Impact of Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality Based on Different Topographic Relief Areas: A Case Study of Chishui River Basin in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
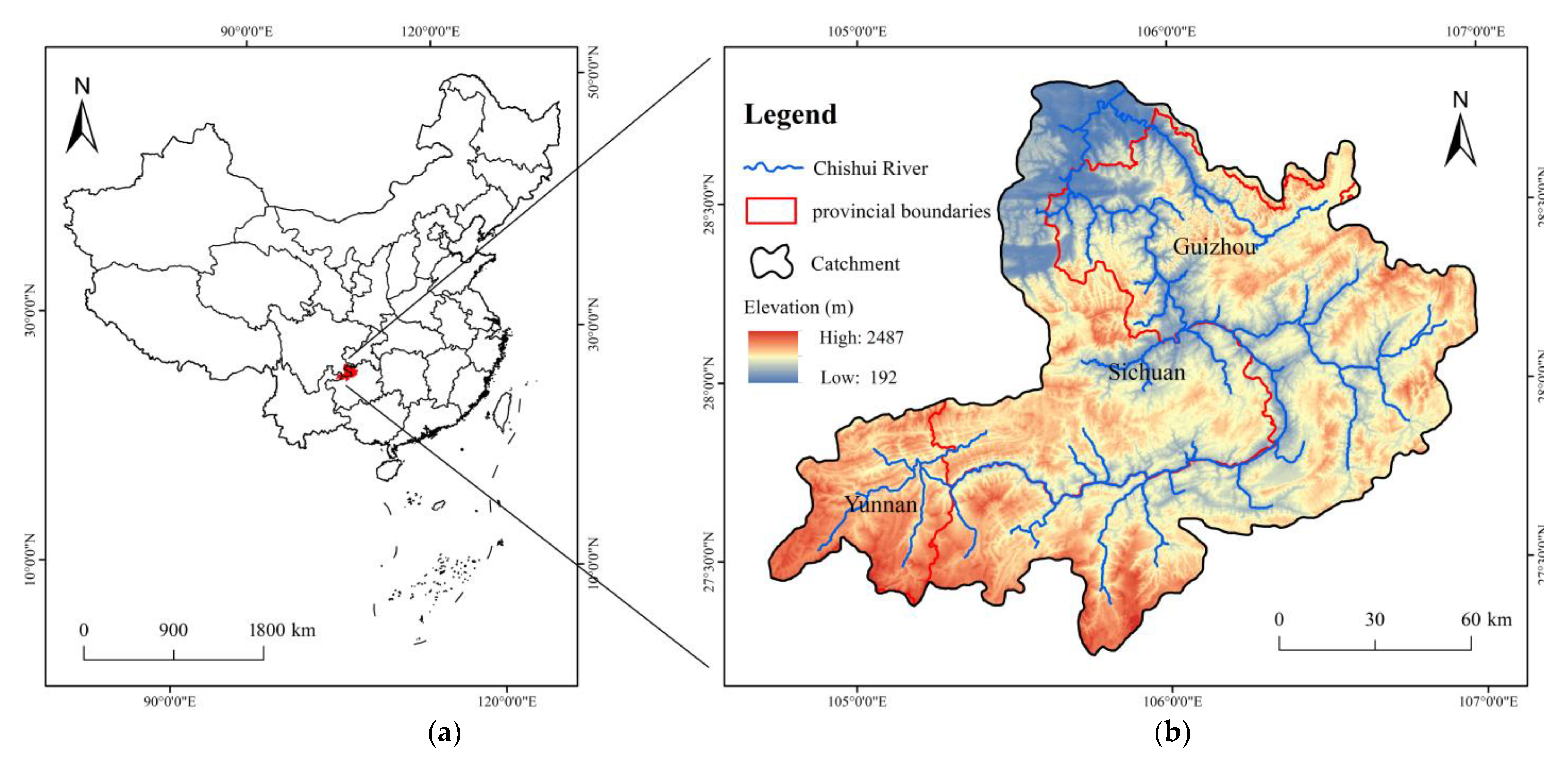
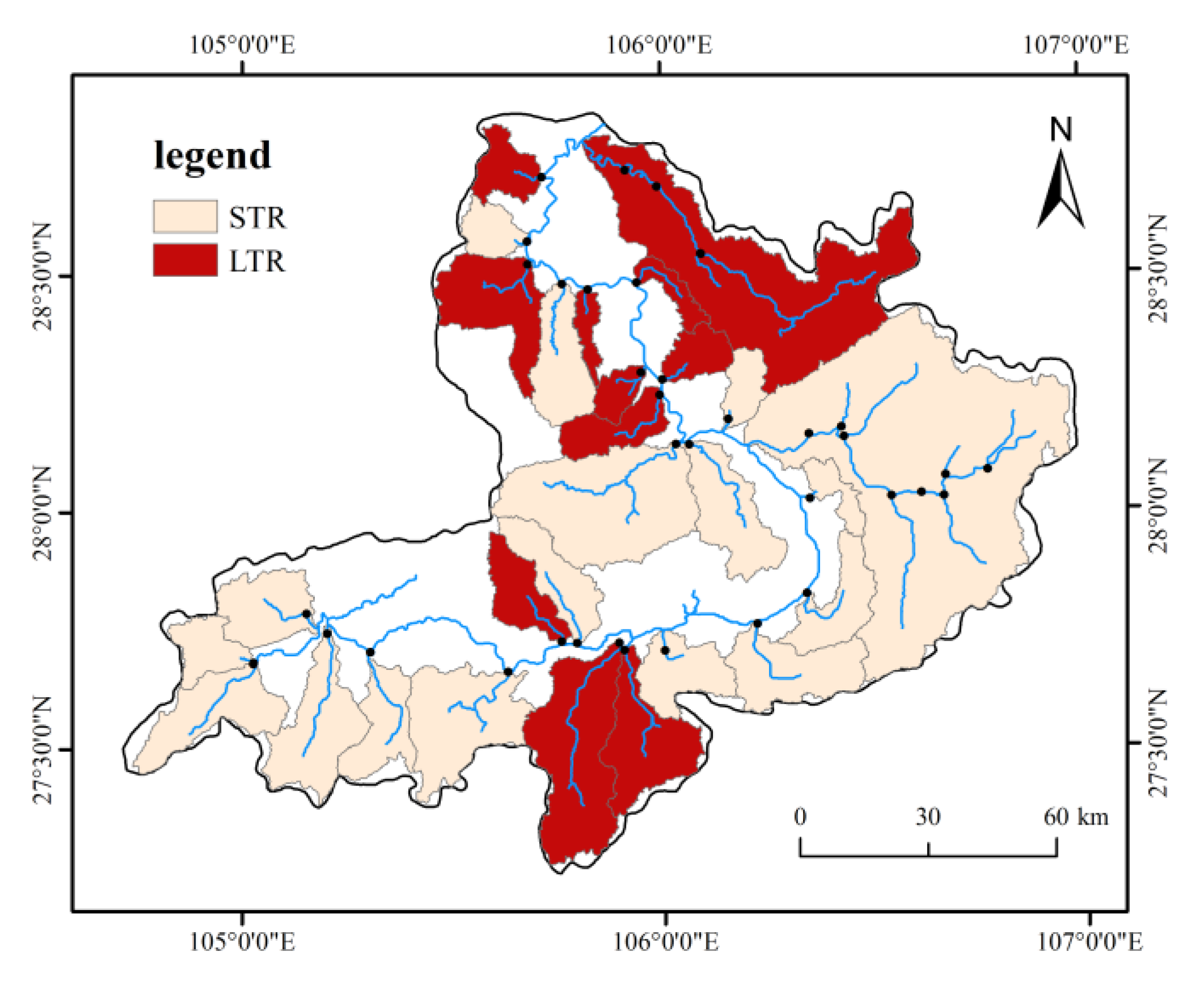
2.1. Study Area
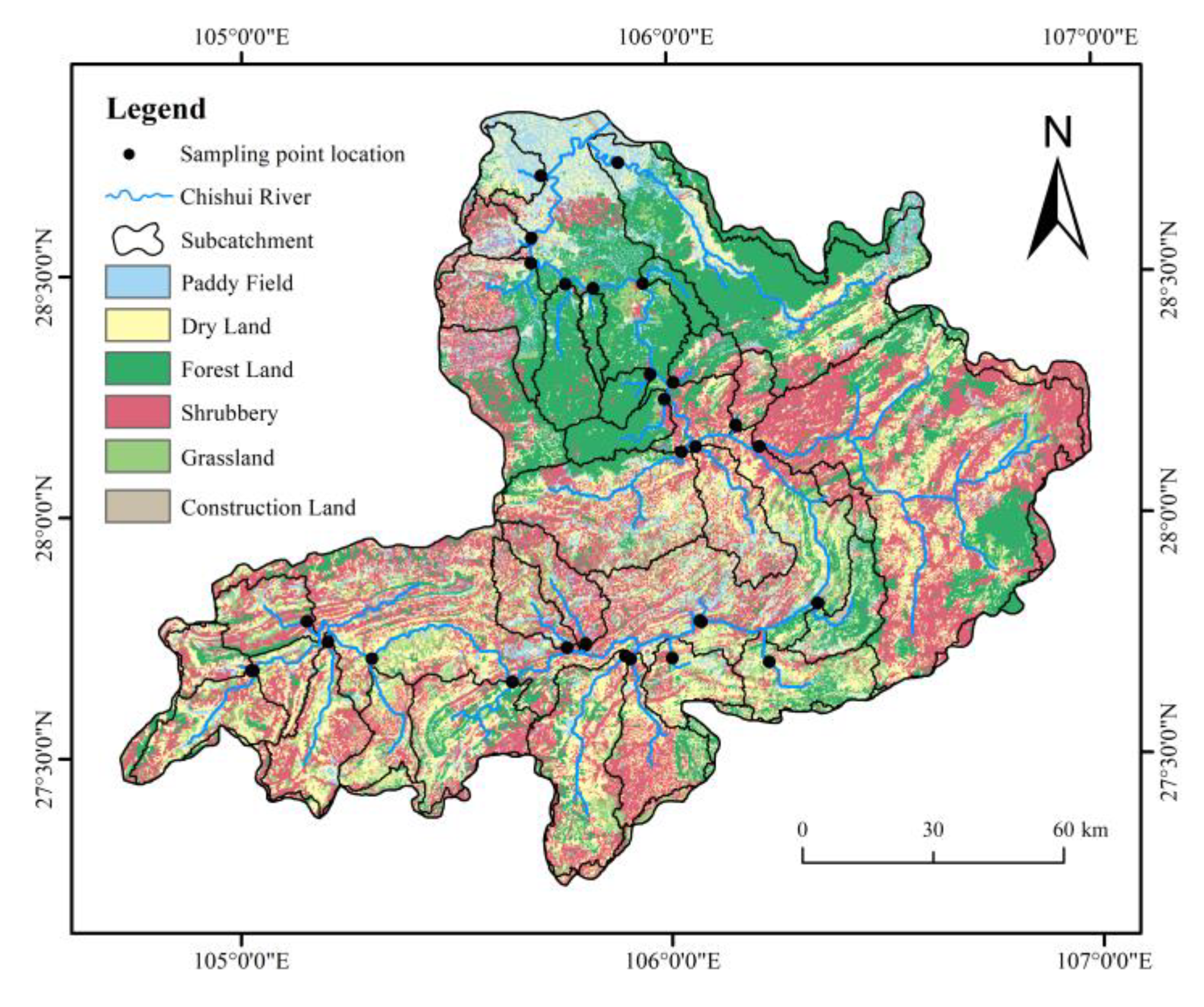
2.2. Water Sample Collection and Water Quality Evaluation
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. Geographic Factor Analysis
2.5. Data Statistics and Processing
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Variations of Water Physic-Chemical Parameters in Different Topographic Relief Areas
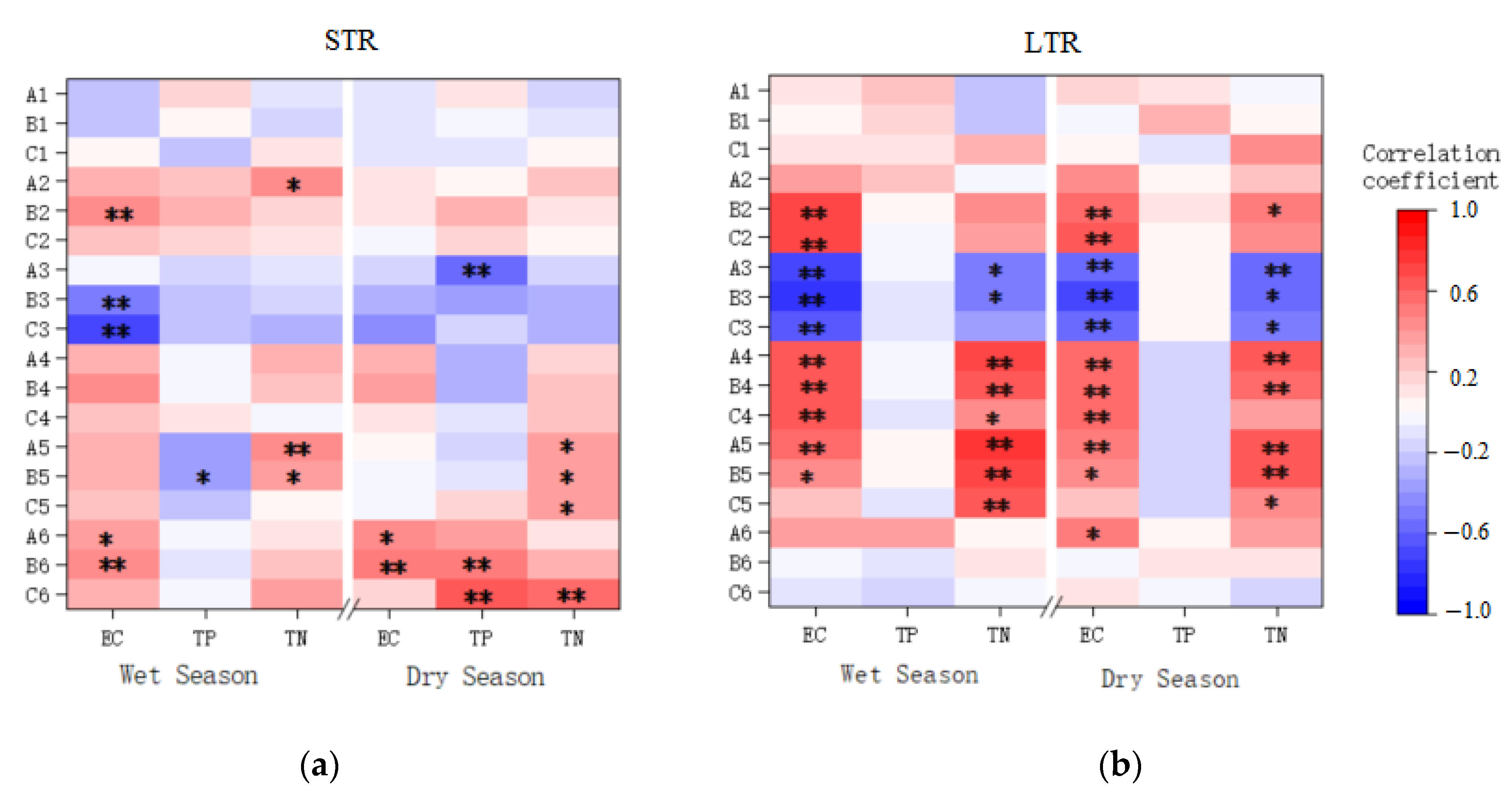
3.2. Relationship between Landscape and Water Quality in Different Topographic Relief Areas
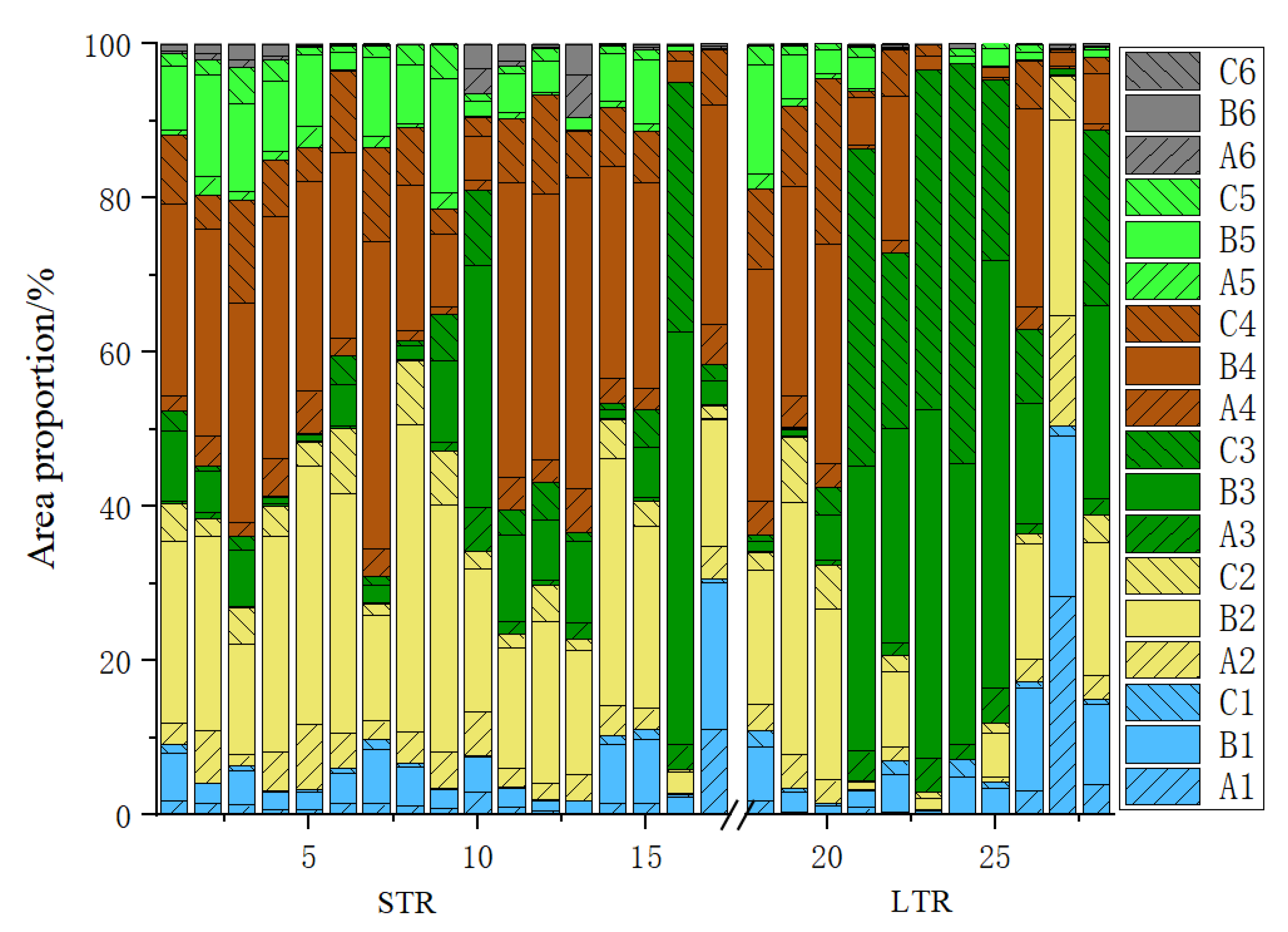
3.3. Relationship between Landscape Pattern and Water Quality in Different Topographic Relief Areas
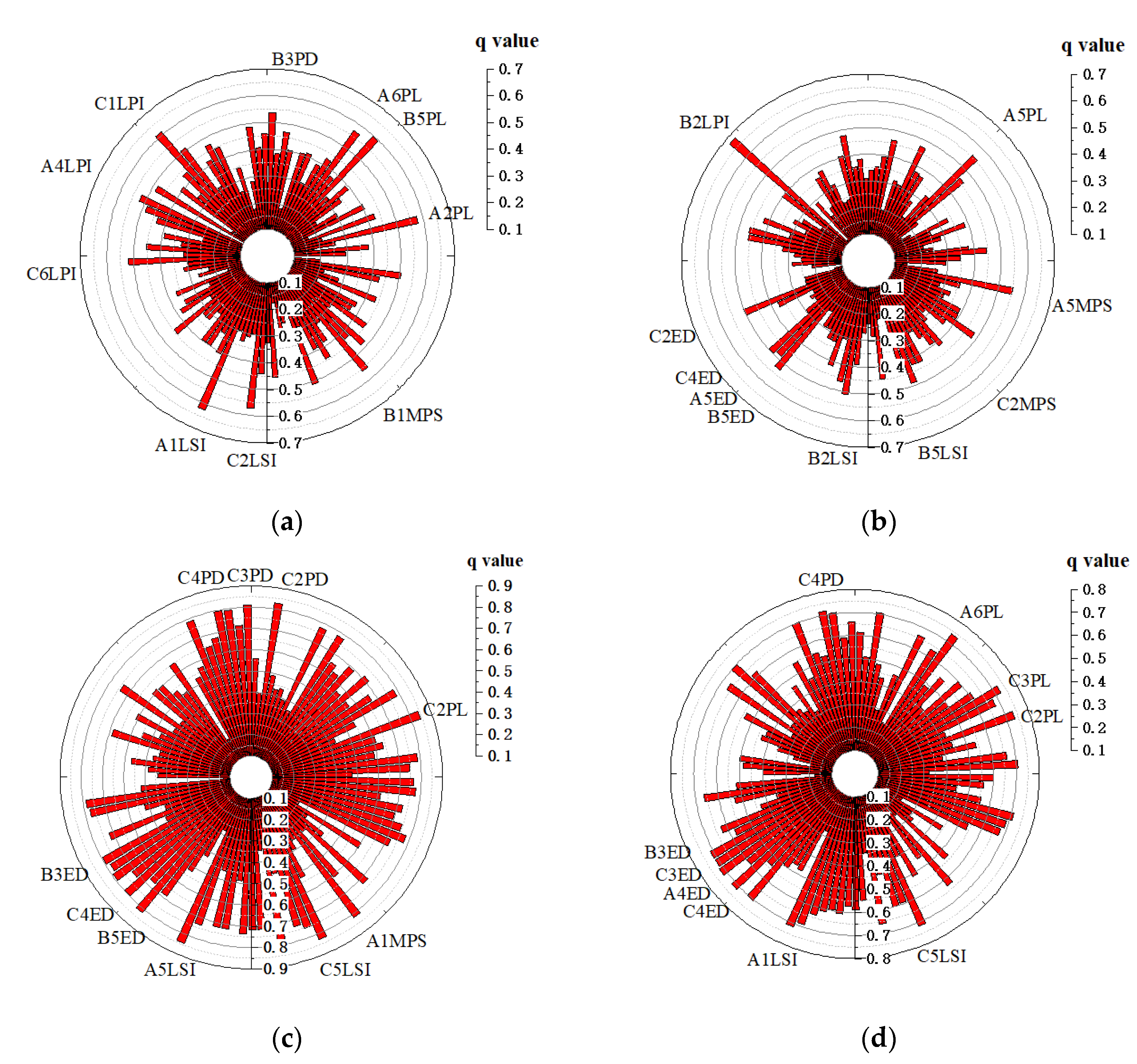
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Water Quality Influencing Factors in Different Topographic Relief Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Analyze the Impact of Slope Landscape on Water Quality in Different Topographic Relief Areas by Combining Various Relevant Factors
4.2. Reasonable Suggestions for Water Quality Protection in Different Terrain Relief Areas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Jin, G.; Yu, Y. Review of River Basin Water Resource Management in China. Water 2018, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; DeFries, R.; Dietz, T.; Mooney, H.A.; Polasky, S.; Reid, W.V.; Scholes, R.J. Ecology. Millennium ecosystem assessment: Research needs. Science 2006, 314, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.H.; Lue, S.B.; Han, Y.P.; Wang, F.Q.; Tang, L. Comprehensive evaluation on water resources carrying capacity based on water-economy-ecology concept framework and EFAST-cloud model: A case study of Henan Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Stevenson, R.J.; Grace, J.B. The importance of natural versus human factors for ecological conditions of streams and rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, X.M.; Kong, B.; Li, R.P.; Wang, G.X. Landscape ecology development supported by geospatial technologies: A review. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 51, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.X.; Wu, X.D.; Ge, X.G.; Lin, G.Y.; Feng, L.; Ma, W.Q.; Xu, D. Study on the Water Quality Characteristics of the Baoan Lake Basin in China under Different Land Use and Landscape Pattern Distributions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Xu, G.C. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, D.; Dufrene, M.; Michez, A.; Lath, A.; Jacobs, S.; Vincke, C.; Dendoncker, N. Forest cover correlates with good biological water quality. Insights from a regional study (Wallonia, Belgium). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 211, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Du, J.L.; Chen, D.C.; Zhang, F. Effects of land use and landscape pattern characteristics on seasonal surface water quality in typical reticulated river network area—A case study of Liyang City, Jiangsu Province. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1524–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.S.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.F.; Huang, J.C. A preliminary analysis on response of river water quality to land use in Riparian Zone of Changzhou. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 2915–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.S.; Yu, W.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.Y. Response of water quality to landscape pattern change in the water source area of upper reaches of Lake Taihu: A case study in the upper reaches of Dongtiaoxi River. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Rickert, B.; van den Berg, H.; Bekure, K.; Girma, S.; Husman, A.M.D. Including aspects of climate change into water safety planning: Literature review of global experience and case studies from Ethiopian urban supplies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, G.R. Climate and rivers. River Res. Appl. 2019, 35, 1119–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.Q.; Zhang, S.L.; Xu, M.X.; He, J.Y.; Li, X.R.; Zhang, J. Response of surface water quality characteristics to socioeconomic factors in Eastern-Central China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhenyao, S.Y.; Yan, T.Z.; Yang, Y.C. Source identification and impact of landscape pattern on riverine nitrogen pollution in a typical urbanized watershed, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Zuo, L.Y.; Liu, W.L. Environmental determinants impacting the spatial heterogeneity of karst ecosystem services in Southwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, B.