Relationship between Learning Strategies and Motivation of University Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
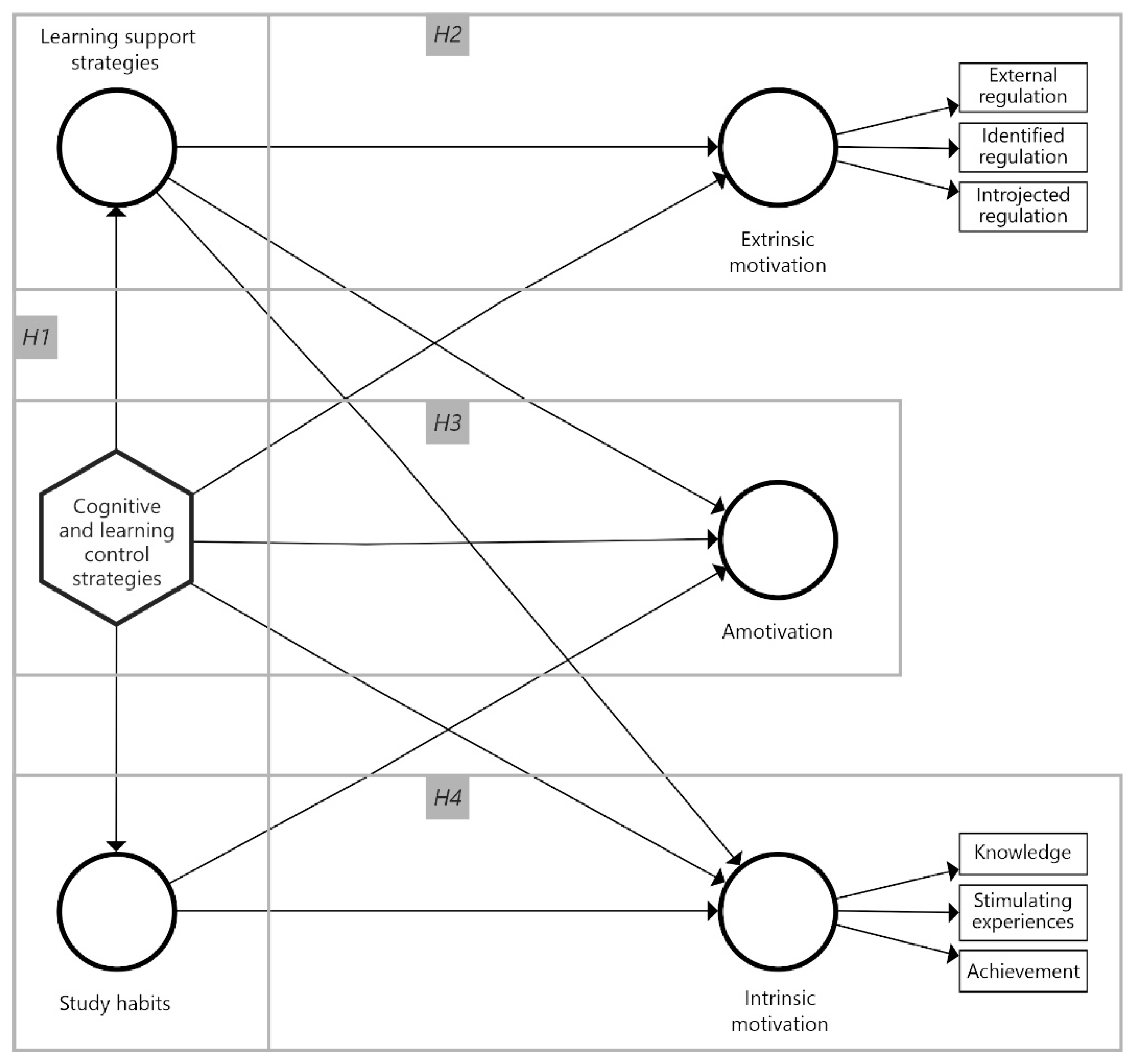
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
Structural Model
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Naqbi, A.K.; Alshannag, Q. The status of education for sustainable development and sustainability knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors of UAE University students. Int. J. Sustain. High. Educ. 2018, 19, 566–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J. Desarrollo sostenible: La lucha por la interpretación. Econ. Ecol. 1995, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Theobald, M. Self-regulated learning training programs enhance university students’ academic performance, self-regulated learning strategies, and motivation: A meta-analysis. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 2021, 66, 101976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégin, C. Les stratégies d’apprentissage: Un cadre de référence simplifié. Rev. Sci. L’éduc. 2008, 34, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo, B.; Suárez, J.; Ferreras, A. Estrategias de aprendizaje y rendimiento académico en estudiantes universitarios. Rev. Investig. Educ. 2007, 25, 421–441. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhretdinova, G.; Zinnatullina, L.M.; Tarasova, E.N. Integrating Sustainability into Language Teaching in Engineering University. In Mobility for Smart Cities and Regional Development—Challenges for Higher Education. ICL 2021; Auer, M.E., Hortsch, H., Michler, O., Köhler, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hye-Sook, C.; Yeo-Hee, Y.; So-Hyun, S.; Gyu-Chul, S. Un estudio sobre la percepción, actitud y voluntad de ejercer para el desarrollo sostenible de docentes de preprimaria. Educ. Ambient. 2010, 23, 129–144. [Google Scholar]
- Jong, Y.; Kim, Y. Perceptions and Approaches of TOEIC Speaking Classes by University Students from Different Academic Disciplines. Res. Chin. Lang. Educ. 2019, 31, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, B.J.; Martinez-Pons, M. Perceptions of efficacy and strategy use in the self-regulation of learning. In Student Perceptions in the Classroom; Schunk, D.H., Meece, J.L., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 185–207. [Google Scholar]
- Svicher, A.; Gori, A.; Di Fabio, A. The Sustainable Development Goals Psychological Inventory: A Network Analysis in Italian University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, A.; Mori, K.; Rustiadi, E.; Muramatsu, S.; Kato, H. Effectiveness of Incorporating the Concept of City Sustainability into Sustainability Education Programs. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca-Lozano, A.; Montes-Oca-Báez, G.; Moreta, Y. Motivación, enfoques de aprendizaje y rendimiento académico: Impacto de metas académicas y atribuciones causales en estudiantes universitarios de educación de la República Dominicana. Rev. Caribeña Investig. Educ. (RECIE) 2019, 3, 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrie Kupczyszyn, K.N.; Bastacini, M.D.C. Autorregulación en estudiantes universitarios: Estrategias de aprendizaje, motivación y emociones. Rev. Educ. 2020, 44, 327–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navea Martín, A. Un Estudio Sobre la Motivación y Estrategias de Aprendizaje en Estudiantes Universitarios de Ciencias de la Salud; Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Broc, M.