Geochemistry Process from Weathering Rocks to Soils: Perspective of an Ecological Geology Survey in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Samples and Methods
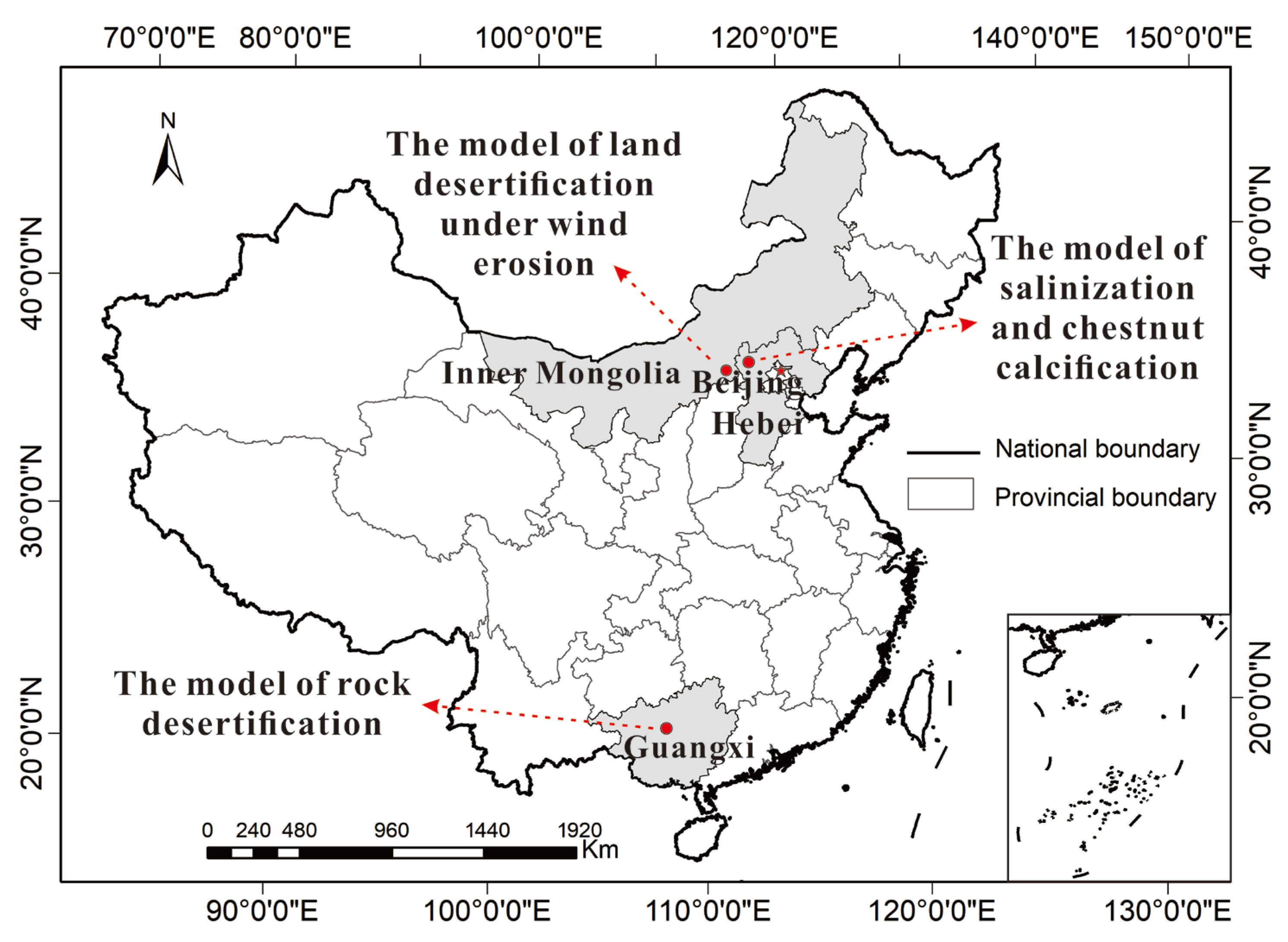
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
- (1)
- Geography and climate at the northern foot of Yinshan Moutain
- (2)
- Geography and climate at Bashang Plateau in Hebei province
- (3)
- Geography and climate in Karst area of Guangxi province
2.2. Analytical Methods and Quality Control
3. Eco-Geology Model for Land Desertification
3.1. Distribution of Major Elements within Soil Particles
3.2. Distribution of Trace Elements within Soil Particles
3.3. Distribution of Soil Grain Sizes
3.4. The Effect of Wind Erosion
3.5. Model Mechanism
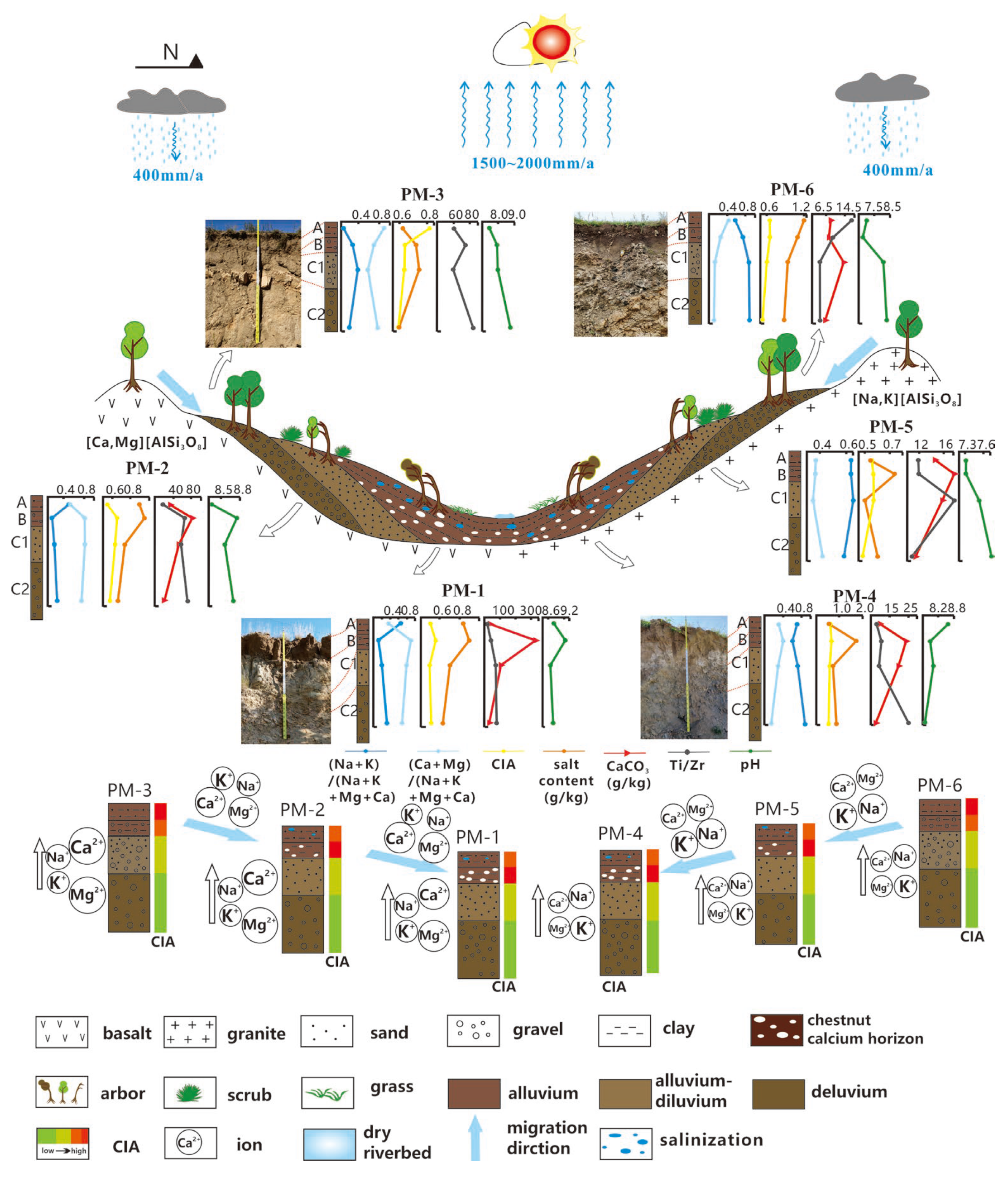
4. Eco-Geology Model for Salinization and Chestnut Calcification
4.1. Source of Salts
4.2. Formation of Calcic Horizon
4.3. Model Mechanism
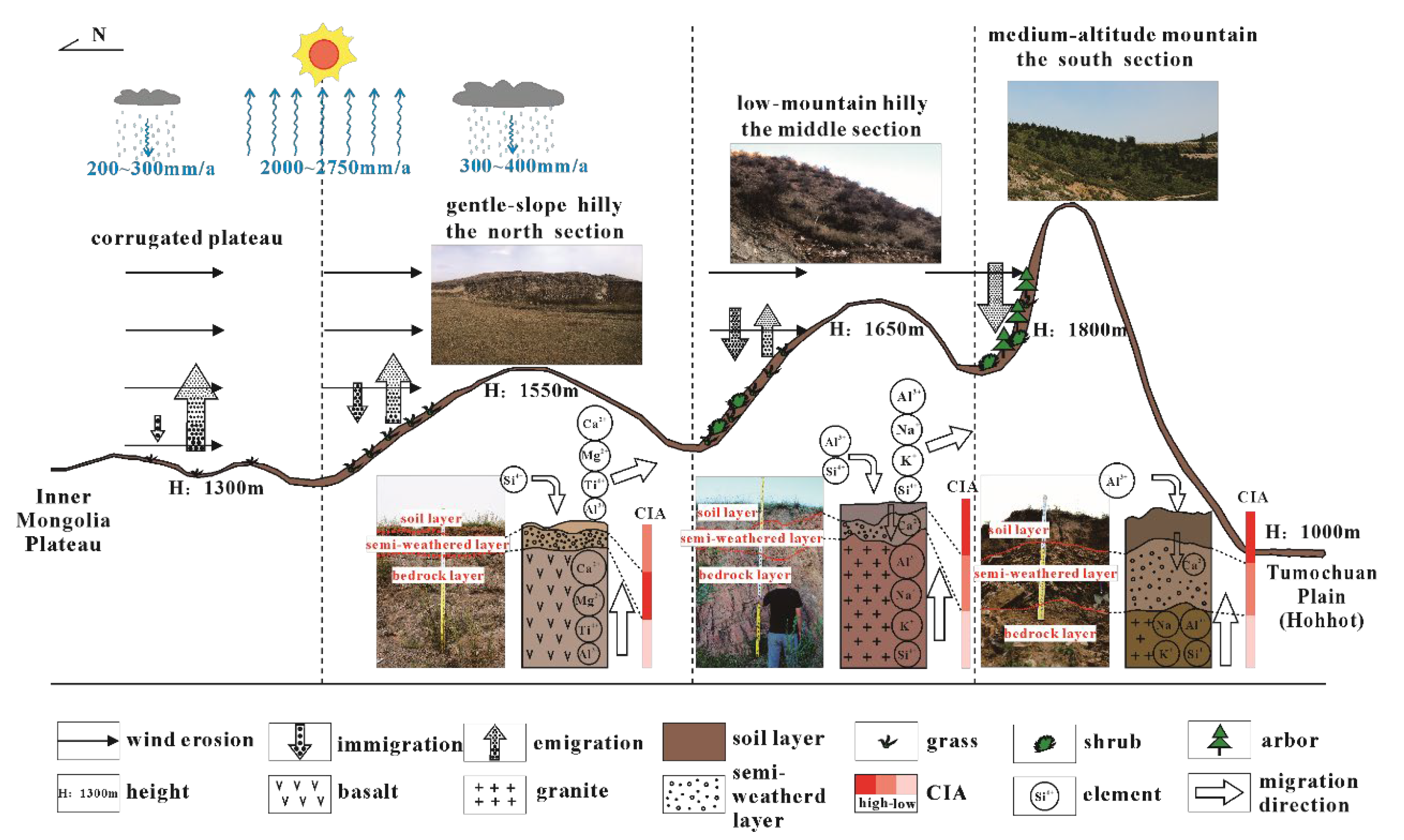
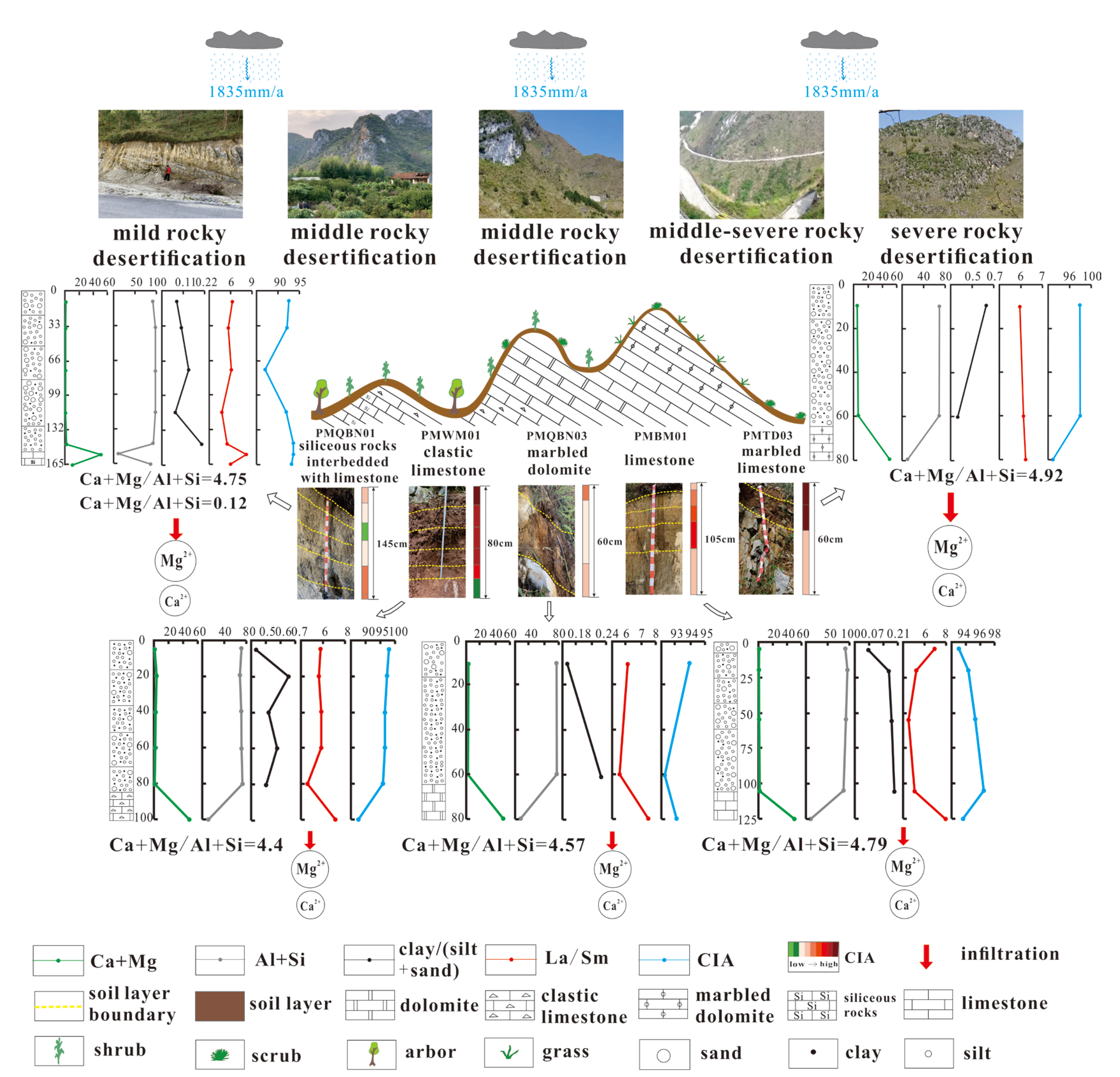
5. Eco-Geology Model for Rocky Desertification
5.1. Soil-Forming Parent Material
5.2. Degree of Soil Weathering
5.3. Model Mechanism
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, H. Eco-environmental geochemistry of Hebei province. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2004, 28, 270–272. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, H.F.; Xiao, C.L.; Ren, W.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Dai, M. Progress and prospect of ecogeological research. Geol. Surv. China 2021, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.P.; Xiong, K.N.; Xu, L.X. Study on the Role of Biological Soil Crust in Ecological Restoration and Its Enlightenment to the Control of Rocky Desertification. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 394–404. [Google Scholar]
- Labianca, C.; De Gisi, S.; Todaro, F.; Notarnicola, M.; Bortone, I. A review of the in-situ capping amendments and modeling approaches for the remediation of contaminated marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meki, K.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S.; Yuan, Y.F. Plant and microbe-assisted biochar amendment technology for petroleum hydrocarbon remediation in saline-sodic soils: A review. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.N.; Ree, R.H.; Spicer, R.A.; Xing, Y.W. Ancient orogenic and monsoon-driven assembly of the world’s richest temperate alpine flora. Science 2020, 369, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshof, C.M.; Spasojevic, M.J. The edaphic control of plant diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1634–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.T. Ecological geology: A novel branch of geological sciences. Earth Sci. Front. 2001, 8, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Banwart, S.A.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Blum, W.E.H.; de Souza, D.M.; Chabaux, F.; Duffy, C.; Kercheva, M.; Krám, P.; Lair, G.J.; Lundin, L.; et al. Chapter One—Soil Functions in Earth’s Critical Zone: Key Results and Conclusions. In Advances in Agronomy; Quantifying and Managing Soil Functions in Earth’s Critical Zone; Banwart, S.A., Sparks, D.