Life Cycle Assessment Research Trends and Implications: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
1.1. Life Cycle Assessment
1.2. Research Gap
1.3. Research Objective
- Research Performance and Progression: Investigate the patterns and shifts in LCA research publications across the years to analyse the performance and progression of research activities.
- Research Trends and Hotspots: Identify major topic clusters within LCA research through a combination of techniques, such as topic clusters prominence indicator, visualisation, knowledge map analysis, and content analysis.
- Database Assessment: Quantitatively assess the factors contributing to disparities in LCA publication counts between Scopus and Web of Science, providing practical recommendations for future LCA bibliometric studies.
1.4. Bibliometric Analysis
2. Materials and Methods
- Research trends
2.1. Database Selection
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Software Tool
3. Results
3.1. Database Assessment
Recommendations
3.2. Data Analysis and Interpretation
3.2.1. Characteristics of Publications
3.2.2. Evolution of Scientific Production
3.2.3. The Most Cited and Prolific Authors
3.2.4. The Most Productive Countries/Territories
3.2.5. The More Productive Institutions and Departments
3.2.6. Knowledge Diffusion and Cooperation Network
3.2.7. Funding Agencies
3.2.8. The Most Researched Areas
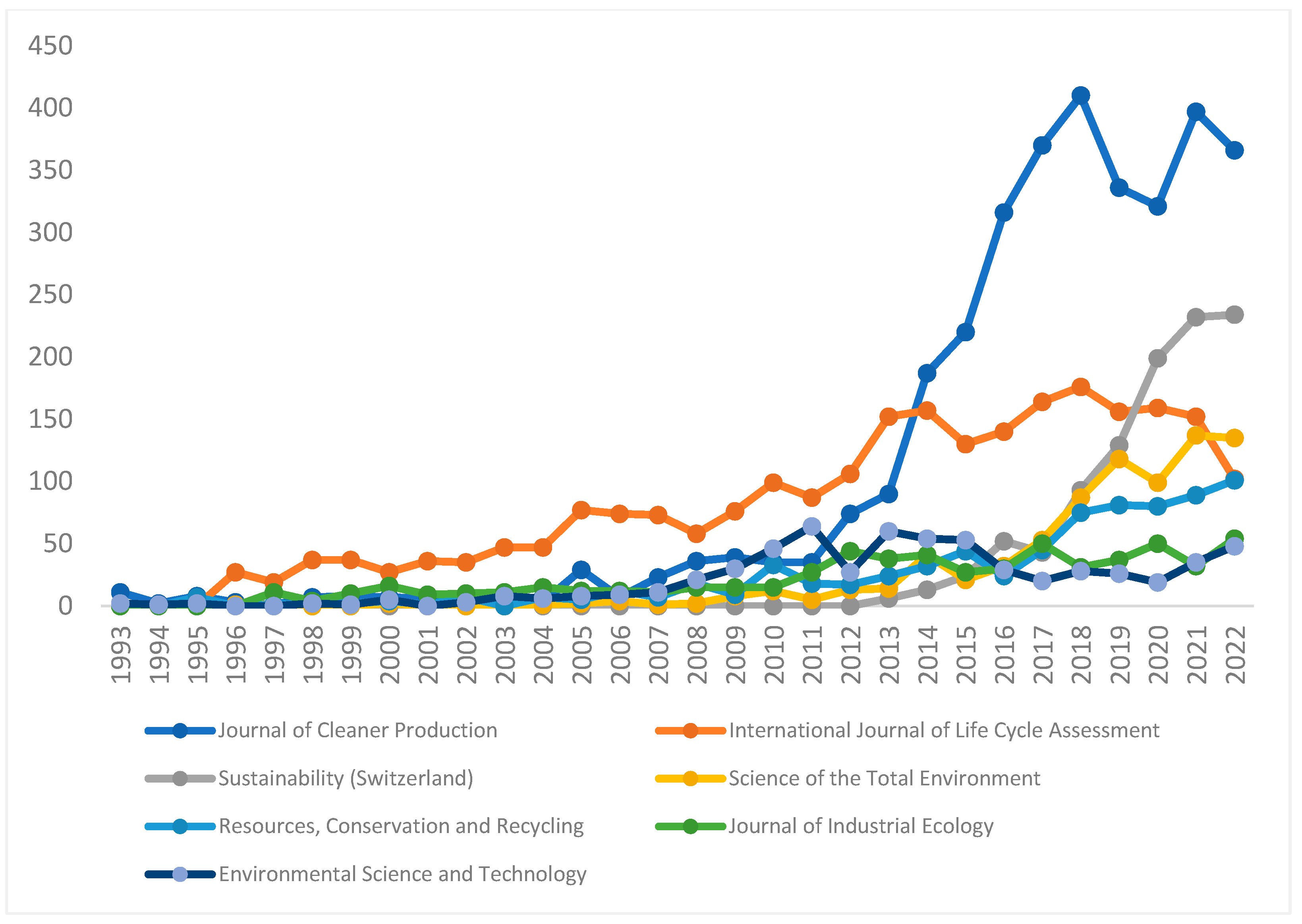
3.2.9. Analysis by Journals Source
3.2.10. Top Cited Articles
3.2.11. The Progression of Research Topics and Hotspots in the Field of LCA
- Keywords co-occurrence analysis
- Period 1992–1997
- Period 1998–2005
- Period 2006–2010
- Period 2011–2015
- Period 2016–2019
3.3. LCA Future Trends: Period 2020—Ongoing
- Cluster 1: LCA methodology
- Cluster 1: Sustainable development and Sustainability
- Cluster 1: Circular economy
- Cluster 2: Agriculture
- Cluster 3: Energy and carbon emissions
- Cluster 4: Waste Management
- Cluster 5: Sustainable Materials and circular economy
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- a.
- Research Trends and Hotspots
- b.
- Research Strength
- Quality Concerns and Collaboration
- Global Engagement and Dynamic Journal Landscape
- c.
- Database Assessment
- d.
- Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO 14044:2006+A2:2020; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. BSI Standards Limited: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Curran, M.A. Broad-based environmental life cycle assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, M.A. EPA’s Life Cycle Methodology: Guidelines for Use in Development of Packaging; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, R.G.; Franklin, W.E. LCA—How it Came about—Personal Reflections on the Origin and the Development of LCA in the USA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 1996, 1, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.G.; Sellers, J.D.; Franklin, W.E. Resource and environmental profile analysis: A life cycle environmental assessment for products and procedures. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 1992, 12, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J.; Heijungs, R.; Huppes, G.; Zamagni, A.; Masoni, P.; Buonamici, R.; Ekvall, T.; Rydberg, T. Life Cycle Assessment: Past, Present, and Future †. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boustead, I. Resource implications with particular reference to energy requirements for glass and plastic milk bottles. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1974, 27, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.G.; James, R.O.W.; Cross, A.; Woodall, A.E. Resource and Environmental Profile Analysis of Nine Beverage Container Alternatives; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Udo de Haes, H.A. Applications of life cycle assessment: Expectations, drawbacks and perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 1993, 1, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.B.; Vanderburg, W.H. Applying environmental life-cycle analysis to materials. JOM 1994, 46, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryshlakivsky, J.; Searcy, C. Fifteen years of ISO 14040: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 57, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedkoop, M.; Spriensma, R. The Eco-Indicator 99: A Damage Oriented Method for Life Cycle Impact Assessment, Methodology Report, 3rd Edition; PRé Consultants, Amersfoort, Netherlands. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/247848113_The_Eco-Indicator_99_A_Damage_Oriented_Method_for_Life_Cycle_Impact_Assessment (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Guinee, J.B. Handbook on life cycle assessment operational guide to the ISO standards. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2002, 7, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliet, O.; Margni, M.; Charles, R.; Humbert, S.; Payet, J.; Rebitzer, G.; Rosenbaum, R. IMPACT 2002+: A new life cycle impact assessment methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2003, 8, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekvall, T.; Finnveden, G. Allocation in ISO 14041—A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2001, 9, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Hauschild, M.; Ekvall, T.; Guinée, J.; Heijungs, R.; Hellweg, S.; Koehler, A.; Pennington, D.; Suh, S. Recent developments in Life Cycle Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levasseur, A.; Lesage, P.; Margni, M.; Deschênes, L.; Samson, R. Considering Time in LCA: Dynamic LCA and Its Application to Global Warming Impact Assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3169–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potting, J.; Hauschild, M.Z. Background for Spatial Differentiation in Life Cycle Impact Assessment. The EDIP2003 Methodology; DTU Library: Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of rare earths: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, Y.; Levy, J.I.; Norris, G.A.; Wilson, A.; Hofstetter, P.; Spengler, J.D. Integrating risk assessment and life cycle assessment: A case study of insulation. Risk Anal. 2002, 22, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, C.; Horvath, A.; Joshi, S.; Lave, L. Economic input-output models for environmental life-cycle assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 184A–191A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, L.; Hendrickson, C.; Matthews, H.S. Economic input-output life-cycle assessment of U.S. residential buildings. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2002, 8, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, M. A guide for compiling inventories in hybrid life-cycle assessments: Some Australian results. J. Clean. Prod. 2002, 10, 545–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Guidance for Data Quality Assessment; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- May, J.R.; Brennan, D.J. Application of data quality assessment methods to an LCA of electricity generation. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2003, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutik, B.; Graham-Jones, J.; Pemberton, R.; Summerscales, J. Quality assessment of life cycle inventory data for composites. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM23), Belfast, Northern Ireland, 30 July–4 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Klöpffer, W. Life-cycle based methods for sustainable product development. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2003, 8, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluch, P.; Baumann, H. The life cycle costing (LCC) approach: A conceptual discussion of its usefulness for environmental decision-making. Build. Environ. 2004, 39, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunkeler, D. Societal LCA methodology and case study. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2006, 11, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöpffer, W. The role of SETAC in the development of LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2006, 11, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoroghi, A.; Rezgui, Y.; Petri, I.; Beach, T. Advances in application of machine learning to life cycle assessment: A literature review. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2022, 27, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elouariaghli, F.N.; Kozderka, S.M.; Quaranta, T.G.; Pena, F.D.; Rose, F.B.; Hoarau, S.Y. Eco-design and Life Cycle Management: Consequential Life Cycle Assessment, Artificial Intelligence and Green IT. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, J.G.; Pamela Del, R.; Petrosa, D.; Traverso, M.; Hatzfeld, T.; Günther, E. Building Sector Issues in about 100 Years: End-Of-Life Scenarios of Carbon-Reinforced Concrete Presented in the Context of a Life Cycle Assessment, Focusing the Carbon Footprint. Processes 2022, 10, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweg, S.; Canals, L.M.I. Emerging approaches, challenges and opportunities in life cycle assessment. Science 2014, 344, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.K. Systematic reviews: Brief overview of methods, limitations, and resources. Nurse Author Ed. 2021, 31, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenluecke, M.K.; Marrone, M.; Singh, A.K. Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Aust. J. Manag. 2019, 45, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.G.; Barbastefano, R.G. Knowledge diffusion and collaboration networks on life cycle assessment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2011, 16, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørn, A.; Owsianiak, M.; Laurent, A.; Molin, C.; Westh, T.B.; Hauschild, M.Z. Mapping and characterization of LCA networks. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2013, 18, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, J. A bibliometric investigation of life cycle assessment research in the web of science databases. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G. Scientometric sorting by importance for literatures on life cycle assessments and some related methodological discussions. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Mao, G.; Zhao, L.; Du, H.; Zuo, J. Mapping the scientific research on life cycle assessment: A bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yu, D. Research trends in life cycle assessment research: A 20-year bibliometric analysis (1999–2018). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2020, 85, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezama, A.; Mittelstädt, N.; Thrän, D.; Balkau, F. Trends and Challenges in Regional Life Cycle Management: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, G.; Bihari Singh, A.; Mistry, S.; Gupta, S.; Dangayach, G.S.; Meena, M.L. Recent progress of scientific research on life cycle assessment. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, S. I publish, therefore I am. Or am I? A reply to A bibliometric investigation of life cycle assessment research in the web of science databases by Chen et al. (2014) and Mapping the scientific research on life cycle assessment: A bibliometric analysis by Hou et al. (2015). Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 1601–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, A. Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics? J. Doc. 1969, 25, 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, D.T. Bibliometrics of the online information retrieval literature. Online Rev. 1978, 2, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żarczyńska, A. Nicola De Bellis: Bibliometrics And Citation Analysis, from the Science Citation Index to Cybermetrics, Lanham, Toronto, Plymouth 2009. Toruńskie Stud. Bibliol. 2012, 5, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadus, R.N. Toward a definition of “bibliometrics”. Scientometrics 1987, 12, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Rodríguez, A.-R.; Ruíz-Navarro, J. Changes in the intellectual structure of strategic management research: A bibliometric study of the Strategic Management Journal, 1980–2000. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 981–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bakker, F.G.A.; Groenewegen, P.; Den Hond, F. A bibliometric analysis of 30 years of research and theory on corporate social responsibility and corporate social performance. Bus. Soc. 2005, 44, 283–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.C.; Glynn, R.W.; O’Briain, D.E.; Felle, P.; McCabe, J.P. The 100 classic papers of orthopaedic surgery: A bibliometric analysis. J. Bone Jt. Surg.-Ser. B 2010, 92, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Tang, M.; Luo, L.; Li, C.; Chiclana, F.; Zeng, X.J. A bibliometric analysis and visualization of medical big data research. Sustainability 2018, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Z.; Wang, M.H.; Ho, Y.S. Mapping of drinking water research: A bibliometric analysis of research output during 1992–2011. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Hong, S. Global biodiversity research during 1900–2009: A bibliometric analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhuri, P.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Abraham, A. Industry 4.0: A bibliometric analysis and detailed overview. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 78, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancino, C.; Merigó, J.M.; Coronado, F.; Dessouky, Y.; Dessouky, M. Forty years of Computers & Industrial Engineering: A bibliometric analysis. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 113, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Munoz, J.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Espejo, A.; Cobo, M. Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. El Prof. De La Inf. 2020, 29, e290103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.d.S. Networks of Scientific Papers. Science 1965, 149, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazov, N.A.; Gureev, V.N.; Glinskikh, V.N. The Methodological Basis of Defining Research Trends and Fronts. Sci. Tech. Inf. Process. 2020, 47, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnine, M.; Tishchenko, A.; Kochiev, L. Visualization of Research Trending Topic Prediction: Intelligent Method for Data Analysis. In Proceedings of the 31th International Conference on Computer Graphics and Vision, Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, 27–30 September 2021; pp. 1028–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Klavans, R.; Boyack, K.W. Research portfolio analysis and topic prominence. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Bote, V.P.; Chinchilla-Rodríguez, Z.; Mendoza, A.; de Moya-Anegón, F. Comparative Analysis of the Bibliographic Data Sources Dimensions and Scopus: An Approach at the Country and Institutional Levels. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2021, 5, 593494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A tale of two databases: The use of Web of Science and Scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotten, M.; el Aisati, M.; Meester, W.; Steiginga, S.; Ross, C. A Brief History of Scopus: The World’s Largest Abstract and Citation Database of Scientific Literature. In Research Analytics; Auerbach Publications: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 31–58. [Google Scholar]
- Toom, K. Chapter 10—Indicators. In Research Management; Andersen, J., Toom, K., Poli, S., Miller, P.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F. Retrieval strategy and possible explanations for the abnormal growth of research publications: Re-evaluating a bibliometric analysis of climate change. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W. Caveats for the use of Web of Science Core Collection in old literature retrieval and historical bibliometric analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2021, 172, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei Chadegani, A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ale Ebrahim, N. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, R.G.; Franklin, W.E. Resource and environmental profile analysis of beer containers. Chemtech 1975, 5, 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Summerscales, J.; Dissanayake, N. Allocation in the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Flax Fibres for the Reinforcement of Composites. In Advances in Natural Fibre Composites: Raw Materials, Processing and Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 223–235. [Google Scholar]
- Gue, I.H.V.; Ubando, A.T.; Cuello, J.L.; Culaba, A.B. Assessing microalgal biodiesel sustainability via MCI and LCA frameworks. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment and Management (HNICEM), Baguio City, Philippines, 29 November–2 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ruben, R.B.; Menon, P.; Sreedharan, R. Development of a Social Life Cycle Assessment framework for manufacturing organizations. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Production and Operations Management Society (POMS 2018), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 14–16 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gear, M.; Sadhukhan, J.; Thorpe, R.; Clift, R.; Seville, J.; Keast, M. A life cycle assessment data analysis toolkit for the design of novel processes—A case study for a thermal cracking process for mixed plastic waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricase, C.; Lamonaca, E.; Ingrao, C.; Bacenetti, J.; Lo Giudice, A. A comparative Life Cycle Assessment between organic and conventional barley cultivation for sustainable agriculture pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3747–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Baceta, M.-A.; Thelwall, M.; Kousha, K. Web of Science and Scopus language coverage. Scientometrics 2019, 121, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Freeman, R. Bigger Than You Thought: China’s Contribution to Scientific Publications and Its Impact on the Global Economy. China World Econ. 2019, 27, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. The changing role of non-English papers in scholarly communication: Evidence from Web of Science’s three journal citation indexes. Learn. Publ. 2016, 30, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelwall, M.; Sud, P. Scopus 1900–2020: Growth in articles, abstracts, countries, fields, and journals. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2022, 3, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. A matter of time: Publication dates in Web of Science Core Collection. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, M.; Goutaudier, V.; Louis, K.; Al-Awadhi, S.; Dubourg, Q.; Truchot, A.; Brousse, R.; Saleh, N.; Giarraputo, A.; Debiais, C.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on publication dynamics and non-COVID-19 research production. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv-Reuven, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Publication patterns’ changes due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A longitudinal and short-term scientometric analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 6761–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Comparing like with like: China ranks first in SCI-indexed research articles since 2018. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, W.; Liu, K. Performance of China’s journals indexed in SCIE: An evaluation based on megajournal metrics. Learn. Publ. 2021, 34, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Blazun Vosner, H. Discrepancies among Scopus, Web of Science, and PubMed coverage of funding information in medical journal articles. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2018, 106, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W. Accuracy of funding information in Scopus: A comparative case study. Scientometrics 2020, 124, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Rincón, L.; Vilariño, V.; Pérez, G.; Castell, A. Life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle energy analysis (LCEA) of buildings and the building sector: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 394–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T.; Prakash, R.; Shukla, K.K. Life cycle energy analysis of buildings: An overview. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernet, G.; Bauer, C.; Steubing, B.; Reinhard, J.; Moreno-Ruiz, E.; Weidema, B. The ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): Overview and methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, D.W.; Potting, J.; Finnveden, G.; Lindeijer, E.; Jolliet, O.; Rydberg, T.; Rebitzer, G. Life cycle assessment Part 2: Current impact assessment practice. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, F.; Guest, G.; Strømman, A.H. Bioenergy from forestry and changes in atmospheric CO2: Reconciling single stand and landscape level approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuer, C.; Keoleian, G.A.; Reppe, P. Life cycle energy and environmental performance of a new university building: Modeling challenges and design implications. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.K.; Dean, A.P.; Osundeko, O. The potential of sustainable algal biofuel production using wastewater resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardon, L.; Hélias, A.; Sialve, B.; Steyer, J.-P.; Bernard, O. Life-Cycle Assessment of Biodiesel Production from Microalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Nei, D.; Orikasa, T.; Xu, Q.; Okadome, H.; Nakamura, N.; Shiina, T. A review of life cycle assessment (LCA) on some food products. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuček, L.; Klemeš, J.J.; Kravanja, Z. A Review of Footprint analysis tools for monitoring impacts on sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.V.; Drzal, L.T.; Mohanty, A.K.; Arora, S. Are natural fiber composites environmentally superior to glass fiber reinforced composites? Composites. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2004, 35, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntzinger, D.N.; Eatmon, T.D. A life-cycle assessment of Portland cement manufacturing: Comparing the traditional process with alternative technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebitzer, G.; Ekvall, T.; Frischknecht, R.; Hunkeler, D.; Norris, G.; Rydberg, T.; Schmidt, W.P.; Suh, S.; Weidema, B.P.; Pennington, D.W. Life cycle assessment Part 1: Framework, goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, and applications. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, N.C.; Nowack, B. Exposure modeling of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4447–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C.K. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, M.E.; Kuiken, T.; Vejerano, E.P.; McGinnis, S.P.; Hochella, M.F., Jr.; Hull, D.R. Nanotechnology in the real world: Redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, E.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wu, F. Sustainable Recycling Technology for Li-Ion Batteries and Beyond: Challenges and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7020–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Okonkwo, E.G.; Huang, G.; Xu, S.; Sun, W.; He, Y. On the sustainability of lithium ion battery industry—A review and perspective. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 36, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkareem, M.A.; Elsaid, K.; Wilberforce, T.; Kamil, M.; Sayed, E.T.; Olabi, A. Environmental aspects of fuel cells: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareiß, K.; de la Rua, C.; Möckl, M.; Hamacher, T. Life cycle assessment of hydrogen from proton exchange membrane water electrolysis in future energy systems. Appl. Energy 2019, 237, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Mehta, N.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Al-Hinai, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Rooney, D.W. Conversion of biomass to biofuels and life cycle assessment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4075–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, H.K.; Chilvers, A.; Azapagic, A. Environmental sustainability of biofuels: A review: Environmental sustainability of biofuels. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 476, 20200351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.; Dubey, B.K. A critical review on operating parameters and strategies to improve the biogas yield from anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Schmid, A.; Tarpani, R.R.Z. Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment in developing countries: A review. Water Res. 2019, 153, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, M.; Saade, M.R.M.; Balouktsi, M.; Rasmussen, F.N.; Birgisdottir, H.; Frischknecht, R.; Habert, G.; Lützkendorf, T.; Passer, A. Embodied GHG emissions of buildings—The hidden challenge for effective climate change mitigation. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zuo, J.; Wu, G.; Huang, C. A bibliometric review of green building research 2000–2016. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2019, 62, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, R.; Choudhary, K.; Srivastava, A.; Sangwan, K.S.; Singh, M. Environmental impact assessment of fly ash and silica fume based geopolymer concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Moreno, F.M.; Rodríguez-Galán, M.; Vega, F.; Alonso-Fariñas, B.; Vilches Arenas, L.F.; Navarrete, B. Carbon capture and utilization technologies: A literature review and recent advances. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 1403–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, S.; Bardow, A. Life-cycle assessment of an industrial direct air capture process based on temperature–vacuum swing adsorption. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. A review of natural fiber composites: Properties, modification and processing techniques, characterization, applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 829–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Deepa, C.; Kumar, L.R.; Sanjay, M.R.; Siengchin, S. Life-cycle and environmental impact assessments on processing of plant fibres and its bio-composites: A critical review. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 5518S–5542S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040:2006/Amd 1:2020; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework—Amendment 1. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- European Commission-Joint Research Centre-Institute for Environment and Sustainability. International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD) Handbook: General Guide for Life Cycle Assessment: Detailed Guidance; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Igos, E.; Benetto, E.; Meyer, R.; Baustert, P.; Othoniel, B. How to treat uncertainties in life cycle assessment studies? Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijungs, R. On the number of Monte Carlo runs in comparative probabilistic LCA. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Li, J.; Bai, Y. Uncertainty analysis in the life cycle assessment of cassava ethanol in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamber, N.; Turner, I.; Arulnathan, V.; Li, Y.; Zargar Ershadi, S.; Smart, A.; Pelletier, N. Comparing sources and analysis of uncertainty in consequential and attributional life cycle assessment: Review of current practice and recommendations. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2020, 25, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D.; Siegel, L.; Rooney-Varga, J.N. Does replacing coal with wood lower CO2 emissions? Dynamic lifecycle analysis of wood bioenergy. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaco, R.; Butnar, I.; Margallo, M.; Laso, J.; Rumayor, M.; Dominguez-Ramos, A.; Irabien, A.; Dodds, P.E. Bringing value to the chemical industry from capture, storage and use of CO2: A dynamic LCA of formic acid production. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.M.; Volpi, L.; Settembre-Blundo, D.; García-Muiña, F.E. Dynamic life cycle assessment (LCA) integrating life cycle inventory (LCI) and Enterprise resource planning (ERP) in an industry 4.0 environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, J.; Oliveira-Esquerre, K.; Medeiros, D. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Life Cycle Assessment Methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1196, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligozat, A.-L.; Lefevre, J.; Bugeau, A.; Combaz, J. Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Impacts of AI Solutions for Environment Life Cycle Assessment of AI Solutions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köck, B.; Friedl, A.; Serna Loaiza, S.; Wukovits, W.; Mihalyi-Schneider, B. Automation of Life Cycle Assessment—A Critical Review of Developments in the Field of Life Cycle Inventory Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Fan, E.; Xue, Q.; Bian, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, R. Toward sustainable and systematic recycling of spent rechargeable batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7239–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenpour, S.F.; Hennige, S.; Willoughby, N.; Adeloye, A.; Gutierrez, T. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kumar, P.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Solid waste management: Scope and the challenge of sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 658–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, A.; Eyckmans, J.; Van Acker, K. Downcycling versus recycling of construction and demolition waste: Combining LCA and LCC to support sustainable policy making. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Koelewijn, S.F.; van den Bossche, G.; van Aelst, J.; van den Bosch, S.; Renders, T.; Navare, K.; Nicolaï, T.; van Aelst, K.; Maesen, M.; et al. A sustainable wood biorefinery for low-carbon footprint chemicals production. Science 2020, 367, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Lin, B.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chu, Y.S.; Ubando, A.T.; Show, P.L.; Ong, H.C.; Chang, J.S.; Ho, S.H.; Culaba, A.B.; et al. Progress in biomass torrefaction: Principles, applications and challenges. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 82, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierling, S.; Knüpffer, E.; Behnsen, H.; Mudersbach, M.; Krieg, H.; Springer, S.; Albrecht, S.; Herrmann, C.; Endres, H.J. Bio-based plastics—A review of environmental, social and economic impact assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, J.G.; Traverso, M. Life cycle sustainability assessment as a metrics towards SDGs agenda 2030. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 38, 100683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado, H.A.; Velásquez, E.I.G.; Monteiro, S.N. Sustainability of additive manufacturing: The circular economy of materials and environmental perspectives. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 8221–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Quinteiro, P.; Dias, A.C. A systematic review of life cycle sustainability assessment: Current state, methodological challenges, and implementation issues. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.I.; Falcone, G.; Stillitano, T.; Iofrida, N.; Strano, A.; Gulisano, G. Evaluation of sustainable innovations in olive growing systems: A Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment case study in southern Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, C.; Civit, B.; Gallego-Schmid, A.; Druckman, A.; Caldeira-Pires, A.; Weidema, B.; Mieras, E.; Wang, F.; Fava, J.; Canals, L.M.; et al. Using life cycle assessment to achieve a circular economy. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2021, 26, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niero, M.; Jensen, C.L.; Fratini, C.F.; Dorland, J.; Jørgensen, M.S.; Georg, S. Is life cycle assessment enough to address unintended side effects from Circular Economy initiatives? J. Ind. Ecol. 2021, 25, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Stijn, A.; Malabi Eberhardt, L.C.; Wouterszoon Jansen, B.; Meijer, A. A Circular Economy Life Cycle Assessment (CE-LCA) model for building components. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Li, L.; Yang, W.; Bian, Y.; Li, C.Q. An analytical review on application of life cycle assessment in circular economy for built environment. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, T.; Leino, R.; Heinonen, J.; Saari, A. Developing Buildings’ Life Cycle Assessment in Circular Economy-Comparing methods for assessing carbon footprint of reusable components. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Osman, A.I.; Murphin Kumar, P.S.; Jamil, F.; Al-Haj, L.; Al Nabhani, A.; Kyaw, H.H.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Mehta, N.; Rooney, D.W. Circular economy approach of enhanced bifunctional catalytic system of CaO/CeO2 for biodiesel production from waste loquat seed oil with life cycle assessment study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, J.; Ye, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Review of waste biorefinery development towards a circular economy: From the perspective of a life cycle assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spierling, S.; Venkatachalam, V.; Mudersbach, M.; Becker, N.; Herrmann, C.; Endres, H.J. End-of-life options for bio-based plastics in a circular economy-status quo and potential from a life cycle assessment perspective. Resources 2020, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Alba, I.; Chia, E.; Andrieu, N. The LCA4CSA framework: Using life cycle assessment to strengthen environmental sustainability analysis of climate smart agriculture options at farm and crop system levels. Agric. Syst. 2019, 171, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Raugei, M.; Zhang, X.; Mellino, S.; Ulgiati, S. Environmental cost and impacts of chemicals used in agriculture: An integration of emergy and Life Cycle Assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recanati, F.; Arrigoni, A.; Scaccabarozzi, G.; Marveggio, D.; Melià, P.; Dotelli, G. LCA Towards Sustainable Agriculture: The Case Study of Cupuaçu Jam from Agroforestry. Procedia Cirp 2018, 69, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benis, K.; Ferrão, P. Potential mitigation of the environmental impacts of food systems through urban and peri-urban agriculture (UPA)—A life cycle assessment approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.; Karunanithi, A. Urban agriculture characterized by life cycle assessment and land use change. In Proceedings of the ICSI 2014: Creating Infrastructure for a Sustainable World, Long Beach, CA, USA, 6–8 November 2014; pp. 