Á. Voluntad para estudiar, regulación del esfuerzo, gestión eficaz del tiempo y rendimiento académico en alumnos universitarios. Revista de Investigación Educativa 2011, 29, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Zare-ee, A. Associations between university students’ beliefs and their leaning strategies use. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2010, 5, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, J.B.; Uriel, F.E.; Freiberg Hoffmann, A.; Fernández Liporace, M.M. Estrategias de aprendizaje y motivación académica en estudiantes universitarios de Buenos Aires. Psicodebate 2015, 15, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente Arias, J.; Justicia Justicia, F. Regulación de la enseñanza para la autorregulación del aprendizaje en la universidad. Aula Abierta 2003, 83, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, J.L.; Martín-Albo, J.; Navarro, J.G. Validación de la versión española de la Échelle de Motivation en Éducation. Psicothema 2005, 17, 344–349. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Seva, U.; Van Ginkel, J.R. Imputación múltiple de valores perdidos en el análisis factorial exploratorio de escalas multidimensionales: Estimación de las puntuaciones de rasgos latentes. Ann. Psychol. 2016, 32, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling; Guildford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P.; Castillo Apraiz, J.; Cepeda Carrión, G.A.; Roldán, J.L. Manual Avanzado de Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); OmniaScience: Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. Issues and Opinion on Structural Equation Modeling. MIS Q. 1998, 22, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ricalde, C.D.L.; López-Hernández, E.S.; Peniche, I.A. Desarrollo sustentable o sostenible: Una definición conceptual. Horiz. Sanit. 2005, 4. Available online: https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/4578/457845044002.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Martínez Ávila, M.; Fierro Moreno, E. Aplicación de la técnica PLS-SEM en la gestión del conocimiento: Un enfoque técnico práctico. Rev. Iberoam. Para Investig. Desarro. Educ. 2018, 8, 130–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez-Asis, E.; Espinoza Maguiña, M.; Esquivel Infantes, S.; Naranjo-Toro, M. Inteligencia emocional, competencias y desempeño del docente universitario: Aplicando la técnica mínimos cuadrados parciales SEM-PLS. Rev. Electrónica Interuniv. Form. Profr. 2020, 23, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jossberger, H.; Brand-Gruwel, S.; Van de Wiel, M.W.; Boshuizen, H.P. Exploring Students’ Self-Regulated Learning in Vocational Education and Training. Vocat. Learn. 2019, 13, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutner, D.; Barthel, A.; Schreiber, B. Students can learn to motivate themselves for learning-A training experiment. Z. Fur. Padagog. Psychol. 2001, 15, 155–167. [Google Scholar]
