Relative Influence of Meteorological Variables of Human Thermal Stress in Peninsular Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
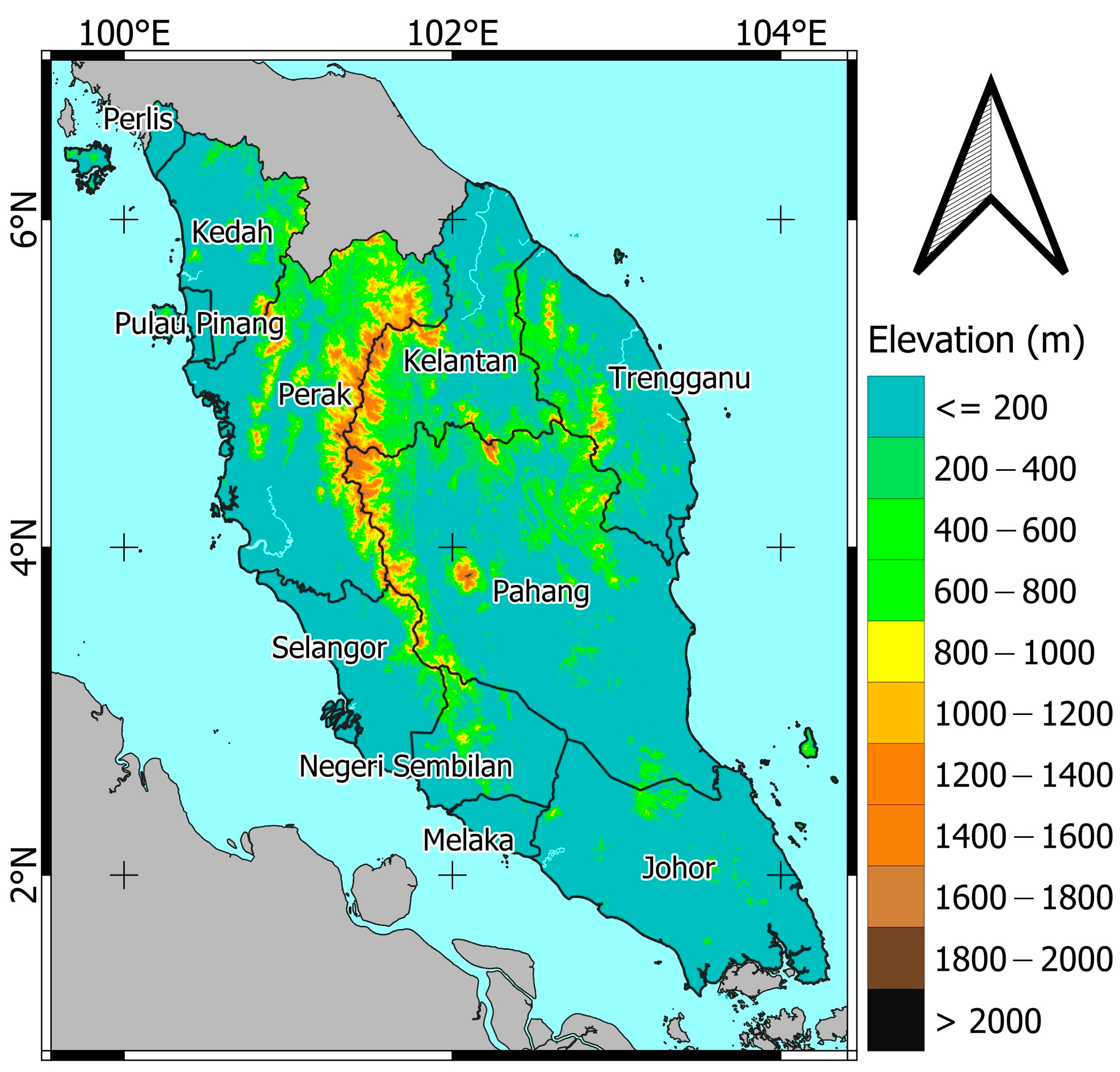
2.1. Peninsular Malaysia
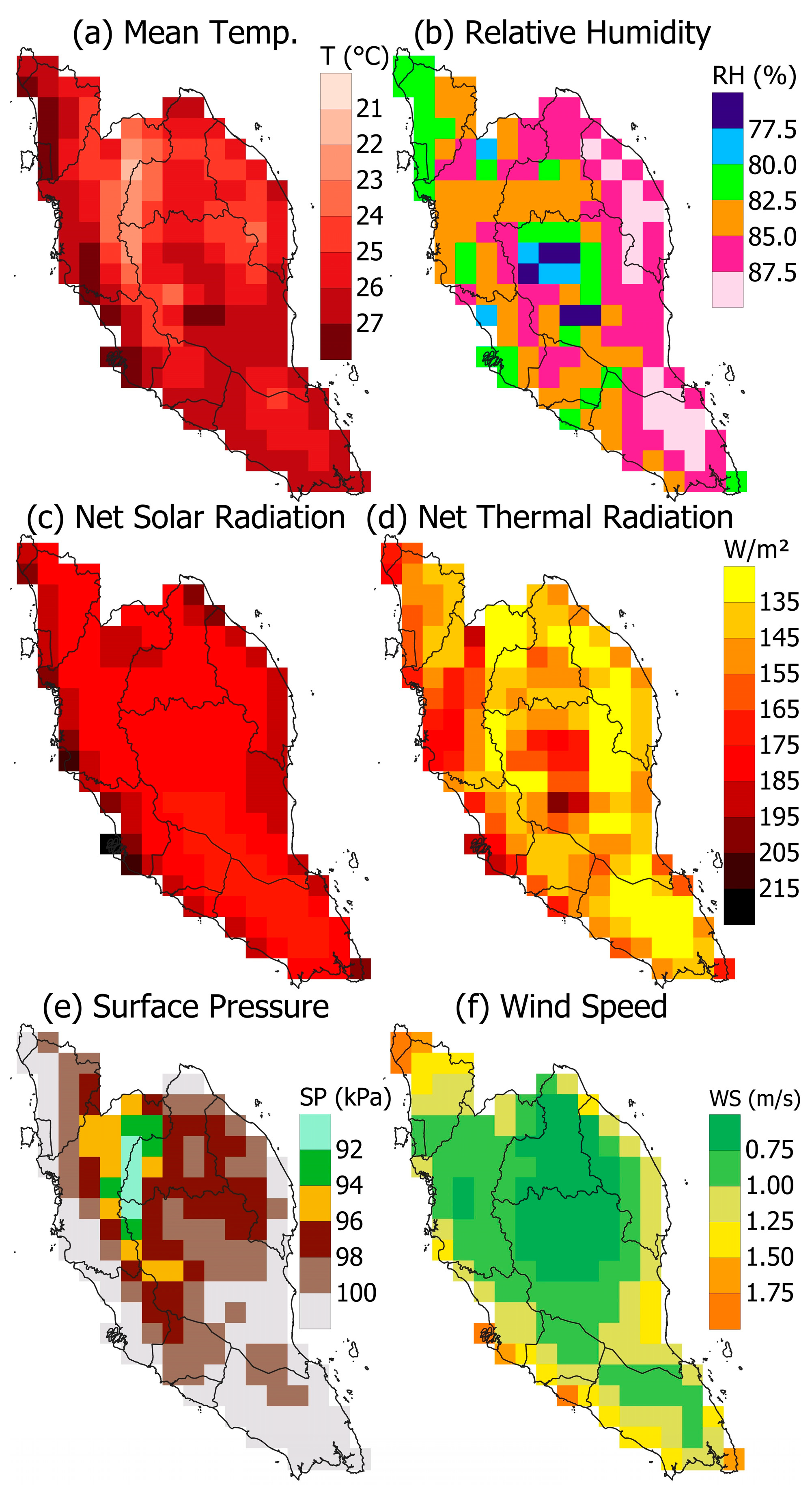
2.2. Dataset
3. Methods
3.1. Wet Bulb Global Temperature
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. Trend Analysis
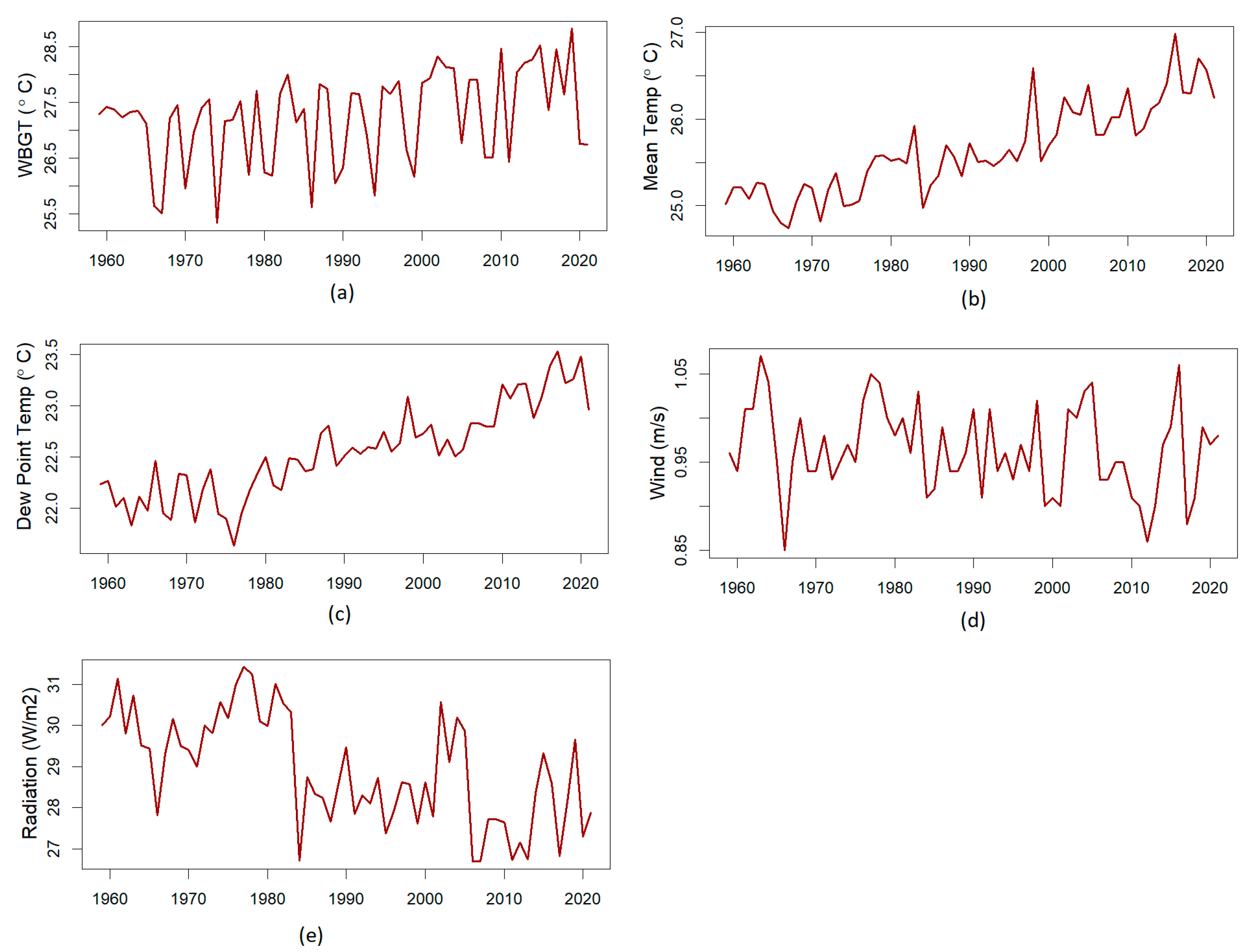
4. Results
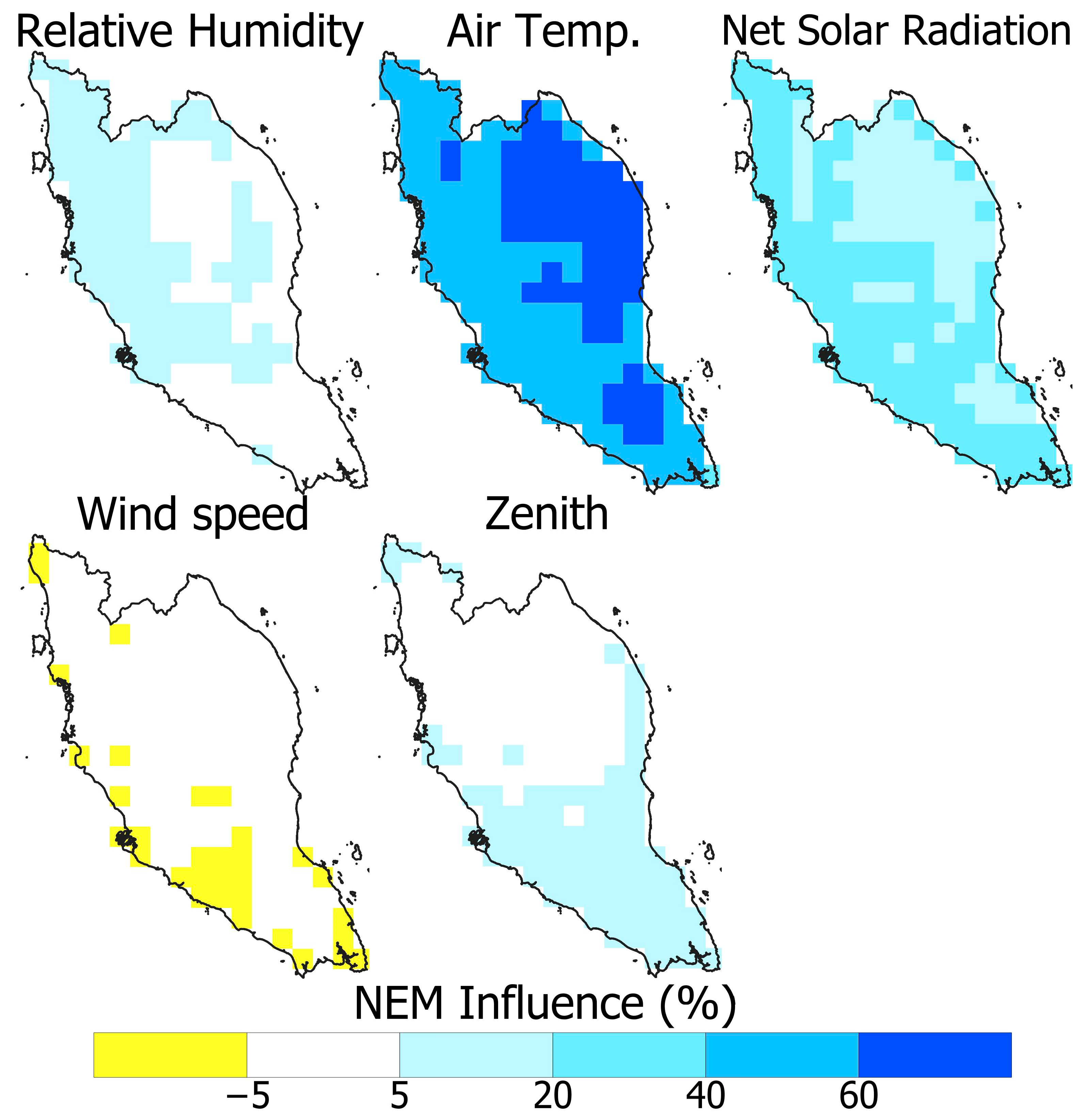
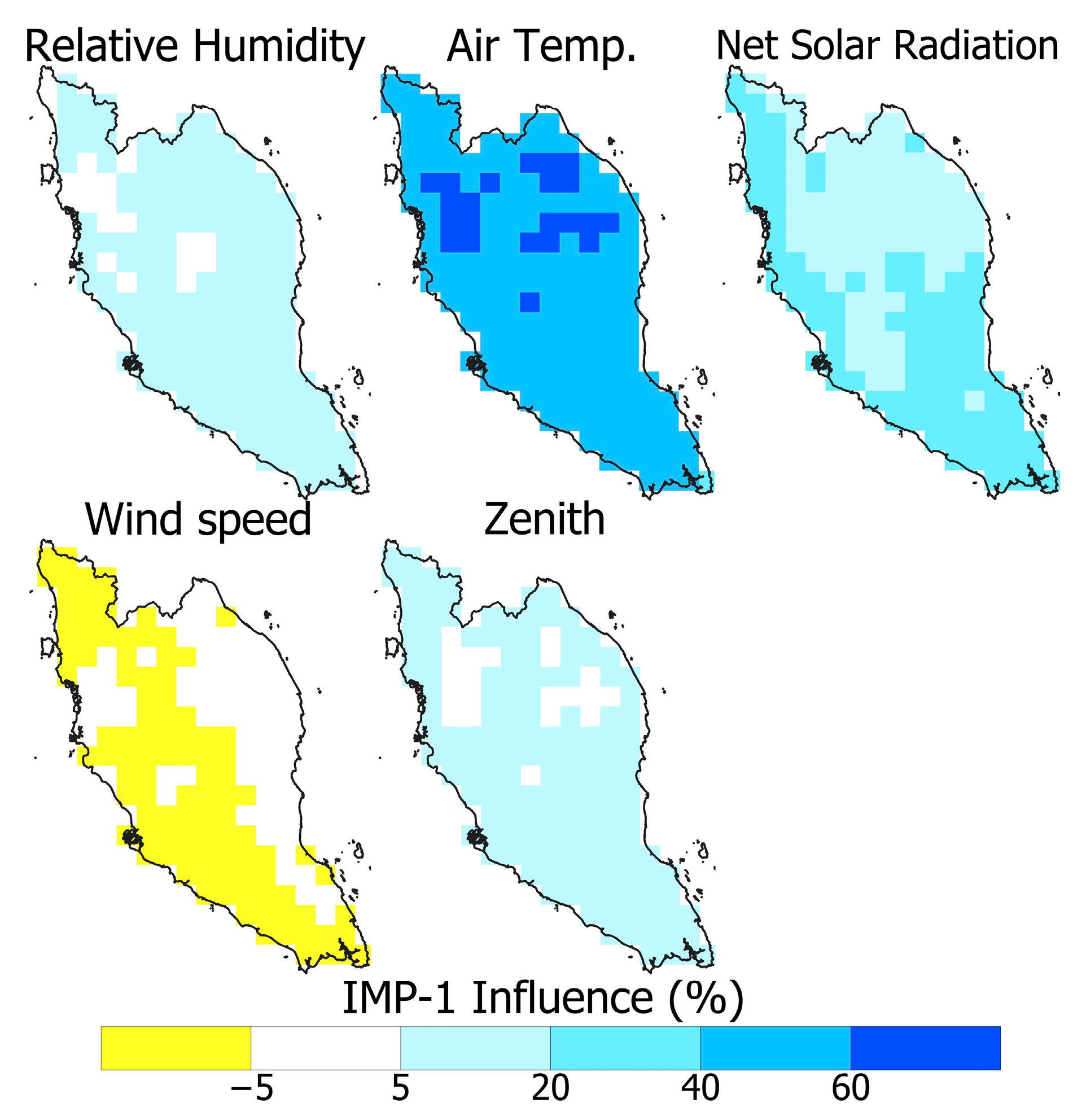
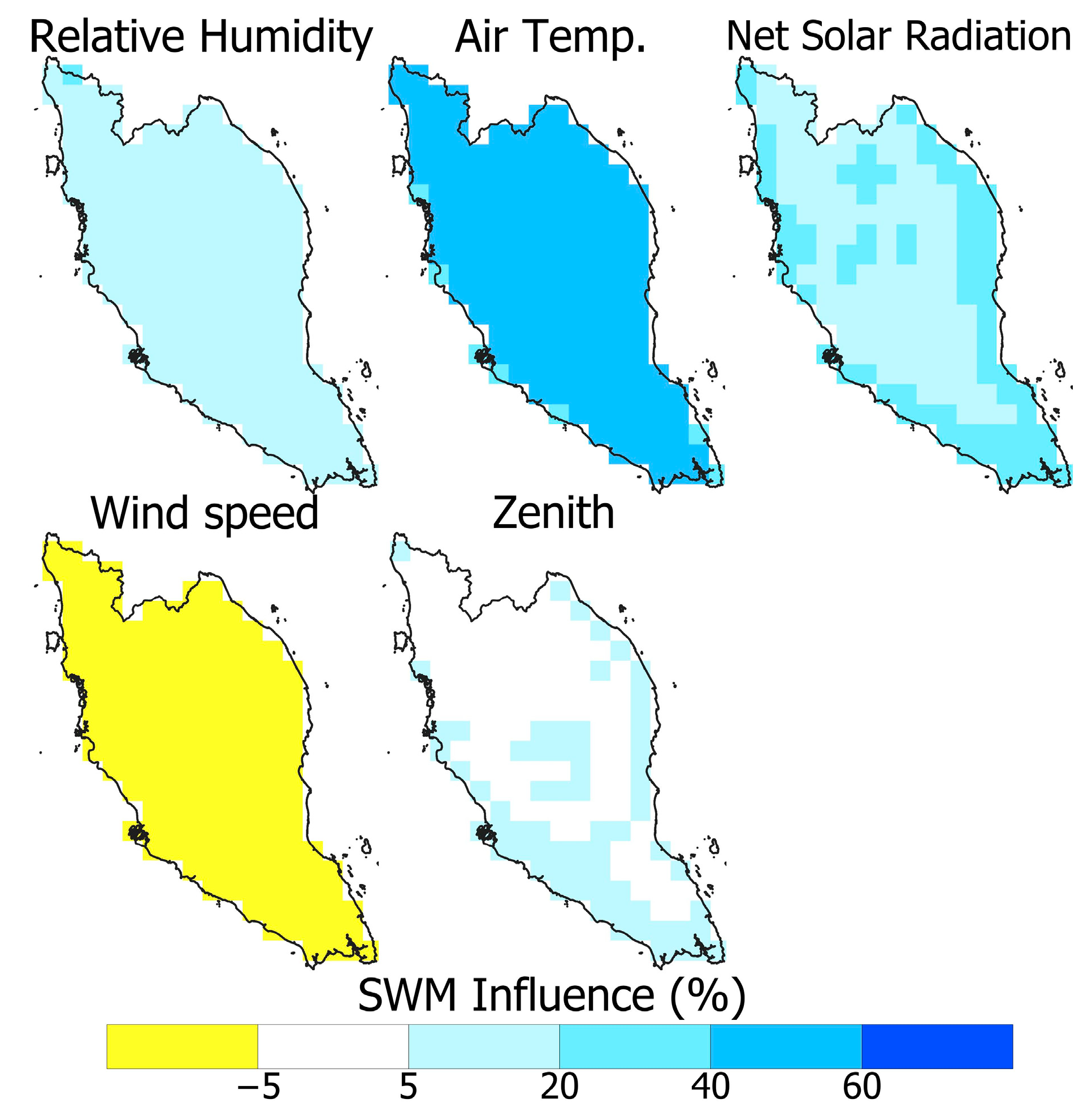
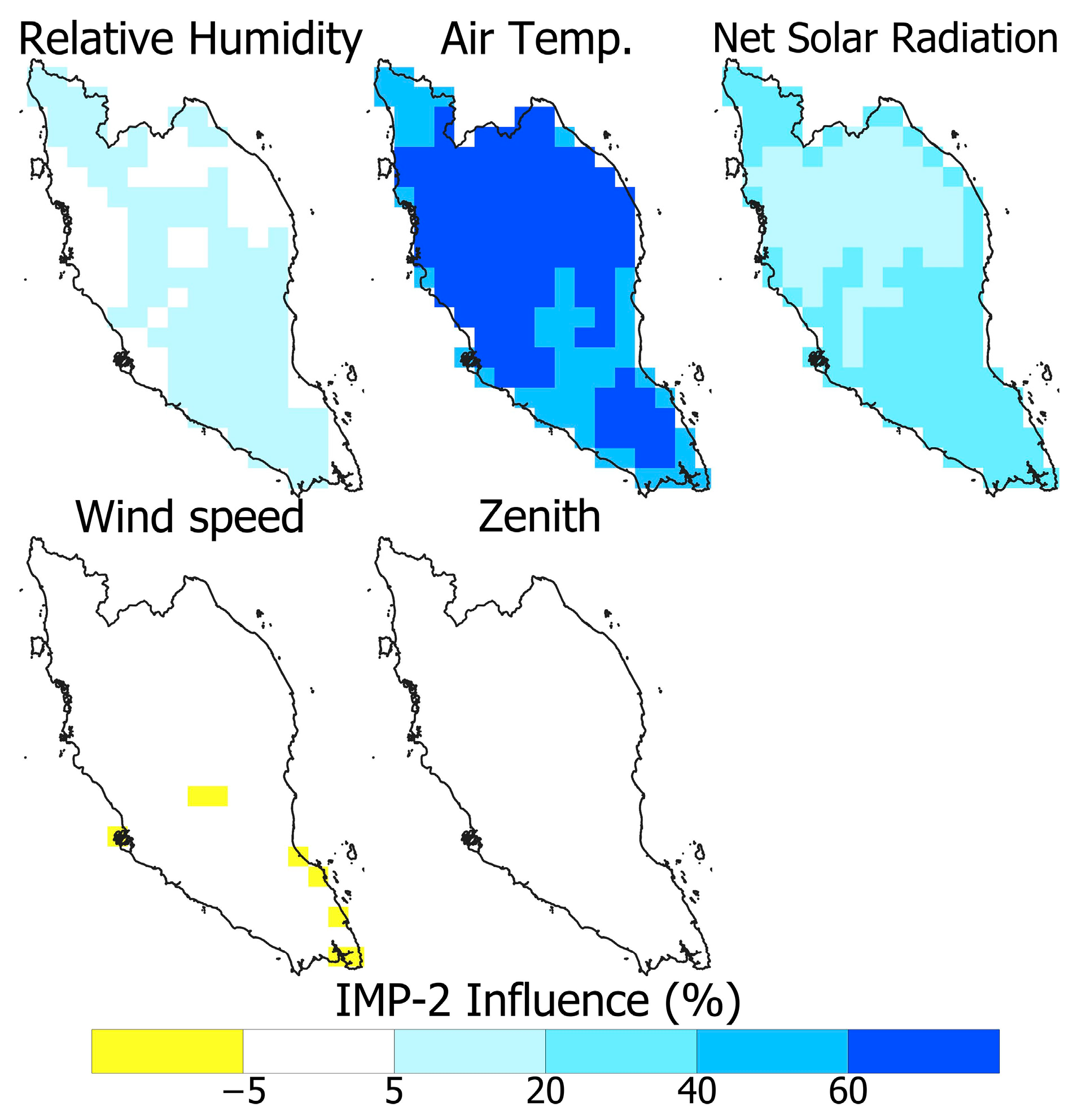
4.1. Spatial Distribution of the Influence of WBGT Drivers
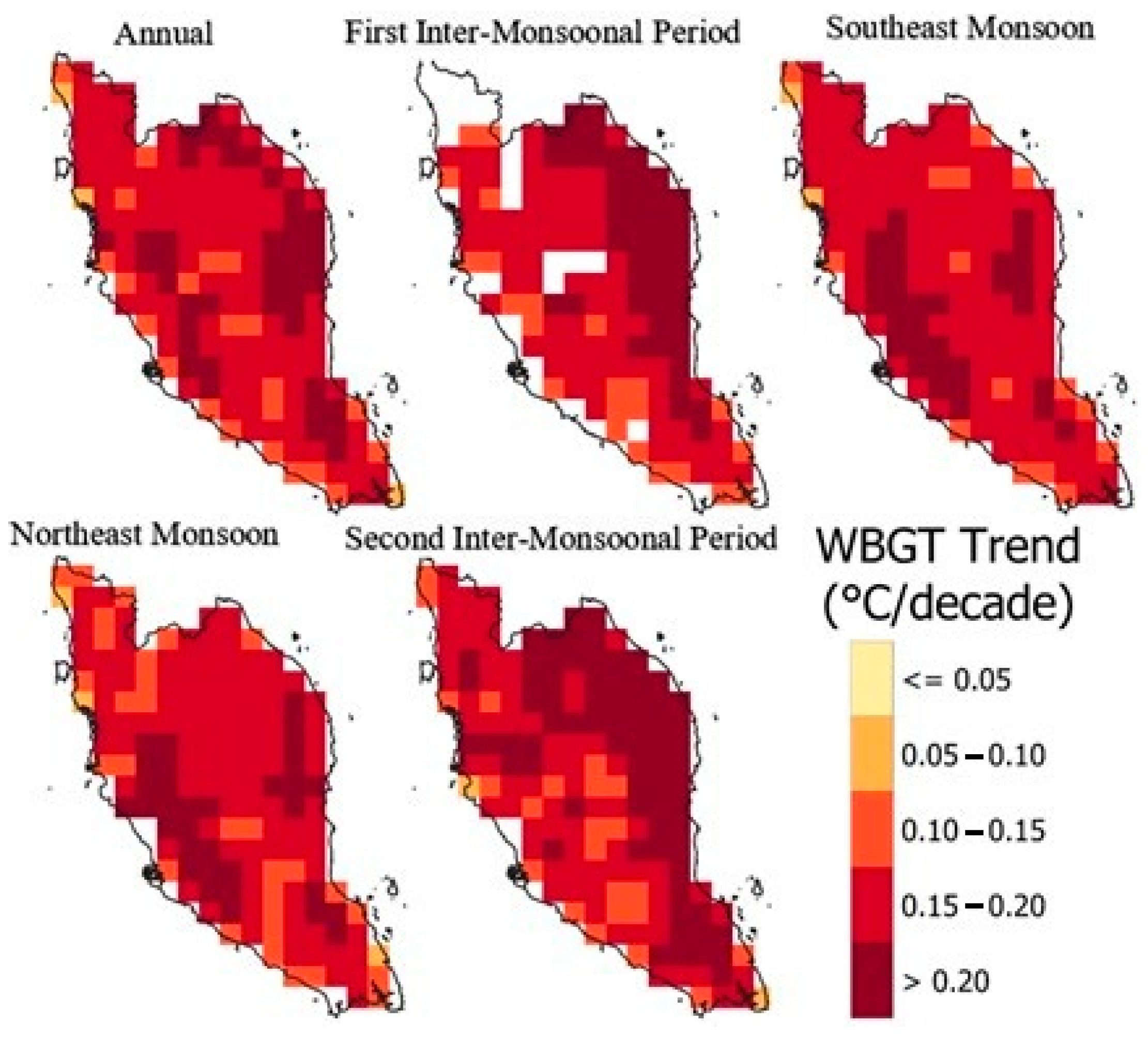
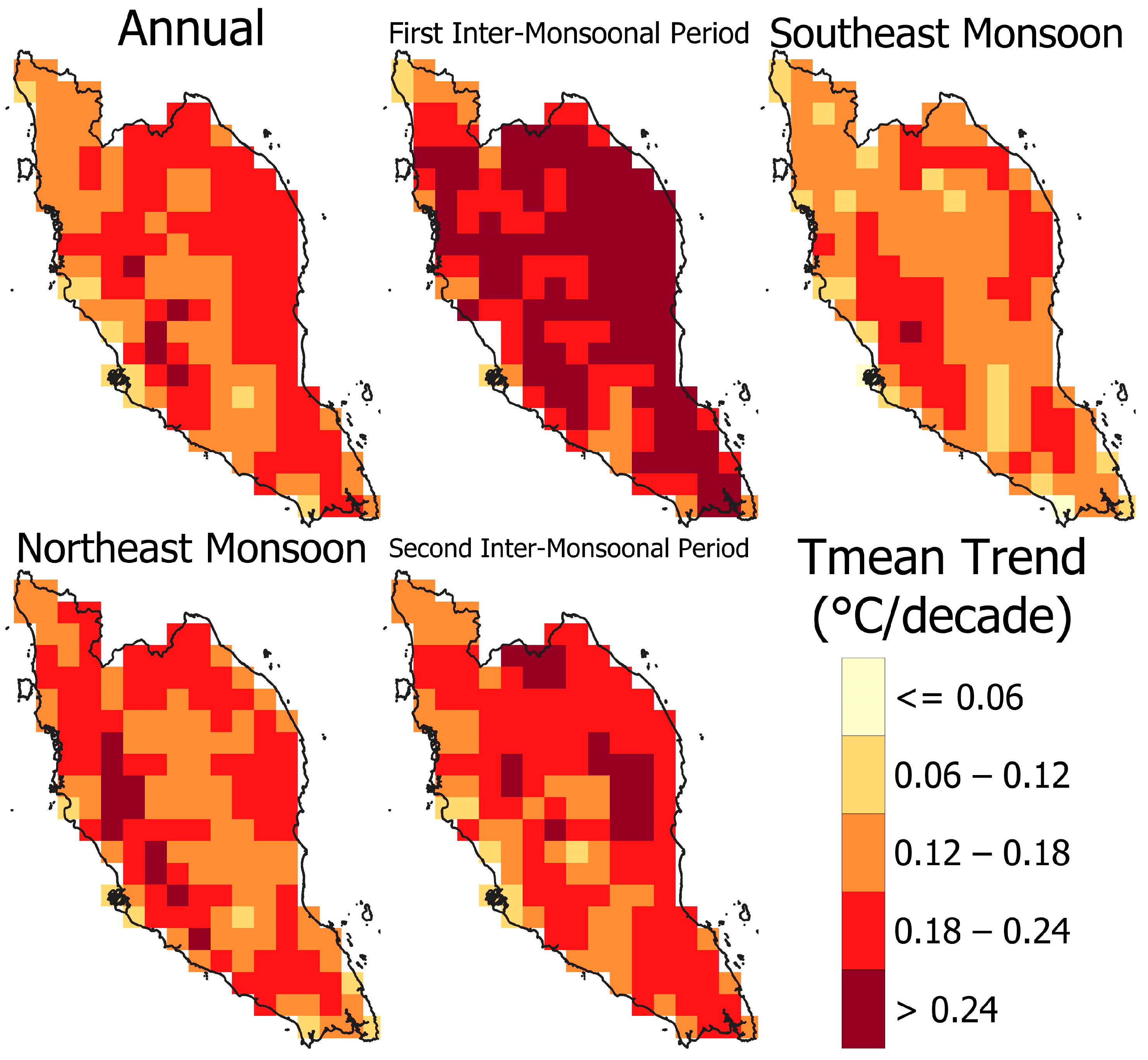
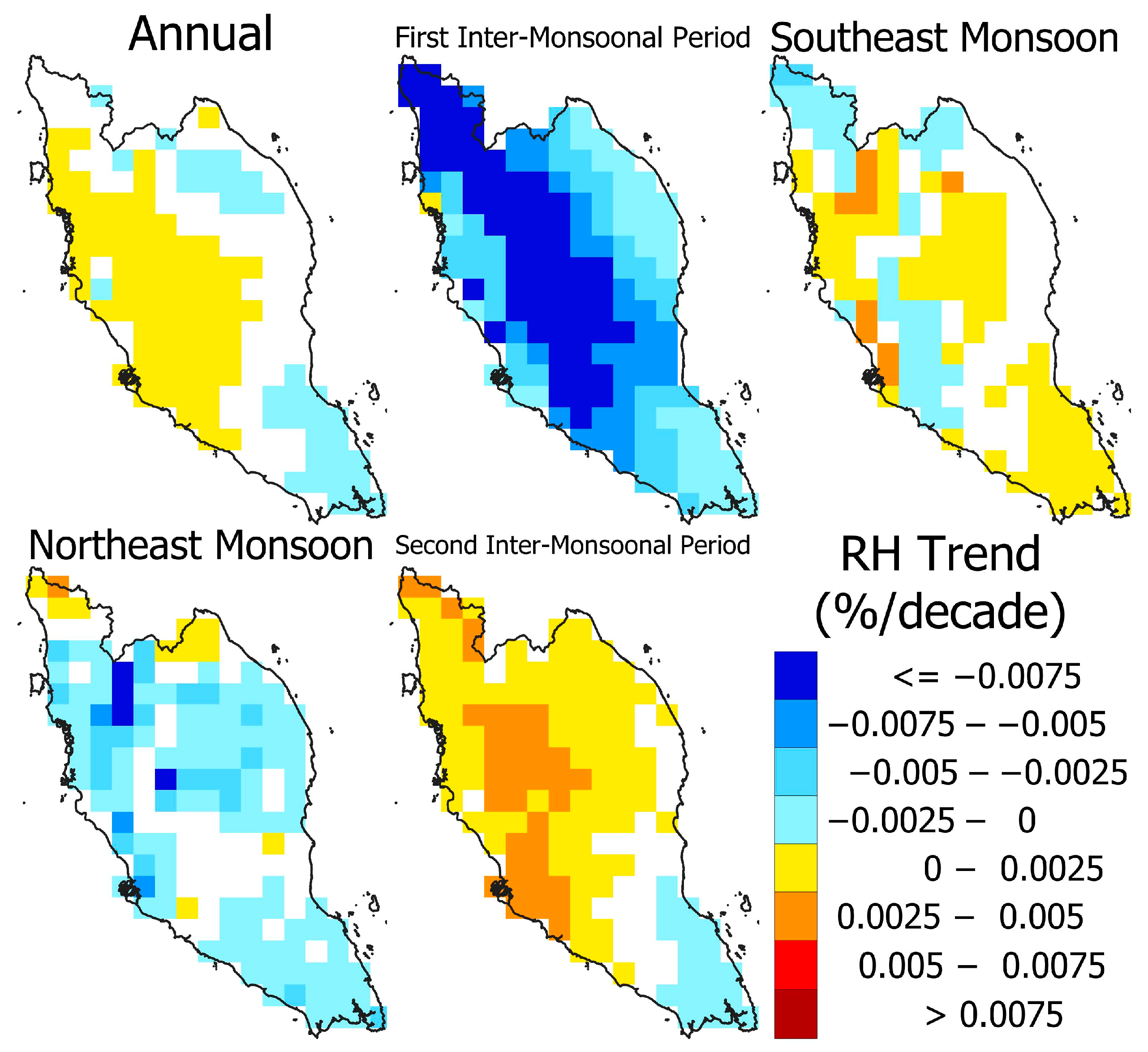
4.2. Spatial Distribution of the Trends in WBGT Drivers
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, T.E.; Iheanacho, I. Heat index and adjusted temperature as surrogates for wet bulb globe temperature to screen for occupational heat stress. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2015, 12, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocherie, F.; Millet, G.P. Is the wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) index relevant for exercise in the heat? Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, T.E.; Ashley, C.D. Short-term heat stress exposure limits based on wet bulb globe temperature adjusted for clothing and metabolic rate. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoi, T.; Mochida, T.; Kurazumi, Y.; Kuwabara, K.; Horiba, Y.; Sawada, S.-I. Heat balance model for a human body in the form of wet bulb globe temperature indices. J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, A.P.; Potter, A.W.; Linnane, D.M.; Xu, X.; Patterson, M.J.; Stewart, I.B. Heat Stress Management in the Military: Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature Offsets for Modern Body Armor Systems. Hum. Factors 2022, 64, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minard, D.; O’brien, R.L. Heat Casualties in the Navy and Marine Corps 1959–1962 with Appendices on the Field Use of the Wet Bulb-Globe Temperature Index. RES REP MR 005. 01-0001. 01, REP N0.7. Res. Summ. 1964, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Powell, J.; Strauch, A.; Roberge, R.; Kenny, G.P.; Kim, J.