Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Data Background
3. Research Methods
3.1. Spatial Interpolation Method
3.2. Sludge Heavy Metal Pollution Index Method
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment Method of Heavy Metals in Sludge
4. Simulation and Results Analysis
4.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metals in Sludge
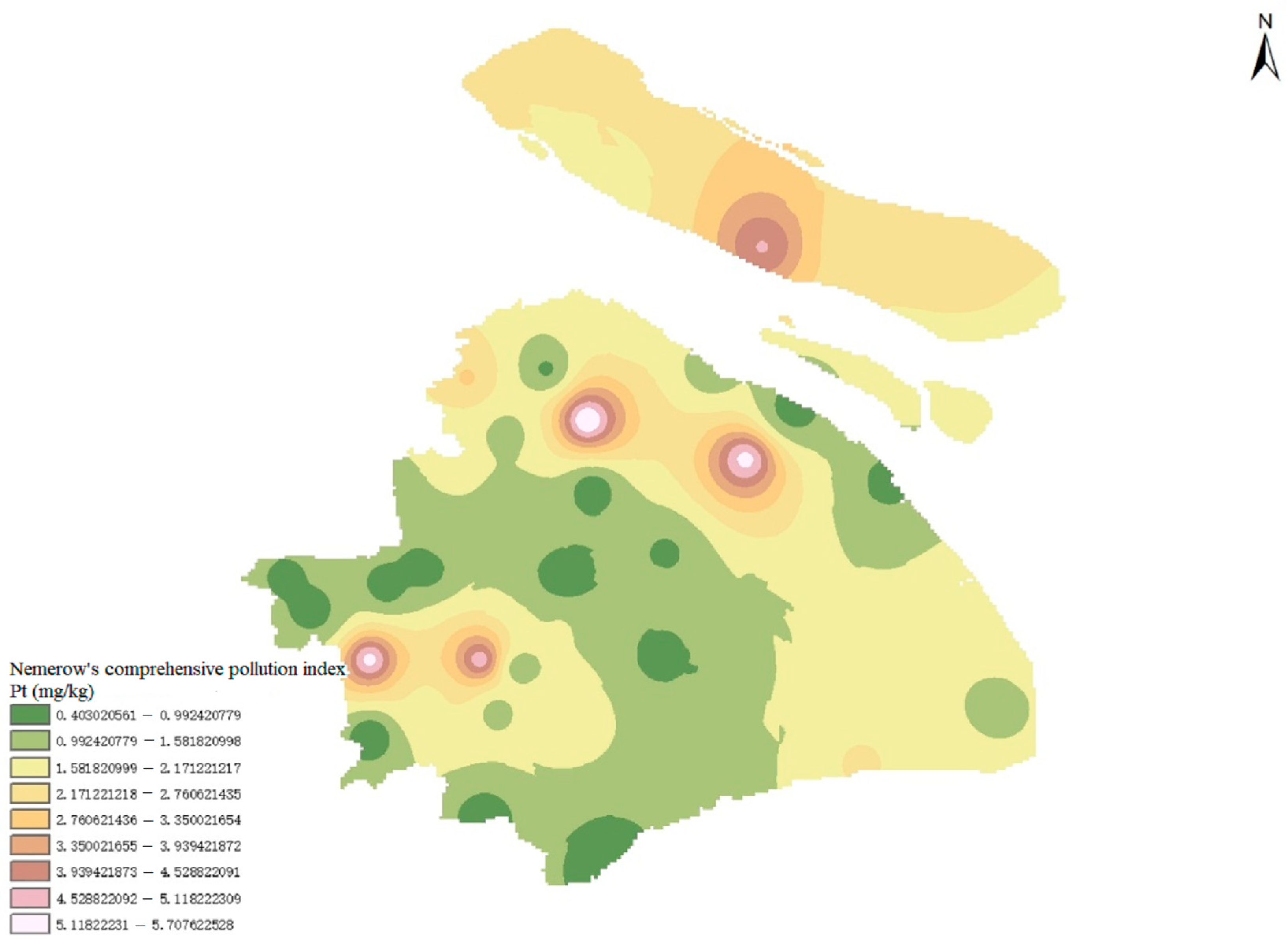
4.2. Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution of Sludge
4.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Propaganda Department of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (Ed.) Readings of General Secretary Xi Jinping’s Series of Important Speeches, 2016th ed.; People’s Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanhong, T.; Huanming, W. Research on performance evaluation of urban wastewater management: Current situation and outlook. J. Tongji Univ. 2017, 28, 94–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, E.; Davidson, C. Introduction to Engineering and the Environment; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhe, X.; Qingrui, Z.; Xuchun, L.; Xianfeng, H. A critical review on chemical analysis of heavy metal complexes in water/wastewater and the mechanism of treatment methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 131688. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaojie, M.; Jianguo, T.; Yue, Z. The transformation mechanism and usable value of sludge stabilization products from urban wastewater treatment plants revealed. Water Supply Drain. 2018, 54, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Ji, F.Y.; Li, J.J. Sludge treatment and disposal and new technologies for resource utilization. Water Supply Drain. 