Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Review the Impact of Livestock Manure on Air and Water
2.3. Assessment of Existing Effects of Livestock Manure
2.3.1. Livestock Manure Generation Estimation
2.3.2. Assessment of District-Wise GHG Emissions
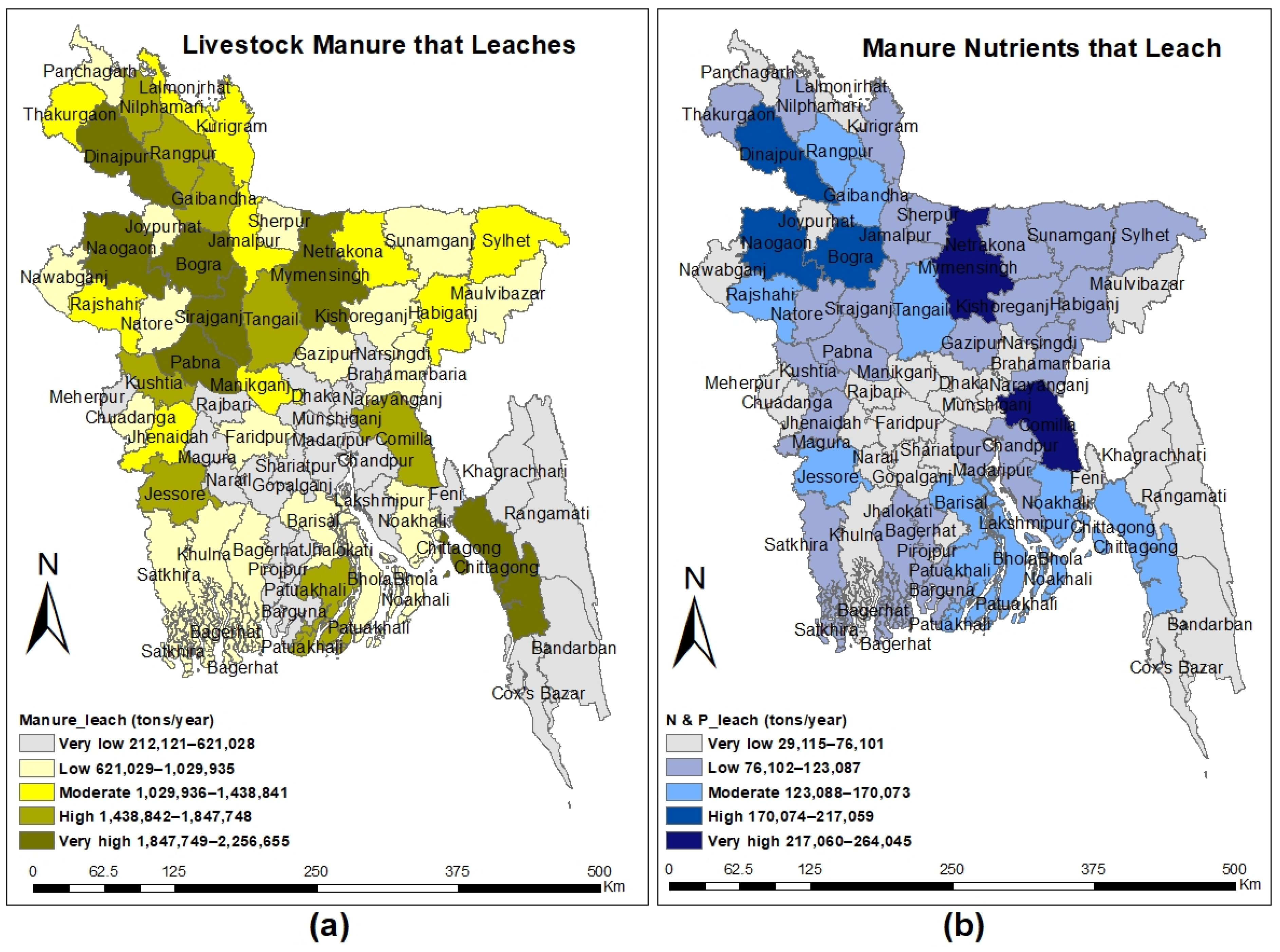
2.3.3. Assessment of District-Wise Manure Nutrients Leaching Out
2.4. Eutrophication Potential Assessment
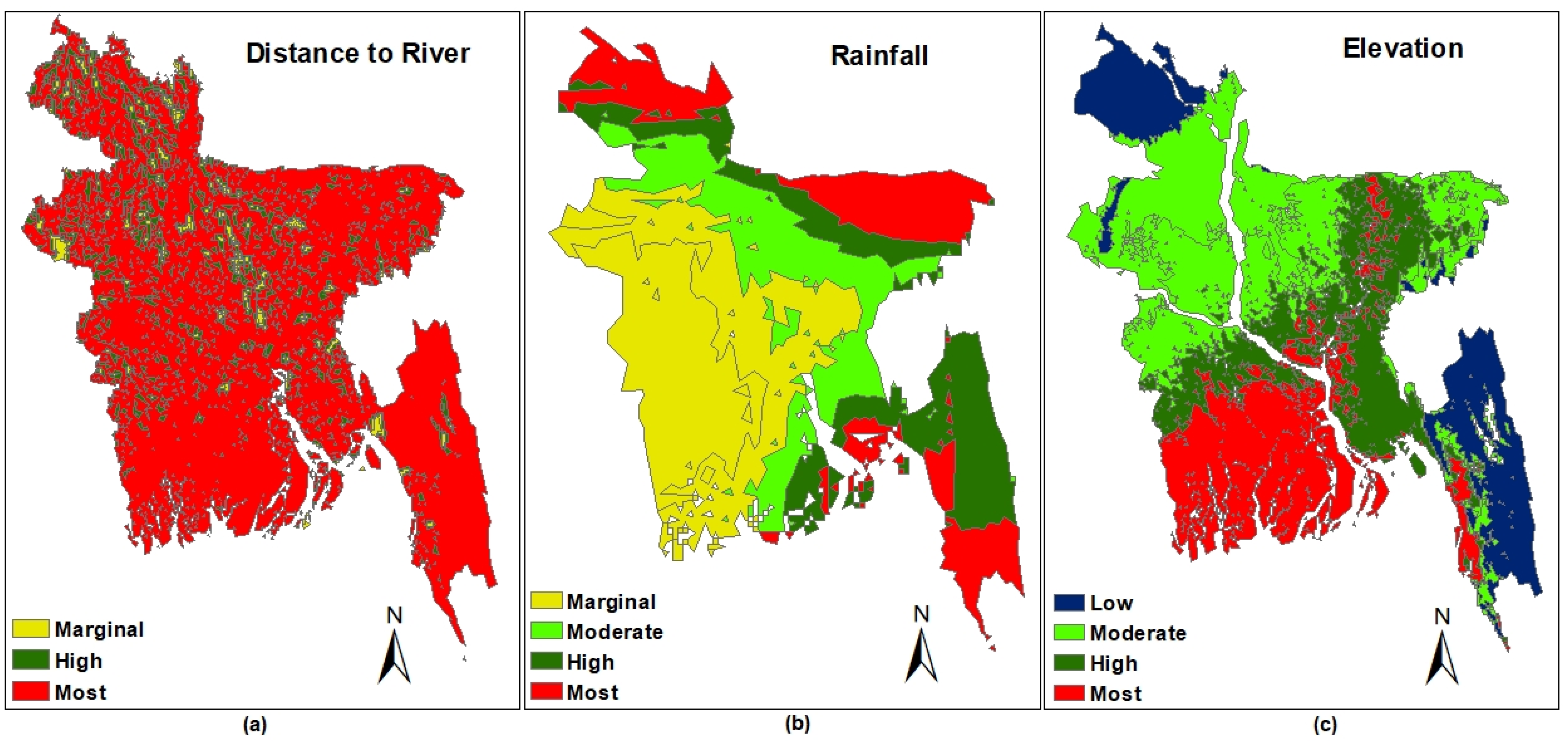
2.5. Eutrophication Susceptibility Analysis
3. Results
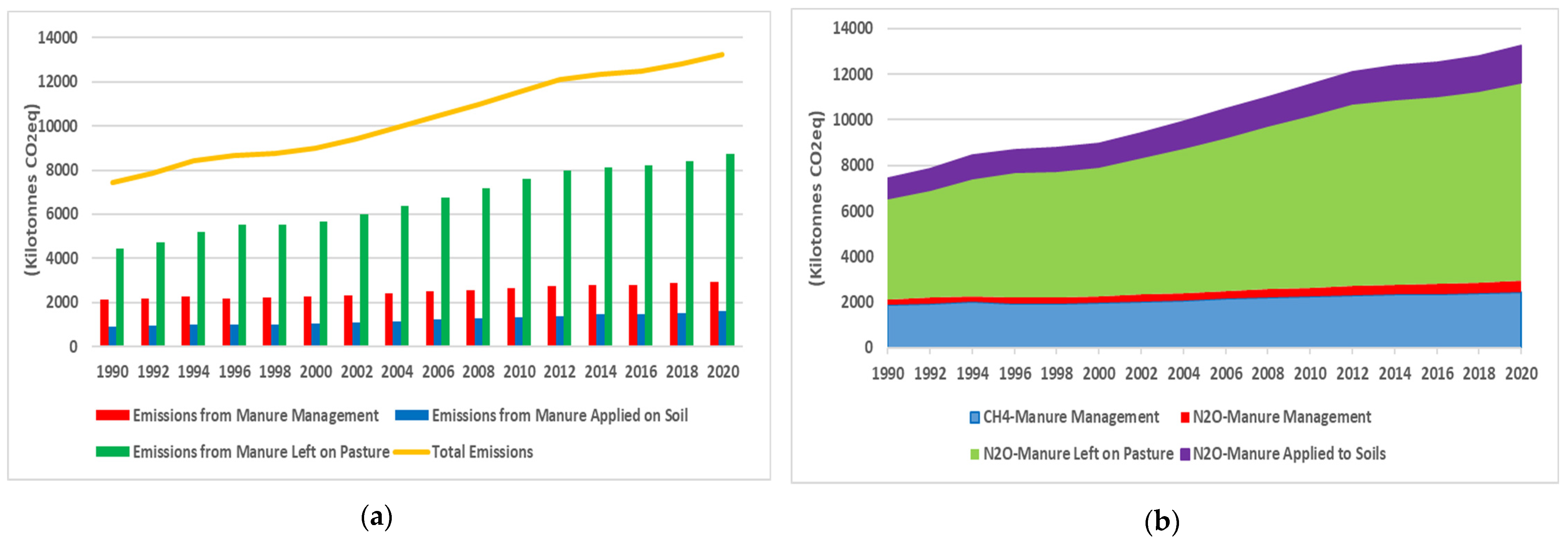
3.1. Impacts on GHG Emissions
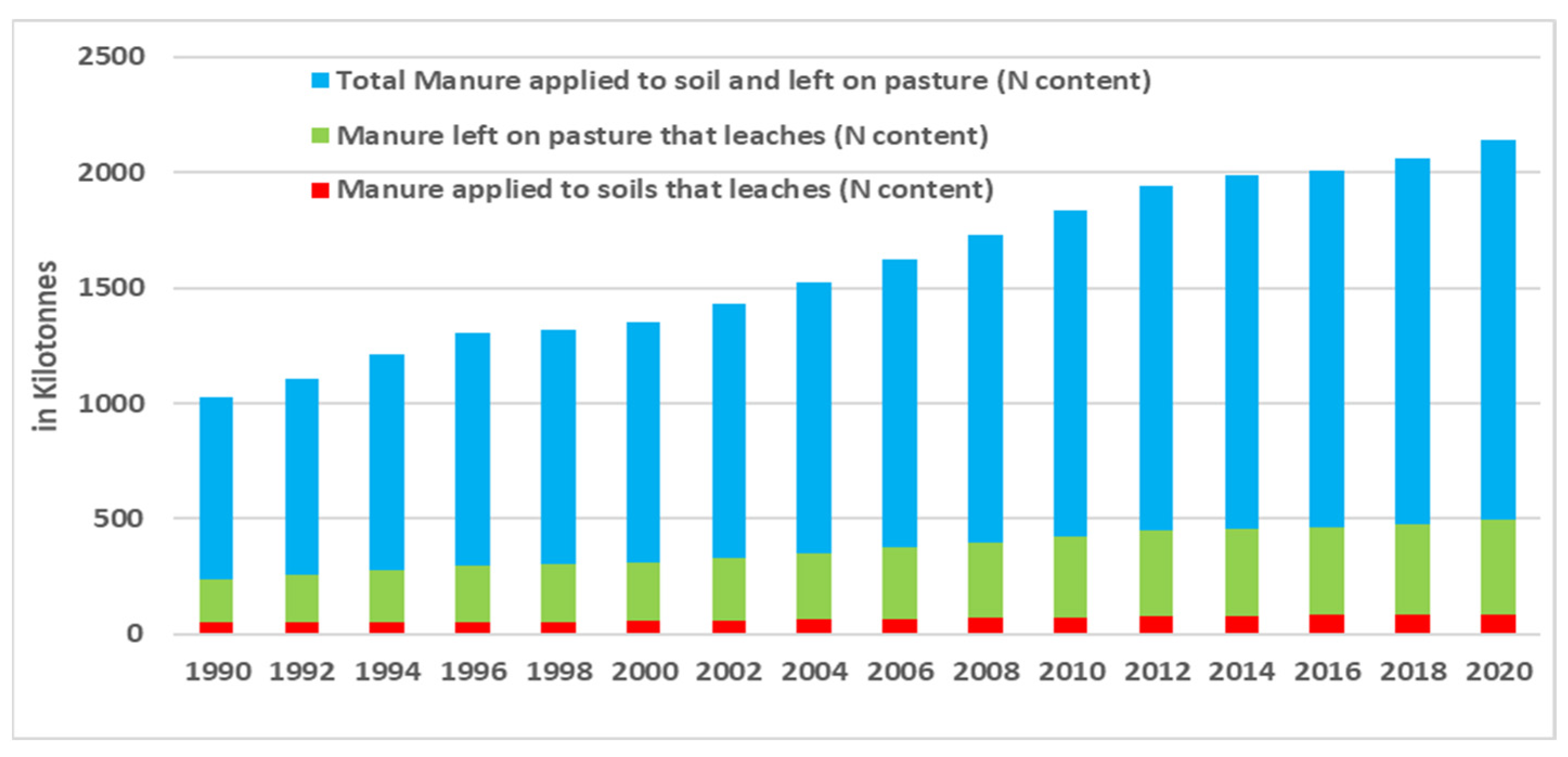
3.2. Impacts on Water Pollution
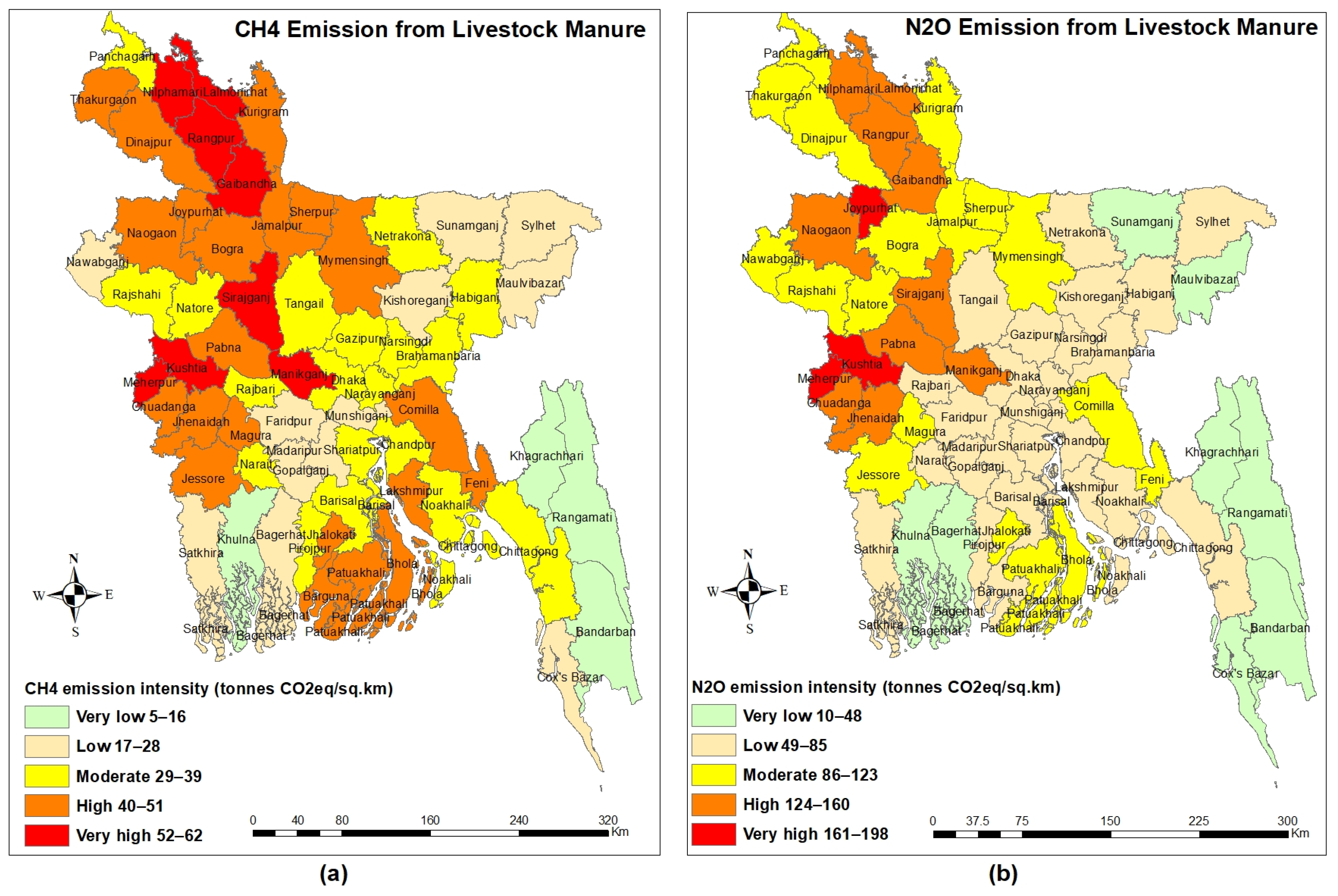
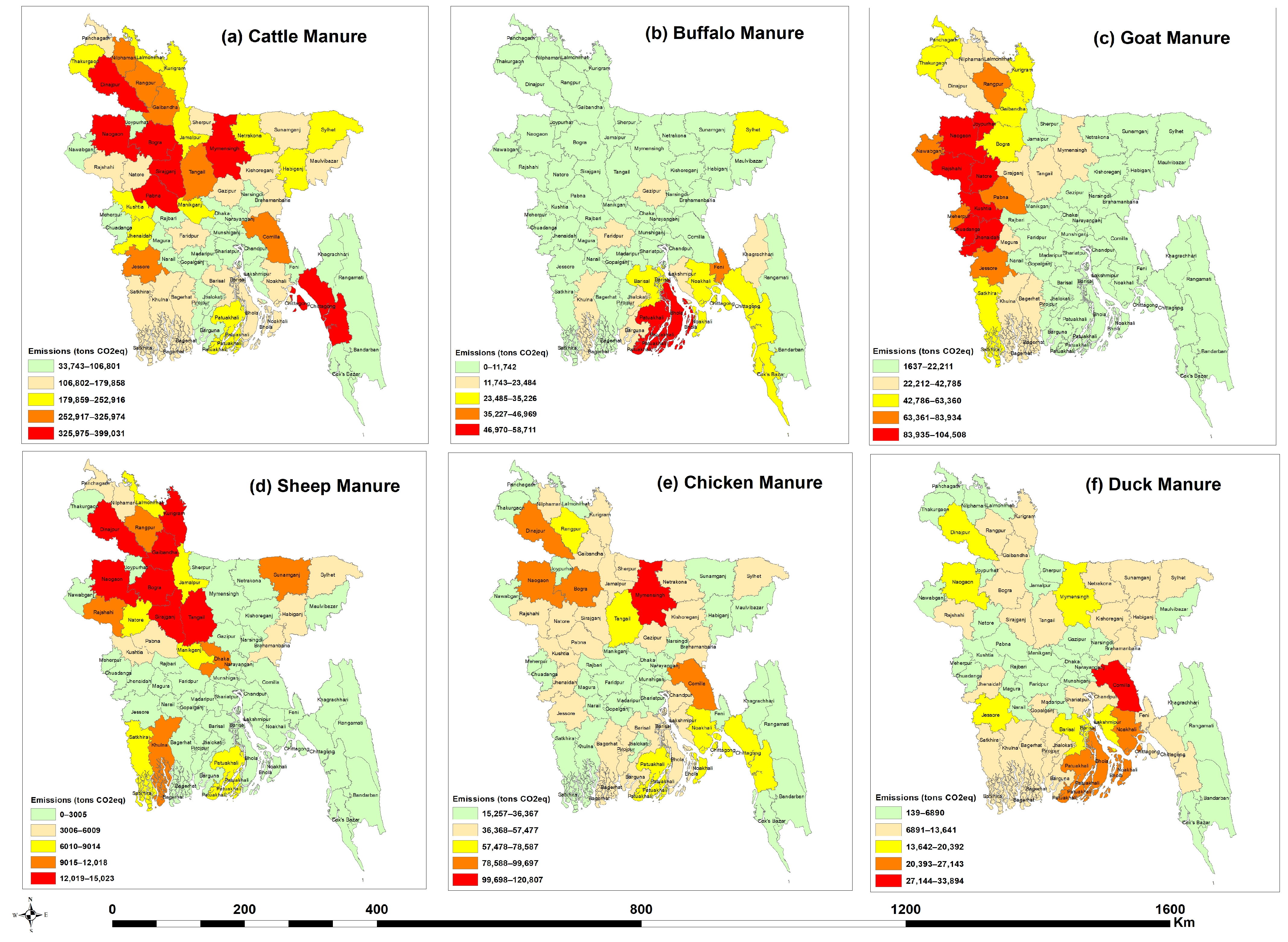
3.3. Regional Pattern of GHG Emissions
3.4. Regional Pattern of Leaching out of Manure
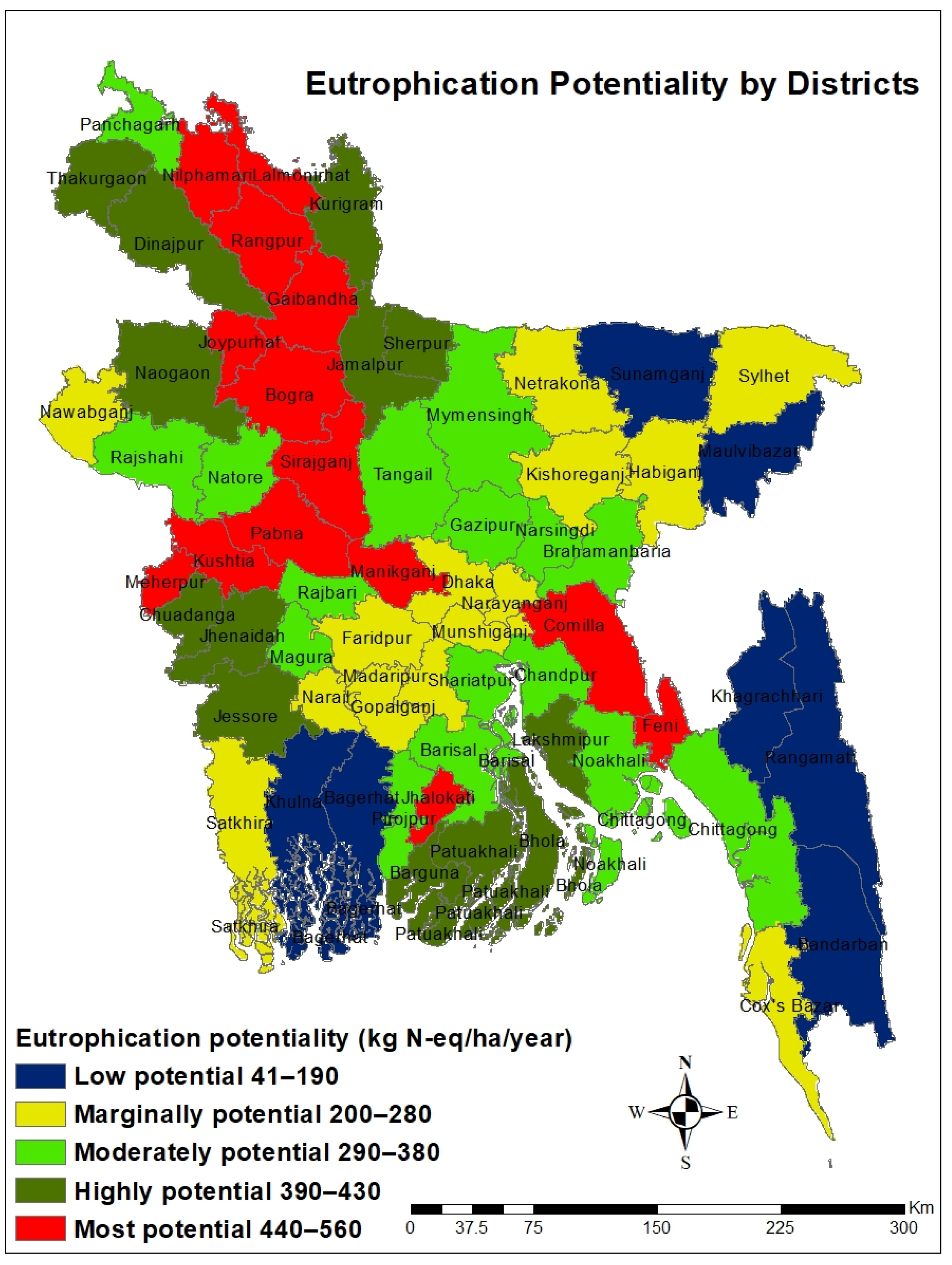
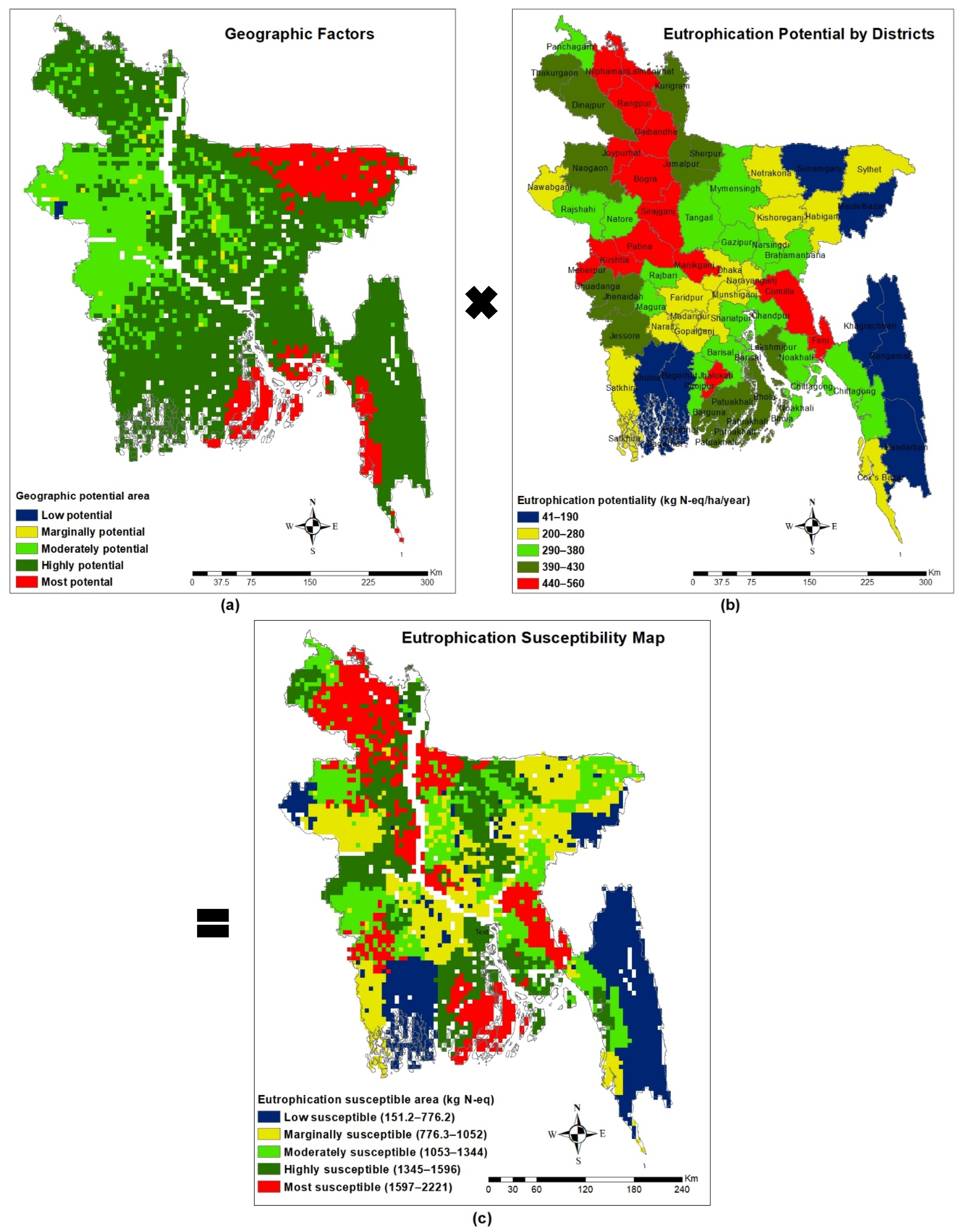
3.5. Spatial Distribution of Eutrophication Potential
3.6. Eutrophication Susceptibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- Livestock manure has an influence on GHG emissions and causes eutrophication susceptibility in waterbodies.
- (b)
- GHG emissions and manure leach-out from livestock showed an increasing trend in production from 1990 to 2020. In 2023, the total GHG emissions were 16.61 million tons CO2eq, and the total leach-out manure was 64.19 million tons in Bangladesh.
- (c)
- GHG emissions from manure were a combination of CH4 emissions (4.84 million tons CO2eq) and N2O emissions (11.76 million tons CO2eq). Leach-out manure nutrients were nitrogen (57.83 million tons) and phosphorus (2.95 million tons).
- (d)
- The EP by leaching manure nutrients and N2O emission was 295.22 kg N-eq ha−1,, and the spatial distribution of eutrophication susceptibility was also categorized into five groups (low-susceptible areas, marginally susceptible areas, moderately susceptible areas, highly susceptible areas, and most susceptible areas).