- Meza, A. Estrategias de aprendizaje. Definiciones, clasificaciones e instrumentos de medición. Propósitos Represent. 2013, 1, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo-Delgado, M.; León-Del-Barco, B.; Mendo-Lázaro, S. Good Practices and Learning Strategies of Undergraduate University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, A.; Lizaso, I.; Iturbe, I. Learning strategies and reasoning skills of university students. Rev. Psicodidáctica 2018, 23, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, N.; Corral, J.; Mata, A. Assessment of the Development of Professional Skills in University Students: Sustainability and Serious Games. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.C. The pro-environmental behavior patterns of college students adapting to climate change. J. Balt. Sci. Educ. 2021, 20, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsóka, Á.; Szerényi, Z.M.; Széchy, A.; Kocsis, T. Greening due to environmental education? Environmental knowledge, attitudes, consumer behavior and everyday pro-environmental activities of Hungarian high school and university students. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 48, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, L. Effects of aviation service commander career selection motivation on autonomy, social support, and adaptation in the university environment. Tour. Manag. Res. 2019, 23, 647–671. [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo, E.M.; Expósito, J.; Romero, J.J.; Pistón, M.D.; Parejo, N. Motivation for Learning among Students Undertaking Basic Vocational Training and University Studies within the Context of COVID-19. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perander, K.; Londen, M.; Holm, G. Supporting students’ transition to higher education. J. Appl. Res. High. Educ. 2021, 13, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Padial-Ruz, R.; González-Valero, G.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Puertas-Molero, P. Motivación y estrategias de aprendizaje en estudiantes de grado en Educación Primaria: Análisis según factores académicos y hábitos saludables. Sportis. Sci. J. Sch. Sport Phys. Educ. Psychomot. 2019, 5, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llauró, A.; Fonseca, D.; Villegas, E.; Aláez, M.; Romero, S. Educational data mining application for improving the academic tutorial sessions, and the reduction of early dropout in undergraduate students. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Technological Ecosystems for Enhancing Multiculturality, Barcelona, Spain, 26–29 October 2021; pp. 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.J.; Rasheed, S. Moderating role of learning strategies between meta-cognitive awareness and study habits among university students. Pak. J. Psychol. Res. 2019, 34, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto Márquez, N.; García-Sinausia, S.; Pérez Nieto, M.A. Relaciones de la motivación con la metacognición y el desempeño en el rendimiento cognitive en estudiantes de educación primaria. An. Psicol. 