Abstract
Many countries are using digital transformation to increase their productivity and organizational performance. In Saudi Arabia, digital transformation is a crucial part of their Saudi Vision 2030 plan, but it is still in its early stages. To understand the factors that affect the adoption of digital transformation. The study used a qualitative interview to identify the critical success factors and challenges in adopting digital transformation at the Ministry of Education of Saudi Arabia. The main results of the study show, first, the seven main success factors include technology, employee engagement, vendor partnerships, budget, top management support, culture, and strategy. Second, the main seven challenges include organizational and strategic stakes, resistance to change, governance, data, cost, and IT infrastructure. The study developed a framework that shows the main success factors and challenges that affect adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. These findings can benefit many individuals and groups, such as academics, business people, and the public, and can apply this research in other contexts. This research aimed to determine the primary factors contributing to the success of digital transformation in the Ministry of Education and the challenges that arise when implementing it, specifically within the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Education.
1. Introduction
The Saudi Arabian government’s digital transformation is not merely a tool to promote change but also a way to redefine and restructure the government’s core function to show how quickly technology is evolving. The Saudi government’s digital transformation program is a comprehensive, decisive, and practical approach that aligns with the Vision 2030 plan and aims to enable and hasten the government’s transformation productively and successfully. Many e-government initiatives have embraced this transition, empowering and assisting various government organizations and authorities. It includes making all government services available online, easily accessible to citizens, and a consistent look and feel focused on live events. The transition has been planned and implemented to retain architecture alignment and suit the digital era, supported using digital tools, skills, and capabilities. The National Transformation Program is an effective and carefully thought-out transformation program provided under Vision 2030. It works to build the necessary infrastructure and create an atmosphere so that the public, commercial, and non-profit sectors may fulfill Vision 2030. Digital transformation in education is highly adopted nowadays in Saudi Arabia. Digital technology has been utilized to its maximum potential [1].
The Ministry offers clients many electronic services inside and outside Saudi Arabia. Therefore, activating electronic services in government sectors is something that the Kingdom is interested in, and the Ministry of Education is interested in making things easier for the clients. The service-level agreement aims to increase customer satisfaction while adhering to the technical specifications established by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and the executive order’s instructions to provide MOE clients with the highest customer service standards. The MOE makes sure that electronic services are delivered using its e-portal and intelligent gadgets to do this. The MOE has also taken all reasonable steps to ease and hasten the conclusion of end-user official transactions by utilizing the Ministry’s electronic services. The study’s final focus is on the factors contributing to adopting digital transformation in an organization’s growth and its challenges [2].
The paper examines the critical success factors (CSFs) and challenges of digital transformation in the Saudi government’s transformation efforts. The government’s comprehensive digital transformation effort, aligned with Vision 2030, intends to redefine fundamental operations and improve services. The study looks specifically at adopting digital transformation in the education sector, with the Ministry of Education leading the development of electronic services. This research intends to contribute to a successful digital transformation journey by identifying CSFs and addressing challenges.
Today, many countries aim to enhance efficiency, improve citizen services, and drive economic growth by using digital technologies to transform their governments and public sectors. This study identifies challenges and critical success factors that can provide valuable guidance for policymakers, government officials, and researchers in other nations.
Moreover, the study’s future scope can involve developing a generalized framework or best practices for digital transformation in the public sector. This framework will be customized to meet the specific needs and challenges that countries encounter at varying stages of development. By considering the research’s global implications and potential applicability, the study becomes a valuable resource for international experts and policymakers seeking to drive digital transformation in their respective countries.
The reason for conducting this research is the importance and relevance of digital transformation in the field of study. With the rapid advancement of technology, governments around the world are adopting digital transformation to increase effectiveness and provide better services to their citizens. The focus of this study is on the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, as it plays a crucial role in offering education-related services to the people.
The Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia provides a variety of electronic services to its customers, both domestically and internationally. These services are aimed at streamlining processes and improving customer satisfaction. The Ministry leverages its e-portal and smart devices to deliver electronic services, making official transactions efficient and timely for end-users.
This research offers significant insights into the Ministry of Education’s digital transformation journey, highlighting critical success factors and challenges. The recommendations and framework presented in this study are applicable not only to Saudi Arabia but also to other countries undergoing comparable transformations. Policymakers, leaders, and researchers can use these findings to develop effective digital transformation strategies in the education sector and beyond.
The research will use a qualitative approach. It allowed the formulation of different types of questions for data collection, increasing the explanations for the responses garnered from the participants. As such, the researcher could interview Saudi leaders across different areas of the organization.
Clustering, depending on the company and its particular environment, several issues and reasons exist for implementing digital transformation. For example, change resistance, a lack of resources or knowledge, problems integrating new technology with legacy systems, and cybersecurity concerns are all common problems businesses face when adopting digital transformation. Furthermore, selecting a digital transformation strategy that matches the needs and goals of a firm may be challenging for some. However, there are many reasons to implement digital transformation. One primary driver is the need to save expenses and increase operational efficiency. Furthermore, increasing agility and creativity due to digital transformation can help firms react more swiftly to shifting market conditions and client expectations. Additionally, businesses may use digital transformation to improve customer satisfaction, boost sales and profits, and obtain a competitive edge in the industry. Consequently, Saudi organizations must keep up with digital developments in their sector and identify the success factors and challenges supporting implementing effectiveness and procedures. Furthermore, to stay competitive in the quickly changing global economy, many companies around the country are focusing on improving their digital transformation process.
This research aims to determine the critical success factors and challenges in adopting digital transformation for Saudi Arabian organizations, using the Ministry of Education as an example. Therefore, the study should also answer two key questions: What are the main success factors for implementing digital transformation? Furthermore, what are the main challenges in implementing digital transformation into practice? However, the goals of this study are to:
- Examine the digital transformation framework’s background, concepts, and case studies.
- Conduct interviews with key stakeholders to identify critical success factors and obstacles.
- Evaluate the responses of the interview respondents to validate the stated essential success elements and difficulties.
- Create a solid framework for digital transformation that efficiently controls and addresses strategic choices for the Ministry of Education.
- Analyze the interview data using established criteria to acquire insights and improve understanding of digital transformation in Saudi Arabian enterprises.
- Based on the analysis and results, fine-tune and align the study’s aims and objectives.
By attaining these objectives, this research aims to increase digital transformation adoption in Saudi Arabian enterprises while offering a better knowledge of managing strategic choices in the context of digital transformation.
