Environmental Impact Assessment of a Dumping Site: A Case Study of Kakia Dumping Site
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.1.1. SW Management and SW Quantities in Makkah
2.1.2. MSW Characteristics in Makkah
2.1.3. Climate and Hydrology in Makkah City
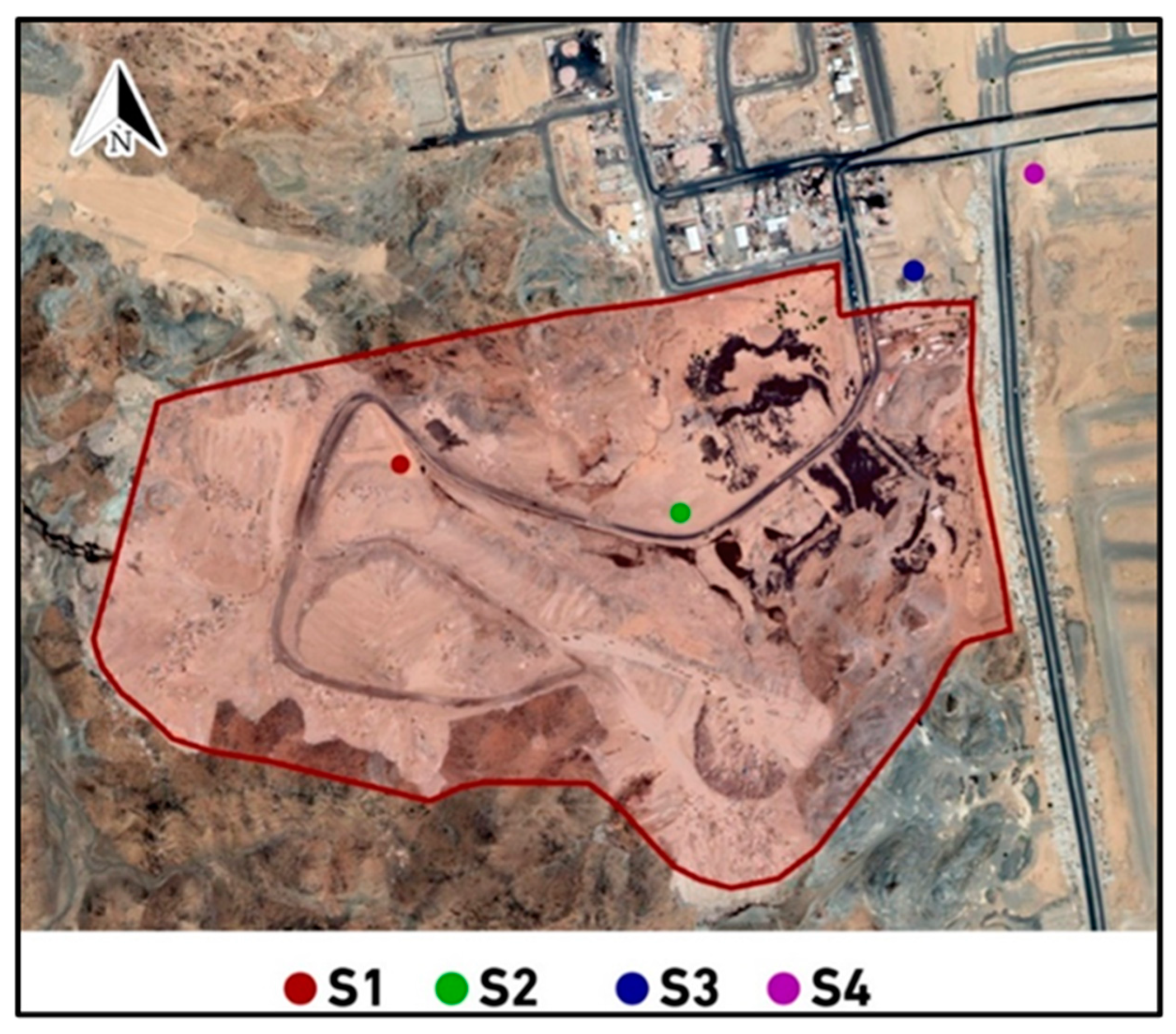
2.2. Sampling
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
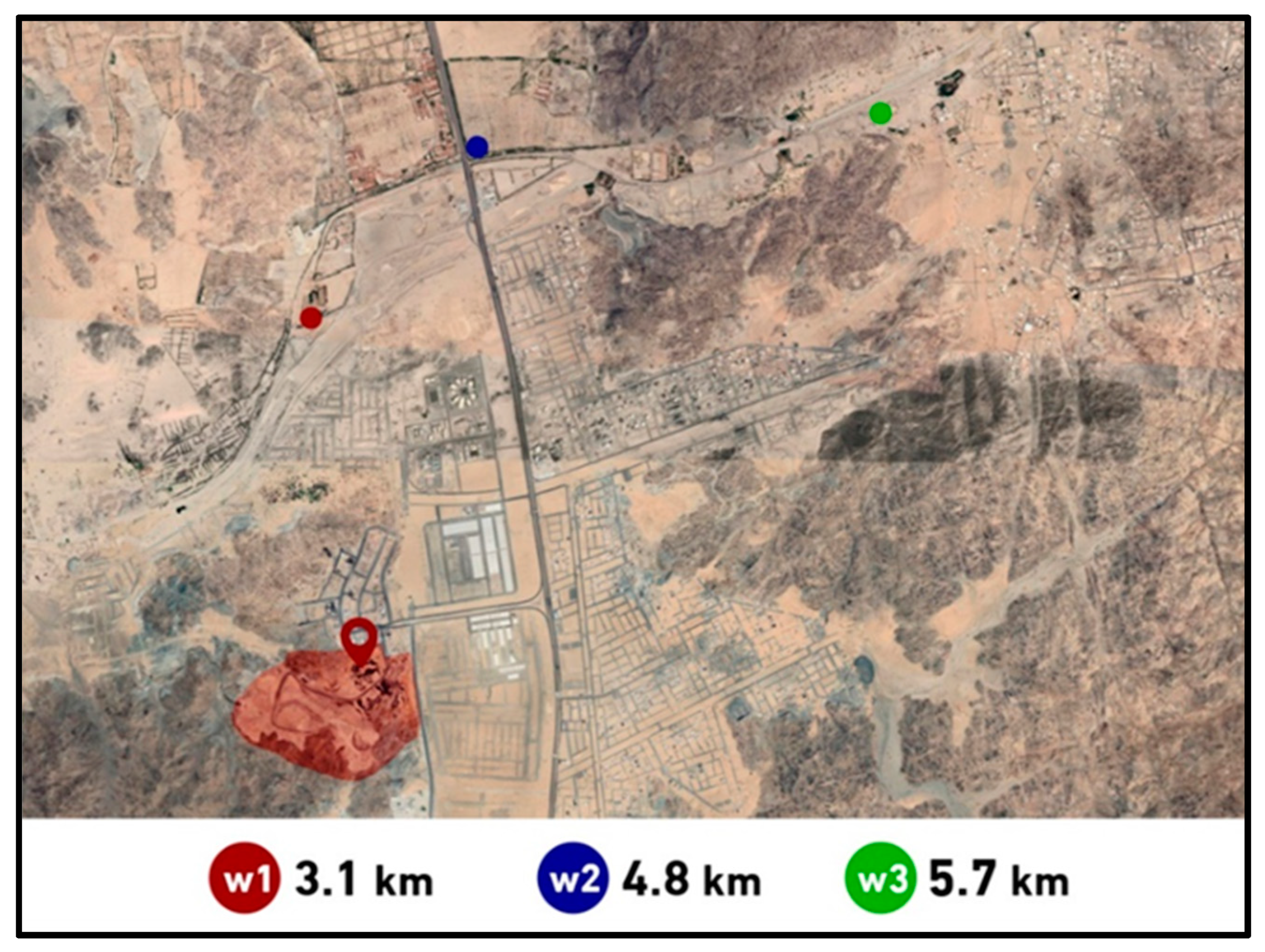
