Study on the Factors Affecting the Green Housing Purchase Intention in Urban Residents—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
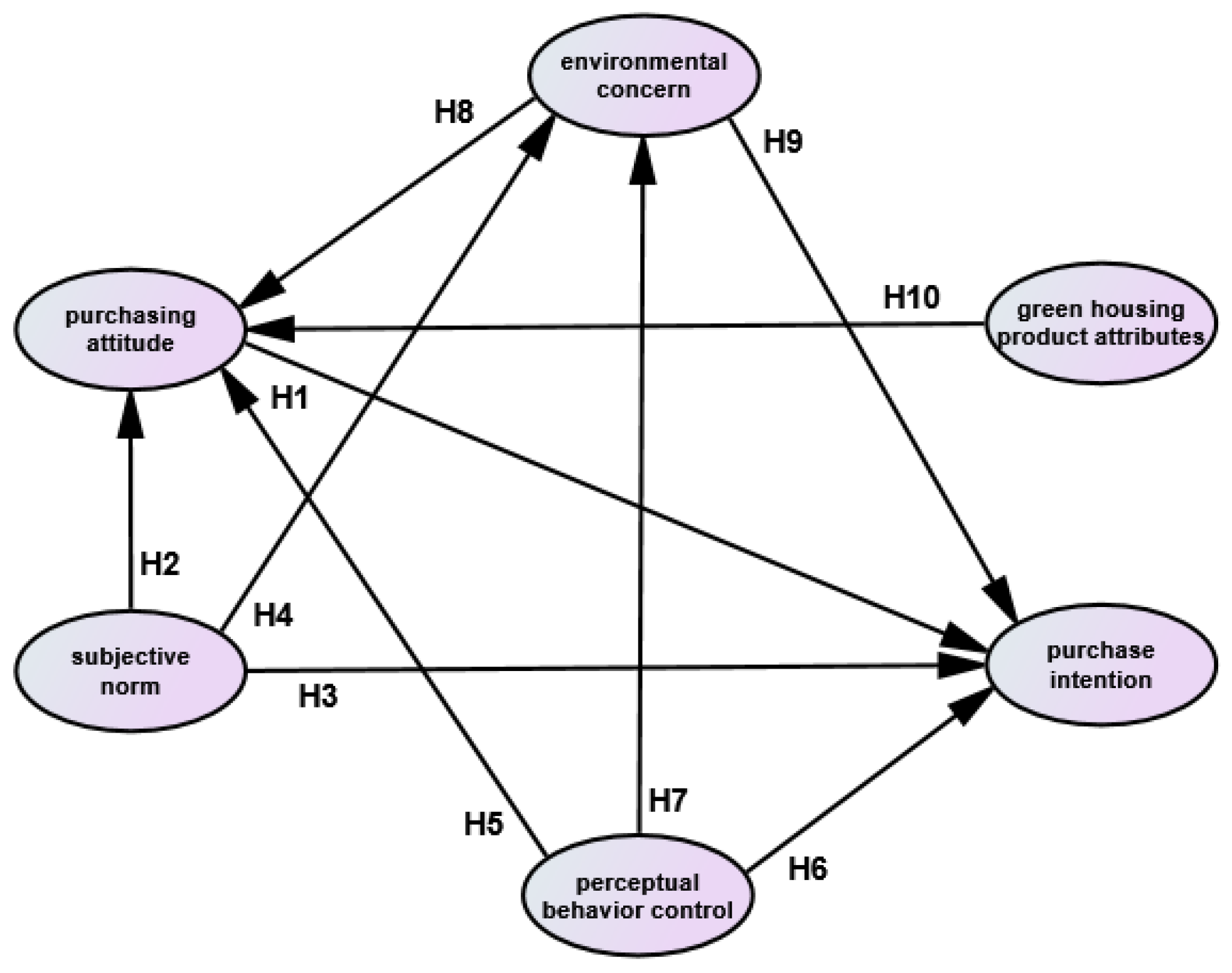
2.1. Influencing Factor Recognition and Research Hypothesis
2.1.1. Research Hypothesis of Purchasing Attitude
2.1.2. Research Hypothesis of Subjective Norm
2.1.3. Research Hypothesis of Perceptual Behavior Control
2.1.4. Research Hypothesis of Environmental Concern
2.1.5. Research Hypothesis of Green House Product Attributes
2.2. Structure Equation Model Construction
2.3. Design and Development of Research Scale
2.4. Sample Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Reliability Test
3.2. Validity Test
3.3. Exploratory Factor Analysis
3.4. Verification Factor Analysis
3.5. Model Adaptability Test
3.6. Model Hypothesis Test
4. Research Results and Discussion
4.1. Results
4.1.1. Impact Path
4.1.2. Influencing Effect
4.2. Discussion
5. Research Conclusions and Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.Q.; Guo, Q.J.; Li, S.L. Research on the Measurement of the Coordinated Development of Construction Industry-Urbanization-Economy—Based on the Empirical Analysis of 31 Provinces of Chine. Mod. Manag. 2022, 2, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.Y.; Chen, X.H. Research on Urbanization and Ecological Environment Coupling Development Based on SD Model: A Case in Eastern Coal-Electricity Base of Heilongjiang Province. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 12, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.T.; Xu, H.Q.; Tang, F.F. Built-up land change and its impact on ecological quality in a fast-growing economic zone: Jinjiang County, Fujian Province, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 4, 1317. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Zhang, Z.F.; Liang, Y.Z.; Huang, Y.F. Assessing the Impact of Urbanization and Eco-Environmental Quality on Regional Carbon Storage: A Multiscale Spatio-Temporal Analysis Framework. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 4007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, M.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal Change of Eco-Environmental Quality in the Oasis City and Its Correlation with Urbanization Based on RSEI: A Case Study of Urumqi, China. Sustainability 2022, 15, 9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D. Understanding the Relationship between China’s Eco-Environmental Quality and Urbanization Using Multisource Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 1, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Wang, D.; Chao, J.F. Energy Efficiency, Economic Growth and Ecological Environment Quality: Based on the DSGE Model Containing Carbon Emissions. J. Technical Econ. Manag. 2022, 10, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, J.M.; Zhao, Y.L. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban green space and ecological quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Taiyuan Univ. Technol. 2023, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, M.D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Q. The impact of eco-environmental quality on urban economic efficiency. Urban Probl. 2022, 1, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.J. Carbon neutral green transition, green investment and ecological environment quality. Stat. Decis. 2021, 18, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Ma, G.W.; He, L.H.; Chen, S.R. Characteristics of Eco-environmental Quality Changes in China During the 13th Five-Year Plan Period. Environ. Monit. China 2021, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.C.; Guo, Y.F.; Wang, L. Dynamic measurement of eco-environmental quality in our country. Stat. Decis. 