Application Study on the Activated Coke for Mercury Adsorption in the Nonferrous Smelting Industry
Abstract
1. Introduction
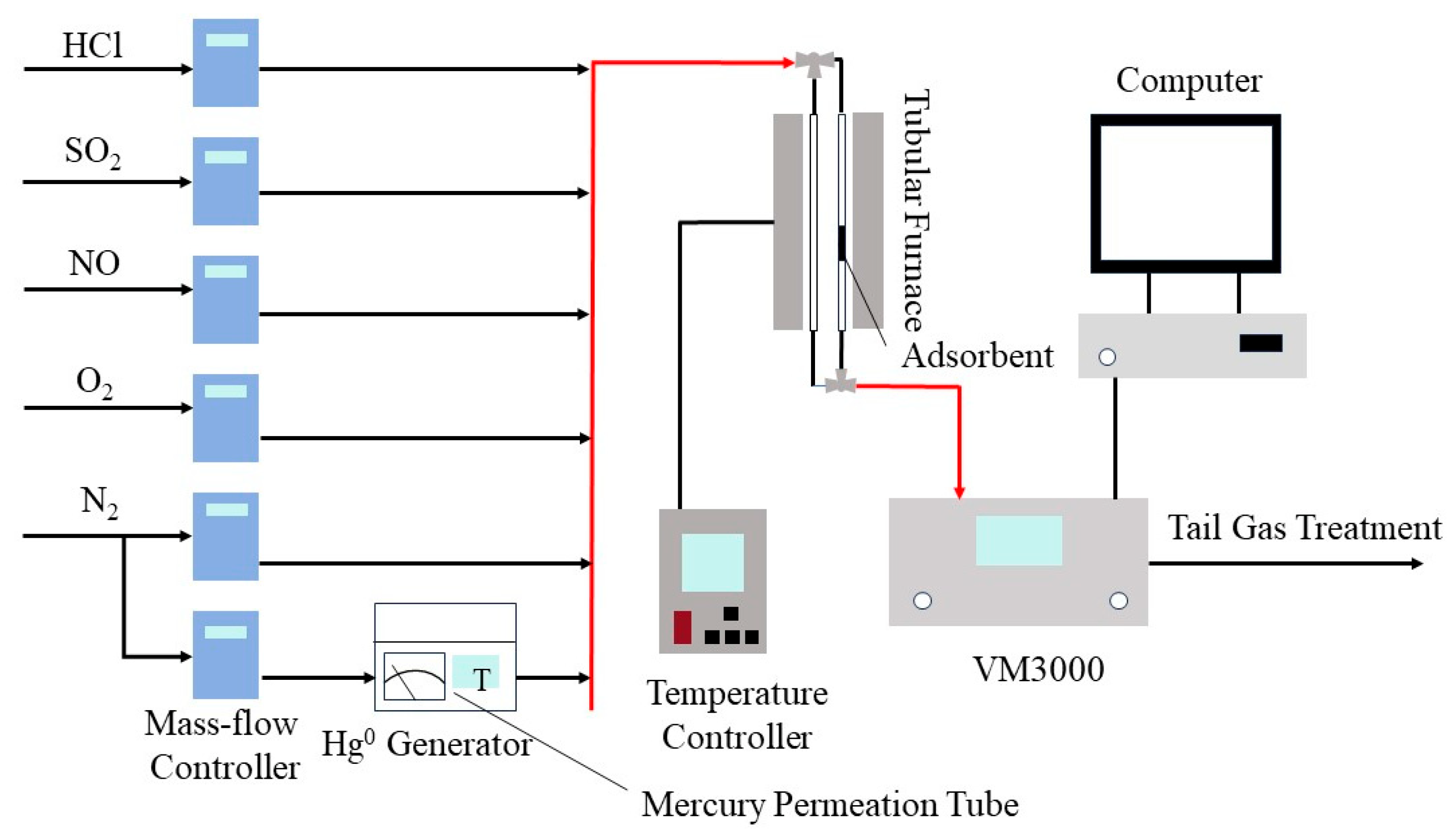
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Material
2.2. Evaluation of Mercury Adsorption Performance
2.3. Sample Characterization
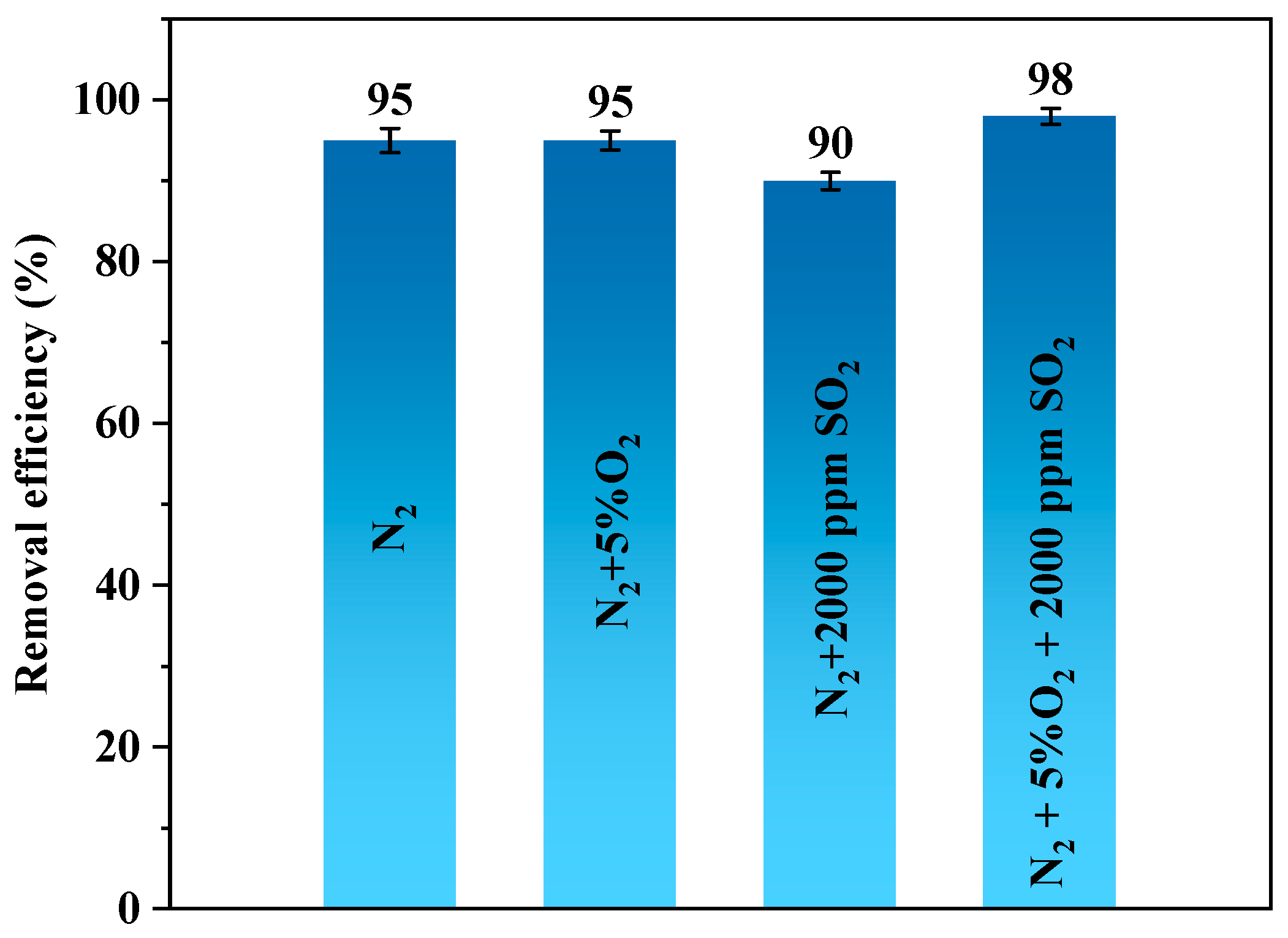
3. Results and Discussion
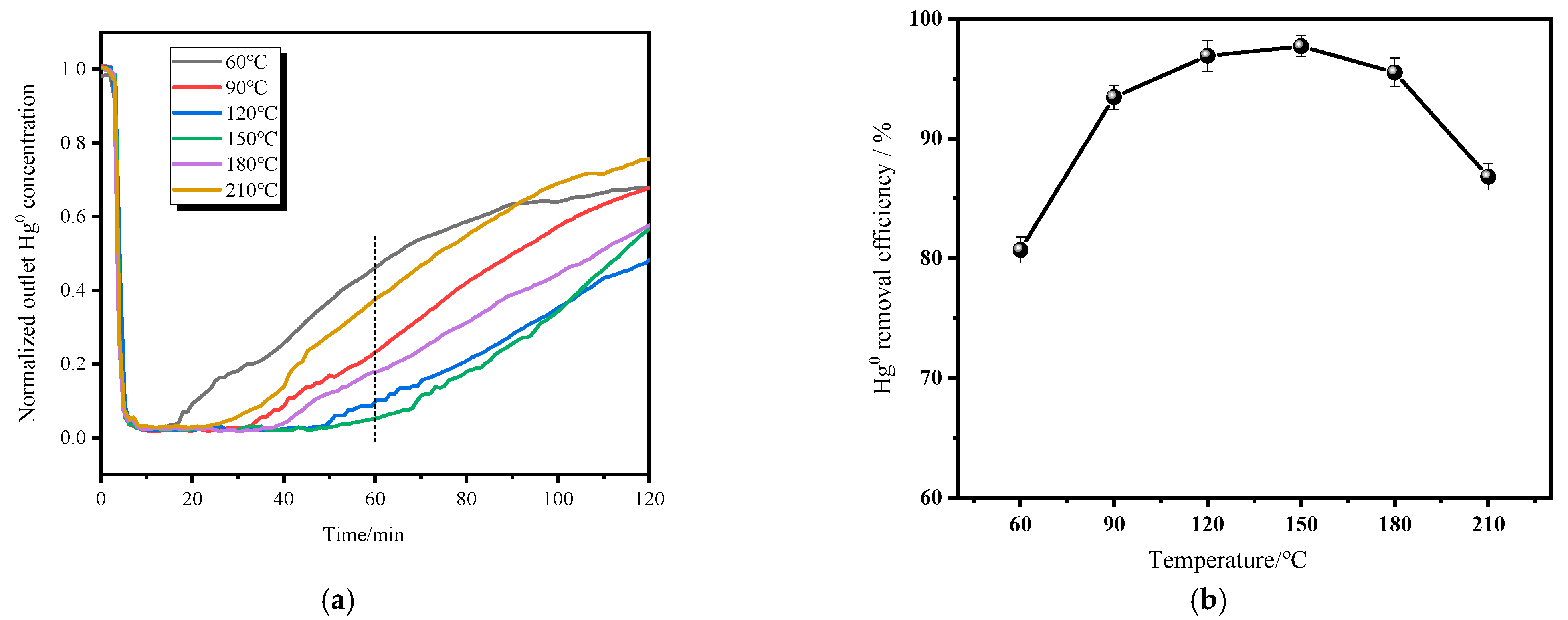
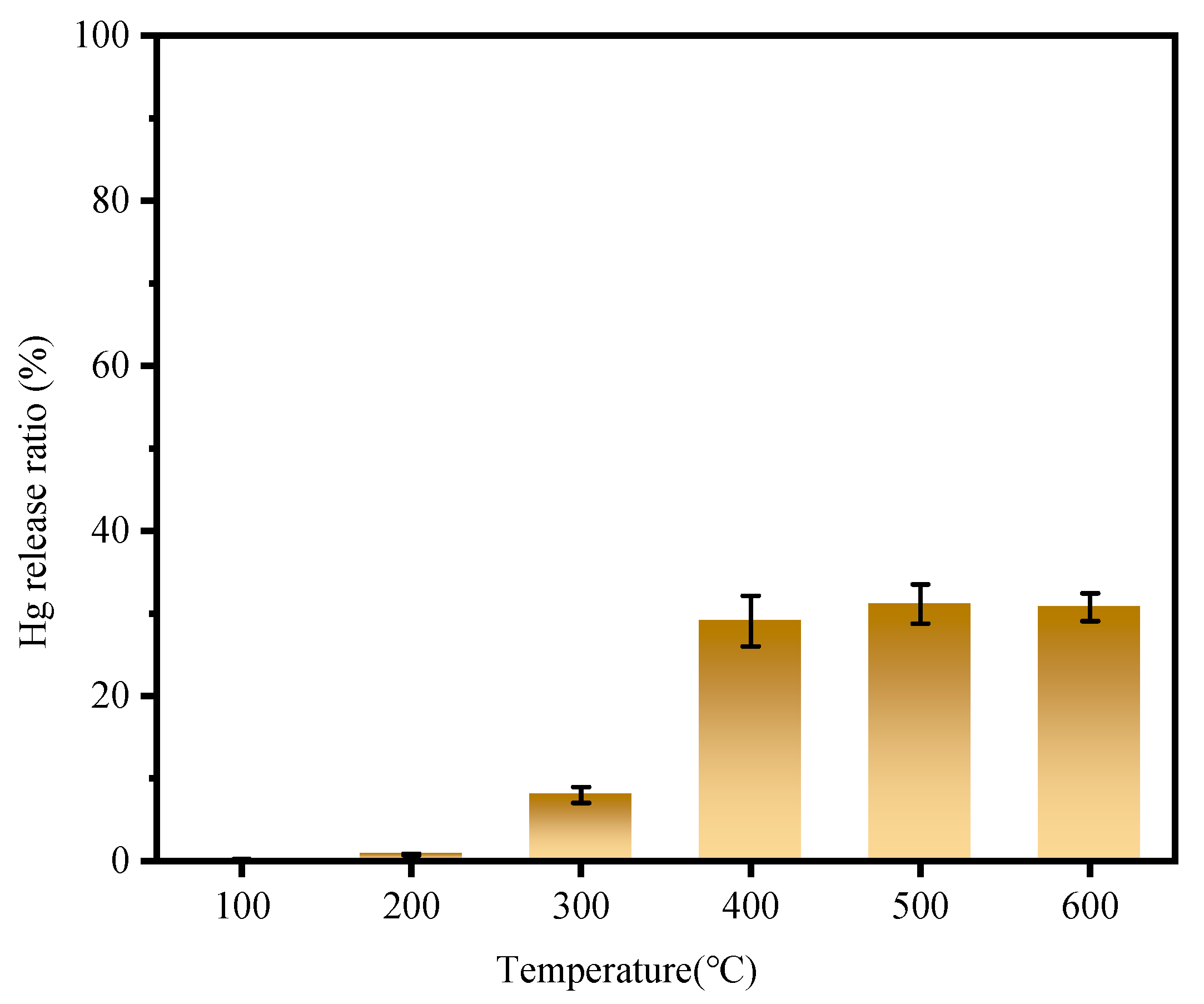
3.1. Effect of Temperature on Mercury Removal Performance
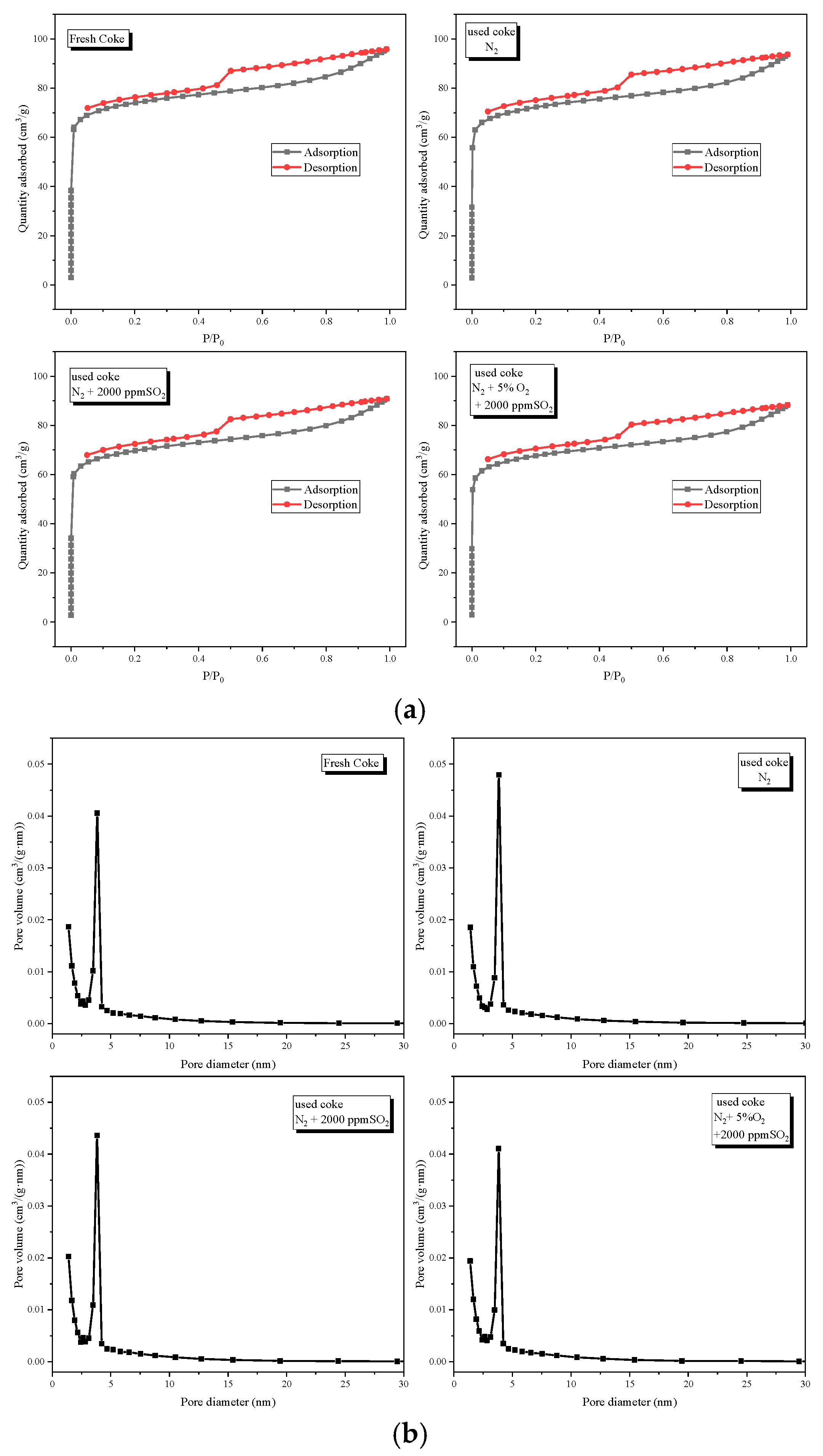
3.2. Specific Surface Area Analysis
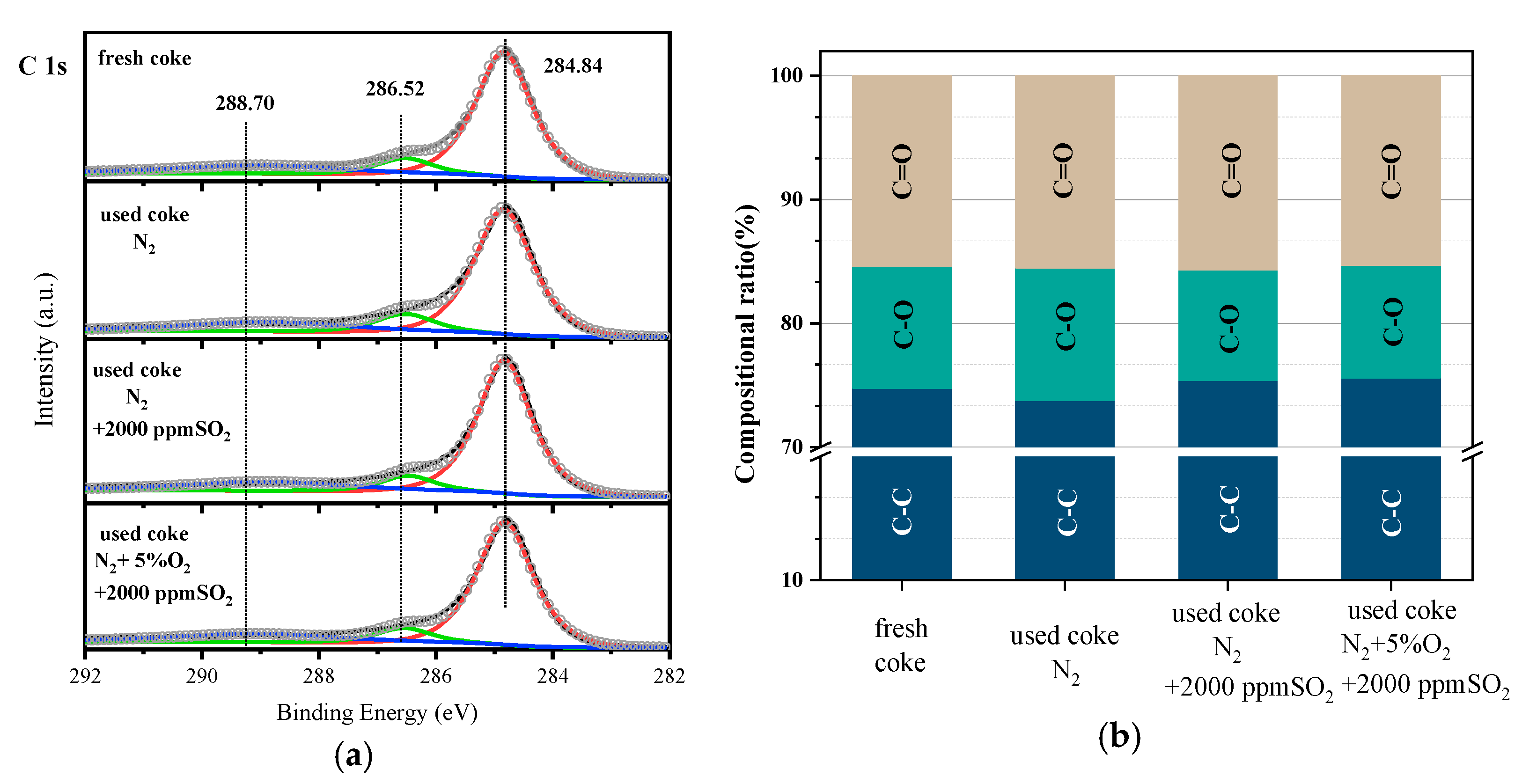
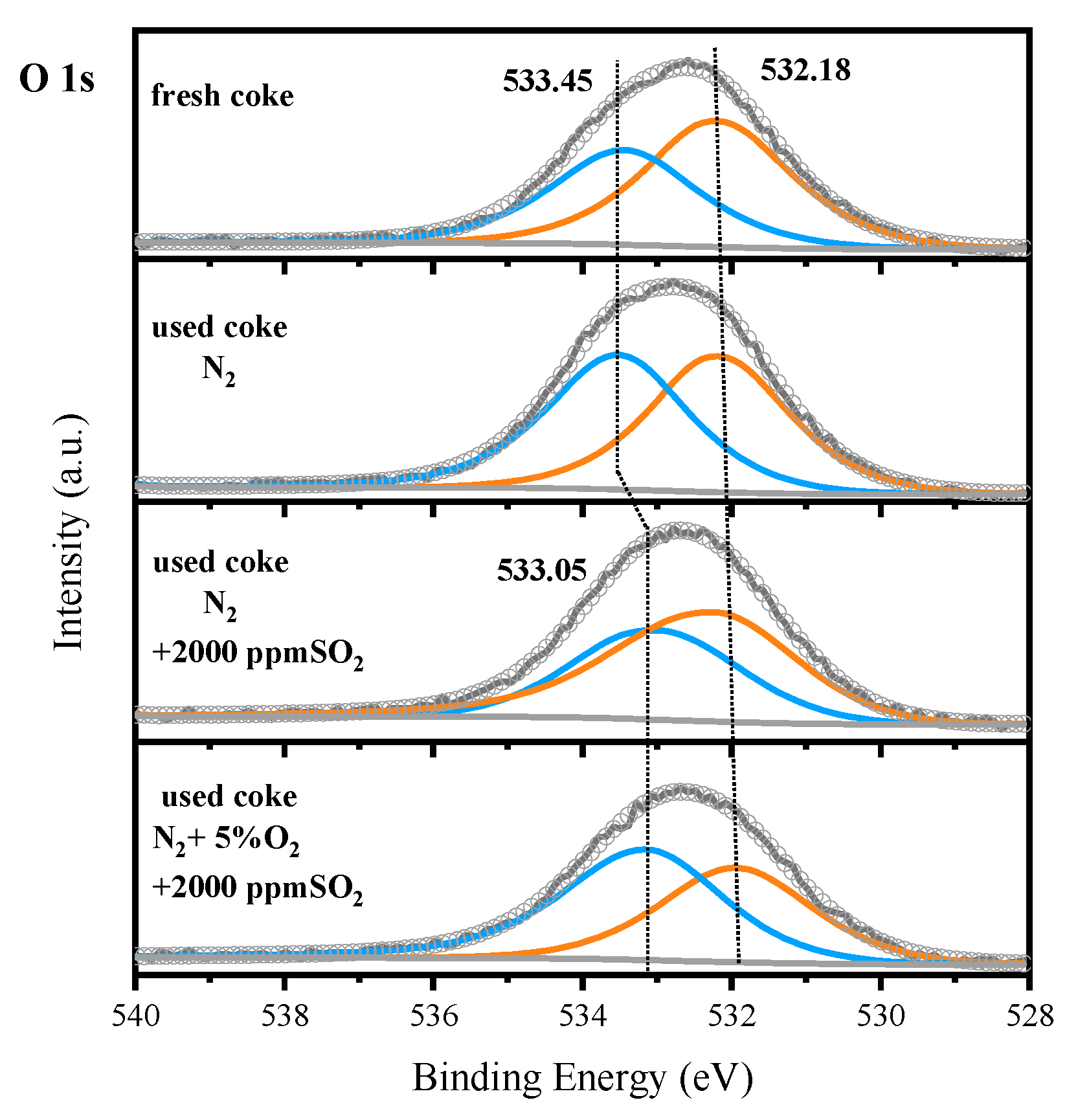
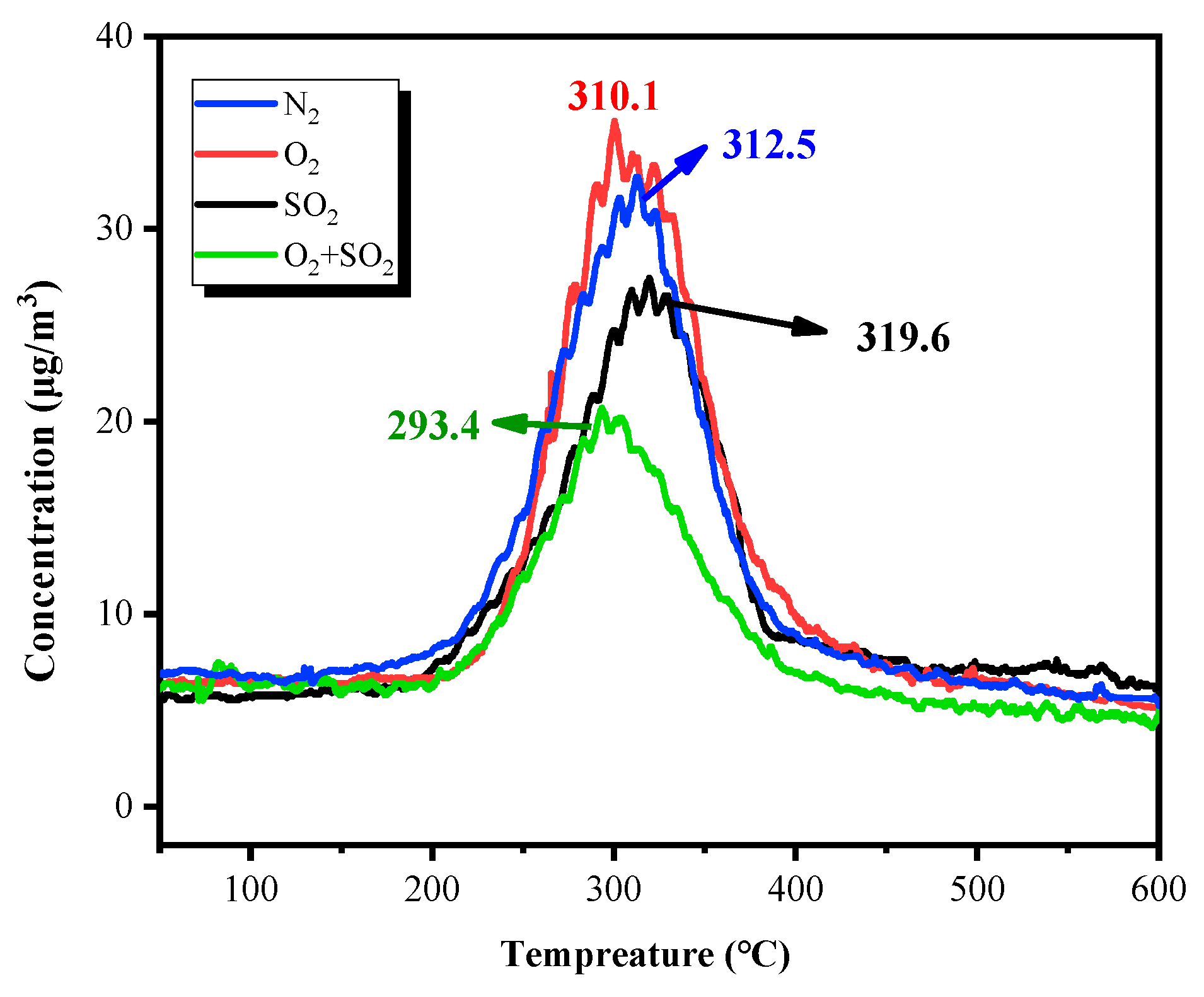
3.3. Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.; Gong, C.; Guan, Y.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Peng, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, T.; Xiang, S.; Gao, Y. Novel bimetallic chalcogenide adsorbents for elemental mercury removal from flue gas: A review. Fuel 2023, 344, 128081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszkiewicz, D.; Jedrusik, M.; Swierczok, A.; Kobylanska-Pawlisz, M. Effect of addition of sulphide based additive to WFGD slurry on mercury removal from flue gas. Energy 2023, 270, 126953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Global Mercury Assessment. 