Enhancing Sales of Green Agricultural Products through Live Streaming in China: What Affects Purchase Intention?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Agricultural Goods Live Streaming
1.2. Participants in Agricultural Livestream Marketing
1.3. Problem Statement
2. Theoretical Framework and Research Hypotheses
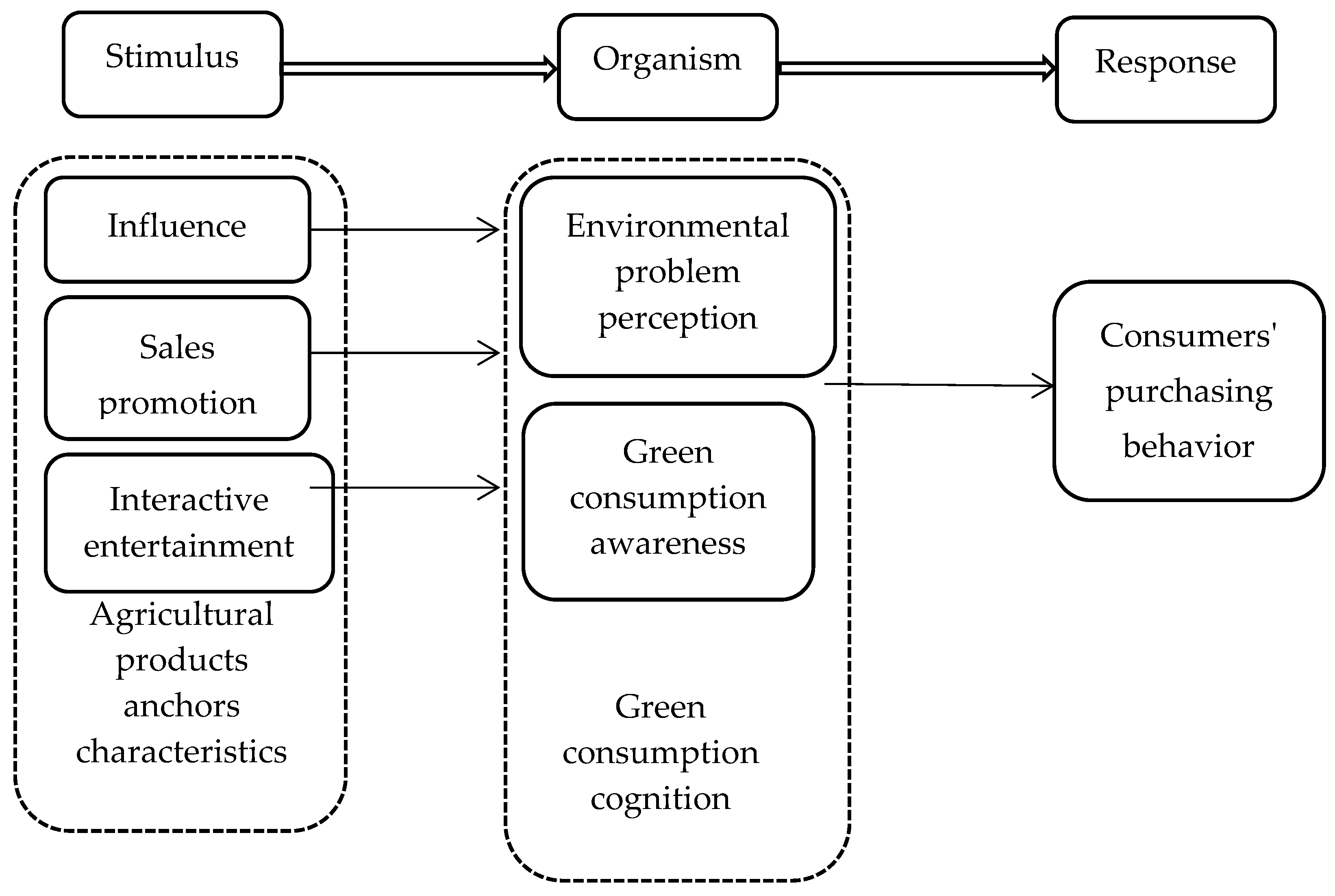
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Research Hypotheses
2.2.1. Influence of Agricultural Products Anchors’ Characteristics on Purchasing Behavior
2.2.2. The Influence of Green Consumption Cognition on Consumer Purchasing Behavior
2.2.3. The Mediating Role of Green Consumption Cognition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Variable Selection
3.3. Reliability and Validity Analysis
3.3.1. Reliability Analysis
3.3.2. Validity Analysis
3.4. Descriptive Analysis
3.5. Model
4. Results
4.1. Difference Test Analysis
4.2. Hypothesis Test Results
4.2.1. Correlation Analysis
4.2.2. Regression Analysis of Agricultural Products Anchors Characteristics’ on Purchasing Behavior
4.2.3. Regression Analysis of the Agricultural Products Anchors’ Characteristics on Green Consumption Cognition