2021, 3, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.X. Urban Carbon Neutralization and Green Building. Urban Dev. Stud. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Wei, H.; Chong, M.; Xing, W.; Li, Y. Demand Analysis and Prospect of High-Quality Development of Green Building in China. Build. Sci. 2018, 9, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Y.X. Factor analysis and relationship research of green housing choice behavior. China Soft Sci. 2017, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Feng, Z.Y. Study on optimal selection of incentive model of green housing from the perspective of dynamic game. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 34, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Gu, J. Overview of green housing development research in our country. Shanghai Real Estate 2019, 47, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q. Discussion on the strategy of green consumption improvement of Chinese residents under the “dual carbon” goal. Bus. Econ. Res. 2022, 6, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Usamah, S. Electric vehicle development in Pakistan: Predicting consumer purchase intention. Clean. Resp. Consump. 2022, 5, 100065. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, J.; Modi, A.; Patel, J. Predicting green product consumption using theory of planned behavior and reasoned action. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2016, 29, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Theoretical logic and practical basis of online marketing of eco-green agricultural products in China. Price Theor. Pract. 2020, 27, 31–34, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Study on consumer behavior of green products from the perspective of environmental Concern. Price Theor. Pract. 2021, 6, 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.W.; Chen, L.W. Influencing Factors and mechanism of green housing purchase Intention: Based on Grounded theory. Bus. Econom. 2020, 235, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, H.Y.; Zheng, S. The role of public information in increasing homebuyers’ willingness-to-pay for green housing: Evidence from Beijing. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 129, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Wang, D.F.; Song, J.Z.; Shi, X. Study on the influence mechanism of green housing purchase intention considering information asymmetry. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 74–79+85. [Google Scholar]
- Matin, A.; Khoshtaria, T.; Marcan, M.; Datuashvili, D. The roles of hedonistic, utilitarian incentives and government policies affecting customer attitudes and purchase intention towards green products. Int. Rev. Public Nonprofit Market. 2021, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amos, D.; Chan, A.P.C. Review of Barriers to Green Building Adoption. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 25, 167–179. [Google Scholar]
- Amos, D.; Zhang, C.Z.; Chan, A.P.C. Drivers for green building: A review of empirical studies. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, J.; Mu, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Liu, W. Strategies for Sustainable Development of Green Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 44, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, J.S. Research on the Development and Countermeasures of Green Building under the Goal of “Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality”. Southwest Finan. 2021, 10, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Narin, G. Real example analysis of housing consumption of dweller of our country town. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2017, 13, 294. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, Y.T. Some thoughts on promoting the healthy development of residential housing consumption. Price Theor. Pract. 2023, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, R.R.; Ding, Z. Temporal and spatial differentiation of the coupling coordination between eco-city urbanization and ecological environment. J. Shand. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 11, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, H.X.; Ma, J.J.; Huang, J.C.; Wei, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Quantization of the coupling mechanism between eco-environmental quality and urbanization from multisource remote sensing data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perloff, R.M. The Dynamics of Persuasion, 7th ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Yoon, H.J. Hotel customers’ environmentally responsible behavioral intention: Impact of key constructs on decision in green consumerism. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2015, 45, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hong, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yan, J.; Qi, J.; Liu, P. Promoting green residential buildings: Residents’ environmental attitude, subjective knowledge, and social trust matter. Energy Policy 2018, 112, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melika, R.; Seyed, M.H.; Iraj, M.M. Proposing a socio-psychological model for adopting green building technologies: A case study from Iran. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 657. [Google Scholar]
- Brenton, M.W.; Deniz, S.O.; Stephan, D. Age and environmental sustainability: A meta-analysis. J. Manag. Psychol. 2013, 7/8, 826. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, R.Y.M. Research on the influence mechanism of customer perception Externalities on green purchasing behavior. Enterp. Econ. 2020, 3, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.D.; Wu, Y.X. Choice Behavior for Green Residential Building: Factors and Relationships. China Soft Sci. 2017, 1, 175. [Google Scholar]
- Tanw, L.; Goh, Y.N. The role of psychological factors in influencing consumer purchase intention towards green residential building. Int. J. Hous. Mark. Anal. 2018, 5, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. Research on Consumers’ Behavior of Green Products from the Perspective of Environmental Concern. Price Theory Pract. 2021, 5, 9197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.M.; Liu, A.D. Empirical study on influencing factors of consumers’ green house purchase behavior. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. Nat. Sci. Edit. 2018, 3, 454. [Google Scholar]
- Gefen, S.B.M. Structural Equation Modeling and Regression: Gridlines for Research Practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2000, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Fit indices in covariance structure modeling. Psychol. Methods 1998, 3, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Bentler, P.M. Cutoff criteria for fit indices in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. 1999, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Potential Variable | Measurement Project |
|---|---|
| Purchasing Attitude (PA) | I think it is wise to buy a green housing (PA1) |
| I think it is beneficial to buy a green housing (PA2) | |
| I think it is a good idea to buy a green housing (PA3) | |
| I think it is pleasant to buy a green housing (PA4) | |
| I think it is very important to buy a green housing (PA5) | |
| Subjective Norm (SN) | The people who are important to me think I should buy a green housing (SN1) |
