Identification of Natural Nearly or Nanoscale Particles in Bituminous Coal: An Important Form of Elements in Coal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
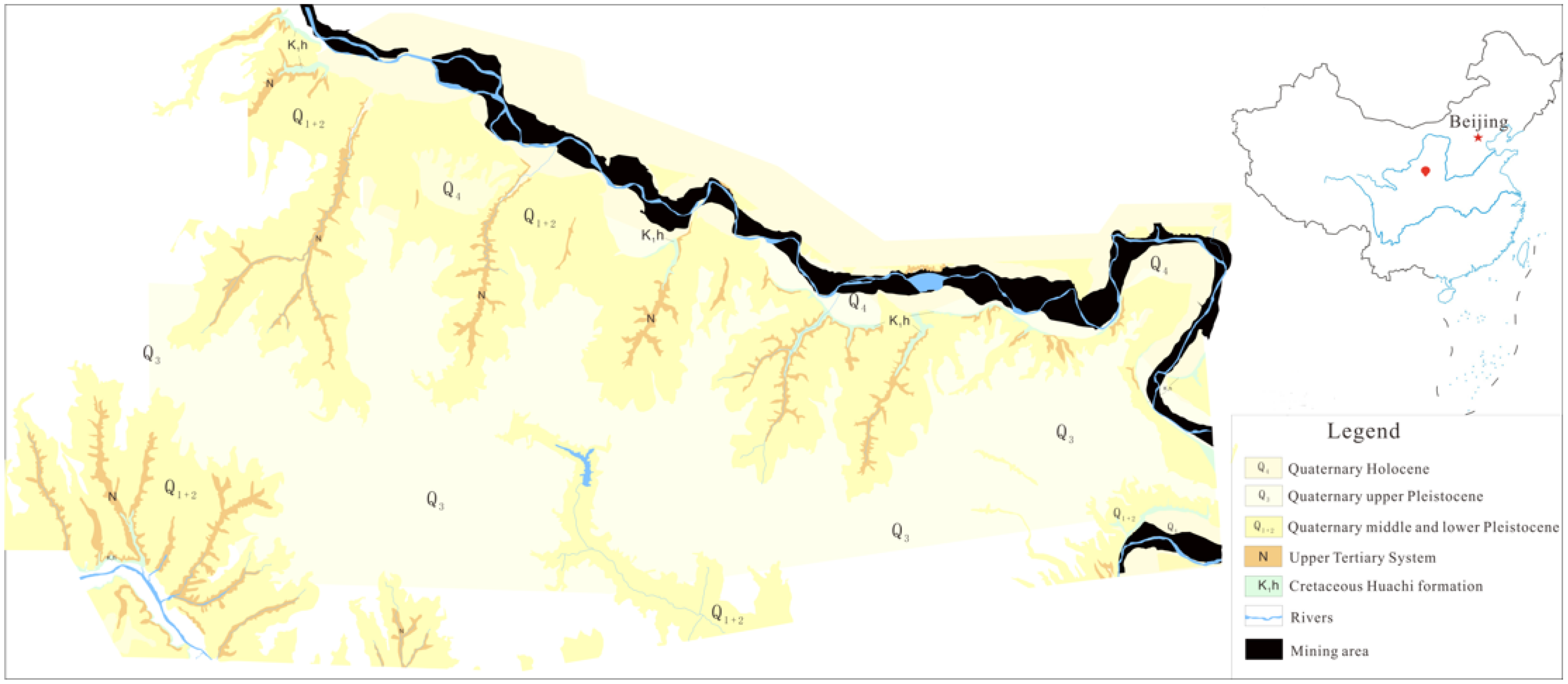
2.1. Sampling Location and Geological Background
2.2. Analytical Methods
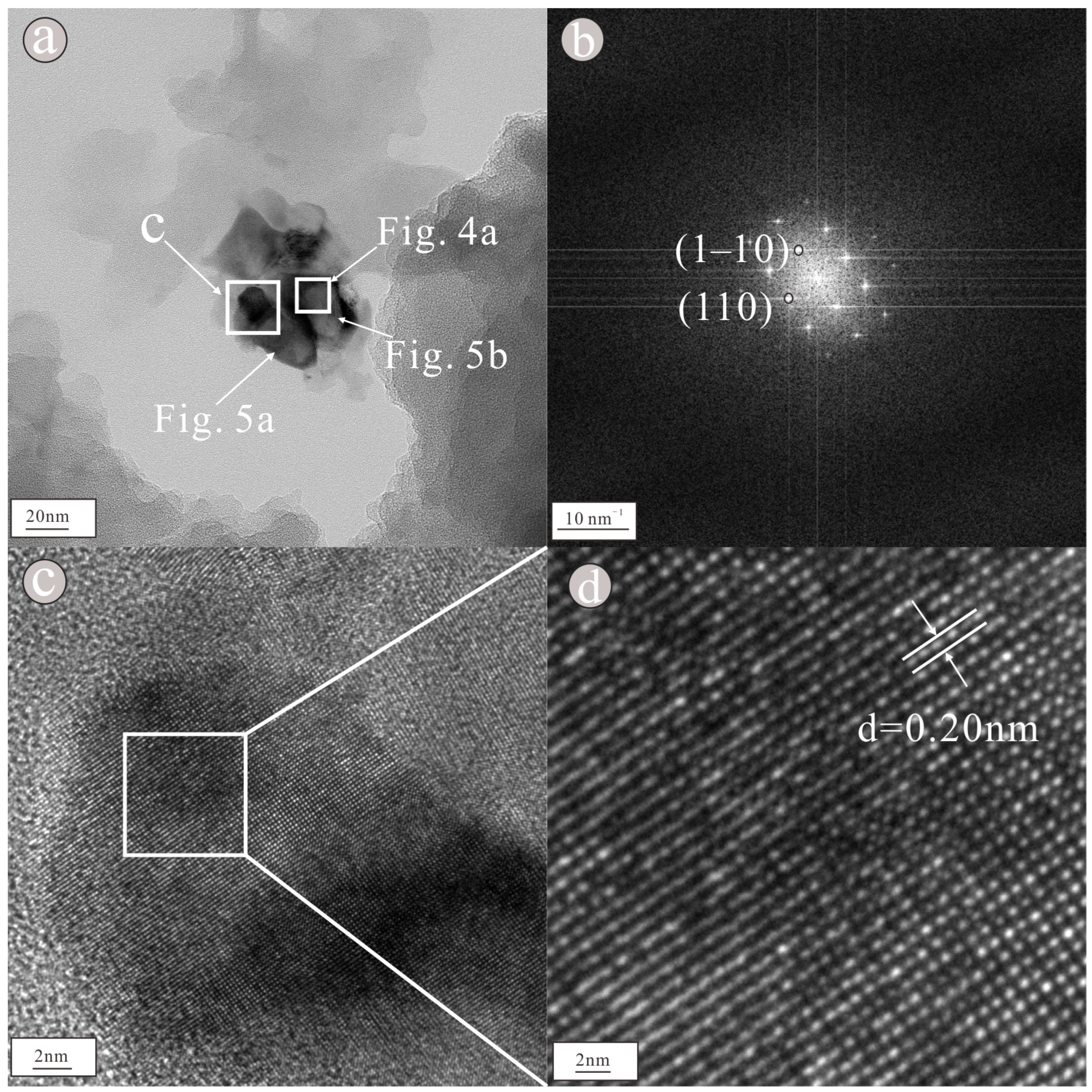
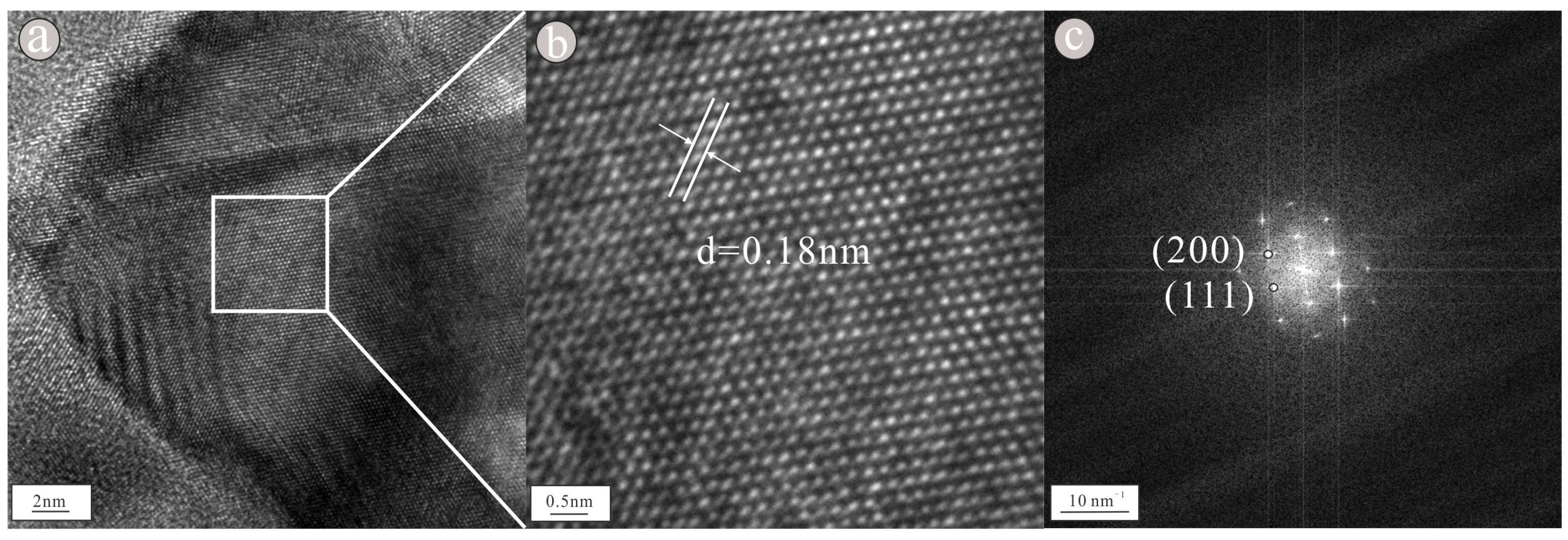
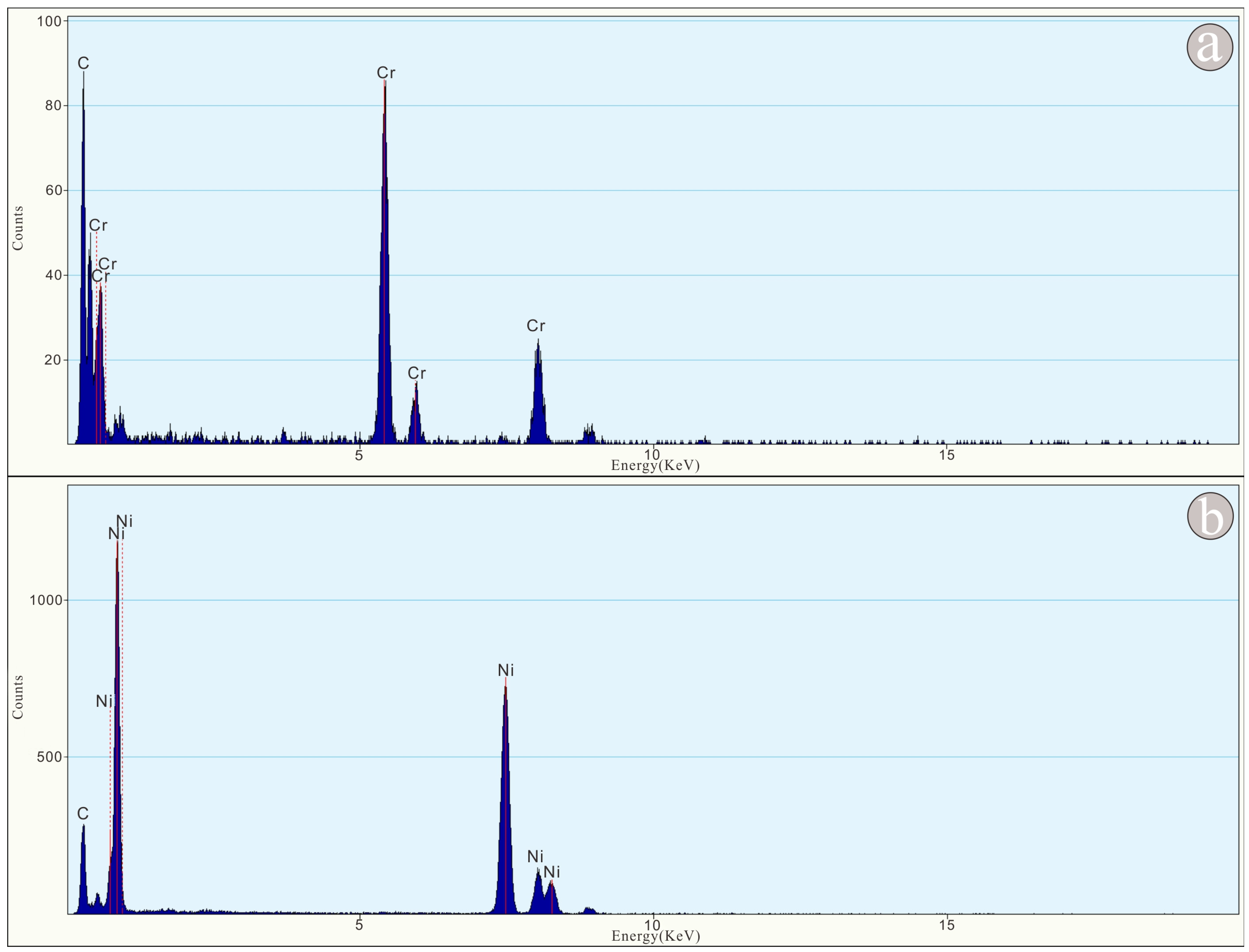
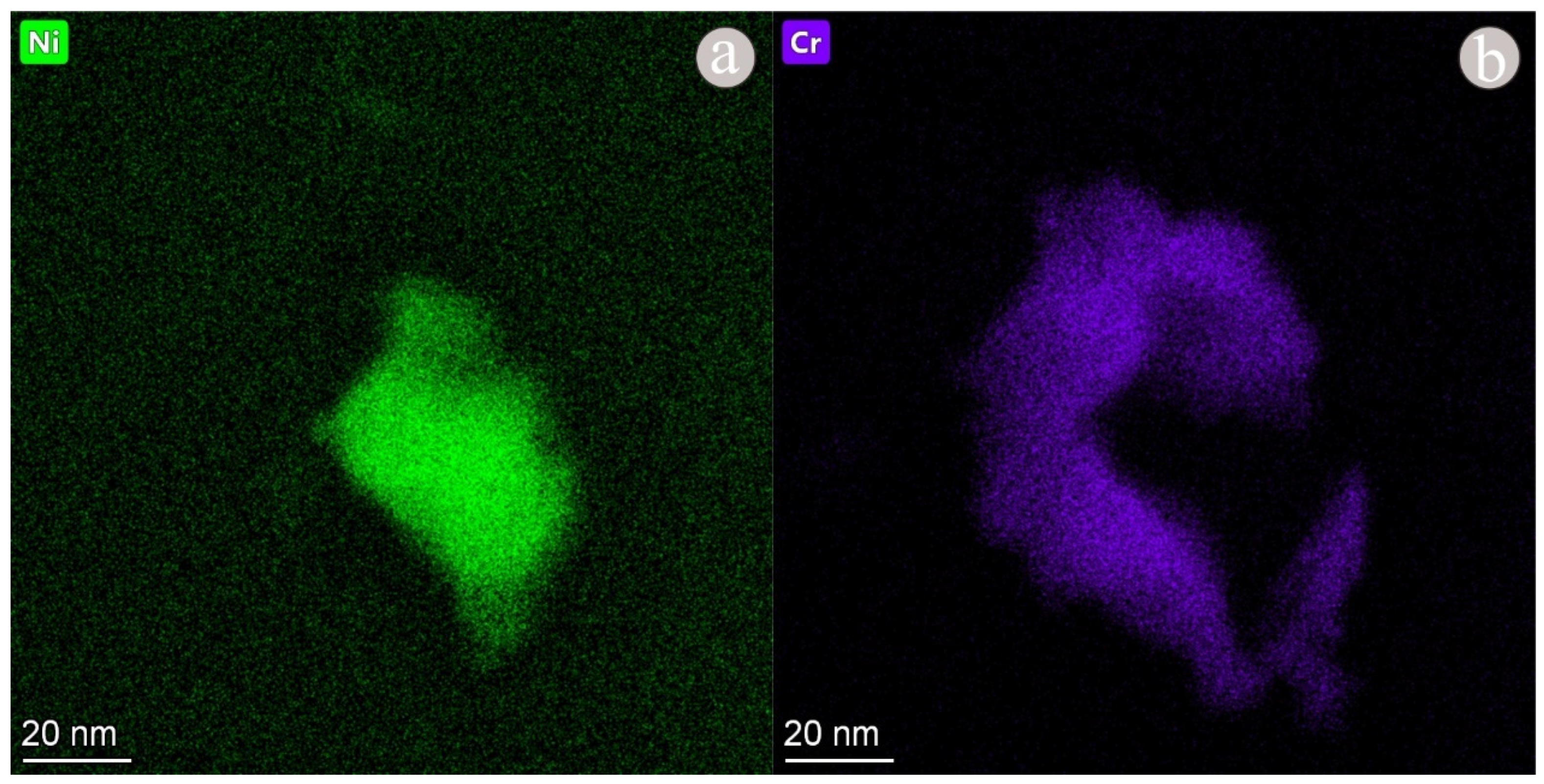
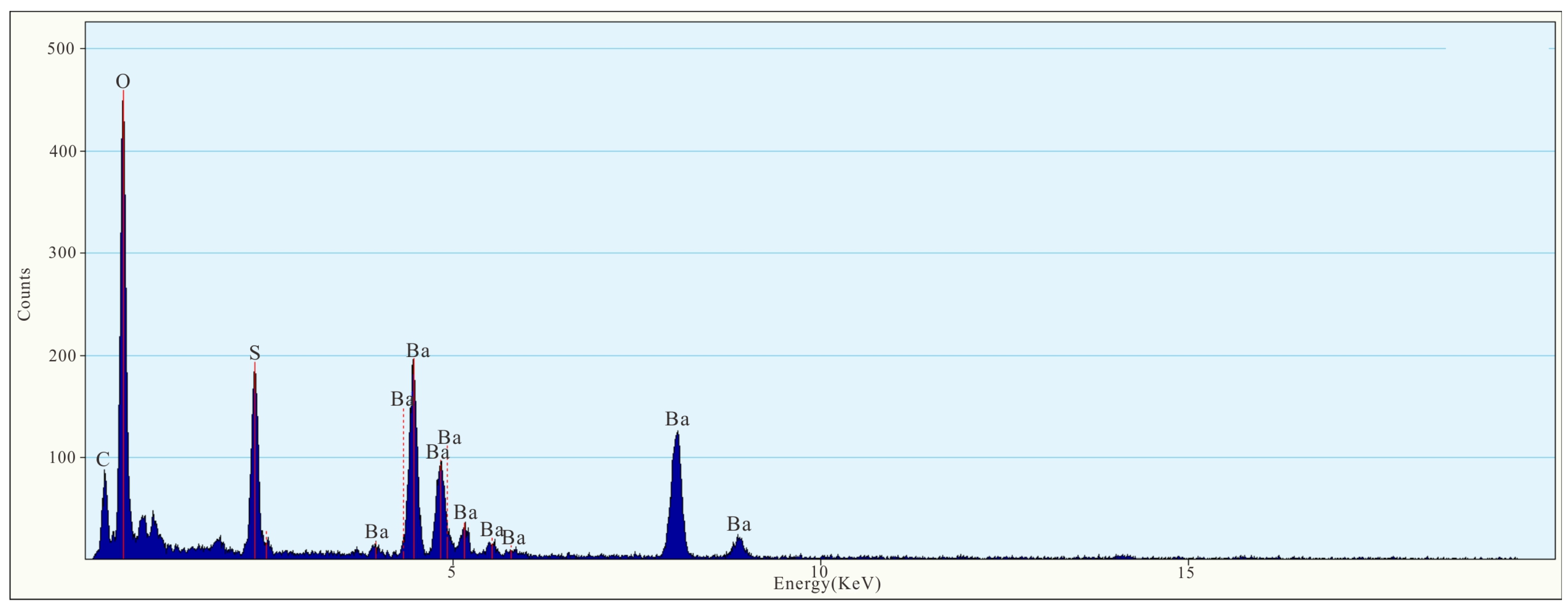
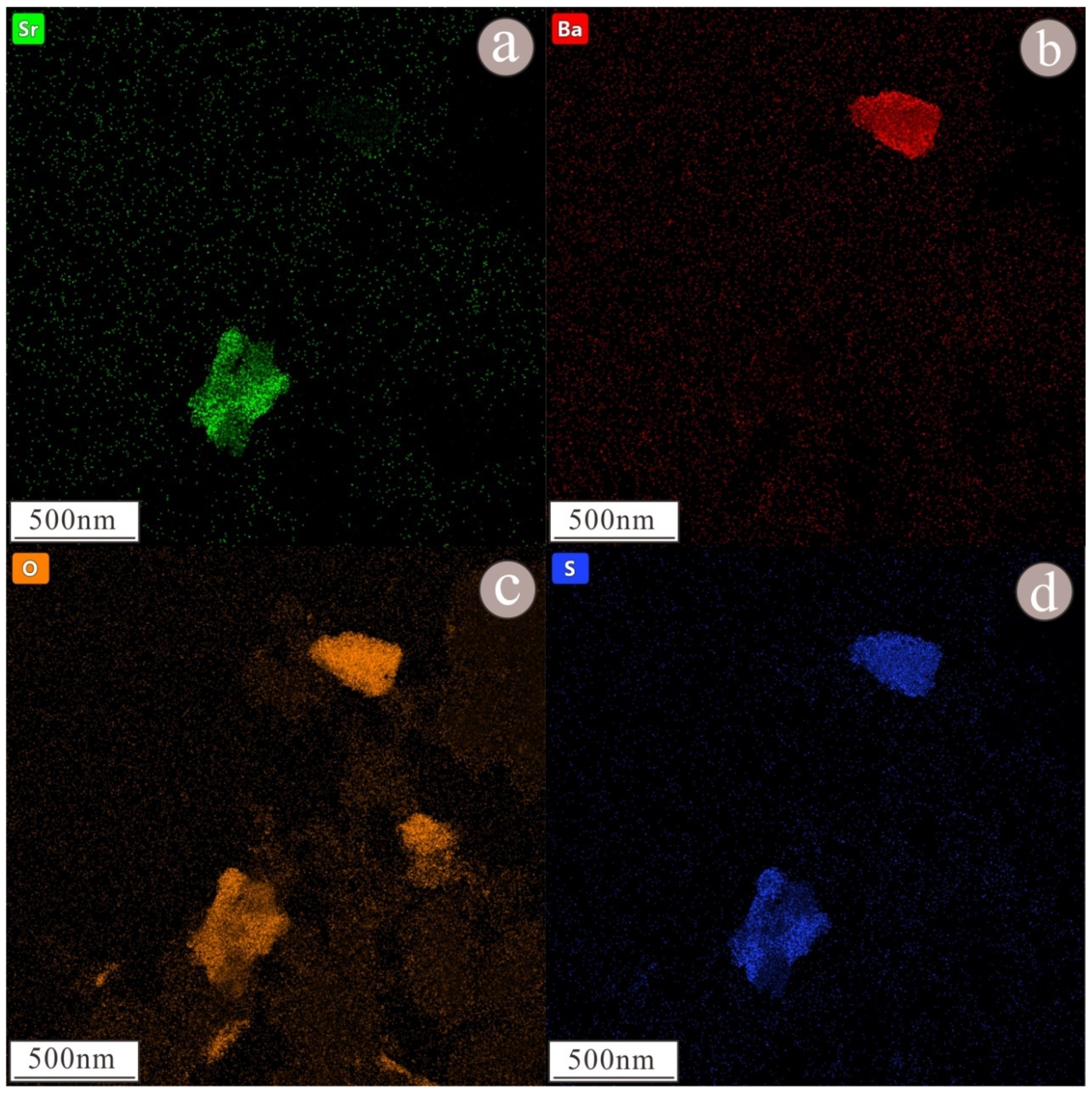
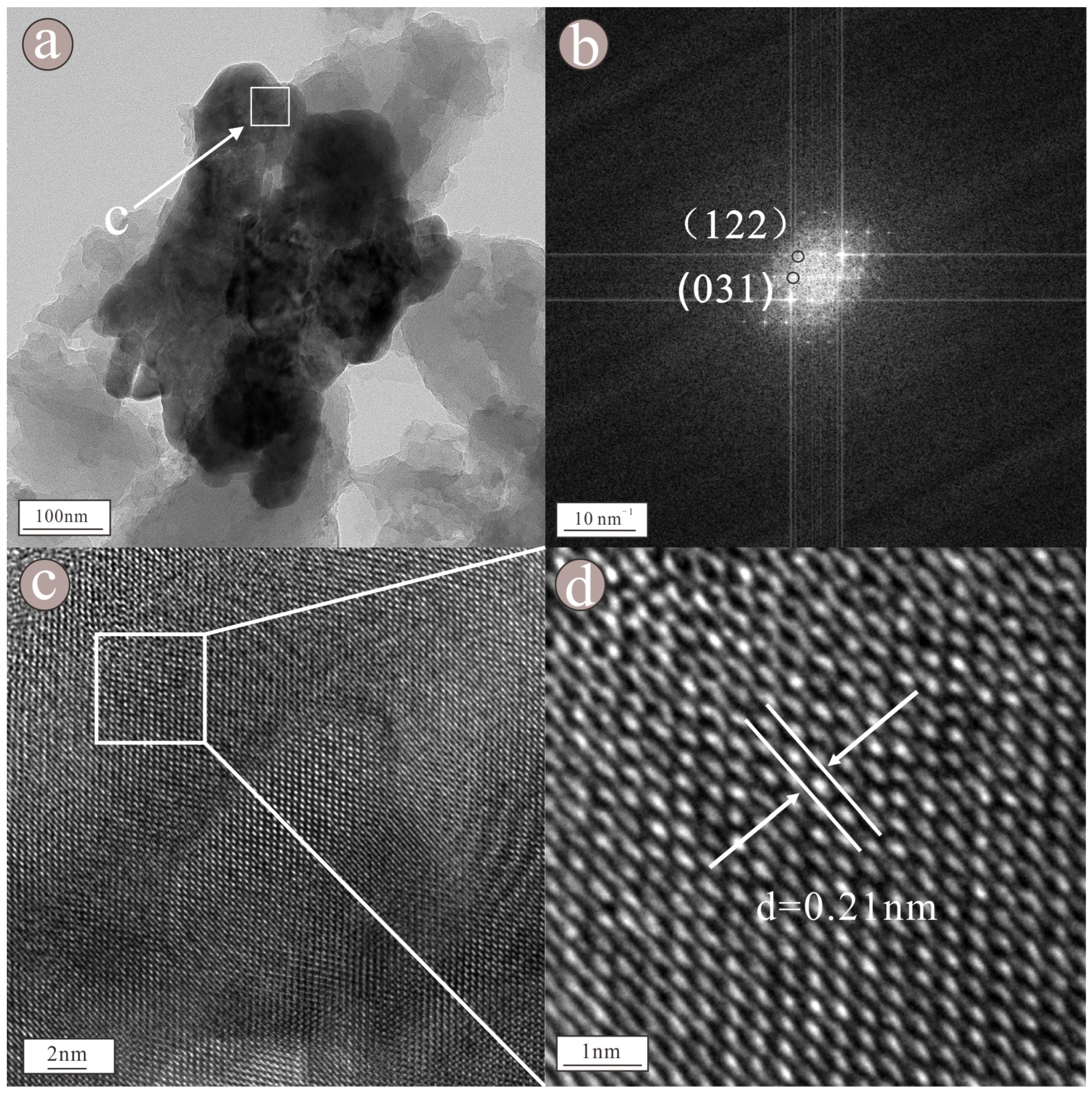
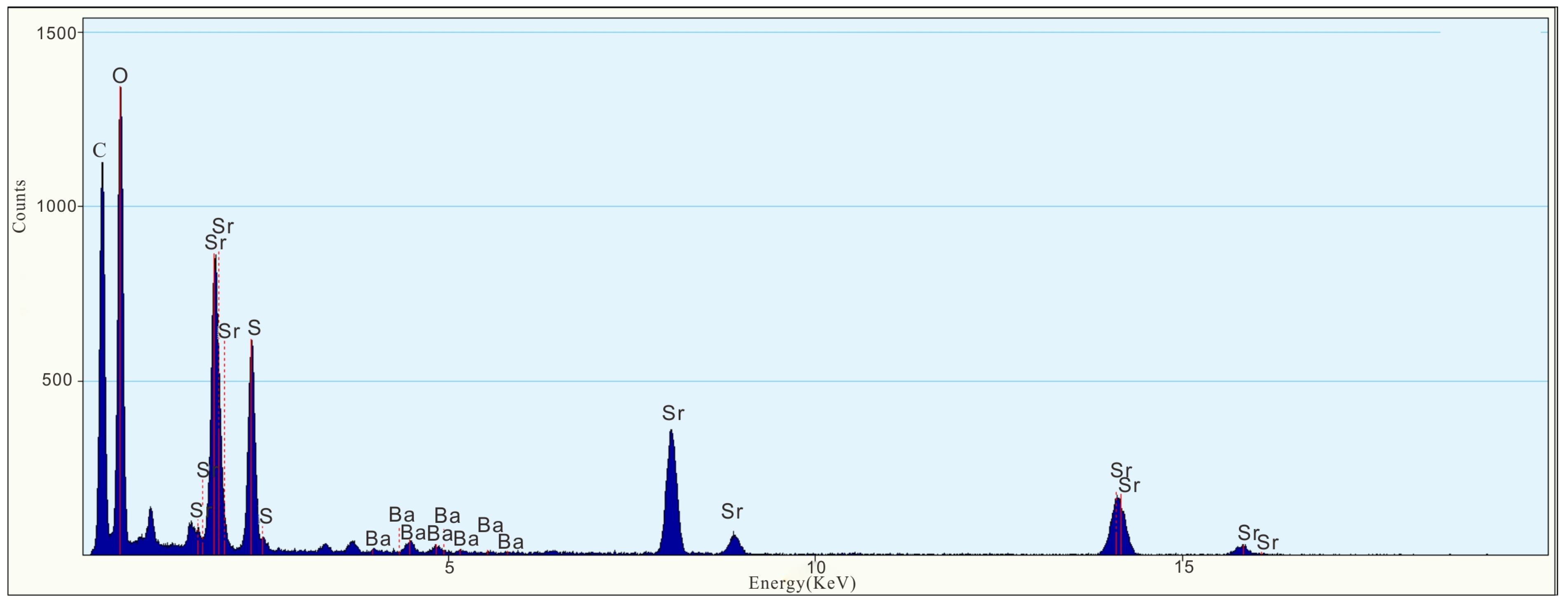
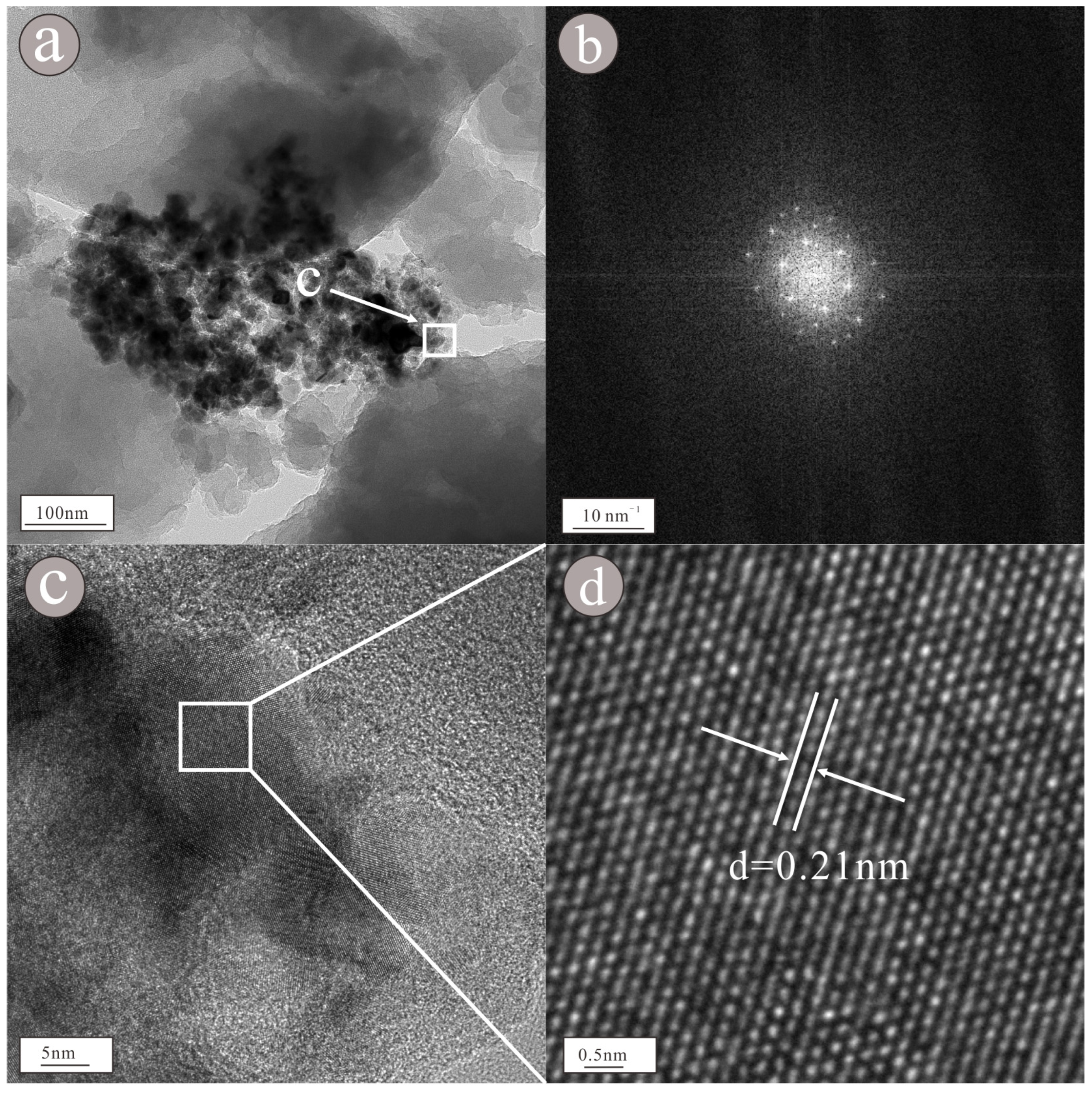
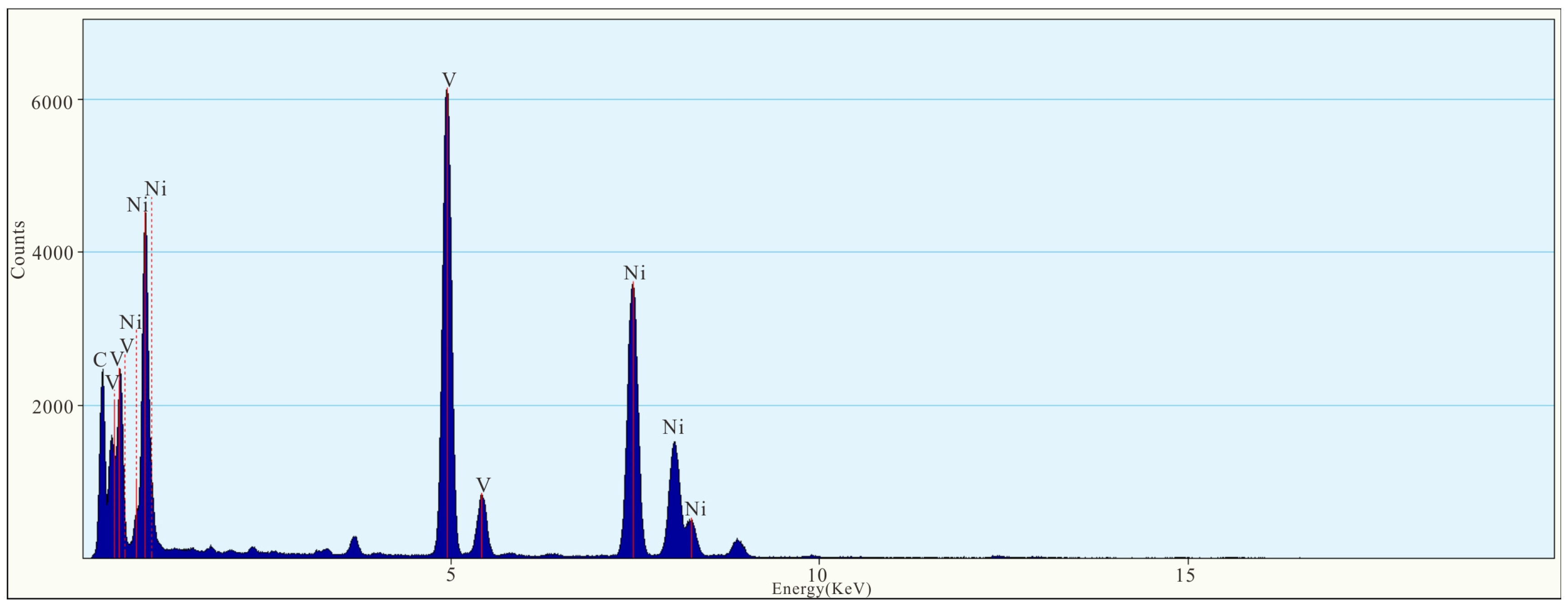
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. A New Form of Elements in Coal
4.2. The Potential Harm of Nanoparticles in Coal to Human Health
4.3. Important Potential Sources of Nanoparticles during Coal Combustion
| Nanoparticles from Coal Combustion | Nanoparticles Occurred in Raw Coal | |
|---|---|---|
| Elemental composition | Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ba, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Sr, Ca, Si, S etc. [37,38]. | Sr, Ba, S, Ni, S, Cr etc. |
| Morphological characteristics | Spherical or single diamond particles and Nanoparticle aggregates [39]. | Spherical or single diamond particles and Nanoparticle aggregates |
