Enhanced Organizational Performance: Integrating Dimensions for Sustainable Growth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. General Systems Theory
2.2. Organizational Performance and SDGs
2.3. Structural Archetypes and Innovative Capacity in the Current Context
2.4. Organizational Performance Measurement and Monitoring Model
3. Methodology
3.1. Methodological Process
3.2. Sample and Data Collection
3.3. Model Construction
3.4. Expert Judgment and AHP Matrix
3.5. Monte Carlo Simulation
3.6. Data Analysis Process
4. Results and Discussion

5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoekman, B.; Taş, B.K.O. Procurement policy and SME participation in public purchasing. Small Bus. Econ. 2020, 58, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghina, Ș.C.; Botezatu, M.A.; Hosszu, A.; Simionescu, L.N. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): The engine of economic growth through investments and innovation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, D.; Recardo, R.J. Corporate Performance Management: How to Build a Better Organization through Measurement-Driven Strategic Alignment; Routledge: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.E.; Kramer, M.R.; Lenssen, G.; Smith, N. Creating shared value. Managing sustainable business. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Abisuga-Oyekunle, O.A.; Patra, S.K.; Muchie, M. SMEs in sustainable development: Their role in poverty reduction and employment generation in sub-Saharan Africa. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2020, 12, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, M.; Chesbrough, H.; Heaton, S.; Teece, D.J. Strategic management of open innovation: A dynamic capabilities perspective. Calif. Manag. Rev. 2019, 62, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalanffy, L.V. General System Theory: Foundations, Development, Applications; Braziller: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sage, A.P.; Rouse, W.B. Handbook of Systems Engineering and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, V.Z. The organization of work: Contributions from open systems theory. In The Unconscious at Work; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.H.; Ahmed, S.A. Systems Thinking—Ludwig Von Bertalanffy, Peter Senge, and Donella Meadows. In Science Education in Theory and Practice: An Introductory Guide to Learning Theory; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 419–436. [Google Scholar]
- Volkova, V.N.; Fleishman, B.S.; Tarasenko, F.P.; Loginova, A.V. Further development of potential feasibility theory for complicated systems according to the unified general-system principle. In International Conference on Professional Culture of the Specialist of the Future; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Garbolino, E.; Chéry, J.P.; Guarnieri, F. The systemic approach: Concepts, method and tools. In Safety Dynamics: Evaluating Risk in Complex Industrial Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- La Scalia, G.; Micale, R.; Miglietta, P.P.; Toma, P. Reducing waste and ecological impacts through a sustainable and efficient management of perishable food based on the Monte Carlo simulation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, A.; Shamayleh, A.; El-Sayegh, S.; Formaneck, S. Prioritizing risks in sustainable construction projects using a risk matrix-based Monte Carlo Simulation approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertalanffy, L.V. The History and Status of General Systems Theory. Acad. Mang. J. 1972, 15, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.B.; Parente, J. Main Street retail system: Theoretical contributions drawn from the general systems theory. ReMark-Rev. Bras. Mark. 2019, 18, 178–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R.; Baker, R.M. Teoría de la complejidad: Una visión general con aplicaciones potenciales para las ciencias sociales. Sistemas 2019, 7, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, T.G. Closed and Open Systems: Organizational. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences; Smelser, N.J., Baltes, P.B., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Greenwood, D.; Kassem, M. Blockchain in the built environment and construction industry: A systematic review, conceptual models and practical use cases. Autom. Constr. 2019, 102, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhoff-Héritier, A. Institutions, interests and political choice. In Political Choice; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 27–52. [Google Scholar]
