Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P along an Altitudinal Gradient in Central Himalaya, India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analyses of Soil Microbial Biomass
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Soil Characteristics
3.2. Microbial C, N and P
3.3. Microbial Biomass and Abiotic Variables
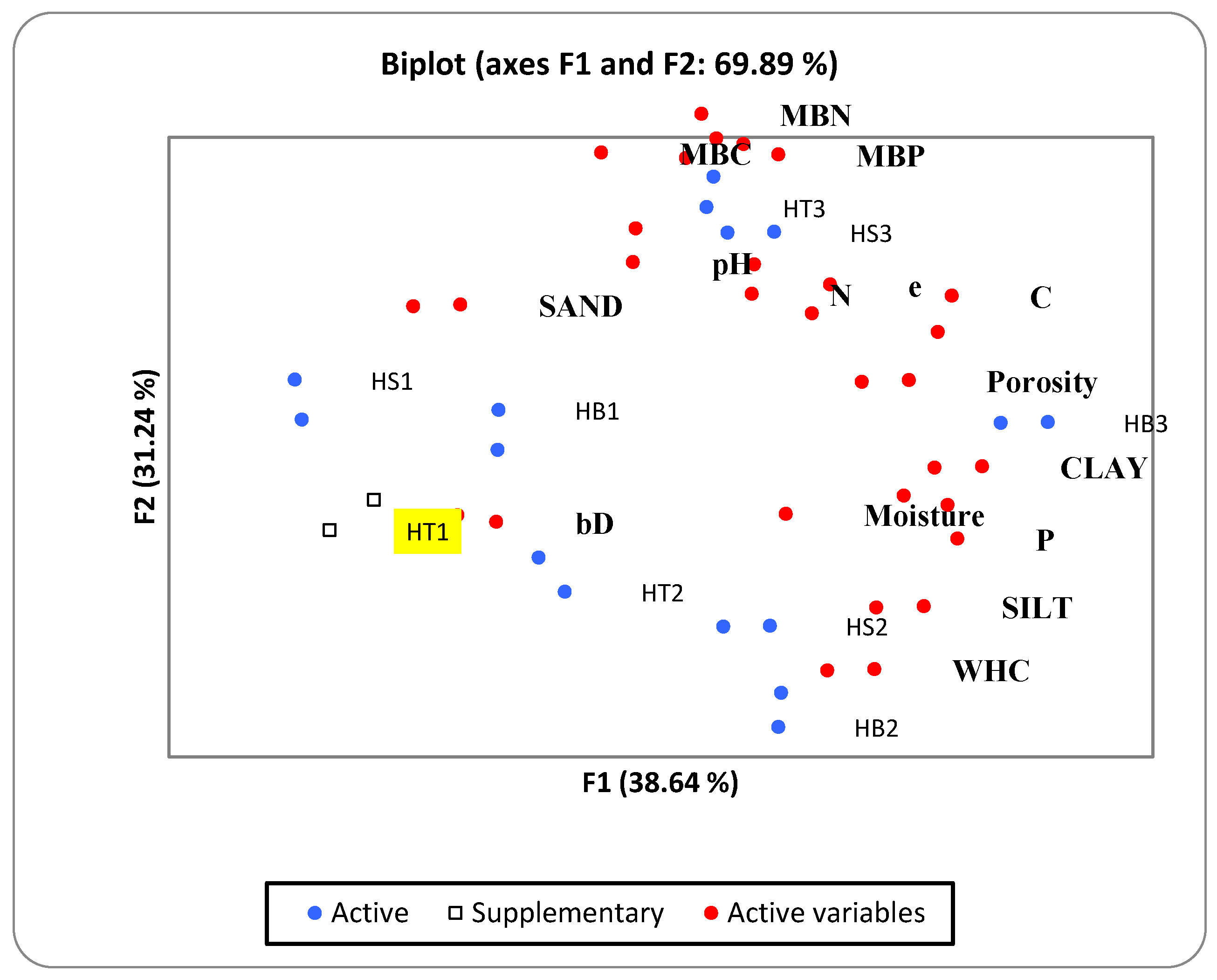
3.4. Multivariate Analyses (PCA) of Microbial Properties of Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Variation in Microbial Biomass
4.2. Effect of Altitude
4.3. Microbial Quotient
4.4. Relationship between Microbial Biomass and Abiotic Variables
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lipson, D.A.; Schadt, C.W.; Schmidt, S.K. Changes in soil microbial community structure and function in an alpine dry meadow following spring snowmelt. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 43, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.S.; Raghubanshi, A.S.; Singh, R.S.; Srivastava, S.C. Microbial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savanna. Nature 1989, 338, 499–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargali, K.; Joshi, B.; Bargali, S.S.; Singh, S.P. Oaks and the Biodiversity They Sustain. Int. Oaks. 2015, 26, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schoenholtz, S.H.; Van Miegroet, H.; Burger, J.A. A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: Challenges and opportunities. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbacher, A.; Rodler, A.; Kuffner, M.; Kitzler, B.; Sessitsch, A.; Zechmeister, B. Experimental warming effects on the microbial community of a temperate mountain forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.A. Dynamics of organic matter in soils. Plant Soil. 1984, 76, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, M.J.; Wollum, A.G.; King, L.D. Soil microbial population and activities in reduced chemical input agroecosystem. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, A.D.; Mullen, M.D.; Ringelberg, D.B.; Tyler, D.D.; Hedrick, D.B.; Gale, P.M.; White, D.C. Soil microbial response to dairy manure or ammonium nitrate application. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1019–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borga, P.; Nilsson, M.; Tunlid, A. Bacterial communities in peat in relation to botanical composition as revealed by phospholipid fatty acid analysis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zogg, G.P.; Zak, D.R.; Ringelberg, D.B.; Macdonald, N.W.; Pregitzer, K.S.; White, D.C. Compositional and functional shifts in microbial communities due to soil warming. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toky, O.P.; Singh, V. Litter dynamics in short rotation high density tree plantations in an arid region of India. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 45, 129–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, R.L.; Maikhuri, R.K.; Rao, K.S.; Sen, K.K.; Saxena, K.G. Leaf litter decomposition and nutrient release patterns of six multipurpose tree species of Central Himalaya, India. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 24, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, P.; Khan, M.L.; Tripathi, R.S. Tree diversity and population structure in undisturbed and human-impacted stands of tropical wet evergreen forest in Arunanchal Pradesh, Eastern Himalayas, India. Biodivers. Conserv. 