2. Literature Review
Organizations must now undergo digital transformation (DT) to remain competitive and relevant in today’s quickly changing business climate. The DT process includes using new technologies like cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics. These innovations can aid companies in decision-making, operational efficiency, and customer service. The authors [3] provided a deep understanding of the concept of DT, specifying its key elements/components/categories. Data analysis is based on pre-determined categories, using inter-rater reliability evaluation techniques and expert surveys to increase the reliability of results. The writers [4] conducted the study using a descriptive research approach using a qualitative narrative review. The study [5] significantly contributes to the body of literature on DT by summarizing existing research and proposing a comprehensive framework for future studies. The authors’ focus on the relationship between technology, strategy, and organizational factors emphasizes the importance of a holistic approach for DT, and their suggested research agenda offers a roadmap for future research on this important topic. The researchers [6] studied the impact of DT on the consumer experience and investigated the role of DT in the enhancement of the consumer experience in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) context. The results show that there is a significant positive relationship between DT and consumer experience. The investigators [7] explored the relationship between digitalization, labor productivity, and unemployment. Examine the impact of DT on the labor market in a variety of sectors. There was also a case study and questionnaire conducted by examining the cloud computing concerns in the public sector organizations of KSA [8] and identifying [9] the key issues for adopting cloud computing in the public sector of KSA.
This review aims to draw the attention of stakeholders to the need to implement digital health technology in academic medical centers in KSA and help improve the quality of healthcare. The writers [10] presented a proposal to apply blockchain technology in the real estate rental sector in the KSA and implement blockchain technology in the management of the rental process. The authors [11] conducted a survey that used the technology organization-environment (TOE) model to determine what factors were influencing the adoption of digital transformation in the KSA Ministry of Education. The other researchers [12] conducted a case study to identify the electronic services or e-services provided by King Abdulaziz University to its students. They analyzed the impact of digital transformation on the organizational and spending efficiency of universities, with a special focus on one particular e-service provided by the Saudi University. This study assumed that it would be expensive to rapidly transition to digitalization without laws and regulations to organize its utilization. According to the study’s findings, a rise in subject withdrawals will damage the university’s financial and administrative effectiveness.
2.1. Digital Transformation Success Factors
The researchers claimed the importance of DT in many aspects and analyzed the most recent empirical contribution on the topic. The study outlined eight success factors: a collaborative and adaptable organizational culture, well-managed transformation activities, knowledge exploitation, management and employee engagement, expansion of IS capabilities, development of dynamic capabilities, creation of a digital business strategy, and alignment of business and IS [13].
The authors conducted a study using the comprehensive TOE framework with personal innovativeness to analyze the factors that affect the decisions of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in rural Saudi Arabia regarding the adoption of information and communication technologies (ICTs). The study discovered a significant association between ICT adoption among SMEs in Saudi Arabia and the success features of relative advantages, top management support, culture, regulatory environment, owner/manager innovativeness, and ICT knowledge. The findings of this research can assist Saudi Arabian SME managers and owners, as well as the Saudi government, in ensuring the successful adoption and spread of ICT in SME establishments situated in rural areas [14].
A study conducted by researchers aimed to identify the key factors contributing to digital transformation’s success in manufacturing businesses. The research involved conducting 20 qualitative interviews using the DeLone and McLean IS success model. The authors identified 13 success criteria from DeLone and McLean’s previous research on e-commerce systems and grouped them into three main areas: organization, environment, and technology. The organization component covered pilot projects, future planning, customer needs, personnel qualifications, autonomy, culture, significant data utilization, management support, usability, and interdisciplinary. The environment dimension included connectedness, openness, and cooperation, while the technology component covered infrastructure, dependability, relevance, flexibility, security, completeness, availability, and real-time data. The study concluded that a successful digital transformation requires collaboration with clients, vendors, and other businesses in the same sector and a culture shift towards more agile working environments and interdisciplinary activities. The authors also emphasized the importance of selecting the appropriate technology but noted that in order to have a successful digital transition, it is necessary to have technological advancements [15].
The authors initiated a study to identify the critical elements required for a successful digital transformation. The authors analyzed 16 case studies from a pool of 89 publications. They identified seven criteria for success: recognizing the digital trigger, cultivating a digital culture, formulating a digital vision, identifying digital drivers, creating a digital organization, pinpointing transformed areas, and assessing impacts. These criteria can serve as a guide for businesses that wish to initiate successful digital transformation projects [16].
A study by researchers presents a two-stage approach to identify barriers and success factors for digital transformation at logistics service providers. The study included numerous case studies involving nine global logistics service companies. The complexity of logistics systems and processes, a lack of resources, reluctance to change, data protection concerns, and the acceptance of new technology are among the five obstacles the authors identified to digital transformation in the logistics services sector. In addition, the study highlighted eight success criteria and best practices for digital transformation, including employee engagement, leadership, organizational culture, process standardization, staff training, agile transformation management, successfully implementing the digital transformation strategy, and a supportive corporate culture was essential. The result of this study contributes to the body of knowledge on supply chain and logistics management’s digital revolution, and they are helpful to practitioners trying to apply it in intricate enterprises [17].
The authors’ work was quantitative research that identified education and training, model construction process, organization development, customer happiness, profitability, and net income as crucial success factors. Using component analysis, the study revealed three success factors: efficient communication, construction techniques, and managerial demands to understand and elevate DT. The authors argue that the construction sector must embrace and leverage this innovation paradigm to benefit from this disruptive time. The study utilized cutting-edge DT and multiple case studies in top-tier logistic service providers (LSP) businesses to make their findings. The authors found that leadership, a supportive organizational culture, employee and partner agreement, aligning business IT strategies, process standardization, employee knowledge, and skills development played a significant role in successfully implementing digital transformation in the industrial sector. The primary challenges LSPs faced were the logistical network’s complexity and a shortage of resources, but having a DT vision and fostering a positive company culture were crucial success factors [18].
The researchers conducted a study that focused on case studies, procedures, and success factors to uncover several elements contributing to the success of digital transformation programs in the public sector. They identified eight factors that are essential for such efforts to succeed. Adopting portfolio, program, and project management, IT leadership, political support, maintaining IT investments, and fostering trust in e-government services were among the success elements in the strategic dimension. In the people dimension, providing team awareness and training via general or specialized training was the most frequently reported success element. Adopting agile methodologies, GDPR compliance, multilevel governance and management structures, transparency, and openness, giving the proper roles to leaders and decision-makers, encouraging integration and rationalization, and multilevel governance and management structures were among the success factors in the organization dimension. In the citizen dimension, citizens are considered co-creators of digital transformation projects and customers. Participation of citizens is crucial for facilitating dialogue and feedback, as well as acceptance, use, and adoption of e-government features. In the ecosystem dimension, working with partners and citizens is essential for constructing an ecosystem and co-creating value. Finally, technology is essential for enabling new services and advancing usability in the technological dimension. The writers also stressed the significance of a sound technological foundation and the importance of looking at developing digital technologies as engines of innovation. The innovation dimension emphasized inspiring others to innovate and comprehending the ongoing cycle that results from the invention. In order to make services’ legal complexity more manageable, the legal and normative dimension was crucial. Practitioners can use this unified framework of success criteria for digital transformation initiatives in the public sector as a checklist of elements to include in their projects to lower the risk of failure and increase the likelihood of success [19].