- López, C.C. Diseño y sistemas complejos: Un enfoque multidimensional en el proceso de Diseño. RChD Creac. Pensam. 2021, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgöwer, F.; de Sousa, J.B.; Kapinski, J.; Mosterman, P.; Oehlerking, J.; Panciatici, P.; Prandini, M.; Rajhans, A.; Tabuada, P.; Wenzelburger, P. Position paper on the challenges posed by modern applications to cyber-physical systems theory. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2019, 34, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C. Critical Systems Thinking and the Management of Complexity; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, E.G.; Giordano, R.; Pagano, A.; Van Der Keur, P.; Costa, M.M. Using a system thinking approach to assess the contribution of nature based solutions to sustainable development goals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siawsh, N.; Peszynski, K.; Young, L.; Vo-Tran, H. Exploring the role of power on procurement and supply chain management systems in a humanitarian organisation: A socio-technical systems view. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 3591–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, M. Qué Aporta el Enfoque Sistémico y Estratégico a las Organizaciones. Management. 2014. Available online: https://mba.americaeconomia.com/articulos/columnas/que-aporta-el-enfoque-sistemico-y-estrategico-lasorganizaciones (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Morales, M. Pensamiento Sistémico en las Organizaciones. UDLAP. 2017. Available online: https://contexto.udlap.mx/pensamiento-sistemico-en-las-organizaciones/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Sieniutycz, S. Complexity and Complex Thermo-Economic Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Herman, J.L.; McCausland, T.C.; Bliton, D. Making a difference in the digital age: Global leadership and multiteam systems. In Research Handbook of Global Leadership; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2020; pp. 126–140. [Google Scholar]
- Fuertes, G.; Alfaro, M.; Vargas, M.; Gutierrez, S.; Ternero, R.; Sabattin, J. Conceptual framework for the strategic management: A literature review—Descriptive. J. Eng. 2020, 2020, 6253013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Bejarano, D.A.; Holguín-García, M.J. Población y desarrollo sostenible en México: Revisión de sus relaciones complejas. Papeles Población 2020, 26, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Dong, T.; Li, B.; Gao, S. Developing a conceptual partner selection framework: Digital green innovation management of prefabricated construction enterprises for sustainable urban development. Buildings 2022, 12, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccho-Huatuco, L.; Ball, P.D. The quest for achieving United Nations sustainability development goals (SDGs) Infrastructure and innovation for responsible production and consumption. RAUSP Manag. J. 2019, 54, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations General Assembly. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 21 October 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Cameron, K.S.; Whetten, D.A. (Eds.) Organizational Effectiveness: A Comparison of Multiple Models; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Eccles, R.G.; Serafeim, G. The performance frontier. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2013, 91, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- Serafeim, G. Public sentiment and the price of corporate sustainability. Financ. Anal. J. 2020, 76, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, T.; Bauer, R.; Orlitzky, M. Sustainable development and financial markets: Old paths and new avenues. Bus. Soc. 2016, 55, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbreath, J. Drivers of green innovations: The impact of export intensity, women leaders, and absorptive capacity. J. Bus. Ethics 2019, 158, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, A.; Matten, D.; Spence, L.J. Corporate social responsibility in a global context. In Corporate Social Responsibility: Readings and Cases in a Global Context; Crane, A., Matten, D., Spence, L.J., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013; Volume 2, pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, I.; Serafeim, G. The Consequences of Mandatory Corporate Sustainability Reporting; Harvard Business School Research Working Paper No. 11-100. 