4.2.4. Regression Analysis of Green Consumption Cognition on Purchasing Behavior
4.3. Mediating Effect Test
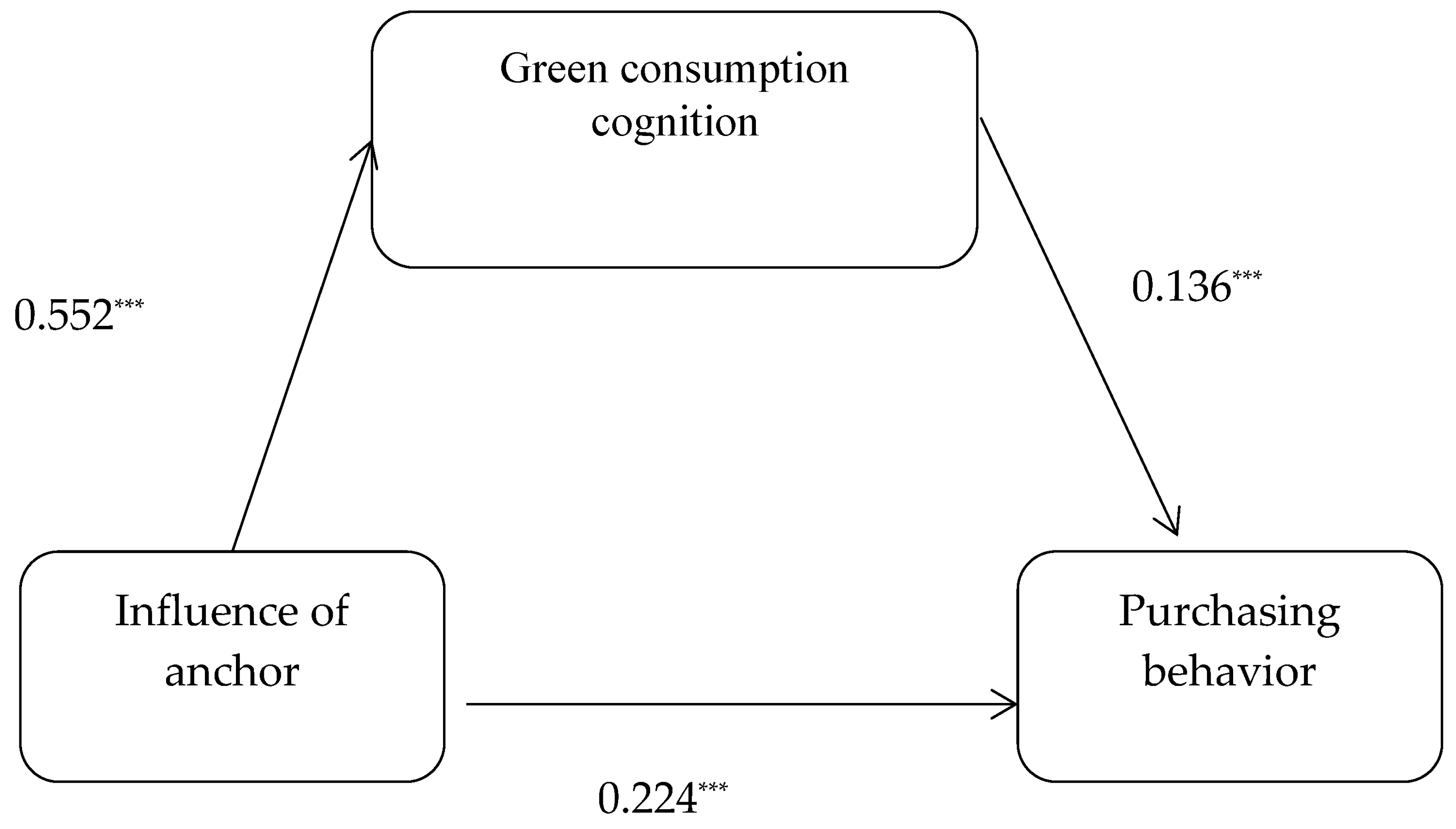
4.3.1. The Mediating Role of Green Consumption Cognition in the Relationship between Influence of Agricultural Product Anchors and Purchasing Behavior
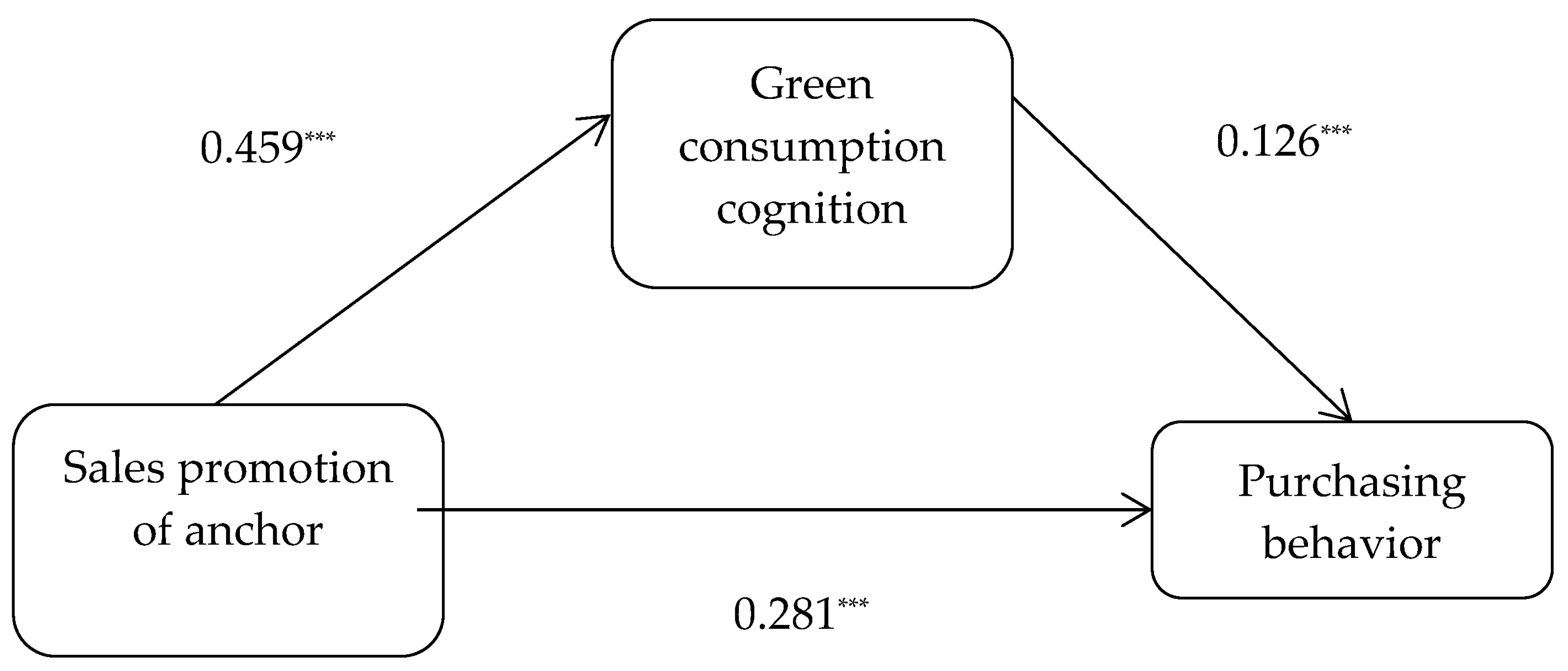
4.3.2. The Mediating Role of Green Consumption Cognition in the Relationship between Sales Promotion of Agricultural Product Anchors and Purchasing Behavior
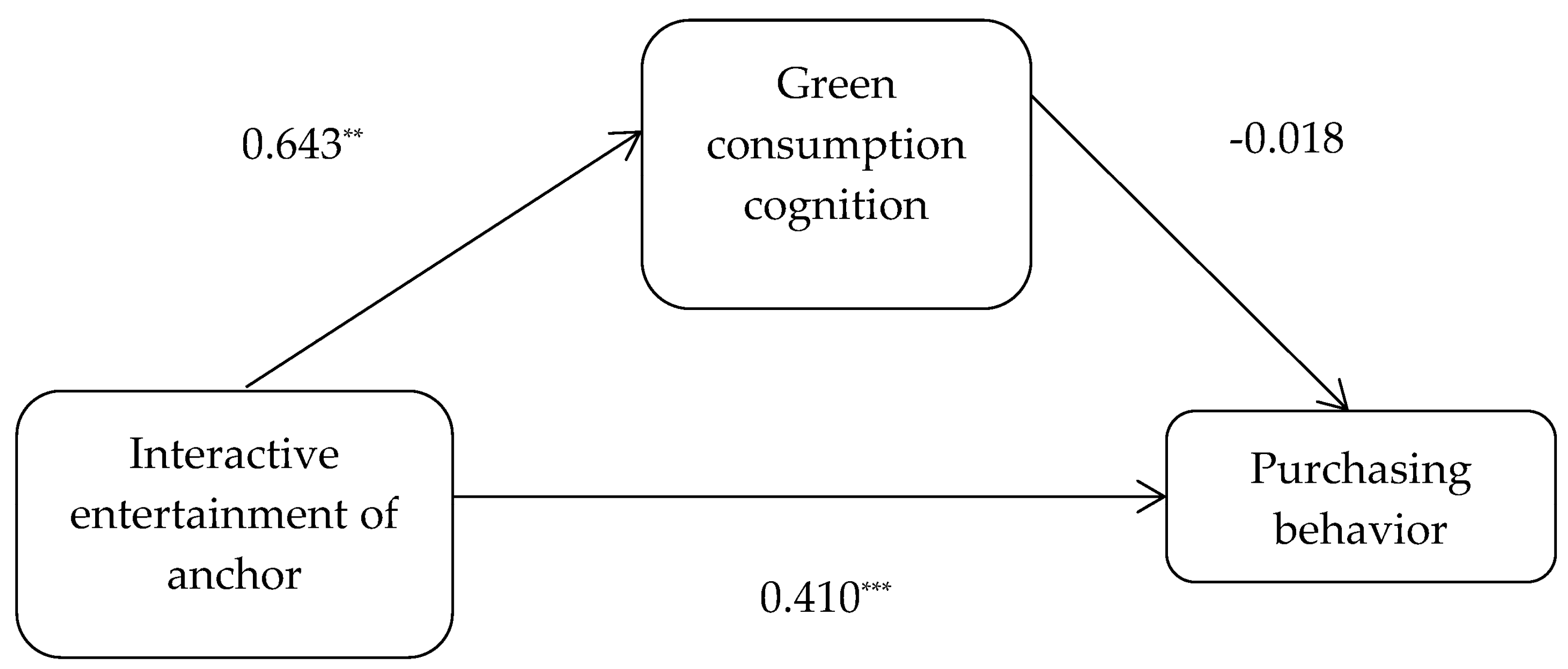
4.3.3. The Mediating Role of Green Consumption Cognition in the Relationship between Interactive Entertainment of Agricultural Product Anchors and Purchasing Behavior
4.4. Hypotheses
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Conclusions
- The influence, sales promotion, and interactive entertainment of agricultural product anchors have a significant positive impact on consumers’ purchase behavior during livestream events selling agricultural products, supporting findings from the literature [4,6,17,20]. The degree of influence from high to low is sales promotion, interactive entertainment, and influence. The real-time shopping environment of the online livestreaming room, promotional opportunities offered by the anchor, and the real-time, two-way, and entertaining experience obtained by consumers through interaction with the anchor can stimulate consumers’ purchasing behavior.
- Green consumption cognition has a positive impact on consumers’ purchasing behavior. The green consumption awareness and environmental problem perception studied in this paper reflect the rational and perceptual aspects of consumers’ green cognition. During the livestream events, agricultural product anchors can stimulate the perceptual side of consumers’ environmental problem perception and increase green consumption awareness, both contributing to increased purchase intentions.
- Green consumption cognition has a mediating effect on the influence of various dimensions of anchor characteristics on consumers’ purchasing behavior. The influence of anchors and their sales promotions both positively affect consumers’ purchasing behavior through green consumption cognition; that is, green consumption cognition plays a mediating role. However, the mediating effect of green consumption cognition between interactive entertainment and consumer purchasing behavior is not significant.