Overall, organizations can improve their chances of embracing digital transformation successfully and getting its benefits by concentrating on critical success criteria.
Based on the literature, a successful adoption of digital transformation in an organization can attributed to several important critical success factors classifications listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Digital transformation Critical success factors classification.
2.2. Digital Transformation Challenges
Based on semi-structured interviews, researchers investigate the implications and effects of digitalization on firms. According to the study’s conclusions, digitization presents businesses with organizational, cultural, and strategic problems that need top management support and involvement. First, the digital transformation of businesses may result in significant changes to their business models, which may impact various factors, including policies, resources, operational methods, and corporate culture. As a result, how to start the digital transformation process will depend on the company’s long-term structure. Businesses must adjust to consumers’ evolving wants and preferences, which are growing more discerning, by putting users at the center of company strategy. Finally, companies must adapt their business processes and match their goods and services to market developments to achieve these expectations [20].
The authors undertook a study that used system analysis, observation, interview, questionnaire, survey, testing, photographing, counting, measuring, and comparing to identify the primary challenges with digital business transformation in the digital economy. The study found that society faces four main challenges regarding digital transformation. Firstly, many companies need an understanding of the necessary procedures. Secondly, there needs to be more awareness about hiring IT professionals for the digital economy. Thirdly, people need complete control over financial transactions in the digital environment. Finally, respondents must know the importance of protecting digital reputation, ethics, and culture [21].
The authors conducted a study highlighting the main challenges of higher education institutions (HEIs) digital transition. First, implementing a digital strategy is a complex process that calls for incremental changes to create the culture, operational procedures, and technological infrastructure necessary for organizations to compete in the current market. Therefore, HEIs need to help develop a strategic vision enabling the institution to collaborate on implementing digital projects. The second challenge is the importance of ensuring that everyone possesses digital literacy. The third barrier is addressing students’ evolving demands and expectations. The fourth issue relates to the technological and financial constraints faced by HEIs. Finally, the fifth challenge is security, compliance, data protection, and regulations. While business process automation and data digitization can increase the agility of HEIs, they also considerably raise the risks and hazards associated with cybersecurity [22].
The authors conducted a study that distributed a questionnaire to 200 Saudi individuals in Riyadh, Qassim, and Jeddah to learn more about the difficulties in adopting DT. The study’s findings indicate that the primary obstacles hindering DT in the context of Vision 2030 are cybersecurity, trustworthiness, usage experience, and Saudi residents’ awareness.
The researchers performed a study examining the challenges businesses, government officials, and educational institutions encounter when implementing digital transformation plans. The authors have identified three significant barriers that prevent the seamless integration of technologies for digital transformation. Successful digital transformation requires addressing three key challenges: culture and skills, infrastructures and technologies, and ecosystems. Regrettably, progress has decelerated, and enhancing strategic efforts in multiple industries is crucial [23].
The authors undertook a study and found that external assistance for digitization is essential for SMEs to undergo a successful digital transformation. They also discovered that operations technology readiness is the most challenging element to succeed in this area [24].
The authors conducted a study. The instructors utilized the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) method called the analytic network process (ANP) to evaluate various challenges in the model and identify the crucial elements that affect the practical application of DT techniques by teachers and students. The challenges that hinder student participation in using digital products and services in HEIs include poor learning performance, insufficient resources, and fear of change. On the other hand, instructors face challenges such as privacy concerns, lack of experience, and resistance to change when using digital products and services in HEIs [25].
The researchers pursued a study to find the barriers preventing design thinking DT applications in corporate settings. The study’s top challenges were organizational commitment, value creation, value proposition, value delivery, value capture, information and technology infrastructure, and data security. As a result, a conceptual framework was established to describe the issues and how they relate to the value architecture of the business model and the various DT stages. Due to its difficulties, DT is a topic of interest for academics and business executives. This increased focus results from the increasing adoption of digital technologies by manufacturing companies [26].
The authors conducted a study that performed a thorough investigation in the healthcare sector that showed the wide-ranging effects of digital technology on healthcare systems. Innovative health technologies, data-enabled and data-collecting technologies, Industry 4.0 tools and technologies, cognitive technologies, and medication and disease technologies all faced technical difficulties throughout implementation. The issues mentioned earlier caused irregularities in the healthcare sector’s value generation, operational effectiveness, and delivery of digital services [27].
Based on the above, organizations may encounter one or more of these concerns while realizing these problems. Therefore, it is essential to acknowledge and resolve those challenges if adopting digital technology and procedures is to be successful. There are a few reasons why digital transformation adoption in a business may be challenging, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Digital transformation challenges classification.
3. Data Collection and Methods
The data will be gathered using a qualitative methodology by conducting interviews with decision-makers due to the study’s experimental character and limited time. The decision to use the qualitative methodology and interviews to collect data was informed by the elements of the study requirements and time limitations relating to data collection. Furthermore, the merits of qualitative research over quantitative were also part of the reasoning for the choice. Qualitative research aims to gather non-numerical data in a structured manner to gain insights. It is a non-statistical and unstructured or semi-structured approach. In developing the questions to be answered, the approach depends on answering the question. In most cases, a researcher uses the approach when they need to describe a topic or phenomenon more than they need to measure it [28]. Consequently, the participants’ opinions, perspectives, and attributes regarding the research topic matter most in this kind of research. As such, one cannot expect charts or graphical representations from qualitative research. Data is collected in the participants’ natural settings without manipulation. It also means that experiments and control groups are not part of such research. Although qualitative approaches also introduce some depth of understanding to the research questions, they may be challenging to analyze, given their extensive reliance on thematic analysis. Nonetheless, qualitative research has multiple benefits when applied in the proper research setup. It assists in interacting with the researcher and the respondents since it relies on people’s views, perceptions, and opinions [29]. The respondents are more involved than in structured surveys since the data collection methods are relatively dynamic [30]. The researcher can investigate further, which allows for presenting more than just the initial rationales and responses. In addition, it can also see and record non-verbal cues, which are vital during discussions and interviews. Interviews can provide crucial information that surveys may need to gather. Using qualitative research as an initial step can help discover problems, and they can obtain opportunities to learn what people are thinking about [28]. However, the research focused on the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia, which required the inclusion of Saudi managers and workers. Consequently, the idea was to identify whether the targeted in MOE had the ideal informed framework to allow informed decision-making or what they felt was necessary to develop an ideal tool to assist them in adopting the DT process. Ultimately, six experts were mainly decision-makers in MOE. The aim was to obtain responses from all levels of leaders, including both top-level and low-level managers. The researcher only considered managers with at least a year of relevant experience. Choosing eight experts was based on the information obtained from Creswell’s research, which recommended 5 to 25 participants, and Boyd, who recommended 2 to 10 participants, provided that the study had thematic redundancy [31]. The interviews focused on two main sections. The Section 1 was an introduction to the study, and it collected data about the participants. Section 2 focused on answering the two interview questions and getting responses to the overall research aim.
