on Belts Using Ultrasonic Sensors. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 95, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X. Coal Weight Measurement Method of Belt Conveyor Based on Binocular Stereo Vision. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Information, Cybernetics, and Computational Social Systems (ICCSS), Guangzhou, China, 13–15 November 2020; pp. 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Liang, B.; Zhang, L.; Hao, B.; Yang, Z. Research on Coal Volume Detection and Energy-Saving Optimization Intelligent Control Method of Belt Conveyor Based on Laser and Binocular Visual Fusion. IEEE Access 2023, 12, 75238–75248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Edge Detection for Conveyor Belt Based on the Deep Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Intelligent Systems Conference; Jia, Y., Du, J., Zhang, W., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 529, pp. 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Q.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Xue, X. Coal Mine Belt Conveyor Foreign Objects Recognition Method of Improved YOLOv5 Algorithm with Defogging and Deblurring. Energies 2022, 15, 9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, D.; Wu, C.; Wu, S.; Yuan, Y. Belt Deviation Detection for Electronic Belt Scales Based on Data Mining. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Qiao, T.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, G. Infrared Spectrum Analysis Method for Detection and Early Warning of Longitudinal Tear of Mine Conveyor Belt. Measurement 2020, 165, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A. The Impact of Atmospheric Pressure Changes on Methane Emission from Goafs to Coal Mine Workings. Energies 2023, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chaulya, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Soni, A. An Approach for Implementation of IoT Enables Smart Environmental Monitoring and Strata Monitoring System for Underground Coal Mines. In Proceedings of the 10th Asian Mining Congress 2023; Sinha, A., Sarkar, B.C., Mandal, P.K., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 165–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.S.; Hariprasadh, R.; Gowthamraj, A.; Harinivash, K. Smart Helmet for Coal Mine Employees: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Innovative Data Communication Technologies and Application (ICIDCA), Uttarakhand, India, 14–16 March 2023; pp. 916–923. [Google Scholar]
- Karthika, S.; Jayabaskaran, G.; Hariharan, M.; Poonthamizhan, M.; Poongothai, G. Realtime Embedded Smart Jacket System for Coal Miners. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 17–18 March 2023; pp. 1655–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Pizer, S.M.; Amburn, E.P.; Austin, J.D.; Cromartie, R.; Geselowitz, A.; Greer, T.; Zuiderveld, K. Adaptive Histogram Equalization and Its Variations. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1987, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Chi, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, T. Underwater Image Enhancement Based on Color Correction and Improved CLAHE Multi-Scale Fusion. Radio Eng. 2024, 54, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Sankaran, P. An Automated Multi Scale Retinex with Color Restoration for Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2012 National Conference on Communications (NCC), Kharagpur, India, 3–5 February 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.; Woodell, G.A. A Multiscale Retinex for Bridging the Gap between Color Images and the Human Observation of Scenes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobson, D.J.; Rahman, Z.; Woodell, G.A. Properties and Performance of a Center/Surround Retinex. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1997, 6, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Liu, D.; Bai, B.; Gu, Q. Image Enhancement Method for Underground Coal Mine Based on the Adaptive MSRCP Algorithm. Min. Res. Dev. 2021, 41, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.; He, H.; Zhuo, W.; Wen, S.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, S.-H.G. Run, Don’t Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03667. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Volume 11211, pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R.-Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. SimAM: A Simple, Parameter-Free Attention Module for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conferenceon Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations From Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, E.; Tian, Q. GhostNets on Heterogeneous Devices via Cheap Operations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1050–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Fan, A.; Baevski, A.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Auli, M. Pay Less Attention with Lightweight and Dynamic Convolutions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.10430. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, C. Channel Prior Convolutional Attention for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.05196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.; Lu, R.; Shen, S.; Xu, T.; Lang, X.; Ren, Z. Mixed Local Channel Attention for Object Detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Tong, J.; Rui, Y.; Cui, Y.; Pu, Y.; Du, J.; Apel, D.B. Step-Path Failure Mechanism and Stability Analysis of Water-Bearing Rock Slopes Based on Particle Flow Simulation. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2024, 131, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).