2018. Available online: https://www.unep.org/resources/publication/global-mercury-assessment-2018 (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Zhao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, J.; Nielsen, C.P. Evaluating the effects of China’s pollution controls on inter-annual trends and uncertainties of atmospheric mercury emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 4317–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Hui, M.; Wang, F.; Hao, J. Flow Analysis of the Mercury Associated with Nonferrous Ore Concentrates: Implications on Mercury Emissions and Recovery in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Ni, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, A.; Quan, Z.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. One Step Interface Activation of ZnS Using Cupric Ions for Mercury Recovery from Nonferrous Smelting Flue Gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4511–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Yi, H.; Shen, F.; Liu, H. Co9S8 nanoparticles-embedded porous carbon: A highly efficient sorbent for mercury capture from nonferrous smelting flue gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 124970–124978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Qu, W.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, S.; Shih, K.; Li, H. Favorably adjusting the pore characteristics of copper sulfide by template regulation for vapor-phase elemental mercury immobilization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 10729–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-h.; Zhang, S.-f.; Wei, Y.-y.; Sher, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.-z.; Wen, L.-y. Preparation of active coke combining coal with biomass and its denitrification performance. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Du, X.; Li, S.; Huang, L. Recycle of waste activated coke as an efficient sorbent for Hg0 removal from coal-fired flue gas. Fuel 2022, 324, 124645–124654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.; Pan, W.-P. A review on adsorbent/catalyst application for mercury removal in flue gas: Effect of sulphur oxides (SO2, SO3). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124220–124238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Sun, X.; Cheng, X.; Cui, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y. Investigation on mercury removal and recovery based on enhanced adsorption by activated coke. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tao, S. Experimental study on Hg0 removal from flue gas over columnar MnOx-CeO2/activated coke. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 333, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yi, H.; Tang, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Gao, F. Copper modified activated coke for mercury removal from coal-fired flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Lu, P.; Gao, L.; Du, X.; Yi, Y. Simultaneous removal of HCHO and elemental mercury from flue gas over Co-Ce oxides supported on activated coke impregnated by sulfuric acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Chuai, X.; Cui, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. A high efficiency and high capacity mercury