Sample
An interview with a few Ministry of Education decision-makers will be conducted to acquire their responses to the questions prepared.
The role of the interviewer may be summaries as follows [32]:
- (1)
- Getting ready for the interview.
- (2)
- Find respondents and solicit their cooperation.
- (3)
- Address any misunderstandings or worries.
- (4)
- Watch the level of the answer’s clarity.
- (5)
- Document the answers to start the analysis phase.
Table 3 displays the individuals overseeing the digital transformation efforts in the Ministry of Education, along with their respective roles and positions as experts.

Table 3.
Expert position in digital transformation management in the Ministry of Education.
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Qualitative Approach
When analyzing the data, the researcher searched for data familiarity, which meant reading the responses and understanding the data offered, impressions, and meaning to obtain all the necessary data from the myriad of information offered [30]. The analysis aided in pinpointing the essential inquiries that required responses. Furthermore, it focused on answering the three interview questions.
Question 1: What are the main success factors in adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education?
Question 2: What are the main challenges in implementing digital transformation in the Ministry of Education?
Coding and indexing data during the analysis process also proved critical as it enabled the information group based on various common elements, including ideas, behaviors, concepts, phases, and interactions The coding technique helps in managing the information and getting the required answers from the bulk of information offered by the interviewees.
During the interviewing process, eight experts participated; each interview took 30 min to an hour. There were three questions, and each expert had a unique take on the responses, given their experience and organizational setup. The organization had representatives from various sectors; it is a typical sample for determining the success factors and challenges of implementing digital transformation within the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Education.
4.2. Interviews Analysis
In this section, when analyzing answers in research studies, particularly those involving interviews, it is important to consider essential factors such as data quality, reliability, and validity of the measures used [33]. Here, are the answers to two main questions related to this topic.
4.2.1. Question One
The first question asked the interviewees about the main success factors in adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. All the interviewees shared their opinions based on what they had experienced within their organizations. For the most part, all the departments represented, and the eight experts shared these factors: technology, people and employee engagement, partnership with vendors, budget, top management support, culture, and strategy (Figure 1).
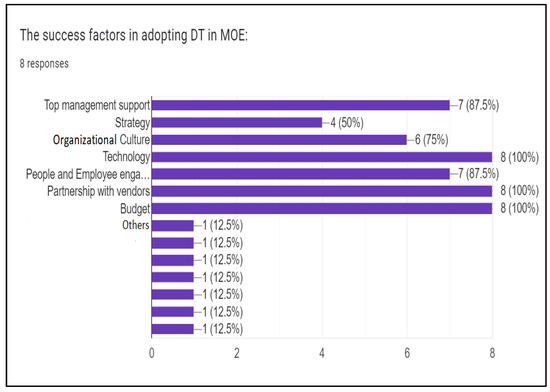
Figure 1.
Statistics of the success factors in adopting DT in MOE.
4.2.2. Critical Success Factor Analysis
According to eight experts from various departments inside the enterprise, the data provided relates to the success factors [34] for adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. The experts identified several essential aspects for successfully embracing digital change: technology, people and employee engagement, vendor partnerships, budget, top management support and culture, and strategy. Most experts agree that using technology to adopt digital transformation is essential. It shows that investments in the latest technologies are significant for the Ministry of Education to accomplish its goals for digital transformation. The experts also highlighted the value of motivating staff members and developing a culture that supports digital transformation, suggesting that the Ministry of Education ensures that its staff is knowledgeable in the latest technologies and inspired to use them. The experts also pointed out the value of working with vendors to give the knowledge and assistance needed to carry out projects for digital transformation. Therefore, the Ministry of Education must establish strong partnerships with vendors to adopt digital transformation effectively.
Furthermore, setting aside a sufficient budget for implementing digital transformation is essential, indicating that the Ministry of Education must allocate adequate resources to support its initiatives. Last, the experts emphasized the significance of top management support and culture, pointing out that the Ministry of Education’s leadership must provide the required support and develop a culture that encourages digital transformation. In addition, the Ministry of Education should have a well-defined plan in place to accomplish its goals for digital transformation, the experts suggested. They also underlined the significance of having a clear strategy for the change. These results indicate that the effective adoption of digital transformation in the Ministry of Education necessitates a comprehensive approach incorporating technology, people, culture, partnerships, and financial support.
Furthermore, to guarantee that staff members have the abilities and knowledge to use new technologies effectively, the Ministry of Education’s leadership must emphasize digital transformation and offer the appropriate assistance, support, and training. The Ministry of Education must also build strategic partnerships with vendors to utilize their expertise and service in implementing digital transformation plans. Finally, the Ministry of Education must also set aside a sufficient budget to support its initiatives for digital transformation while creating a clear strategy that aligns with its aims and objectives.
Technology
Technology is essential in embracing digital transformation, as it helps businesses automate their operations, improve efficiency, and spur innovation. All experts agree that technology is a key success factor.
E1 stated,
“Choosing the right technology is critical to achieving digital transformation”. This technology can facilitate the development of novel business models. Improve processes, and enhance customer experiences”.
E2 mentioned,
“Technology is the foundation of digital transformation, but it is not enough by itself”. A flexible attitude and a creative environment are critical to realizing its full potential”.
E4 noted,
“To compete in today’s digital landscape, organizations must invest in the right technology”. It can assist firms in gaining a strategic advantage, improving operational efficiency, and driving growth”.
E6 said,
“Access to technical resources like hardware, software, and networks is crucial for success”.
People and Employee Engagement
To effectively carry out a digital transformation, it is vital to give top priority to people and employee engagement [35]. This approach will encourage a cultural shift and a mindset change necessary for embracing new technologies and work practices. Most of the experts shared similar feelings about this factor.
E4 said,
“Employee engagement and empowerment to embrace change are essential to success. Especially the entry of young Saudi men and women”.
E5 stated,
“Digital transformations prioritizing people tend to be the most successful”. Employees engaged and empowered within the Ministry can effect significant change”.
E6 mentioned,
“Technology alone is insufficient; a successful digital transformation requires combining technology and people”.
E7 noted,
“Employee engagement is the driving force behind digital transformation”. Without their employees’ participation, the Ministry of Education is unlikely to succeed in their change efforts”.
Partnership with Vendor
Collaborating with vendors is a crucial element in embracing digital transformation. It gives organizations access to expertise, technology, and resources required to implement and sustain digital initiatives. All experts had a consensus about the factor of necessity.
E1 stated,
“Collaborating with the business sector to promote job opportunities and technology is crucial for achieving success in adopting digital transformation, exemplified by TETCO and TCO”.
E2 said,
“Partnerships with vendors such as (TETCO and TCO companies, ministries, and government agencies) Digital transformation relies heavily on their contribution to success”.