| The size of granule | Spherical or single diamond particles: 20–50 nm Nanoparticle aggregates: <500 nm [39]. | Spherical or single diamond particles: 40–70 nm Nanoparticle aggregates: 200–500 nm |
5. Conclusions and Prospection
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, H. Analysis on the Present Situation and Development Prospect of Coal Chemical Industry. Mod. Chem. Res. 2020, 17, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.L.; Wu, T.S.; Tang, M. Research on advance of health effects of nanoparticles on air pollution in China. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, S.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Ali, A.Y.S.; Musarrat, J. Characterization of coal fly ash nanoparticles and induced oxidative DNA damage in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Hower, J.; Schindler, M.; Winkler, C.; Brandt, J.; Giulio, R.D.; Ge, J.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y. Discovery and ramifications of incidental Magnéli phase generation and release from industrial coal-burning. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Liu, Y.J.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y.C. In Vitro Toxicity of Naturally Occurring Silica Nanoparticles in C1 Coal in Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Chin. J. Lung Cancer 2012, 15, 561–568. [Google Scholar]
- Lengke, M.; Southam, G. Bioaccumulation of gold by sulfate-reducing bacteria cultured in the presence of gold (I)-thiosulfate complex. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3646–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenik, C.S.; Utsunomiya, S.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Wang, L.; Ewing, R.C. “Invisible” gold revealed: Direct imaging of gold nanoparticles in a Carlin-type deposit. Am. Miner. 2004, 89, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lähde, A.; Gudmundsdottir, S.S.; Joutsensaari, J.; Tapperd, U.; Ruusunen, J.; Ihalainen, M.; Karhunen, T.; Torvela, T.; Jokiniemi, J.; Järvinen, K.; et al. In vitro evaluation of pulmonary deposition of airborne volcanic ash. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, R.M.; Noble, R.R.P.; Hitchen, G.J.; Hart, R.; Reddy, S.M.; Saunders, M.; Clode, P.; Vaughan, D.; Lowe, J.; Gray, D.J.; et al. Naturally occurring gold nanoparticles and nanoplates. Geology 2008, 36, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.; Masood, M.I.; Nasim, M.J.; Sarfraz, M.; Jacob, C. Natural nanoparticles: A particular matter inspired by nature. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Dewers, T.; Reches, Z.; Brune, J. Particle size and energetics of gouge from earthquake rupture zones. Nature 2005, 434, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Cao, J. Occurrence and significance of natural ore-related Ag nanoparticles in groundwater systems. Chem. Geol. 2019, 515, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hower, J.C.; Graham, U.M.; Dozier, A.; Tseng, M.T.; Khatri, R.A. Association of the sites of heavy metals with nanoscale carbon in a Kentucky electrostatic precipitator fly ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8471–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.; Flores, D.; Ward, C.R.; Silva, L.F. Identification of nanominerals and nanoparticles in burning coal waste piles from Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6032–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.F.; da Boit, K.M. Nanominerals and nanoparticles in feed coal and bottom ash: Implications for human health effects. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 174, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.G. Study on Controlling Effect of Sedimentary Microfacies to Rock Burst in Gaojiapu Coal Mine; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L. Study on the Law of Sandstone Sedimentation Control in Luohe Group in Gaojiabao Coal Mine; Xi’an University of Science and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.F.; Ren, D.Y.; Tang, Y.G. Modes of occurrence of major elements in coal and their study significance. Coal Geol. Explor. 2005, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.H. Study on the Mechanism of Distributions and Occurrences of Hazardous Minor and Trace Elements in Coal and Leaching Experiments of Coal Combustion Residues; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev, S.V.; Eskenazy, G.M.; Vassileva, C.G. Contents, modes of occurrence and origin of chlorine and bromine in coal. Fuel 2000, 79, 903–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Fundamental Research on Propagation Law of Ultra-Wideband Radar Wave in Coal and Localiztion; Xi’an University of Science and Technology: Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.H. The Coal Quality and Its Controlling Factors in the Main Coalfields of Junggar and Yili Basins, Northern Xinjiang Province; China University of Geosciences: Wuhan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.W. The Dynamic Differentiation Characteristics and Mechanisms of Stress-Sensitive Elements and Minerals in Tectonically Deformed Coals; China University of Mining and Technology: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.F. Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Trace Elements in Coals from the Taiping Coal Mine in Panzhihua, Sichuan Province; Anhui University of Science and Technology: Huainan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.M. Pollution and harm of chromium. Hanzhong Sci. Technol. 