2016, 52, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Yuanmeng, G.; Chuanbing, Z.; Yong, Z.; Doudou, H.; Shuxiao, Y.; Tengfei, S.; Liu, C.; Jing, W.; Yuxiang, M. Speciation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in the municipal sewage sludge of China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4834–4843. [Google Scholar]
- Qingfang, L.; Jing, Y.; Xiaorong, H.; Yongjiang, Z.; Xianliang, L.; Weihua, S.; Xiangbing, W. Ecological risk evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the sludge of Qianjiang District wastewater treatment plant. J. Southwest. Univ. 2019, 41, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Jing, C.; Xuesong, J.; Hengzhen, Q.; Zhiming, B. Occurrence characterist and ecological risk assessment of organic pollutants in sewage sludge of Zibo city. Environ. Monit. China 2022, 38, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, S.-B.; Zhou, J.-L.; Zeng, Y.-Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Du, J.-Y.; Cao, A.-N. Characteristics and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of Minfeng County, Xinjiang. Arid. Zone Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Huang, H.J.; Lai, F.Y. Pollution hazards of heavy metals in sludge from Nanchang wastewater treatment plant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 2249–2259. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusheng, W.; Hongyan, L.; Li, R.; Junbo, Y.; Jiang, D. Characterization of heavy metal composition of urban sludge in Guizhou Province and evaluation of the risk of agricultural use. Yangtze River Basin Resour. Environ. 