E3 mentioned,
“Collaboration with other ministries is essential, such as the Ministry of Health, and government organizations, such as the Digital Government Authority and STC, accelerated and succeeded in the Ministry of Education’s digital transformation”.
E4 stated,
“Collaborating with suppliers is vital to success. We can see this in how we bring data from credible sources”.
Budget
Budget is an important consideration when implementing digital transformation. It allows businesses to invest in the technology, talent, and resources required to drive innovation and meet business goals. All experts showed their agreement upon the importance of this factor.
E1 said,
“Having a realistic budget is critical for the success of digital transformation initiatives”. Having sufficient funds ensures that projects are completed on time and launched successfully. Also, reduce wastage”.
E2 noted,
“Budget constraints can limit the scope and quality of digital transformation efforts”. Therefore, organizations must establish their priorities and distribute resources accordingly”.
E4 stated,
“A long-term commitment and sustained investment are important for adopting digital transformation”. Organizations must guarantee that their budget is adaptable to shifting circumstances”.
E7 mentioned,
“A well-planned budget can assist organizations in achieving their objectives while successfully managing expenditures”.
E8 cited,
“Budgeting for digital transformation is about managing risks and optimizing returns, not just allocating funds”. Therefore, to evaluate the effectiveness of their efforts, organizations need to establish specific metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs)”.
Top Management Support
Top management support is critical in implementing digital transformation because it establishes the tone, vision, and direction for the organization’s digital activities and ensures agreement and alignment at all levels [36]. Most of the experts considered top management support as a key factor.
E1 stated,
“To successfully undergo digital transformation, it is crucial to receive support from upper management. It includes providing guidance to leaders and utilizing the resources available within the organization to ensure the change is successful and the benefits realized”.
E2 mentioned,
“Leadership support is crucial for any successful digital transformation initiative. In early 2020, the Department of Digital Transformation within the Ministry of Education received significant backing from the minister and other leaders. Establishing the organization’s culture and setting the standard and resources for success is essential”.
E3 cited,
“Top management support is critical in advancing digital transformation”. Digital Transformation Department at MOE received support from leaders at the level of the Minister of Education, general supervisors, and principals”. It offers staff the resources, advice, and motivation they need to embrace change and adopt new technology”.
E4 said,
“Getting government support and collaboration with other ministries, such as integrating government technical resources, is one of the success factors influencing the effectiveness of the Ministry of Education’s digital transformation”.
E8 cited,
“The Governance and Strategy Office receives the support of top management and leaders, ensuring the success of the Ministry of Education’s digital transformation”.
Organizational Culture
Culture has a significant impact on digital transformation. It shapes the attitudes, actions, and principles needed to welcome progress, creativity, and sustained development. Most of the experts shared similar feelings about this factor.
E4 cited,
“The existence of a culture of change, which we see in the awareness of employees and the demand for change, is among the main factors for adopting digital transformation”.
E7 stated,
“The leader of the digital transformation process will demonstrate that investing in cultural transformation is more important than investing in digital transformation procedures”.
Strategy
Having a clear strategy is crucial when implementing digital transformation. It outlines the objectives, priorities, and plans for an organization’s digital initiatives while ensuring they align with the overall business strategy. Half of the experts had a consensus about the essential of this factor.
E1 stated,
“One of the factors considered for success was ensuring that the digital transformation strategy of the Ministry of Education aligned with the Vision 2030 strategy”.
E2 cited,
“The digital transformation program’s strategic tasks and objectives are taken very seriously and responsibly”.
Other Success Factors
The interview covered several success-related factors. E1 and E7 brought up the COVID-19 pandemic [37], the 2030 vision, juggling several tasks across technical departments, and embracing the fourth industrial revolution. E3 emphasized the significance of taking responsibility for carrying out the duties and goals related to digital transformation. E4 highlighted the need to use trustworthy data sources, evaluate data accuracy, and involve Saudi men and women in digital transformation. E5 and E6 shared the same idea of the value of data integration and the accessibility of technical resources, such as hardware, software, networks, data centers, and passionate staff members [38,39]. E7 mentioned the significance of raising employee understanding of the fourth industrial revolution, support from the government, and employee awareness of digital transformation. Lastly, E8 stressed the importance of digital transformation planning, leadership development, governance for digital transformation, and enhancing capabilities that support digital transformation. The following table shows the distribution of the success factors among experts given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Success factors classification table.
4.2.3. Question Two
The second question investigated the challenges when implementing digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. The eight experts and most of the departments present shared these challenges: organizational stakes, strategic stakes, resistance to change, information technology and infrastructure, data, digital transformation governance, and cost are the biggest challenges in implementing digital transformation in the Ministry of Education (Figure 2).
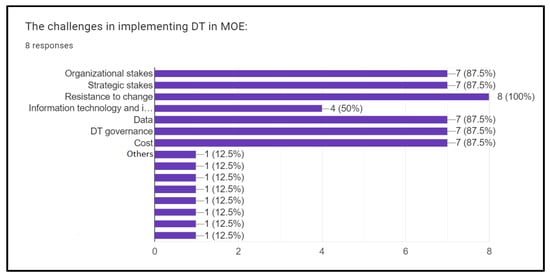
Figure 2.
Statistics of the challenges in implementing DT in MOE.
4.2.4. Challenges Analysis
There are particular challenges to consider when implementing digital transformation at the Ministry of Education, based on the information gathered from the interviews with eight experts and representatives from different departments. Additionally, all experts agreed that many challenges needed to be resolved: organizational stakes, strategic stakes, change resistance, information technology and infrastructure, data, governance of the digital transformation, and cost. Furthermore, dealing with resistance to change is critical, which is a significant challenge. According to the interview results, developing strategies and solutions to address these issues is required to provide a seamless shift to digital transformation at the Ministry of Education. Every stakeholder, including representatives, experts, and IT professionals, must work together to overcome these challenges. In conclusion, this interview emphasizes how critical it is for the Ministry of Education to recognize and address the challenges raised by digital transformation.
Organizational Stakes
Organizational stakes in digital transformation relate to the potential risks and rewards that an organization or its stakeholders may experience while developing and adopting digital technology and processes [20]. Implementing digital transformation in an organization is challenging due to structural constraints. Therefore, balancing short-term gains with long-term benefits is crucial. Most experts had comparable opinions regarding this aspect.
E1 stated,
“The Ministry of Education’s agencies and departments require significant services, which also applies to the external beneficiaries and the time needed to implement these services”.
E3 cited,
“Due to its large size, the Ministry of Education faces a challenge in implementing digital transformation. The Ministry has numerous agencies and departments, as well as many employees and external parties that it handles daily. Additionally, the Ministry receives many external requests from government entities like NIC and SDAIA”.