| Under social pressure, I think I should buy a green housing (SN2) | |
| Under social pressure, I think many people will buy green housing (SN3). | |
| If I buy a green housing, those who are important to me will fully agree (SN4) | |
| Perceptual Behavior Control (PBC) | I think I have a lot of control over buying a green housing (PBC1) |
| If I want to, it is easy for me to buy a green housing (PBC2) | |
| Whether to buy a green housing or not mainly depends on myself (PBC3) | |
| Environmental Concern (EC) | I often pay attention to environmental information and reports and advertisements related to green products (EC1) |
| I often talk to others about environmental problems or green products (EC2) | |
| I think I am an environmentally friendly consumer (EC3) | |
| I think I am a person who is very concerned about environmental issues (EC4) | |
| Green House Product Attributes (GPA) | I think green housing has better water-saving and energy-saving performance than ordinary housing (GPA1) |
| I think green housing are more comfortable than ordinary housing (GPA2) | |
| I think green housing has better greening effect than ordinary housing (GPA3) | |
| I think the development of green housing is conducive to the overall improvement of the current social environment (GPA4) | |
| I think the development of green housing can improve the overall public’s awareness of environmental protection (GPA5) | |
| Purchase Intention (PI) | I want to live in a green housing (PI1) |
| I am willing to buy a green housing in the future (PI2) | |
| I would consider a green house for my next home purchase (PI3) | |
| I plan to buy a green housing (PI4) |
| Potential Variables | Standardized Cronbach’s α | Number of Measurement Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Attitude (PA) | 0.601 | 5 |
| Subjective Norm (SN) | 0.661 | 4 |
| Perceptual Behavior Control (PBC) | 0.580 | 3 |
| Environmental Concern (EC) | 0.690 | 4 |
| Green Housing Product Attributes (GPA) | 0.624 | 5 |
| Purchase Intention (PI) | 0.606 | 4 |
| Total | 0.818 | 25 |
| Potential Variables | KMO Value | Bartlett Sphere Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approximate Champion | Degree of Freedom | Significant Level | ||
| Purchasing Attitude (PA) | 0.714 | 113.043 | 10 | 0.000 |
| Subjective Norm (SN) | 0.686 | 156.213 | 6 | 0.000 |
| Perceptual Behavior Control (PBC) | 0.619 | 74.854 | 3 | 0.000 |
| Environmental Concern (EC) | 0.727 | 165.979 | 6 | 0.000 |
| Green Housing Product Attributes (GPA) | 0.681 | 152.800 | 10 | 0.000 |
| Purchase intention (PI) | 0.628 | 128.437 | 6 | 0.000 |
| Total | 0.790 | 1516.807 | 300 | 0.000 |
| Research Variables | Measurement Items | Factor Load Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Purchasing Attitude (PA) | PA1 | 0.495 | 0.580 | ||||
| PA3 | 0.670 | ||||||
| PA4 | 0.514 | ||||||
| PA5 | 0.676 | ||||||
| Subjective Norm (SN) | SN 1 | 0.515 | |||||
| SN 2 | 0.813 | ||||||
| SN 3 | 0.783 | ||||||
| SN 4 | 0.522 | 0.310 | |||||
| Perceptual Behavior Control (PBC) | PBC1 | 0.609 | |||||
| PBC2 | 0.737 | ||||||
| PBC3 | 0.715 | ||||||
| Environmental Concern (EC) | EC1 | 0.741 | |||||
| EC2 | 0.628 | ||||||
| EC3 | 0.675 | ||||||
| EC4 | 0.689 | ||||||
| Green House Product Attributes (GPA) | GPA1 | 0.748 | |||||
| GPA3 | 0.411 | 0.619 | |||||
| GPA5 | 0.618 | ||||||
| Purchase Intention (PI) | PI 1 | 0.517 | 0.388 | ||||
| PI 2 | 0.765 | ||||||
| PI 3 | 0.668 | ||||||
| Variance Interpretation Rate (%) | 10.310% | 9.628% | 9.139% | 9.136% | 8.502% | 8.300% | |
| Cumulative Variance Interpretation Rate (%) | 10.310% | 19.938% | 29.077% | 38.214% | 46.716% | 55.016% | |