2017. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=1799589 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Bansal, P.; DesJardine, M.R. Business sustainability: It is about time. Strateg. Organ. 2014, 12, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jia, J.; Chapple, L. The corporate sustainability committee and its relation to corporate environmental performance. Meditari Account. Res. 2022, 31, 1292–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, J.; Daniels, J. The role of universities and educators in developing and implementing sustainable developmental goals. Andragoška Spoznanja 2019, 25, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickel, J.; Kallis, G. Is green growth possible? New Pol. Econ. 2020, 25, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, H.; Di Minin, A. Open social innovation. New Front. Open Innov. 2014, 16, 301–315. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbour, C.J.C.; Sarkis, J.; de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.L.; Renwick, D.W.S.; Singh, S.K.; Grebinevych, O.; Kruglianskas, I.; Godinho Filho, M. Who is in charge? A review and a research agenda on the ‘human side’of the circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukker, A. Product services for a resource-efficient and circular economy—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 97, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mont, O.; Neuvonen, A.; Lähteenoja, S. Sustainable lifestyles 2050: Stakeholder visions, emerging practices and future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 63, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Lasrado, F.; Hafeez, K. The effect of TQM on organisational performance: Empirical evidence from the textile sector of a developing country using SEM. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2019, 30, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dhone, N.C. Industry 4.0 and lean manufacturing practices for sustainable organisational performance in Indian manufacturing companies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 1319–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethibe, T.; Steyn, R. Innovation and organisational performance: A critical review of the instruments used to measure organisational performance. South. Afr. J. Entrep. Small Bus. Manag. 2016, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadi, A.; Kamble, S.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Gunasekaran, A.; Ndubisi, N.O.; Venkatesh, M. Manufacturing and service supply chain resilience to the COVID-19 outbreak: Lessons learned from the automobile and airline industries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 163, 120447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, J.; Sağsan, M. Impact of knowledge management practices on green innovation and corporate sustainable development: A structural analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Chen, J.; Del Giudice, M.; El-Kassar, A.N. Environmental ethics, environmental performance, and competitive advantage: Role of environmental training. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccanto, F.F.; Vera, F.R.; Vera, R.P.R.; Vera, A.M.R. Gestión de Innovación tecnológica y globalización como factores impulsadores de la calidad de servicio y competitividad. Rev. Venez. Gerenc. 2019, 24, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, J.A.N.; Khan, N.A. Exploring the role of social media in collaborative learning the new domain of learning. Smart Learn. Environ. 2020, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M. The Theory of Social and Economic Organization; Parsons: New York, NY, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.A. Strategy and Structure, Chapters in the History of the American Industrial Enterprise; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, M.Y. Modelo de Gestión del Teletrabajo en Contexto de Contingencias para la Educación Superior en Costa Rica: El Caso de la Universidad Nacional. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Costa Rica, Heredia, Costa Rica, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Martorell, F.J.B.; Arcos, F.J.M.; García, L.M.R.; Torralba, L.T.; Forteza, C.M. Turismo post COVID-19. El turismo después de la pandemia global. Análisis Perspect. Vías Recuper. 2020, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phimister, A.; Torruella, A. El Libro de la Innovación: Guía Práctica para Innovar en tu Empresa; Libros de Cabecera: Barcelona, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, T.; Stalker, G.M. Mechanistic and organic systems. In Classics of Organizational Theory; Routledge: London, UK, 1961; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, S.; Soto-Acosta, P.; Palacios-Marqués, D. A discriminant analysis of high and low-innovative firms: The role of IT, human resources, innovation strategy, intellectual capital and environmental dynamism. J. Knowl. Manag. 2022, 26, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlechter, D.; Agoff, S.; Anzoátegui, M.; Bauni, N.; Blugerman, L.; Caravaca, E.; Chosco Díaz, C.; Espejo, V.; Gibert, G.; Iorio, S.; et al. Teorías de las Organizaciones: Un Enfoque Crítico, Histórico y Situado; Universidad Nacional de General Sarmiento: Los Polvorines, Argentina, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Castrillón, M.A.G. Propuesta de modelo de ambidestreza organizacional. New Bus. Rev. 2020, 6, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traba, L.A. Teoría (y Práctica) de las Organizaciones: Herramientas para la Gestión de la Calidad; Universidad Nacional del Litoral: Santa Fe, Argentina, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Perilla, R.B.; González, M.B. La innovación organizacional examinada desde las teorías del diseño, el cambio, la cognición y aprendizaje organizacionales. ESPACIOS 2021, 42, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez-de-Lema, D.; Ruiz-Palomo, D.; Diéguez-Soto, J. Analysing the roles of CEO’s financial literacy and financial constraints on Spanish SMEs technological innovation. Technol. Soc. 2021, 64, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuren, F.H.; Campos, D.B.D.; Fagundes, A.B.; Kohlbeck, E.; Pereira, D. Minimização das Barreiras na Implantação de um Sistema Produto Serviço Através da Economia Circular e dos Objetivos do Desenvolvimento Sustentável. ENSUS 2021—IX Encontro de Sustentabilidade em Projecto. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.ufsc.br/handle/123456789/228943 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Hamadamin, H.H.; Atan, T. The impact of strategic human resource management practices on competitive advantage sustainability: The mediation of human capital development and employee commitment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepez-Moreira, R.I.; Muyulema-Allaica, J.C.; Ormaza-Morejón, F.M.; Sánchez-Macías, R.A. Instrumento de diagnóstico para el análisis y mejora de las operaciones de confección. RIIIT Rev. Int. Inv. Innov. Tecnol. 2019, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, F.; Montoya, D.C.B. Diseño de un modelo de gestión aplicado a una PYME en el sector eléctrico. Relig. Rev. Cien. Soci. Hum. 2023, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teves, L.S.; Castro, M.D.P.; Morgante, M.G. Circulación e intercambios desde Análisis de Redes Sociales (ARS): Revisión de modelos en clave relacional. In Poder, Circulación y Comunidades en América del Sur: Reflexiones Teórico-Metodológicas Desde el Análisis de Redes Sociales; 2020. Available online: https://ri.conicet.gov.ar/handle/11336/161462 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Ballina, F. ¿Hacia una teoría de la administración en América Latina? Ens. Econ. 2021, 31, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdi, B.; Alshurideh, M. Employee retention and organizational performance: Evidence from banking industry. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2020, 10, 3981–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.; Frow, P.; Steinhoff, L.; Eggert, A. Toward a comprehensive framework of value proposition development: From strategy to implementation. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 87, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engert, S.; Rauter, R.; Baumgartner, R.J. Exploring the integration of corporate sustainability into strategic management: A literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2833–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koontz, H.; Weihrich, H. Essentials of Management: An International, Innovation, and Leadership Perspective; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Velarde, O.; Bernete, F.; Casas-Más, B. Las interacciones virtuales con personas conocidas que no son amigas. Rev. Lat. Com. Soc. 2019, 74, 668–691. [Google Scholar]