2.2.2. Groundwater Sampling
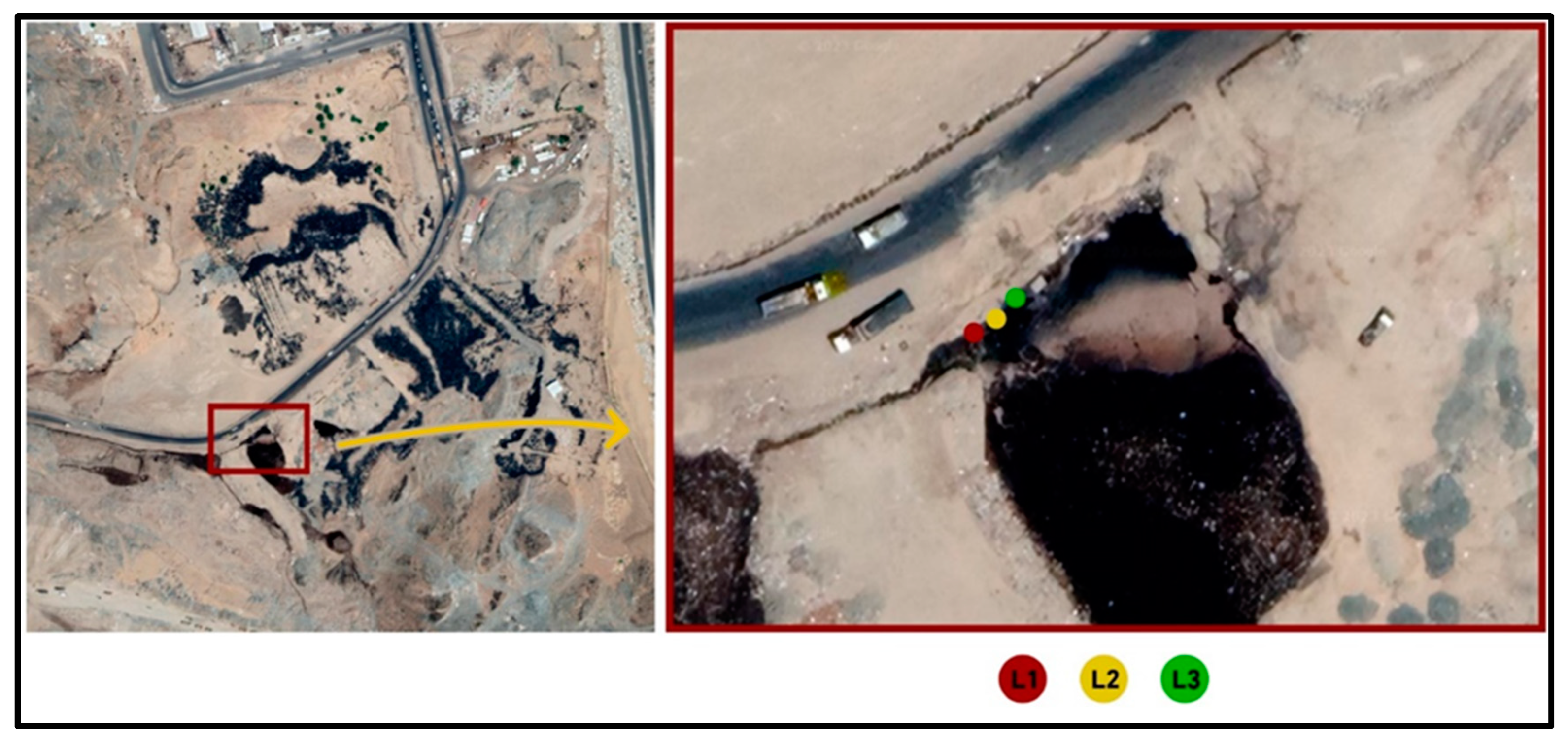
2.2.3. Leachate Sampling
2.2.4. Air Sampling
3. Results and Discussion
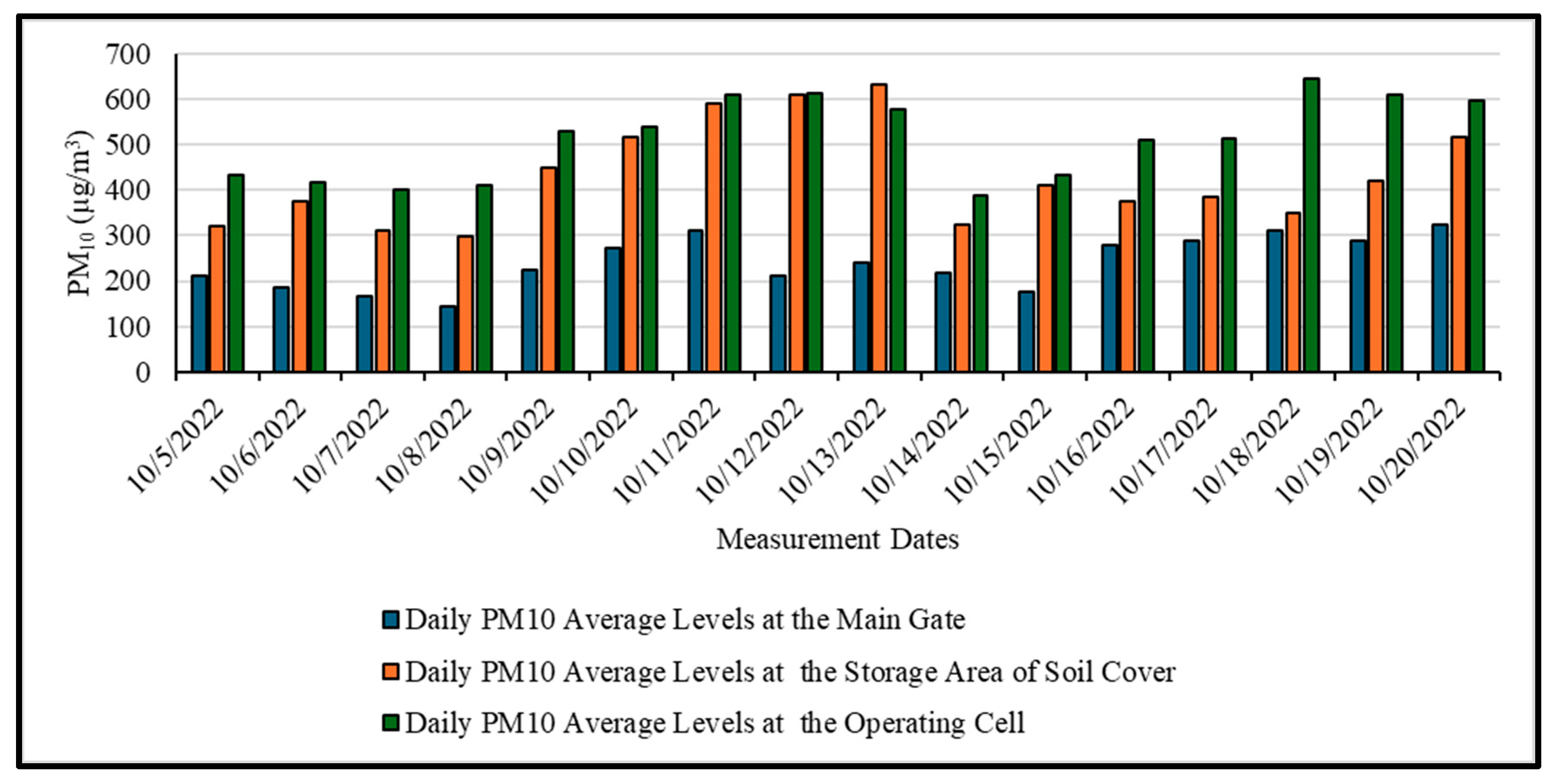
3.1. Assessment of Air Quality Levels
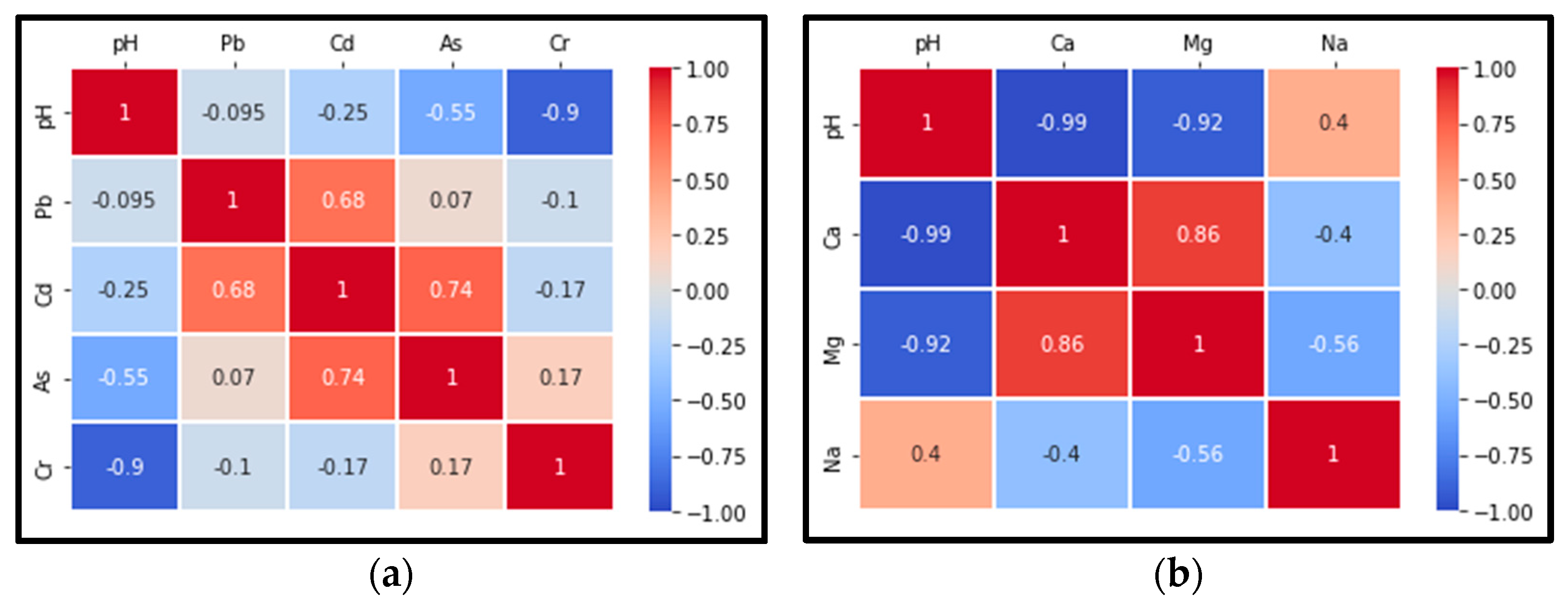
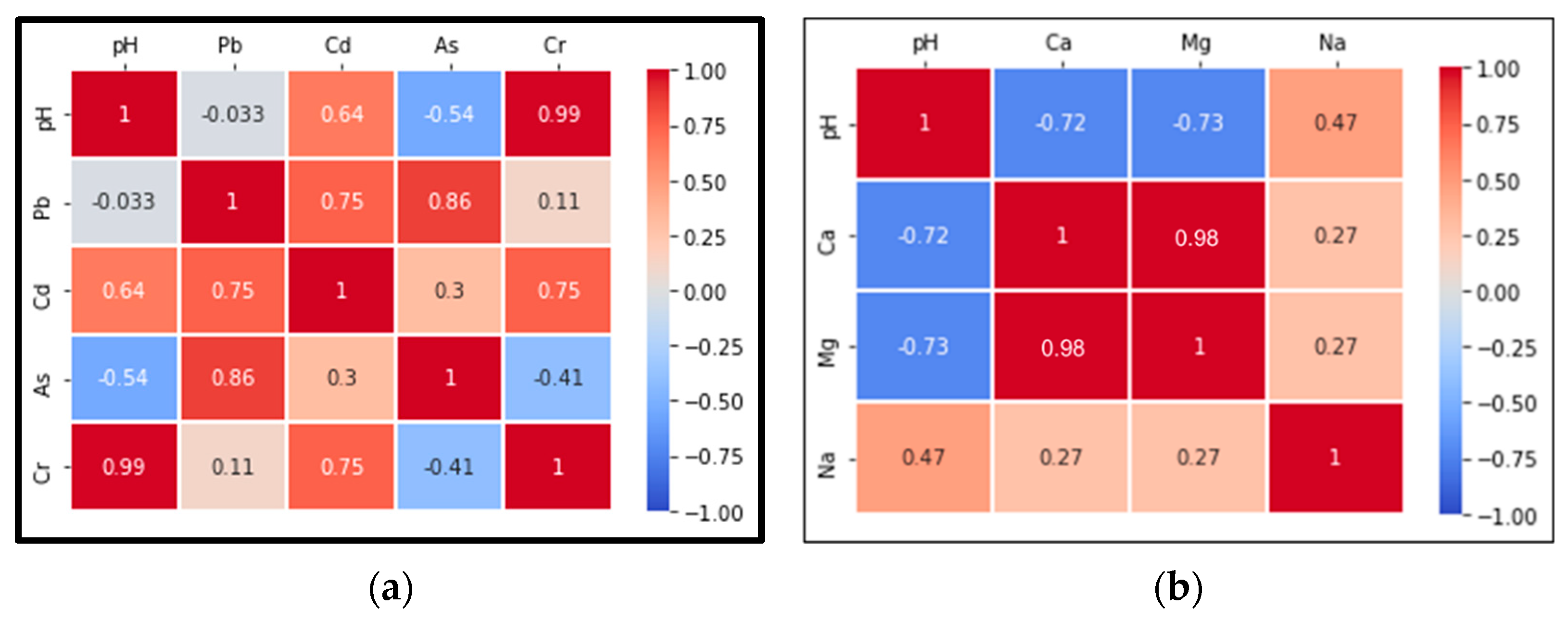
3.2. Assessment of Soil Pollution
- Soil sodicity—sodium ions displace calcium and magnesium from soil binding sites, leading to clay dispersion and reduced soil stability, disrupting drainage, aeration, and nutrient availability for plants [72];
- Potential impact on surrounding areas—the elevated SAR values for S3 and S4, which are outside the dumping site’s boundaries, suggest that leachate or other contaminants have migrated beyond the dump, impacting surrounding soil quality.