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Llorach-Massana, P.; Muñoz, P.; Riera, M.R.; Gabarrell, X.; Rieradevall, J.; Montero, J.I.; Villalba, G. N2O emissions from protected soilless crops for more precise food and urban agriculture life cycle assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Beltran, A.; Padró, R.; La Rota-Aguilera, M.J.; Marull, J.; Eckelman, M.J.; Cirera, J.; Giocoli, A.; Villalba, G. Displaying geographic variability of peri-urban agriculture environmental impacts in the Metropolitan Area of Barcelona: A regionalized life cycle assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufí-Salís, M.; Petit-Boix, A.; Villalba, G.; Gabarrell, X.; Leipold, S. Combining LCA and circularity assessments in complex production systems: The case of urban agriculture. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 166, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyé-Mengual, E.; Oliver-Solà, J.; Montero, J.I.; Rieradevall, J. An environmental and economic life cycle assessment of rooftop greenhouse (RTG) implementation in Barcelona, Spain. Assessing new forms of urban agriculture from the greenhouse structure to the final product level. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, H.M.G.; Knudsen, M.T.; Cederberg, C. Towards better representation of organic agriculture in life cycle assessment. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteinis, S.; Chatzisymeon, E. Life cycle assessment of organic versus conventional agriculture. A case study of lettuce cultivation in Greece. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 2462–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludin, N.A.; Mustafa, N.I.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Asri Mat Teridi, M.; Sepeai, S.; Zaharim, A.; Sopian, K. Prospects of life cycle assessment of renewable energy from solar photovoltaic technologies: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 96, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanali, M.; Kokei, D.; Aghbashlo, M.; Nasab, F.K.; Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H.; Tabatabaei, M. Energy flow modeling and life cycle assessment of apple juice production: Recommendations for renewable energies implementation and climate change mitigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 118997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chai, Y.; Shen, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, Y. Environmental impact evaluation of distributed renewable energy system based on life cycle assessment and fuzzy rough sets. Energies 2019, 12, 4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijó, L.; González-García, S.; Lovarelli, D.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G.; Bacenetti, J. Life Cycle Assessment of Renewable Energy Production from Biomass. In Life Cycle Assessment of Energy Systems and Sustainable Energy Technologies. Green Energy and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 6, pp. 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubando, A.T.; Rivera, D.R.T.; Chen, W.H.; Culaba, A.B. A comprehensive review of life cycle assessment (LCA) of microalgal and lignocellulosic bioenergy products from thermochemical processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.M.; Sowlati, T.; Salazar, J. Life cycle assessment of forest-based biomass for bioenergy: A case study in British Columbia, Canada. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, F.; Bhandari, R.; Gäth, S. Critical review on life cycle assessment of conventional and innovative waste-to-energy technologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B. The hotspots of life cycle assessment for bioenergy: A review by social network analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusenza, M.A.; Bobba, S.; Ardente, F.; Cellura, M.; Di Persio, F. Energy and environmental assessment of a traction lithium-ion battery pack for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, M.; Peters, J.F.; Baumann, M.; Weil, M. Toward a cell-chemistry specific life cycle assessment of lithium-ion battery recycling processes. J. Ind. Ecol. 2020, 24, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, Z.; Cui, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Li, S. Life cycle assessment of end-of-life treatments of waste plastics in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antelava, A.; Damilos, S.; Hafeez, S.; Manos, G.; Al-Salem, S.M.; Sharma, B.K.; Kohli, K.; Constantinou, A. Plastic Solid Waste (PSW) in the Context of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Sustainable Management. Environ. Manag. 2019, 64, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paes, M.X.; de Medeiros, G.A.; Mancini, S.D.; Bortoleto, A.P.; Puppim de Oliveira, J.A.; Kulay, L.A. Municipal solid waste management: Integrated analysis of environmental and economic indicators based on life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 119848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yang, J.X.; Wang, R.S. Life cycle assessment for municipal solid waste treatment and utilization. J. Environ. Sci. 2000, 12, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, A.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.H. Municipal solid waste: Review of best practices in application of life cycle assessment and sustainable management techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, H.; Krüger, C.; Russ, M.; Horlacher, M.; Antony, F.; Hann, S.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental impacts of chemical recycling via pyrolysis of mixed plastic waste in comparison with mechanical recycling and energy recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Tang, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Chi, Y.; Weiss-Hortala, E.; Ni, M. Life cycle assessment of pyrolysis, gasification and incineration waste-to-energy technologies: Theoretical analysis and case study of commercial plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, A.; Veksha, A.; Yin, K.; Weerachanchai, P.; Giannis, A.; Lisak, G. Environmental impact assessment of converting flexible packaging plastic waste to pyrolysis oil and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, K.; Sinkko, T.; Luostarinen, S.; Tampio, E.; Joensuu, K. LCA of anaerobic digestion: Emission allocation for energy and digestate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, S.; Ma, X.; Mosley, J.; Garland, J.; Crone, B.; Xue, X. Energy and greenhouse gas life cycle assessment and cost analysis of aerobic and anaerobic membrane bioreactor systems: Influence of scale, population density, climate, and methane recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 254, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Dhar, D.W. Overview of carbon capture technology: Microalgal biorefinery concept and state-of-the-art. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Mohanty, K. A comprehensive review on microalgal harvesting strategies: Current status and future prospects. Algal Res. 2019, 44, 101683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijnders, L. Life cycle assessment of microalgae-based processes and products. In Handbook of Microalgae-Based Processes and Products: Fundamentals and Advances in Energy, Food, Feed, Fertilizer, and Bioactive Compounds; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 823–840. [Google Scholar]
