Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
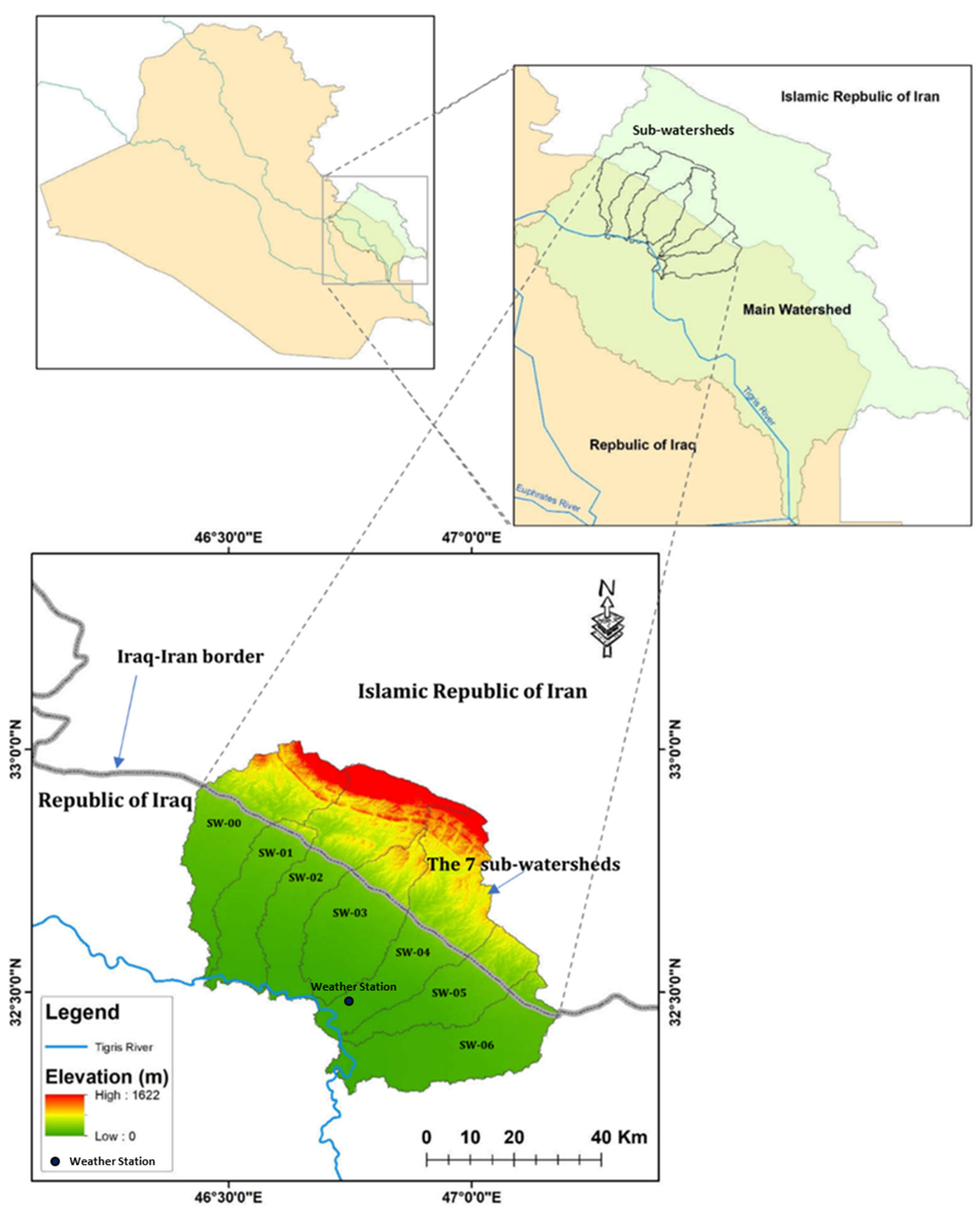
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Techniques and Data Used
3. Results
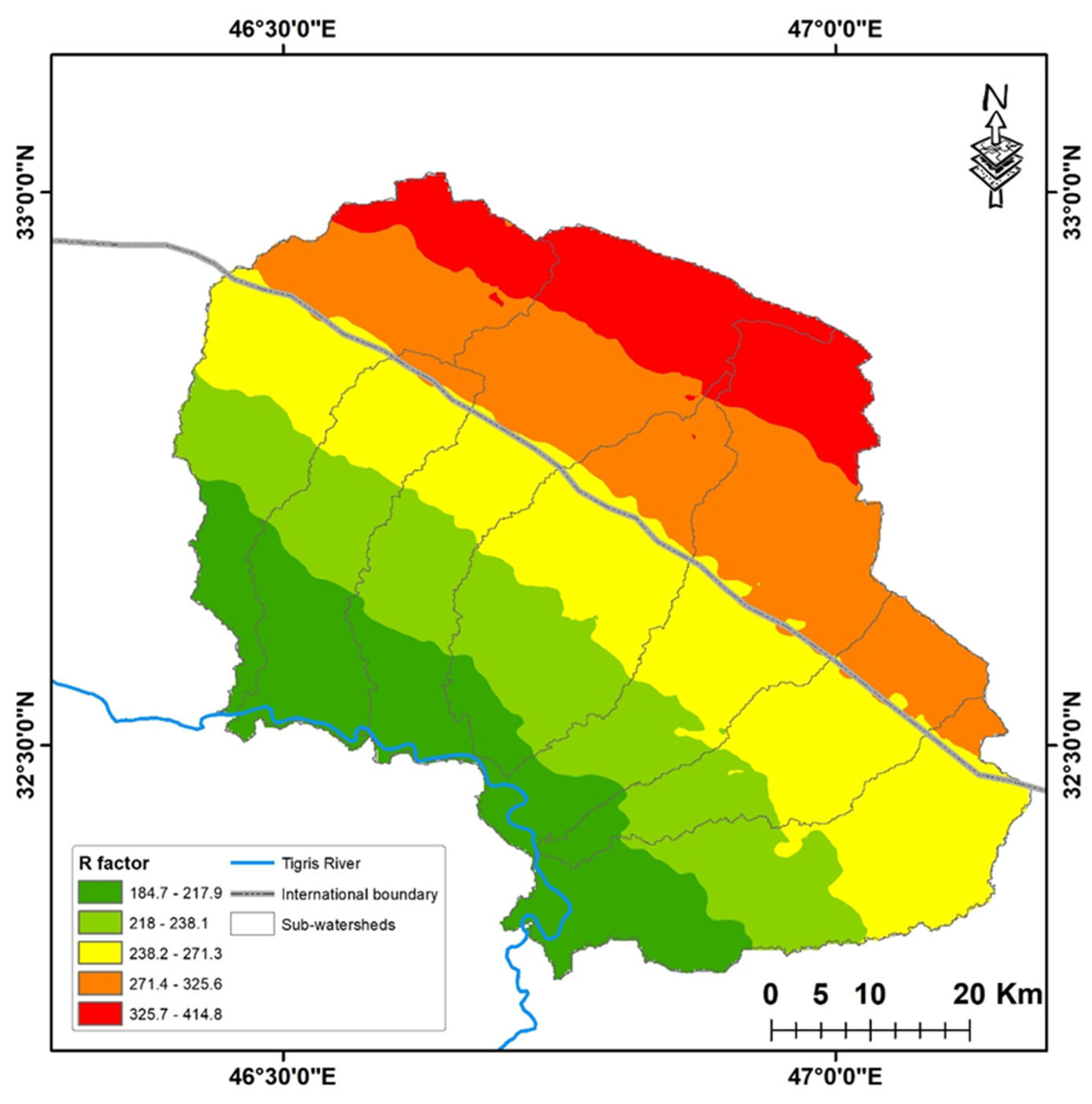
3.1. Rainfall Erosivity (R)
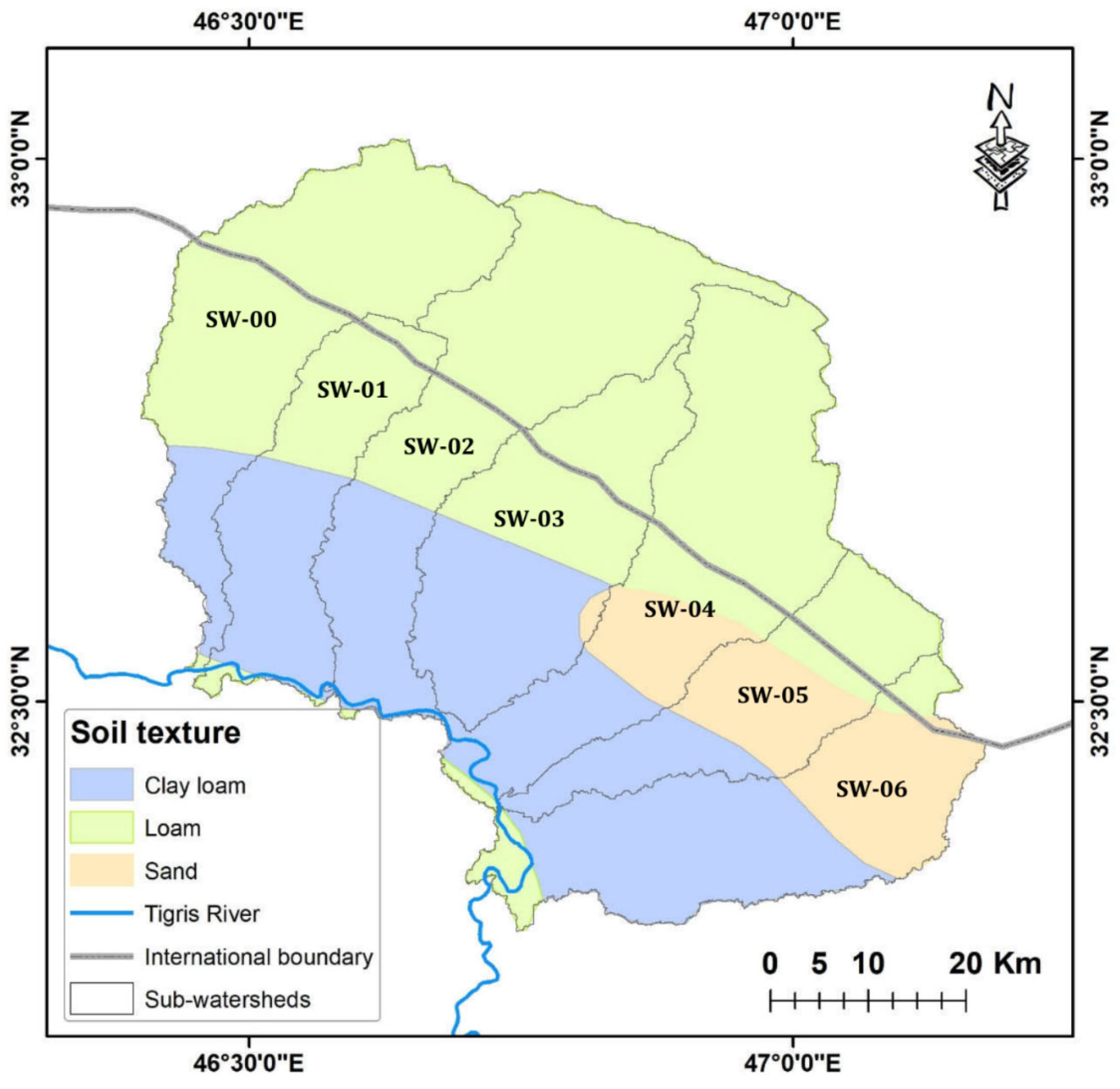
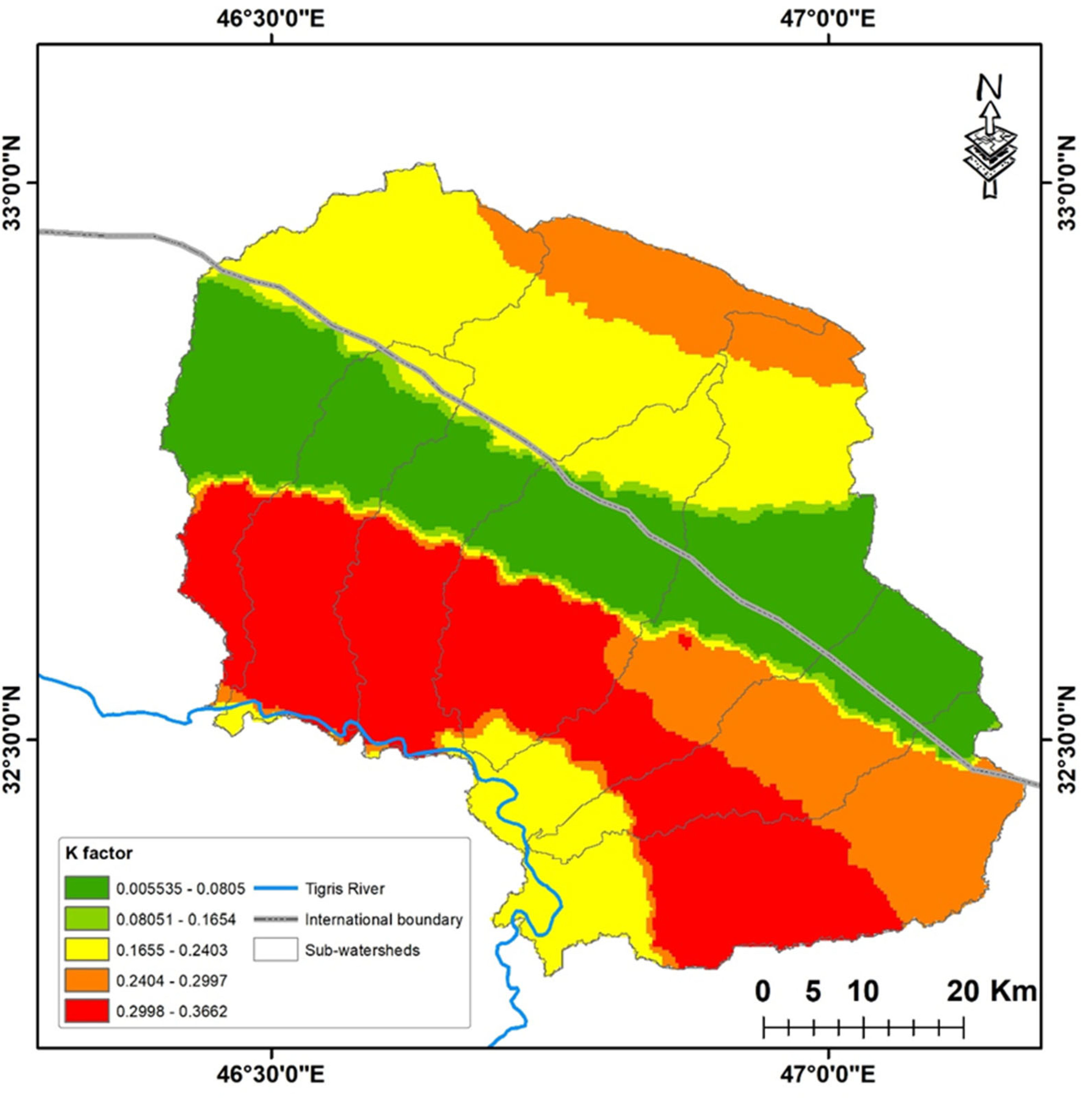
3.2. Soil Erodibility (K)
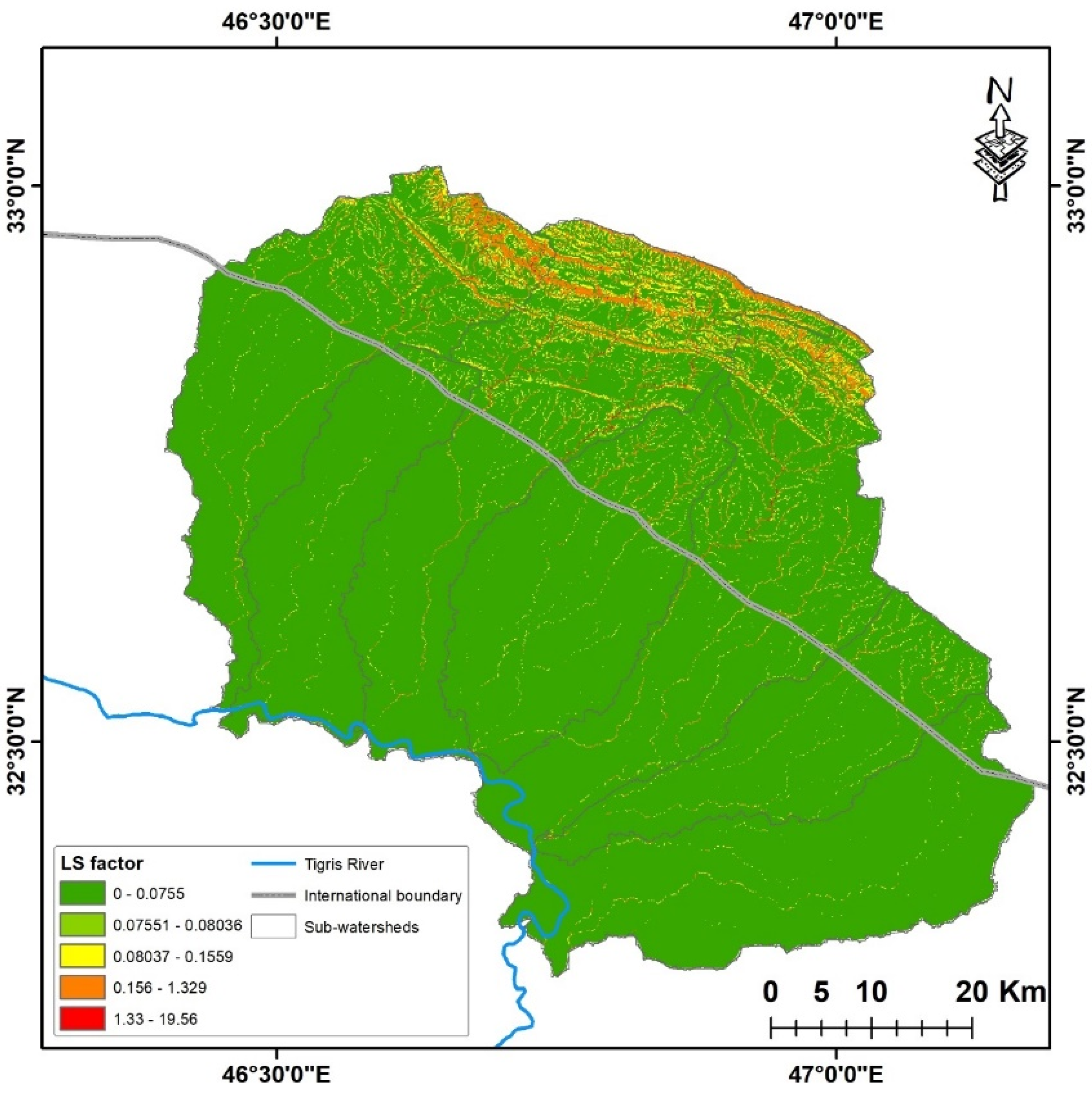
3.3. Topographic Factor
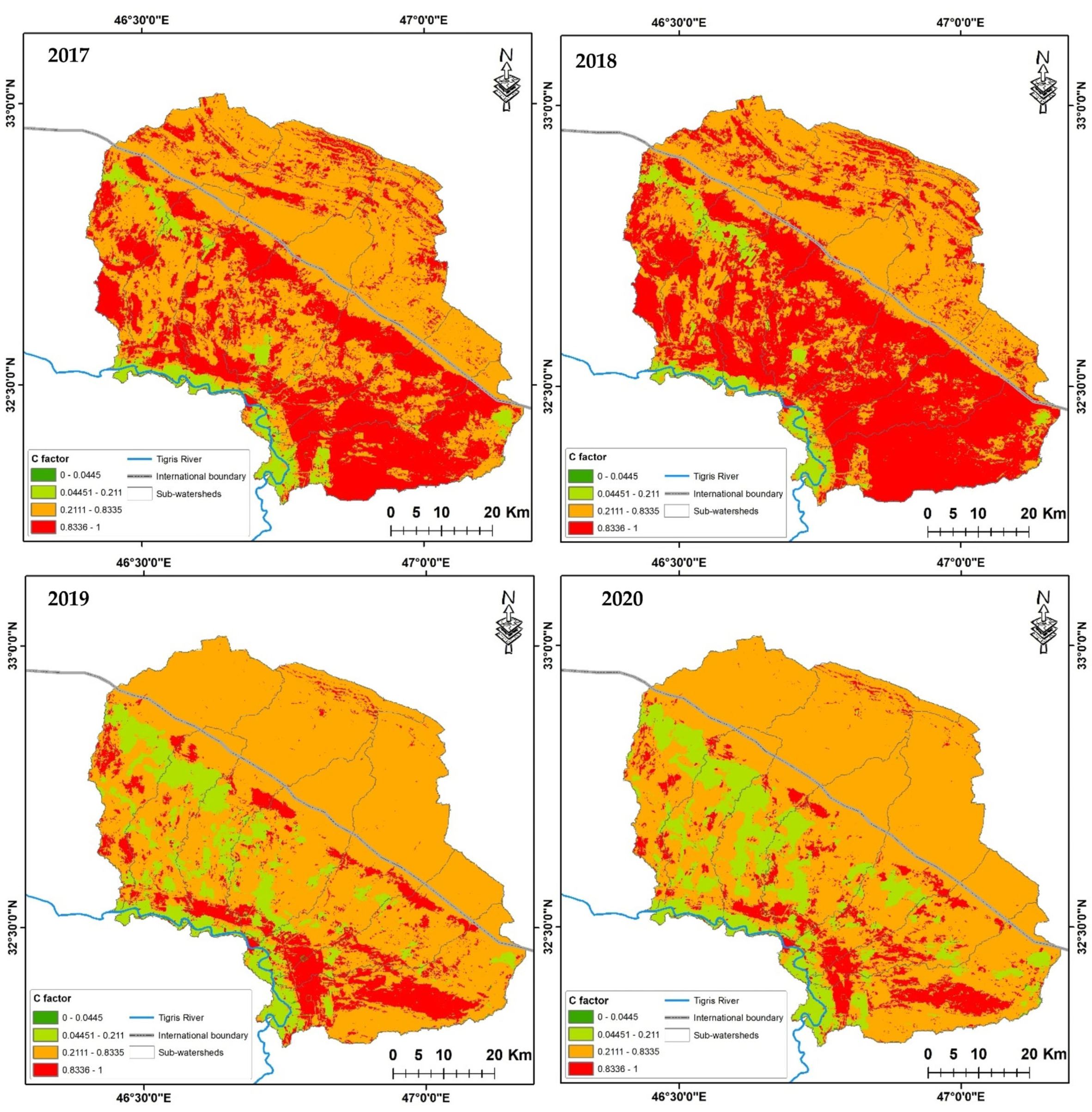
3.4. Crop Management Factor (C)
3.5. Practice Support Factor (P)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vahabi, J.; Nikkami, D. Assessing dominant factors affecting soil erosion using a portable rainfall simulator. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C.; Panagos, P.; Montanarella, L. Wind erosion susceptibility of European soils. Geoderma 2014, 232, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shi, P.; Meadows, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Z. Measuring compound soil erosion by wind and water in the eastern agro–pastoral Ecotone of northern China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohun, B.J.; Anifowose, A.Y.; Odeyemi, C.; Aladejana, O.O.; Aladeboyeje, A.I. GIS-based estimation of soil erosion rates and identification of critical areas in Anambra sub-basin, Nigeria. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelder, B.; Sklenar, T.; James, D.; Herzmann, D.; Cruse, R.; Gesch, K.; Laflen, J. The Daily erosion project-daily estimates of water runoff, soil detachment, and erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 43, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.S.; Mustafa, F.B.; Muhammad Yusoff, S.; Didams, G. A systematic review of soil erosion control practices on the agricultural land in Asia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Alexandridis, V.; Ghosal, K. Assessment of Water-Induced Soil Erosion as a Threat to Natura 2000 Protected Areas in Crete Island, Greece. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgiazzi, A.; Panagos, P. Soil biodiversity and soil erosion: It is time to get married. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2018, 27, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Vijith, H.; Abinod, S.; Geetha, N. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, V.M.; Chakraborthy, D.; Jeyaram, A.; Murthy, Y.V.; Sharma, J.R.; Dadhwal, V.K. Multi-criteria decision making approach for watershed prioritization using analytic hierarchy process technique and GIS. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3555–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aher, P.; Adinarayana, J.; Gorantiwar, S. Quantification of morphometric characterization and prioritization for management planning in semi-arid tropics of India: A remote sensing and GIS approach. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Gupta, V.; Moharana, P. Watershed prioritization using remote sensing and geographical information system: A case study from Guhiya, India. J. Arid. Environ. 2001, 49, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R. Soil and Water Assessment Tool Theoretical Documentation Version; Texas Water Resources Institute: Holleman, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, J.; von Werner, M.; Michael, A. EROSION 2D/3D—A Computer Model to Simulate Water Erosion—Parameter Catalogue; Saxon State Institute for Agriculture: Freiberg, Germany, 1996; Volume II. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook #507; U.S. Department of Agriculture, U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G.; Ferreira, V.A. RUSLE model description and database sensitivity. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gertner, G.; Fang, S.; Anderson, A.B. Mapping multiple variables for predicting soil loss by Geostatistical methods with TM images and a slope map. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, N. Spatial modeling of soil erosion potential in a tropical watershed of the colombian Andes. CATENA 2005, 63, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, O.; Antronico, L.; Coscarelli, R.; Iaquinta, P. Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: An application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 112, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhangara, P.; Kakembo, V.; Lim, K.J. Soil erosion risk assessment of the Keiskamma catchment, South Africa using GIS and remote sensing. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 65, 2087–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoma, H.; Suryabhagavan, K.V.; Balakrishnan, M. Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Huluka watershed, central Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Shi, Z.; Chongfa, C. Soil erosion hazard evaluation—An integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiyan, F.; Liying, S. Modelling soil erosion and its response to the soil conservation measures in the Black soil catchment, northeastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, H.; He, H. Soil erosion processes and geographical differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, N.; Jiao, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Soil erosion and sediment interception by check dams in a watershed for an extreme rainstorm on the Loess Plateau, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eniyew, S.; Teshome, M.; Sisay, E.; Bezabih, T. Integrating RUSLE model with remote sensing and GIS for evaluation soil erosion in Telkwonz watershed, northwestern Ethiopia. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, H. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in the Taohe river basin using the RUSLE model and Google Earth engine. Water 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayneh, M.; Yirgu, T.; Tsegaye, D. Potential soil erosion estimation and area prioritization for better conservation planning