3.3. Assessment of Groundwater Pollution
3.4. Assessment of Generated Leachate
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
- Reduce the quantity of respirable dust particles disturbed by the movement of compactors and trucks during unloading, and squeeze and compact sand cover deposits and MSW through the occasional wetting of the operational area and the pavement of the roads, where possible, with asphalt.
- Frequently spray water around the entry area of the dumping site and the weighing site for trucks.
- Conduct regular follow-ups and repairs of the entire road network and the operating cells of the dumping site.
- Regularly spray water to minimize and mitigate the potential for the resuspension of particulate matter to avert and minimize the risk of human exposure for workers in the landfill/dumping sites.
- Plant more trees and expand the green landscape in/around the landfill/dumping site to minimize the levels of ambient particulate matter by means of the dust retention capacity of the foliage of shrubs and trees.
- Generally, the studied site is in need of a plan for preserving the current natural resources (soil, groundwater, and air).
- Encourage the optimum scenario for the management of MSW with the 3Rs concept (reduce, reuse, and recycle) and conduct waste sorting and treatment before disposal.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamović, V.M.; Antanasijević, D.Z.; Ćosović, A.R.; Ristić, M.Đ.; Pocajt, V.V. An artificial neural network approach for the estimation of the primary production of energy from municipal solid waste and its application to the Balkan countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C. Evaluating greenhouse gas emissions and energy recovery from municipal and industrial solid waste using waste-to-energy technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohalidanond, K.; Chaiyawong, P.; Kerdsuwan, S. Municipal solid waste characteristics and green and clean energy recovery in Asian megacities. Energy Procedia 2015, 79, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, S.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Hasan, M.A.; Shoaib, S.A.; Rushd, S. Greenhouse gas emissions from solid waste management in Saudi Arabia—Analysis of growth dynamics and mitigation opportunities. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinti, G.; Vaccari, M. Solid waste management in rural communities of developing countries: An overview of challenges and opportunities. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1138–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, A.; Patil, D.; Argade, K. Municipal solid waste management. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.H. Municipal solid waste: Review of best practices in application of life cycle assessment and sustainable management techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, S.; Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Irabien, A. From linear to circular integrated waste management systems: A review of methodological approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 135, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hipel, K.W. Exploring social dimensions of municipal solid waste management around the globe–A systematic literature review. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S. Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breukelman, H.; Krikke, H.; Löhr, A. Failing services on urban waste management in developing countries: A review on symptoms, diagnoses, and interventions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.N.; Noor, Z.Z.; Abba, A.H.; Yusuf, R.O.; Hassan, M.A.A. Review on life cycle assessment of integrated solid waste management in some Asian countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 41, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, I.A.; Arafat, H.A.; Basheer, T.; Shawahneh, H.; Salahat, A.; Eid, J.; Ali, W. Trends and problems of solid waste management in developing countries: A case study in seven Palestinian districts. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Bank. Trends in Solid Waste Management. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html#:~:text=The%20world%20generates%202.01%20billion,from%200.11%20to%204.54%20kilograms (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill impacts on the environment. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.H. The ethics of working with wicked urban waste problems: The case of Singapore’s Semakau Landfill. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 154, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osra, F.A.; Ozcan, H.K.; Alzahrani, J.S.; Alsoufi, M.S. Municipal solid waste characterization and landfill gas generation in kakia landfill, makkah. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M. Greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste management: A review of global scenario. In Carbon Footprint Case Studies: Municipal Solid Waste Management, Sustainable Road Transport and Carbon Sequestration; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2021; pp. 123–160. [Google Scholar]
- Ergül, M. Düzenli Depolama Sahalarının Tasarımı ve Örnek bir Uygulama. Master’s Thesis, Namık Kemal Üniversitesi, Tekirdağ, Turkey, 2018. (In Turkish). [Google Scholar]
- Sumathi, V.R.; Natesan, U.; Sarkar, C. GIS-based approach for optimized siting of municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2146–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.R. Sanitary Landfill Leachate: Generation, Control and Treatment; Routledge: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rajoo, K.S.; Karam, D.S.; Ismail, A.; Arifin, A. Evaluating the leachate contamination impact of landfills and open dumpsites from developing countries using the proposed Leachate Pollution Index for Developing Countries (LPIDC). Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, S. Temporal and spatial variation of greenhouse gas emissions from a limited-controlled landfill site. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Un, C. A Sustainable Approach to the Conversion of Waste into Energy: Landfill Gas-to-Fuel Technology. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.C. Religious tourism and its management: The hajj in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2011, 13, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolecka, K.; Rusin, A. Potential hazards posed by biogas plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, D.; Arya, S.; Kumar, S. Open dumping of organic waste: Associated fire, environmental pollution and health hazards. In Advanced Organic Waste Management; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ilmasari, D.; Kamyab, H.; Yuzir, A.; Riyadi, F.A.; Khademi, T.; Al-Qaim, F.F.; Kirpichnikova, I.; Krishnan, S. A review of the biological treatment of leachate: Available technologies and future requirements for the circular economy implementation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiriga, D.; Vestgarden, L.S.; Klempe, H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: Effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krčmar, D.; Tenodi, S.; Grba, N.; Kerkez, D.; Watson, M.; Rončević, S.; Dalmacija, B. Preremedial assessment of the municipal landfill pollution impact on soil and shallow groundwater in Subotica, Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundhoo, Z.M. Solid waste management in least developed countries: Current status and challenges faced. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Kumar, S.; Lokhandwala, S. Advanced oxidation processes for treatment of leachate from hazardous waste landfill: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Singh, D.; Shukla, S.K. Assessment of human health risk due to leachate contaminated soil at solid waste dumpsite, Kanpur (India). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 21, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzo, L.; Manno, V.; Iavarone, I.; Minelli, G.; De Santis, M.; Beccaloni, E.; Scaini, F.; Miotto, E.; Airoma, D.; Comba, P. The health impact of hazardous waste landfills and illegal dumps contaminated sites: An epidemiological study at ecological level in Italian Region. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 996960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chireshe, A.; Shabani, T.; Shabani, T. Safety and health risks associated with illegal municipal solid waste disposal in urban Zimbabwe. “A case of Masvingo City”. Saf. Extrem. Environ. 2023, 5, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibade, F.O.; Adelodun, B.; Ajibade, T.F.; Lasisi, K.H.; Abiola, C.; Adewumi, J.R.; Akinbile, C.O. The threatening effects of open dumping on soil at waste disposal sites of Akure city, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2021, 27, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, B.; Mani, S.; Madguni, O. Open dumping of waste and its impact on our water resources and health—A case of New Delhi, India. In Recent Developments in Waste Management: Select Proceedings of Recycle 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 127–154. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Chokhandre, P.; Salve, P.S.; Rajak, R. Open dumping site and health risks to proximate communities in Mumbai, India: A cross-sectional case-comparison study. Clin. Epidemiol. Global Health 2020, 9, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Tabinda, A.B.; Qadir, A.; Butt, T.E.; Siddique, S.; Mahmood, A. Ecological risk assessment of an open dumping site at Mehmood Booti Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17889–17899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Ahmad, M.; Rasheed, H.; Rafique, M.I.; Ahmad, J.; Usman, A.R. Environmental Issues Due to Open Dumping and Landfilling. In Circular Economy in Municipal Solid Waste Landfilling: Biomining & Leachate Treatment: Sustainable Solid Waste Management: Waste to Wealth; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 65–93. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqua, A.; Hahladakis, J.N.; Al-Attiya, W.A.K. An overview of the environmental pollution and health effects associated with waste landfilling and open dumping. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58514–58536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, S.; Joseph, C.P. Potential hazards due to municipal solid waste open dumping in India. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2021, 101, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Aziz, H.; Isa, M.; Kadir, O.; Nordin, N.; Daud, W.; Alsebaei, A.; Abu-Rizaiza, A. Study of baseline data regarding solid waste management in the holy city of Makkah during Hajj. In The Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques Institute of the Hajj Research; Universiti Sains Malaysia: Penang, Malaysia, 2007; (Unpunished Report). [Google Scholar]
- Nizami, A.S.; Rehan, M.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Almeelbi, T.; Ouda, O.K.M. Waste biorefinery in Makkah: A solution to convert waste produced during Hajj and Umrah Seasons into wealth. In Proceedings of the Conference: 15th Scientific Symposium for Hajj, Umrah and Madinah Visit, Medina, Saudi Arabia, 27–28 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- MEP. The Eighth Development Plan for 2005–2009; Ministry of Economy and Planning: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2005.
