Intelligent-Technology-Empowered Active Emergency Command Strategy for Urban Hazardous Chemical Disaster Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. UHCDM
2.2. Intelligent Technologies for Disaster Management
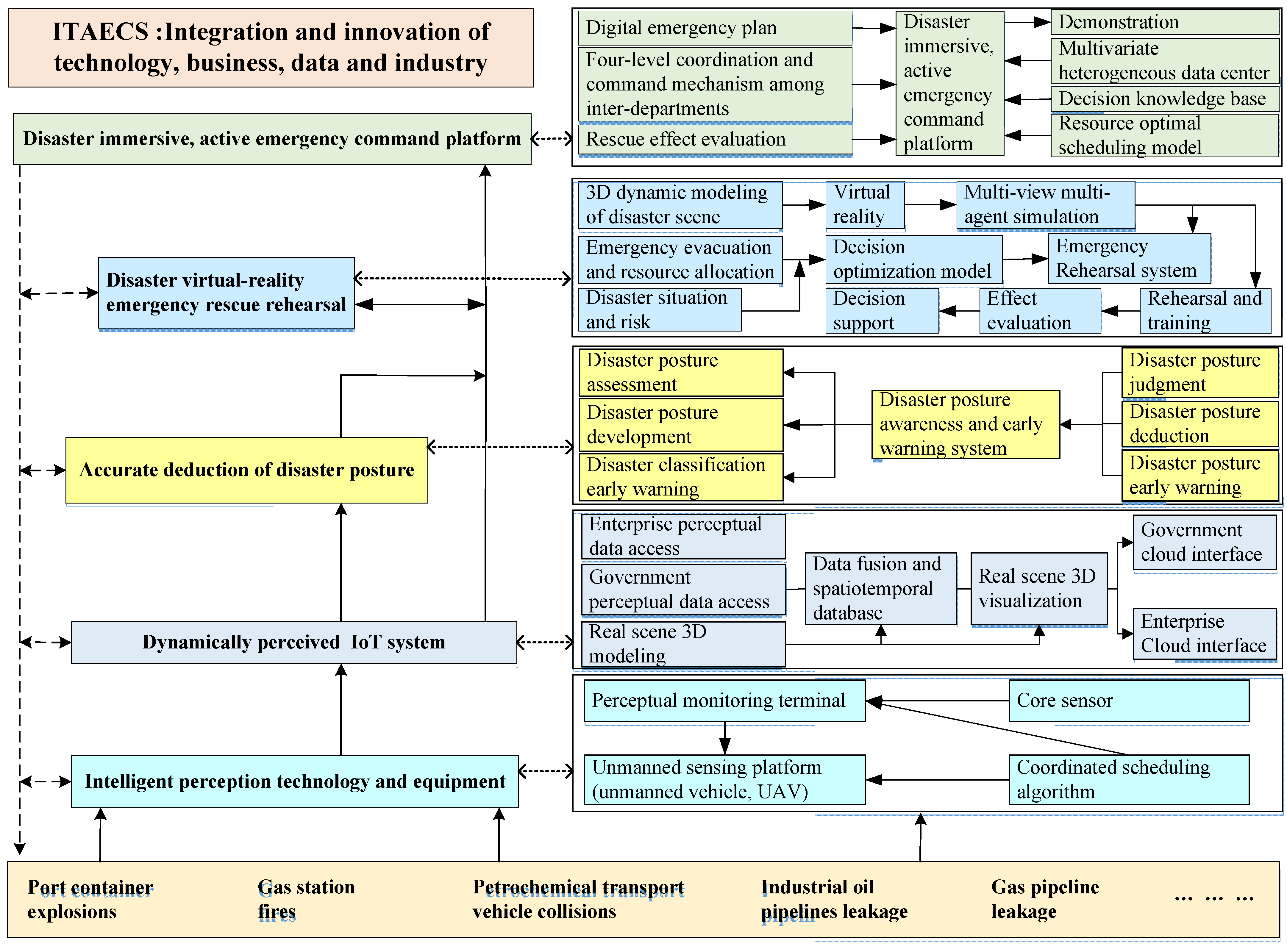
3. ITAECS Theoretical Framework for UHCDM
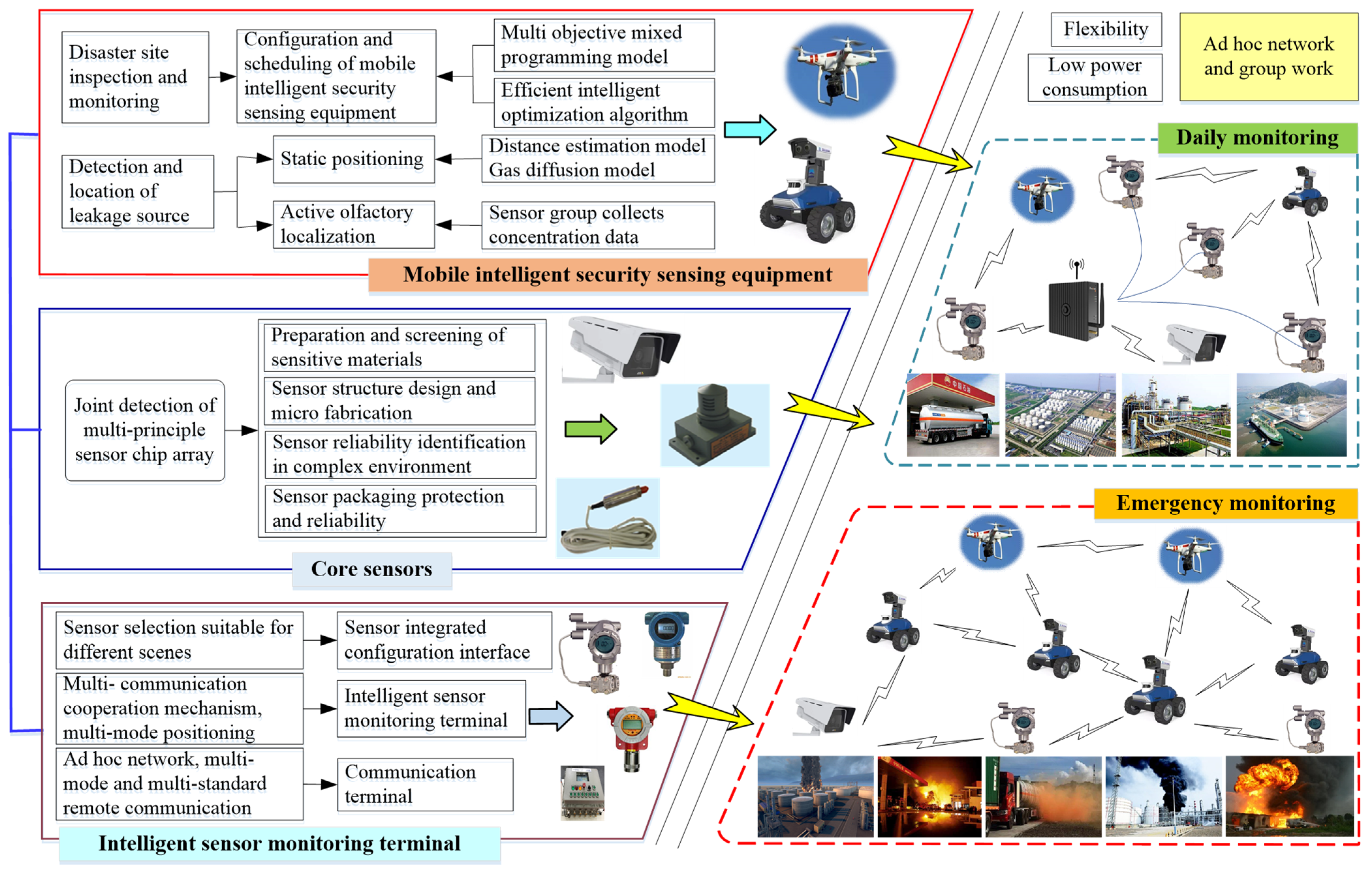
3.1. Strategy of Intelligent Perception Technology and Equipment for UHCDM
3.1.1. Core Sensors
3.1.2. Intelligent Sensor Monitoring Terminals (ISMT)
3.1.3. Mobile Intelligent Security Sensing Equipment
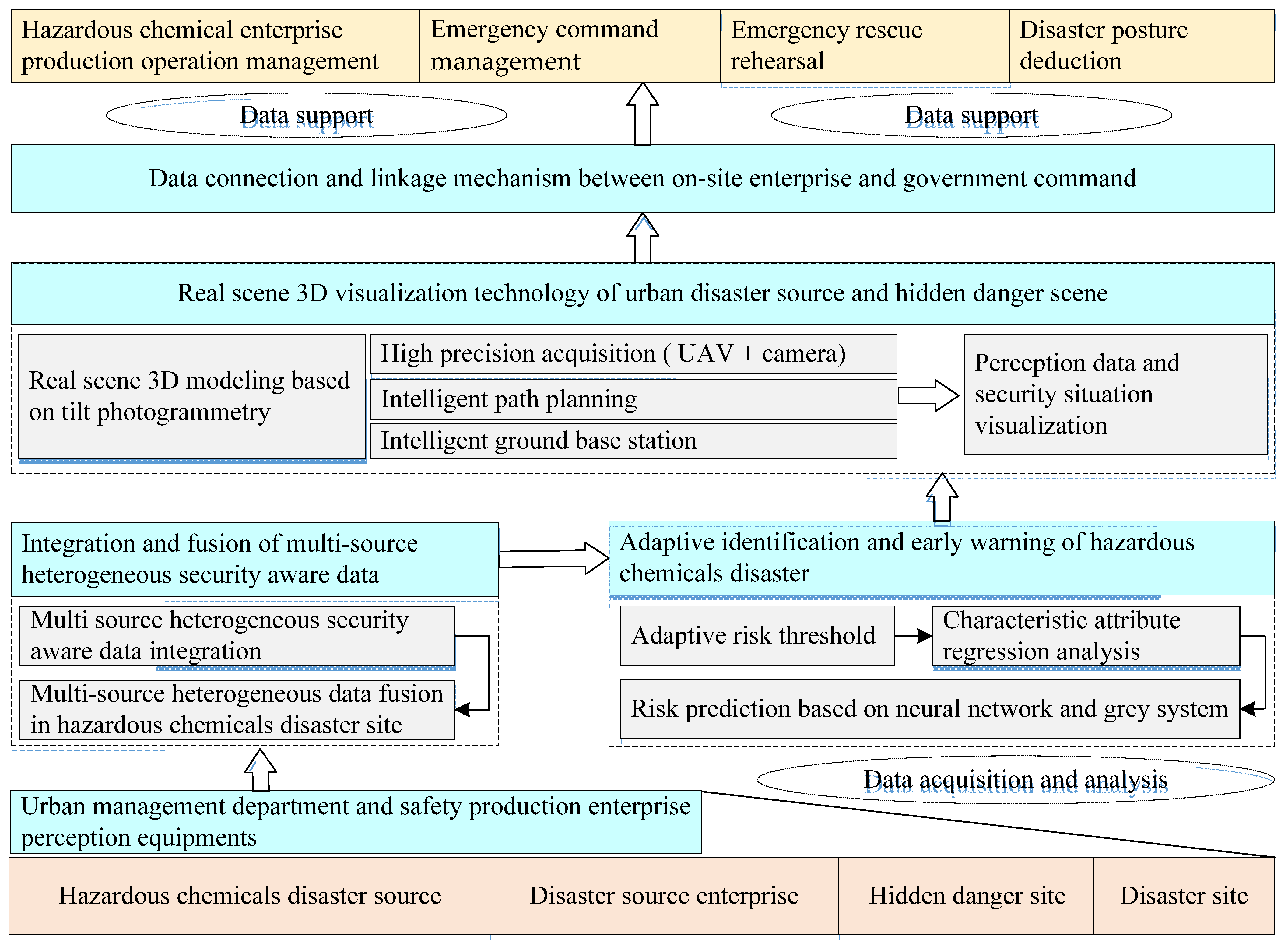
3.2. Strategy of the Dynamically Perceived IoT System for UHCDM
3.2.1. Multi-Source Heterogeneous Security-Aware Data Integration and Fusion
3.2.2. Real-Time Monitoring Digital Map of Disaster Source and Hidden Danger Site
3.2.3. Safety Early Warning Model of the Hazardous Chemical Disaster Site
3.2.4. Data Connection and Linkage Mechanism between on-Site Enterprise and Government Command
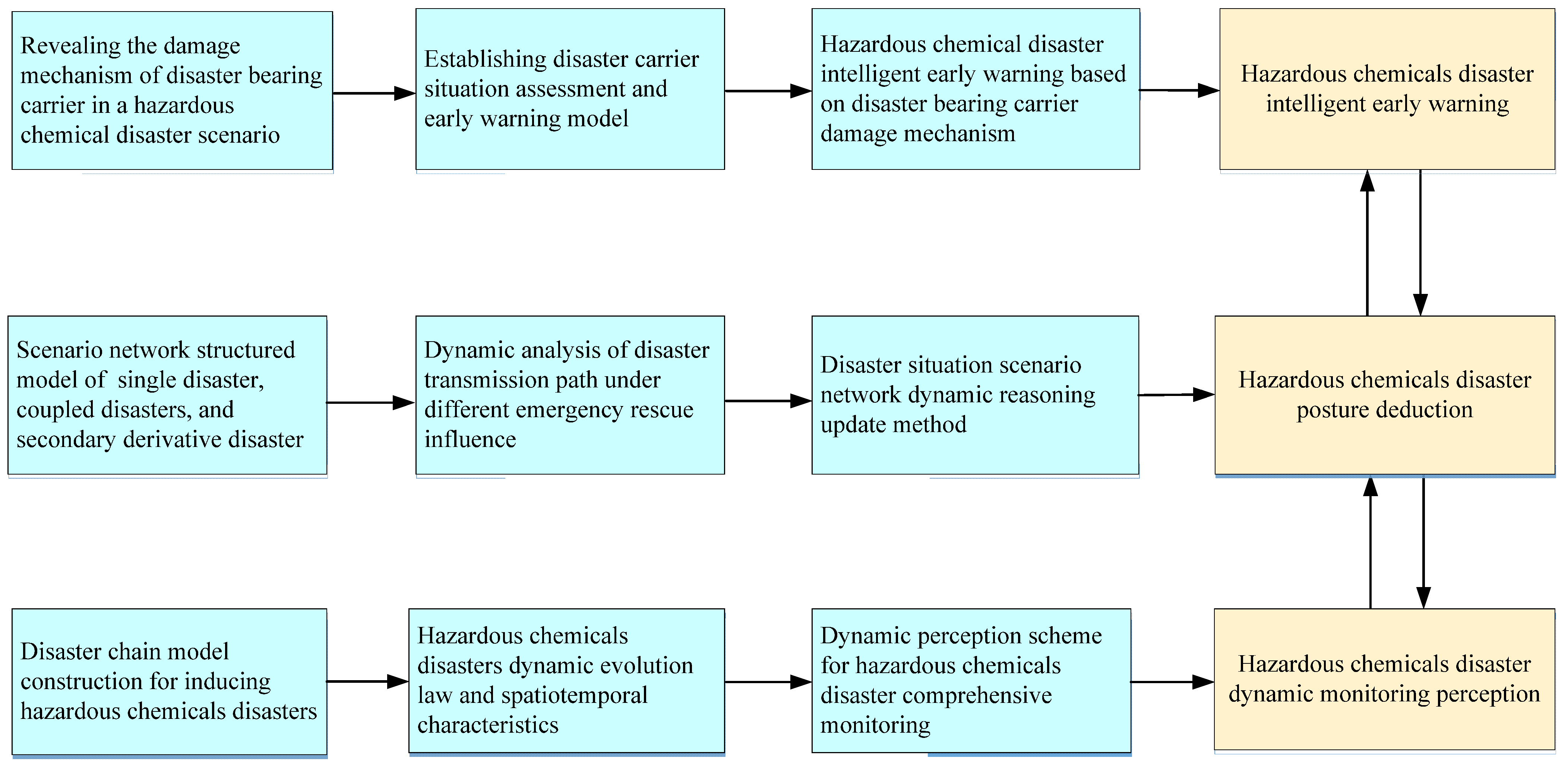
3.3. Strategy of the Accurate Posture Deduction for UHCDM
3.3.1. Life Cycle Dynamic Monitoring Perception Method of Hazardous Chemical Disasters’ Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics
3.3.2. Deduction Model for Hazardous Chemical Disaster under Multi-Source Heterogeneous Big Data Fusion
3.3.3. Intelligent Early Warning Strategy of Hazardous Chemical Disasters Based on Damage Mechanism of Disaster Carrier
3.4. Strategy of Virtual Reality Emergency Rescue Rehearsal for UHCDM
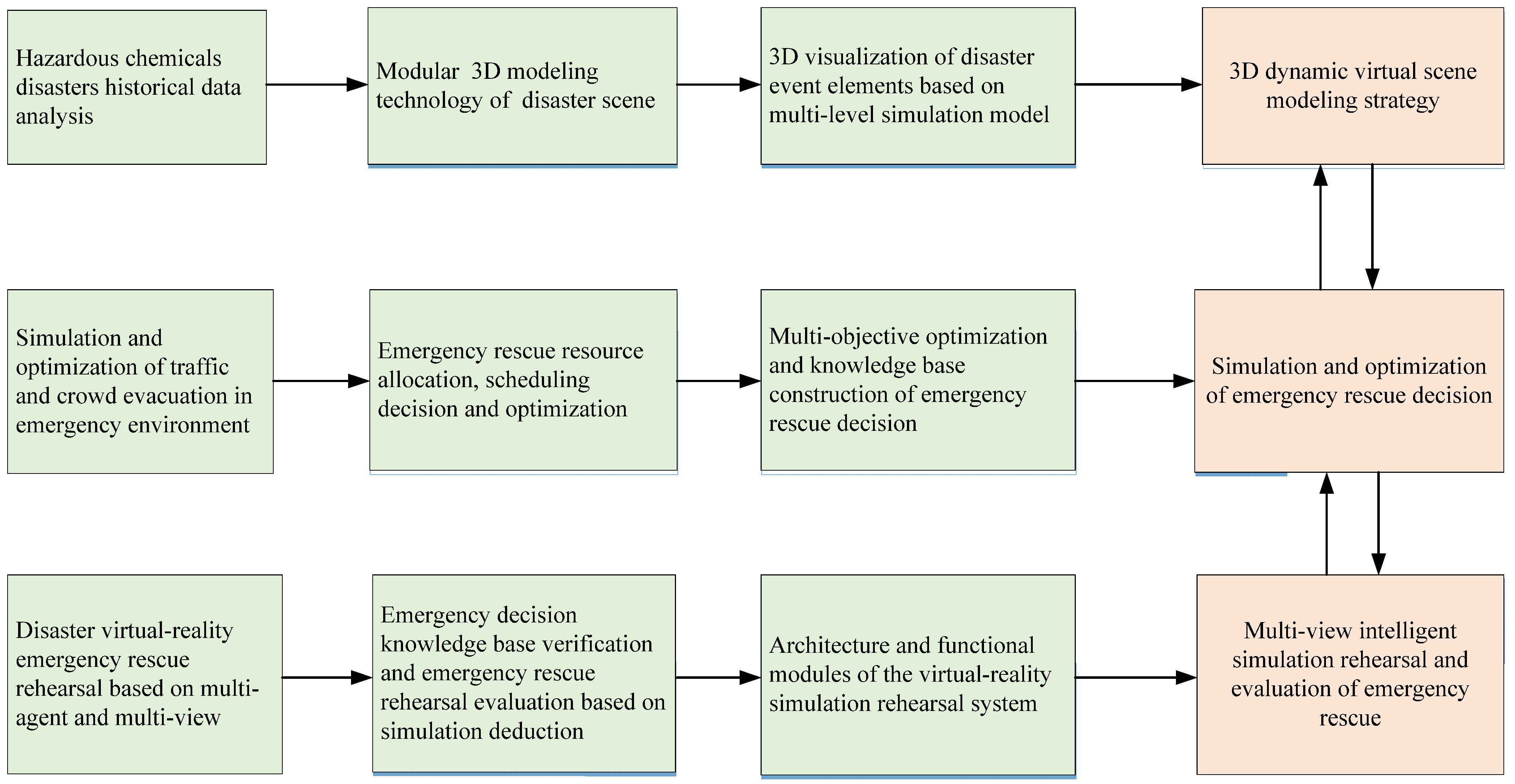
3.4.1. The 3D Dynamic Virtual Scene Modeling Strategy
3.4.2. Simulation and Optimization of Emergency Rescue Decisions
3.4.3. Multi-View Intelligent Simulation Rehearsal and Evaluation Strategy of Emergency Rescue
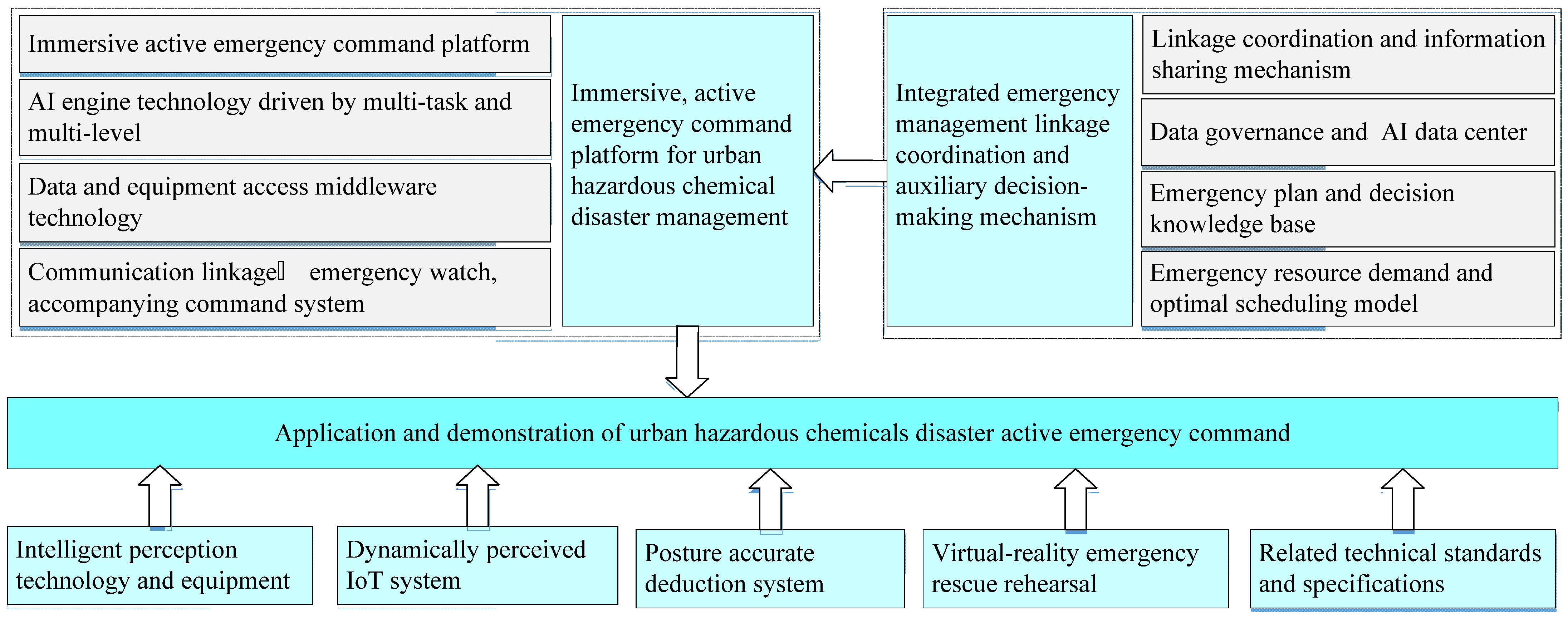
3.5. Strategy of Immersive, Active Emergency Command Platform for UHCDM
3.5.1. Integrated Emergency Management Linkage Coordination and Auxiliary Decision-Making Mechanism
3.5.2. Development of Immersive, Active Emergency Command Platforms
4. Key Scientific and Technological Issues in ITAECS
4.1. Group Coordinated Operation and Disaster Tracing Location Technology of Mobile Sensing Equipment under Complex Disaster Conditions
4.2. Intelligent Terminal and ISSE Multi-Point Delivery ad Hoc Network Technology
4.3. DT Modeling Technology for Urban Disaster Source and Hidden Danger Scene Dynamic Real-Time Perception
4.4. Situation Deduction and Intelligent Early Warning Technology Based on Damage Mechanism of Disaster Carrier and Real-Time Data of Disaster Site
4.5. A 3D Dynamic Scene Modeling and Virtual Reality Fusion Simulation Rehearsal Technology Based on Complex Disaster Characteristics and Disaster Scenes
4.6. AI Data Center Based on Knowledge Graph and Emergency Plan Digitization Technology
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huimin, G.; Lianhua, C.; Shugang, L.; Haifei, L. Regional risk assessment methods in relation to urban public safety. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamsen, E.B.; Abrahamsen, H.B.; Milazzo, M.F.; Selvik, J.T. Using the ALARP principle for safety management in the energy production sector of chemical industry. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2018, 169, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, C.; Reniers, G.; Huang, L.; Kang, L.; Zhang, L. The future of hazardous chemical safety in China: Opportunities, problems, challenges and tasks. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ghoshal, S.K. Hydrogen the future transportation fuel: From production to applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Zheng, X.P. Characteristics of hazardous chemical accidents in China: A statistical investigation. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2012, 25, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Characteristics of hazardous chemical accidents during hot season in China from 1989 to 2019: A statistical investigation. Saf. Sci. 2020, 129, 104788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellasio, R.; Bianconi, R. On line simulation system for industrial accidents. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, F.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Z.; Qiao, X.; Meng, Q.; Chen, Q. Construction and spatio-temporal derivation of hazardous chemical leakage disaster chain. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2021, 12, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallinger, D.; Gutmann, B.; Kappe, C.O. The concept of chemical generators: On-site on-demand production of hazardous reagents in continuous flow. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavlock, R.J.; Bahadori, T.; Barton-Maclaren, T.S.; Gwinn, M.R.; Rasenberg, M.; Thomas, R.S. Accelerating the pace of chemical risk assessment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Chen, G.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Q. The situation of hazardous chemical accidents in China between 2000 and 2006. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qian, Y.; Hu, Q.M.; Jiang, R.; Li, M.; Wang, X. An analysis of hazardous chemical accidents in China between 2006 and 2017. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Woo, J.; Kang, C. Analysis of severe industrial accidents caused by hazardous chemicals in South Korea from January 2008 to June 2018. Saf. Sci. 2020, 124, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, K. Disaster governance: Social, political, and economic dimensions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Xiao, L.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, D.; Wang, J. A statistical analysis of hazardous chemical fatalities (HCFs) in China between 2015 and 2021. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B. Facts and lessons related to the explosion accident in Tianjin Port, China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Yan, M. Anatomy of Tianjin Port fire and explosion: Process and causes. Process Saf. Prog. 2016, 35, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, R. Public attitudes toward technological hazards after a technological disaster: Effects of the 2015 Tianjin Port explosion, Tianjin, China. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2019, 28, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaito, M.A.; Al-Hajj, S. A brief report on the Beirut port explosion. Mediterr. J. Emerg. Med. Acute Care 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, F.T.; Haidar, R.; Mansour, F.; Elbejjani, M.; El Khoury, J.; Khoury, B.; Ghandour, L.A. Anxiety, depression and PTSD in children and adolescents following the Beirut port explosion. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 302, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, C.K.; Nastacă, C.C. The Beirut port explosion: Social, urban and economic impact. Theor. Empir. Res. Urban Manag. 2021, 16, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Tao, G. Smart chemical industry parks in China: Current status, challenges, and pathways for future sustainable development. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2023, 83, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.I.; Fumei, S.; Song, B.A.I. Study on emergency disposal process and mechanism for hazardous chemicals storage areas. China Saf. Sci. J. 2020, 30, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Kapucu, N. Disaster and emergency management systems in urban areas. Cities 2012, 29, S41–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccaro, G.; Leone, M.F.; Martucci, C. Future research and innovation priorities in the field of natural hazards, disaster risk reduction, disaster risk management and climate change adaptation: A shared vision from the ESPREssO project. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 51, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.; Liu, C.; Thomas, P.; Chen, W.H. Unmanned aerial vehicle-based hazardous materials response: Information-theoretic hazardous source search and reconstruction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2019, 27, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. A systematic review of prediction methods for emergency management. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 62, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Gai, W.M.; Cheng, W.Y.; Deng, Y.F. Hazardous chemical leakage accidents and emergency evacuation response from 2009 to 2018 in China: A review. Saf. Sci. 2021, 135, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, R.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H. Multi-hazard disaster scenario method and emergency management for urban resilience by integrating experiment–simulation–field data. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 2021, 2, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiqi, W.; Yanmei, Z.; Shouyi, S.; Guoqiang, X. Design of mine safety dynamic diagnosis system based on cloud computing and internet of things technology. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 5837–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erd, M.; Schaeffer, F.; Kostic, M.; Reindl, L.M. Event monitoring in emergency scenarios using energy efficient wireless sensor nodes for the disaster information management. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2016, 16, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Choi, S.D. Emergency evacuation plan for hazardous chemicals leakage accidents using GIS-based risk analysis techniques in South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Optimization of emergency supplies scheduling for hazardous chemicals storage considering risk. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Ma, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T. Scenario deduction on fire accidents for oil–gas storage and transportation based on case statistics and a dynamic bayesian network. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2020, 24, 04020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, N.; Bose, I. Exploring the role of deep neural networks for post-disaster decision support. Decis. Support Syst. 2020, 130, 113234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; Chang, Y.Y. Organizational Innovation of Functional Orientation Mechanism for Cross-Regional Governance: Case Study of The Regional Emergency Operation Centers (REOS) in TATIWAN. Available online: https://www.ijoi-online.org/attachments/article/55/FINAL%20ISSUE%20VOL%2010%20NUM%203%20JANUARY%202018%20SECTION%20A.pdf#page=28. (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Dhall, S.; Mehta, B.R.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sood, K. A review on environmental gas sensors: Materials and technologies. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzolla, A.; Spadavecchia, M. Wireless sensor networks for environmental monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte-Luis, J.; Gómez-Galán, J.A.; Gómez-Bravo, F.; Sánchez-Raya, M.; Alcina-Espigado, J.; Teixido-Rovira, P.M. An efficient wireless sensor network for industrial monitoring and control. Sensors 2018, 18, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Chakraborty, D.; Law, A. Artificial intelligence in Internet of things. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2018, 3, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P.; Mukherjee, M.; Shu, L. Internet of things for disaster management: State-of-the-art and prospects. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18818–18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Kumar, P.; Rana, N.P.; Islam, R.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Impact of internet of things (IoT) in disaster management: A task-technology fit perspective. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 283, 759–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Seker, D.Z.; Hameed, S.; Draheim, D. The rising role of big data analytics and IoT in disaster management: Recent advances, taxonomy and prospects. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54595–54614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial internet of things: Challenges, opportunities, and directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Yu, F.R.; Deng, G.; Luo, C.; Ming, Z.; Yan, Q. Industrial internet: A survey on the enabling technologies, applications, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 1504–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.K.; Sharma, R.; Singh, R.; Gehlot, A.; Satapathy, S.C.; Alnumay, W.S.; Pelusi, D.; Ghosh, U.; Nayak, J. Industrial Internet of Things and its applications in industry 4.0: State of the art. Comput. Commun. 2021, 166, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, M.A.; Tan, T.K. Artificial intelligence and sustainable development. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2020, 18, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Han, F.; Liu, H. Challenges of big data analysis. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamola, V.; Hassija, V.; Gupta, S.; Goyal, A.; Guizani, M.; Sikdar, B. Disaster and pandemic management using machine learning: A survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 16047–16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batty, M. Digital twins. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yin, S.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Kaynak, O. Industrial applications of digital twins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20200360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramu, S.P.; Boopalan, P.; Pham, Q.V.; Maddikunta, P.K.; Huynh-The, T.; Alazab, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Gadekallu, T.R. Federated learning enabled digital twins for smart cities: Concepts, recent advances, and future directions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Qi, Q. Make more digital twins. Nature 2019, 573, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahat, E.; Hyun C, T.; Yeom, C. City digital twin potentials: A review and research agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Z.; Hanqiang, D.; Jialong, G.; Jian, H. Dynamic Target Assignment of Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Based on Clustering of Network Nodes. J. Syst. Simul. 2023, 35, 695. [Google Scholar]