-H. Heat stress assessment during intermittent work under different environmental conditions and clothing combinations of effective wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT). J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2019, 16, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, R.; Matthew, W.T.; Christiansen, J.; Brown, B.; Smith, J.; Thomas, G.; Rose, M.S.; Szlyk, P.C.; Armstrong, L.; Schatzle, F.J. Field assessment of wet bulb globe temperature: Present and future. Mil. Med. 1991, 156, 535–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.W.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Gohlke, J.M.; Wang, S.; Richardson, M.B. Methods for estimating wet bulb globe temperature from remote and low-cost data: A comparative study in Central Alabama. GeoHealth 2020, 4, e2019GH000231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Kume, M.; Tuneoka, H.; Yoshida, T. Differences in the heat stress associated with white sportswear and being semi-nude in exercising humans under conditions of radiant heat and wind at a wet bulb globe temperature of greater than 28 °C. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundstein, A.; Cooper, E. Assessment of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology wet bulb globe temperature model using weather station data. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohraz, M.H.; Ghahri, A.; Karimi, M.; Golbabaei, F. The past and future trends of heat stress based on wet bulb globe temperature index in outdoor environment of Tehran City, Iran. Iran. J. Public Health 2016, 45, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.; Fang, Y.; Michalak, A.M. Recent very hot summers in Northern Hemispheric land areas measured by wet bulb globe temperature will be the norm within 20 years. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, J.L.; Pryor, R.R.; Grundstein, A.; Casa, D.J. The heat strain of various athletic surfaces: A comparison between observed and modeled wet-bulb globe temperatures. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakoi, T.; Mochida, T. Concept of the equivalent wet bulb globe temperature index for indicating safe thermal occupational environments. Build. Environ. 2013, 67, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.F.A.; Silveira, I.H.; Feitosa, R.C.; Horta, M.A.P.; Junger, W.L.; Hacon, S. Human Heat stress risk prediction in the Brazilian semiarid Region based on the Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2019, 91, e20180748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, S.; Rayner, D.; Palm, G.; Lindberg, F.; Carlström, E.; Börjesson, M.; Nilson, F.; Khorram-Manesh, A.; Holmer, B. Is Physiological Equivalent Temperature (PET) a superior screening tool for heat stress risk than Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) index? Eight years of data from the Gothenburg half marathon. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.T.; Havenith, G.; Kenney, W.L. Relatively minor influence of individual characteristics on critical wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) limits during light activity in young adults (PSU HEAT Project). J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 134, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.S.; Pandolf, K.B.; Shapiro, Y.; Heled, Y.; Shani, Y.; Mathew, W.; Gonzalez, R. An environmental stress index (ESI) as a substitute for the wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT). J. Therm. Biol. 2001, 26, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paengkaew, W.; Limsakul, A.; Junggoth, R.; Pitaksanurat, S. Empirically Derived Equation from Simple Heat Index for Calculating Wet Bulb Globe Temperature: A Case Study of Thailand. Appl. Environ. Res. 2020, 42, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanos, J.K.; Grundstein, A.J. Variations in athlete heat-loss potential between hot-dry and warm-humid environments at equivalent wet-bulb globe temperature thresholds. J. Athl. Train. 2020, 55, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, N.N.; Pitman, A.J.; Ukkola, A.M. High impact compound events in Australia. Weather. Clim. Extrem. 2022, 36, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabara, J.W. Comparison of the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature and a Modified Botsball Thermometer in an Outdoor Environment. Appl. Ind. Hyg. 1988, 3, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, D.J.; Adams, W.C. Wet bulb globe temperature index and performance in competitive distance runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.S.; Pandolf, K.B. Wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT)—To what extent is GT essential? Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 1999, 70, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Prost, G.; Davezies, P. L’indice WBGT. Arch. Mal. Prof. Médecine Trav. Sécurité Soc. 1985, 46, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Brimicombe, C.; Lo, C.H.B.; Pappenberger, F.; Di Napoli, C.; Maciel, P.; Quintino, T.; Cornforth, R.; Cloke, H.L. Wet Bulb Globe Temperature: Indicating extreme heat risk on a global grid. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2022GH000701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, A.K.; Hamed, M.M.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Shahid, S. Spatiotemporal changes in population exposure to heat stress in south Asia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 93, 104544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Kim, I.