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Hutchins, M.G.; Miller, J. An empirical investigation of climate and land-use effects on water quantity and quality in two urbanising catchments in the southern United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Cao, H.M.; Tang, M.F.; Deng, H.B. The Human Threat to River Ecosystems at the Watershed Scale: An Ecological Security Assessment of the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Water 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhail, H.A.; Yang, R.; Chen, H.L.; Rao, G. The impact of river capture on the landscape development of the Dadu River drainage basin, eastern Tibetan plateau. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 198, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Li, W.J.; Yu, J.; Wu, C.Z. Ecological Sensitivity Evaluation of Tourist Region Based on Remote Sensing Image—Taking Chaohu Lake Area as a Case Study. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-3, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Lasco, R.D.; Myint, S.W.; Pulhin, F.B.; Wang, C.Y.; Ooba, M.; Hijioka, Y. Changes in the landscape pattern of the La Mesa Watershed—The last ecological frontier of Metro Manila, Philippines. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 430, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zinda, J.A.; Yang, Z.J.; Yin, M.; Ou, X.K.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Q.C. Effects of topographic attributes on landscape pattern metrics based on redundancy ordination gradient analysis. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; dos Santos, A.C.A.; Vettorazzi, C.A. Effects of land use and land cover on water quality of low-order streams in Southeastern Brazil: Watershed versus riparian zone. Catena 2018, 167, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.Y.; Dong, R.Z.; Jiang, C.S.; Ni, M.F. Influences of land use metrics at multi-spatial scales on seasonal water quality: A case study of river systems in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 206, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, S.L.; Zhong, J.; Li, C. Spatial scale effects of the variable relationships between landscape pattern and water quality: Example from an agricultural karst river basin, Southwestern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Shen, S.Z.; Xu, X. Effects of land use changes on water quality of the plain area in Taihu basin. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2017, 36, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.H.; Cai, H.; Lin, G.M.; Wu, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y. Influences of landscape on river quality under different geomorphological conditions. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hao, Y.H.; Zhang, M. Characterizing the heterogeneous correlations between the landscape patterns and seasonal variations of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in a peri-urban watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 34067–34077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Lin, G.M.; Kang, W.H. The effects of sloping landscape features on water quality in the upper and middle reaches of the Chishui River Watershed. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 704–716. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Cai, H.; Yin, J.Y. Spatio-temporal changes of land use on sloping land in the Chishui River Basin based on topographic relief. J. Geomat. 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogeraphica Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; Hu, M.G.; Zhang, F.S.; Gao, B.B. Influential factors detection for surface water quality with geographical detectors in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M.H. Impacts of land use and population density on seasonal surface water quality using a modified geographically weighted regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.L.; Ji, Q. The inluence of sloping landscape features on riverine water quality in upper Yangte River. Acta Eologica Sin. 2022, 42, 6704–6717. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.P.; Yao, Y.H. Implications of mass elevation effect for the altitudinal patterns of global ecology. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, W.B.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, L.Q.; Li, M.J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.D. Spatial variations of terrain and their impacts on landscape patterns in the transition zone from mountains to plains-A case study of Qihe River Basin in the Taihang Mountains. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, M.; Jiao, K.Q.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Q.Q. Characteristics of terrain factors and their effects on landscape pattern in Zhangjiang River, Upper of Ganjiang River. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.J.; Gao, J.B.; Wu, S.H. Quantitative Analysis of the Influencing Factors and Their Interactions in Runoff Generation in a Karst Basin of Southwestern China. Water 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.Y.; Lei, X.T.; Zhou, L.N.; He, J.Q.; Jia, A.P.; Yu, J.J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, F. Effects of tillage measures on soil nutrients distribution and fertilizer use efficiency on gentle slope farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.M.; Jiang, N.; Jiang, G.Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, J.L. Influencing factors and sensitivity analysis of cultivated-layer quality of purple soil slope farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; Shi, D.M.; Xia, R.; Ni, S.H.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, R.H. Evolution characteristics and driving mechanism for the spatiotemporal pattern of sloping farmland in Chongqing based on geodetector. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 280–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.Q.; Wen, Y.; Wei, J.B.; Wu, Z.F.; Lu, Q.; Cheng, J. Relationships between landscape spatial characteristics and surface water quality in the Lin Xi River watershed. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.S.; Dai, E.F.; Zheng, D.; Dong, Y.X.; Yin, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.X.; Pan, L.H.; Qin, S.P. Spatial simulation of “Grain to Green Program” implementation in a typical region based on agent-based model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1983–1995. [Google Scholar]

| Code | Classification | Slope /(°) | Division Basis |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | flat land | 0~6 | there is no water and soil loss or slight soil erosion can occur |
| B | gentle slope land | 6~25 | Moderate to severe water and soil loss, and the soil erosion area increases with the increase of slope |