- Pantoja-Aguilar, M.P.; Garza-Treviño, J.R.S. Etapas de la administración: Hacia un enfoque sistémico. Rev. EAN 2019, 87, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle Barco, J.A.; Sandoval Cabeza, C.J. Microempresa Comercial del Mercado Modelo de la Ciudad de Chiclayo Como Sistema Complejo Adaptativo. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Católica Santo Toribio de Mogrovejo, Chiclayo, Peru, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno Monsalve, N.A.; Sánchez Ayala, L.M.; Velosa García, J.D. Introducción a la Gerencia de Proyectos: Conceptos y Aplicación. Ediciones EAN. 2019. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10882/9547 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Greenwood, R.C. Management by objectives: As developed by Peter Drucker, assisted by Harold Smiddy. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1981, 6, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinzant, J.C.; Vinzant, D.H. Strategic management spin-offs of the Deming approach. J. Manag. Hist. 1999, 5, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, A.; Guttman, I.; Marinovic, I. Earnings management and earnings quality: Theory and evidence. Account. Rev. 2019, 94, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Spiegel, M.; De Boer, W.J.; Luning, P.A.; Ziggers, G.W.; Jongen, W.M.F. Validation of the instrument IMAQE-Food to measure effectiveness of food quality management. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2007, 24, 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, P.J.R. La teoría de sistemas aplicada en la administración reflexiones desde la perspectiva transcompleja. Revista Cient. e-Locução 2022, 1, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela-Jiménez, L.F.; Giner-Fillol, A.; Ripoll Feliu, V. Una propuesta metodológica para la gestión integral de los puertos marítimos. Criterio Libre 2019, 17, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Sierra, J.M. Sistema de Gestión de Eficiencia Global (Overall Equipment Effectiveness, OEE) en Tiempo Real para Industria. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de València, Valencia, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ottogalli, D.; Rohvein, C.; Roark, G.; Urrutia, S.; Paravié, D.; Corres, G. Desarrollo y madurez de las actividades de un conglomerado de pymes industriales argentinas. Rev. Ing. Ind. 2016, 15, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Garrote, P.R.; del Carmen Rojas, M. La validación por juicio de expertos: Dos investigaciones cualitativas en Lingüística aplicada. Rev. Nebrija Lingüística Apl. Enseñanza Leng. 2015, 18, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanasreh, E.; Moles, R.; Chen, T.F. Evaluation of methods used for estimating content validity. Res. Soc. Adm. Pharm. 2019, 15, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; King, B.; Silverberg, J.I.; Beck, L.A.; Bieber, T.; Reich, K.; Kabashima, K.; et al. The Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (vIGA-AD): The development and reliability testing of a novel clinical outcome measurement instrument for the severity of atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-Velasco, A. Modelo de Salud y Seguridad en el Trabajo con Gestión Integral para la Sustentabilidad de las organizaciones (SSeTGIS). Cienc. Trab. 2017, 19, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1990, 48, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Serv. Sci. 2008, 1, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 1987, 9, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L.; Kearns, K.P. Analytical Planning; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T. That is not the analytic hierarchy process: What the AHP is and what it is not. J. Multi-Criteria Decis. Anal. 1997, 6, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parejo, I.