-G.; Kim, H.-M.; Lee, D.-G.; Lee, H.-C.; Choi, G. Spatio-temporal patterns of the minimum rest time for outdoor workers exposed to summer heat stress in South Korea. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houmsi, M.R.; Ismail, Z.; Othman, L.K.; Ishak, D.S.M.; Hamed, M.M.; Iqbal, Z.; Syamsunur, D.; Shahid, S. Spatiotemporal changes in Hourly Wet Bulb Globe temperature in Peninsular Malaysia. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 2327–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.; Horta, A.; Khan, M.R.; Crabbe, R.A. Spatial Analysis of Outdoor Wet Bulb Globe Temperature under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 Scenarios for 2041–2080 across a Range of Temperate to Hot Climates. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2022, 35, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljegren, J.C.; Carhart, R.A.; Lawday, P.; Tschopp, S.; Sharp, R. Modeling the wet bulb globe temperature using standard meteorological measurements. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2008, 5, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, H.; Mortazavi, S.B.; Jafari, M.J.; Maracy, M.R. Evaluation of wet bulb globe temperature index for estimation of heat strain in hot/humid conditions in the Persian Gulf. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2012, 17, 1108. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Z. A Simplified Method to Calculate the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature. J. Civ. Archit. Environ. Eng. 2015, 5, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Meng, Q.; Lu, S.; Zhong, K. Simplified calculation method of outdoor wet bulb globe temperature for areas with low latitude and high latitude. J. Chongqing Univ. 2020, 43, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Takane, Y.; Kusaka, H.; Takaki, M.; Okada, M.; Abe, S.; Fuji, Y.; Iizuka, S.; Nagai, T. Observational Study and Numerical Prediction Experiments on Wet-Bulb Globe Temperature in Tajimi, Gifu Prefecture: Consideration of Uncertainty with a Physics Parameterization Scheme and Horizontal Resolution of the Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Jpn. Prog. Climatol. = Jpn. Prog. Climatol. 2013, 2013, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, S.; Bell, M.L.; Lee, J.-T. Comparison of health risks by heat wave definition: Applicability of wet-bulb globe temperature for heat wave criteria. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneau, P.D.; Bishop, P.A. A review of the suggested wet bulb globe temperature adjustment for encapsulating protective clothing. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1996, 57, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroter, R.; Marlin, D.; Jeffcott, L. Use of the wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT) index to quantify environmental heat loads during three-day-event competitions. Equine Vet. J. 1996, 28, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dally, M.; Butler-Dawson, J.; Sorensen, C.J.; Van Dyke, M.; James, K.A.; Krisher, L.; Jaramillo, D.; Newman, L.S. Wet bulb globe temperature and recorded occupational injury rates among sugarcane harvesters in southwest Guatemala. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbary Sartang, A.; Dehghan, H. Investigating relationship between perceptual strain index with indices heat strain score index, wet bulb globe temperature in experimental hot condition. Int. J. Environ. Health Eng. 2015, 4, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Bitencourt, D.P. Maximum wet-bulb globe temperature mapping in central–south Brazil: A numerical study. Meteorol. Appl. 2019, 26, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dernedde, E. A correlation of the wet-bulb globe temperature and botsball heat stress indexes for industry. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1992, 53, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.F.; Blackadder-Coward, J.; Pynn, H. Measuring wet bulb globe temperatures at point-of-exertion in worldwide UK military settings: A longitudinal observational study determining the accuracy of a portable WBGT monitor. BMJ Mil. Health 2023, 169, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Golbabaei, F.; Shamsipour, A.; Forushani, A.R.; Gaeini, A. Consistency between sweat rate and wet bulb globe temperature for the assessment of heat stress of people working outdoor in arid and semi-arid regions. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brake, D. Calculation of the natural (unventilated) wet bulb temperature, psychrometric dry bulb temperature and wet bulb globe temperature from standard psychrometric measurements. J. Mine Vent. Soc. S. Afr. 2001, 54, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi, Y.; Kawabe, T.; Shigeta, Y.; Hirano, Y.; Kusaka, H.; Fudeyasu, H.; Fukao, K. Evaluation of urban thermal environments in commercial and residential spaces in Okayama City, Japan, using the wet-bulb globe temperature index. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 95, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ding, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Field study on the effect of space type, exercise intensity, and wet bulb globe temperature on thermal responses of exercisers. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Abdullah, R.A.; Ibrahim, I.S.; Lai, G.T.; Chaudry, M.H.; Junaid, M.; Iqbal, Z.; Jamal, N.; Aziz, A.F.A.; Salim, A. Effect of Stress Ratio K due to Varying Overburden Topography on Crack Intensity of Tunnel Liner. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2023, 37, 04023026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.; Kuehn, L.; Howat, M. A direct-reading mercury thermometer for the wet bulb globe temperature index. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1969, 47, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyer, H.; Georgescu, M.; Hondula, D.M.; Wardenaar, F.; Vanos, J. Identifying the need for locally-observed wet bulb globe temperature across outdoor athletic venues for current and future climates in a desert environment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.C.; Lau, K.K.-L.; Ren, C.; Ng, E. Characterizing prolonged heat effects on mortality in a sub-tropical high-density city, Hong Kong. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Gu, X.; Song, X. A simplified indoor wet-bulb globe temperature formula to determine acceptable hot environmental parameters in naturally ventilated buildings. Energy Build. 2019, 196, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Zwiers, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Wu, H. Rapid warming in summer wet bulb globe temperature in China with human-induced climate change. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5697–5711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, L.; Stubbs, R.; MacHattie, L. A nomogram for calculation of the wet bulb–globe temperature index. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1970, 48, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Huber, M. Explicit calculations of wet-bulb globe temperature compared with approximations and why it matters for labor productivity. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarh, G.F.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Dewan, A.; Nashwan, M.S.; Shahid, S. Integration of catastrophe and entropy theories for flood risk mapping in peninsular Malaysia. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, B.; Kjellstrom, T. Calculating workplace WBGT from meteorological data: A tool for climate change assessment. Ind. Health 2012, 50, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossent, J.; Elsen, P.; Bauwens, W. Sobol’ sensitivity analysis of a complex environmental model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2011, 26, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Sakamoto, H. Monte Carlo sensitivity analysis method for the effective delayed neutron fraction with the differential operator sampling method. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 140, 107108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, I.M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates. Math. Comput. Simul. 2001, 55, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangang, F.T.; Juneng, L.; Salimun, E.; Sei, K.; Halimatun, M. Climate change and variability over Malaysia: Gaps in science and research information. Sains Malays. 2012, 41, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Masron, T.; Yaakob, U.; Ayob, N.M.; Mokhtar, A.S. Population and spatial distribution of urbanization in Peninsular Malaysia 1957–2000. Geogr. Malays. J. Soc. Space 2012, 8, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ariffin, E.H.; Mathew, M.J.; Roslee, A.; Ismailluddin, A.; Yun, L.S.; Putra, A.B.; Yusof, K.M.K.K.; Menhat, M.; Ismail, I.; Shamsul, H.A.; et al. A multi-hazards coastal vulnerability index of the east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 84, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, P.; Lim, K.C.; Jamei, E. Urban heat island and wind flow characteristics of a tropical city. Sol. Energy 2014, 107, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, Z.A.; Kafy, A.-A.; Saha, M.; Rahim, A.A.; Almulhim, A.I.; Rahaman, S.N.; Fattah, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; S, K.; Faisal, A.-A.; et al. Assessing the impacts of vegetation cover loss on surface temperature, urban heat island and carbon emission in Penang city, Malaysia. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budd, G.M. Wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT)—Its history and its limitations. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.S.M.M.; Shahid, S.; Fahim, A.K.F. Changes in Wet Bulb Globe Temperature and Risk to Heat-Related Hazards: An Overview of Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the OHOW 2022—The 1st International Symposium on One Health, One World, Pattaya City, Thailand, 8–10 December 2022; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sakoi, T.; Mochida, T.; Kurazumi, Y.; Sawada, S.