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Volume 142, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Rahbek, C.; Borregaard, M.K.; Antonelli, A.; Colwell, R.K.; Holt, B.G.; Nogues-Bravo, D.; Rasmussen, C.M.O.; Richardson, K.; Rosing, M.T.; Whittaker, R.J.; et al. Building mountain biodiversity: Geological and evolutionary processes. Science 2019, 365, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Ding, H.; Liu, T.Z.; Long, T.C.; Ling, F.B.; Lu, H. Geochemical Behavior of Rare-Earth Element During the Weathering of Granite under Different Climatic Conditions. Acta Mineral Sin. 2016, 36, 125–137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.K.; Ji, H.B.; Liu, X.M.; Wei, X.; Luo, G.; Shijie, W.; Trung, N.D.; Dinh, N.Q. Genetic mechanism and elemental evolution of weathering laterite crust overlying carbonate rocks in tropical areas. Geol. China 2021, 48, 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, V.T. The ecological-geological system, its types and position in the structure of an ecosystem. Mosc. Univ. Geol. Bull. 2009, 64, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.d.B.; Billings, S.A. “One physical system”: Tansley’s ecosystem as Earth’s critical zone. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Gillings, M.; Simonet, P.; Stekel, D.; Banwart, S.; Penuelas, J. Human dissemination of genes and microorganisms in Earth’s Critical Zone. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Li, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Nie, Q. Spatial Change of the Farming–Pastoral Ecotone in Northern China from 1985 to 2021. Land 2022, 11, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyun, D.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.X.; Hou, A.H.; Crusiol, L.G.T.; Yu, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, Z. The spatiotemporal change of cropland and its impact on vegetation dynamics in the farming-pastoral ecotone of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.L.; Wang, A.T.; Zhang, R.Q.; Li, J.R.; Gao, T.M. Characteristics of wind regime and drift potential of the desert steppe in northern slope of Yinshan Mountains, Inner Mongolia. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2022, 36, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.D.; Zhang, Y.J. Experimental analysis on soil wind-erosion amount in Siziwang Banner North Yinshan Mountain, Inner Mongolia. Arid Land Geogr. 2006, 29, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.; Lan, D.M.; Zhao, H.S.; Zhao, X.H.; Guo, L. Floristic analysis of woody plants in the northern foot of Yinshan Mountain. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.X.; Yu, E.F.; Shi, S.B.; Mao, Y.F. Strategies for Rejuvenation of Degenerated Natural Grassland Within Northern Agro-grazing Ecotone of Yinshan Mountains, Inner Mongolia. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2002, 9, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Tuo, D.B.; Zhao, P.Y. Strategy of Optimum Land Utilization Structure to Prevent Wind Erosion and Desertification in North Foot of Yinshan Mountain. Inn. Mong. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2003, 5, 1–3+9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Ma, C.M.; Di, K.; Cheng, Y.M.; Sun, S.J.; Yan, T.F. Soil Properties of Degraded Shelter Forests in Bashang Plateau of Northwestern Hebei Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.Y.; Xu, Z.Q.; Ma, C.M.; Sun, S.J.; Yan, T.F. The Factors Influencing the Poplar Shelterbelt Degradation in the Bashang Plateau of Northwest Hebei Province. For. Resour. Manag. 2018, 1, 9–15+147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhao, W.S.; Cai, H.Y. In Situ Measurement Based Study on Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity at Small Scale in Bashang Region of Hebei Province. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 30, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- D’Avello, T.P.; Waltman, W.J.; Waltman, S.W.; Thompson, J.A.; Brennan, J. Revisiting the Pedocal/Pedalfer boundary and Soil Moisture Regimes using the javaNewhall simulation model and PRISM data. Geoderma 2019, 353, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.C.; Luo, W.Q.; Xiao, Q.; Hu, Z.X.; Wu, H.Y. Subsoil carbonate dissolution rates and their determining factors in a karst drainage basin, SW China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Wang, H.B.; Song, B.; Jia, G.D.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yu, X.X.; Zeng, J. Water utilization characteristics of the degraded poplar shelterbelts in Zhangbei, Hebei, China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao, J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, Q.; Tong, X.H. Study on the influence of topographic factors on the distribution and yield of rice in Guangxi. J. Shaanxi Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2020, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Lu, J.; Li, Y.L.; He, J.L.; Huang, X.S.; Huang, Z.; Zhuo, M.L. Climate survey of Guangxi in 2020. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2021, 42, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.X.; Xiong, L.M.; Wei, C.H.; Tan, H.; Yang, S.; Nong, M.L.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, G.Q.; Zhao, Q.G. Changes of soil fertility and its comprehensive evaluation under different stands in typical types of soils in Guangxi Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 5229–5233. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.G.; Xiong, X.J.; Hu, B.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Y.L.; He, T.X. Variation of Vegetation Cover on Various Lithology and Its Response to Human Activities in Guangxi. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 34, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.T.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, G.L.; Albanese, S.; Petrik, A. Geo-statistical and multivariate analyses of potentially toxic elements’ distribution in the soil of Hainan Island (China): A comparison between the topsoil and subsoil at a regional scale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.; Young, G. Early proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, S.M. Weathering and Global Denudation. J. Geol. 1993, 101, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.J.; Pagel, M.; Herbilln, A.; Rosin, C. Mobilization and redistribution of REEs and thorium in a syenitic lateritic profile: A mass balance study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 4419–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.D.; Zhou, S.Z.; Li, F.Q.; Ye, W.; Cui, Q. The elemental transport features of red earth from TX-Section and its Paleo-climatic implications. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2007, 27, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.T.; Huang, C.M. Quantitatives studies on development of tropical soils: A case study in northern Hainan Island. First Earth Sci. 2001, 26, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Cao, J.; Li, B.G.; Xu, F.L.; Chen, W.Y. Distribution pattern of trace elements in soil from Shenzhen area. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2001, 38, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepil, W.S. Dynamics of wind erosion: I. Nature of movement of soil by wind. Soil Sci. 1945, 60, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Ji, H.B.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhou, D.Q.; Zhen, L.P.; Li, T.Y. Preliminary study on weathering and pedogenesis of carbonate rock. Sci. China Ser. Earth Sci. 1999, 42, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, D.Q.; Li, R.L.; Li, Y.L. Differential weathering and pedogenetic characterisitics of carbinate rocksand their effect on the development of rock desertification in karst regions. Acta Mineral Sin. 2002, 22, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.H.; Yuan, D.X.; Pan, G.X. Some soil features in karst ecosystem. Adv. Earth Sci. 2003, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
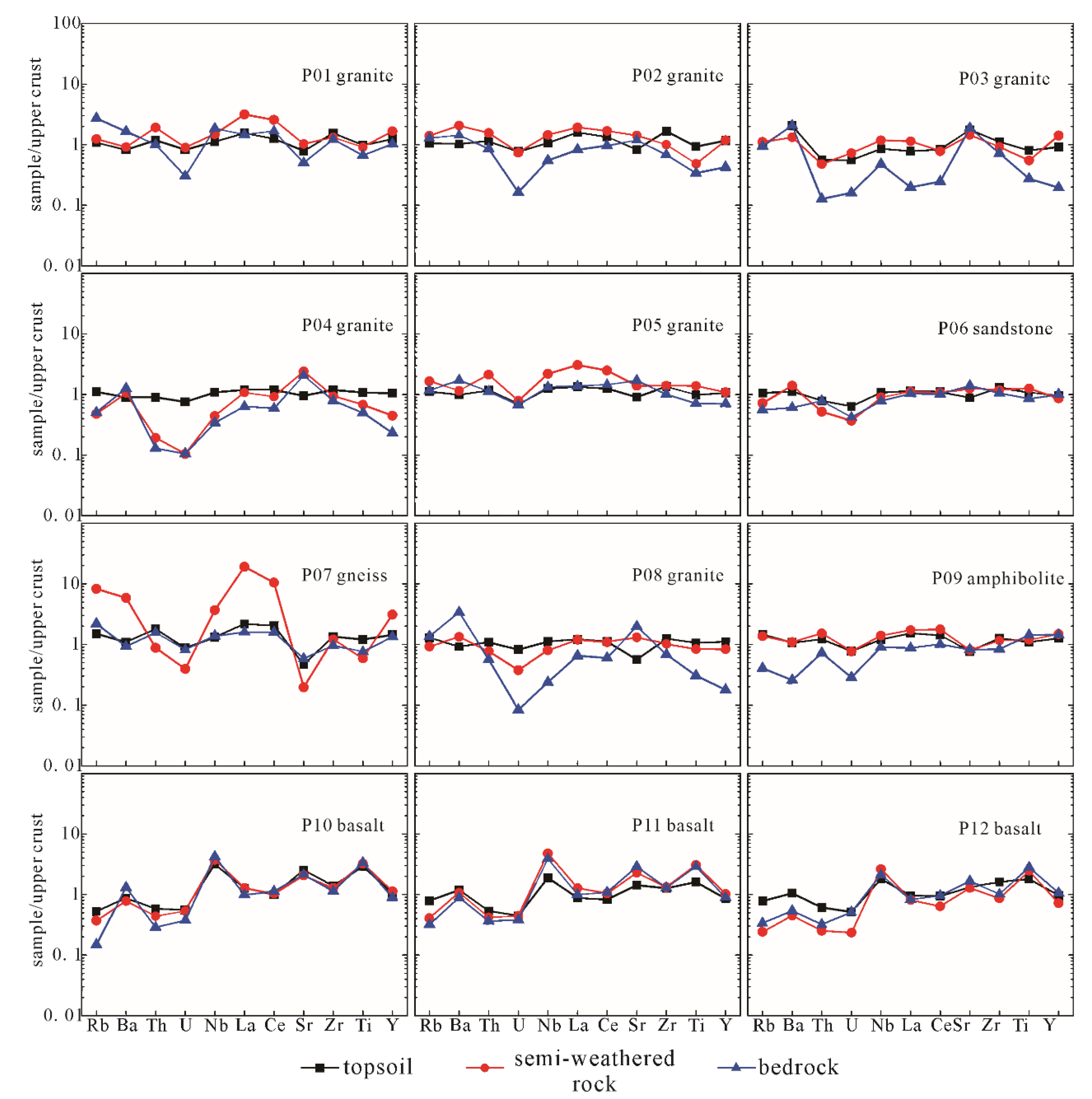
| Profile | Lithology | Layer | SiO2 % | Al2O3 % | Fe2O3 % | MgO % | CaO % | Na2O % | K2O % | CIA % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-mountain hilly landform | ||||||||||
| P01 | granite | soil layer | 60.0 | 10.9 | 5.13 | 2.23 | 4.65 | 2.20 | 2.16 | 53.4 |
| semi-weathered layer | 55.6 | 11.0 | 4.41 | 1.92 | 8.37 | 2.24 | 2.58 | 51.9 | ||
| bedrock | 67.6 | 13.6 | 2.12 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 3.46 | 5.95 | - | ||
| P02 | granite | soil layer | 61.1 | 11.5 | 4.30 | 1.78 | 3.27 | 2.25 | 2.48 | 53.4 |
| semi-weathered layer | 62.0 | 12.5 | 2.43 | 0.88 | 6.07 | 2.74 | 3.78 | 48.8 | ||
| bedrock | 70.4 | 13.2 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 1.58 | 3.90 | 4.00 | - | ||
| P03 | granite | soil layer | 60.3 | 13.2 | 4.36 | 2.69 | 2.86 | 3.38 | 3.07 | 48.3 |
| semi-weathered layer | 69.9 | 10.1 | 3.99 | 3.41 | 4.62 | 2.72 | 5.16 | 40.9 | ||
| bedrock | 67.3 | 14.4 | 1.58 | 0.33 | 0.73 | 5.14 | 5.47 | - | ||
| P04 | granite | soil layer | 57.4 | 13.1 | 5.62 | 2.17 | 2.60 | 2.25 | 2.13 | 57.5 |
| semi-weathered layer | 58.9 | 14.7 | 4.46 | 1.93 | 3.89 | 3.78 | 1.88 | 50.4 | ||
| bedrock | 64.3 | 15.1 | 2.87 | 1.62 | 2.87 | 4.95 | 2.11 | - | ||
| P05 | granite | soil layer | 59.9 | 13.4 | 4.98 | 1.84 | 2.09 | 2.62 | 2.63 | 54.9 |
| semi-weathered layer | 55.3 | 14.1 | 7.27 | 2.03 | 2.96 | 3.77 | 3.07 | 48.7 | ||
| bedrock | 63.5 | 13.7 | 3.82 | 1.72 | 3.00 | 4.25 | 4.04 | - | ||
| Medium-altitude mountain | ||||||||||
| P06 | sandstone | soil layer | 60.8 | 12.8 | 5.50 | 2.34 | 1.71 | 2.70 | 2.41 | 55.8 |