5.2. Challenges and Recommendations
5.2.1. Challenges
5.2.2. Recommendations
Recommendations for Agricultural Product Anchors
Recommendations for Agricultural Product e-Commerce Companies
Recommendations for Government
Recommendations for Consumers
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ming, J.; Jianqiu, Z.; Bilal, M.; Akram, U.; Fan, M. How social presence influences impulse buying behavior in live streaming commerce? The role of S-O-R theory. Int. J. Web Inf. Syst. 2021, 17, 300–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkitrungrueng, A.; Assarut, N. The role of live streaming in building consumer trust and engagement with social commerce sellers. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 117, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qu, J. Research on sustainable development of live-streaming marketing to help agriculture. People’s Tribune, 2020; 74–76. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhao, H. Marketing by live streaming: How to interact with consumers to increase their purchase intentions. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 933633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Zhu, Q. Research on influence and mechanism of external clues on customers’ online purchase intention of agricultural products with geographical indications. China Bus. Mark. 2020, 34, 37–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Duan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lü, K.; Chen, S. The impact of online celebrity in livestreaming e-commerce on purchase intention from the perspective of emotional contagion. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2021, 63, 102733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, C. Consumer empowerment in live-streaming marketing mode and the empirical validation. China Bus. Mark. 2021, 35, 43–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Osman, S.; Cheng, K.W.; Sam, T.H.; Ruiteng, X.; Rajanthran, S.K. Factors Influencing Live-Stream Shopping Behaviour among Malaysian Consumers. Res. Mil. 2023, 13, 1548–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.X.; Hoo, W.C. A Study on Purchase Intention of Agricultural Produce on Shopee Live-Streaming in Malaysia. Int. J. E Serv. Mob. Appl. 2022, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wen, T.; Wei, H.; Du, Z.; Li, C.; Jin, W. Speeding up the modernization of agriculture and rural areas: An in-depth interpretation by authoritative experts of the spirit of China’s No.1 Central Document. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2021, 4, 2–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ji, P.; Liu, L. Case research of ‘Internet + Modern Agricultural Park’. Econ. Rev. 2016, 96–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, K. The determinants of purchase intention on agricultural products via public-interest live streaming for farmers during COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, L.; Jiang, J.; Ren, S. Purchase Intention in Agricultural Products Live-Streaming Commerce: A S-O-R Model. In HCI International 2022—Late Breaking Papers: HCI for Today’s Community and Economy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Based on the Perspective of Rural Revitalization, the Current Situation and Countermeasures of Rural Live-Streaming in China; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, X. Problems and countermeasures of agricultural products live-broadcast with goods. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2022, 5, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, M.; Wang, Z. E-commerce live streaming of agricultural products: A new mode of poverty alleviation. Issues Agric. Econ. 2020, 11, 77–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sun, N. Unprofessional or admirable? Determinants of purchasing behavior in government officials’ livestreamed shopping. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. The impact of network spokesperson characteristics on consumer brand relationship investment from the consumer perceived perspective. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2018, 21, 64–72. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Bai, Y.; Yi, H.; He, M.; Li, X. Research on Purchase Intention of Fresh Agricultural Products Based on SOR Theory under Live Broadcast Situation. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on E-Commerce and Internet Technology (ECIT), Hangzhou, China, 5–7 March 2021; pp. 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, T. The role of live-streaming e-commerce on consumers’ purchasing intention regarding green agricultural products. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, X. An empirical study on how livestreaming can contribute to the sustainability of green agri-food entrepreneurial firms. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.B. Psychology as the behaviorist views It. Psychol. Rev. 1913, 20, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Deng, P.; Chen, B.; Liang, Q.; Deng, G. Research on tik tok platform live streaming e-commerce to help rural revitalization based on SOR model. Acad. J. Bus. Manag. 2021, 3, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, S.A.; Machleit, K.A.; Davis, L.M. Atmospheric qualities of online retailing: A conceptual model and implications. J. Bus. Res. 2001, 54, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.A.; Khalid, M.J.; Awan, H.M.; Attiq, S.; Rasool, H.; Kiran, M. Consumer’s Perceptions of Website’s Utilitarian and Hedonic Attributes and Online Purchase Intentions: A Cognitive–Affective Attitude Approach. Span. J. Mark. ESIC 2017, 21, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.T.; Jacob, J. The relationship between green perceived quality and green purchase intention: A three-path mediation approach using green satisfaction and green trust. Int. J. Bus. Innov. Res. 2018, 15, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Zhang, Q. Green purchase intention: Effects of electronic service quality and customer green psychology. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Cao, Y. Understanding consumer online impulse buying in live streaming e-commerce: A stimulus-organism-response framework. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Liu, L.; Liu, C. Consumers’ impulsive purchase intention from the perspective of affection in livestreaming e-commerce. China Bus. Mark. 2022, 36, 33–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, B.; Wang, K. Consumers’ Intention to Buy Agricultural Products via Livestreaming Platforms in Southern China. In Design, Operation and Evaluation of Mobile Communications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hua, Y. The influence of presence on purchase intention in live streaming commerce: From the perspective of vicarious learning. China Bus. Mark. 2021, 35, 81–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. To shop or not: Understanding Chinese consumers’ live-stream shopping intentions from the perspectives of uses and gratifications, perceived network size, perceptions of digital celebrities, and shopping orientations. Telemat. Inform. 