- MOMRA. Cleanliness Projects and Sanitary Landfill in Saudi Arabia; Ministry of Municipal and Rural Affairs in Saudi Arabia: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2013.
- GCC. Municipal Solid Waste Management Guidelines in the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf; Department of Human Affairs and Environment—The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, (GCC): Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mashat, B. Effective Microorganisms (EM) Technology as a Pathway to Improve Municipal Solid Waste of Makkah City (Saudi Arabia) and as Foul Odor Eliminator’. In Proceedings of the Clute Institute International Academic Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–12 June 2014; pp. 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Osra, F. Optimizing the Suitable Site (S) for Landfill by Multi-Criteria Decision and Investigating Biogasification Potential of the Waste in Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Doctoral Dissertation, Institute of Graduate Studies in Science and Engineering, Istanbul University, Istanbul, Türkiye, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, W.R.; Hadley, D.G.; Anderson, R.E.; Fleck, R.J.; Schmidt, D.L. A Discussion on global tectonics in Proterozoic times-Late Proterozoic cratonization in southwest Saudi Arabia. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1976, 280, 517–527. [Google Scholar]
- Sonbul, A.R. Engineering Geology as Applied to Urban Development of the North-Western Area of The Holy City of Makkah; Faculty of Earth Sciences, King Abdul-Aziz University: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Osra, F.A.; Kajjumba, G.W. Landfill site selection in Makkah using geographic information system and analytical hierarchy process. Waste Manag. Res. 2020, 38, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, N.; Mangi, S.A. Municipal solid waste management practices and opportunities in Saudi Arabia. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 4516–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzammil, A.; Rashid, M.; Muhammad, W.; Ijaz, A.; Ziad, O.A.A.; Asad, S.A.; Mohamed, A.B.; Tasneem, A. Solid waste management in Saudi Arabia: A review. J. Appl. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, E.A. Geo-Environmental Evaluation of the Kaakia Landfill, Southwest Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2022, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Pal, J.S.; Eltahir, E.A. Future heat stress during Muslim pilgrimage (Hajj) projected to exceed “extreme danger” levels. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10094–10100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajbar, A.H.; Ali, E. Water demand prediction for touristic Mecca city in Saudi Arabia using neural networks. Int. J. Geol. Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Huang, Y.; Al-Ansari, N.; Knutsson, S. Dust Emissions from Landfill Deposition: A Case Study in Malmbetget mine, Sweden. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2011, 3, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2. 5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnama, E.; Bazrafshan, O.; Asadollahfardi, G. Application of data-driven methods to predict the sodium adsorption rate (SAR) in different climates in Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, R.; de Oliveira, M.W.; de Freitas Santos, D. Irrigation Water–Quality Issues, Limits, and Way Forward. DELOS Desarro. Local Sosten. 2023, 16, 2941–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hadidi, N.; Al Hadidi, M. Suitability of reclaimed wastewater effluent from decentralized wastewater plant for irrigation. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Health Nexus. Sodium Adsorption Ratio and Sodicity. 2020. Available online: https://soilhealthnexus.org/resources/soil-properties/soil-chemical-properties/sodium-adsorption-ratio-and-sodicity/ (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Environmental Saudi Standards, Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Environmental Saudi Standards. Available online: https://ncec.gov.sa/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Preventing-and-treating-soil-pollution.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Nhung, T.C.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Rangasamy, G. A review on landfill system for municipal solid wastes: Insight into leachate, gas emissions, environmental and economic analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T.H.; Kjeldsen, P.; Bjerg, P.L.; Jensen, D.L.; Christensen, J.B.; Baun, A.; Albrechtsen, H.J.; Heron, G. Biogeochemistry of landfill leachate plumes. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 659–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chai, J.; Cao, J.; Qin, Y.; Dang, M.; Geng, K.; Wei, Y. Landfill leachate generation mechanism study: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 9271–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wdowczyk, A.; Szymańska-Pulikowska, A. Differences in the composition of leachate from active and non-operational municipal waste landfills in Poland. Water 2020, 12, 3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Grattan, S.R.; Fulton, A. Agricultural Salinity and Drainage; University of California, University of California Irrigation Program: Davis, CA, USA, 1999; 159p. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Kharche, V.K. Soil salinity and sodicity. Soil Sci. Introd. 2018, 12, 353–384. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwar, P.; Singh, R.; Trivedi, M.; Tiwari, R.K. Sodic soil: Management and reclamation strategies. In Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development: Volume 2: Biodiversity, Soil and Waste Management; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2020; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Nkwunonwo, U.C.; Odika, P.O.; Onyia, N.I. A review of the health implications of heavy metals in food chain in Nigeria. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 6594109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hembrom, S.; Singh, B.; Gupta, S.K.; Nema, A.K. A comprehensive evaluation of heavy metal contamination in foodstuff and associated human health risk: A global perspective. In Contemporary Environmental Issues and Challenges in Era of Climate Change; Springer Nature: London, UK, 2020; pp. 33–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jayakumar, M.; Surendran, U.; Raja, P.; Kumar, A.; Senapathi, V. A review of heavy metals accumulation pathways, sources and management in soils. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okereafor, U.; Makhatha, M.; Mekuto, L.; Uche-Okereafor, N.; Sebola, T.; Mavumengwana, V. Toxic metal implications on agricultural soils, plants, animals, aquatic life and human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, R.; Aravindan, S.; Shankar, K.; Balamurugan, P. Suitability of groundwater quality for irrigation in and around the main Gadilam river basin on the east coast of southern India. Arch. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2020, 5, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iddrisu, U.F.; Mbatchou, V.C.; Armah, E.K.; Amedorme, B.S. Groundwater quality assessment for sustainable irrigation in Nanton district, Ghana. Water Pract. Technol. 