in Gumara watershed using RUSLE and GIS techniques’. Environ. Syst. Res. 2019, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T.B.; Tefera, S.A. Comparing potential risk of soil erosion using RUSLE and MCDA techniques in central Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 7, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.P.; Chatzichristaki, C.A.; Stefanidis, P.S. An ArcGIS Toolbox for Estimation and Mapping Soil Erosion. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2021, 22, 689–696. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Wu, B. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment delivery ratio using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of upstream Chaobaihe river catchment, north China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.D.; Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Agapiou, A. Integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and precipitation data for the assessment of soil erosion rate in the catchment area of “Yialias” in Cyprus. Atmos. Res. 2013, 131, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, H.; Salloum, J. Spatial assessment of soil erosion in Alqerdaha basin (Syria). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2017, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahi, K.A.; Al-Madhhachi, A.T.; Al-Hussaini, S.N. Assessment of surface water resources of eastern Iraq. Hydrology 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, P.A.; Ahamed, S.; Carré, F.; Hartemink, A.E.; Hempel, J.; Vanlauwe, B.; Walsh, M.G.; Zhang, G.L. Digital Soil Map of the World. Science 2009, 25, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S.F.A. Tectonic and structural evolution of the Mesopotamia Foredeep, Iraq. Iraqi Bull. Geol. 2010, 2, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Falcon, N. Zagros mountains, Mesozoic-Cenozoic orogenic belts. Geol. Soc. 1974, 4, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Garzic, E.; Vergés, J.; Sapin, F.; Saura, E.; Meresse, F.; Ringenbach, J. Evolution of the NW Zagros fold-and-Thrust belt in Kurdistan region of Iraq from balanced and restored crustal-scale sections and forward modeling. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 124, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R. Soil conservation: Principles of erosion by water. Dryland Agric. 1983, 23, 155–176. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Freimund, J.R. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R-factor in the revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Chen, S.; McCool, D.K. Modeling the impacts of no-till practice on soil erosion and sediment yield with RUSLE, SEDD, and ArcView GIS. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 85, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Jae Lim, K.; Ballabio, C. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. A Universal Soil-Loss Estimating Equation to Guide Conservation Form Planning. 7th Conger. Intern. Soil Sci. Soc. Trans. 1961, 1, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Roose, E. Land Husbandry: Components and Strategy; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Wilson, J.P. Length-slope factors for the revised universal soil loss equation: Simplified method of estimation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 47, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Modelling erosion and deposition: Topographic effects. Trans. ASAE 1986, 29, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G. Hydrology and Soil Conservation Engineering: Including Watershed Management; PHI Learning Pvt: Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shalini Tirkey, A.; Pandey, A.; Nathawat, M. Use of satellite data, GIS and RUSLE for estimation of average annual soil loss in Daltonganj watershed of Jharkhand (India). J. Remote Sens. Technol. 2013, 1, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); United States Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Namdar, F.; Mahmoudi, S.; Esmali Ouri, A.; Pazira, E. Investigating the effect of land use changes on soil erosion using RS-GIS and AHP-fuzzy based techniques (Case study: Qaresu watershed, Ardabil, Iran). Nexo Rev. Científica 2020, 33, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, H.K.; Klik, A. Predicting the spatial distribution of soil erodibility factor using USLE nomograph in an agricultural watershed, Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) universal soil loss equation ((R)USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulabian, S.; Shadmehri Toosi, A.; Humberto Calbimonte, G.; Ghasemi Tousi, E.; Alaghmand, S. Projected climate change impacts on soil erosion over Iran. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Moore, D.; He, P.; Geissen, V. Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Tresch, S.; Meusburger, K. Modification of the RUSLE slope length and steepness factor (LS-factor) based on rainfall experiments at steep Alpine grasslands. MethodsX 2019, 6, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Luukkanen, O.; Tokola, T.; Nieminen, J. Effect of vegetation cover on soil erosion in a mountainous watershed. CATENA 2008, 75, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Motamedi, A.; Galoie, M. Impact of C factor of USLE technique on the accuracy of soil erosion modeling in elevated mountainous area (case study: The Tibetan Plateau). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 12615–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int. Yearb. Cart. 1967, 7, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- El-Hassanin, A.; Labib, T.; Gaber, E. Effect of vegetation cover and land slope on runoff and soil losses from the watersheds of Burundi. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 43, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadat, F.M.; Taimeh, A.Y. Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Data | Spatial Resolution | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | 30 m × 30 m | USGS. http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 18 April 2022). |