| semi-weathered layer | 55.8 | 12.9 | 6.31 | 2.79 | 1.72 | 3.12 | 2.17 | 54.8 | ||
| bedrock | 50.9 | 11.2 | 3.69 | 2.42 | 11.8 | 3.43 | 1.71 | - | ||
| P07 | gneiss | soil layer | 57.4 | 13.5 | 6.73 | 2.57 | 1.73 | 1.47 | 2.61 | 63.7 |
| semi-weathered layer | 47.9 | 9.4 | 3.66 | 6.10 | 2.58 | 0.21 | 6.62 | 54.4 | ||
| bedrock | 63.4 | 14.3 | 4.00 | 2.15 | 1.67 | 4.69 | 2.95 | - | ||
| P08 | granite | soil layer | 60.9 | 13.3 | 5.49 | 2.16 | 1.51 | 1.97 | 2.50 | 60.5 |
| semi-weathered layer | 63.8 | 13.9 | 5.02 | 1.84 | 1.91 | 3.41 | 2.47 | 54.1 | ||
| bedrock | 72.9 | 13.4 | 1.57 | 0.77 | 1.51 | 3.57 | 4.89 | - | ||
| P09 | amphibolite | soil layer | 58.3 | 13.6 | 6.67 | 2.25 | 2.38 | 2.53 | 2.68 | 54.9 |
| semi-weathered layer | 56.3 | 14.5 | 7.00 | 2.23 | 2.24 | 2.71 | 2.66 | 55.9 | ||
| bedrock | 54.1 | 12.6 | 9.35 | 2.89 | 5.54 | 3.80 | 1.23 | - | ||
| Gentle-slope hilly landform | ||||||||||
| P10 | basalt | soil layer | 49.2 | 14.7 | 9.05 | 2.94 | 5.39 | 1.95 | 1.70 | 64.0 |
| semi-weathered layer | 47.9 | 15.6 | 9.43 | 3.07 | 6.75 | 1.78 | 1.55 | 67.4 | ||
| bedrock | 43.2 | 14.9 | 9.98 | 3.21 | 13.6 | 2.26 | 1.14 | - | ||
| P11 | basalt | soil layer | 57.1 | 12.3 | 5.96 | 2.34 | 4.54 | 2.18 | 2.40 | 55.8 |
| semi-weathered layer | 45.6 | 15.1 | 10.5 | 2.64 | 8.80 | 2.14 | 2.09 | 61.9 | ||
| bedrock | 47.4 | 14.1 | 9.99 | 4.07 | 9.50 | 3.51 | 2.25 | - | ||
| P12 | basalt | soil layer | 56.4 | 13.0 | 7.23 | 2.66 | 3.55 | 2.20 | 1.97 | 58.1 |
| semi-weathered layer | 43.9 | 12.7 | 9.11 | 3.24 | 11.38 | 1.86 | 1.39 | 63.0 | ||
| bedrock | 49.1 | 14.9 | 9.64 | 3.82 | 8.94 | 3.65 | 1.46 | - | ||
| Clay | Silt | Very Fine Sand | Fine Sand | Medium Sand | Coarse Sand | Very Coarse Sand | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.002 mm | 0.002–0.05 mm | 0.05–0.1 mm | 0.1–0.25 mm | 0.25–0.5 mm | 0.5–1 mm | 1–2 mm | |
| Low-mountain hilly landform | |||||||
| P01 | 4.45 | 48.4 | 34.5 | 12.6 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| P02 | 4.52 | 47.6 | 32.8 | 11.8 | 2.16 | 1.13 | 0.00 |
| P03 | 3.93 | 62.2 | 17.8 | 8.97 | 6.00 | 1.10 | 0.00 |
| P04 | 3.66 | 71.7 | 19.9 | 3.39 | 1.29 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| P05 | 5.27 | 58.45 | 20.8 | 6.81 | 2.93 | 5.33 | 0.43 |
| Medium-altitude mountain | |||||||
| P06 | 5.13 | 60.5 | 13.9 | 9.99 | 8.21 | 2.17 | 0.00 |
| P07 | 4.11 | 64.7 | 18.4 | 5.72 | 3.58 | 3.12 | 0.36 |
| P08 | 6.97 | 71.0 | 18.2 | 3.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| P09 | 4.39 | 64.5 | 16.3 | 6.43 | 5.56 | 2.78 | 0.03 |
| Gentle-slope hilly landform | |||||||
| P10 | 5.70 | 68.6 | 18.8 | 6.40 | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| P11 | 5.67 | 62.4 | 16.4 | 12.1 | 3.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| P12 | 4.82 | 63.3 | 16.9 | 7.40 | 6.85 | 0.74 | 0.00 |
| Profile | Layer | Na2O (%) | K2O (%) | MgO (%) | CaO (%) | (Na + K)/ (Na + K +Mg + Ca) | (Ca + Mg)/ (Na + K + Mg + Ca) | Salt Content (g/kg) | CaCO3/ (g/kg) | pH | CIA % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM-1 | soil layer A | 1.91 | 2.88 | 0.61 | 2.07 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.84 | 29.9 | 8.81 | 50.5 |