| C | steep slope land | >25 | Reaching the critical slope of soil erosion, the reclamation of slope land is not strictly prohibited above 25 ° |
| Index | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Percentage of land use (PL) | PL = Ai/A | Area percentage of land use for the corresponding land use type. |
| Patch density (PD) | PD = ni/A | Number of patches per unit area of the corresponding land use type. |
| Largest patch index (LPI) | LPI = amax/A*100 | Quantifies the percentage of total landscape area comprised by the largest patch at the class level. |
| Edge density (ED) | ED = E/A | Reflects the degree of landscape fragmentation. |
| Landscape shape index (LSI) | LSI = E/√A | Reflects the complexity of landscape patch shapes and provides a measure of class aggregation. |
| Mean Patch Size (MPS) | MPS = Ai/ni | Calculate the horizontal patch area of the category, and the result is inversely proportional to the fragmentation degree of such landscape. |
| Sub-Basin | Mean Elevation (m) | SD of Elevation (m) | Mean RDLS (m) | SD of RDLS (m) | Regions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1510 | 156 | 121 | 48 | areas with small topographic relief (SRA) |
| 2 | 1585 | 147 | 91 | 40 | |
| 3 | 1348 | 149 | 133 | 49 | |
| 4 | 1549 | 201 | 103 | 52 | |
| 5 | 1490 | 175 | 85 | 45 | |
| 6 | 1312 | 191 | 124 | 54 | |
| 7 | 1197 | 194 | 115 | 50 | |
| 8 | 950 | 185 | 122 | 47 | |
| 9 | 993 | 196 | 119 | 54 | |
| 10 | 1030 | 197 | 99 | 56 | |
| 11 | 958 | 222 | 106 | 43 | |
| 12 | 1078 | 246 | 132 | 56 | |
| 13 | 1158 | 193 | 88 | 41 | |
| 14 | 991 | 220 | 111 | 44 | |
| 15 | 957 | 290 | 118 | 56 | |
| 16 | 1091 | 257 | 151 | 55 | |
| 17 | 504 | 163 | 92 | 53 | |
| 18 | 1199 | 199 | 115 | 60 | areas with large topographic relief (LRA) |
| 19 | 1380 | 303 | 120 | 61 | |
| 20 | 1265 | 270 | 141 | 66 | |
| 21 | 1109 | 389 | 172 | 74 | |
| 22 | 887 | 293 | 154 | 72 | |
| 23 | 1144 | 273 | 176 | 68 | |
| 24 | 1021 | 271 | 207 | 74 | |
| 25 | 1001 | 243 | 139 | 62 | |
| 26 | 631 | 255 | 123 | 61 | |
| 27 | 403 | 149 | 70 | 61 | |
| 28 | 976 | 342 | 142 | 82 |
| Description | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2) < Min(q(X1), q(X2)) | Weaken, nonlinear |
| Min(q(X1), q(X2)) < q(X1∩X2) < Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Weaken, univariate |