| Crop Management Factor (C) | - | USLE fact sheet (http://www.omafra.gov.on.ca/english/engineer/facts/12-051.htm, accessed on 18 April 2022), U.N, Food and Agriculture Organization (http://www.fao.org/docrep/T1765E/t1765e0c.htm, accessed on 18 April 2022) |
| Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R) | 1 km × 1 km | European Soil Data Center (ESDAC) (https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/content/global-rainfall-erosivity, accessed on 18 April 2022) |
| Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) | 10 m × 10 m | Sentinel-2 10m Land Use/Land Cover Time Series https://www.arcgis.com/apps/mapviewer/index.html?layers=d3da5dd386d140cf93fc9ecbf8da5e31 (accessed on 18 April 2022) |
| Soil Erodibility Factor | - | Sanchez et al., 2009 [35]; https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/en/ (accessed on 18 April 2022) |
| Textural Class | Soil Composition | Mean K (Based on % Organic Material) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | Unknown | <2% | ≥2% | |
| Clay | 0–45 | 0–40 | 40–100 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| Sandy Clay | 45–65 | 0–20 | 35–55 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.200 |
| Silty Clay | 0–20 | 40–60 | 40–60 | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.26 |
| Sand | 68–100 | 0–14 | 0–10 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Sandy Loam | 50–70 | 0–50 | 0–20 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Clay Loam | 20–45 | 15–52 | 27–40 | 0.30 | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| Loam | 23–52 | 28–50 | 7–27 | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| Loamy Sand | 70–86 | 0–30 | 0–15 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Sandy Clay Loam | 45–80 | 0–28 | 20–35 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Silty Clay Loam | 0–20 | 40–73 | 27–40 | 0.32 | 0.35 | 0.30 |
