Influences of Flow Channel on Electrochemical Characteristics of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Humidified with NaCl Contained H2O
Abstract
1. Introduction
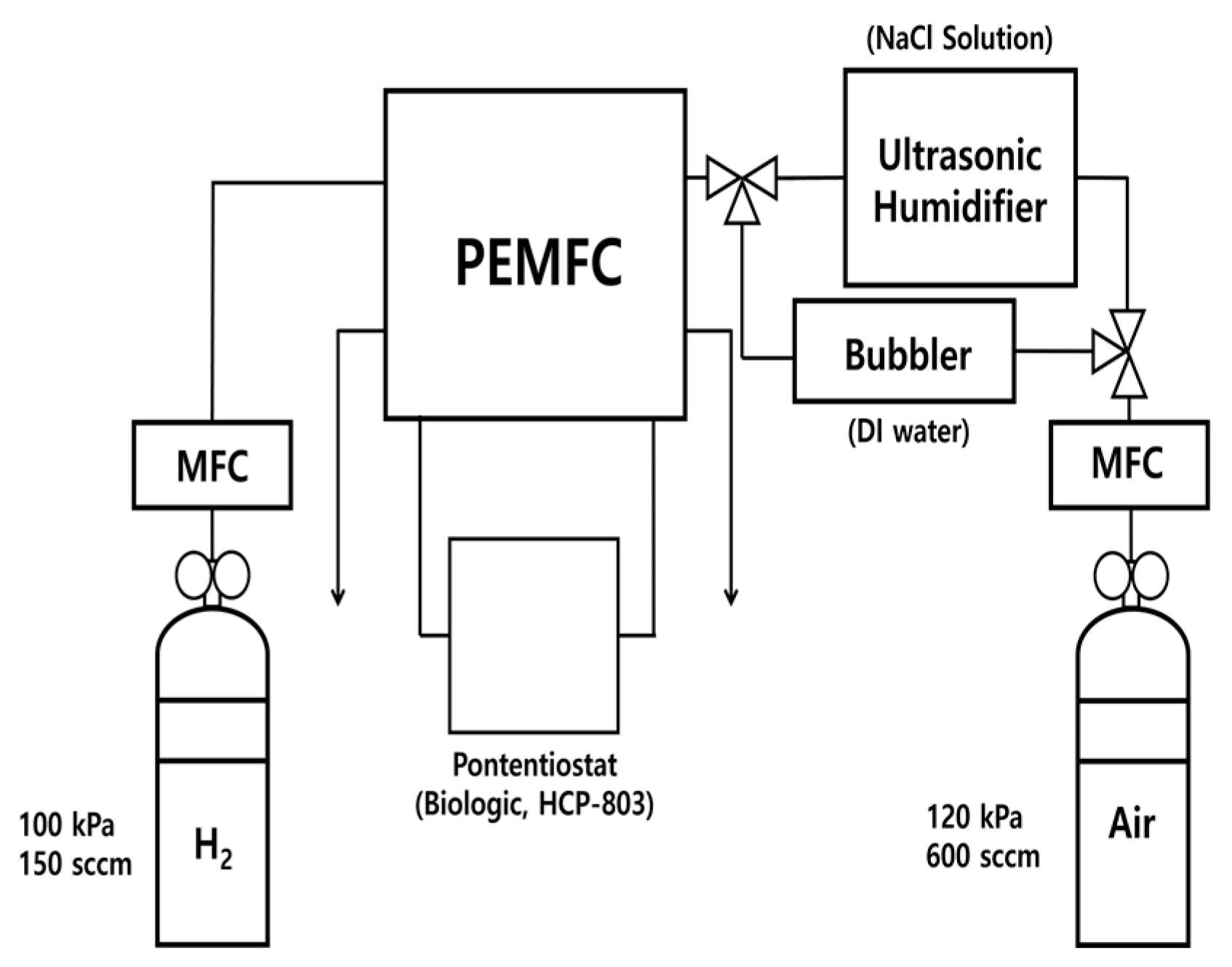
2. Experiments
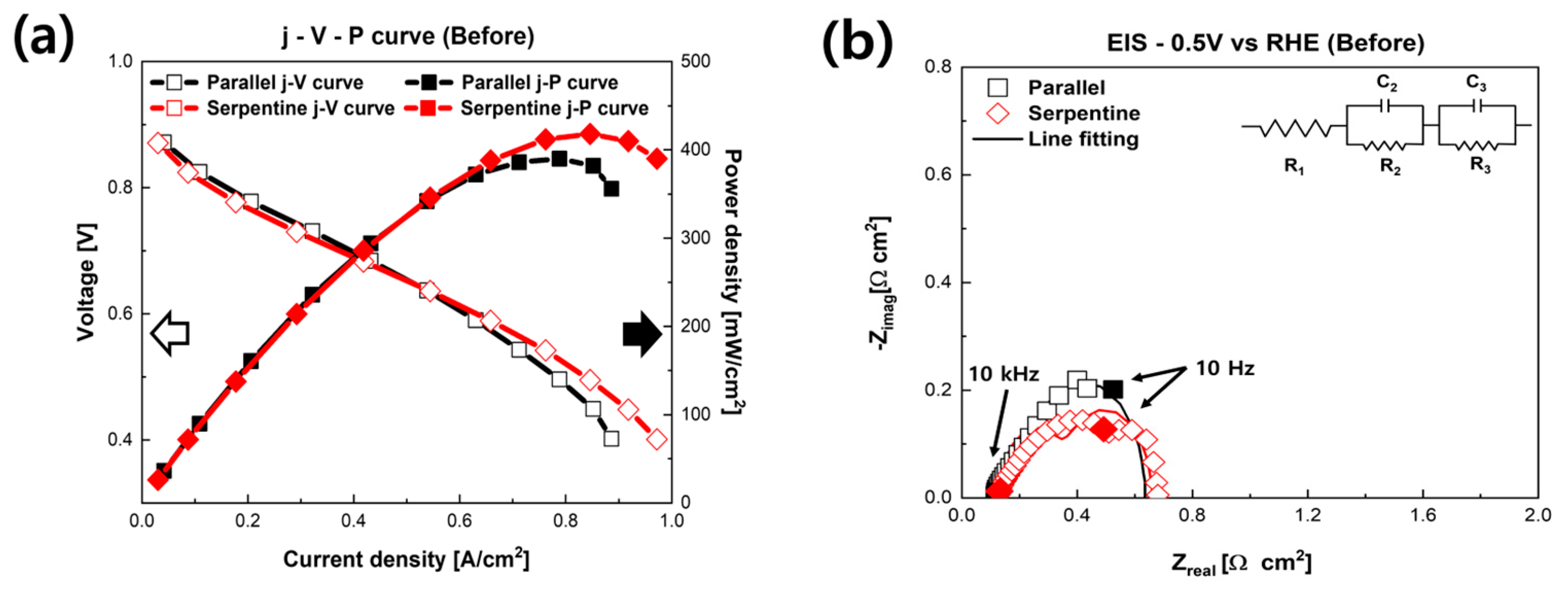
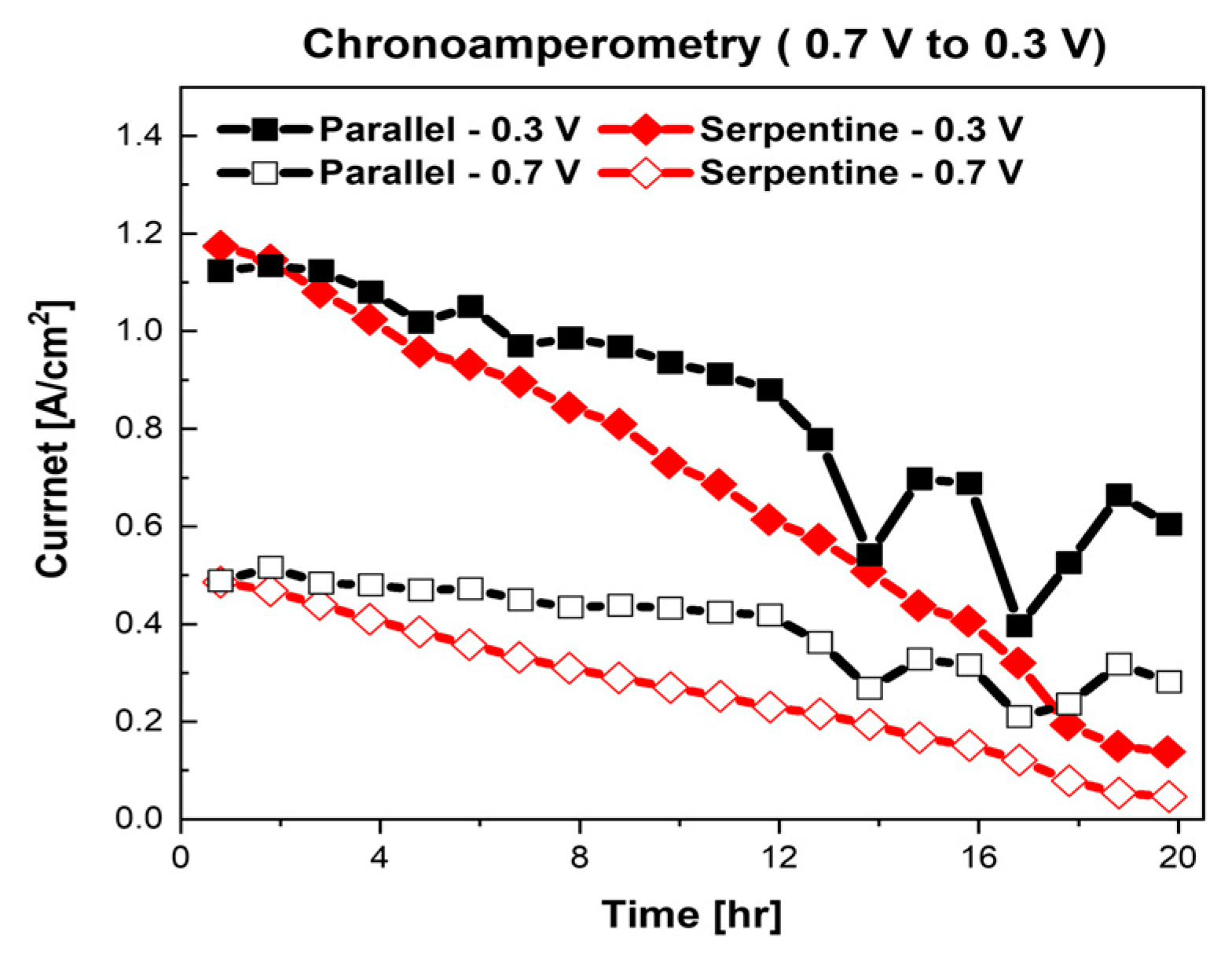
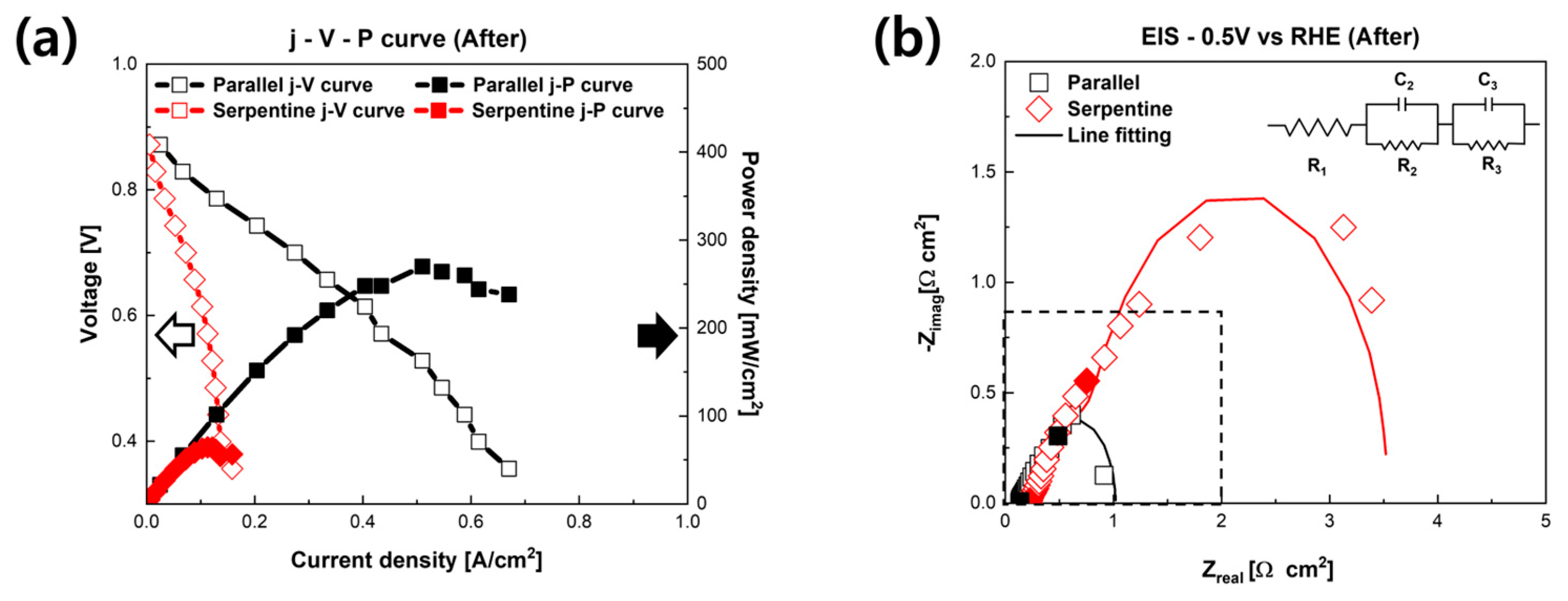
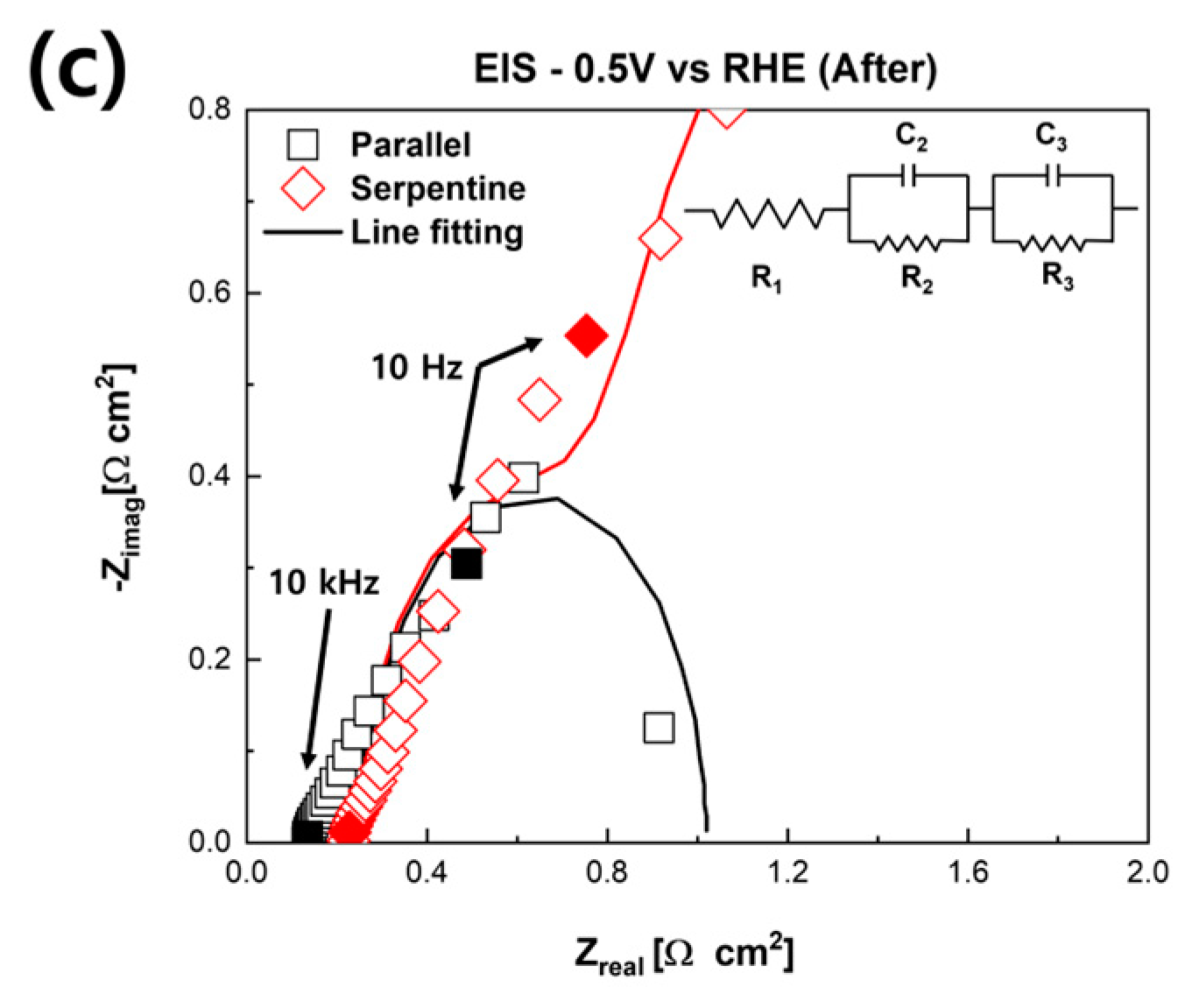
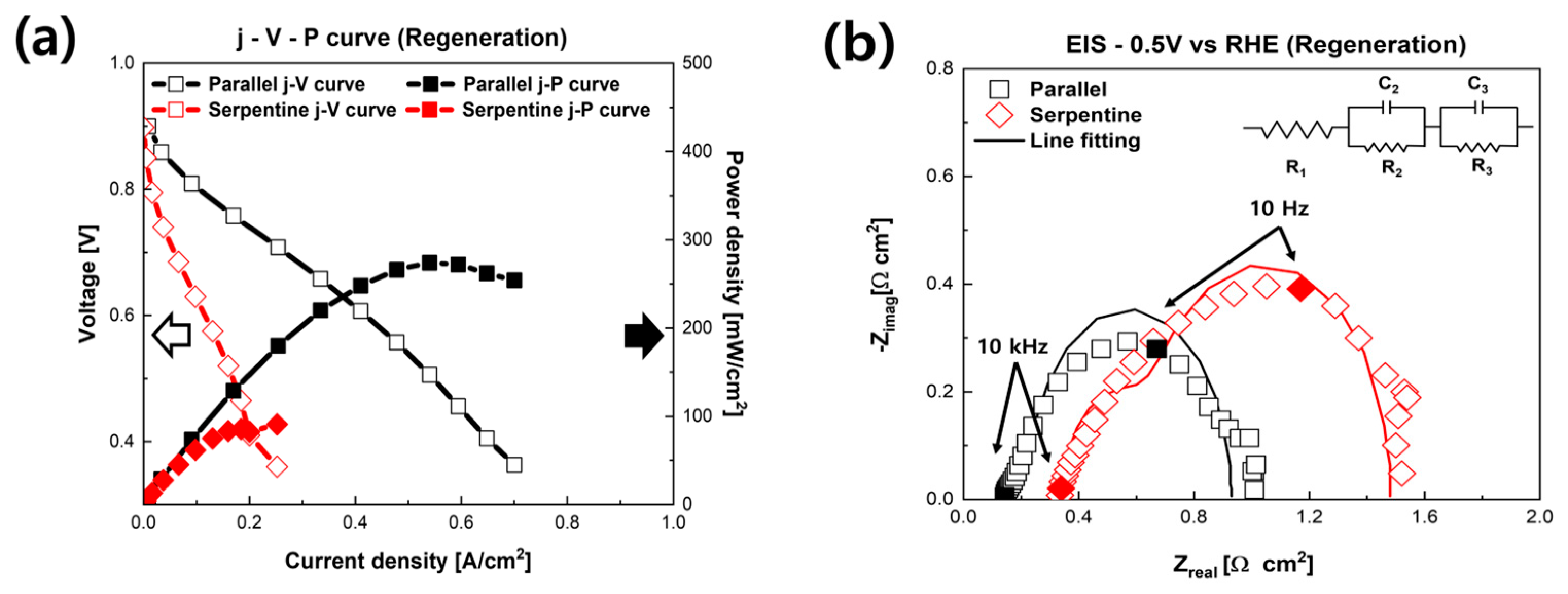
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Hayre, R.; Cha, S.-W.; Colella, W.; Prinz, F.B. Fuel Cell Fundamentals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costamagna, P.; Srinivasan, S. Quantum jumps in the PEMFC science and technology from the 1960s to the year 2000. J. Power Sources 2001, 102, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubakaran, A.; Jain, S.; Nema, R.K. A review on fuel cell technologies and power electronic interface. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.S.; Dubois, T.G.; Sifer, N.; Bostic, E.; Gardner, K.; Quah, M.; Bolton, C. Portable fuel cell systems for America’s army: Technology transition to the field. J. Power Sources 2004, 136, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Pan, M.; Wan, Z. Experimental investigation on the dynamic performance of a hybrid PEM fuel cell/battery system for lightweight electric vehicle application. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, N.-C.; Weng, B.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Hsiao, Y.