2021, 59, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Meng, L.; Chen, S.; Duan, S. The impact of network celebrities’ information source characteristics on purchase intention. Chin. J. Manag. 2020, 17, 94–104. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, R.J.; Maeng, A. A tiger and a president: Imperceptible celebrity facial cues influence trust and preference. J. Consum. Res. 2012, 39, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y. The research on referral’s influence on consumers’ purchase decision in virtual community. J. Bus. Econ. 2007, 50–55+80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xiao, J.; Jin, Y. Study on the influencing factors of consumers’ continuous buying intention on social e-commerce platform based on S-O-R theory. Soft Sci. 2020, 34, 115–121. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Lei, B. Opinion leader traits, promotion stimulus and purchasing intention of social e-commerce consumers: Based on the survey of consumers on WeChat group. J. Manag. 2021, 34, 99–110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q. Research on the influence of KOL on consumers’ purchase intention from the perspective of new media: From the perspective of e-commerce live broadcast. Technol. Ind. Across Straits 2020, 3, 10–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ye, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J. Research on the influencing mechanism of atmosphere clue on impulse purchase intention in live streaming context. Chin. J. Manag. 2019, 16, 875–882. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z. Webcasting and the development of online retailers of fresh agricultural products: Driving mechanism and empirical test. China Soft Sci. 2021, 18–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. The new turn of platform labor: The dynamics, mechanism and direction of live streaming sales of officials. J. Shenzhen Univ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2022, 39, 15–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiao, L. Analysis of college students’ consumption participation behavior and driving factors in the context of e-commerce live streaming. J. Commer. Econ. 2021, 55–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, M.; Wu, F. An empirical study on the influence of network broadcast marketing on purchase intention. Manag. Obs. 2018, 41–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Lu, G.; Pang, K.; Yao, Q. Optimal farmer’s income from farm products sales on live streaming with random rewards: Case from china’s rural revitalisation strategy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 189, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C. The influence of Webcast characteristics on consumers’ purchase intention under e-commerce live broadcasting mode: The mediating role of consumer perception. China Bus. Mark. 2021, 35, 52–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, M.; Liu, B. Research on the influence of anchor characteristics on consumers’ impulse purchase intention in e-commerce livestreaming. China Bus. Mark. 2022, 36, 32–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, H.; Cai, J. The influence of Webcast on consumer’s purchase intention. J. Beijing Inst. Fash. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 40, 88–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, M. The formation of online impulse purchase tendency: An empirical study of the social commerce. Jinan J. Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2019, 41, 17–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, Q. The psychology of peasant religious conversion for the purpose of disease control: The role of ‘belief’ in understanding Chinese rural religious practices. Chin. J. Sociol. 2017, 37, 474–508. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.Y.; Huang, C.W.; Chang, H.J. The influence of green consumption cognition of consumers on behavioural intention-A case study of the restaurant service industry. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2012, 6, 7888–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J. Analysis of the related concepts of green consumption behavior and green consumption psychology. Knowl. Econ. 2014, 18–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Zhao, C. Analysis of green agricultural product consumption intention and consumption behavior. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2008, 44–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Analyzing the formation mechanism of consumers’ green consumption behavior: From the perspective of group pressure and environment perception. Consum. Econ. 2009, 25, 75–77+96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Liu, N.; Lu, G.; Wu, X. Studies on theory and actuality of green consumption behavior. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2009, 35, 37–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. Study on Consumers’ Purchase Intention can Be Influenced by Web Celebrity Sales Promotion in Live Streaming. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 15 October 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- He, A.; Du, J.; Chen, M. The mechanism on the impact of retailers’ green perception and emotion on green behavior. China Soft Sci. 2013, 117–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Luo, Y. Research on green consumption consciousness and behavior of urban residents—A case study of Changchun city. China Mark. 2013, 64–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, S.; Wang, X. Analysis and Research on User of Agricultural Products Live Streaming of E-Commerce Under the Background of China’s Rural Revitalization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Economy, Data Modeling and Cloud Computing, ICIDC 2022, Qingdao, China, 13 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Item |
|---|---|
| Influence of anchors | Q1 The anchor has a high reputation and influence in the field of live streaming of agricultural products |
| Q2 The anchor is very professional and has rich practical experience in the field of live streaming of agricultural products | |
| Q3 The anchor always patiently explains the information of agricultural products and attracts me | |
| Q4 The anchor pays attention to self-improvement and is enthusiastic about public welfare, which attracted me | |
| Sales promotion of anchors | Q5 I will buy agricultural products because the anchor runs a special flash sale during the live streaming |