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J. Creating a Sustainable Food Future “A Menu of Solutions to Feed Nearly 10 Billion People by 2050”; World Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; Available online: https://agritrop.cirad.fr/593176/1/WRR_Food_Full_Report_0.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2024).
- Venier, F.; Yabar, H. Renewable energy recovery potential towards sustainable cattle manure management in Buenos Aires Province: Site selection based on GIS spatial analysis and statistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1317–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wu, H. Assessment of pollution from livestock and poultry breeding in China. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2013, 70, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodele, T.R.; Ogunjuyigbe, A.S.O.; Alao, M.A. Economic and environmental assessment of electricity generation using biogas from organic fraction of municipal solid waste for the city of Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 718–735. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652618326337 (accessed on 16 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ouyang, W.; Hao, F.; Ren, X.; Yang, S. The non-point source pollution in livestock-breeding areas of the Heihe River basin in Yellow River. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2007, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DLS. Livestock Economy at a Glance; Department of Livestock Services: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023. Available online: http://dls.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/dls.portal.gov.bd/page/ee5f4621_fa3a_40ac_8bd9_898fb8ee4700/2023-07-23-12-04-afbcccb96f8b27d4bab6501aa8c2c2ff.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2024).
- FAO. FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/EK (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Sapkota, T.B.; Vetter, S.H.; Jat, M.L.; Sirohi, S.; Shirsath, P.B.; Singh, R.; Jat, H.S.; Smith, P.; Hillier, J.; Stirling, C.M. Cost-effective opportunities for climate change mitigation in Indian agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, P.; Vellinga, T.; Opio, C.; Steinfeld, H. Productivity gains and greenhouse gas emissions intensity in dairy systems. Livest. Sci. 2011, 139, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou-Ttofa, L.; Foteinis, S.; Seifelnasr Moustafa, A.; Abdelsalam, E.; Samer, M.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Life cycle assessment of household biogas production in Egypt: Influence of digester volume, biogas leakages, and digestate valorization as biofertilizer. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.; Ren, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, R.; Stajic, M.; Blagojević, B.; Bezdan, A.; Vranesevic, M.; Nikolić Jokanović, V.; Baumgertel, A.; Bubalo Kovačić, M.; Horvatinec, J.; Ondrasek, G. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Concentrations and Their Ratios as Indicators of Water Quality and Eutrophication of the Hydro-System Danube–Tisza–Danube. Agriculture 2022, 12, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Scherer, L.; Van Bodegom, P.M.; Beusen, A.; Mogollón, J.M. Regionalized nitrogen fate in freshwater systems on a global scale. J. Ind. Ecol. 2022, 26, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, B.; Hawkins, T.R.; Niblick, B.; Henderson, A.D.; Golden, H.E.; Compton, J.E.; Cooter, E.J.; Bare, J.C. Critical Review of Eutrophication Models for Life Cycle Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9562–9578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBS. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics-Government of the People\’s Republic of Bangladesh. 