E4 said,
“Digital transformation presents several challenges, including managing many internal and external stakeholders. The fast-paced and frequent changes in systems, businesses, and services can be overwhelming, especially when they need to be thoroughly analyzed and studied. Additionally, it is crucial to define and clarify the roles and tasks within the digital transformation organization for all departments that benefit from the services”.
E5 mentioned,
“When working with stakeholders during digital transformation, it can be challenging to accurately describe services and the various segments of beneficiaries and customers. Additionally, it is essential to have a large group of staff members spread across the Ministry’s geographical area to manage work and understand the services provided efficiently”.
E6 noted,
“Making changes within an organization can be challenging, but undergoing digital transformation is an even more demanding task. To successfully implement digital projects, leaders must be intentional, forward-thinking, and unwavering in bringing about cultural and structural changes”.
Strategic Stakes
In digital transformation, strategic stakes involve aligning digital projects with an organization’s goals and considering how digital technologies and processes will influence long-term success. Achieving digital transformation requires clear goals, targets, and measurements and aligning digital initiatives with company strategy [20]. Most of the experts considered strategic stakes as a key factor.
E2 stated,
“Digital transformation faces challenges due to a need for more clarity in its vision and complete maturity”.
E3 cited,
“Implementing digital transformation poses a challenge for the Ministry of Education due to the complexity of governing the procedures involved and the requirement for a well-defined message, vision, and strategic goals”.
E6 said,
“A significant challenge in digital transformation is the need for clarity surrounding each department’s strategic objectives, mission, vision, policies, and responsibilities”.
E7 mentioned,
“Developing a strategy is the biggest hurdle in achieving digital transformation. It’s crucial to have a well-planned approach, encourage a culture of experimentation, and maintain a constant learning and improvement mindset to remain competitive”.
Resistance to Change
Implementing digital transformation can be challenging due to resistance to change. This resistance can stem from fear, uncertainty, and doubt among employees, stakeholders, and consumers. Most of the experts considered resistance to change as a critical factor.
E1 stated,
“One of the biggest challenges in digital transformation is the reluctance to change. To overcome this hurdle, leaders must build trust, communicate clearly, and foster a culture encouraging innovation”.
E3 cited,
“One of the challenges of introducing digital transformation is the resistance to change since skills and personnel must align with digital transformation initiatives”.
E4 said,
“A major challenge in digital transformation is people’s reluctance to change because they fear losing their job duties and responsibilities”.
E7 mentioned,
“Achieving digital transformation is a significant challenge that requires a shift in people’s thinking and work methods. Though difficult, showing the advantages and engaging employees to succeed is crucial”.
Digital Transformation Governance
Digital transformation governance is a set of policies, procedures, and decision-making processes that guide an organization in creating, implementing, and managing digital transformation initiatives. Digital transformation governance poses a challenge in effectively monitoring, administering, and coordinating digital activities while balancing agility with risk management and compliance. The majority of experts acknowledge the importance of this factor.
E1 cited,
“Digital transformation requires proper governance, efficient use of resources such as technology, systems, and personnel, and hiring internal programmers”.
E4 stated,
“Establishing appropriate procedures and governance for the services offered by departments and agencies within the Ministry is crucial. Often, service requests are made based on personal preferences rather than a systematic process. Therefore, it is vital to thoroughly and accurately implement the enterprise architecture concept”.
E5 said,
“Proper governance to guide the process is a significant challenge in achieving digital transformation”.
E6 mentioned,
“One of the challenges in implementing digital transformation is managing its governance. Therefore, we must establish a framework to solve this issue to manage risks, ensure compliance, and align digital initiatives with Vision 2030 goal”.
Data
Managing data volume, velocity, diversity, and veracity can be challenging when implementing digital transformation. However, ensuring data quality, security, and privacy is essential, and using data insights to create business value. Many experts view data as a crucial factor.
E2 stated,
“Multiple challenges come with digital transformation in dealing with big data; access to this data requires approvals and agreements, which causes delays in analyzing, interpreting, and storing it”.
E3 cited,
“When working on projects outside of the Ministry, a significant obstacle we encounter is bringing in and retrieving data and ensuring its accuracy and reliability”.
E4 said,
“Our daily challenge on the Fares system is sourcing and integrating data from external systems”.
E5 mentioned,
“Digital transformation poses a challenge in maintaining data quality, which is difficult to control”.
E8 noted,
“Digital transformation can make managing data complicated. It is essential to have reliable, easily accessible, and valuable data. In addition, it is crucial to clearly understand data from the moment it is collected, processed, and presented. Therefore, prioritizing data governance, management, and comprehension is essential”.
Cost
The difficulty in implementing digital transformation lies in balancing the cost of investing in technology, talent, and resources with the organization’s budget and expected return on investment. According to many experts, cost is an essential factor to consider.
E2 cited,
“A significant hurdle in executing digital transformation is the potential need to allocate more funds to cover planned initiatives’ expenses, especially considering the ministry’s magnitude”.
E4 mentioned,
“Investing in projects, innovation, and growth is necessary to achieve digital transformation and requires ongoing costs”.
E7 stated,
“Investing in digital transformation may seem expensive, but not transforming can cost even more. Therefore, organizations must be willing to allocate resources toward technology and talent to stay competitive in the current digital world”.
E8 stated,
“One of the significant obstacles to achieving digital transformation is the financial expense. Therefore, the Ministry must balance investing in digital projects and achieving immediate results while creating long-term value”.
IT and Infrastructure
Achieving digital transformation in IT and infrastructure requires modernizing legacy systems, integrating new technologies, and ensuring the digital infrastructure’s scalability, security, and resilience. Half of the experts had a consensus about this factor.
E1 stated,
“Keeping infrastructure consistent is challenging for digital transformation. Therefore, prioritizing cybersecurity measures is essential to ensure safety”.
E7 cited,
“Implementing digital transformation poses a significant challenge, particularly in IT infrastructure, which serves as its backbone. Hence, enabling the Ministry to utilize data effectively, automate processes, and offer personalized experiences to customers and employees is crucial”.
E8 mentioned,
“Digital transformation can be challenging, with IT and infrastructure being the most difficult aspects. Moving away from traditional on-premises systems and adopting modern cloud-native architectures requires a new mindset, skillset, and working strategy for IT and infrastructure teams”.
Other Challenges
The interview covered several challenges. E1 emphasized the following challenges: insufficient resource utilization, a lack of in-house programmers, cybersecurity and privacy concerns, and scope creep in IT projects. E2 mentioned difficulties such as inadequate planning, a lack of understanding of digital transformation, and limited access to data. E3 highlighted challenges with managing legacy systems and working with several external parties. E4 discussed the challenges, such as needing more Enterprise Architecture applications, decision-making based on personal preferences rather than work system preferences, and unplanned and unorganized changes to systems and enterprises. E5 pointed out challenges with the concept of digital transformation’s maturity, the ownership of data shared across stakeholders, and the need for more extensive automation. E6 highlighted the need for a management structure for digital transformation. E7 listed several key challenges, including improving enterprise architecture, implementing user experience management, hiring more people in various departments such as business analysts, system analysts, and software developers, changing work methodologies such as Scrum Master and Agile, and addressing cybersecurity and privacy concerns. Finally, E8 mentioned challenges, including operations management, project management, business continuity, and risk management, and enhancing the quality of digital services. The table below shows the distribution of the challenges among expert responses (Table 5).