-C. Development of a small fuel cell underwater vehicle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 11138–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.F.; An, L.; Wen, C.Y. Recent advances in fuel cells- based propulsion systems for unmanned aerial vehicles. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, M.; Kallo, J.; Friedrich, K.A.; Werner, C.; Saballus, M.; Gores, F. Multifunctional fuel cell system in an aircraft environment: An investigation focusing on fuel tank inerting and water generation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; You, Y.; Becker, S. Current technologies and challenges of applying fuel cell hybrid propulsion systems in unmanned aerial vehicles. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2020, 116, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Iqbal, S.; Naqvi, I.J.; Usman, M.; Ashiq, M.N.; Elnaggar, A.Y.; El-Bahy, Z.M. Highly dispersed active sites of Ni nanoparticles onto hierarchical reduced graphene oxide architecture towards efficient water oxidation. Fuel 2022, 312, 122926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Maqbool, A.; Hussain, M.A.; Pashameah, R.A.; Shahzadi, A.; Nazar, N.; Iqbal, S.; Alanazi, A.K.; Ashiq, M.N.; Abo-Dief, H.M. One-pot solvothermal synthesis of highly catalytic Janus transition metal phosphides (TMPs) for high per-formance OER. Fuel 2023, 331, 125913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetenko, T.V.; Bender, G.; Bethune, K.; Rocheleau, R. A segmented cell approach for studying the effects of serpentine flow field parameters on PEMFC current distribution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spernjak, D.; Prasad, A.K.; Advani, S.G. In