Ground-Level Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Mapping in the Central and South Zones of Peninsular Malaysia Using a Geostatistical Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
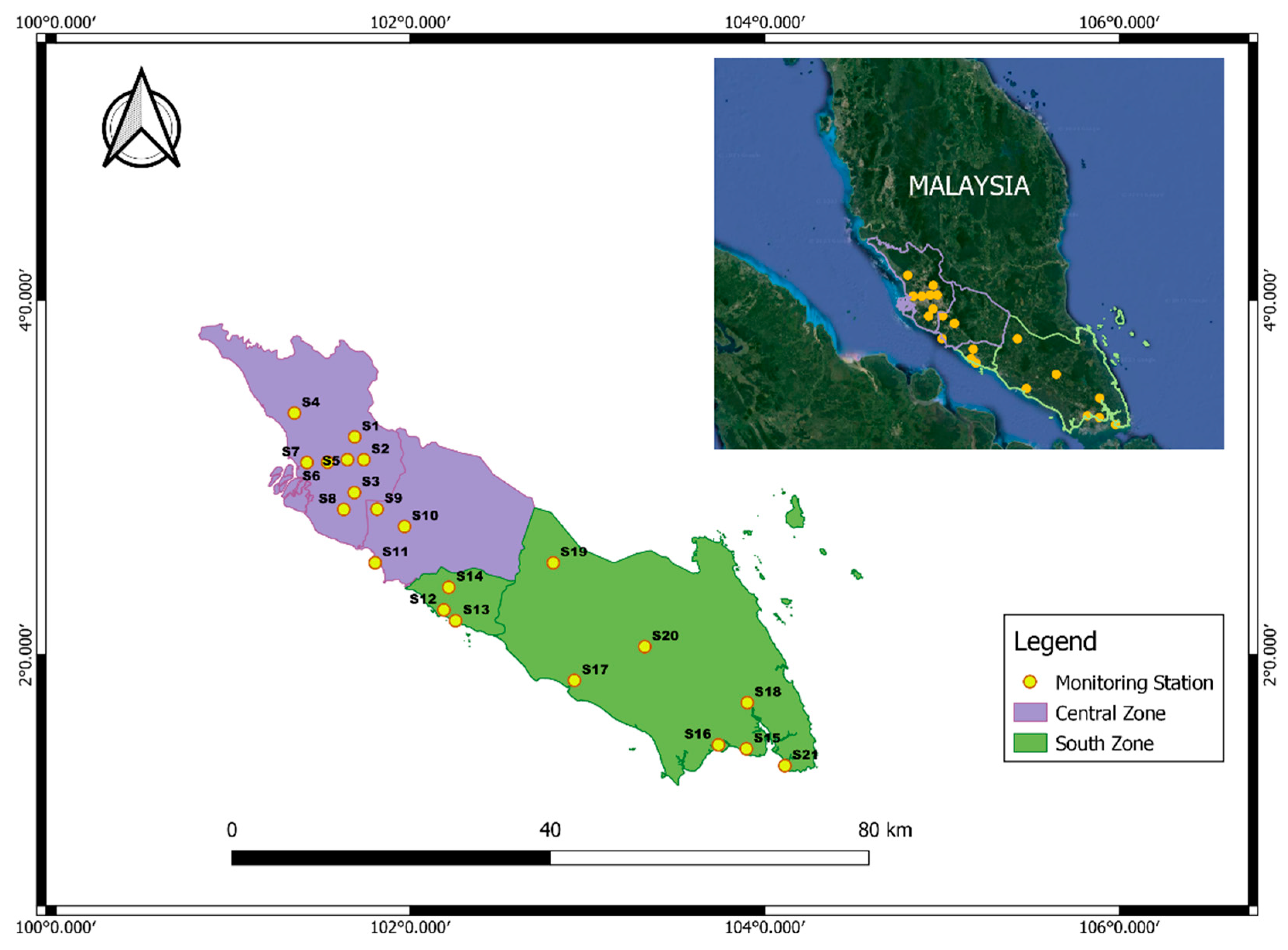
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Classification Breakpoint of PM2.5 Concentrations in the Air Pollutant Index (API)
2.4. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.4.1. Moran’s