2014, 23, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Jiang, L.; Xing, W.; Qingqing, Z. Distribution of heavy metal forms in sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Guizhou Province and evaluation of their potential ecological risks. China Rural. Water Conserv. Hydropower 2016, 67–73, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Aizetz, M.T.; Mamuti, A.; Buyati, A.; Guofei, M. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk of oasis farmland soils in the Bosten Lake basin. J. Geogr. 2017, 72, 1680–1694. [Google Scholar]
- Bingbo, D.; Chao, T.; Youbin, S. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Hefei and its ecological risk evaluation. Environ. Pollut. Prev. 2015, 37, 46–51, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Yani, G.; Qingfang, L.; Ningning, Y.; Jie, D.; Jun, Z. Spatial distribution, sources and health risks of dust heavy metals in urban areas of Baoji City. Earth Environ. 2019, 47, 696–706. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Yu Yixuan Wang, L.J.; Han, J.B.; Tao, P. Analysis of heavy metal pollution of sludge from urban sewage treatment plants in coastal areas of China and its disposal. Environ. Sci. 2013, 34, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Yu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.Y. Heavy metal contamination in sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants and its characteristics. Environ. Sci. Res. 2010, 23, 696–702. [Google Scholar]
- Jiancheng, T.; Qingliang, Z.; Qianqian, Y. Morphological distribution of heavy metals in sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants in Northeast China and evaluation of their potential ecological risks. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.W.; Huanxin, W.; Jinjun, Z. Regional characteristics and changes of heavy metals and nutrients in urban sludge in China. China Environ. Sci. 2011, 31, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Jiangmin, S.; Qunqun, L.; Yanqing, S. Comparision of ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in dredged sediment treated by different methods. Environ. Eng. 2021, 39, 141–146+152. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.N.; Guo, X.M.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, X.L.; Miao, J.; He, W.L. Evaluation of heavy metal morphology and potential ecological risk in sludge from Luoyang urban wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Eng. 2017, 11, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Junxiao, L.; Chaokui, L.; Wisdom, Y. Kriging interpolation method based on ArcGIS and its application. Mapp. Bull. 2013, 87–90, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Guanjiu, H.; Sulan, C.; Xi, C.; Bo, C.; Jie, W.; Jinli, S.; Yunrui, G. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and ecological risk of sludge from chemical park sewage treatment plants in Jiangsu Province. Yangtze River Basin Resour. Environ. 2015, 24, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Yanyan, Y.; Jinxiang, L.; Yaping, L.; Yongchen, F.; Tong, C.; Zhaoying, L.; Gang, C. Analysis of heavy metal contamination status and potential ecological risk in sludge from urban wastewater treatment plants in Beijing. Environ. Pollut. Prev. 2019, 41, 1098–1102+1107. [Google Scholar]