Table 5.
Challenges classification table.
Finally, Table 6 depicts the interview questions and the interviewees’ responses to each question.

Table 6.
A summary of each participant’s response to all interview questions.
5. Discussion
This examines and compares the main findings of the literature and this research. The results concentrated on the main success factors and challenges that affected DT in the MOE.
5.1. Research Approach
This research aimed to identify the main factors that lead to successful digital transformation in the Ministry of Education and the challenges that may arise during the implementation. In order to gather data, the researcher conducted qualitative interviews with eight decision-makers who were leaders and managers in four relevant departments. Each interviewee was asked three semi-structured questions related to the topic.
5.2. Success Factors
This section analyzes and discusses the information provided by eight experts to determine the critical success factors classification [40] in adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. They include budget, vendor partnerships, top management support, and technology.
Overall, all Experts agree that technology is a success factor for adopting digital transformation. By leveraging automation, the Ministry can improve efficiency and drive innovation. However, it is necessary to recognize employees’ crucial role in implementing new technology and processes.
In order to succeed in its digital initiatives, the Ministry of Education needs to establish positive relationships. This requires a strong focus on the vendor’s expertise [41], their technology capabilities, and their resources. Budgeting for technology and personnel is also crucial to achieving organizational objectives.
It is important to have top management support, which sets the tone, vision, and direction of the organization’s digital initiatives, ensuring alignment and agreement at all levels. A clear strategy, which outlines the organization’s goals, priorities, and plans, is essential when implementing digital transformation.
Other success factors are also covered in the results, including the importance of reliable data sources, data accuracy, and involving Saudi women and men in digital transformation. Accessibility of technical resources, employee knowledge of the fourth Industrial Revolution, government support, COVID-19 adaptation, and employee awareness are all-important.
The results are a valuable insight into the factors that will determine the success of digital transformation at the Ministry of Education. The research emphasizes technology, employee engagement, and vendor partnerships as well as budget, top-management support, culture, and strategy.
5.3. Challenges
This research report examines the challenges of implementing digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. It is based on eight interviews conducted with experts and representatives of various departments. The report analyzes and identifies several factors that must be addressed. These include organizational stakes (including strategic stakes), resistance to change, governance of digital transformation, data, costs, and IT infrastructure.
Overall, the research shows that the Ministry of Education is facing significant challenges because of its size. It includes numerous departments, agencies, employees, and external parties it deals with daily. To achieve digital transformation, it is important to balance short-term gains and long-term benefits. It also requires developing clear goals and targets and measuring them. Digital initiatives must be aligned with the organization’s strategy. Building trust, communicating clearly, and cultivating a culture of innovative thinking are all ways to address resistance to change. The research emphasizes the importance of recruiting internal programmers, establishing adequate governance, and efficiently using resources such as technology and systems to achieve digital transformation. Data volume, velocity, and diversity can all be challenging to manage. It is also critical to protect data security and privacy. The paper emphasizes the difficulty of balancing talent, technology, and resource investment against the MOE’s budget and desired return. The results analyze the challenges in implementing digital transformation in MOE of integrating legacy systems with new technology and emphasize the importance of ensuring that the digital infrastructure can be scaled, secured, and durable. In order to support a seamless transformation, the research emphasizes that MOEs need to address and improve DT barriers via collaborations and the development of solutions and policies.
Based on comprehensive research and analyzing the results of our discussion, the researcher developed a framework that outlines the main success factors and challenges for adopting digital transformation in the Ministry of Education. A framework of the main success factors and challenges findings in (Figure 3).
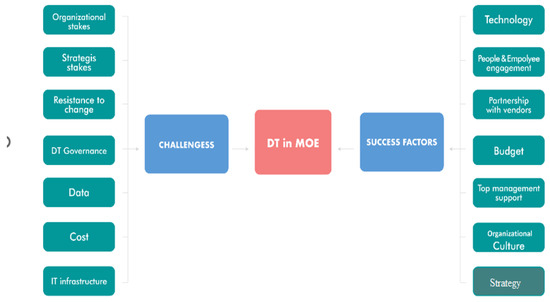
Figure 3.
A framework for main success factors and challenges in adopting DT in MOE.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, this research aimed to determine the primary factors contributing to the success of digital transformation in the Ministry of Education and the challenges that arise when implementing it, specifically within the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Education. Using qualitative interviews, the study found that the seven main success factors were technology, employee engagement, vendor partnerships, budget, top management support, culture, and strategy. On the other hand, the seven main challenges included organizational and strategic stakes, resistance to change, governance, data, cost, and IT infrastructure. The study created a framework that outlines these success factors and challenges, which can be applied to other sectors and industries. Future studies can use models like Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) to examine individual perspectives, and other analyses can rank factors according to their significance. The Ministry of Education can use these insights to create a digital transformation strategy that aligns with its objectives, focusing on good governance, efficient resource usage, data quality, and privacy management.