I Method
2.4.2. Variogram
- Exponential model
- Gaussian model
- Stable model
2.5. Spatial Interpolation
2.5.1. Ordinary Kriging
2.5.2. Simple Kriging
2.5.3. Universal Kriging
2.6. Performance Indicator
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis of PM2.5 Concentrations
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
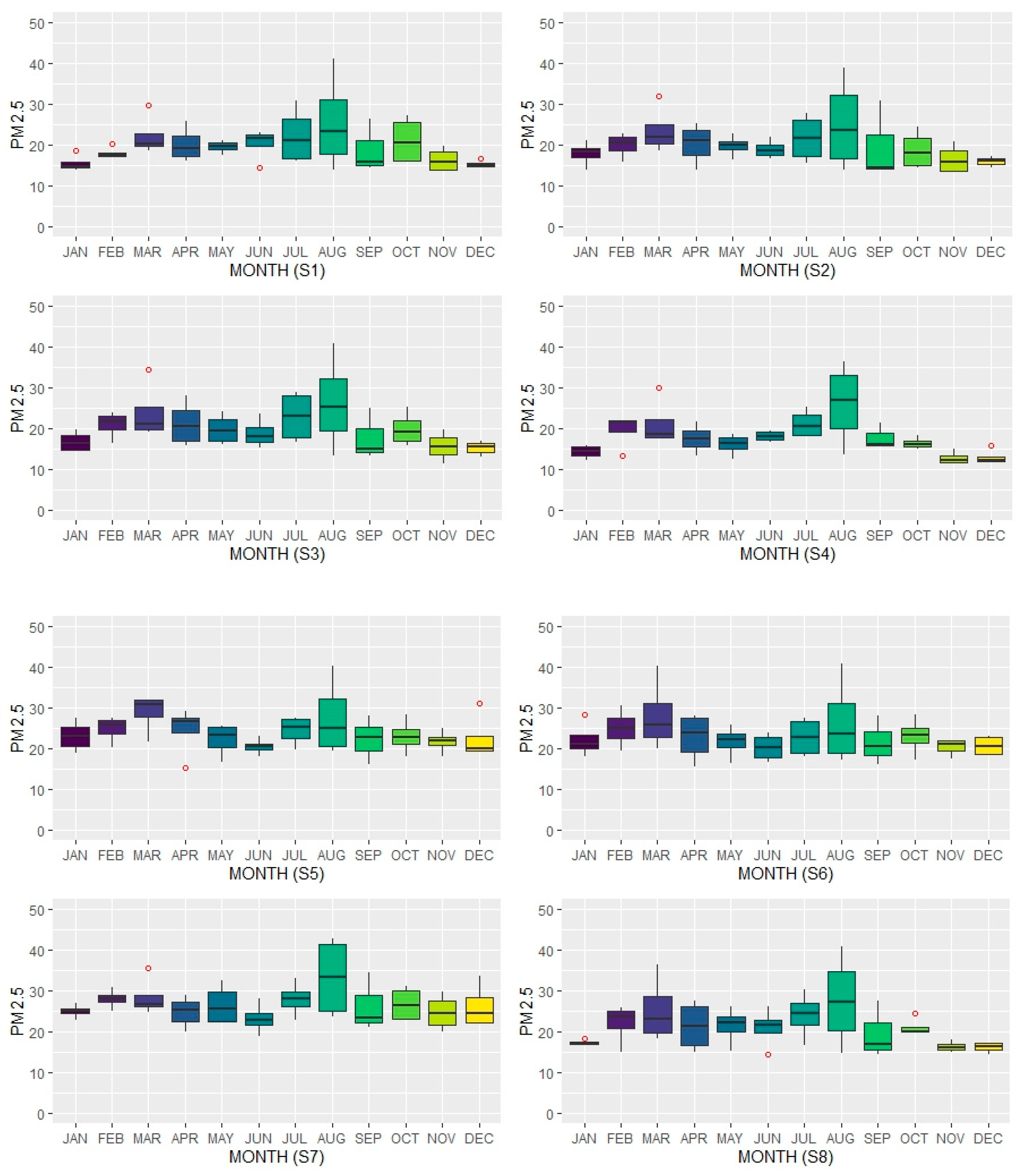