- Shanghai Municipal People’s Government. Statistical Bulletin on National Economic and Social Development of Shanghai in 2018. (2019-03-01) [2019-06-17]. Available online: https://tjj.sh.gov.cn/tjgb/20191115/0014-1003219.html (accessed on 15 November 2019).
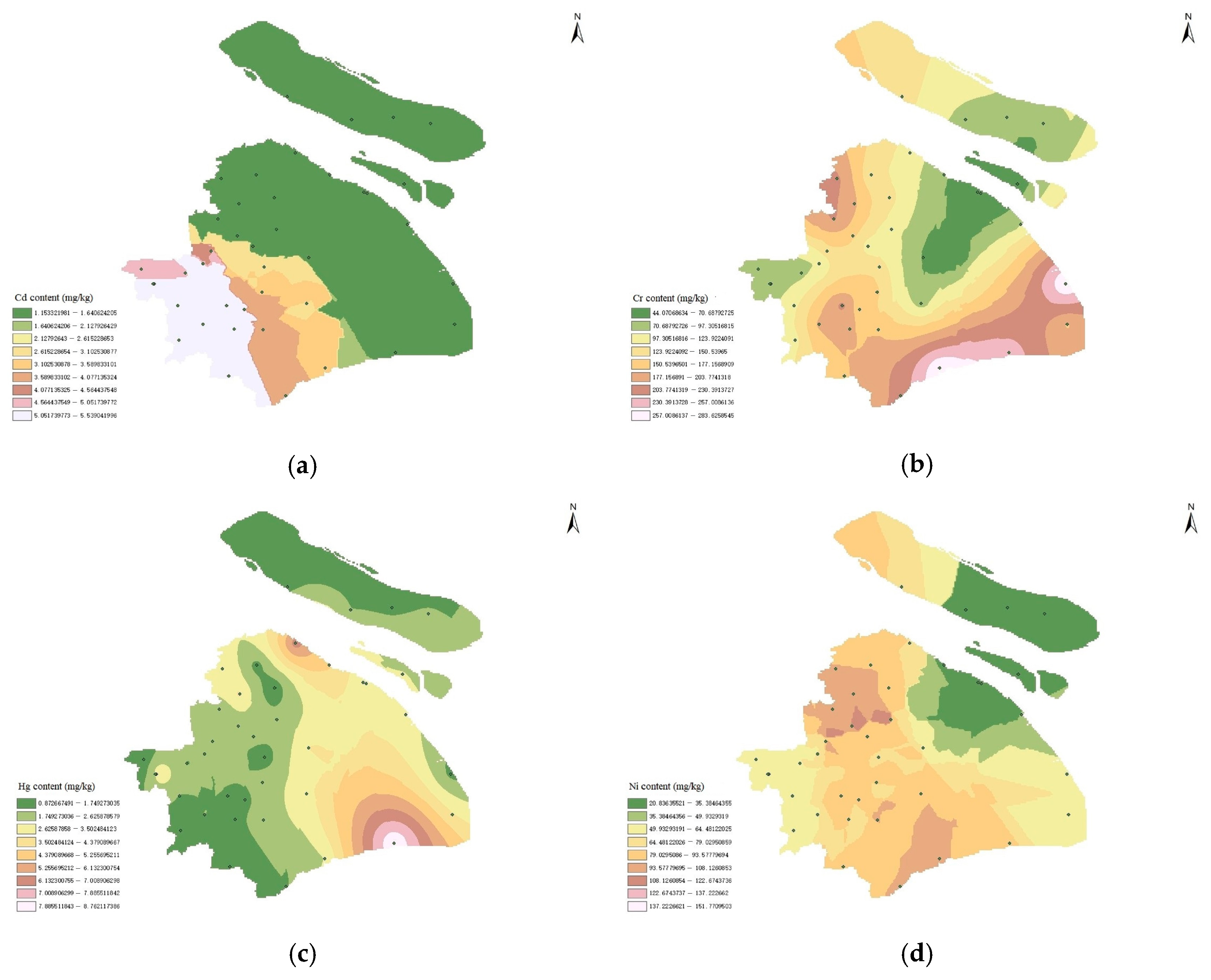
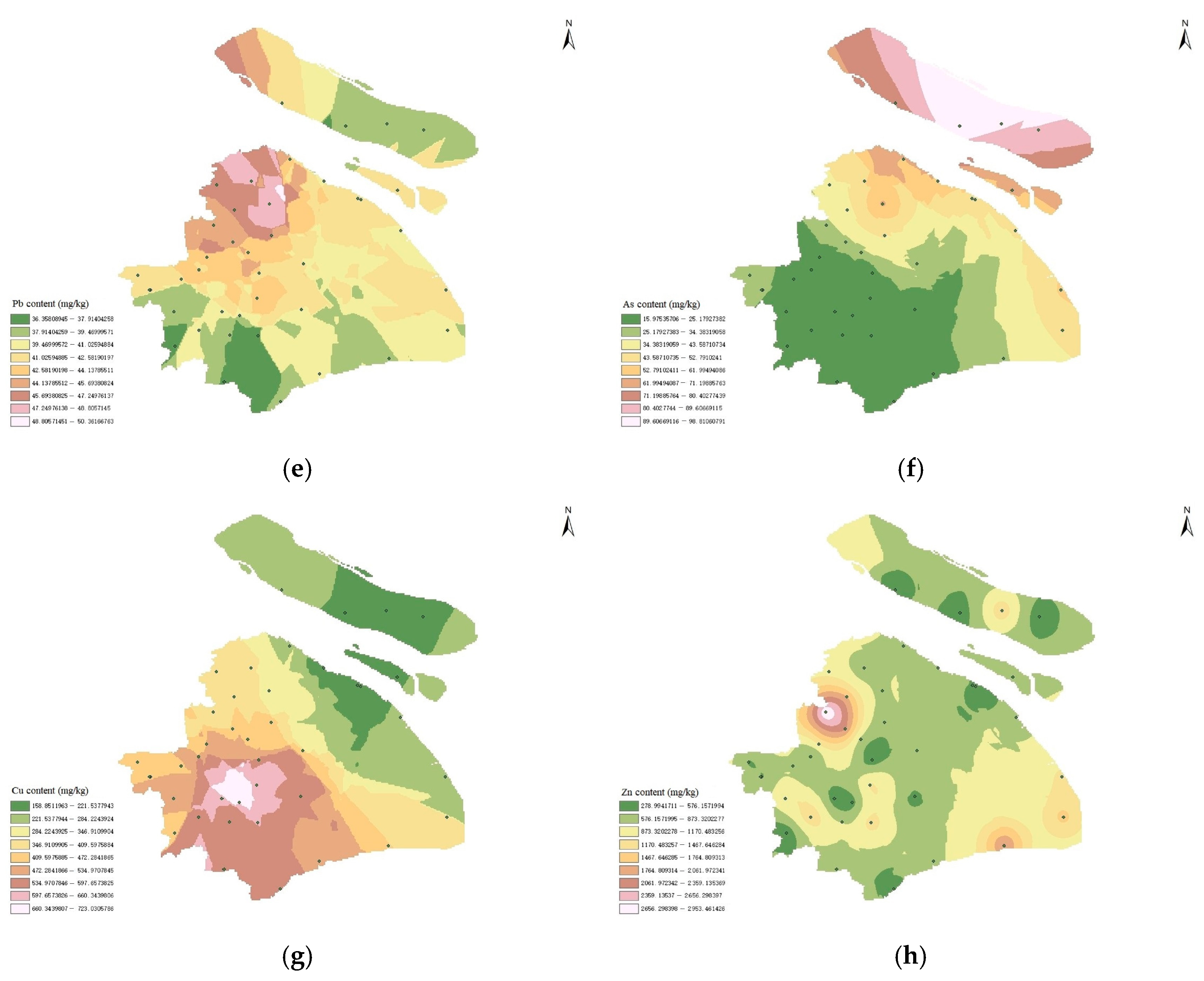
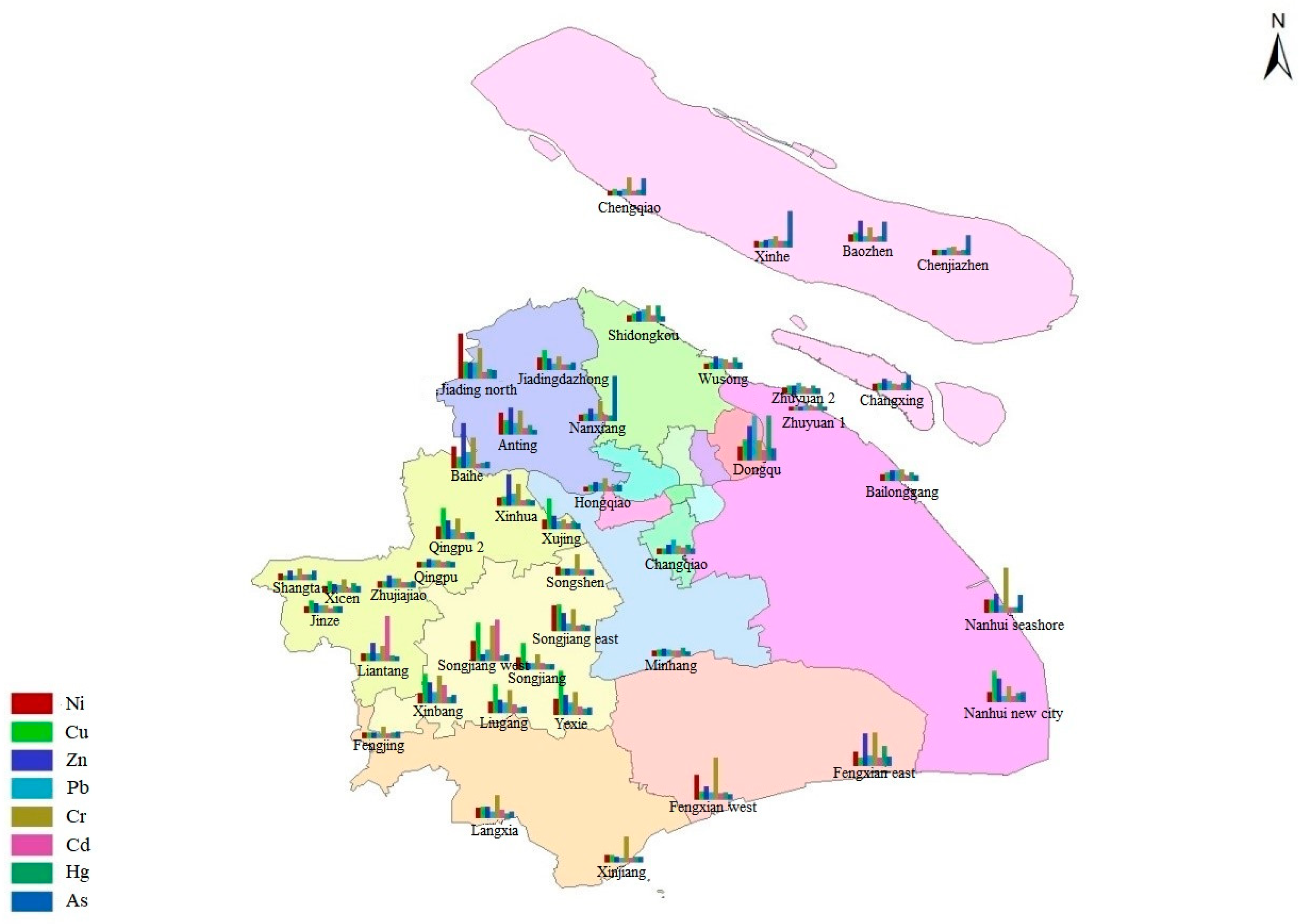
| Minimum Heavy Metal | Minimum | Maximum | Weighted Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.55 | 22.24 | 1.59 |
| Cr | 25.40 | 357.50 | 110.60 |
| Hg | 0.70 | 21.88 | 3.12 |
| Ni | 10.36 | 381.33 | 51.25 |
| Pb | 16.87 | 190.80 | 41.26 |
| As | 9.69 | 239.28 | 21.02 |
| Cu | 79.48 | 1383.33 | 278.33 |
| Zn | 258.00 | 2970.00 | 709.70 |
| Ni | Cu | Zn | Cr | Pb | Cd | Hg | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental quality | 100 | 500 | 1200 | 500 | 300 | 3 | 3 | 30 |
| Grade Classification | Pollution Index | Comprehensive Pollution Index | Pollution Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Security | ||
| 2 | Alert level | ||
| 3 | Light pollution | ||
| 4 | Moderate pollution | ||
| 5 | Severe pollution |
| Ni | Cu | Zn | Cr | Pb | Cd | Hg | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy metal toxicity response factor | 5 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 30 | 40 | 10 |
| Heavy metal evaluation reference values | 40 | 30 | 80 | 60 | 25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 15 |
| Degree of Potential Ecological Risk | ||
|---|---|---|
| Low | ||
| Mid | ||
| High | ||
| Very high | ||
| Strongly high |
| Sewage Treatment Plant | Comprehensive Pollution Index | Pollution Level |
|---|---|---|
| Langxia, Zhuyuan 2, Zhujiajiao, Fengting, Hongqiao, Fengjing, Qingpu, Xinjiang, Songshen, and Xingta. | Safety | |