Future Work
The improvements involve creating a five-year plan, clarifying goals and strategies, and introducing new projects. The Enterprise Architecture Office will document work procedures, inventory services, and technical resources, while performance indicators and criteria will measure the quality of digital transformation’s quality. Departments must focus on SLA, BPR, and Business Systems to enhance efficiency, promote internal development and data improvement, standardization of digital systems, and create a customer experience department. The Ministry must collaborate with third-party suppliers such as Apple to exchange experiences. The Ministry should invest in training and development and use modern AI technologies. In addition, focusing on the diversity of work methodologies like Agile and Scrum, innovation, and application workshops will improve system-level products. Additionally, enhance performance criteria KPIs and develop them to reflect the quality of digital transformation outputs accurately. An Agile Squad must perform with one member from each Digital Transformation Department to handle urgent and emergency digital requests, and Matter-most will enhance communication. Lastly, the Ministry will eliminate the digital transformation discourse within the department.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and J.A.; Methodology, M.A. and S.B.K.; Validation, M.A.; Formal analysis, J.A. and S.B.K.; Data curation, J.A.; Writing—original draft, M.A. and J.A.; Writing—review & editing, S.B.K.; Visualization, J.A.; Supervision, S.B.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, “Ministry of Education” in Saudi Arabia, for funding this research (IFKSUOR3-176-2023-3).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data has been well referenced in the paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, “Ministry of Education” in Saudi Arabia, for funding this research (IFKSUOR3-176-2023-3).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Digital Transformation Vision 2030. Available online: https://dga.gov.sa/en/digital-transformation (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Education, M. of. (n.d.). المملكة العربية السعودية. وزارة التعليم. Available online: https://moe.gov.sa/en/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Verina, N.; Titko, J. Digital Transformation: Conceptual Framework. In Proceedings of the 6th International Scientific Conference Contemporary Issues in Business, Management and Economics Engineering 2019, Vilnius, Lithuania, 9–10 May 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tonder, C.; Schachtebeck, C.; Nieuwenhuizen, C.; Bossink, B. A framework for digital transformation and Business Model Innovation. Management 2020, 25, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Li, W. Digital Transformation: A review and research framework. Front. Bus. Econ. Manag. 2022, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudairi, S.A. The impact of digital transformation on the consumer experience in Saudi Arabia 2021. مجلة العلوم الإقتصادية و الإدارية و القانونية 2022, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabdeen, M.; Alofaysan, H. Investigating the impact of digital transformation on the labor market in the era of Changing Digital Transformation Dynamics in Saudi Arabia. Economies 2023, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ruithe, M.; Benkhelifa, E.; Hameed, K. Key issues for embracing the cloud computing to adopt a digital transformation: A Study of Saudi Public Sector. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 130, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kuwaiti, A.; Al Muhanna, F.A.; Al Amri, S. Implementation of Digital Health Technology at Academic Medical Centers in Saudi Arabia. Oman Med. J. 2018, 33, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrahili, M.; Aldahawi, H. Developing the real estate rental sector in line with the digital transformation of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia a proposed study for the application of Blockchain technology. J. Inf. Stud. Technol. (JIST) 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, R. The Adoption of Digital Transformation in the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia. 2021. Available online: https://tuengr.com/V12/12A8L.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Brdesee, H. A divergent view of the impact of digital transformation on academic organizational and spending efficiency: A review and Analytical Study on a university E-Service. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmundsen, K.; Iden, J.; Bygstad, B. Digital Transformation: Drivers, Success Factors, and Implications. AIS Electronic Library (AISeL), 2018. Available online: https://aisel.aisnet.org/mcis2018/37/ (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- AlBar, A.M.; Hoque Md, R. Factors affecting the adoption of information and communication technology in small and Medium Enterprises: A perspective from rural Saudi Arabia. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2017, 25, 715–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Qiu, K.; Zhu, Y. The measurements and decomposition of innovation inequality: Based on Industry—University—Research perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakanyane, R.; O’Reilly, P.; Mcavoy, J.; Grace, A. Determining Digital Transformation Success Factors. Handle Proxy. 7 January 2020. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10125/64274 (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Cichosz, M.; Wallenburg, C.M.; Knemeyer, A.M. Digital Transformation at Logistics Service Providers: Barriers, success factors and leading practices. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2020, 31, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, A.E.; Aliu, J.; Onajite, S.; Simeon, M. Success factors of digital technologies (DT) tools adoption for sustainable construction in a developing economy. Constr. Innov. 2022; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar, F.; Almeida WH, C.; Varajão, J. Digital transformation success in the Public Sector: A systematic literature review of cases, processes, and success factors. Inf. Polity 2023, 28, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunis, M.; Markarian, C.; El-Kassar, A.N. A conceptual model for sustainable adoption of ehealth: Role of digital transformation culture and healthcare provider’s readiness. Proc. IMCIC 2020, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Saab, S., Jr.; Fu, Y.; Ray, A.; Hauser, M. A dynamically stabilized recurrent neural network. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 54, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.S. Challenges of digital transformation in Higher Education Institutions: A brief discussion. In Proceedings of the 30th IBIMA Conference, Madrid, Spain, 8–9 November 2017; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.22/15234 (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Brunetti, F.; Matt, D.T.; Bonfanti, A.; De Longhi, A.; Pedrini, G.; Orzes, G. Digital transformation challenges: Strategies emerging from a multi-stakeholder approach. TQM J. 2020, 32, 697–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M. Digital transformation success under Industry 4.0: A strategic guideline for manufacturing SMEs. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2021, 32, 1533–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhubaishy, A.; Aljuhani, A. The challenges of instructors’ and students’ attitudes in Digital Transformation: A case study of Saudi universities. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2021, 26, 4647–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favoretto, C.; Mendes GH, D.S.; Filho, M.G.; Gouvea de Oliveira, M.; Ganga, G.M.D. Digital transformation of business model in manufacturing companies: Challenges and research agenda. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2022, 37, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Mas, F.; Massaro, M.; Rippa, P.; Secundo, G. The challenges of digital transformation in healthcare: An interdisciplinary literature review, framework, and future research agenda. Technovation 2023, 123, 102716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, G.; Kong, M.; Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Developing Multi-Labelled Corpus of Twitter Short Texts: A Semi-Automatic Method. Systems 2023, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, C.; Palmgren, P.J.; Liljedahl, M. Twelve tips for conducting qualitative research interviews. Med. Teach. 2019, 41, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woiceshyn, J.; Daellenbach, U. Evaluating Inductive versus Deductive Research in Management Studies: Implications for Authors, Editors, and Reviewers. Qual. Res. Organ. Manag. Int. J. 2018, 13, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubrium, J.F.; Holstein, J.A.; Marvasti, A.B.; McKinney, K.D. The SAGE Handbook of Interview Research: The Complexity of the Craft; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacherjee, A. “Social Science Research: Principles, Methods, and Practices” 2012. Open Access Textbooks. Book 3. Available online: http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/oa_textbooks/3 (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Erlingsson, C.; Brysiewicz, P. A hands-on guide to doing content analysis. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 7, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Ouyang, T.; Balozian, P.; Zhang, S. The role of managerial cognitive capability in developing a sustainable innovation ecosystem: A case study of Xiaomi. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, Z.B.; Farah, M.F.; Daouk, S. The effect of e-retailers’ innovations on shoppers’ impulsiveness and addiction in web-based communities: The case of Amazon’s Prime Now. Int. J. Web Based Communities 2019, 15, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuni, I.Y. A systematic review of the critical success factors for implementing circular economy in construction projects. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 31, 1195–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhini, A.; Harfouche, A.; De Marco, M. Artificial intelligence-based digital transformation for sustainable societies: The prevailing effect of COVID-19 crises. Pac. Asia J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Altamimi, S.A.; Alkayyal, N.A.; Alshehri, E.; Alabbad, D.A. Digital Transformation and Cybersecurity Challenges for Businesses Resilience: Issues and Recommendations. Sensors 2023, 23, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenezi, M.; Akour, M. Digital Transformation Blueprint in Higher Education: A Case Study of PSU. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, T.; Zhou, G.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Emotion classification for short texts: An improved multi-label method. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.C. Individual investors’ trading behavior and gender difference in tolerance of sex crimes: Evidence from a natural experiment. J. Empir. Financ. 2023, 73, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
