Green Loans in Bank Portfolio: Financial and Marketing Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Sustainable Development Based on Green Finance
2.2. The Green Loans Concept
2.3. The Relationship between Green Loans and Bank Profitability
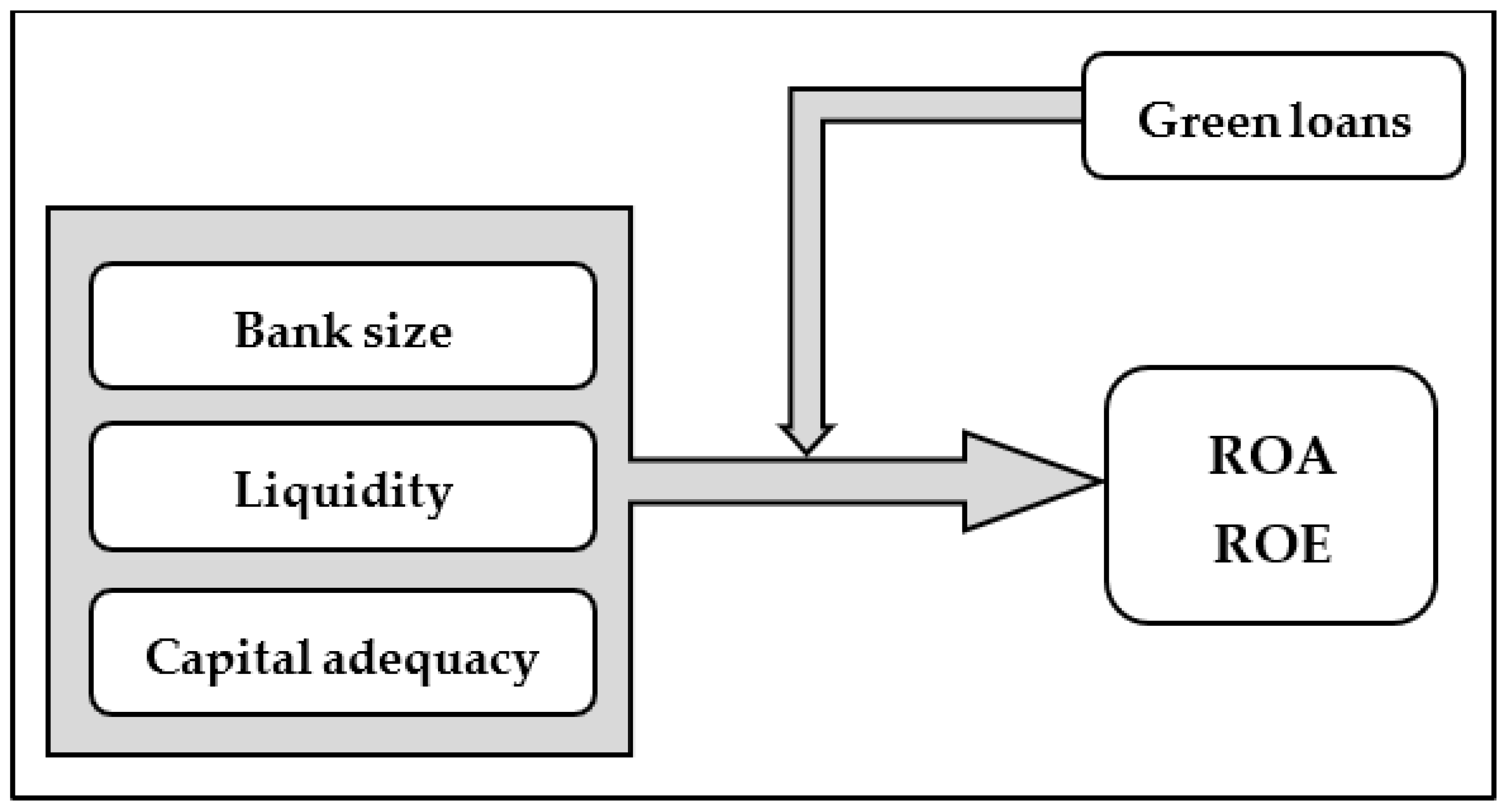
2.4. Conceptual Model and Hypotheses
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical and Methodological Implications
5.2. Practical and Managerial Implications
5.3. Marketing Implications
5.4. Limitations of the Conducted Research
5.5. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Siddik, A.B.; Zheng, G.-W.; Masukujjaman, M.; Bekhzod, S. The Effect of Green Banking Practices on Banks’ Environmental Performance and Green Financing: An Empirical Study. Energies 2022, 15, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Caldecott, B.; Hoepner, A.G.F.; Wang, Y. Bank green lending and credit risk: An empirical analysis of China’s Green Credit Policy. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbanee, F.K.; Haque, M.M.; Banik, S.; Islam, M.M. Managing engagement in an emerging economy service. J. Serv. Theory Pract. 2019, 29, 610–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Lee, C.-C.; Zhou, F. Green credit policy, credit allocation efficiency and upgrade of energy-intensive enterprises. Energy Econ. 2021, 94, 105099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Deng, X.; Wu, R. Comparing the Influence of Green Credit on Commercial Bank Profitability in China and Abroad: Empirical Test Based on a Dynamic Panel System Using GMM. Int. J. Financ. Stud. 2019, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liu, R.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Xia, Y. Can green financial development promote renewable energy investment efficiency? A consideration of bank credit. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Bai, Y.; Qiao, G.; Popp, J.; Oláh, J. Financial inclusion technological Innovation and Environmental Quality Analyzing the Role of Green Openness. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 80, 851263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasterolo, I.; Zheng, J.; Battiston, S. Climate Transition Risk and Development Finance: A Carbon Risk Assessment of China’s Overseas Energy Portfolios. China World Econ. 2018, 26, 116–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilliers, E.J.; Diemont, E.; Stobbelaar, D.J.; Timmermans, W. Sustainable green urban planning. The Geen Credit Tool. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2010, 3, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.; Kamran, M.; Djajadikerta, H.G.; Sarker, T. Can Banks Sustain the Growth in Renewable Energy Supply? An International Evidence. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 2021, 35, 20–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.D.; Rahman, S.M.; Mamoon, M. Green banking: The case of commercial banking sector in Oman. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 2681–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, J.; Permatasari, P.; Sharma, U. Exploring sustainability and green banking disclosures: A study of banking sector. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 24, 11153–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tripe, D. Green credit policy and corporate access to bank loans in China: The role of environmental disclosure and green innovation. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2021, 77, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, V.; Laktionova, O.; Atstaja, D.; Grasis, J.; Lomachynska, I.; Shchur, R. Green Financial Instruments of Cleaner Production Technologies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Q. The local-neighborhood effect of green credit on green economy: A spatial econometric investigation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65776–65790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Zhu, Z.; Kirkulak-Uludag, B.; Zhu, Y. The determinants of green credit and its impact on the performance of Chinese banks. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 28, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yu, S.; Zhou, G. Does green credit improve the core competence of commercial banks? Based on quasi-natural experiments in China. Energy Econ. 2021, 100, 105335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, M.; Yang, C. Green Credit, Green Stimulus, Green Revolution? China’s Mobilization of Banks for Environmental Cleancup. J. Environ. Dev. 2010, 19, 119–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Bi, J. Tracking the implementation of green credit policy in China: Top-down perspective and bottom-up reform. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, T.; Lin, J.-H. Bank Interest Margin and Green Lending Policy under Sunflower Management. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Jiang, S. Green credit and high-quality sustainable development of banks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80871–80881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bank of Serbia. Available online: https://www.nbs.rs/en/finansijske-institucije/banke/izvestaji-i-analize/ (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Al-Homaidi, E.A.; Tabash, M.I.; Farhan, N.H.; Almaqtari, F.A. The determinants of liquidity of Indian listed commercial banks: A panel data approach. Cogent Econ. Financ. 2019, 7, 1616521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, Y. Macroeconomic, Institutional and Bank-Specific Determinants of Non-Performing Loans in Emerging Market Economies: A Dynamic Panel Regression Analysis. J. Cent. Bank. Theory Pract. 2019, 8, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akomea-Frimpong, I.; Adeabah, D.; Ofosu, D.; Tenakwah, E.J. A review of studies on green finance of banks, research gaps and future directions. J. Sustain. Financ. Investig. 2021, 12, 1241–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, K. Green Loans and Green Innovations: Evidence from China’s Equator Principles Banks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caby, J.; Ziane, Y.; Lamarque, E. The impact of climate change management on banks profitability. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 142, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, T.; Kassim, S. Exploring green banking performance of Islamic banks vs conventional banks in Bangladesh based on Maqasid Shariah framework. J. Islam. Mark. 2020, 11, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairunnessa, F.; Vazquez-Brust, D.A.; Yakovleva, N. A Review of the Recent Developments of Green Banking in Bangladesh. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Choubey, A. Green banking initiatives: A qualitative study on Indian banking sector. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Rabbani, M.R.; Ahmad, N.; Sial, M.S.; Cheng, G.; Zia-Ud-Din, M.; Fu, Q. CSR, Co-Creation and Green Consumer Loyalty: Are Green Banking Initiatives Important? A Moderated Mediation Approach from an Emerging Economy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, J.D. Transition towards green banking: Role of financial regulators and financial institutions. Asian J. Sustain. Soc. Responsib. 