| Silt | 0–20 | 88–100 | 0–12 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.37 |
| Silty Loam | 20–50 | 74–88 | 0–27 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.37 |
| LULC Class Number | Class Name | C Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water | 0 |
| 2 | Trees | 0.025 |
| 4 | Flooded Vegetation | 1 |
| 5 | Crops | 0.05 |
| 7 | Build Area | 1 |
| 8 | Bare Ground | 1 |
| 9 | Snow/ice | 0 |
| 10 | Clouds | 0 |
| 11 | Rangeland | 0.4 |
| Soil Texture | SNUM | Soil Composition | OM | K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||||
| Loam | 3122 | 40 | 39 | 21 | 2.01 | 0.26 |
| Clay | 3136 | 37 | 46 | 17 | 5.40 | 0.21 |
| Clay | 3254 | 18 | 61 | 21 | 60.66 | 0.21 |
| Loamy Sand | 3529 | 86 | 10 | 4 | 3.38 | 0.04 |
| Clay Loam | 3554 | 40 | 39 | 21 | 2.01 | 0.28 |
| Clay | 3627 | 26 | 63 | 11 | 1.97 | 0.33 |
| Clay | 3634 | 37 | 46 | 17 | 5.40 | 0.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.A.; Al-Abbadi, A.M.; Jabbar, F.K.; Alzahrani, H.; Hamad, S. Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031776
Ali AA, Al-Abbadi AM, Jabbar FK, Alzahrani H, Hamad S. Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(3):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031776
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Ammar Ak., Alaa M. Al-Abbadi, Fadhil K. Jabbar, Hassan Alzahrani, and Samie Hamad. 2023. "Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model" Sustainability 15, no. 3: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031776
APA StyleAli, A. A., Al-Abbadi, A. M., Jabbar, F. K., Alzahrani, H., & Hamad, S. (2023). Predicting Soil Erosion Rate at Transboundary Sub-Watersheds in Ali Al-Gharbi, Southern Iraq, Using RUSLE-Based GIS Model. Sustainability, 15(3), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15031776