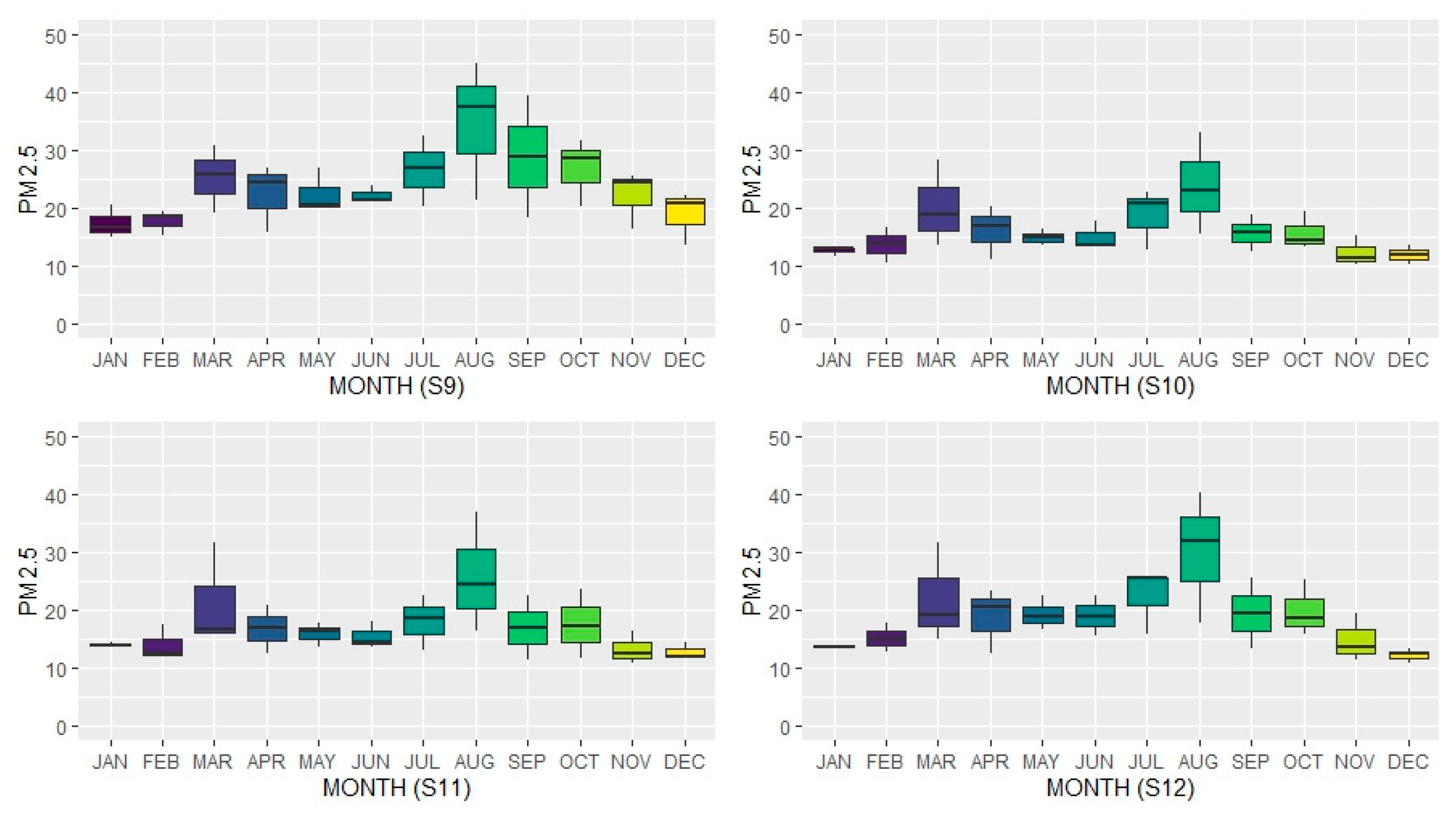
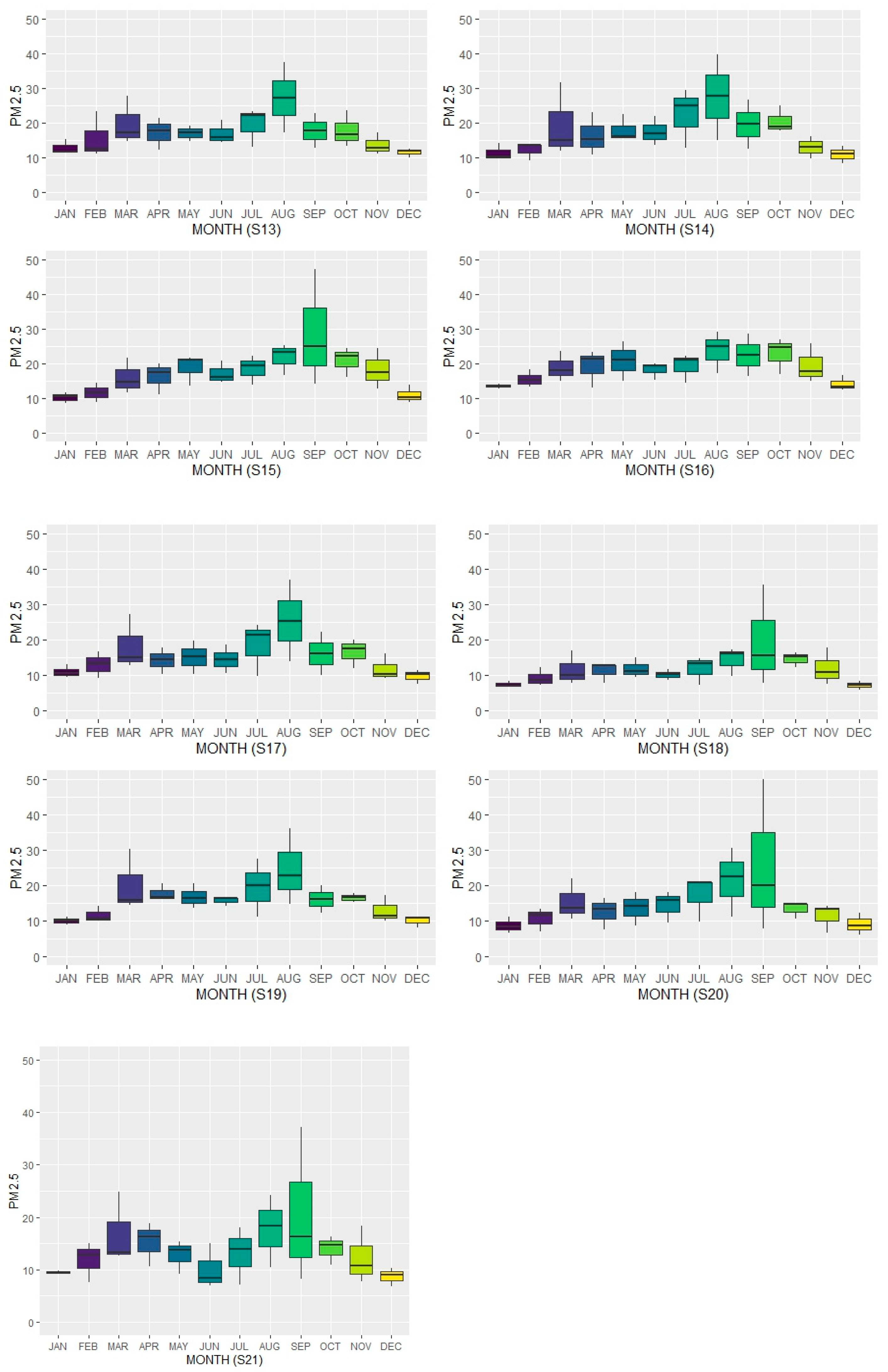
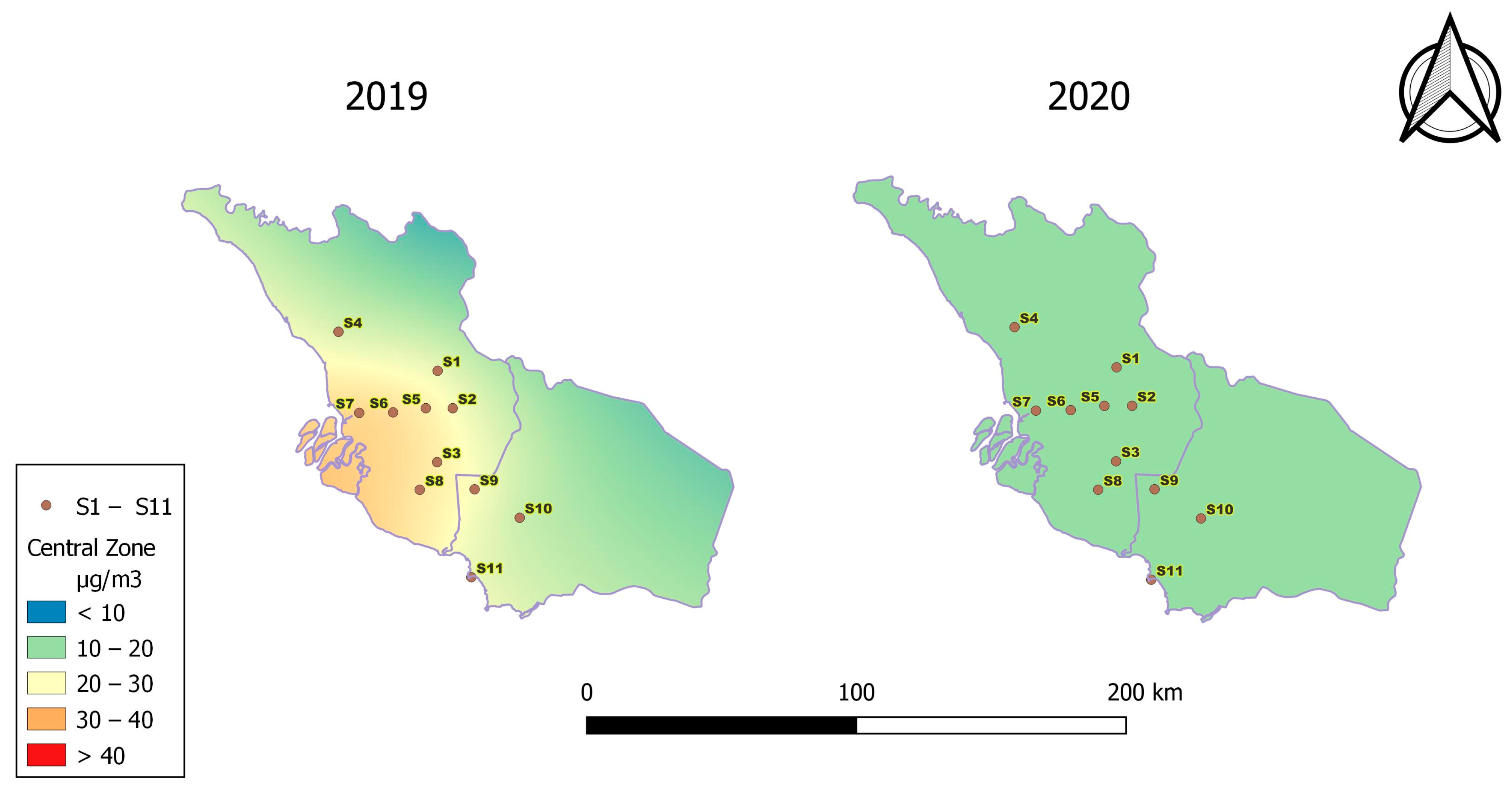
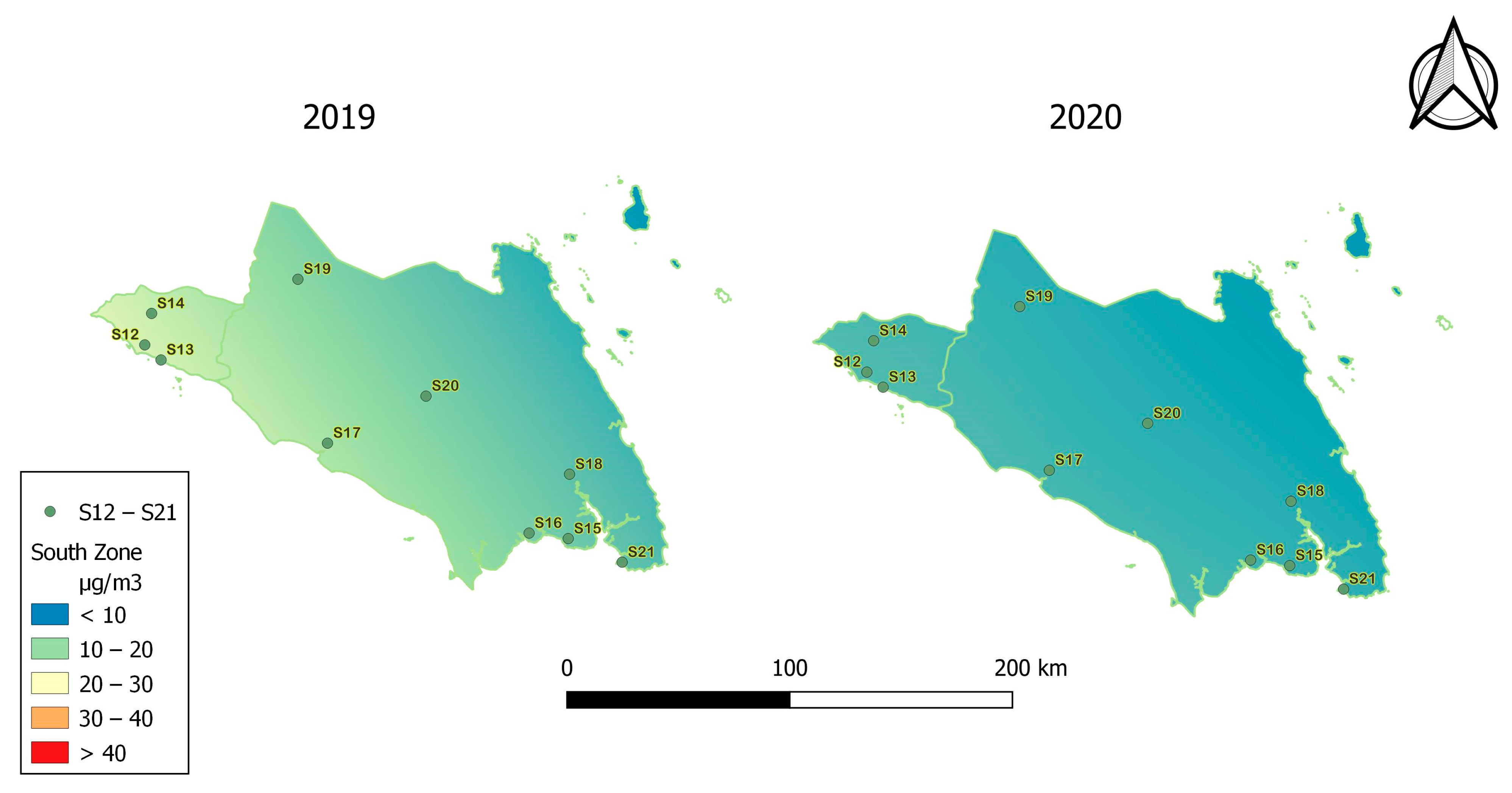
3.3. Temporal Changes in PM2.5
- 1.
- Central Zone
- 2.