2020, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Yoshino, N. Sustainable Solutions for Green Financing and Investment in Renewable Energy Projects. Energies 2020, 13, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tara, K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, R. Green Banking for Environmental Management: A Paradigm Shift. Curr. World Environ. 2015, 10, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Li, B.; Song, D.; Chen, X. Green Credit Financing versus Trade Credit Financing in a Supply Chain with Carbon Emission Limits. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 292, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelyazkova, V.; Kitanov, Y. Green banking—Definition, scope and proposed business model. Ecol. Saf. 2015, 9, 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist, D.; Yu, J.; Zhong, R. The Limits of Green Finance: A Survey of Literature in the Context of Green Bonds and Green Loans. Sustainability 2021, 13, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBRD. Green Economy Financing Facility. European Bank for Reconstruction and Development. Available online: https://ebrdgeff.com/ (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Scholtens, B.; Dam, L. Banking on the equator: Are banks that adopted the equator principles different from non-adopters. World Dev. 2007, 35, 1307–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Xia, Y.; Fan, Y.; Lin, S.-M.; Wu, J. Assessment of a green credit policy aimed at energy-intensive industries in China based on a financial CGE model. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, W. Will the implementation of green credit affect the profitability of commercial banks? Financ. Regul. Res. 2016, 7, 92–110. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W. Turning coporate environmental ethics into firm performance: The role of green marketing programs. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2019, 28, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Greobey, S.; Weber, O.; Lin, H. The Impact of Green Lending on Credit Risk in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasari, T.; Surwanti, A.; Pribadi, F. Implementation of Green Banking and Financial Performance on Commercial Banks in Indonesia. In Recent Developments in Asian Economics International Symposia in Economic Theory and Econometrics (International Symposia in Economic Theory and Econometrics); Barnett, W.A., Sergi, B.S., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2021; Volume 28, pp. 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, M.; Lagasio, V. Environmental, social, and governance and company profitability: Are financial intermediaries different? Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangi, F.; Meles, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Daniele, L.M. Sustainable development and corporate governance in the financial system: Are environmentally friendly banks less risky? Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2019, 26, 526–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ye, T. How does green credit affect the financial performance of commercial banks? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, B.L.; Previtali, D.; Sampagnaro, G.; Verdoliva, V.; Vigne, S. Syndicated green lending and lead bank performance. J. Int. Financ. Manag. Account. 2022, 33, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, A.; Sharma, M. Green banking: The case of the commercial banking sector in Delhi NCR. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2021, 65, 1975–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M. Green credit, green reputation, and corporate financial performance: Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2401–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X. Research on the Influence of Green Credit on the Profitability of Chinese Commercial Banks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Informatization in Education, Management and Business, Suzhou, China, 5–6 June 2021; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ranning, Z. Research on the Impact of Green Credit on the Profitability of Commercial Banks. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Education, Management and Social Science, Suzhou, China, 25–26 June 2022; pp. 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Almaqtari, F.A.; Al-Homaidi, E.A.; Tabash, M.I.; Farhan, N.H. The determinants of profitability of Indian commercial banks. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2019, 24, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.T.M.; Guerreiro, J.P.S.M. Internal and external determinants of banks’ profitability: The Portuguese case. J. Econ. Stud. 2016, 43, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampara, K.; Giannopoulos, M.; Koufopolulos, D.N. Macroeconomic and Industry-Specific Determinants of Greek Bank Profitability. Int. J. Bus. Econ. Sci. Appl. Res. 2017, 10, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, K.P.; Pathneja, S. Effect of bank-specific and governance-specific variables on the productivity and profitability of banks. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2016, 65, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.K. An empirical analysis of macroeconomic and bank-specific factors affecting liquidity of Indian banks. Future Bus. J. 2016, 2, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasiouras, F.; Kosmidou, K. Factors influencing the profitability of domestic and foreign commercial banks in the European Union. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2007, 21, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, A.; Wanzenried, D. The determinants of commercial banking profitability in low-, middle-, and high-income countries. Q. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2014, 54, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salike, N.; Ao, B. Determinants of bank’s profitability: Role of poor asset quality in Asia. China Financ. Rev. Int. 2018, 8, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, A.; Dobromirov, D. The determinants of Serbian banking industry profitability. Econ. Res.-Ekon. Istraživanja 2016, 29, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidanoski, F.; Choudhry, M.; Davidović, M.; Sergi, B.S. What does affect profitability of banks in Croatia? Compet. Rev. 2018, 28, 338–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asteriou, D.; Stephen, H. Applied Econometrics, 3rd ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harbi, A. The determinants of conventional banks profitability in developing and underdeveloped OIC countries. J. Econ. Financ. Adm. Sci. 2019, 24, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Baloch, Q.B.; Khan, A.W. Factors affecting banks’ profitability in Pakistan. Int. J. Bus. Stud. Rev. 2017, 2, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.S.; Shin, H.Y. Loan-to-Deposit Ratio vs. Basel III Net Stable Funding Ratio: Case in Korean Banks. Korea World Econ. 2017, 18, 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Lymperopoulos, C.; Chaniotakis, I.E.; Soureli, M. A model of green bank marketing. J. Financ. Serv. Mark. 2012, 17, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R. Investment in environmental governance and asset quality of banks: Analysis from the perspective of green credit. Financ. Forum 2016, 11, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Batae, O.M.; Dragomir, V.D.; Feleaga, L. The relationship between environmental, social, and financial performance in the banking sector: An European Study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, P.M.P.; Fernando, K.S.D. Study of Green Banking Practices in the Sri Lankan Context: A Critical Review. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Conference on Economics & Finance, Singapore, 27–28 July 2017; pp. 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzert, N. The impact of corporate reputation and reputation damaging events on financial performance: Empirical evidence from the literature. Eur. Manag. J. 2015, 33, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; García, J.A.; Revilla, A.J. Antecedents and consequences of bank reputation: A comparison of the United Kingdom and Spain. Int. Mark. Rev. 2016, 33, 781–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramburu, I.A.; Pescador, I.G. The effects of corporate social responsibility on customer loyalty: The mediating effect of reputation in cooperative banks versus commercial banks in the Basque Country. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 154, 701–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.A.A.; Hashim, F.; Amran, A. Green Banking: A road map for adoption. Int. J. Ethics Syst. 2020, 36, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufique, K.M.R. Integrating environmental values and emotion in green marketing communications inducing sustainable consumer behaviour. J. Mark. Commun. 2020, 28, 272–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, X.; Yang, S.; Siddik, A.B. Do Green Banking Activities Improve the Banks’ Environmental Performance? The Mediating Effect of Green Financing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshebami, A.S. Evaluating the relevance of green banking practices on Saudi Banks’ green image: The mediating effect of employees’ green behavior. J. Bank. Regul. 2021, 22, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Notation | Calculation |
|---|---|---|
| Dependent | ||
| Return on assets | ROA | |
| Return on equity | ROE | |
| Independent | ||
| Bank size | SIZE | Log of total assets |
| Liquidity | LDR | |
| Capital Adequacy | CA | |
| Dummy | ||
| Green loans | GL | 0—banks without green loans in bank’s portfolio, 1—banks with green loans in bank’s portfolio |
| Variables | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROA | −0.009 | 0.115 | −1.421 | 0.121 |
| ROE | −0.047 | 0.658 | −8.333 | 0.477 |
| SIZE | 17.871 | 1.342 | 14.438 | 20.316 |
| LDR | 2.41 | 1.374 | 1.11 | 11.2 |
| CA | 0.205 | 0.112 | 0.069 | 0.988 |
| Variables | VIF | 1/VIF |
|---|---|---|
| SIZE | 1.82 | 0.5507 |
| GL | 1.60 | 0.6258 |
| CA | 1.15 | 0.8724 |
| LDR | 1.13 | 0.8859 |
| Mean VIF | 1.42 |
| Variables | FT Test | Inverse Chi-Squared (p) | Inverse Normal (Z) | Inverse Logit (L) | Modified Inv. Chi-Squared (Pm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROA | 290.15 (0.000) | −9.08 (0.000) | −16.11 (0.000) | 26.24 (0.000) | |
| ROE | 231.96 (0.000) | −6.49 (0.000) | −12.15 (0.000) | 20.03 (0.000) | |
| SIZE | 171.23 (0.000) | 0.396 (0.654) | −4.41 (0.000) | 13.56 (0.000) | |
| LDR | 178.39 (0.000) | −4.36 (0.000) | −8.23 (0.000) | 14.32 (0.000) | |
| CA | 265.21 (0.000) | −4.09 (0.000) | −10.99 (0.000) | 23.58 (0.000) |
| Variables | ADF Test | 1% | 5% | 10% | KT Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROA | −38.583 (0.000) | −5.347 | −4.859 | −4.607 | −0.505 (0.011) |
| ROE | −48.310 (0.000) | −5.347 | −4.859 | −4.607 | −0.026 (0.070) |
| SIZE | −5.126 (0.000) | −5.347 | −4.859 | −4.607 | −2.185 (0.140) |
| LDR | −6.428 (0.000) | −5.347 | −4.859 | −4.607 | −2.182 (0.000) |