| Q6 I will continue to watch live streaming and buy agricultural products because the anchors issue livestreaming-exclusive coupons | |
| Q7 I will buy agricultural products because, when I place an order to buy agricultural products during the live streaming, I will receive a gift | |
| Q8 I will buy agricultural products because there are occasional draws during the live streaming | |
| Q9 I was attracted to buy agricultural products by the ‘limited time, limited purchase and limited sales’ promotion in the live streaming | |
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | Q10 I would like to actively participate in the interaction during the live streaming and share my shopping experience and usage experience |
| Q11 The questions I have during the live streaming can be answered immediately by the anchor | |
| Q12 My questions in the live streaming room can be answered immediately by other consumers online | |
| Q13 I am relaxed and happy while watching the anchor’s live stream | |
| Q14 I think it is interesting to watch the anchors live | |
| Q15 The anchor uses humorous language in the live streaming to make the livestreaming room more joyful | |
| Environmental problem perception | Q16 I pay close attention to news reports related to the environment |
| Q17 I often discuss environmental issues with my family, friends, and relatives | |
| Q18 I get angry when I think about the damage pollution does to plants and animals | |
| Q19 When I see familiar person doing something damaging to the environment, I will stop him/her | |
| Q20 I know which products are more environmentally friendly to buy/consume | |
| Green consumption awareness | Q21 I think green consumption is a very meaningful thing for environmental protection |
| Q22 I think green consumption is very closely related to my life | |
| Q23 I follow and am interested in learning more about products with environmental value | |
| Purchasing behavior | Q24 Frequency of purchasing agricultural products in the livestreaming room |
| Q25 Percentage of agricultural products purchased online that were purchased via live streaming. |
| Dimension | Cronbach’s Alpha | Items |
|---|---|---|
| Influence of anchors | 0.804 | 4 |
| Sales promotion of anchors | 0.846 | 5 |
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | 0.848 | 6 |
| Environmental problem perception | 0.877 | 5 |
| Green consumption awareness | 0.864 | 3 |
| Purchasing behavior | 0.805 | 2 |
| Item | First Factor | Second Factor | Third Factor | Common Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5 I will buy agricultural products because the anchor runs a special flash sale during the live streaming | 0.577 | 0.536 | ||
| Q6 I will continue to watch live streaming and buy agricultural products because the anchors issue livestreaming-exclusive coupons | 0.658 | 0.626 | ||
| Q7 I will buy agricultural products because when I place an order to buy agricultural products during the live streaming, I will receive a gift | 0.759 | 0.671 | ||
| Q8 I will buy agricultural products because there are occasional draws during the live streaming | 0.813 | 0.707 | ||
| Q9 I was attracted to buy agricultural products by limited time, limited purchase, and limited sales in the live streaming | 0.737 | 0.625 | ||
| Q10 I would like to actively participate in the interaction during the live streaming and share my shopping experience and usage experience | 0.575 | 0.547 | ||
| Q11 The questions I have during the live streaming can be answered immediately by the anchor | 0.762 | 0.629 | ||
| Q12 My questions in the live streaming room can be answered immediately by other consumers online | 0.748 | 0.63 | ||
| Q13 I am relaxed and happy while watching the anchor’s live stream | 0.69 | 0.646 | ||
| Q14 I think it is interesting to watch the anchors live | 0.649 | 0.609 | ||
| Q15 The anchor uses humorous language in the live streaming to make the livestreaming room more joyful | 0.575 | 0.557 | ||
| Q1 The anchor has a high reputation and influence in the field of live streaming of agricultural products | 0.571 | 0.418 | ||
| Q2 The anchor is very professional and has rich practical experience in the field of live streaming of agricultural products | 0.728 | 0.608 | ||
| Q3 The anchor always patiently explains the information of agricultural products and attracts me | 0.772 | 0.693 | ||
| Q4 The anchor pays attention to self-improvement and is enthusiastic about public welfare, which attracted me | 0.743 | 0.663 | ||
| Eigenvalue | 3.10 | 3.08 | 2.99 | |
| Variance percentage | 20.64 | 20.52 | 19.94 | |
| Cumulative variance percentage | 20.64 | 41.15 | 61.10 |
| Item | First Factor | Second Factor | Common Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q16 I pay close attention to news reports related to the environment | 0.834 | 0.739 | |
| Q17 I often discuss environmental issues with my family, friends, and relatives | 0.734 | 0.585 | |
| Q18 I get angry when I think about the damage pollution does to plants and animals | 0.786 | 0.749 | |
| Q19 When I see familiar person doing something damaging to the environment I will stop him/her | 0.752 | 0.696 | |
| Q20 I know which products are more environmentally friendly to buy/consume | 0.700 | 0.609 | |
| Q21 I think green consumption is a very meaningful thing for environmental protection | 0.843 | 0.799 | |
| Q22 I think green consumption is very closely related to my life | 0.889 | 0.856 | |
| Q23 I follow and am interested in learning more about products with environmental value | 0.75 | 0.704 | |
| Eigenvalue | 3.20 | 2.54 | |
| Variance percentage | 40.03 | 31.68 | |
| Cumulative variance percentage | 40.03 | 71.71 |
| Variable | Definition | Number of People | Proportion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 299 | 43% |
| Age | Under 25 | 65 | 9% |
| 25–35 | 158 | 23% | |
| 35–45 | 238 | 34% | |
| Above 45 | 230 | 33% | |
| Education | High school or below | 253 | 37% |
| College | 144 | 21% | |
| Undergraduate | 232 | 34% | |
| Graduate or above | 62 | 9% | |
| Monthly income (RMB) | ≤3000 | 232 | 34% |
| 3000–5000 | 182 | 26% | |
| 5000–8000 | 153 | 22% | |
| ≥8000 | 124 | 18% | |
| Employment | Government civil servants | 38 | 6% |
| Business | 191 | 28% | |
| Doctors, teachers, and personnel of public institution | 104 | 15% | |
| Other | 358 | 52% |
| Variable | Dimension | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | Influence of anchors | 3.323 | 0.600 |
| Sales promotion of anchors | 3.214 | 0.634 | |
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | 3.379 | 0.593 | |
| Mediating | Environmental problem perception | 3.492 | 0.655 |
| Green consumption awareness | 3.711 | 0.710 | |
| Green consumption cognition | 3.574 | 0.619 | |
| Dependent | Purchasing behavior | 2.574 | 0.834 |