2003, 12, 1753–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, O.; Bolat, I. The effect of different land uses on soil microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in Bartin province. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2008, 32, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Salunkhe, O.; Kharem, P.K.; Kumari, R.; Khan, M.L. A systemic review on the aboveground biomass and carbon stocks of Indian forest ecosystems. Ecol. Process. 2018, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.K.; Ladha, J.K.; Gami, S.K. Total and organic soil carbon in cropping systems of Nepal. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 2006, 75, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Tsai, S.H.; Fan, H.Y.; Yang, C.K.; Hung, W.L.; Cho, S.T. Seasonal variation of microbial ecology in hemlock soil of Tatachia mountain, Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 39, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kujur, M.; Patel, A.K. Quantifying the contribution of different soil properties on microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous in dry tropical ecosystem. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 2272–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Joergensen, R.G.; Anderson, T.H.; Wolters, T. Carbon and nitrogen relationships in the microbial biomass of soils in beech (Fagus sylvatica) forests. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1995, 19, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Chapin, F.S., III; Pons, T.L. Mineral Nutrition. In Plant Physiological Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 239–298. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, A.; Schlesinger, W.H. Factors limiting microbial biomass in the mineral soil and forest floor of a warm-temperate forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettema, C.H.; Wardle, D.A. Spatial soil ecology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J.; Roda, F. Changes in nutrient status, retranslocation and use efficiency in young post-fire regeneration Pinus halepensis in response to sudden N and P input, irrigation and removal of competing vegetation. Trees 2005, 19, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Putten, W.H.; Bardgett, R.D.; De Ruiter, P.C.; Hol, W.H.G.; Meyer, K.M.; Bezemer, T.M.; Bradford, M.A.; Christensen, S.; Eppinga, M.B.; Fukami, T.; et al. Empirical and theoretical challenges in aboveground-belowground ecology. Oecologia 2009, 161, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiya, K.S. Geology of Kumaun Lesser Himalaya; Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology: Dehra Dun, India, 1980; Volume 66, pp. 323–348. [Google Scholar]
- Medlicott, H.B. On the geology, structure and relations of the southern portion of the Himalayan Range between the rivers Ganges and Ravee. Mem. Geol. Suvey India 1864, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.C.; Singh, J.S. Effect of cultivation on microbial carbon and nitrogen in dry tropical forest soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 1989, 8, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargali, S.S.; Padalia, K.; Bargali, K. Effects of tree fostering on soil health and microbial biomass under different land use systems in central Himalaya. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1984–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indian Standard: 2720; Part IV: Grain Size Analysis. Indian Standard Institute: New Delhi, India, 1965.