2021, 37, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Yao, M.; Zhang, X. The dampening effects of perceived teacher enthusiasm on class-related boredom: The mediating role of perceived autonomy support and task value. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, M.; Ono, Y. Estudio sobre estrategias de aprendizaje en educación física en la escuela primaria. Rev. Educ. Física Y Deporte 2021, 20, 3211–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Magen-Nagar, N. Los efectos de las estretagias de aprendizaje en la competencia matemática: Una comparación entre países de bajo y alto rendimiento. Rev. Int. Investig. Educ. Cienc. 2016, 2, 306–321. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.W.; Reynolds, B.L. Un studio sobre la relación entre el uso de la estrategia de escritura EFL de los estudiantes universitarios taiwaneses, la capacidad de escritura y la dificultad de escritura. Enseñanza Aprendiz. Inglés 2017, 41, 31–67. [Google Scholar]

| Latent Factor | Indicator | α | ω | Estimate | SE | Z | p | β | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive and learning control strategies | Item 8 | 0.899 | 0.905 | 0.740 | 0.0808 | 9.17 | <0.001 | 0.594 | 0.541 | 0.885 |
| Item 9 | 0.899 | 0.905 | 0.793 | 0.0863 | 9.19 | <0.001 | 0.595 | |||
| Item 10 | 0.900 | 0.905 | 0.882 | 0.0955 | 9.24 | <0.001 | 0.597 | |||
| Item 11 | 0.898 | 0.903 | 0.767 | 0.0702 | 10.92 | <0.001 | 0.681 | |||
| Item 12 | 0.898 | 0.903 | 0.726 | 0.0665 | 10.91 | <0.001 | 0.680 | |||
| Item 13 | 0.897 | 0.902 | 0.812 | 0.0711 | 11.42 | <0.001 | 0.703 | |||
| Item 14 | 0.894 | 0.899 | 0.921 | 0.0657 | 14.02 | <0.001 | 0.812 | |||
| Item 16 | 0.899 | 0.905 | 0.830 | 0.0915 | 9.07 | <0.001 | 0.588 | |||
| Item 17 | 0.900 | 0.905 | 0.710 | 0.0773 | 9.19 | <0.001 | 0.595 | |||
| Item 18 | 0.899 | 0.905 | 0.813 | 0.0842 | 9.66 | <0.001 | 0.619 | |||
| Item 6 | 0.900 | 0.905 | 0.745 | 0.0839 | 8.87 | <0.001 | 0.577 | |||
| Learning support strategies | Item 27 | 0.898 | 0.904 | 0.742 | 0.0770 | 9.64 | <0.001 | 0.631 | 0.604 | 0.835 |
| Item 34 | 0.898 | 0.904 | 0.816 | 0.0697 | 11.72 | <0.001 | 0.729 | |||
| Item 35 | 0.901 | 0.906 | 0.730 | 0.0709 | 10.30 | <0.001 | 0.662 | |||
| Item 36 | 0.899 | 0.903 | 0.773 | 0.0592 | 13.07 | <0.001 | 0.789 | |||
| Item 37 | 0.900 | 0.905 | 0.664 | 0.0569 | 11.67 | <0.001 | 0.728 | |||
| Study habits | Item 40 | 0.902 | 0.907 | 1.592 | 0.1374 | 11.59 | <0.001 | 1.086 | 0.838 | 0.908 |
| Item 41 | 0.905 | 0.910 | 0.971 | 0.1100 | 8.83 | <0.001 | 0.705 |
| Latent Factor | Indicator | α | ω | Estimate | SE | Z | p | β | AVE | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amotivation | Item 5 | 0.872 | 0.885 | 1.165 | 0.0734 | 15.9 | <0.001 | 0.871 | 0.752 | 0.924 |
| Item 19 | 0.869 | 0.883 | 1.312 | 0.0827 | 15.9 | <0.001 | 0.870 | |||
| Item 26 | 0.871 | 0.884 | 1.360 | 0.0798 | 17.0 | <0.001 | 0.909 | |||
| Item 12 | 0.871 | 0.884 | 1.252 | 0.0873 | 14.3 | <0.001 | 0.816 | |||