adsorbent based on elemental selenium loaded SiO2 and its application in coal-fired flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.C.; Shetty, S.; Chu, H.W.; Lin, C.J.; Hopper, J.R. Simulation of mercury emission control by activated carbon under confined-bed operations. Powder Technol. 2008, 180, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, P.; Chen, S.; Shi, L. Research on Mercury Emissions Regularity and Adsorbing Mercury by Activated Carbon in Coal-fired Power Plants. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284–286, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graydon, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Kirk, D.W.; Jia, C.Q. Sorption and stability of mercury on activated carbon for emission control. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Long, Y.; Ding, J. Interface reaction activity of recyclable and regenerable Cu-Mn spinel-type sorbent for Hg0 capture from flue gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodeno, R. Projected global mercury supply, demand, and excess to 2050 based on impacts of the Minamata Convention. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 3608–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q. Impacts of Removal Compensation Effect on the Mercury Emission Inventories for Nonferrous Metal (Zinc, Lead, and Copper) Smelting in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Huang, W.; Ji, L.; Xu, H.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Establishing a self-supporting system of H2S production from SO2 with induced catalytic reduction process for mercury capture with super-large enrichment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141493–141503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dang, J.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Zhang, Q. Theoretical insight into the influence of SO2 on the adsorption and oxidation of mercury over the MnO2 surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 626, 157216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Wattimena, Y.; Erdiwansyah; Mahidin; Muhibbuddin; Riza, M. Simultaneous sulfur dioxide and mercury removal during low-rank coal combustion by natural zeolite. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07052–e07058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Peng, X.; An, M.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W. Negative effect of SO2 on mercury removal over catalyst/sorbent from coal-fired flue gas and its coping strategies: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Z.; Gao, H.L.; Wang, Q.H.; Cen, K.F. Factors affecting amount of activated carbon injection for flue gas mercury control. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2005, 56, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Xu, L. Experimental research of removing mercury from flue gas by activated carbon fibers. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 2006, 34, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Goci, M.C.; Leudjo Taka, A.; Martin, L.; Klink, M.J. Chitosan-Based Polymer Nanocomposites for Environmental Remediation of Mercury Pollution. Polymers 2023, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Park, S.