- Walkley, A.; Black, C.A. An experiment of Degtjareff methods for determining soil organic matter and proposed modification of the chronic acid titration methods. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Prentice Hall, Inc.: Englewood Clift, NJ, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Peach, K.; Tracey, M.V. Modern Methods of Plant Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Adelaide, Australia, 1956; Volume III and IV, p. 368. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Kragt, J.F.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloroform fumigation and release of soil nitrogen: The effect of fumigation time and temperature. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1985, 17, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, D.S.; Ladd, J.N. Microbial biomass in soil: Measurement and treatment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1981, 5, 415–417. [Google Scholar]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. Microbial biomass measurements in forest soils: The use of the chloroform fumigation incubation method for strongly acid soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrot, J.; Robertson, G.P. Vegetation removal in two soils of the humid tropics: Effect on microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, A.; Arunachalam, K. Influence of gap size and soil properties on microbial biomass in a subtropical humid forest of North-east India. Plant Soil 2000, 223, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martikainen, P.J.; Palojarvi, A. Evaluation of the fumigation extraction method for the determination of microbial C and N in a range of forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ravina, M.; Carballas, T.; Acea, M.J. Microbial biomass and metabolic activity in four acid soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioli, D.; Schulz, E.; Lentendu, G.; Wubet, T.; Buscot, F.; Reitz, T. Mineral vs. organic amendments: Microbial community structure, activity and abundance of agriculturally relevant microbes are driven by long-term fertilization strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, X.; Alexander, T.W.; Thomas, B.W.; Shi, X.; Lupwayi, N.Z. Long-term and legacy effects of manure application on soil microbial community composition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalia, K. Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon and Nitrogen under Different Cropping System of Kumaun Himalaya. Ph.D. Thesis, Kumaun University, Nainital, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, B.N.; Yadava, P.S. Seasonal dynamics in soil microbial biomass C, N and P in a mixed-oak forest ecosystem of Manipur, North-east India. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2006, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, V. A comparative Account of the Microbial Biomass Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Soils of Natural Forests in Kumaun Himalaya. Ph.D. Thesis, Kumaun University, Nainital, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bargali, K.; Manral, V.; Padalia, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Upadhyay, V.P. Effect of vegetation type and season on microbial biomass carbon in Central Himalaya forest soils, India. Catena 2018, 171, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratchandra, S.U.; Perrott, K.W.; Upsdell, M.P. Microbiological and biochemical characteristics of a range of New Zealand soils under stabilized pasture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1984, 16, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ravina, M.; Acea, M.J.; Carballas, T. Seasonal changes in microbial biomass and nutrient flush in forest soils. Biol. Fertil. Soil 1995, 19, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, T.I.; Zhelezova, A.D. The dynamics of soil microbial communities on different timescales: A review. Eurasia Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, K.A.; Jefferies, R.L. Inter-annual and seasonal dynamics of soil microbial biomass and nutrients in wet and dry low-Arctic sedge meadows. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, O.; Tscherko, D.; Kandeler, E. Temperature sensitivity of microbial respiration, nitrogen mineralization, and potential soil enzyme activities in organic alpine soils. Glob. Biogeochem. Cyc. 2007, 21, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, G. Measurements of nitrogen isotope composition of plants and surface soils along the altitudinal transect of the eastern slope of Mount Gongga in southwest China. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Kumar, J.I.N.; Kumar, R.N.; Bhoi, R.K. Seasonal and temporal variation in soil microbial biomass C, N and P in different types land uses of dry deciduous forest ecosystem of Udaipur, Rajasthan, Western India. Appl. Ecol. Env. Res. 2010, 8, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, D.A. Controls of temporal variability of the soil microbial biomass: A global-scale synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, A.; Pandey, H.N. Ecosystem restoration of Jhoom fallows in Northeast India: Microbial C and N along altitudinal and successional gradients. Restor. Ecol. 2003, 11, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, V.; Bargali, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Shahi, C. Changes in soil biochemical properties following replacement of Banj oak forest with Chir pine in Central Himalaya, India. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.R.; Karlen, D.L.; Veum, K.S.; Moorman, T.B.; Cambardella, C.A. Biological soil health indicators respond to tillage intensity: A US meta-analysis. Geoderma 2020, 369, 114335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, J.J.; Yan, Q.L. Changes of soil P chemistry as affected by conversion of natural secondary forests to larch plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Dongsheng, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhonggui, L. Variation in soil microbial biomass carbon and soil dissolved organic carbon in the re-vegetation of Hilly slope with purple soil. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padaliya, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Bargali, K.; Manral, V. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus under different land use systems of Central Himalaya. Trop. Ecol. 2022, 63, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