| External regulation | Item 8 | 0.858 | 0.872 | 1.138 | 0.0857 | 13.3 | <0.001 | 0.796 | 0.653 | 0.849 |
| Item 15 | 0.860 | 0.875 | 1.016 | 0.0798 | 12.7 | <0.001 | 0.767 | |||
| Item 22 | 0.856 | 0.872 | 1.443 | 0.0973 | 14.8 | <0.001 | 0.859 | |||
| Introjected regulation | Item 7 | 0.854 | 0.869 | 1.237 | 0.0982 | 12.6 | <0.001 | 0.760 | 0.557 | 0.834 |
| Item 14 | 0.854 | 0.870 | 1.126 | 0.1019 | 11.0 | <0.001 | 0.690 | |||
| Item 21 | 0.852 | 0.868 | 1.165 | 0.0981 | 11.9 | <0.001 | 0.732 | |||
| Item 28 | 0.853 | 0.867 | 1.187 | 0.0880 | 13.5 | <0.001 | 0.799 | |||
| Identified regulation | Item 17 | 0.861 | 0.874 | 0.890 | 0.0871 | 10.2 | <0.001 | 0.670 | 0.528 | 0.690 |
| Item 24 | 0.860 | 0.872 | 0.930 | 0.0772 | 12.1 | <0.001 | 0.779 | |||
| Knowledge | Item 9 | 0.858 | 0.870 | 0.963 | 0.0704 | 13.7 | <0.001 | 0.807 | 0.648 | 0.846 |
| Item 16 | 0.859 | 0.871 | 1.071 | 0.0759 | 14.1 | <0.001 | 0.828 | |||
| Item 23 | 0.859 | 0.871 | 0.982 | 0.0762 | 12.9 | <0.001 | 0.778 | |||
| Achievement | Item 6 | 0.856 | 0.868 | 1.118 | 0.0804 | 13.9 | <0.001 | 0.825 | 0.694 | 0.819 |
| Item 13 | 0.859 | 0.870 | 1.052 | 0.0737 | 14.3 | <0.001 | 0.841 | |||
| Stimulating experiences | Item 11 | 0.866 | 0.879 | 1.190 | 0.0933 | 12.8 | <0.001 | 0.797 | 0.729 | 0.842 |
| Item 18 | 0.862 | 0.876 | 1.373 | 0.0921 | 14.9 | <0.001 | 0.906 |
| Variable | α | Composite Reliability Index (IFC) | Rho_A | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amotivation | 0.923 | 0.945 | 0.948 | 0.812 |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies | 0.921 | 0.930 | 0.925 | 0.551 |
| Extrinsic motivation | 0.781 | 0.864 | 0.897 | 0.679 |
| Intrinsic motivation | 0.771 | 0.862 | 0.852 | 0.680 |
| Learning support strategies | 0.867 | 0.891 | 0.875 | 0.509 |
| Study habits | 0.764 | 0.842 | 0.774 | 0.520 |
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amotivation | 0.901 | |||||
| Cognitive and learning control strategies | −0.194 | 0.592 | ||||
| Extrinsic motivation | −0.093 | 0.362 | 0.824 | |||
| Intrinsic motivation | −0.201 | 0.501 | 0.627 | 0.825 | ||
| Learning support strategies | −0.304 | 0.748 | 0.428 | 0.595 | 0.640 | |
| Study habits | −0.099 | 0.561 | 0.263 | 0.397 | 0.564 | 0.721 |
| Variable | Amotivation | Cognitive and Learning Control Strategies | Extrinsic Motivation | Intrinsic Motivation | Learning Support Strategies | Study Habits |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amotivation | 0.867 | −0.166 | −0.068 | −0.171 | −0.242 | −0.078 |
| 0.899 | −0.155 | −0.028 | −0.107 | −0.237 | −0.029 | |
| 0.917 | −0.161 | −0.095 | −0.177 | −0.246 | −0.099 | |
| 0.920 | −0.206 | −0.129 | −0.246 | −0.344 | −0.136 | |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies | −0.026 | 0.536 | 0.150 | 0.212 | 0.356 | 0.314 |
| −0.096 | 0.650 | 0.261 | 0.294 | 0.455 | 0.325 | |
| −0.096 | 0.665 | 0.221 | 0.245 | 0.459 | 0.347 | |
| −0.153 | 0.738 | 0.272 | 0.419 | 0.521 | 0.401 | |
| −0.124 | 0.776 | 0.306 | 0.347 | 0.598 | 0.415 | |
| 0.008 | 0.620 | 0.236 | 0.355 | 0.457 | 0.425 | |
| −0.111 | 0.582 | 0.206 | 0.273 | 0.431 | 0.320 | |
| −0.029 | 0.626 | 0.242 | 0.353 | 0.471 | 0.304 | |