2023. Available online: http://bbs.portal.gov.bd/site/page/6b4c2697-452b-4bc6-9ee2-1fb5e0fc66c0/- (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- DLS. Department of Livestock Services. Available online: https://dls.gov.bd/ (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- DIVA. Download Data by Country|DIVA-GIS. Available online: https://www.diva-gis.org/gdata (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Avcioğlu, A.O.; Türker, U. Status and potential of biogas energy from animal wastes in Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaygusuz, K. Renewable and sustainable energy use in Turkey: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2002, 6, 339–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afazeli, H.; Jafari, A.; Rafiee, S.; Nosrati, M. An investigation of biogas production potential from livestock and slaughterhouse wastes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeshahian, P.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Potential of biogas production from farm animal waste in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoEFCC. Second National Communication of Bangladesh to the United Nations Framework on Convention on Climate Change; Ministry of Environment and Forest: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, S.; Zerhusen, B.; Zehetmeier, M.; Effenberger, M. Distribution of specific greenhouse gas emissions from combined heat-and-power production in agricultural biogas plants. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 133, 105443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. EFDB—Main Page, Emission Factor Database. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2024. Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/EFDB/main.php (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Cestonaro, T.; Costa, M.S.S.D.M.; Costa, L.A.D.M.; Pereira, D.C.; Rozatti, M.A.T.; Martins, M.F.L. Addition of cattle manure to sheep bedding allows vermicomposting process and improves vermicompost quality. Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Bahar, M.M.; Sarkar, B.; Donne, S.W.; Wade, P.; Bolan, N. Assessment of the fertilizer potential of biochars produced from slow pyrolysis of biosolid and animal manures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 155, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C. Available Nutrients and Value for Manure; The Ontario Ministry of Agriculture and Food and the Ministry of Rural Affairs: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013; Available online: https://fieldcropnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Nutrient-Value-of-Manure.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Leikam, D.F.; Lamond, R.E. Estimating Manure Nutrient Availability; Report No.: MF-2562; Kansas State University, Department of Agronomy: Manhattan, Kansas, 2003; Available online: https://bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/download/estimating-manure-nutrient-availability_MF2562 (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Raza, S.T.; Tang, J.L.; Ali, Z.; Yao, Z.; Bah, H.; Iqbal, H.; Ren, X. Ammonia Volatilization and Greenhouse Gases Emissions during Vermicomposting with Animal Manures and Biochar to Enhance Sustainability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Tool for Reduction and Assessment of Chemicals and Other Environmental Impacts (TRACI). 2015. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/tool-reduction-and-assessment-chemicals-and-other-environmental-impacts-traci (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Lipiatte, B.C. Building for Environmental and Economic Sustainability, Technical Manual and User Guide; (BEES 3.0). Report No.: NISTIR 6916; U.S. Department of Commerce: National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2002. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/9400081C.TXT?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=2000+Thru+2005&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5Czyfiles%5CIndex%20Data%5C00thru05%5CTxt%5C00000035%5C9400081C.