- Arkin, W.M. Unmanned: Drones, Data, and the Illusion of Perfect Warfare; Hachette: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Li, X. Precise point positioning with the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sensors 2014, 14, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, J.; Cao, H.; Shi, J. Broadband LEO satellite communications: Architectures and key technologies. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, Y. Study on artificial intelligence: The state of the art and future prospects. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021, 23, 100224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Mehmood, R.; Corchado, J.M. Green artificial intelligence: Towards an efficient, sustainable and equitable technology for smart cities and futures. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.K.; Sulaiman, N.; Chan, S.W.; Nazir, U.; Abid, M.; Han, H.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Vega-Muñoz, A. Toward an integrated disaster management approach: How artificial intelligence can boost disaster management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, W.; Bai, R.; Chen, A. Application of computational intelligence technologies in emergency management: A literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 2131–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Tran Tuan, V.; Quoc Tran, D.; Park, M.; Park, S. Conceptual framework of an intelligent decision support system for smart city disaster management. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Christie, G.A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Freeman, J.D.; Hsu, E.B. Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in disasters and public health emergencies. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2022, 16, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian, S.; Rezaie Farhadabad, A.; Kerle, N. Post-disaster recovery monitoring with google earth engine. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian, S.; Roy, D.; Filatova, T.; Kerle, N. Agent-based modelling of post-disaster recovery with remote sensing data. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Loukatos, D.; Bartzanas, T.; Arvanitis, K.G. Applications of artificial intelligence in fire safety of agricultural structures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasan, M.; Muthu, B.; Sivaparthipan, C.B.; Sundarasekar, R.; Kadry, S.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Dasel, A.A. Detection of flood disaster system based on IoT, big data and convolutional deep neural network. Comput. Commun. 2020, 150, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lmalawi, A.; Alsolami, F.; Khan, A.I.; Alkhathlan, A.; Fahad, A.; Irshad, K.; Qaiyum, S.; Alfakeeh, A.S. An IoT based system for magnify air pollution monitoring and prognosis using hybrid artificial intelligence technique. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangra, A.; Sehgal V, K. Natural disasters management using social internet of things. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 34447–34461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. An IoT-Based Intelligent Geological Disaster Application Using Open-Source Software Framework. Sci. Program. 2022, 2022, 9285258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y.; Vijjapu, M.T.; Yuvaraja, S.; Surya, S.G.; Salama, K.N.; Dong, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gas sensing materials roadmap. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2021, 33, 303001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Sha, F. Accurate Concentration Measurement Model of Multicomponent Mixed Gases during a Mine Disaster Period. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 25443–25457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, X. Satellites Based Edge Computing Dynamic Warning Terminal for Hazardous Chemicals Storage and Transportation Safety. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 126, 104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Q. Using multi-robot active olfaction method to locate time-varying contaminant source in indoor environment. Build. Environ. 