Á.B.; Núñez, W.A.N.; Núñez, L.D.N. Inserción del análisis financiero en PyMes colombianas como mecanismo para promover la sostenibilidad empresarial. Desarro. Gerenc. 2021, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahul Hameed, N.S.; Salamzadeh, Y.; Abdul Rahim, N.F.; Salamzadeh, A. El impacto de la reingeniería de procesos de negocio en el desempeño organizacional durante la pandemia de coronavirus: Papel moderador del pensamiento estratégico. Previsión 2022, 24, 637–655. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, U.; Lee, S.; Salik, M. La influencia de la innovación en la gestión y la innovación tecnológica en el desempeño de la organización. Un papel mediador de la sostenibilidad. Sostenibilidad 2019, 11, 495. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Khan, M.S.; Thitivesa, D.; Siraphatthada, Y.; Phumdara, T. Impacto del compromiso de los empleados y el intercambio de conocimientos en el desempeño organizacional: Estudio de los desafíos de recursos humanos en la pandemia de COVID-19. Gest. Sist. Hum. 2020, 39, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Akdere, M.; Egan, T. Liderazgo transformacional y desarrollo de recursos humanos: Vincular el aprendizaje de los empleados, la satisfacción laboral y el desempeño organizacional. Hum. Resour. Dev. Q. 2020, 31, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Coelho, A.; Moutinho, L. Dynamic capabilities, creativity and innovation capability and their impact on competitive advantage and firm performance: The moderating role of entrepreneurial orientation. Technovation 2020, 92, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibidunni, A.S.; Ogundana, O.M.; Okonkwo, A. Entrepreneurial competencies and the performance of informal SMEs: The contingent role of business environment. J. Afr. Bus. 2021, 22, 468–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, P.A.; Odunukan, K.; Rahman, M.; Rugara, D.G.; Ochinanwata, C. How entrepreneurship ecosystem influences the development of frugal innovation and informal entrepreneurship. Thunderbird Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 62, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urribarri, A.C.; Vera, K.J.C.; Reyes, C.A.R.; Cubas, M.R. Desempeño innovador para el fortalecimiento de la cultura de emprendimiento en Peru. Rev. Venez. Gerenc. RVG 2022, 27, 1837–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
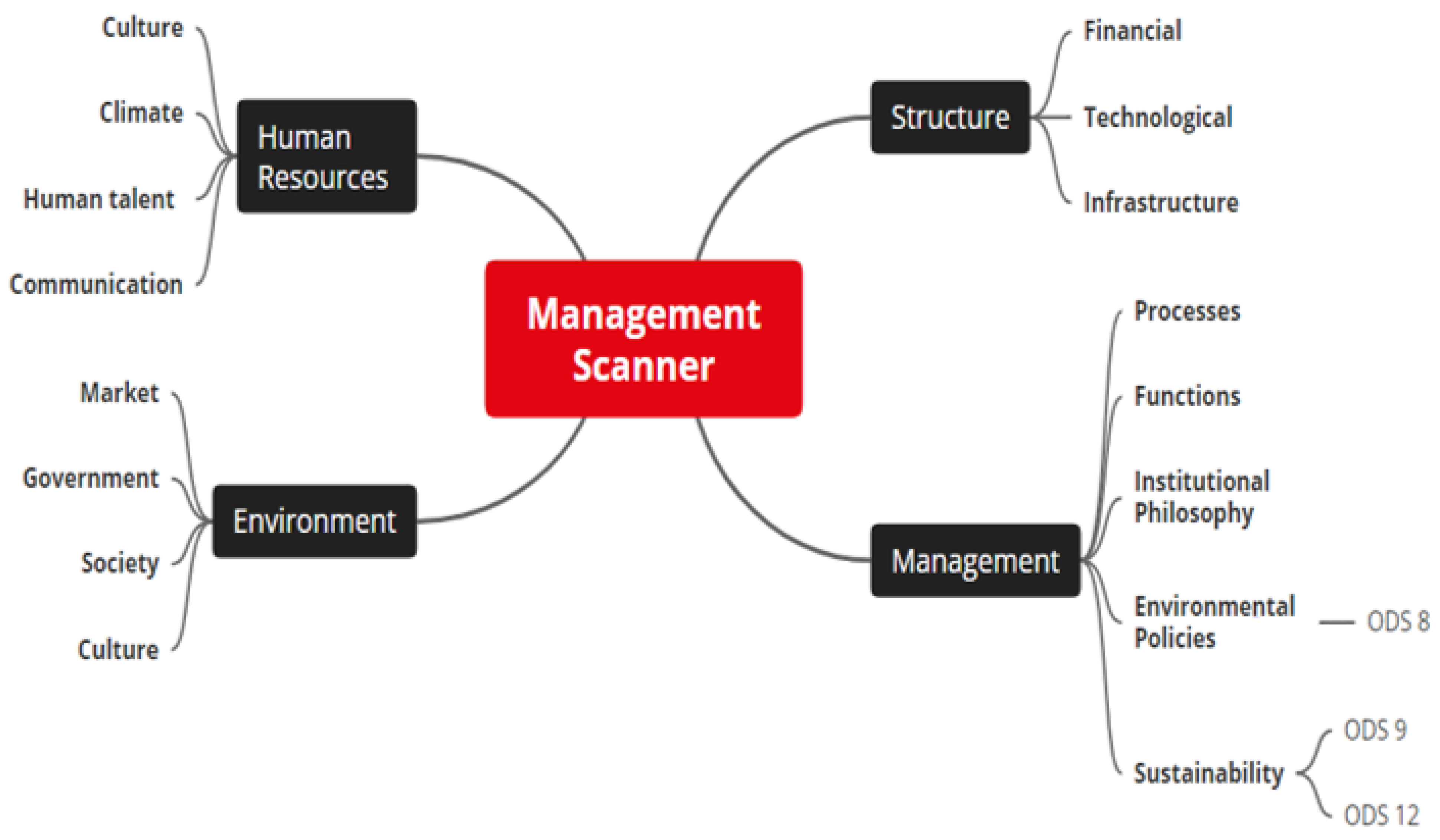






|
|
|
|
|
| Dimension | Attribute | Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Financial Technological Infrastructure | Funds internal generation Company liquidity Business cycle Business profitability vs. non-quality costs Fulfillment of strategic organizational objectives Clean technology Technological innovation Computer equipment Manufacturing technology or servo production Digitalization Strategic location vs. suppliers and customers The physical structure in harmony with nature Spaces (areas): Use of physical spaces Information safety |
| Management | Processes Functions Philosophy Environmental Policies Sustainability | Management processes Mission processes Support processes Strategic functions Tactical functions Operational functions Vision Mission Principles Values Policies Environmental policies Environmental behavior Environmental attitude Environmental knowledge Sustainability benefits |
| Human Resources | Culture Climate Human talent Communication | Intrapersonal ties Interpersonal links Interorganizational linkages Cohabitation Stimulus Competences Compensation Formation Media Participation Impact |
| Environment | Market Government United Nations Culture | Clients Suppliers Government policies Stimuli Support entities Stakeholders Internship SDG 8–SDG 9 and SDG 12 |
| Valuation | Operationalization |
|---|---|
| Enhanced | Aspects of the company that are perceived as outstanding and reflect the company’s great achievements in the evaluation process. |
| Factors that are given a very high rating between 8.0 and 9.0, which are high-value aspects of the company. | |