| q(X1∩X2) > Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Enhance, bivariate |
| q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independent |
| q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Enhance, nonlinear |
| Time | Water Physic-Chemical Parameters | STR | LTR | Standard III | Kruskal–Wallis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max | Mean | S.D. | H | p-Value | |||
| Wet season | WT (°C) | 16.70 | 27.50 | 21.49 | 2.63 | 20.40 | 24.10 | 21.28 | 1.32 | - | 2.35 | 0.126 |
| pH | 7.40 | 8.38 | 7.97 | 0.31 | 7.42 | 8.30 | 7.90 | 0.29 | - | 0.22 | 0.638 | |
| EC (μs/cm) | 100 | 560 | 439 | 107 | 110 | 480 | 281 | 139 | - | 7.99 | 0.005 ** | |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | ≤0.2 | 3.85 | 0.050 ** | |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.01 | 4.93 | 2.42 | 1.64 | 0.96 | 3.77 | 1.87 | 0.87 | ≤1.0 | 5.15 | 0.023 ** | |
| Ip | 0.16 | 4.95 | 2.35 | 1.20 | 0.76 | 2.98 | 1.50 | 0.66 | ||||
| Dry season | WT (°C) | 8.00 | 12.80 | 10.65 | 1.43 | 9.00 | 11.50 | 10.15 | 0.85 | - | 1.03 | 0.311 |
| pH | 7.81 | 8.43 | 8.10 | 0.16 | 7.66 | 8.47 | 8.05 | 0.29 | - | 0.14 | 0.706 | |
| EC (μs/cm) | 87 | 1115 | 503 | 213 | 98 | 485 | 294 | 146 | - | 7.446 | 0.006 ** | |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 | ≤0.2 | 0.641 | 0.670 | |
| TN (mg/L) | 1.44 | 10.45 | 4.04 | 2.01 | 1.55 | 4.08 | 2.27 | 0.85 | ≤1.0 | 7.064 | 0.008 ** | |
| Ip | 1.17 | 8.47 | 2.8 | 1.39 | 1.00 | 3.25 | 1.65 | 0.60 | ||||
| Regions | Slope | Land Use Type | Landscape Indicators (Source-Sink Landscape) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL | PD | LPI | ED | LSI | MPS | |||
| STR | 0–6 (A) | Dry land | 3.70 | 3.16 | 0.45 | 16.21 | 42.72 | 1.20 |
| Shrubbery | 2.86 | 3.52 | 0.42 | 15.31 | 46.74 | 0.77 | ||
| Construction land | 0.60 | 0.14 | 0.32 | 1.41 | 7.75 | 3.42 | ||
| Forest land | 0.95 | 1.41 | 0.26 | 5.39 | 25.00 | 0.69 | ||
| 6–25 (B) | Dry land | 21.93 | 1.52 | 2.77 | 41.82 | 45.55 | 15.87 | |
| Shrubbery | 24.27 | 1.15 | 4.68 | 43.97 | 46.94 | 21.98 | ||
| Construction land | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 2.03 | 9.13 | 5.89 | ||
| Forest land | 9.38 | 0.54 | 3.04 | 17.28 | 26.74 | 17.73 | ||
| >25 (C) | Dry land | 3.67 | 1.49 | 0.32 | 11.73 | 31.45 | 2.44 | |