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=1&SeekPage=x&ZyPURL# (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Heijungs, R.; Guinée, J.B.; Huppes, G.; Lankreijer, R.M.; Udo de Haes, H.A.; Wegener Sleeswijk, A.; Ansems, A.M.M.; Eggels, P.G.; van Duin, R.; de Goede, H.P. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Products: Guide and Backgrounds (Part 1). 1992. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/1887/8061 (accessed on 24 April 2024).
- Nikou, S.; Mezei, J. Evaluation of mobile services and substantial adoption factors with Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). Telecommun. Policy 2013, 37, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherobim, V.F.; Huang, C.-H.; Favaretto, N. Tillage system and time post-liquid dairy manure: Effects on runoff, sediment and nutrients losses. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 184, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yao, Y.; Kang, X.; Niu, Y.; Wang, K. Effect of rainfall–runoff process on sources and transformation of nitrate at the urban catchment scale. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.N.; Sarker, T.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Atri, A.C.; Alam, M.S. Renewable energy generation from livestock waste for a sustainable circular economy in Bangladesh. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.L.; Hao, X.; Gross, C.D.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Chang, S.X. The Effect of Manure from Cattle Fed Barley- vs. Corn-Based Diets on Greenhouse Gas Emissions Depends on Soil Type. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, M.; Tayà, C.; Burgos, L.; Morey, L.; Noguerol, J.; Provolo, G.; Cerrillo, M.; Bonmatí, A. Assessing Ammonia and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Livestock Manure Storage: Comparison of Measurements with Dynamic and Static Chambers. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamati, K.; Laliotis, G.P.; Bizelis, I. Greenhouse Gas Emissions of the Poultry Sector in Greece and Mitigation Potential Strategies. Gases 2023, 3, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economic Review. Finance Division, Ministry of Finance. 2023. Available online: https://mof.portal.gov.bd/site/page/28ba57f5-59ff-4426-970a-bf014242179e/Bangladesh-Economic-Review (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Balasuriya, B.T.G.; Ghose, A.; Gheewala, S.H.; Prapaspongsa, T. Assessment of eutrophication potential from fertiliser application in agricultural systems in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 154993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Elser, J.J. Intensification of phosphorus cycling in China since the 1600s. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2609–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Xu, L. Spatially eutrophication potential and policy implication of nitrogen emission for surface water: A case study in Guangzhou city, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Type of Livestock | EFMT (kg/Head/Year) * | EFNT (kg N2O-N/kg Nitrogen Excretion) * | NE (kg N/Head/Year) ** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large animals | 2–6 | 0.005–0.02 | 50 |
| Small animals | 0.10–0.22 | 0.005–0.02 | 12 |
| Poultry | 0.012–0.023 | 0.001–0.02 | 0.6 |
| Components | N (%) | P (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large animal manure | 2.7 | 0.624 | [26] |
| 1.79 | 1.68 | [27] | |
| 0.92 | 0.33 | [28] | |
| 0.55 | 0.90 | [29] | |
| Small animal manure | 1.94 | 0.99 | [27] |
| 1.04 | 0.28 | [28] | |
| 1.82 | 0.59 | [30] | |
| Poultry manure | 4.52 | 1.68 | [27] |
| 2.7 | 1.32 | [28] | |
| 1.65 | 2.40 | [29] |
| 1 kg of Substance | EPi (kg N-eq) |
|---|---|
| Nitrous Oxides (as N2O to air) | 0.09 |
| Nitrogen to water (as nitrate, as nitrite) | 0.275 (0.23, 0.32) |
| Phosphorus to water | 7.29 |
| Criteria | Comments | Weights |
|---|---|---|
| Distance to river | The closer to the river, the higher the susceptibility. | 48.6% |