2023, 18, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhisheka, V.R.; Binoj Kumar, R.B. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Domestic and Irrigational Suitability in Kallada River Basin, South Kerala, India. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2018, 17, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Jat Baloch, M.Y.; Zhang, W.; Chai, J.; Li, S.; Alqurashi, M.; Rehman, G.; Tariq, A.; Talpur, S.A.; Iqbal, J.; Munir, M.; et al. Shallow groundwater quality assessment and its suitability analysis for drinking and irrigation purposes. Water 2021, 13, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 29 Rev. 1; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Ančić, M.; Huđek, A.; Rihtarić, I.; Cazar, M.; Bačun-Družina, V.; Kopjar, N.; Durgo, K. PHYSICO chemical properties and toxicological effect of landfill groundwaters and leachates. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, P.; Mor, S.; Ravindra, K. Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality in three cities of North India and health risk assessment. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 1455–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.H.; Kavianpour, M.R.; Alcaraz, J.L.G.; Yamini, O.A. System dynamics modeling for effective strategies in water pollution control: Insights and applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budi, S.; Suliasih, B.A.; Othman, M.S.; Heng, L.Y.; Surif, S. Toxicity identification evaluation of landfill leachate using fish, prawn and seed plant. Waste Manag. 2016, 55, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmunnaher, T.; Chowdhury, M.A.I. Correlation study for assessment of water quality and its parameters of Kushiyara River, Sylhet, Bangladesh. Int. J. New Technol. Res. 2017, 3, 263179. [Google Scholar]
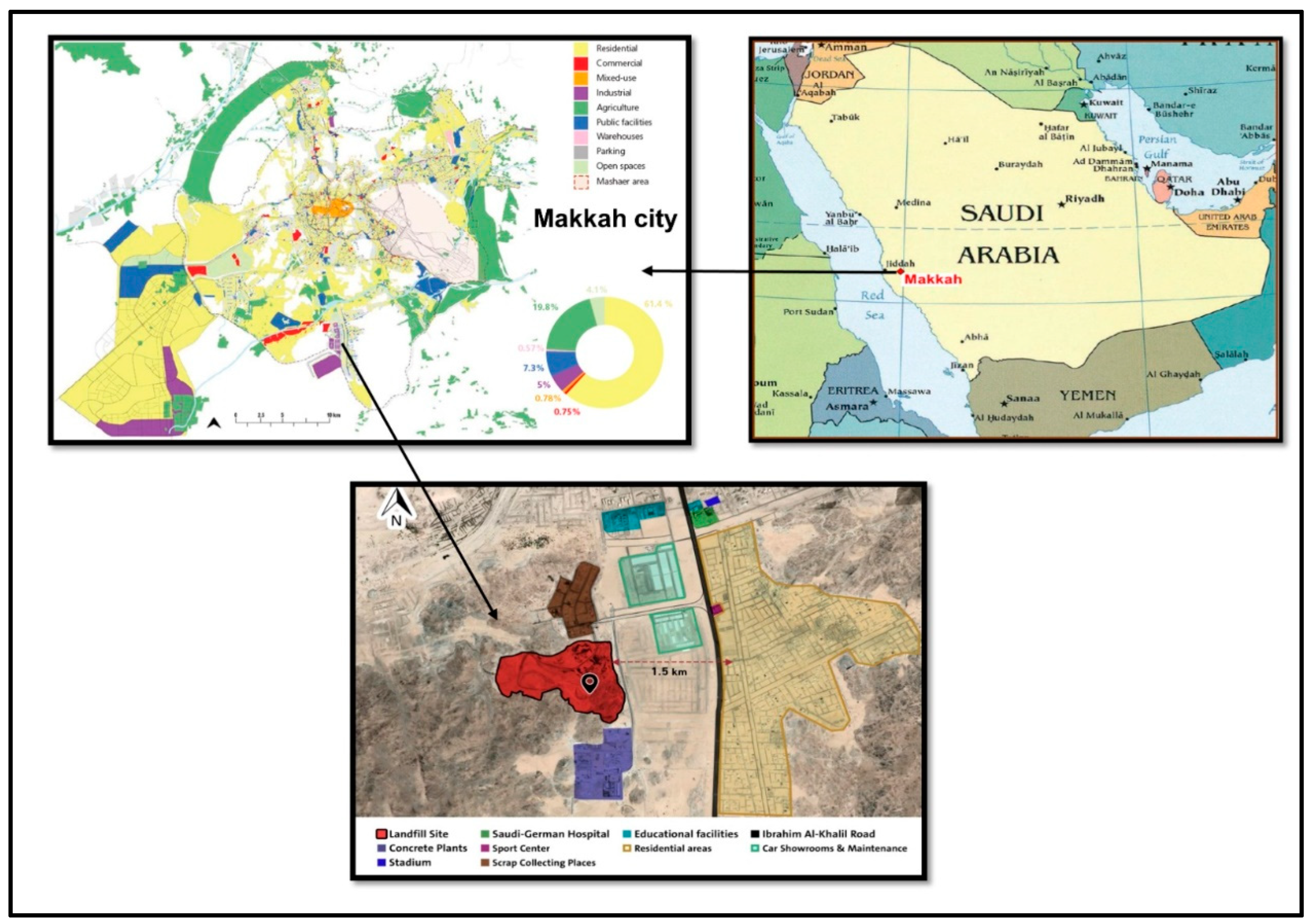
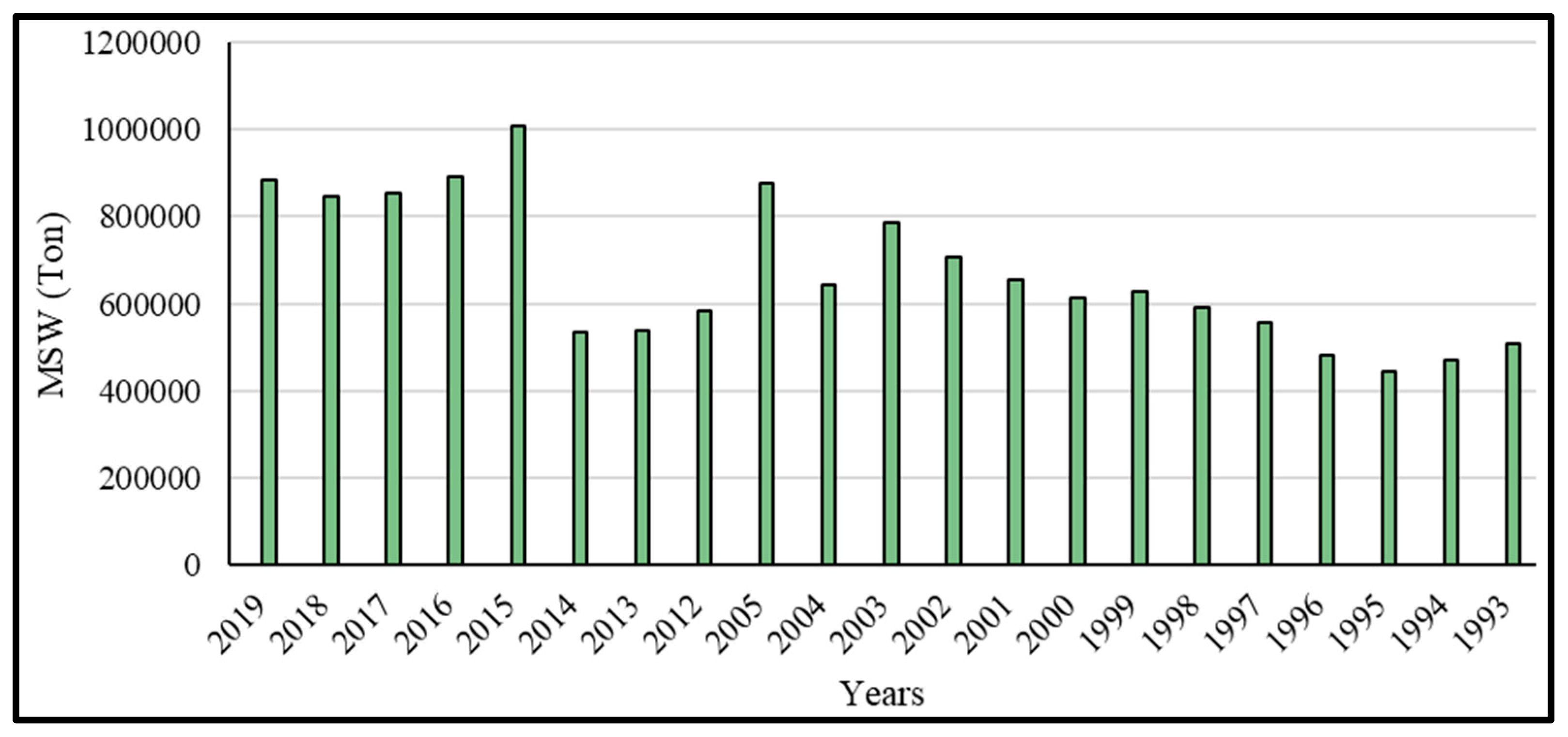
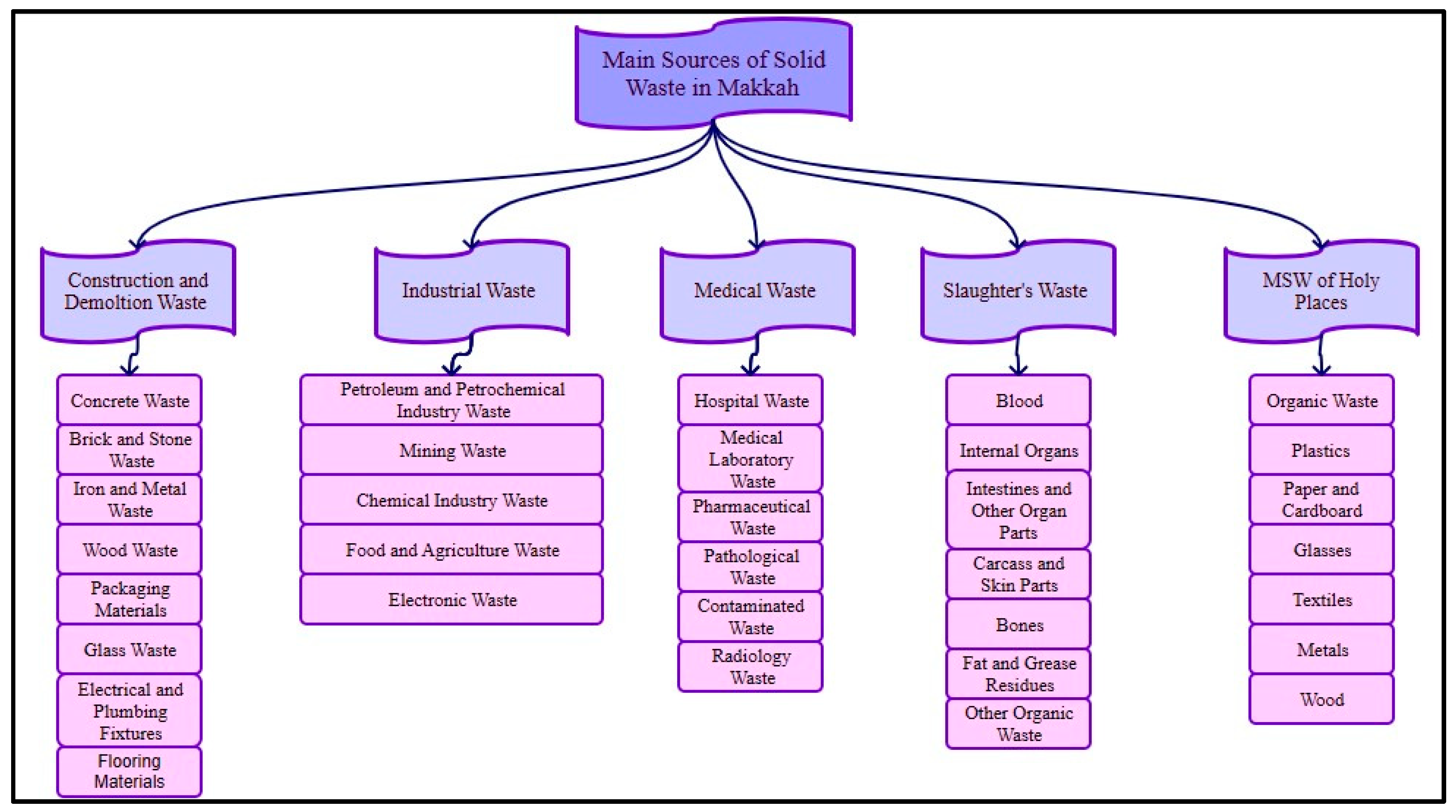
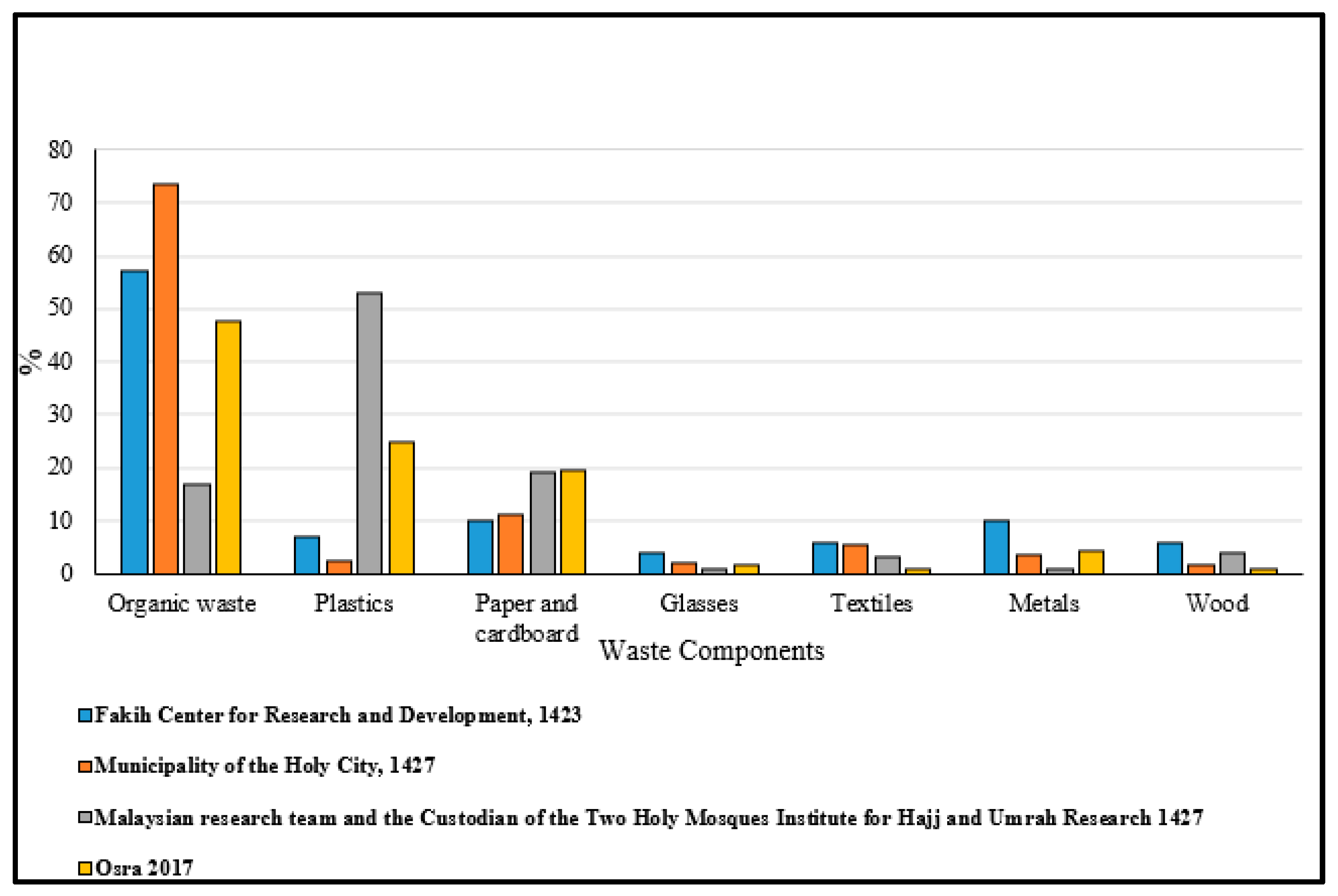


| Parameter | Pollutant Parameters and Analysis Methods for Soil Samples (a) | Pollutant Parameters and Analysis Methods for Groundwater Samples (b) | Pollutant Parameters and Analysis Methods for Leachate Samples (c) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Unit | Method | Unit | Method | Unit | |
| pH | APHA 9040 B | - | APHA 9040 B | - | APHA 9040 B | - |
| Calcium (Ca) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Magnesium (Mg) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Sodium (Na) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Lead (Pb) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Cadmium (Cd) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Arsenic (As) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| Chromium (Cr) | EPA 200.7 | mg/kg | EPA 200.7 | mg/L | EPA 200.7 | mg/L |
| (A) | ||||
| Test Name | Unit | Result | Result | Saudi Standards for Protecting Soil from Pollution |
| (S1) | (S2) | |||
| pH | - | 8.45 | 9 | 8.50 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg/kg | 52,400 | 29,900 | - |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg/kg | 20,600 | 11,100 | - |
| Sodium (Na) | mg/kg | 17,700 | 18,200 | - |
| Lead (Pb) | mg/kg | 10 | 12 | 600 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | mg/kg | <1 | <1 | 22 |
| Arsenic (As) | mg/kg | <0.001 | <0.001 | 26 |
| Chromium (Cr) | mg/kg | 45.96 | 33.86 | 87 |
| SAR (Sodium Adsorption Ratio) | meq/L | 16.55 | 22.78 | <13 |
| (B) | ||||
| Test Name | Unit | Result | Result | Saudi Standards for Protecting Soil from Pollution |