- South Zone
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Jin, L.; Kan, H. Air Pollution: A Global Problem Needs Local Fixes. Nature 2019, 570, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Jaffe, D.A.; Qiao, X.; Miao, Y.; Tang, Y. Prediction of Potentially High PM2.5 Concentrations in Chengdu, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal Variations of Six Ambient Criteria Air Pollutants from 2015 to 2018, Their Spatial Distributions, Health Risks and Relationships with Socioeconomic Factors During 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, N.T.; Pan, C.-H.; Chen, W.-L.; Wang, C.-C.; Liang, C.-W.; Chien, C.-Y.; Chuang, K.-J.; Thao, H.N.X.; Dung, H.B.; Thuy, T.P.C. Associations of PM2.5 with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Shipyard Workers: A Cohort Study. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, N.L.; Nolte, C.G.; Sarofim, M.C.; Martinich, J.; Nassikas, N.J. Associations between Simulated Future Changes in Climate, Air Quality, and Human Health. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2032064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyankara, S.; Senarathna, M.; Jayaratne, R.; Morawska, L.; Abeysundara, S.; Weerasooriya, R.; Knibbs, L.D.; Dharmage, S.C.; Yasaratne, D.; Bowatte, G. Ambient Pm2. 5 and Pm10 Exposure and Respiratory Disease Hospitalization in Kandy, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, A.S. Identification of Air Pollution Sources and Temporal Assessment of Air Quality at a Sector in Mosul City Using Principal Component Analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, D.; Fan, L.; Li, F.; Wang, W.; Bai, H.; Tang, J. Spatiotemporal Estimates of Daily PM2.5 Concentrations Based on 1-Km Resolution Maiac Aod in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, China. Environ. Chall. 2022, 8, 100548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Nie, D.; Zhang, S.; Yu, W.; Ge, X.; Song, N. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Air Pollutants and Their Health Effects in China During 2019–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amil, N.; Latif, M.T.; Khan, M.F.; Mohamad, M. Seasonal Variability of PM2.5 Composition and Sources in the Klang Valley Urban-Industrial Environment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5357–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeli, M.I.; Pahrol, M.A.; Shakor, A.S. a. A.; Kanniah, K.D.; Omar, M.A. Cardiovascular, Respiratory and All-Cause (Natural) Health Endpoint Estimation Using a Spatial Approach in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hong, C.; Pandey, M.R.; Smith, K.R. Indoor Air Pollution in Developing Countries. World Health Stat. Q. 1990, 43, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; An, X.; Cai, X.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, H. The Impact of New Urbanization on PM2.5 Concentration Based on Spatial Spillover Effects: Evidence from 283 Cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 90, 104386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Che, J.; Wang, Z. Differential Effects of Urbanization on Air Pollution: Evidences from Six Air Pollutants in Mainland China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Geng, G.; Liang, F.; Wang, X.; Lv, Z.; Lei, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; He, K. Changes in Spatial Patterns of PM2.5 Pollution in China 2000–2018: Impact of Clean Air Policies. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.M.C.a.C.; Nascimento, R.C.; Da Silva, Y.J.a.B.; Barbosa, R.S.; Da Silva, Y.J. a B.; Do Nascimento, C.W.A.; Van Straaten, P. Combining Geospatial Analyses to Optimize Quality Reference Values of Rare Earth Elements in Soils. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Lv, B.; Wang, R. Impact of Motor Vehicle Exhaust on the Air Quality of an Urban City. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Wei, H.; Tan, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Qian, Y. Linking Urbanization and Air Quality Together: A Review and a Perspective on the Future Sustainable Urban Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 130988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Urban Air Quality Index During Haze Pollution Episodes in China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; He, X.; Le, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Driving Forces of Air Quality in Jiangsu Province, China, 2014. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 4076–4083. [Google Scholar]
- Danek, T.; Weglinska, E.; Zareba, M. The Influence of Meteorological Factors and Terrain on Air Pollution Concentration and Migration: A Geostatistical Case Study from Krakow, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hu, X.; He, L. Performance Analysis of Different Kriging Interpolation Methods Based on Air Quality Index in Wuhan. In Proceedings of the 2015 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Wuhan, China, 26–28 November 2015; pp. 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, M.K.B.M.; Yusof, F.; Daud, Z.M.; Yusop, Z.; Kasno, M.A. Comparison of Semivariogram Models in Rain Gauge Network Design. MATEMATIKA 2019, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, A.K.; Jain, K.G.; Shaw, N.; Tuluri, F.; Tchounwou, P.B. Kriging Analysis for Spatio-Temporal Variations of Ground Level Ozone Concentration. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 9, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gia Pham, T.; Kappas, M.; Van Huynh, C.; Hoang Khanh Nguyen, L. Application of Ordinary Kriging and Regression Kriging Method for Soil Properties Mapping in Hilly Region of Central Vietnam. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Mouni, L. Spatial Distribution of the Groundwater Quality Using Kriging and Co-Kriging Interpolations. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, A.a.A.; Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Azhari, A.; Baharudin, N.H.; Hanif, N.M.; Chung, J.X.; Juneng, L. Spatiotemporal Variations of Particulate Matter and Their Association with Criteria Pollutants and Meteorology in Malaysia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, E.A.; Hamzah, F.M.; Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D. Assessment of Pm2. 5 Patterns in Malaysia Using the Clustering Method. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Ahamad, F.; Khan, M.F.; Juneng, L.; Hamzah, F.M.; Nadzir, M.S.M. Long Term Assessment of Air Quality from a Background Station on the Malaysian Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Calder, C.A.; Cressie, N. Beyond Moran’s I: Testing for Spatial Dependence Based on the Spatial Autoregressive Model. Geogr. Anal. 2007, 39, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.A. Notes on Continuous Stochastic Phenomena. Biometrika 1950, 37, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Kumar, P.; Mann, G.S.; Khare, M. Mapping Spatial Distribution of Particulate Matter Using Kriging and Inverse Distance Weighting at Supersites of Megacity Delhi. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Lloyd, C.D.; Mckinley, J.M. Increasing the Accuracy of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Pollution Mapping Using Geographically Weighted Regression (Gwr) and Geostatistics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.; Webster, R. A Tutorial Guide to Geostatistics: Computing and Modelling Variograms and Kriging. Catena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyana, T.J. Spatial Analysis with R: Statistics, Visualization, and Computational Methods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.-P.; Chen, J.-S.; Chien, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-F. Spatial Analysis of the Risk to Human Health from Exposure to Arsenic Contaminated Groundwater: A Kriging Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Huang, B.; Peng, C.; Lin, J.; Liao, Y. Simulation of Average Monthly Ozone Exposure Concentrations in China: A Temporal and Spatial Estimation Method. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, D.W.; Afifah, N.; Anggarani, S.M.; Chamidah, N. Prediction Concentration of PM2.5 in Surabaya Using Ordinary Kriging Method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2329, 060030. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Scrimshaw, M.; Emmerson, R.; Lester, J. Geostatistical Analysis of Sampling Uncertainty at the Tollesbury Managed Retreat Site in Blackwater Estuary, Essex, UK: Kriging and Cokriging Approach to Minimise Sampling Density. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 221, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’amor, A.; Noor, N.M.; Jafri, I.a.M.; Addiena, N.A.; Saufie, A.Z.U.; Amin, N.A.; Boboc, M.; Deak, G. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) and Its Health Effects During the Haze Event in Malaysia. J. Atmos. Sci. Res. 2023, 6, 26–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redzuan, S.N.; Noor, N.M.; Rahim, N.a.a.A.; Jafri, I.a.M.; Baidrulhisham, S.E.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Sandu, A.V.; Vizureanu, P.; Zainol, M.R.R.M.A.; Deák, G. Characteristics of PM10 Level During Haze Events in Malaysia Based on Quantile Regression Method. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafri, I.a.M.; Noor, N.M.; Rahim, N.a.a.A.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Hassan, Z.; Deak, G. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Particulate Matter (PM10) in Urban-Industrial Environment During Episodic Haze Events in Malaysia. Environ. Asia 2023, 16, 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zainal, S.; Zamre, N.M.; Khan, M. Emission Level of Air Pollutants During 2019 Pre-Haze, Haze, and Post-Haze Episodes in Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya. Malays. J. Chem. Eng. Technol. (MJCET) 2021, 4, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K. Changes in Us Air Pollution During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139864. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Dahu, B.M.; Scott, G.J. A Spatio-Temporal Study of Changes in Air Quality from Pre-Covid Era to Post-COVID Era in Chicago, USA. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkepli, N.F.S.; Noorani, M.S.M.; Razak, F.A.; Ismail, M.; Alias, M.A. Cluster Analysis of Haze Episodes Based on Topological Features. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3985. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Hawari, N.S.S.L.; Mohtar, A.A.A.; Othman, M. The Concentration of Major Air Pollutants During the Movement Control Order Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic in the Klang Valley, Malaysia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102660. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, M.; Zheng, M. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Global Air Quality and Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142533. [Google Scholar]