-W.; Kim, H.S.; Alam, T.; Lee, S.Y. Oxidation Enhancement of Gaseous Elemental Mercury Using Waste Steel Slag under Various Experimental Conditions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, R. Enhanced adsorption of gaseous mercury on activated carbon by a novel clean modification method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122885–122896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, C.; Schramm, A.; Hubalkova, J.; Brachhold, N.; Giesche, H.; Aneziris, C.G. Impact of carbon binders and carbon fillers on mercury intrusion and extrusion porosimetry of carbon-bonded alumina. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 6264–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Long, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, J. Joint Characterization and Fractal Laws of Pore Structure in Low-Rank Coal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumari, G.; Rajarajan, M.; Senthilvelan, S. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of activated carbon-zirconium-incorporated CeO2 nanocomposites for photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2023, 49, 3539–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Tan, J. High Resolution XPS Quantitative Study on Surface Elements and Chemical States of Novel Carbon Materials. Chemistry 2023, 86, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Nolan, M.; Detavernier, C. A step toward correct interpretation of XPS results in metal oxides: A case study aided by first-principles method in ZnO. J. Chem. Phys. 2023, 159, 34702–34713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumayor, M.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Lopez-Anton, M.A.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Mercury compounds characterization by thermal desorption. Talanta 2013, 114, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumayor, M.; Gallego, J.R.; Rodríguez-Valdés, E.; Díaz-Somoano, M. An assessment of the environmental fate of mercury species in highly polluted brownfields by means of thermal desorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 325, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Groups | Gas Conditions | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| I | N2 | 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210 |
| II | N2 + 5% O2 | 150 |
| III | N2 + 2000 ppm SO2 | 150 |
| IV | N2 + 5% O2 + 2000 ppm SO2 | 150 |
| V | II–IV + N2 | 50–600, 10 °C/min |
| Raw Material Source | Means of Treatment | Adsorption Efficiency | Adsorption Capacity (μg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| commercial cokes from Shanxi Xinhua Chemical Co., Ltd., Taiyuan, China | Separation and washing | 98% | 742.2 | This work |
| Zhundong lignite | Separation and purification | 91% | 30.72 | [12] |
| commercial cokes from Inner Mongolia Kexing Carbon Industry Co., Ltd., Hohhot, China | Mn-Ce impregnation | 94.87% | No data | [13] |