-I.; Horiba, Y.; Kuwabara, K. Expansion of effective wet bulb globe temperature for vapor impermeable protective clothing. J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 71, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, K.M.; Sherwood, S. Exceedance of heat index thresholds for 15 regions under a warming climate using the wet-bulb globe temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kim, K.R.; Shin, J.-Y. Event-based heat-related risk assessment model for South Korea using maximum perceived temperature, wet-bulb globe temperature, and air temperature data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, S.; Hasheminejad, N.; Bateni, M.; Baneshi, M.R.; Shirvan, H.E.; Hemmatjo, R. The association between wet-bulb globe temperature and other thermal indices (DI, MDI, PMV, PPD, PHS, PSI and PSIhr): A field study. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2020, 26, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, C.; Prange, M.; Varma, V.; Steinke, S.; Hebbeln, D.; Mohtadi, M. Holocene variations of thermocline conditions in the eastern tropical Indian Ocean Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015, 114, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houmsi, M.R.; Ismail, Z.b.; Ziarh, G.F.; Hamed, M.M.; Ishak, D.S.b.M.; Muhammad, M.K.I.; Mokhtar, M.Z.b.; Sa’adi, Z.; Shahid, S. Relative Influence of Meteorological Variables of Human Thermal Stress in Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12842. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712842
Houmsi MR, Ismail Zb, Ziarh GF, Hamed MM, Ishak DSbM, Muhammad MKI, Mokhtar MZb, Sa’adi Z, Shahid S. Relative Influence of Meteorological Variables of Human Thermal Stress in Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability. 2023; 15(17):12842. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712842
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoumsi, Mohamad Rajab, Zulhilmi bin Ismail, Ghaith Falah Ziarh, Mohammed Magdy Hamed, Daeng Siti binti Maimunah Ishak, Mohd Khairul Idlan Muhammad, Muhamad Zulhasif bin Mokhtar, Zulfaqar Sa’adi, and Shamsuddin Shahid. 2023. "Relative Influence of Meteorological Variables of Human Thermal Stress in Peninsular Malaysia" Sustainability 15, no. 17: 12842. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712842
APA StyleHoumsi, M. R., Ismail, Z. b., Ziarh, G. F., Hamed, M. M., Ishak, D. S. b. M., Muhammad, M. K. I., Mokhtar, M. Z. b., Sa’adi, Z., & Shahid, S. (2023). Relative Influence of Meteorological Variables of Human Thermal Stress in Peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability, 15(17), 12842. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712842