situ comparison of water content and dynamics in parallel, single-serpentine, and interdigitated flow fields of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 3553–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Park, J.; Li, X. Experimental investigations on liquid water removal from the gas diffusion layer by reactant flow in a PEM fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2770–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.D.; Zhou, B. A general model of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2008, 182, 197–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, R.; Técher, L.; Cui, X. Experimental study of variable operating parameters effects on overall PEMFC performance and spatial performance distribution. Energy 2016, 115, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Kojima, K. Toyota MIRAI Fuel Cell Vehicle and Progress Toward a Future Hydrogen Society. Interface Mag. 2015, 24, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.T.; Sauriol, P.; Stumper, J. Two-phase flow distributors for fuel cell flow channels. Particuology 2010, 8, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddu, R.; Marupakula, U.K.; Summers, B.; Majumdar, P. Development of bipolar plates with different flow channel configurations for fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2009, 189, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.H.; Majlan, E.H.; Daud, W.R.W.; Husaini, T.; Rosli, M.I. Effects of flow field design on water management and reactant distribution in PEMFC: A review. Ionics 2016, 22, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misran, E.; Hassan, N.S.M.; Daud, W.R.W.; Majlan, E.H.; Rosli, M.I. Water transport characteristics of a PEM fuel cell at various operating pressures and temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Koh, J.S.; Kim, M.S.; Song, H.H. Experimental and computational study on the dynamic interaction be-tween load variation and back pressure control in a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell for automotive application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, P.; Juarez-Robles, D.; Wang, K.; Hernandez-Guerrero, A. Experimental Study and Comparison of Various De-signs of Gas Flow Fields to PEM Fuel Cells and Cell Stack Performance. Front. Energy Res. 2014, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sando, Y. Research and Development of Fuel Cell Vehicles at Honda. ECS Trans. 2009, 25, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larminie, J.; Dicks, A. Fuel Cell Systems Analysed, Fuel Cell Systems Explained; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.D.; Zhou, B. Fundamental understanding of liquid water effects on the performance of a PEMFC with serpentine-parallel channels. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2137–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-D.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Yan, W.