- Arif, Z.U.; Khalid, M.Y.; Sheikh, M.F.; Zolfagharian, A.; Bodaghi, M. Biopolymeric sustainable materials and their emerging applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pozzo, A.; Carabba, L.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Tugnoli, A. Life cycle assessment of a geopolymer mixture for fireproofing applications. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, D.A.; Ramirez, A.D.; Ulloa, N.; Baykara, H.; Boero, A.J. Life cycle assessment of geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tong, L.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Zheng, Y. Eco-friendly geopolymer materials: A review of performance improvement, potential application and sustainability assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaidi, S.M.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Isleem, H.F.; de Azevedo, A.R.G.; Ahmed, H.U.; Emad, W. Sustainable utilization of red mud waste (bauxite residue) and slag for the production of geopolymer composites: A review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckin, D.; Tillman, A.M. Environmental assessment of additive manufacturing in the automotive industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, A.C.M.; Verlinden, J.C. Life cycle assessment of wire + arc additive manufacturing compared to green sand casting and CNC milling in stainless steel. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafara, M.; Süchting, M.; Kemnitzer, J.; Westermann, H.H.; Steinhilper, R. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Conventional and Additive Manufacturing in Mold Core Making for CFRP Production. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 8, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Author | Title/Theme | Time Span | Database and Records | Publications Search Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaurav et al. [46] | Recent progress of scientific research on life cycle assessment | 1991–2018 | Scopus: 10,524 WoS: 7726 | Within: Title, keywords, and abstract fields of a publication Language: All Search String: “Life cycle assessment *” OR “life cycle analysis *” OR “life cycle sustainability assessment *” OR “life cycle sustainability analys *” OR “ecobalanc *” OR “eco balanc *” OR “eco-balanc *” OR “Resource * and environmental profile analys *” OR “cradle-to-grave analys *” OR “cradle to grave analys *” OR “LCA” OR “Life-cycle assessment *” OR “life-cycle analys *” OR “life-cycle sustainability assessment *” OR “life-cycle sustainability analys *” |
| He and Yu [44] | Research trends in life cycle assessment research: A 20-year bibliometric analysis (1999–2018) | 1999–2018 | Web of Science: 20,153 | Within: Title, keywords, and abstract fields of a publication and Keywords Plus®. Language: English Document Type: (Article OR Review OR Proceeding papers) Search String: “life cycle assessment *” OR “life cycle analys *” OR “Life cycle sustainability assessment *” OR “life cycle sustainability analys *” OR “life cycle inventory” OR “life cycle impact assessment” OR (“eco balanc *” OR “ecobalanc *”) |
| Hou et al. [43] | Mapping the scientific research on life cycle assessment: A bibliometric analysis | 1998–2013 | Web of Science: 6616 | Within: Title, keywords, and abstract fields of a publication Language: All Document type: All Search String: “Life cycle assessment” OR “life-cycle assessment” |
| Chen et al. [41] | A bibliometric investigation of life cycle assessment research in the web of science databases | 1998–2013 | Web of Science: 7782 | Within: Title, keywords, and abstract fields of a publication Language: English Document type: All Search String: “life cycle assessment *” OR “life cycle analys *” OR “life cycle sustainability assessment *” OR “life cycle sustainability analys *” OR (“eco balanc *” OR “ecobalanc *”) |
| Databases | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Scopus | WoS | ||
| Publications | 3107 | 1750 | 1357 | |
| Deduplicated publications | Encompassed within Scopus (not referenced in WoS) | Encompassed within WoS (not referenced in Scopus) | Main Driven Factors | |
| Difference in articles | 776 (25%) | 676 | 100 |
|
| Difference in Conference papers | 155 (5%) | 154 | 1 |
|
| Difference in Reviews | 62 (2%) | 62 | 0 |
|
| Chinese language papers | 28 (1%) | 28 | 0 |
|
| French, German, Polish, Spanish, Korean, Japanese Language papers | 14 | 11 | 3 |
|
| 1992–2018 | 2019–2022 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | No. of Publications | % | No. of Publications | % |
| English | 11,632 | 96 | 8003 | 99 |
| Chinese | 241 | 2 | 79 | 1 |
| Japanese | 75 | 1 | 2 | - |
| German | 38 | - | 9 | - |
| Spanish | 32 | - | 12 | - |
| Portuguese | 22 | - | 11 | - |
| French | 16 | - | 3 | - |
| Korean | 8 | - | 2 | - |
| Author Name | TP | Institution | Country | h- Index | Documents and Citations Trend (A Graphical Summary Showcasing an Author’s Yearly Publications Alongside Their Cumulative Citations). |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moreira, M.T. | 68 | University of Santiago De Compostela | Spain | 65 |  |
| Feijoo, G. | 57 | University of Santiago De Compostela | Spain | 65 |  |
| Finkbeiner, M. | 50 | Technical University of Berlin | Germany | 44 |  |
| Azapagic, A. | 48 | University of Manchester | England | 62 |  |
| Dewulf, J. | 41 | Ghent University | Belgium | 63 |  |
| Aldaco, R. | 38 | Universidad de Cantabria | Spain | 28 |  |
| Hong, J. | 38 | Shandong University | China | 35 |  |
| Gheewala, S.H. | 36 | King Mongkuts Univ Technol Thonburi | Thailand | 50 |  |
| González-García, S. | 36 | Universidade de Santiago de Compostela | Spain | 44 |  |
| Freire, F. | 35 | Universidade de Coimbra | Portugal | 30 |  |
| Habert, G. | 35 | ETH Zurich | Switzerland | 45 |  |
| Sonnemann, G. | 35 | Institut des Sciences Moléculaires | France | 31 |  |
| Margallo, M. | 34 | Universidad de Cantabria | Spain | 22 |  |
| Passer, A. | 33 | Graz University of Technology | Austria | 17 |  |
| Iribarren, D. | 32 | Madrid Institute for Advanced Studies in Energy | Spain | 40 |  |
| Sala, S. | 32 | European Commission Joint Research Centre | EU, Belgium | 49 |  |
| Silvestre, J.D. | 32 | Universidade de Lisboa | Portugal | 34 |  |
| Birkved, M. | 31 | University of Southern Denmark | Denmark | 31 |  |
| Cellura, M. | 31 | University of Palermo | Italy | 45 |  |
| Margni, M. | 31 | University of Applied Sciences Western Switzerland | Switzerland | 45 |  |
| Rank 1–10 | 10–20 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Institution | Count | % | Country | Institution | Count | % | Country |
| Ministry of Education China | 192 | 2.45 | China | Universiteit Gent | 89 | 1.14 | Belgium |
| Technical University of Denmark | 161 | 2.06 | Denmark | University of Tehran | 88 | 1.12 | Iran |
| ETH Zürich | 149 | 1.90 | Switzerland | The Royal Institute of Technology KTH | 86 | 1.10 | Sweden |
| Chinese Academy of Sciences | 137 | 1.75 | China | Universidad de Santiago de Compostela | 86 | 1.10 | Spain |
| CNRS Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique | 116 | 1.48 | France | The University of Manchester | 84 | 1.07 | UK |
| Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet | 108 | 1.38 | Norway | University of Michigan, Ann Arbor | 83 | 1.06 | USA |
| Tsinghua University | 107 | 1.37 | China | Aalborg University | 81 | 1.04 | Denmark |
| Technische Universität Berlin | 99 | 1.27 | Germany | Universidade de Lisboa | 81 | 1.04 | Portugal |
| Politecnico di Milano | 93 | 1.19 | Italy | KU Leuven | 78 | 1.00 | Belgium |
| Chalmers University of Technology | 91 | 1.16 | Sweden | European Commission Joint Research Centre | 78 | 1.00 | EU Belgium |
| Funding Sponsor | Documents | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| National Natural Science Foundation of China | 732 | 9.50 |
| Horizon 2020 Framework Programme | 397 | 5.15 |
| European Commission | 375 | 4.87 |
| European Regional Development Fund | 309 | 4.01 |
| National Key Research and Development Program of China | 258 | 3.35 |
| National Science Foundation | 239 | 3.10 |
| Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico | 191 | 2.48 |
| Horizon 2020 | 188 | 2.44 |
| Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior | 187 | 2.43 |
| Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia | 184 | 2.39 |
| Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council | 143 | 1.86 |
| Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities | 139 | 1.80 |
| US Department of Energy | 139 | 1.80 |
| Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad | 135 | 1.75 |
| Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada | 126 | 1.64 |
| Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung | 117 | 1.52 |
| National Research Foundation of Korea | 88 | 1.14 |
| China Scholarship Council | 82 | 1.06 |
| Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades | 79 | 1.03 |
| National Institute of Food and Agriculture | 72 | 0.93 |
| Subject Area | Count | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Science | 5004 | 27.27% |
| Engineering | 3369 | 18.36% |
| Energy | 3204 | 17.46% |
| Business, Management, and Accounting | 1140 | 6.21% |
| Social Sciences | 999 | 5.44% |
| Chemical Engineering | 48 | 3.53% |
| Materials Science | 86 | 3.19% |
| Agricultural and Biological Sciences | 28 | 2.88% |
| Chemistry | 40 | 2.40% |
| Computer Science | 67 | 2.54% |
| Mathematics | 71 | 2.02% |
| Economics, Econometrics, and Finance | 307 | 1.67% |
| Earth and Planetary Sciences | 85 | 2.10% |
| Physics and Astronomy | 58 | 1.41% |
| Biochemistry, Genetics, and Molecular Biology | 61 | 0.88% |
| Decision Sciences | 12 | 0.61% |
| Medicine | 49 | 0.81% |
| Multidisciplinary | 6 | 0.36% |
| Arts and Humanities | 0 | 0.11% |
| Immunology and Microbiology | 8 | 0.15% |
| Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Pharmaceutics | 3 | 0.18% |
| Veterinary | 0 | 0.16% |
| Health Professions | 4 | 0.13% |
| Nursing | 7 | 0.09% |
| Neuroscience | 2 | 0.01% |
| Psychology | 2 | 0.01% |
| Journal | Contribution | Publisher | Quartiles | CiteScore |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Journal Of Cleaner Production | 16.21% | Elsevier | Q1 | 15.8 |
| Sustainability Switzerland | 7.21% | MDPI | Q2 | 5 |
| International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment | 6.65% | Springer | Q1 | 8.4 |
| Science Of the Total Environment | 6.31% | Elsevier | Q1 | 14.1 |
| Resources Conservation and Recycling | 4.53% | Elsevier | Q1 | 17.9 |
| Energies | 3.60% | MDPI | Q2 | 5 |
| Journal Of Environmental Management | 2.07% | Elsevier | Q1 | 11.4 |
| Journal Of Industrial Ecology | 2.05% | Wiley-Blackwell | Q1 | 12 |
| ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering | 1.89% | American Chemical Society | Q1 | 14.5 |
| Renewable And Sustainable Energy Reviews | 1.71% | Elsevier | Q1 | 28.5 |
| Author and Year of Publication | Total | Title | Journal | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chong, et al., (2010) | 3879 | Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review [106] | Water Research | TiO2; Photocatalysis; Water treatment; Photocatalytic reactors; Kinetic modelling; Water qualities; Life cycle analysis; Mineralisation; Disinfection |
| Wernet et al., (2016) | 2189 | The Ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): Overview and methodology [96] | IJLCA | Ecoinvent version 3; Life Cycle Assessment (LCA); Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) database; Parametrisation; Regionalisation; System model |
| Finnveden et al., (2009) | 2060 | Recent developments in Life Cycle Assessment [16] | Journal of Environmental Management | Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Strategic; Environmental Assessment; Risk assessment; LCC; Ecological footprint; Exergy analysis; Valuation; Weighting |
| Joshi et al., (2004) | 1700 | Are natural fibre composites environmentally superior to glass fibre reinforced composites? [104] | Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing | Natural fibres; A. Glass fibres |
| Binnemans et al., (2013) | 1494 | Recycling of rare earths: A critical review [19] | Journal Of Cleaner Production | Balance problem; Lanthanides; Rare earths; Recycling; Resource; Recovery; Urban mining |
| Mueller and Nowack (2008) | 1476 | Exposure modelling of engineered nanoparticles in the environment [108] | Environmental Science and Technology | Environmental Exposure; Nanoparticles |
| Zhu et al., (2016) | 1420 | Sustainable polymers from renewable resources [109] | Nature | Catalysis; manufacturing; polymer; polymerisation; renewable resource; sustainability |
| Al-Salem et al., (2009) | 1372 | Recycling and recovery routes of Plastic Solid Waste (PSW): A review [110] | Waste Management | Municipal solid waste; plastic waste; polymer; recycling; sustainability; waste treatment |
| Rebitzer et al., (2004) | 1300 | Life cycle assessment Part 1: Framework, goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, and applications [107] | Environment international | Environmental impact; human activity; inventory; life cycle analysis; pollution effect; sustainable development |
| Vance et al., (2015) | 1298 | Nanotechnology in the real world: Redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory [111] | Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology | Consumer products; database; inventory; nanoinformatics; nanomaterials |
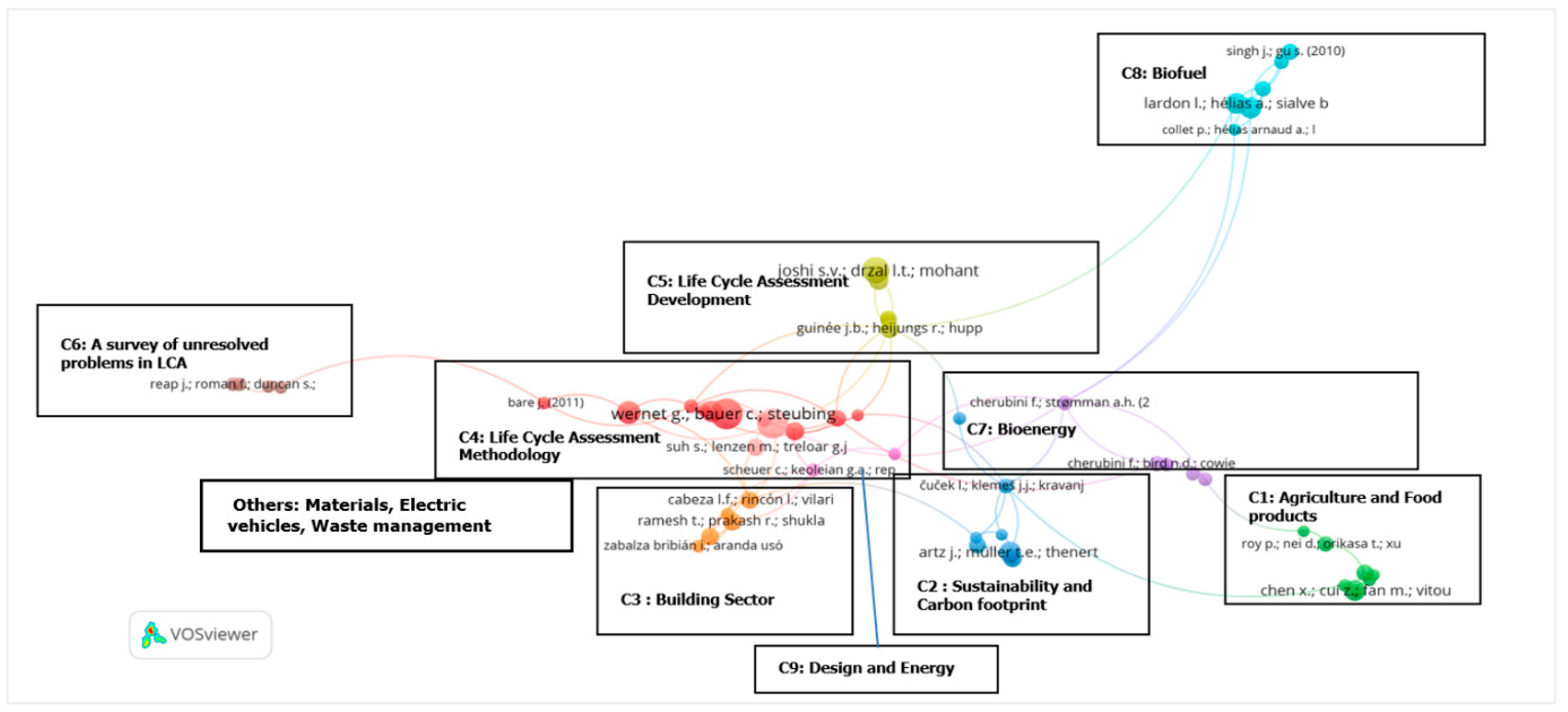
| Cluster | Main Keywords | Theme |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Circular economy—comparative LCA—Ecodesign—Sensitivity—Uncertainty analysis—Sustainability— Sustainable Development— | LCA methodology; Sustainable Development; Circular economy |
| 2 | Agriculture—Animal— Energy consumption—Fertilisers—Water—Toxicity—Land Use—Ozone depletion— Sustainability | Environmental Impact Assessment in Agricultural Systems |
| 3 | Biofuel—Biomass—Carbon footprint—Energy—Fossil fuels—GHG—Renewable energy—Sustainability | Energy and carbon emissions |
| 4 | Anaerobic digestion—incineration—landfill—municipal—solid waste—waste disposal—Economic aspect— Sustainability | Waste Management and Resource Utilisation |
| 5 | Bio-Based—Biopolymers—Circular economy—Composites—Plastic waste—Polymers—Textile— Waste Technology—Recycling—Polyethelene | Sustainable Materials and circular economy |
| Others: Agricultural wastes—Bioenergy—Biomass—Bioethanol—Techno Economic analysis—Feedstocks—Pyrolysis | ||
| Topic Cluster | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Life Cycle; Sustainable Development; Sustainability | 98.28 | 98.23 | 98.55 | 98.79 | 97.91 | 97.76 | 97.8 |
| Life Cycle Assessment; Photovoltaic System; Solar Collectors | 98.74 | 98.72 | 98.97 | 99.07 | 98.91 | 99.09 | 99.07 |
| Solid Waste Management; Life Cycle Assessment; Municipal Solid Waste; Circular economy | 99.23 | 99.38 | 99.64 | 99.6 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.69 |
| Biopolymer; Bioplastics; Biodegradable Plastics | 83.06 | 89.8 | 93.02 | 93.4 | 92.65 | 96.94 | 96.76 |
| Anaerobic Digestion; Biofuel; Life Cycle Assessment | 98.28 | 98.23 | 98.55 | 98.79 | 97.91 | 97.76 | 97.8 |
| Sustainability; Ecodesign; Cradle-To-Cradle cycle | 95.13 | 96.95 | 97.42 | 95.26 | 94.6 | 95.93 | 94.64 |
| Sustainability; United Nations Environment Program; Social Indicators; Life cycle sustainability assessment | 93.75 | 93.76 | 97.6 | 97.45 | 95.19 | 95.78 | 97.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moutik, B.; Summerscales, J.; Graham-Jones, J.; Pemberton, R. Life Cycle Assessment Research Trends and Implications: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813408
Moutik B, Summerscales J, Graham-Jones J, Pemberton R. Life Cycle Assessment Research Trends and Implications: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813408
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoutik, Badr, John Summerscales, Jasper Graham-Jones, and Richard Pemberton. 2023. "Life Cycle Assessment Research Trends and Implications: A Bibliometric Analysis" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813408
APA StyleMoutik, B., Summerscales, J., Graham-Jones, J., & Pemberton, R. (2023). Life Cycle Assessment Research Trends and Implications: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability, 15(18), 13408. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813408