| soil layer B | 1.55 | 1.22 | 1.65 | 19.68 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 323 | 9.24 | 55.2 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 2.95 | 1.07 | 2.72 | 12.44 | 0.21 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 103 | 8.72 | 52.8 | |
| weathered layer C2 | 3.63 | 1.28 | 3.17 | 7.54 | 0.31 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 30.9 | 8.79 | 51.6 | |
| PM-2 | soil layer A | 2.10 | 2.51 | 1.34 | 3.21 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 30.9 | 8.35 | 54.3 |
| soil layer B | 1.86 | 0.96 | 4.82 | 8.69 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.96 | 81.7 | 8.75 | 65.2 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 1.84 | 0.83 | 4.89 | 6.07 | 0.20 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 54.9 | 8.57 | 63.7 | |
| weathered layer C2 | 2.75 | 1.21 | 5.29 | 6.84 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.66 | 19.7 | 8.7 | 57.9 | |
| PM-3 | soil layer A | 0.59 | 0.51 | 5.70 | 2.71 | 0.11 | 0.89 | 0.62 | - | 7.45 | 82.7 |
| soil layer B | 1.83 | 1.36 | 3.17 | 4.21 | 0.30 | 0.70 | 0.72 | - | 7.96 | 64.3 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 1.84 | 1.82 | 2.52 | 2.83 | 0.41 | 0.59 | 0.74 | - | 7.98 | 63.8 | |
| weathered layer C2 | 2.67 | 1.02 | 3.90 | 8.43 | 0.23 | 0.77 | 0.60 | - | 8.76 | 60.2 | |
| PM-4 | soil layer A | 2.15 | 2.87 | 0.84 | 1.29 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.54 | 9.72 | 8.58 | 60.9 |
| soil layer B | 2.20 | 2.61 | 1.43 | 1.87 | 0.59 | 0.41 | 1.74 | 23.8 | 7.88 | 65.4 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 2.27 | 3.59 | 0.86 | 1.42 | 0.72 | 0.28 | 0.74 | 19.7 | 8.02 | 58.3 | |
| weathered layer C2 | 3.18 | 5.97 | 0.3 | 1.10 | 0.87 | 0.13 | 0.88 | 7.77 | 7.63 | 53.9 | |
| PM-5 | soil layer A | 2.89 | 2.72 | 1.47 | 1.75 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 14.6 | 7.31 | 56.2 |
| soil layer B | 2.98 | 2.62 | 1.43 | 1.79 | 0.64 | 0.36 | 0.74 | 17.8 | 7.31 | 57.2 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 4.72 | 1.96 | 1.19 | 2.37 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 15.8 | 7.53 | 50.9 | |
| weathered layer C2 | 4.39 | 2.34 | 1.98 | 2.84 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.60 | 11.4 | 7.73 | 48.8 | |
| PM-6 | soil layer A | 1.56 | 2.44 | 1.51 | 1.48 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 1.20 | 8.50 | 7.01 | 65.3 |
| soil layer B | 2.20 | 3.54 | 1.27 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.26 | 1.10 | 7.77 | 6.75 | 64.2 | |
| weathered layer C1 | 2.59 | 4.70 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.88 | 0.12 | 0.94 | 14.1 | 8.08 | 60.5 |
| Desertification Grade | Profile with Different Parent Rock | Soil Thick-ness (cm) | SiO2 % | Al2O3 % | CaO % | MgO % | (Ca + Mg) /(Si + Al) | Clay/ (Silt + Sand) | CIA % | La/Sm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Siliceous rocks interbedded with limestone | |||||||||
| PMQBN01-1 | 10.0 | 87.4 | 4.50 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 92.5 | 6.26 | ||
| PMQBN01-2 | 35.0 | 93.9 | 3.73 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 92.1 | 5.67 | ||
| PMQBN01-3 | 75.0 | 93.7 | 3.78 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 86.9 | 6.09 | ||