-M. Novel serpentine-baffle flow field design for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, G.H.; Kwon, O.; Cha, H.; Choi, H.; Yoo, H.; Park, T. Mass diffusion characteristics on perfor-mance of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells with serpentine channels of different width. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 183, 122106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpalee, S.; Vanzee, J. Numerical studies on rib & channel dimension of flow-field on PEMFC performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Hemminger, J.C. Physical Chemistry of Airborne Sea Salt Particles and Their Components. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 11463–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Qian, W.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, X.Z.; Wang, H.; Jiang, M.; Wessel, S.; Cheng, T.T.H. Impacts of operating conditions on the effects of chloride contamination on PEM fuel cell performance and durability. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkola, M.S.; Rockward, T.; Uribe, F.A.; Pivovar, B.S. The Effect of NaCl in the Cathode Air Stream on PEMFC Performance. Fuel Cells 2007, 7, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.T.; Li, Q.; Pan, C.; Jensen, J.O.; Nielsen, L.P.; Møller, P. Effect of chloride impurities on the performance and durability of polybenzimidazole-based high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.-M.; Chu, H.-S.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, F.; Jang, J.-H. Effects of chlorides on the performance of proton exchange mem-brane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 5435–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Farro, W. Influence of seawater and its aerosols on copper patina composition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 10072–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carton, J.G.; Olabi, A.G. Design of experiment study of the parameters that affect performance of three flow plate con-figurations of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energy 2010, 35, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahad, H.A.; Alawee, W.H.; Hassan, A.K. Experimental study of the effect of flow field design to PEM fuel cells performance. Renew. Energy Focus 2019, 30, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, F.; Rahman, M.A.; Mora, J.M.; Ocon, J.D.; Chuang, P.Y.A. Experimental Study of Three Channel Designs with Model Comparison in a PEM Fuel Cell. Fuel Cells 2020, 20, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, M.; Karthikeyan, P.; Muthukumar, M.; Kannan, V.M.; Thanarajan, K.; Maiyalagan, T.; Hong, C.W.; Jothi, V.R.; Yi, S.C. Adoption of novel porous inserts in the flow channel of pem fuel cell for the mitigation of cathodic flooding. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 7863–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, H.; Kermani, M.J.; Advani, S.G.; Prasad, A.K. Experimental investigation of in-line and staggered blockages in parallel flowfield channels of PEM fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 6885–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Hwang, S.S. Performance Characteristics of a PEM Fuel Cell with Parallel Flow Channels at Different Cath-ode Relative Humidity Levels. Sensors 2009, 11, 9104–9121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Canut, J.-M.; Abouatallah, R.M.; Harrington, D.A. Detection of Membrane Drying, Fuel Cell Flooding, and Anode Catalyst Poisoning on PEMFC Stacks by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Kwon, O.; Yoo, H.; Kim, H.; Cha, H.; Park, T. Observation of flooding-induced performance enhancement in PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 6259–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, H.J.; Cho, G.Y. Influences of Flow Channel on Electrochemical Characteristics of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Humidified with NaCl Contained H2O. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032415
Yoo HJ, Cho GY. Influences of Flow Channel on Electrochemical Characteristics of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Humidified with NaCl Contained H2O. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032415
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Ho Jun, and Gu Young Cho. 2023. "Influences of Flow Channel on Electrochemical Characteristics of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Humidified with NaCl Contained H2O" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032415
APA StyleYoo, H. J., & Cho, G. Y. (2023). Influences of Flow Channel on Electrochemical Characteristics of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells Humidified with NaCl Contained H2O. Sustainability, 15(3), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032415