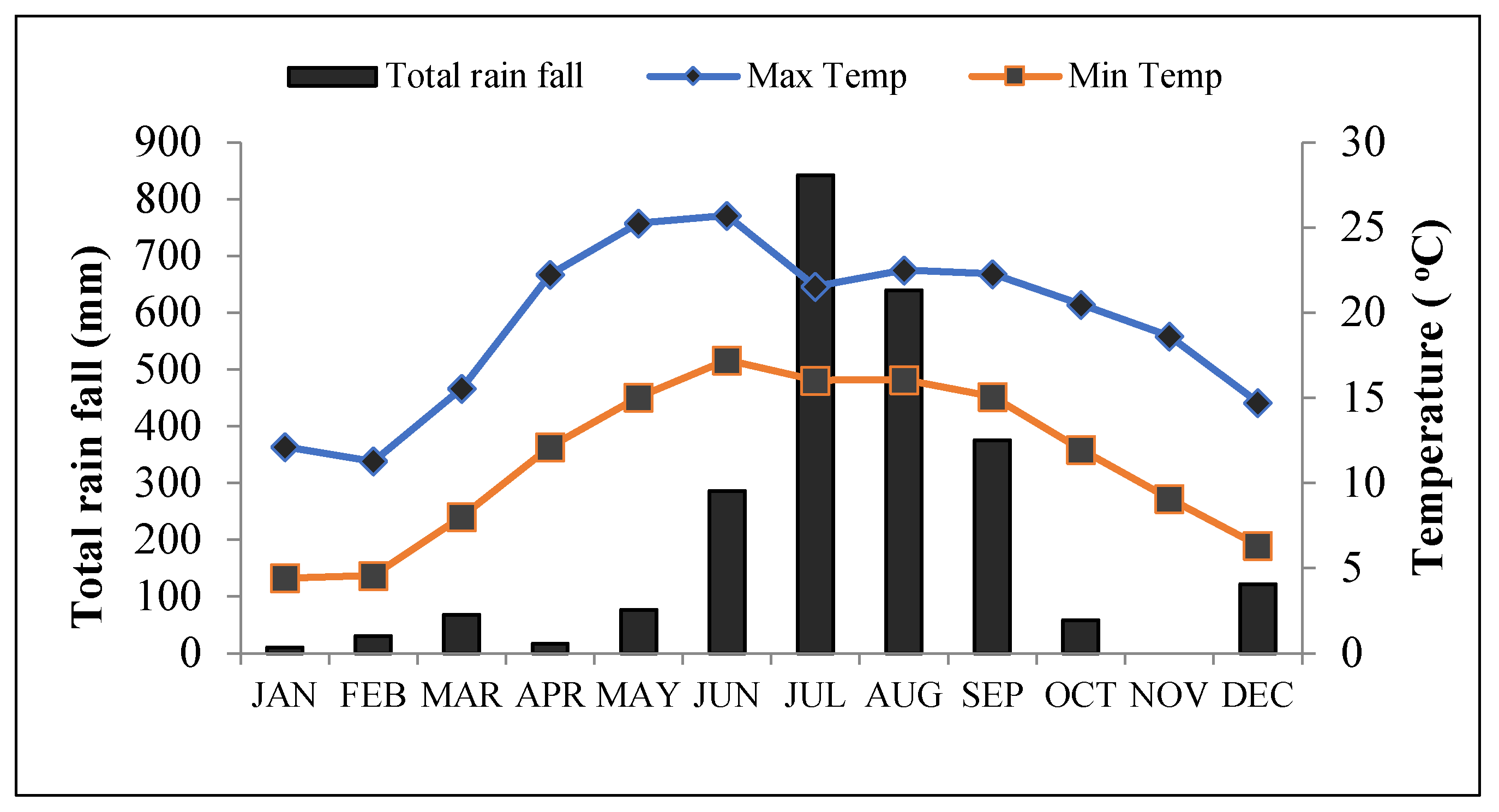
| Site | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Stand I (HB) | Stand II (HS) | Stand III (HT) | ANOVA | |
| Soil | F Value | p Value | |||
| sand (%) | 70 a ± 0.88 | 78 b ± 0.88 | 78 b ± 0.88 | 48.077 | 0.000 |
| silt (%) | 18 b ± 0.88 | 12 a ± 0.88 | 12 a ± 0.58 | 11.645 | 0.009 |
| clay (%) | 13 a ± 1.76 | 11 a ± 0.33 | 10 a ± 0.33 | 1.837 | 0.239 |
| bulk density (g cm−3) | 0.65 b ± 0.01 | 0.60 b ± 0.09 | 0.42 a ± 0.01 | 66.690 | 0.000 |
| WHC (%) | 45.65 b ± 0.43 | 42.76 ab ± 0.61 | 41.47 a ± 0.69 | 6.201 | 0.035 |
| moisture (%) | 22.48 c ± 0.37 | 14.70 b ± 0.19 | 11.36 a ± 0.35 | 68.044 | 0.000 |
| porosity | 75.35 a ± 0.33 | 77.23 a ± 3.28 | 84.28 b ± 0.33 | 11.986 | 0.008 |
| pH | 5.67 a ± 0.03 | 5.87 b ± 0.03 | 6.13 c ± 0.03 | 30.659 | 0.001 |
| organic C (%) | 5.24 c ± 0.09 | 3.75 b ± 0.07 | 3.24 a ± 0.04 | 1008.148 | 0.000 |
| total N (%) | 0.38 b ± 0.01 | 0.38 b ± 0.01 | 0.17 a ± 0.01 | 85.809 | 0.000 |
| total P (%) | 0.09 c ± 0.00 | 0.06 b ± 0.00 | 0.04 a ± 0.00 | 324.328 | 0.000 |
| C:N | 13.4 a ± 0.17 | 9.8 b ± 0.13 | 18.2 c ± 0.15 | 743.831 | 0.000 |
| Vegetation | |||||
| Tree species richness | 05 (Boehrmeria regulosa, Myrica esculenta, Pinus roxburghii, Quercus leucotrichophora, Rhus valagaris) | 03 (Boehrmeria regulosa, Pinus roxburghii, Quercus leucotrichophora) | 02 (Pinus roxburghii, Quercus leucotrichophora) | ||
| Tree density (stems ha−1) | 670 | 590 | 570 | ||
| Basal area (m2 ha−1) | 32.39 | 27.73 | 27.20 | ||
| Stand I (HB) | Stand II (HS) | Stand III (HT) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microbial biomass carbon (MBC) | |||
| Rainy | 751 ± 2.58 | 737 ± 1.02 | 697 ± 0.55 |
| Winter | 730 ± 0.86 | 718 ± 1.32 | 681 ± 1.81 |
| Summer | 738 ± 1.39 | 725 ± 1.18 | 685 ± 2.01 |
| Annual mean | 739.67 ± 6.12 | 726.67 ± 5.55 | 687.67 ± 4.81 |
| Microbial biomass nitrogen (MBN) | |||
| Rainy | 143 ± 8.54 | 111 ± 4.43 | 99 ± 2.14 |
| Winter | 111 ± 1.78 | 93 ± 1.41 | 73 ± 1.38 |
| Summer | 120 ± 1.45 | 103 ± 1.42 | 89 ± 1.07 |
| Annual mean | 124.67 ± 9.53 | 102.33 ± 5.21 | 87.00 ± 7.57 |
| Microbial biomass phosphorus (MBP) | |||
| Rainy | 72 ± 3.03 | 49 ± 3.69 | 36 ± 1.86 |
| Winter | 53 ± 1.57 | 38 ± 1.53 | 23 ± 1.55 |
| Summer | 65 ± 1.79 | 45 ± 1.91 | 26 ± 1.73 |
| Annual mean | 63.33 ± 5.55 | 44.00 ± 3.21 | 28.33 ± 3.93 |
| Microbial C:N | |||
| Rainy | 5.25 ± 0.33 | 6.63 ± 0.26 | 7.04 ± 0.15 |
| Winter | 6.57 ± 0.10 | 7.72 ± 0.13 | 9.33 ± 0.19 |
| Summer | 6.15 ± 0.08 | 7.03 ± 0.07 | 7.69 ± 0.08 |
| Annual mean | 6.16 ± 0.39 | 7.23 ± 0.32 | 8.19 ± 0.22 |
| Microbial C:P | |||
| Rainy | 10.66 ± 0.40 | 14.31 ± 1.21 | 19.71 ± 0.98 |
| Winter | 13.81 ± 0.41 | 18.41 ± 0.74 | 35.89 ± 2.42 |
| Summer | 11.42 ± 0.33 | 16.43 ± 0.70 | 27.56 ± 1.75 |