| CA | −10.062 (0.000) | −5.347 | −4.859 | −4.607 | −0.033 (0.030) |
| Model Specification (ROA) | Results | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Random-effects model vs Fixed-effects model | Chi2(3) = (b − B)′[(V_b − V_B)^(−1)](b − B) = 17.70 | Fixed-effects model is an appropriate |
| Prob > chi2 = 0.0005 | ||
| Model Specification (ROE) | Results | Conclusion |
| Random-effects model vs Fixed-effects model | Chi2(3) = (b − B)′[(V_b − V_B)^(−1)](b − B) = 13.11 | Fixed-effects model is an appropriate |
| Prob > chi2 = 0.0044 |
| Breusch–Pagan Lagrange Multiplier Test | ROA | ROE |
|---|---|---|
| Results | Chibar 2(01) = 0.04 | Chibar 2(01) = 0.01 |
| Prob > chibar2 = 0.4235 | Prob > chibar2 = 0.4547 |
| ROA | Coef. | Std. Err. | T | p > t | [95% Conf. Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL#c.LDR | ||||||
| 0 | −0.000342 | 0.022077 | −0.02 | 0.988 | −0.04397 | 0.043294 |
| 1 | −0.062855 | 0.014041 | −4.48 | 0.000 | −0.09061 | −0.035100 |
| Diff. | −0.062513 | 0.026164 | −2.39 | 0.018 | −0.11422 | −0.01079 |
| GL#c.SIZE | ||||||
| 0 | 0.0022474 | 0.017639 | 0.13 | 0.899 | −0.03261 | 0.037113 |
| 1 | 0.0849045 | 0.069275 | 1.23 | 0.222 | −0.05202 | 0.221832 |
| Diff. | 0.082657 | 0.071486 | 1.16 | 0.249 | −0.05864 | 0.223954 |
| GL#c.CA | ||||||
| 0 | −0.012866 | 0.146839 | −0.09 | 0.930 | −0.30310 | 0.277373 |
| 1 | 0.358793 | 0.222235 | 1.61 | 0.109 | −0.08047 | 0.798058 |
| Diff. | 0.371659 | 0.266354 | 1.40 | 0.165 | −0.15483 | 0.898150 |
| R-squared | 0.281 | |||||
| Prob > F | 0.000 | |||||
| ROE | Coef. | Std. Err. | T | p > t | [95% Conf. Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL#c.LDR | ||||||
| 0 | 0.010339 | 0.1299481 | 0.08 | 0.937 | −0.24651 | 0.267191 |
| 1 | −0.324939 | 0.0826515 | −3.93 | 0.000 | −0.48830 | −0.16157 |
| Diff. | −0.335279 | 0.1540058 | −2.18 | 0.031 | −1.78662 | 1.63014 |
| GL#c.SIZE | ||||||
| 0 | 0.0142653 | 0.1038278 | 0.14 | 0.891 | −0.19095 | 0.219488 |
| 1 | −0.460871 | 0.4077633 | −1.13 | 0.260 | −0.34510 | 1.266846 |
| Diff. | 0.4466059 | 0.4207744 | 1.06 | 0.290 | −0.38508 | 1.278298 |
| GL#c.CA | ||||||
| 0 | −0.078243 | 0.022876 | −0.09 | 0.928 | −1.78662 | 1.603014 |
| 1 | 2.356895 | 1.308105 | 1.80 | 0.074 | −0.22867 | 4.942462 |
| Diff. | 2.435138 | 1.567858 | 1.55 | 0.123 | −0.66385 | 5.534126 |
| R-squared | 0.252 | |||||
| Prob > F | 0.000 | |||||
| Moderating Effects of Green Loans When It Comes to the Influence of Bank-Specific Determinants | On ROA | On ROE |
|---|---|---|
| Bank size (SIZE) | H1.1.1 Rejected | H1.2.1 Rejected |
| Liquidity (LDR) | H1.1.2 Supported | H1.2.2 Supported |
| Capital adequacy (CA) | H1.1.3 Rejected | H1.2.3 Rejected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirovic, V.; Kalas, B.; Djokic, I.; Milicevic, N.; Djokic, N.; Djakovic, M. Green Loans in Bank Portfolio: Financial and Marketing Implications. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075914
Mirovic V, Kalas B, Djokic I, Milicevic N, Djokic N, Djakovic M. Green Loans in Bank Portfolio: Financial and Marketing Implications. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075914
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirovic, Vera, Branimir Kalas, Ines Djokic, Nikola Milicevic, Nenad Djokic, and Milos Djakovic. 2023. "Green Loans in Bank Portfolio: Financial and Marketing Implications" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075914
APA StyleMirovic, V., Kalas, B., Djokic, I., Milicevic, N., Djokic, N., & Djakovic, M. (2023). Green Loans in Bank Portfolio: Financial and Marketing Implications. Sustainability, 15(7), 5914. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075914