| Jinze, Jiadingdazhong, Shangta, Changqiao, Minhang, Bailonggang, Zhuyuan 1, Xicen | Alert level | |
| Baihe, Changxing, Songjiang east, Shidongkou, Fengxian west, Lingang new city, Qingpu 2, Xujing, Liugang, Anting, Xinhua, Songjiang, and Wusong. | Mild pollution | |
| Jiading north, Baozhen, Chenjiazhen, Fengxian east, Nanhui seashore, Yexie, Xinbang, Chengqiao | Moderate pollution | |
| Nanxiang, Dongqu, Liantang, Songjiang west, and Xinhe. | Heavy pollution |
| Sewage Treatment Plant | Pollution Level | |
|---|---|---|
| Low | ||
| Shangta, Xingta | Mid | |
| Xujing, Huaxin, Xicen, Xinhe, Songjiang, Zhuyuan 2, Nanxiang, Baihe, Nanhui seashore, Chenjiazhen, Fengting, Qingpu, Baozhen, Jiadingdazhong, Zhujiajiao, Hongqiao, Langxia, Xinjiang, Chengqiao, Fengjing, and Songshen. | High | |
| Xinbang, Lingang new city, Wusong, Jiading north, Yexie, Anting, Jinze, Changqiao, Qingpu 2, Fengxian west, Songjiang east, Zhuyuan 1, Bailonggang, Minhang, Liugang, and Changxing. | Very high | |
| Dongqu, Songjiang west, Liantang, Fengxian east, and Shidongkou. | Strongly high |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043465
Zhang J, Xu X. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043465
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinling, and Xu Xu. 2023. "Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043465
APA StyleZhang, J., & Xu, X. (2023). Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Potential Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sludge of Shanghai Sewage Treatment Plant: A Case Study. Sustainability, 15(4), 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043465