| Annual mean | 11.96 ± 0.95 | 16.38 ± 1.18 | 27.72 ± 1.54 |
| Microbial N:P | |||
| Rainy | 1.98 ± 0.11 | 2.26 ± 0.10 | 2.75 ± 0.18 |
| Winter | 2.09 ± 0.09 | 2.45 ± 0.13 | 3.17 ± 0.28 |
| Summer | 1.85 ± 0.06 | 2.29 ± 0.11 | 3.42 ± 0.19 |
| Annual mean | 1.97 ± 0.04 | 2.33 ± 0.08 | 3.11 ± 0.15 |
| Variables | Source | Sum of Squares | Df | Mean Square | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC | S | 1598.06 | 2 | 799.03 | 113.52 | 0.000 |
| A | 13274.20 | 2 | 6637.10 | 942.92 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 25.87 | 4 | 6.47 | 0.92 | 0.474 | |
| MBN | S | 2818.66 | 2 | 1409.33 | 38.63 | 0.000 |
| A | 6575.10 | 2 | 3287.55 | 90.10 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 237.36 | 4 | 59.34 | 1.63 | 0.211 | |
| MBP | S | 1162.40 | 2 | 581.20 | 40.27 | 0.000 |
| A | 6135.68 | 2 | 3067.84 | 212.58 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 73.51 | 4 | 18.38 | 1.27 | 0.317 | |
| Microbial C:N | S | 10.59 | 2 | 5.30 | 56.13 | 0.000 |
| A | 18.88 | 2 | 9.44 | 100.06 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 1.66 | 4 | 0.42 | 4.40 | 0.012 | |
| Microbial C:P | S | 330.30 | 2 | 165.15 | 26.51 | 0.000 |
| A | 1238.75 | 2 | 619.37 | 99.44 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 218.53 | 4 | 54.63 | 8.77 | 0.000 | |
| Microbial N:P | S | 1.28 | 2 | 0.64 | 8.89 | 0.002 |
| A | 10.18 | 2 | 5.09 | 70.63 | 0.000 | |
| S × A | 1.34 | 4 | 0.33 | 4.65 | 0.009 |
| Altitude | Sand | Silt | Clay | WHC | bD | Mo | Po | pH | C | N | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBC | 0.985 ** | −0.720 * | 0.685 * | 0.455 | 0.822 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.916 ** | −0.819 ** | −0.967 ** | 0.897 ** | 0.939 ** | 0.908 ** |
| MBN | 0.963 ** | −0.905 ** | 0.907 ** | 0.496 | 0.928 ** | 0.650 | 0.987 ** | −0.649 | −0.890 ** | 0.992 ** | 0.734 * | 0.992 ** |
| MBP | 0.948 ** | −0.957 ** | 0.898 ** | 0.624 | 0.920 ** | 0.619 | 0.987 ** | −0.619 | −0.884 ** | 0.987 ** | 0.685 * | 0.984 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manral, V.; Bargali, K.; Bargali, S.S.; Karki, H.; Chaturvedi, R.K. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P along an Altitudinal Gradient in Central Himalaya, India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021651
Manral V, Bargali K, Bargali SS, Karki H, Chaturvedi RK. Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P along an Altitudinal Gradient in Central Himalaya, India. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021651
Chicago/Turabian StyleManral, Vijyeta, Kiran Bargali, Surendra Singh Bargali, Himani Karki, and Ravi Kant Chaturvedi. 2023. "Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P along an Altitudinal Gradient in Central Himalaya, India" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021651
APA StyleManral, V., Bargali, K., Bargali, S. S., Karki, H., & Chaturvedi, R. K. (2023). Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C, N and P along an Altitudinal Gradient in Central Himalaya, India. Sustainability, 15(2), 1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021651