- Nadzir, M.S.M.; Ooi, M.C.G.; Alhasa, K.M.; Bakar, M.a.A.; Mohtar, A.a.A.; Nor, M.F.F.M.; Latif, M.T.; Abd Hamid, H.H.; Ali, S.H.M.; Ariff, N.M. The Impact of Movement Control Order (Mco) During Pandemic Covid-19 on Local Air Quality in an Urban Area of Klang Valley, Malaysia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar]
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | Mean | Median | SD | Min | Max | Mean | Median | SD | Min | Max |
| S1 | 28.39 | 23.95 | 16.90 | 14.60 | 76.60 | 17.50 | 16.95 | 2.61 | 14.00 | 22.10 |
| S2 | 28.23 | 23.00 | 16.07 | 16.40 | 75.00 | 15.78 | 15.65 | 1.70 | 13.70 | 18.50 |
| S3 | 29.79 | 24.60 | 16.85 | 16.20 | 78.60 | 16.62 | 16.25 | 2.11 | 14.30 | 21.30 |
| S4 | 24.12 | 19.70 | 14.83 | 11.70 | 65.10 | 15.23 | 14.50 | 3.06 | 11.70 | 22.00 |
| S5 | 30.09 | 25.80 | 15.93 | 19.10 | 77.10 | 19.97 | 19.10 | 4.37 | 15.30 | 31.10 |
| S6 | 32.18 | 28.20 | 15.46 | 18.80 | 76.40 | 18.07 | 18.05 | 1.63 | 15.50 | 20.70 |
| S7 | 33.07 | 30.35 | 14.34 | 18.90 | 74.10 | 23.23 | 22.75 | 1.98 | 19.90 | 26.90 |
| S8 | 29.32 | 25.15 | 15.66 | 14.50 | 72.60 | 17.02 | 16.70 | 2.22 | 14.50 | 22.00 |
| S9 | 30.14 | 25.01 | 18.64 | 13.68 | 82.46 | 18.91 | 19.50 | 2.38 | 15.21 | 22.30 |
| S10 | 22.56 | 17.44 | 15.33 | 10.27 | 66.32 | 12.67 | 12.87 | 1.49 | 10.18 | 15.59 |
| S11 | 24.10 | 19.33 | 15.76 | 11.75 | 67.66 | 13.08 | 12.75 | 1.70 | 10.71 | 16.36 |
| S12 | 25.92 | 22.80 | 14.64 | 10.95 | 64.82 | 14.37 | 14.28 | 1.99 | 11.42 | 17.79 |
| S13 | 23.46 | 20.28 | 14.36 | 10.03 | 62.05 | 13.21 | 12.95 | 1.78 | 11.20 | 17.25 |
| S14 | 25.07 | 22.79 | 15.05 | 8.44 | 64.49 | 12.48 | 12.18 | 2.67 | 9.126 | 17.73 |
| S15 | 21.06 | 20.84 | 9.91 | 8.87 | 47.29 | 12.69 | 13.21 | 2.66 | 8.536 | 16.54 |
| S16 | 24.66 | 23.49 | 11.46 | 12.60 | 56.86 | 14.78 | 14.96 | 1.47 | 12.80 | 17.19 |
| S17 | 22.08 | 18.80 | 12.90 | 7.49 | 54.97 | 10.64 | 10.24 | 1.51 | 9.122 | 14.00 |
| S18 | 14.82 | 14.18 | 7.60 | 5.92 | 35.51 | 8.27 | 7.789 | 1.46 | 6.95 | 12.07 |
| S19 | 23.72 | 19.21 | 16.40 | 7.97 | 68.71 | 12.96 | 12.90 | 2.55 | 9.92 | 16.63 |
| S20 | 19.28 | 16.07 | 11.44 | 6.11 | 49.49 | 8.64 | 8.60 | 1.53 | 6.72 | 11.07 |
| S21 | 16.94 | 14.31 | 8.54 | 6.89 | 37.17 | 9.16 | 9.13 | 1.72 | 6.99 | 12.67 |
| 2019 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|
| Observed | 0.37 | −0.06 |
| Expected | −0.05 | −0.05 |
| Standard deviation | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| z-score | 6.20 | −0.16 |
| p-value | 5.62 × 10−10 | 0.87 |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | MSE | RMSE | NRMSE | MSE | RMSE | NRMSE |
| Exponential | 15.1349 | 3.8903 | 20.1584 | 321.8418 | 17.9400 | 90.9503 |
| Gaussian | 14.7645 | 3.8425 | 19.9101 | 42.2593 | 6.5007 | 32.9561 |
| Stable | 15.1398 | 3.9810 | 20.1616 | 19.8337 | 4.4535 | 22.5780 |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | MSE | RMSE | NRMSE | MSE | RMSE | NRMSE |
| Exponential | 12.6802 | 3.5610 | 31.9423 | 90.4825 | 9.5122 | 146.1614 |
| Gaussian | 12.6796 | 3.5609 | 31.9416 | 57.0498 | 7.5531 | 116.0586 |
| Stable | 12.6811 | 3.5611 | 31.9435 | 8.8766 | 2.9793 | 45.7799 |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | OK | SK | UK | OK | SK | UK |
| MSE | 19.8333 | 31.4175 | 13.9549 | 15.5617 | 19.8691 | 15.1398 |
| RMSE | 4.4535 | 5.6051 | 3.7356 | 3.9450 | 4.4574 | 3.8909 |
| NRMSE | 22.5780 | 28.4163 | 18.9385 | 20.4406 | 23.0969 | 20.1616 |
| Ranking | 2 | 3 | 1 * | 2 | 3 | 1 * |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | OK | SK | UK | OK | SK | UK |
| MSE | 14.7124 | 22.4445 | 12.6811 | 8.8766 | 7.8602 | 5.7940 |
| RMSE | 3.8357 | 4.7375 | 3.5610 | 2.9793 | 2.8036 | 2.4070 |
| NRMSE | 34.4068 | 42.4970 | 31.9435 | 45.7798 | 43.0793 | 36.9861 |
| Ranking | 2 | 3 | 1 * | 2 | 3 | 1 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusmili, S.H.A.; Mohamad Hamzah, F.; Choy, L.K.; Azizah, R.; Sulistyorini, L.; Yudhastuti, R.; Chandraning Diyanah, K.; Adriyani, R.; Latif, M.T. Ground-Level Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Mapping in the Central and South Zones of Peninsular Malaysia Using a Geostatistical Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16169. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316169
Rusmili SHA, Mohamad Hamzah F, Choy LK, Azizah R, Sulistyorini L, Yudhastuti R, Chandraning Diyanah K, Adriyani R, Latif MT. Ground-Level Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Mapping in the Central and South Zones of Peninsular Malaysia Using a Geostatistical Approach. Sustainability. 2023; 15(23):16169. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316169
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusmili, Siti Hasliza Ahmad, Firdaus Mohamad Hamzah, Lam Kuok Choy, R. Azizah, Lilis Sulistyorini, Ririh Yudhastuti, Khuliyah Chandraning Diyanah, Retno Adriyani, and Mohd Talib Latif. 2023. "Ground-Level Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Mapping in the Central and South Zones of Peninsular Malaysia Using a Geostatistical Approach" Sustainability 15, no. 23: 16169. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316169
APA StyleRusmili, S. H. A., Mohamad Hamzah, F., Choy, L. K., Azizah, R., Sulistyorini, L., Yudhastuti, R., Chandraning Diyanah, K., Adriyani, R., & Latif, M. T. (2023). Ground-Level Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Mapping in the Central and South Zones of Peninsular Malaysia Using a Geostatistical Approach. Sustainability, 15(23), 16169. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316169