| −0.180 | 0.619 | 0.255 | 0.317 | 0.459 | 0.318 | |
| −0.128 | 0.595 | 0.278 | 0.292 | 0.443 | 0.294 | |
| −0.131 | 0.584 | 0.219 | 0.302 | 0.452 | 0.294 | |
| Extrinsic motivation | ||||||
| External regulation | 0.108 | 0.199 | 0.784 | 0.284 | 0.243 | 0.140 |
| Identified regulation | −0.272 | 0.416 | 0.882 | 0.611 | 0.466 | 0.285 |
| Introjected regulation | 0.098 | 0.197 | 0.803 | 0.590 | 0.270 | 0.176 |
| Intrinsic motivation | ||||||
| Knowledge | −0.215 | 0.474 | 0.588 | 0.914 | 0.564 | 0.354 |
| Stimulating experiences | 0.058 | 0.210 | 0.223 | 0.661 | 0.255 | 0.211 |
| Achievement | −0.232 | 0.479 | 0.622 | 0.877 | 0.566 | 0.380 |
| Learning support strategies | −0.266 | 0.601 | 0.423 | 0.526 | 0.710 | 0.367 |
| −0.275 | 0.548 | 0.291 | 0.406 | 0.764 | 0.431 | |
| −0.204 | 0.521 | 0.261 | 0.347 | 0.658 | 0.302 | |
| −0.293 | 0.539 | 0.371 | 0.386 | 0.705 | 0.417 | |
| −0.209 | 0.497 | 0.259 | 0.379 | 0.673 | 0.392 | |
| Study habits | −0.062 | 0.444 | 0.183 | 0.298 | 0.493 | 0.795 |
| 0.031 | 0.350 | 0.123 | 0.207 | 0.313 | 0.813 |
| Relation between Variables | Path Coefficient (β) | Standard Deviation (σ) | Statistic t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cognitive and learning control strategies -> Amotivation | 0.045 | 0.098 | 0.457 | 0.648 | |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies -> Extrinsic motivation | 0.096 | 0.107 | 0.897 | 0.370 | |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies -> Intrinsic motivation | 0.105 | 0.093 | 1.122 | 0.263 | |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies -> Learning support strategies | 0.748 | 0.040 | 18.736 | *** | |
| Cognitive and learning control strategies -> Study habits | 0.561 | 0.056 | 10.009 | *** | |
| Learning support strategies -> Amotivation | −0.391 | 0.091 | 4.306 | *** | |
| Learning support strategies -> Extrinsic motivation | 0.356 | 0.090 | 3.946 | *** | |
| Learning support strategies -> Intrinsic motivation | 0.478 | 0.086 | 5.588 | *** | |
| Study habits -> Amotivation | 0.096 | 0.069 | 1.399 | 0.162 | |
| Study habits -> Intrinsic motivation | 0.069 | 0.068 | 1.012 | 0.312 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Navío, E.; Gavín-Chocano, Ó.; Checa-Domene, L.; Prieto, M.G.-V. Relationship between Learning Strategies and Motivation of University Students. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043497
Pérez-Navío E, Gavín-Chocano Ó, Checa-Domene L, Prieto MG-V. Relationship between Learning Strategies and Motivation of University Students. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043497
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Navío, Eufrasio, Óscar Gavín-Chocano, Lara Checa-Domene, and Marina García-Valdecasas Prieto. 2023. "Relationship between Learning Strategies and Motivation of University Students" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043497
APA StylePérez-Navío, E., Gavín-Chocano, Ó., Checa-Domene, L., & Prieto, M. G.-V. (2023). Relationship between Learning Strategies and Motivation of University Students. Sustainability, 15(4), 3497. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043497