| (S3) | (S4) | |||
| pH | - | 8.67 | 8.94 | 8.50 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg/kg | 41,100 | 33,700 | - |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg/kg | 21,200 | 12,800 | - |
| Sodium (Na) | mg/kg | 17,500 | 18,700 | - |
| Lead (Pb) | mg/kg | 26 | 13 | 70 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | mg/kg | <1 | <1 | 1.4 |
| Arsenic (As) | mg/kg | <0.001 | <0.001 | 17 |
| Chromium (Cr) | mg/kg | 37.14 | 28.42 | 64 |
| SAR (Sodium Adsorption Ratio) | meq/L | 17.44 | 21.95 | <13 |
| Test Name | Unit | Result | Result | Result | Saudi Standards for Irrigation Water | Saudi Standards for Potable Groundwater |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (W1) | (W2) | (W3) | ||||
| pH | - | 6.83 | 7.46 | 7.05 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–9 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg/L | 433.42 | 223.92 | 206.45 | - | 10–100 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg/L | 173.81 | 90.5 | 84.14 | - | - |
| Sodium (Na) | mg/L | 819.56 | 1049.34 | 329.72 | - | 150 |
| Lead (Pb) | mg/L | 0.00019 | 0.00016 | <0.0001 | 5 | 0.0075 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | mg/L | 0.00013 | 0.00019 | <0.0001 | 0.01 | 0.003 |
| Arsenic (As) | mg/L | 0.00333 | 0.00193 | 0.00131 | 0.1 | 0.0075 |
| Chromium (Cr) | mg/L | 0.00096 | 0.00388 | 0.00159 | 0.1 | 0.037 |
| SAR (Sodium Absorption Rate) | meq/L | 8.39 | 14.93 | 4.88 | <9 | - |
| Test Name | Unit | Result (L1) | Result (L2) | Result (L3) | Saudi Standards for Potable Groundwater | Saudi Standards for Irrigation Water | Saudi Standards for Surface Water (Non-Potable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.19 | 7.23 | 7.23 | 6.5–9 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–9 |
| Calcium (Ca) | mg/L | 1171 | 1083 | 1099 | 10–100 | - | 10–100 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | mg/L | 481 | 461 | 473 | - | - | - |
| Sodium (Na) | mg/L | 4588 | 4789 | 5034 | 150 | - | 150 |
| Lead (Pb) | mg/L | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.0075 | 5 | 0.01 |
| Cadmium (Cd) | mg/L | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.000025 |
| Arsenic (As) | mg/L | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.0075 | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| Chromium (Cr) | mg/L | 0.98 | 0.957 | 0.989 | 0.037 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| SAR (Sodium Absorption Rate) | meq/L | 28.45 | 30.66 | 31.92 | - | <9 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osra, F.A.; Elbisy, M.S.; Mosaıbah, H.A.; Osra, K.; Ciner, M.N.; Ozcan, H.K. Environmental Impact Assessment of a Dumping Site: A Case Study of Kakia Dumping Site. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16103882
Osra FA, Elbisy MS, Mosaıbah HA, Osra K, Ciner MN, Ozcan HK. Environmental Impact Assessment of a Dumping Site: A Case Study of Kakia Dumping Site. Sustainability. 2024; 16(10):3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16103882
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsra, Faisal A., Moussa Sobh Elbisy, Hasan Abdullah Mosaıbah, Khalid Osra, Mirac Nur Ciner, and H. Kurtulus Ozcan. 2024. "Environmental Impact Assessment of a Dumping Site: A Case Study of Kakia Dumping Site" Sustainability 16, no. 10: 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16103882
APA StyleOsra, F. A., Elbisy, M. S., Mosaıbah, H. A., Osra, K., Ciner, M. N., & Ozcan, H. K. (2024). Environmental Impact Assessment of a Dumping Site: A Case Study of Kakia Dumping Site. Sustainability, 16(10), 3882. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16103882