| PMQBN01-4 | 115 | 94.1 | 3.53 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 91.9 | 4.77 | ||
| PMQBN01-5 | 145 | 88.1 | 4.85 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 93.6 | 5.47 | ||
| PMQBN01-6R ** | 155 | 7.36 | 3.33 | 50.5 | 0.31 | 4.75 | - | 93.6 | 8.17 | |
| PMQBN01-7R ** | 165 | 83.3 | 3.03 | 10.0 | 0.09 | 0.12 | - | 93.2 | 5.95 | |
| Middle | Clastic limestone | |||||||||
| PMWM01-1 | 5.00 | 42.3 | 28.9 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 97.9 | 5.78 | ||
| PMWM01-2 | 20.0 | 41.4 | 27.0 | 3.19 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 97.3 | 5.62 | ||
| PMWM01-3 | 40.0 | 43.2 | 27.6 | 1.54 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 96.6 | 5.84 | ||
| PMWM01-4 | 60.0 | 43.5 | 27.9 | 1.31 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 96.7 | 5.81 | ||
| PMWM01-5 | 80.0 | 44.0 | 29.1 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.50 | 95.9 | 4.60 | ||
| PMWM01-6R ** | 100 | 7.54 | 3.56 | 48.6 | 0.23 | 4.40 | - | 87.5 | 7.11 | |
| Marbled dolomite | ||||||||||
| PMQBN03-1 | 10.0 | 60.2 | 16.5 | 0.96 | 1.86 | 0.16 | 93.9 | 6.06 | ||
| PMQBN03-2 | 60.0 | 59.3 | 17.9 | 0.43 | 1.70 | 0.23 | 92.2 | 5.51 | ||
| PMQBN03-3R ** | 80.0 | 7.62 | 3.44 | 30.0 | 20.6 | 4.57 | - | 93.0 | 7.48 | |
| Middle- severe | Limestone | |||||||||
| PMBM01-1 | 5.00 | 84.2 | 5.95 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 0.07 | 92.8 | 6.90 | ||
| PMBM01-2 | 20.0 | 90.2 | 4.80 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 0.16 | 94.1 | 5.21 | ||
| PMBM01-3 | 55.0 | 83.4 | 8.19 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 0.18 | 95.1 | 4.49 | ||
| PMBM01-4 | 105 | 75.0 | 11.2 | 0.98 | 1.10 | 0.19 | 96.3 | 5.05 | ||
| PMBM01-5R ** | 125 | 7.28 | 3.29 | 50.3 | 0.31 | 4.79 | - | 93.4 | 7.94 | |
| Severe | Marbled limestone | |||||||||
| PMTD03-1 | 10.0 | 44.0 | 25.4 | 3.49 | 1.39 | 0.63 | 97.9 | 5.95 | ||
| PMTD03-2 | 60.0 | 43.2 | 25.3 | 5.22 | 1.24 | 0.37 | 97.9 | 6.11 | ||
| PMTD03-3R ** | 80.0 | 7.10 | 3.05 | 49.7 | 0.29 | 4.92 | - | 92.9 | 6.21 | |
| Sample | N | P | K2O | CaO | MgO | S | Fe2O3 | B | Mn | Cu | Zn | Mo | Cl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/g | μg/g | % | % | % | μg/g | % | μg/g | μg/g | μg/g | μg/g | μg/g | μg/g | |
| Mild rocky desertification Siliceous rocks interbedded with limestone | |||||||||||||
| PMQBN01-1 | 2481 | 375 | 0.05 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 269 | 0.99 | 12.3 | 208 | 12.2 | 45.9 | 0.41 | 38.2 |
| PMQBN01-2 | 235 | 67.0 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 51.0 | 0.73 | 10.6 | 100 | 5.50 | 24.4 | 0.24 | 10.9 |
| PMQBN01-3 | 182 | 68.0 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.13 | 46.0 | 0.86 | 10.5 | 151 | 7.70 | 30.3 | 0.39 | 28.2 |
| PMQBN01-4 | 145 | 50.0 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 42.0 | 0.43 | 12.0 | 73.0 | 9.10 | 22.6 | 0.30 | 10.8 |
| PMQBN01-5 | 305 | 185 | 0.15 | 1.59 | 0.19 | 57.0 | 1.07 | 14.0 | 218 | 25.5 | 77.9 | 0.41 | 10.6 |
| PMQBN01-6R | 63.0 | 98.0 | 0.05 | 50.5 | 0.31 | 77.0 | 0.21 | 2.50 | 53.0 | 5.20 | 8.10 | 0.34 | 69.1 |
| PMQBN01-7R | 50.0 | 47.0 | 0.05 | 10.0 | 0.09 | 58.0 | 0.12 | 3.60 | 18.0 | 3.60 | 8.60 | 0.36 | 51.4 |