2017, 118, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Khan, S.; Palade, V.; Mehmood, I.; De Albuquerque, V.H. Edge intelligence-assisted smoke detection in foggy surveillance environments. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poslad, S.; Middleton, S.E.; Chaves, F.; Tao, R.; Necmioglu, O.; Bugel, U. A semantic IoT early warning system for natural environment crisis management. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2015, 3, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Awais, M.; Ali, K.; Aslam, N.; Paranthaman, V.V.; Imran, M.; Ali, F. Establishing effective communications in disaster affected areas and artificial intelligence based detection using social media platform. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 112, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, L.; D’Oro, S.; Bonati, L.; Cuomo, F.; Melodia, T. HIRO-NET: Heterogeneous intelligent robotic network for internet sharing in disaster scenarios. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 21, 4367–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydher, H.; Jayakody, D.N.K.; Hemachandra, K.T.; Samarasinghe, T. Intelligent UAV deployment for a disaster-resilient wireless network. Sensors 2020, 20, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Garg, S.; Wang, X.; Bradai, A.; Lin, H.; Hossain, M.S. Learning-based IoT data aggregation for disaster scenarios. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 128490–128497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M.; Lakshmanna, K.; Thippa, R.G.; Pham, Q.-V.; Maddikunta, P.K.R. Multi-objective cluster head selection using fitness averaged rider optimization algorithm for IoT networks in smart cities. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Xi, C. Application of Digital Twin in Handling and Transportation of Hazardous Chemicals. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Gupta, S.; Gupta S, K. Multi-hazard disaster studies: Monitoring, detection, recovery, and management, based on emerging technologies and optimal techniques. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 47, 101642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Tian, Y.; Wei, G. Deduction of sudden rainstorm scenarios: Integrating decision makers’ emotions, dynamic bayesian network and DS evidence theory. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 2935–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.; Reniers, G. An event-driven probabilistic methodology for modeling the spatial-temporal evolution of natural hazard-induced domino chain in chemical industrial parks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 226, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.D.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, D. Analysis on the disaster chain evolution from gas leak to explosion in urban utility tunnels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 140, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.; Chen, G.; Zeng, T. Multi-Hazard Coupling Effects in Chemical Process Industry—Part II: Research Advances and Future Perspectives on Methodologies. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 17, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Sun, N.; Cao, C.; Hou, S.; Gong, Y. Review on visualization technology in simulation training system for major natural disasters. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 1851–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; He, Z. Digital twin-driven intelligence disaster prevention and mitigation for infrastructure: Advances, challenges, and opportunities. Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yu, P.; Wan, C.; Wang, D.; Shi, W.; Shou, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Integrating virtual reality and building information modeling for improving highway tunnel emergency response training. Buildings 2022, 12, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, X. Multi-objective scheduling of priority-based rescue vehicles to extinguish forest fires using a multi-objective discrete gravitational search algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, G.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Baboli, A.; Najafi, M. A decision support model for robust allocation and routing of search and rescue resources after earthquake: A case study. Oper. Res. 2022, 22, 1039–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Reniers, G. Petri net simulation of multi-department emergency response to avert domino effects in chemical industry accidents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Reniers, G.; Khakzad, N. A dynamic multi-agent approach for modeling the evolution of multi-hazard accident scenarios in chemical plants. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 207, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiao, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, P. Data-driven AI emergency planning in process industry. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2022, 76, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Mesicek, L.; Bae, K.; Ko, H. AI advisor platform for disaster response based on big data. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2023, 35, e6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboualola, M.; Abualsaud, K.; Khattab, T.; Zorba, N.; Hassanein, H.S. Edge Technologies for Disaster Management: A Survey of Social Media and Artificial Intelligence Integration. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 73782–73802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. UrbanKG: An Urban Knowledge Graph System. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2023, 14, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, J.; Ren, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, J. A BN-based risk assessment model of natural gas pipelines integrating knowledge graph and DEMATEL. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 171, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Multi-source knowledge graph reasoning for ocean oil spill detection from satellite SAR images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.; Sen, S. A dynamic trust management model for vehicular ad hoc networks. Veh. Commun. 2023, 41, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yin, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Min, G.; Fan, Q. Three-dimensional geographic routing in wireless mobile ad hoc and sensor networks. IEEE Netw. 2016, 30, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Review of ZnO-based nanomaterials in gas sensors. Solid State Ion. 2021, 360, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, C.; Lei, M.; Gao, Q.; Nie, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Reduced graphene oxide-based highly sensitive pressure sensor for wearable electronics via an ordered structure and enhanced interlayer interaction mechanism. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2150–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, T.; Ge, Z. Recent Advances in the Development of Flexible Sensors: Mechanisms, Materials, Performance Optimization, and Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 6735–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shamsi M, H. Biosensors-on-chip: A topical review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Cassandras C, G. Distributed coverage control and data collection with mobile sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes, H.; Brand, O.; Waelti, M. Packaging of CMOS MEMS. Microelectron. Reliab. 2000, 40, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Sen, J. Internet of things: Applications and challenges in technology and standardization. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2011, 58, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J. Towards robust and stealthy communication for wireless intelligent terminals. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 11791–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Liang, T.; Zheng, J. Group key agreement protocol among terminals of the intelligent information system for mobile edge computing. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 10442–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.K.; Rashid, M.; Khan, A.; Manjul, M. Unmanned aerial vehicles integrated HetNet for smart dense urban area. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Gao, P.; Hua, X.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, T. Multi-UAV network assisted intelligent edge computing: Challenges and opportunities. China Commun. 2022, 19, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, K.G.; Das, S.; Sen, D.; Arif, W. Design and deployment of UAV-aided post-disaster emergency network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 102985–102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, Y.-P.; Zhang, S.-Q. Multiclass dynamic emergency traffic collaborative optimization considering multiple solutions with stage-based algorithm. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2022, 608, 128281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ueda, T. A review study on unmanned aerial vehicle and mobile robot technologies on damage inspection of reinforced concrete structures. Struct. Concr. 