2011, 6, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.Y.; Zhao, F.H.; Dai, S.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Luo, K.L. Trace Element Geochemistry of Coal; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.H.; Huang, Q.C.; Su, X.F. Review on the Toxicological Effect and the Mechanism of Nickel to the Human Health. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2008, 33, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J. Occupational hazards of vanadium compounds. Ind. Health Occup. Dis. 1998, 24, 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, K.; Stone, V.; Borm, P.J.A.; Jimenez, L.A. William MacNee, Oxidative stress and calcium signaling in the adverse effects of environmental particles (PM10). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwinn, M.R.; Vallyathan, V. Nanoparticles: Health effects—Pros and cons. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffin, R.; Mills, N.L.; Donaldson, K. Nanoparticles—A thoracic toxicology perspective. Yonsei Med. J. 2007, 48, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Abou-Tarboush, F.M.; Azam, A.; Musarrat, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in human amnion epithelial (WISH) cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, M.I.; O’Connor, S.; Dick, C.A.J.; Miller, C.A.; Linak, W.P. Differential pulmonary inflammation and in vitro cytotoxicity of size-fractionated fly ash particles from pulverized coal combustion. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G.; Oberdorster, E.; Oberdorster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Persp. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.J. Properties and Control of Fine Particulate Matter During the Combustion of High Ash Fusion Temperature Coal; Anhui University of Science and Technology: Huainan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Y. Distribution and Environmental Impact of Metal Containing Nanoparticles in Coal Fly Ashes from Coal Fired Power Plants; East China Normal University: Shanghai, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Tou, F.; Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Vast emission of Fe-and Ti-containing nanoparticles from representative coal-fired power plants in China and environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.F.O.; Pinto, D.; Lima, B.D. Implications of iron nanoparticles in spontaneous coal combustion and the effects on climatic variables. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Xu, M.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, K.; Wen, C.; Li, L. Physicochemical properties and potential health effects of nanoparticles from pulverized coal combustion. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Zuo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Tao, D.; Chen, Z.; Tao, G.; Wang, K. Identification of Natural Nearly or Nanoscale Particles in Bituminous Coal: An Important Form of Elements in Coal. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076276
Zhang P, Lu J, Zuo L, Wang Y, Liu R, Tao D, Chen Z, Tao G, Wang K. Identification of Natural Nearly or Nanoscale Particles in Bituminous Coal: An Important Form of Elements in Coal. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):6276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076276
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Jing Lu, Lei Zuo, Yaqin Wang, Rui Liu, Dongping Tao, Zhaoying Chen, Gang Tao, and Kun Wang. 2023. "Identification of Natural Nearly or Nanoscale Particles in Bituminous Coal: An Important Form of Elements in Coal" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 6276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076276
APA StyleZhang, P., Lu, J., Zuo, L., Wang, Y., Liu, R., Tao, D., Chen, Z., Tao, G., & Wang, K. (2023). Identification of Natural Nearly or Nanoscale Particles in Bituminous Coal: An Important Form of Elements in Coal. Sustainability, 15(7), 6276. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076276