| Shrubbery | 7.10 | 1.59 | 0.57 | 18.31 | 35.58 | 4.50 | ||
| Construction land | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 3.27 | 0.79 | ||
| Forest land | 4.33 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 9.12 | 20.30 | 6.14 | ||
| LTR | 0–6 (A) | Dry land | 2.86 | 1.83 | 0.56 | 11.54 | 30.13 | 1.25 |
| Shrubbery | 1.57 | 1.96 | 0.35 | 8.19 | 28.66 | 0.83 | ||
| Construction land | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 3.95 | 2.08 | ||
| Forest land | 1.78 | 3.08 | 1.51 | 10.51 | 29.71 | 0.58 | ||
| 6–25 (B) | Dry land | 12.50 | 1.33 | 1.42 | 26.57 | 33.75 | 8.81 | |
| Shrubbery | 12.59 | 0.89 | 1.84 | 25.58 | 31.24 | 13.68 | ||
| Construction land | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.30 | 4.27 | 4.35 | ||
| Forest land | 21.58 | 1.27 | 5.42 | 41.44 | 34.56 | 19.58 | ||
| >25 © | Dry land | 2.65 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 8.11 | 22.71 | 3.22 | |
| Shrubbery | 5.07 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 11.98 | 22.42 | 3.88 | ||
| Construction land | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 0.54 | ||
| Forest land | 18.8 | 0.91 | 3.96 | 28.60 | 24.29 | 15.87 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Cai, H.; Tu, H. Impact of Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality Based on Different Topographic Relief Areas: A Case Study of Chishui River Basin in Southwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021476
Zhang X, Cai H, Tu H. Impact of Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality Based on Different Topographic Relief Areas: A Case Study of Chishui River Basin in Southwest China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021476
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuzhao, Hong Cai, and Haomiao Tu. 2023. "Impact of Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality Based on Different Topographic Relief Areas: A Case Study of Chishui River Basin in Southwest China" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021476
APA StyleZhang, X., Cai, H., & Tu, H. (2023). Impact of Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality Based on Different Topographic Relief Areas: A Case Study of Chishui River Basin in Southwest China. Sustainability, 15(2), 1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021476