| Middle rocky desertification Clastic limestone | |||||||||||||
| PMWM01-1 | 2728 | 814 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 294 | 10.70 | 47.5 | 7199 | 72.3 | 353 | 2.83 | 63.6 |
| PMWM01-2 | 2142 | 884 | 0.54 | 3.19 | 0.48 | 246 | 11.00 | 48.7 | 7908 | 77.7 | 369 | 2.95 | 35.3 |
| PMWM01-3 | 1701 | 909 | 0.75 | 1.54 | 0.52 | 182 | 10.50 | 54.3 | 7109 | 78.5 | 361 | 2.44 | 26.7 |
| PMWM01-4 | 1461 | 866 | 0.73 | 1.31 | 0.50 | 143 | 10.50 | 54.7 | 6905 | 77.8 | 347 | 2.43 | 17.5 |
| PMWM01-5 | 1477 | 1061 | 1.01 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 108 | 10.60 | 61.5 | 5751 | 85.4 | 369 | 2.30 | 25.3 |
| PMWM01-6R | 90.0 | 175 | 0.13 | 48.6 | 0.23 | 76.0 | 0.40 | 4.20 | 199 | 2.40 | 8.40 | 0.26 | 93.1 |
| Middle rocky desertification Marbled dolomite | |||||||||||||
| PMQBN03-1 | 3309 | 672 | 0.61 | 0.96 | 1.86 | 370 | 6.59 | 65.6 | 1362 | 15.1 | 371 | 0.80 | 31.3 |
| PMQBN03-2 | 1116 | 407 | 0.99 | 0.43 | 1.70 | 135 | 7.23 | 74.4 | 934 | 15.3 | 324 | 0.95 | 16.6 |
| PMQBN03-3R | 87.0 | 66.0 | 0.05 | 30.0 | 20.6 | 77.0 | 0.10 | 2.50 | 19.0 | 2.30 | 7.80 | 0.13 | 278 |
| Middle-severe rocky desertification Limestone | |||||||||||||
| PMBM01-1 | 3121 | 294 | 0.09 | 0.50 | 0.77 | 307 | 1.71 | 14.7 | 84.0 | 15.4 | 105.0 | 1.71 | 70.7 |
| PMBM01-2 | 429 | 75.0 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.58 | 67.0 | 1.21 | 13.8 | 41.0 | 11.0 | 74.3 | 2.61 | 33.4 |
| PMBM01-3 | 437 | 204 | 0.17 | 0.43 | 0.92 | 70.0 | 2.84 | 19.6 | 188 | 23.6 | 154 | 5.30 | 19.8 |
| PMBM01-4 | 612 | 462 | 0.25 | 0.98 | 1.10 | 95.0 | 4.18 | 20.6 | 312 | 38.9 | 226 | 8.44 | 20.2 |
| PMBM01-5R | 62.0 | 114 | 0.06 | 50.3 | 0.31 | 76.0 | 0.19 | 2.30 | 35.0 | 2.00 | 6.60 | 0.18 | 57.8 |
| Severe rocky desertification Marbled limestone | |||||||||||||
| PMTD03-1 | 2654 | 1340 | 0.36 | 3.49 | 1.39 | 333 | 10.5 | 66.6 | 2789 | 32.6 | 511.0 | 0.89 | 13.5 |
| PMTD03-2 | 2479 | 1051 | 0.35 | 5.22 | 1.24 | 300 | 9.48 | 60.2 | 2347 | 29.6 | 451.0 | 0.88 | 11.3 |
| PMTD03-3R | 59.0 | 41.0 | 0.05 | 49.7 | 0.29 | 51.0 | 0.06 | 1.8 0 | 18.0 | 1.1.0 | 6.40 | 0.10 | 117 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.-Y.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.-H.; Yuan, G.-L.; Zheng, J.-L.; Liu, Z.-J. Geochemistry Process from Weathering Rocks to Soils: Perspective of an Ecological Geology Survey in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021002
Guo X-Y, Li J, Jia Y-H, Yuan G-L, Zheng J-L, Liu Z-J. Geochemistry Process from Weathering Rocks to Soils: Perspective of an Ecological Geology Survey in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(2):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiao-Yu, Jun Li, Yan-Hui Jia, Guo-Li Yuan, Ji-Lin Zheng, and Zhi-Jie Liu. 2023. "Geochemistry Process from Weathering Rocks to Soils: Perspective of an Ecological Geology Survey in China" Sustainability 15, no. 2: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021002
APA StyleGuo, X.-Y., Li, J., Jia, Y.-H., Yuan, G.-L., Zheng, J.-L., & Liu, Z.-J. (2023). Geochemistry Process from Weathering Rocks to Soils: Perspective of an Ecological Geology Survey in China. Sustainability, 15(2), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021002