2023, 24, 536–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraereh, O.A.; Alsaraira, A.; Khan, I.; Uthansakul, P. Performance evaluation of UAV-enabled LoRa networks for disaster management applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W. Research on a mixed gas recognition and concentration detection algorithm based on a metal oxide semiconductor olfactory system sensor array. Sensors 2018, 18, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; An, Y.; Zhao, H.; Miao, X.; Liu, R.; Fortino, G. Multi-sensor information fusion based on machine learning for real applications in human activity recognition: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 2022, 80, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, W.; Azam, M.A.; Saadat, S.; Iqbal, F.; Hanan, A. Unmanned aerial vehicles enabled IoT platform for disaster management. Energies 2019, 12, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lei, Z.; Cao L E, I. Visual simulation method of runoff in landscape space based on UAV tilt photography. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 249, 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X. Regional Geological Disasters Emergency Management System Monitored by Big Data Platform. Processes 2022, 10, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, K.; Touseau, L.; Donsez, D. Combining heterogeneous service technologies for building an Internet of Things middleware. Comput. Commun. 2012, 35, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirre, A.; Parra, J.; Armentia, A.; Estévez, E.; Marcos, M. QoS aware middleware support for dynamically reconfigurable component based IoT applications. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2016, 12, 2702789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Batty, M.; Goodchild, M.F. Real-time GIS for smart cities. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.N.; Wolf, C.M. Smart cities with digital twin systems for disaster management. J. Manag. Eng. 2020, 36, 04020027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, C.; Yahja, A.; Mostafavi, A. Disaster city digital twin: A vision for integrating artificial and human intelligence for disaster management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Roy, S.; DasBit, S. A post-disaster demand forecasting system using principal component regression analysis and case-based reasoning over smartphone-based DTN. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2018, 66, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiophuead, T.; Kunsuwan, N. Logistic regression analysis of factors affecting travel mode choice for disaster evacuation. Eng. J. 2019, 23, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Li, L.; Guo, W. Cascading disasters risk modeling based on linear uncertainty distribution. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 43, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Blockchain: A potential technology to improve the performance of collaborative emergency management with multi-agent participation. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 72, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, Z.; Pei, Z.; Liu, D. Emergency relief chain for natural disaster response based on government-enterprise coordination. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, M.; Meng, Y.; Qin, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, D. Coupling evolution effect between security system vulnerability and security incident in petrochemical plants. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2022, 75, 104682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Q.; Qian, X.; Li, M.; Shi, T. Cause analysis and damage mechanism of explosive destruction with case investigation involving LPG tank trailer. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 133, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, W.; Wang, S.; Qi, W.; Li, X.; Wang, C. Disaster chain analysis of landfill landslide: Scenario simulation and chain-cutting modeling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J. Disaster chain scenarios evolutionary analysis and simulation based on fuzzy petri net: A marine oil spill disaster case study. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 183010–183023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Qin, Y. A simulation method for the dynamic evolution of domino accidents in chemical industrial parks. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 168, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Z.; Rong, L. A scenario modelling method for regional cascading disaster risk to support emergency decision making. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 77, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, X.; Suo, W. Construction of risk response scenarios for the emergency material support system. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 221, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzali, N.; Lavasani, M.R.M.; Ghodousi, J. Safety barriers analysis of offshore drilling system by employing Fuzzy Event Tree Analysis. Saf. Sci. 2015, 78, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liang, J.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z. Scenario-driven methodology for cascading disasters risk assessment of earthquake on chemical industrial park. Processes 2022, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, B.K.; Arshad, F.M.; Noh, K.M. System dynamics. Model. Simul. 2017, 274. Available online: https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-981-10-2045-2 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- He, S.; Song, D.; Mitri, H.; He, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Chen, T. Integrated rockburst early warning model based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 142, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, Y.; Story, B.A. Competitive probabilistic neural network. Integr. Comput. Aided Eng. 2017, 24, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. ParaViewWeb architecture method of power security emergency drill platform based on VR technology. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Va, H.; Choi M, H.; Hong, M. Real-time surface-based colume constraints on mass-spring model in Unity3D. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 17857–17869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Sotiriadis, S.; Asimakopoulou, E.; Li, M.; Bessis, N. CLOTHO: A large-scale Internet of Things-based crowd evacuation planning system for disaster management. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 3559–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Gai, Y.; Wang, H. Allocation of Resources for Emergency Response to Coal-to-Oil Hazardous Chemical Accidents under Railway Transportation Mode. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Gai, W.; Xu, K. Bi-objective rescue path selection optimization for mine fires based on quantitative risk assessment. Saf. Sci. 2022, 146, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liang, X.; Zhou, L.; Men, J. A dynamic risk-based routing approach for multi-source and multi-sink evacuation problem in chemical industrial parks. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2022, 77, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekihara, K.; Haneishi, H.; Ohyama, N. Details of simulated annealing algorithm to estimate parameters of multiple current dipoles using biomagnetic data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1992, 11, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, C. Building an improved artificial neural network model based on deeply optimizing the input variables to enhance rutting prediction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A. Study on the decision-making behavior of evacuation for coastal residents under typhoon storm surge disaster. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 45, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.A.; Maitland, C.F.; Tapia, A.H. Collaborative systems development in disaster relief: The impact of multi-level governance. Inf. Syst. Front. 2010, 12, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, J.; Zhou, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, B. Intelligent-Technology-Empowered Active Emergency Command Strategy for Urban Hazardous Chemical Disaster Management. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914369
Lyu J, Zhou S, Liu J, Jiang B. Intelligent-Technology-Empowered Active Emergency Command Strategy for Urban Hazardous Chemical Disaster Management. Sustainability. 2023; 15(19):14369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Jieyin, Shouqin Zhou, Jingang Liu, and Bingchun Jiang. 2023. "Intelligent-Technology-Empowered Active Emergency Command Strategy for Urban Hazardous Chemical Disaster Management" Sustainability 15, no. 19: 14369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914369
APA StyleLyu, J., Zhou, S., Liu, J., & Jiang, B. (2023). Intelligent-Technology-Empowered Active Emergency Command Strategy for Urban Hazardous Chemical Disaster Management. Sustainability, 15(19), 14369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914369