| Rainfall | The higher the intensity of rainfall, the higher the susceptibility. | 31.3% |
| Elevation | The higher elevation has lower susceptibility. | 20.1% |
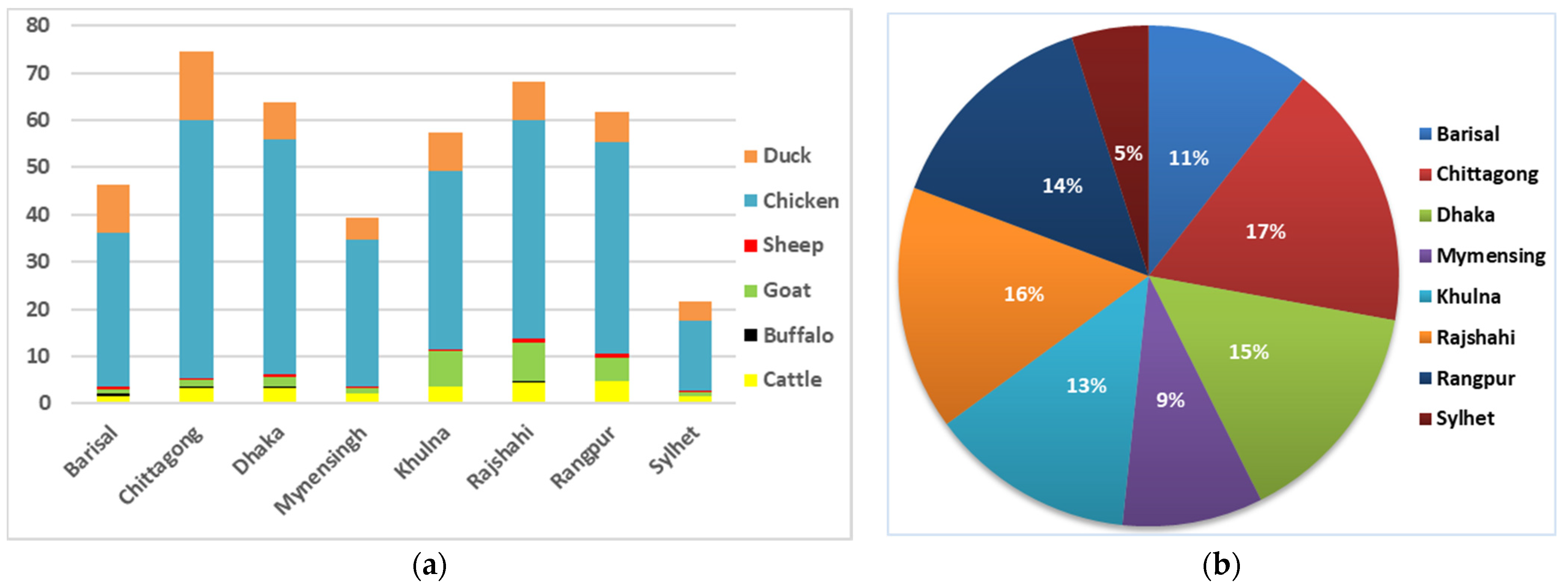
| Divisions | Total Livestock (in Million) | Manure Generation (Tons) | Total Emissions (Tons CO2eq) | CH4 Emissions (Tons CO2eq) | N2O Emissions (Tons CO2eq) | Manure Leach-Out (Tons) | Nutrients (NPK) Leach-Out (Tons) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barisal | 45.83 | 16,995,264.91 | 1,327,327.39 | 441,282.51 | 886,044.89 | 5,021,514.02 | 714,723.61 |
| Chittagong | 74.57 | 29,984,169.28 | 2,276,643.84 | 749,585.23 | 1,527,058.61 | 8,859,286.82 | 1,176,343.82 |
| Dhaka | 63.75 | 28,318,250.85 | 2,151,818.26 | 671,869.26 | 1,479,949.01 | 8,367,065.44 | 999,756.18 |
| Khulna | 57.31 | 31,122,759.98 | 2,529,102.32 | 656,594.94 | 1,872,507.39 | 9,195,701.06 | 838,454.98 |
| Mymensingh | 39.30 | 18,447,865.41 | 1,361,829.30 | 429,557.36 | 932,271.95 | 5,450,707.32 | 626,538.91 |
| Rajshahi | 68.25 | 39,232,203.66 | 3,111,780.65 | 813,419.99 | 2,298,360.66 | 1,159,1761.7 | 1,013,972.18 |
| Rangpur | 61.88 | 39,424,912.04 | 2,905,683.93 | 801,969.93 | 2,103,714.01 | 11,648,700.4 | 974,739.39 |
| Sylhet | 21.50 | 13,448,865.60 | 941,463.53 | 280,367.74 | 661,095.79 | 3,973,675.46 | 354,026.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahal, Z.; Yabar, H.; Mizunoya, T. Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135479
Mahal Z, Yabar H, Mizunoya T. Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135479
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahal, Zinat, Helmut Yabar, and Takeshi Mizunoya. 2024. "Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135479
APA StyleMahal, Z., Yabar, H., & Mizunoya, T. (2024). Spatial Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Eutrophication Potential from Livestock Manure in Bangladesh. Sustainability, 16(13), 5479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135479