| Dimension | Age | Mean | Std | F | p | Multiple Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influence of anchors | Under 25 | 2.900 | 0.838 | 12.751 | <0.001 | 1 < (2, 3, 4) |
| 25–35 | 3.362 | 0.584 | ||||
| 35–45 | 3.346 | 0.563 | ||||
| Above 45 | 3.392 | 0.519 | ||||
| Sales promotion of anchors | Under 25 | 2.883 | 0.753 | 7.158 | <0.001 | 1 < (2, 3, 4) |
| 25–35 | 3.291 | 0.703 | ||||
| 35–45 | 3.252 | 0.599 | ||||
| Above 45 | 3.214 | 0.552 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | Under 25 | 3.131 | 0.824 | 5.065 | 0.002 | 1 < 2 |
| 25–35 | 3.466 | 0.613 | ||||
| 35–45 | 3.373 | 0.585 | ||||
| Above 45 | 3.395 | 0.486 | ||||
| Environmental problem perception | Under 25 | 3.049 | 0.978 | 11.609 | <0.001 | 1 < (2, 3, 4) |
| 25–35 | 3.554 | 0.611 | ||||
| 35–45 | 3.513 | 0.608 | ||||
| Above 45 | 3.551 | 0.569 | ||||
| Green consumption awareness | Under 25 | 3.343 | 0.984 | 8.084 | <0.001 | 1 < (2, 3, 4) |
| 25–35 | 3.848 | 0.754 | ||||
| 35–45 | 3.730 | 0.665 | ||||
| Above 45 | 3.702 | 0.591 | ||||
| Purchasing behavior | Under 25 | 2.562 | 0.950 | 0.343 | 0.794 | / |
| 25–35 | 2.529 | 0.882 | ||||
| 35–45 | 2.613 | 0.825 | ||||
| Above 45 | 2.567 | 0.775 |
| Dimension | Income (RMB) | Mean | Std | F | p | Multiple Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influence of anchors | 3000 | 3.248 | 0.652 | 2.533 | 0.056 | |
| 3000–5000 | 3.313 | 0.524 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 3.381 | 0.534 | ||||
| 8000 | 3.407 | 0.665 | ||||
| Sales promotion of anchors | 3000 | 3.182 | 0.607 | 1.271 | 0.283 | |
| 3000–5000 | 3.201 | 0.600 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 3.301 | 0.583 | ||||
| 8000 | 3.184 | 0.775 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | 3000 | 3.331 | 0.625 | 0.819 | 0.484 | |
| 3000–5000 | 3.391 | 0.547 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 3.414 | 0.517 | ||||
| 8000 | 3.409 | 0.679 | ||||
| Environmental problem perception | 3000 | 3.379 | 0.696 | 4.353 | 0.005 | 1 < (3, 4) |
| 3000–5000 | 3.492 | 0.540 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 3.565 | 0.622 | ||||
| 8000 | 3.611 | 0.738 | ||||
| Green consumption awareness | 3000 | 3.504 | 0.722 | 23.221 | <0.001 | (1, 2) < 3 < 4 |
| 3000–5000 | 3.634 | 0.601 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 3.791 | 0.642 | ||||
| 8000 | 4.113 | 0.741 | ||||
| Purchasing behavior | 3000 | 2.547 | 0.880 | 7.188 | <0.001 | (1, 2, 4) < 3 |
| 3000–5000 | 2.508 | 0.786 | ||||
| 5000–8000 | 2.830 | 0.803 | ||||
| 8000 | 2.403 | 0.788 |
| Dimension | Job | Mean | Std | F | p | Multiple Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influence of anchors | Government | 3.086 | 1.144 | 3.011 | 0.030 | 1 < (3, 4) |
| Business | 3.283 | 0.565 | ||||
| Public institution | 3.325 | 0.556 | ||||
| Other | 3.369 | 0.540 | ||||
| Sales promotion of anchors | Government | 3.126 | 0.977 | 4.370 | 0.005 | 2 < 3 |
| Business | 3.086 | 0.564 | ||||
| Public institution | 3.304 | 0.570 | ||||
| Other | 3.265 | 0.632 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment of anchors | Government | 3.211 | 1.051 | 1.621 | 0.183 | |
| Business | 3.343 | 0.504 | ||||
| Public institution | 3.406 | 0.547 | ||||
| Other | 3.408 | 0.583 | ||||
| Environmental problem perception | Government | 3.205 | 1.050 | 3.075 | 0.027 | 1 < (2, 3, 4) |
| Business | 3.555 | 0.570 | ||||
| Public institution | 3.473 | 0.634 | ||||
| Other | 3.494 | 0.644 | ||||
| Green consumption awareness | Government | 3.535 | 1.120 | 2.362 | 0.070 | |
| Business | 3.805 | 0.670 | ||||
| Public institution | 3.744 | 0.638 | ||||
| Other | 3.670 | 0.692 | ||||
| Purchasing behavior | Government | 2.763 | 1.107 | 3.626 | 0.013 | (2, 4) < 3 |
| Business | 2.524 | 0.812 | ||||
| Public institution | 2.784 | 0.902 | ||||
| Other | 2.520 | 0.781 |
| Dimension | Purchasing Behavior | Influence | Sales Promotion | Interactive Entertainment | Environ. Problem Perception | Green Consumption Awareness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purchasing behavior | 1 | |||||
| Influence | 0.278 *** | 1 | ||||
| Sales promotion | 0.325 *** | 0.584 *** | 1 | |||
| Interactive entertainment | 0.389 *** | 0.623 *** | 0.598 *** | 1 | ||
| Environ. problem perception | 0.231 *** | 0.545 *** | 0.452 *** | 0.633 *** | 1 | |
| Green consumption awareness | 0.205 *** | 0.494 *** | 0.399 *** | 0.554 *** | 0.663 *** | 1 |
| Dependent Variable | Purchasing Behavior | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||||
| Variable | Β | t | Β | t | Β | T | Β | T |
| Control variables | ||||||||
| Gender | −0.059 | −1.540 | −0.067 | −1.817 | −0.074 | −2.048 | −0.072 * | −2.04 |
| Age | 0.022 | 0.566 | −0.027 | −0.701 | −0.017 | −0.448 | −0.004 | −0.102 |
| Education | −0.018 | −0.354 | −0.035 | −0.734 | −0.023 | −0.503 | −0.011 | −0.241 |
| Income | 0.004 | 0.086 | −0.027 | −0.592 | −0.028 | −0.620 | −0.034 | −0.765 |
| Job | −0.051 | −1.280 | −0.088 | −2.287 | −0.100 | −2.652 | −0.096 ** | −2.623 |
| Independent variables | ||||||||
| Influence | 0.299 *** | 7.959 | 0.150 ** | 3.340 | 0.024 | 0.493 | ||
| Sales promotion | 0.253 *** | 5.744 | 0.149 *** | 3.228 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment | 0.296 *** | 6.184 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.006 | 0.090 | 0.132 | 0.178 | ||||
| Adj. R2 | −0.002 | 0.082 | 0.123 | 0.168 | ||||
| F | 0.791 | 11.277 *** | 14.831 *** | 18.466 *** | ||||
| Dependent Variable | Environmental Problem Perception | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||||
| Variable | β | T | Β | t | β | t | β | T |
| Control variable | ||||||||
| Gender | 0.037 | 0.976 | 0.023 | 0.723 | 0.018 | 0.556 | 0.021 | 0.734 |
| Age | 0.144 *** | 3.73 | 0.057 | 1.717 | 0.066 * | 2.007 | 0.086 ** | 2.906 |
| Education | 0.015 | 0.302 | −0.016 | −0.386 | −0.006 | −0.158 | 0.013 | 0.364 |
| Income | 0.145 ** | 3.073 | 0.089 * | 2.213 | 0.089 * | 2.246 | 0.080 * | 2.222 |
| Job | 0.044 | 1.116 | −0.022 | −0.647 | −0.032 | −0.961 | −0.026 | −0.862 |
| Independent variable (anchors) | ||||||||
| Influence | 0.528 *** | 16.15 | 0.404 *** | 10.307 | 0.203 *** | 5.172 | ||
| Sales promotion | 0.212 *** | 5.487 | 0.045 | 1.200 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment | 0.472 *** | 12.094 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.043 | 0.307 | 0.337 | 0.454 | ||||
| Adj. R2 | 0.036 | 0.301 | 0.330 | 0.447 | ||||
| F | 6.212 *** | 50.609 *** | 49.526 *** | 70.836 *** | ||||
| Dependent Variable | Green Consumption Awareness | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | ||||
| Variable | Β | T | Β | T | Β | T | β | T |
| Control variable | ||||||||
| Gender | 0.072 * | 1.98 | 0.060 | 1.882 | 0.055 | 1.753 | 0.058 * | 1.97 |
| Age | 0.070 | 1.878 | −0.007 | −0.213 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.018 | 0.570 |
| Education | 0.067 | 1.428 | 0.040 | 0.966 | 0.048 | 1.183 | 0.065 | 1.697 |