| Viable | The company’s characteristics are perceived as good; some achievements have been made and indicate normal functioning of the company. |
| There is room for improvement since the optimal level for the company has not yet been reached. | |
| Aspects with a score between 6.0 and 7.9 that reflect good performance but can be improved upon. | |
| Warning | Characteristics of companies for which there are certain difficulties in implementation; at this level are factors that have demonstrated some failures and indicate early warnings. |
| Aspects rated to values between 4.0 and 5.9. This scale indicates failures in the company’s various processes and reflects errors that have occurred. | |
| High Risk | Characteristics of the company that can cause significant problems and place the company in a vulnerable situation. |
| Typically scored between 0.0 and 3.9 and reflect negligence, poor practices, mistakes with serious consequences, and omissions that leave a negative image and affect the stability of the organization. |
| Dimensions/Variables | Minimum Value | Most Likely | Maximum Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Environment (SDG 12) | 4.25 | 5.03 | 5.80 |
| 1.1 Context | 5.75 | 6.57 | 7.39 |
| 1.2 International | 1.92 | 2.47 | 3.02 |
| 1.3 Legal | 5.33 | 6.26 | 7.19 |
| 1.4 Socioenvironmental | 3.90 | 4.75 | 5.60 |
| 2. Structure (SDG 8) | 5.71 | 6.45 | 7.20 |
| 2.1 Finance | 6.16 | 6.76 | 8.01 |
| 2.2 Infrastructure and production | 5.84 | 6.64 | 7.45 |
| 2.3 Technology | 5.09 | 5.94 | 6.80 |
| 3. Management | 4.37 | 5.59 | 6.81 |
| 3.1 Institutional philosophy | 4.37 | 5.53 | 6.69 |
| 3.2 Functions | 5.04 | 6.15 | 7.26 |
| 3.2 Processes | 4.13 | 5.42 | 6.72 |
| 4. People (SDG 9) | 4.51 | 5.43 | 6.34 |
| 4.1 Organizational climate | 4.65 | 5.51 | 6.37 |
| 4.2 Organizational culture | 4.78 | 5.69 | 6.60 |
| 4.3 Human resources management | 4.26 | 5.22 | 6.19 |
| Organizational performance | 4.73 | 5.63 | 6.53 |
| High Risk | International (Within the Environmental Dimension/SDG 12) | 2.47 |
| Warning | Environmental dimension (SDG 12) | 5.03 |
| Socioenvironmental (within the environmental dimension/SDG 12) | 4.75 | |
| Technology (within the structural dimension/SDG 8) | 5.94 | |
| Management | 5.59 | |
| Institutional philosophy (within the management dimension) | 5.53 | |
| Processes (within the management dimension) | 5.42 | |
| People (SDG 9) | 5.43 | |
| Organizational climate (people dimension/SDG 9) | 5.51 | |
| Organizational culture (people/SDG 9 dimension) | 5.69 | |
| Human resources management (people dimension/SDG 9) | 5.22 | |
| Organizational performance | 5.63 | |
| Viable | Context (within the environmental dimension/SDG 12) | 6.57 |
| Legal (within the environmental dimension/SDG 12) | 6.26 | |
| Structure (SDG 8) | 6.45 | |
| Finance (structural dimension/SDG 8) | 6.76 | |
| Infrastructure and production (structural dimension/SDG 8) | 6.64 | |
| Functions (within the management dimension) | 6.15 | |
| Enhanced | None of the dimensions/variables reach the level of excellence | |
| Organizational performance | 5.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Restrepo-Morales, J.A.; Giraldo-Betancur, E.A.; López-Cadavid, D.A.; Grados-Vásquez, M.M.; Olórtiga-Cóndor, L.W. Enhanced Organizational Performance: Integrating Dimensions for Sustainable Growth. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115186
Restrepo-Morales JA, Giraldo-Betancur EA, López-Cadavid DA, Grados-Vásquez MM, Olórtiga-Cóndor LW. Enhanced Organizational Performance: Integrating Dimensions for Sustainable Growth. Sustainability. 2023; 15(21):15186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115186
Chicago/Turabian StyleRestrepo-Morales, Jorge Aníbal, Emerson Andrés Giraldo-Betancur, Diego Alejandro López-Cadavid, Martín Manuel Grados-Vásquez, and Lucio Wilfredo Olórtiga-Cóndor. 2023. "Enhanced Organizational Performance: Integrating Dimensions for Sustainable Growth" Sustainability 15, no. 21: 15186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115186
APA StyleRestrepo-Morales, J. A., Giraldo-Betancur, E. A., López-Cadavid, D. A., Grados-Vásquez, M. M., & Olórtiga-Cóndor, L. W. (2023). Enhanced Organizational Performance: Integrating Dimensions for Sustainable Growth. Sustainability, 15(21), 15186. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152115186