| Research Variables | Measurement Items | Standardized Factor Load | Standard Error (S.E.) | Critical Ratio (C.R.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Attitude (PA) | PA1 | 0.627 | -- | -- |
| PA3 | 0.456 | 0.147 | 5.319 | |
| PA4 | 0.447 | 0.137 | 5.224 | |
| PA5 | 0.437 | 0.176 | 4.965 | |
| Subjective Norm (SN) | NA1 | 0.434 | -- | -- |
| NA2 | 0.745 | 0.368 | 5.337 | |
| NA3 | 0.625 | 0.313 | 5.248 | |
| NA4 | 0.504 | 0.224 | 5.110 | |
| Perceptual Behavior Control (PBC) | PBC1 | 0.492 | -- | -- |
| PBC2 | 0.498 | 0.348 | 4.798 | |
| PBC3 | 0.707 | 0.350 | 4.523 | |
| Environmental Concern (EC) | EC1 | 0.615 | -- | -- |
| EC2 | 0.549 | 0.149 | 6.620 | |
| EC3 | 0.626 | 0.145 | 6.891 | |
| EC4 | 0.581 | 0.138 | 6.695 | |
| Green House Product Attributes (GPA) | GPA1 | 0.592 | -- | -- |
| GPA3 | 0.605 | 0.178 | 5.958 | |
| GPA5 | 0.489 | 0.159 | 5.492 | |
| Purchase Intention (PI) | PW1 | 0.743 | -- | -- |
| PW2 | 0.493 | 0.108 | 6.077 | |
| PW3 | 0.518 | 0.104 | 6.400 |
| Fitting Index | Χ2/df | GFI | RMSEA | RMR | CFI | PGFI | NNFI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptation Critical Value | <3 | >0.80 | <0.08 | <0.10 | >0.80 | >0.50 | >0.80 |
| Verify the Model | 1.923 | 0.892 | 0.059 | 0.086 | 0.832 | 0.687 | 0.802 |
| Hypothesis | Path Coefficient | C.R. | p | Hypothetical Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: Purchasing Intention ← Purchasing Attitude | 0.228 | 1.430 | 0.153 | Rejection |
| H2: Purchasing Attitude ← Subjective Norm | 0.350 | 2.994 | 0.003 | Support |
| H3: Purchasing Intention ← Subjective Norm | −0.040 | −0.359 | 0.720 | Rejection |
| H4: Environmental Concern ← Subjective Norm | 0.350 | 3.345 | *** | Support |
| H5: Purchasing Attitude ← Perceptual Behavior Control | 0.147 | 1.234 | 0.217 | Rejection |
| H6: Purchase Intention ← Perceived Behavior Control | −0.071 | −0.626 | 0.531 | Rejection |
| H7: Environmental Concern ← Perceptual Behavior Control | 0.446 | 3.931 | *** | Support |
| H8: Purchasing Attitude ← Environmental Concern | −0.022 | −0.168 | 0.867 | Rejection |
| H9: Purchasing Intention ← Environmental Concerns | 0270 | 2.318 | 0.020 | Support |
| H10: Purchasing Attitude ← Green Housing Product Attributes | 0.562 | 4.375 | *** | Support |
| H11: Purchasing Intention ← Green Housing Product Attributes | 0.601 | 3.646 | *** | Support |
| Potential Variables | Direct Influence Effect | Indirect Influence Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchasing Attitude | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Subjective Norm | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Perceptual Behavior Control | 0.00 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Environmental Concern | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.25 |
| Green Housing Product Attribute | 0.78 | 0.00 | 0.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, W.; Wang, Y. Study on the Factors Affecting the Green Housing Purchase Intention in Urban Residents—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043735
Ren W, Wang Y. Study on the Factors Affecting the Green Housing Purchase Intention in Urban Residents—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043735
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Wei, and Yaxiao Wang. 2023. "Study on the Factors Affecting the Green Housing Purchase Intention in Urban Residents—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043735
APA StyleRen, W., & Wang, Y. (2023). Study on the Factors Affecting the Green Housing Purchase Intention in Urban Residents—Taking the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region as an Example. Sustainability, 15(4), 3735. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043735