| commercial cokes from Inner Mongolia Taixi Group Xingtai Coal Chemistry Co., Ltd., Alxa, China | Cu impregnation | >90% | No data | [14] |
| commercial cokes from Gongyi Zhongya water purification materials Co., Ltd., Gongyi, China | Co-Ce impregnation | 71.07% | No data | [15] |
| Samples | Specific Surface Areas (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh coke | 231.45 | 0.055 | 3.43 |
| Used coke N2 | 231.46 | 0.054 | 3.26 |
| Used coke N2 + 2000 ppm SO2 | 213.69 | 0.052 | 3.28 |
| Used coke N2 + 5% O2 + 2000 ppm SO2 | 209.41 | 0.051 | 3.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yue, T. Application Study on the Activated Coke for Mercury Adsorption in the Nonferrous Smelting Industry. Sustainability 2024, 16, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010421
Zheng Y, Li G, Jiang J, Zhang L, Yue T. Application Study on the Activated Coke for Mercury Adsorption in the Nonferrous Smelting Industry. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010421
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yang, Guoliang Li, Jiayan Jiang, Lin Zhang, and Tao Yue. 2024. "Application Study on the Activated Coke for Mercury Adsorption in the Nonferrous Smelting Industry" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010421
APA StyleZheng, Y., Li, G., Jiang, J., Zhang, L., & Yue, T. (2024). Application Study on the Activated Coke for Mercury Adsorption in the Nonferrous Smelting Industry. Sustainability, 16(1), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010421