| Income | 0.269 *** | 5.861 | 0.219 *** | 5.428 | 0.218 *** | 5.500 | 0.211 *** | 5.666 |
| Job | 0.031 | 0.820 | −0.027 | −0.812 | −0.036 | −1.083 | −0.031 | −0.996 |
| Independent variable | ||||||||
| Influence | 0.471 *** | 14.429 | 0.364 *** | 9.243 | 0.195 *** | 4.800 | ||
| Sales promotion | 0.183 *** | 4.728 | 0.043 | 1.116 | ||||
| Interactive entertainment | 0.395 *** | 9.788 | ||||||
| R2 | 0.101 | 0.311 | 0.332 | 0.415 | ||||
| Adj. R2 | 0.094 | 0.304 | 0.326 | 0.408 | ||||
| F | 15.332 *** | 51.338 *** | 48.572 *** | 60.374 *** | ||||
| Dependent Variable | Purchasing Behavior | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | |||
| Variable | β | t | β | t | Β | T |
| Control variable | ||||||
| Gender | −0.059 | −1.540 | −0.068 | −1.822 | −0.074 * | −1.98 |
| Age | 0.022 | 0.566 | −0.013 | −0.327 | −0.010 | −0.262 |
| Education | −0.018 | −0.354 | −0.021 | −0.438 | −0.028 | −0.581 |
| Income | 0.004 | 0.086 | −0.031 | −0.659 | −0.052 | −1.086 |
| Job | −0.051 | −1.280 | −0.061 | −1.588 | −0.062 | −1.604 |
| Independent variable | ||||||
| Environmental problem perception | 0.243 *** | 6.406 | 0.167 ** | 3.332 | ||
| Green consumption awareness | 0.119 * | 2.304 | ||||
| R2 | 0.006 | 0.062 | 0.069 | |||
| Adj. R2 | −0.002 | 0.054 | 0.060 | |||
| F | 0.791 | 7.536 *** | 7.259 *** | |||
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Purchasing Behavior | Green Consumption Cognition | Purchasing Behavior | |||
| Variable | Β | t | Β | t | β | t |
| Gender | −0.067 * | −1.817 | 0.041 | 1.334 | −0.073 ** | −1.978 |
| Age | −0.027 | −0.701 | 0.035 | 1.083 | −0.032 | −0.828 |
| Education | −0.035 | −0.734 | 0.007 | 0.166 | −0.036 | −0.757 |
| Income | −0.027 | −0.592 | 0.153 *** | 3.936 | −0.048 | −1.036 |
| Job | −0.088 ** | −2.287 | −0.026 | −0.804 | −0.084 ** | −2.207 |
| Influence of anchor | 0.299 *** | 7.959 | 0.552 *** | 17.513 | 0.224 *** | 4.981 |
| Green consumption cognition | 0.136 *** | 3.003 | ||||
| R2 | 0.300 | 0.597 | 0.319 | |||
| Adj. R2 | 0.090 | 0.357 | 0.102 | |||
| F | 11.277 *** | 63.238 *** | 11.068 *** | |||
| Effect | Effect Value | SE | t | LLCI | ULCI | Effect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.415 | 0.052 | 7.959 *** | 0.313 | 0.517 | |
| Direct | 0.311 | 0.062 | 4.981 *** | 0.188 | 0.433 | 74.88% |
| Indirect | BootSE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | |||
| 0.104 | 0.042 | 0.019 | 0.185 | 25.12% |
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Purchasing Behavior | Green Consumption Cognition | Purchasing Behavior | |||
| Variable | β | t | Β | t | Β | t |
| Gender | −0.074 ** | −2.025 | 0.036 | 1.099 | −0.078 ** | −2.161 |
| Age | 0.003 | 0.082 | 0.100 *** | 2.949 | −0.010 | −0.254 |
| Education | −0.014 | −0.294 | 0.044 | 1.035 | −0.019 | −0.414 |
| Income | −0.018 | −0.390 | 0.182 *** | 4.410 | −0.041 | −0.886 |
| Job | −0.091 ** | −2.417 | −0.013 | −0.366 | −0.090 ** | −2.390 |
| Anchor sales promotion | 0.338 *** | 9.320 | 0.459 *** | 13.942 | 0.281 *** | 5.426 |
| Green consumption cognition | 0.126 *** | 6.860 | ||||
| R2 | 0.343 | 0.524 | 0.360 | |||
| Adj. R2 | 0.118 | 0.275 | 0.129 | |||
| F | 15.218 *** | 43.142 *** | 14.484 *** | |||
| Effect | Effect Value | SE | t | LLCI | ULCI | Effect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.445 | 0.048 | 9.320 *** | 0.351 | 0.539 | |
| Direct | 0.369 | 0.054 | 4.981 *** | 0.264 | 0.475 | 82.94% |
| Indirect | BootSE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | |||
| 0.076 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.135 | 17.08% |
| Model | M1 | M2 | M3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Purchasing Behavior | Green Consumption Cognition | Purchasing Behavior | |||
| Variable | β | t | Β | t | β | t |
| Gender | −0.067 * | −1.884 | 0.044 | 1.563 | −0.066 * | −1.857 |
| Age | 0.004 | 0.109 | 0.096 *** | 3.350 | 0.006 | 0.156 |
| Education | −0.009 | −0.198 | 0.053 | 1.457 | −0.008 | −0.177 |
| Income | −0.031 | −0.686 | 0.156 *** | 4.439 | −0.028 | −0.614 |
| Job | −0.084 ** | −2.282 | −0.011 | −0.369 | −0.084 ** | −2.285 |
| Interactive entertainment | 0.398 *** | 11.301 | 0.643 *** | 23.100 | 0.410 *** | 8.712 |
| Green consumption cognition | −0.018 | −0.374 | ||||
| R2 | 0.403 | 0.690 | 0.403 | |||
| Adj. R2 | 0.162 | 0.477 | 0.162 | |||
| F | 22.066 *** | 103.839 *** | 18.910 *** | |||
| Effect | Effect Value | SE | T | LLCI | ULCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.560 | 0.050 | 11.301 *** | 0.463 | 0.657 |
| Direct | 0.576 | 0.066 | 8.712 *** | 0.446 | 0.706 |
| Indirect | BootSE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | ||
| −0.016 | 0.047 | −0.109 | 0.073 |
| Hypothesis | Result |
|---|---|
| H1 Influence of agricultural anchors positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H2 Sales promotion of agricultural anchors positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H3 Interactive entertainment of agricultural anchors positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H4 Green consumption cognition positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H4a Environmental problem perception positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H4b Green consumption awareness positively affects purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H5 Green consumption cognition plays a mediating role between the influence of agricultural product anchors and purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H6 Green consumption cognition plays a mediating role between the sales promotion of agricultural product anchors and purchasing behavior. | Supported |
| H7 Green consumption cognition plays a mediating role between the interactive entertainment of agricultural product anchors and purchasing behavior. | Not supported |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.; Lyu, X.; Wang, J.; Wachenheim, C. Enhancing Sales of Green Agricultural Products through Live Streaming in China: What Affects Purchase Intention? Sustainability 2023, 15, 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075858
Zheng S, Lyu X, Wang J, Wachenheim C. Enhancing Sales of Green Agricultural Products through Live Streaming in China: What Affects Purchase Intention? Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075858
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Shi, Xinyang Lyu, Jie Wang, and Cheryl Wachenheim. 2023. "Enhancing Sales of Green Agricultural Products through Live Streaming in China: What Affects Purchase Intention?" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075858
APA StyleZheng, S., Lyu, X., Wang, J., & Wachenheim, C. (2023). Enhancing Sales of Green Agricultural Products through Live Streaming in China: What Affects Purchase Intention? Sustainability, 15(7), 5858. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075858






