Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values and Driving Mechanism in the Yan River Basin from 1990 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
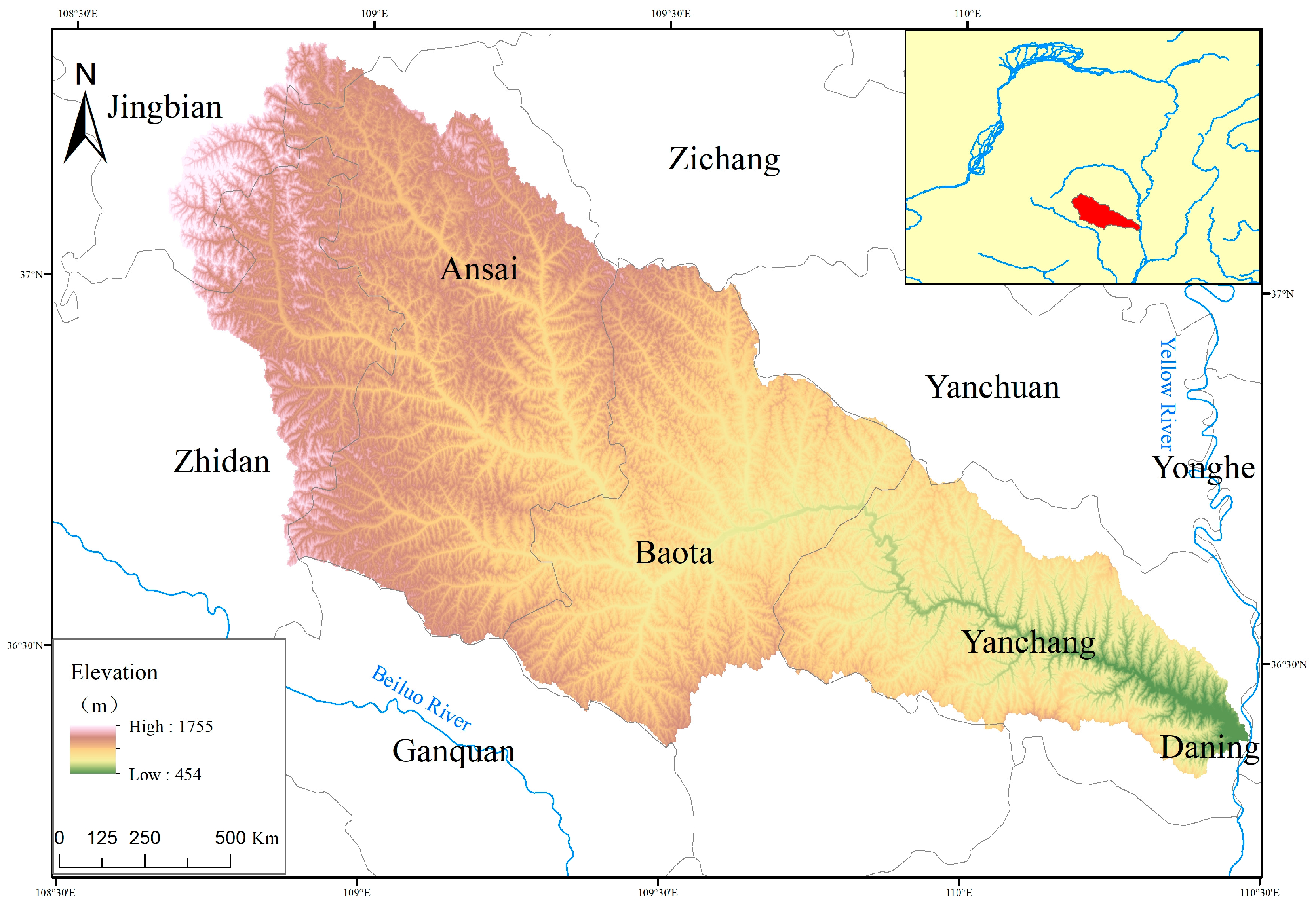
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Construction of the Driving Index System
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Land-Use Structural Information Entropy
2.3.2. ESV Accounting
2.3.3. Elasticity Coefficient
2.4. Geographical Detectors
3. Results
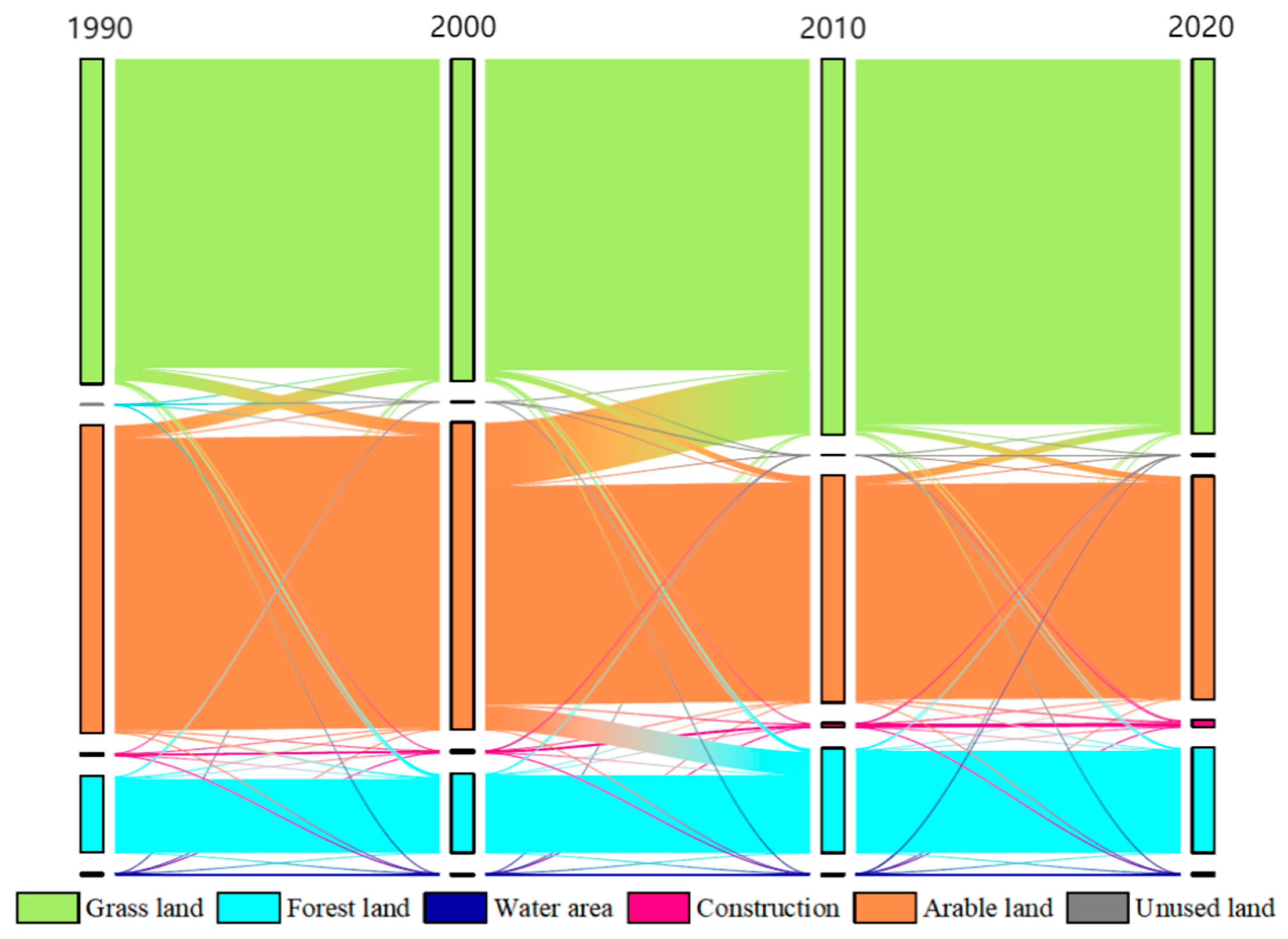
3.1. Changes in Land-Use Structure Characteristics
3.2. The ESV Evolution Characteristics
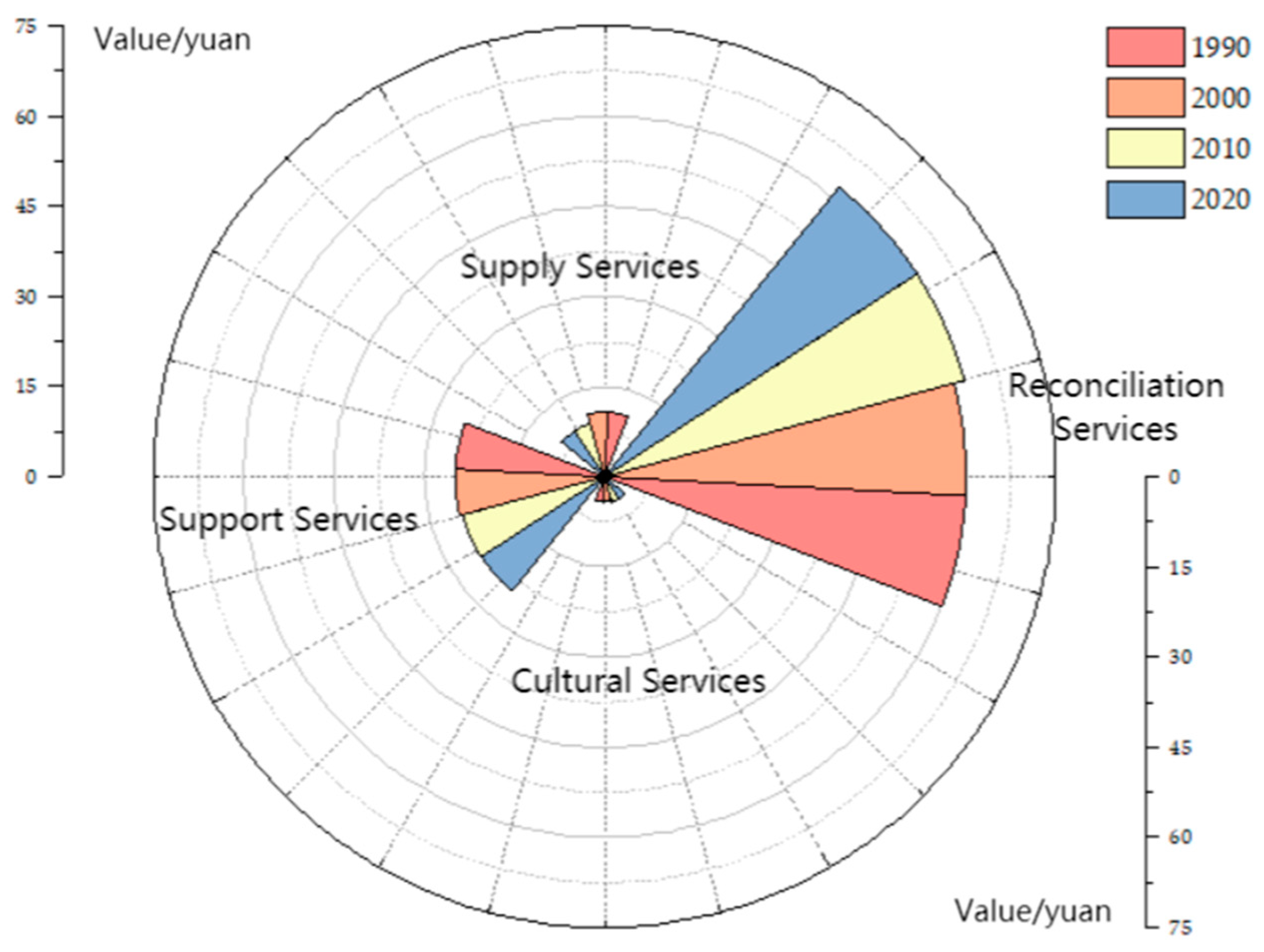
3.2.1. The ESV Temporal Evolution
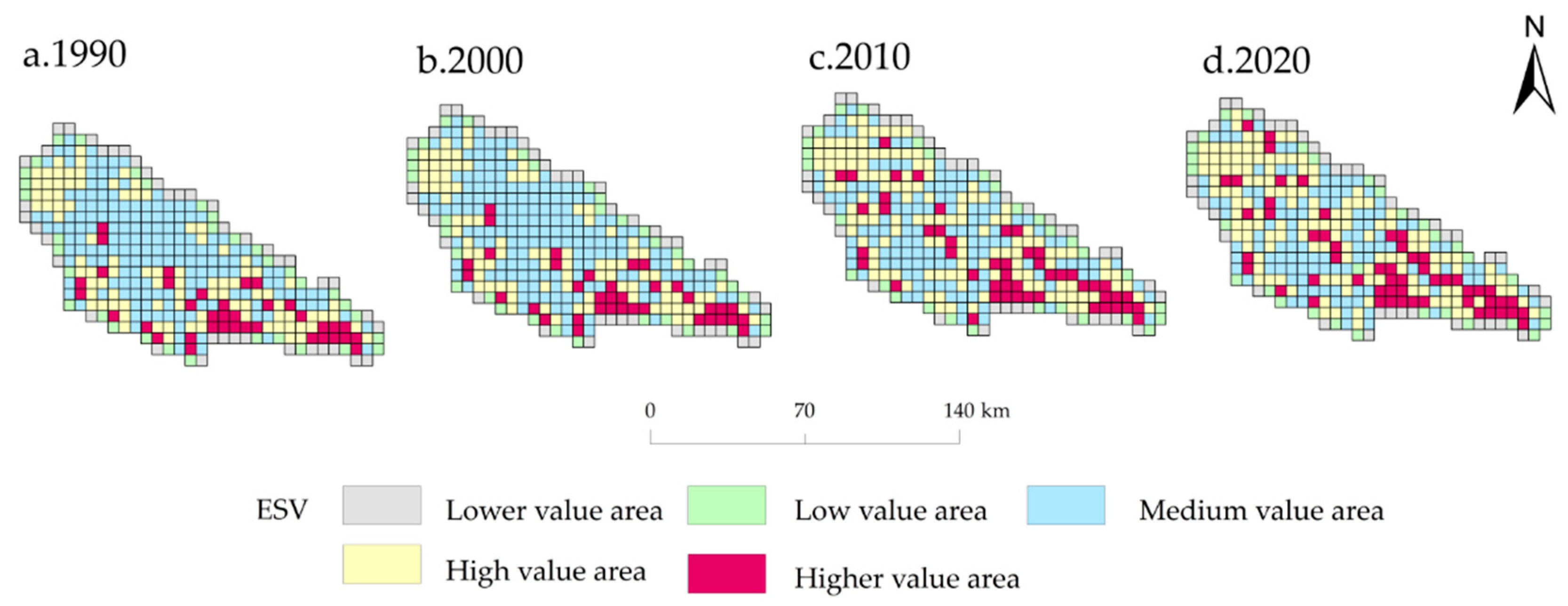
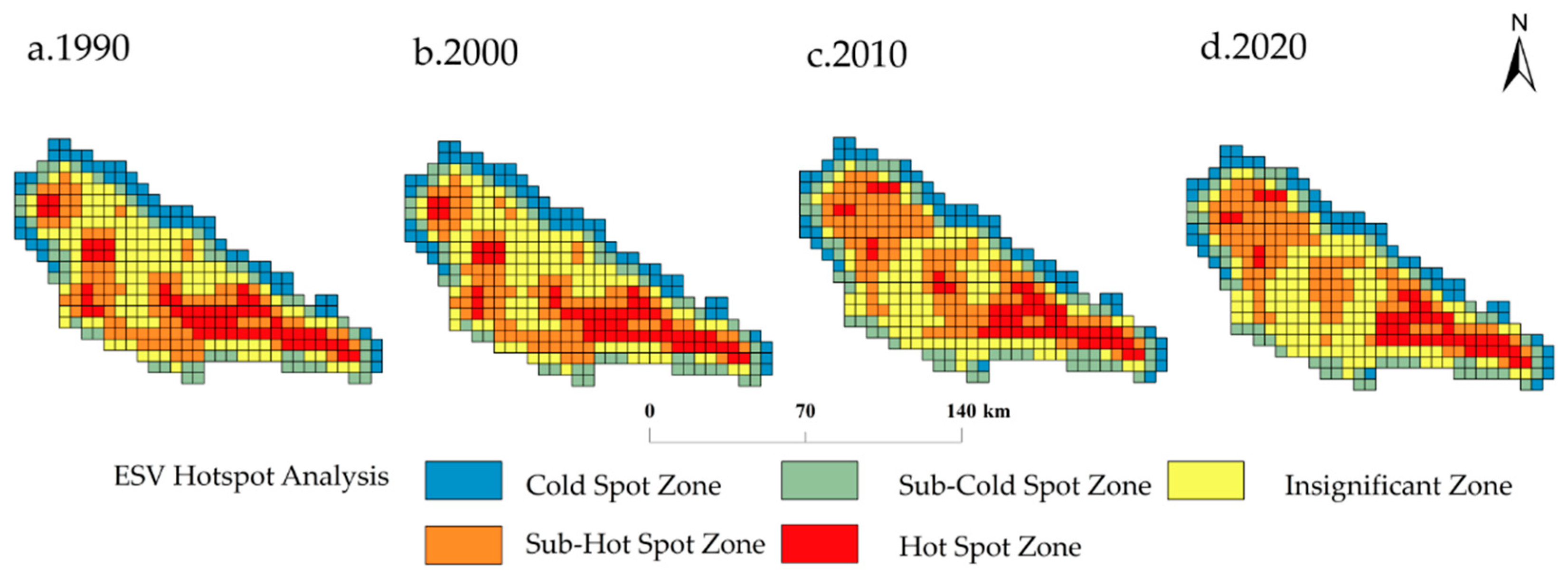
3.2.2. Spatial ESV Land Distribution
3.3. ESV Response to Land-Use Changes
3.4. Driving Mechanisms of Ecosystem Service Values
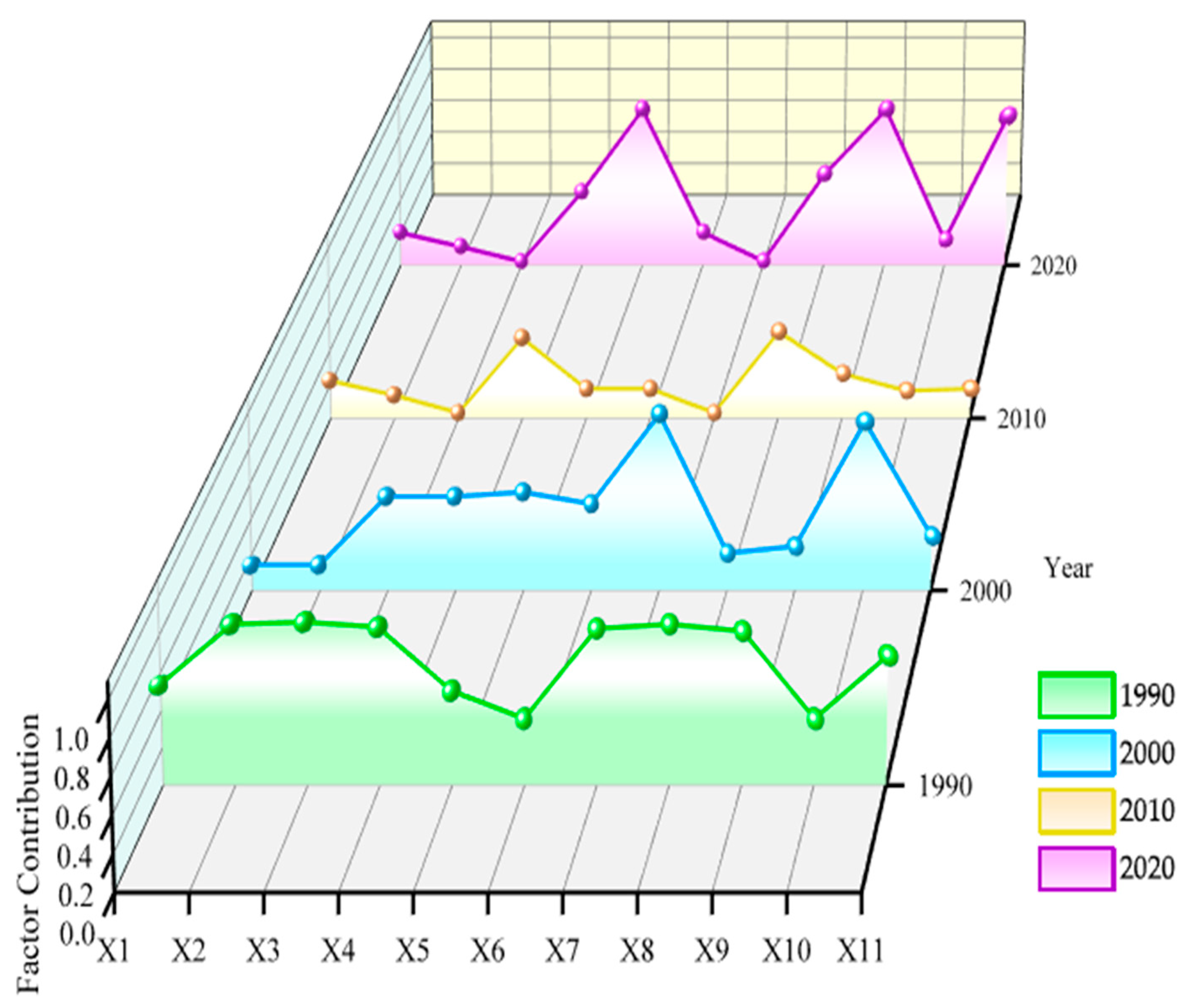
3.4.1. Factor Detection
3.4.2. Interaction Factor Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Pan, J. Impacts and Projections of Land Use and Demographic Changes on Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in the Guanzhong Region, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.W.; Pan, J.F.; Cai, S.Q.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, Y. Trade-offs and Synergies between Social Value and Ecological Value of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Potatso National Park. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dade, M.C.; Mitchell, M.G.E.; McAlpine, C.A.; Rhodes, J.R. Assessing ecosystem service trade-offs and synergies: The need for a more mechanistic approach. Ambio 2018, 48, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.C.; Xi, F.M.; Wang, J.Y.; Bing, L.F.; Du, L.Y. Application of Ecosystem Value in Policy System Design: A Case Study of Fuzhou City, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3815–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, R.; Brander, L.; van der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global estimates of the value of ecosystems and their services in monetary units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G. The relationship between social values for ecosystem services and global land cover: An empirical analysis. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y. Modern Human-earth Relationship and Human-earth System Science. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhang, L.W. Land-use Change and Ecosystem Services: Concepts, Methods and Progress. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, R.; Berrens, R.; Cerda, A.; Li, H.W.; Klingeman, P.C. Developing a bioeconomic model for riverine management: Case of the John Day River, Oregon. Rivers 1993, 4, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Miao, H. A Primary Study on Chinese Terrestrial Ecosystem Services and their Ecological-economic Values. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1999, 5, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.X. Study on Ecosystem Services Value of Food Production in China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2005, 13, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Zhang, L.M.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.M. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Yao, L.Y.; Lang, L.M.; Zhao, M.J. Revaluation of Ecosystem Services in Inland River Basins of China: Based on Meta-Regression Analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 1040–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.J.; Bai, Y.P.; Hu, Y.C.; Deng, X.Z.; Wei, L. Valuation of Ecosystem Services in China under Different SSP-RCP Scenarios. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Jiang, A.X.; Yu, Y.H. Temporal and Spatial Dynamics of Ecosystem Service Value in Benghe River Basin based on Land Use Change. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 269–275+283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, C. Study on Ecosystem Service Value (ESV) Spatial Transfer in the Central Plains Urban Agglomeration in the Yellow River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Ding, J.L.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, G.L. Impact of LUCC on Ecosystem Services Values in the Yili River Basin based on an Intensity Analysis Model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 3106–3118. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.T.; Sun, T.; Wang, J.X.; Fu, Q.; An, C.Y. Annual Dynamic Monitoring of Regional Ecosystem Service Value based on Multi-source Remote Sensing Data: A Case of Central Plains Urban Agglomeration Region. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2019, 39, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Wang, D.C.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, F.C.; Hu, B.X.; Chen, J.H.; Sun, Z.C. Estimation of the Ecosystem Service Value of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration based on Multi-boundary Improvement. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 4192–4204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.T.; Wang, S.J.; Fang, C.L. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Mechanism of Ecosystem Service Value in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 76, 2797–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.Q.; Han, Y.X.; Gao, N.; Ji, L.S.; Gao, H.B.; Tan, X.Q.; Xu, Y.T. Quantity and Equilibrium of Ecosystem Service Value and their Spatial Distribution Patterns in Shandong Province. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.F.; Li, P.J.; Liu, L.C.; Wang, W.T. Ecological Restoration Zoning of Provincial Territorial Space in the Ecologically Fragile Areas of Northwest China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 254–263. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.M.; Lu, X.; Ma, Q. Study on Eco-economic Value Evaluation and Compensation from the Perspective of Small Watershed: A Case Study of Zhuanghe City in Liaoning province. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, T.Y.; Hui, B.H. Economic Value of Forest Ecosystem Services in Huangshan City based on Meta-Analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 42, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Q.; Zhang, J.Q.; Jie, G.; Qian, C.Y. Spatial and Temporal Relations among Land-use Intensity, Ecosystem Services, and Human Well-being in the Longzhong Loess Hilly Region: A Case Study of the Anding District, Gansu Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, B.P.; Pei, T.T.; Ren, X.J.; He, Y. Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Land Use Transition and Ecosystem Service Value in Yuzhong County. Ecol. Sci. 2022, 41, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.H.; Liu, J.; Zhai, L. Reclamation Project Monitoring and Ecosystem Servive Value Change Analysis. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2020, 45, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, Z.X.; Zhu, Q.; Bai, J.Z. Spatiotemporal Change of Soil Conservation Service in Yanhe Watershed. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 28, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.L.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.J.; Lv, Y.H.; Yan, J.W.; Zhang, W.B.; Jin, Z.; Lan, Z.Y. Land Use/Cover Change in the Yellow River Basin based on Google Earth Engine and Complex Network. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, Z.X.; Li, Z.B.; Yu, K.X.; Li, P.; Gao, H.D.; Yao, J.W. Impact of land Use Change on Ecosystem Services Value in Northern Shaanxi. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.Y.; Jiao, C.M.; Han, X.Y.; Jiao, F. Spatio-temporal Transmutation and Impact Factors of Ecosystem Servive Value in Yan’an City from the Perspective of Entropy. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Changes in Farmland Ecosystem Services Value and its Influencing Factors in Xinjiang. J. Shihezi Univ. 2020, 38, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and Prospective. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.P.; Zhang, G.H.; Yang, Q.K. Characteristics of Runoff and Sediment Variation in Yanhe River Basin in Last 50 Years. J. China Hydrol. 2012, 32, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, L.P.; Wen, Z.M.; Zhang, L. Study on the Relationship between Vegetation Change and Runoff-Sediment: A Case of the Yanhe Basin. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2015, 29, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, D.C.; Yao, W.Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, X.M.; Lv, X.Z. Effect of Forest-grass Vegetation on Reducing Flood and Sediment from 1997 to 2006 in Yanhe Basin. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Q. Characteristics of Runoff and Sediment Transport during 1960-2010 and its Response to Grain for Green Project in Yanhe River. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.H.; Zheng, L.N. Soil Erosion Changes in the Yanhe Watershed from 2001 to 2010 based on RUSLE Model. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Wang, F.; Mu, X.M.; Li, R.; He, Y. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Land Use/Land Cover Change (LUCC) over the Past 25 Years in the Yan River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 19, 148–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, H.Z.; Yang, S.T.; Zhou, Q.W.; Luo, Y.; Hou, L.P. Analysis of the Land Use/Cover Change and Driving Forces in Yan River Basin from 2000 to 2010. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.J.; Zheng, F.L.; Yin, R.S. Trend Analysis of Precipitation and Streamflow during 1952–2008 in Yanhe River Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 25, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.H. Variation Characteristics of the Stoichiometry Characterustics of Zonalvegetation Community and Soil in the Yan River Catchment. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, F.L.; Yang, A.M.; Yan, D.H. Impact of Soil and Water Conservation on Runoff and Sediment in Yan River Basin. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J. Temporal Information Entropy and its Application in the Evaluation of Ecological Environment Quality in Yan Watershed. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, Z.X.; Liu, T.; Bai, J.Z. Vegetation Restoration and Ecosystem Soil Conservation Service Value Increment in Yan Watershed, Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2557–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, H. The Impact of Socio-Economic Factors on Sediment Load: A Case Study of the Yanhe River Watershed. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Zhu, Y.N.; Li, T.; Yang, C.R. Response of Ecological Service Value and Quality to Land Use Change in China′s Loess Plateau. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 29, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Y.; Yue, W.Z.; Fang, B.; Feng, S.R. Scale Response Characteristics and Geographic Exploration Mechanism of Spatial Differentiation of Ecosystem Service Values in Dabie Mountain Area, Central China from 1970 to 2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 1904–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.R.; Tang, Q. Human Activity Intensity of Land Surface: Concept, Methods and Application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Li, Y. Evaluating the effectiveness of landscape metrics in quantifying spatial patterns. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.C.; Guo, G.C. Research on Spatio-temporal Evolution of Urban Land-use Structure in Inter-Provincial Border Areas and the Influencing Factors: Based on Information Entropy Theory. Urban Probl. 2022, 33–42+65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, X.Y.; Yu, H.Y. Analysis of Urban Land Use Change based on ArcGIS and Information Entropy Method in Jilin Province. China Soft Sci. Mag. 2020, S1, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.Y.; Fang, B.; Yue, W.Z.; Feng, S.R. Spatial Differentiation of Ecosystem Service Values and its Geographical Detection in Chaohu Basin during 1995–2017. Geogr. Res. 2019, 74, 1904–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.L.; Wu, N. Evaluation of Ecosystem Services Value of Eco-redline Region in Anhui Province. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.X.; Wang, Y.X. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and its Spatial Heterogeneity Mechanism in the Dongjiang River Basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhu, C.A.-O.; Yang, L.; Xie, F. Responses of Ecosystem Services to Urbanization-Induced Land Use Changes in Ecologically Sensitive Suburban Areas in Hangzhou, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.H.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Kuang, B.; Cai, D.W.; Hou, J. Driving Factors and Spatial Differentiation of Urban Land Green Use Efficiency in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; He, Z.Q.; Zhang, T.H. Spatio-temporal Variation of NDVI and Geographical Detection of its Driving Factors in the ‘Grain for Green’ Project in Northern Shaanxi. Ecol. Sci. 2022, 41, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Ma, X.; Feng, M.; Zhou, C.W.; Fu, B.J. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Trade-off and Synergy of Ecosystem Services in Key Vulnerable Ecological Areas in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 7344–7355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Lv, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Yin, L.C.; Yu, D.D. The Effects of Vegetation Coverage Changes on Ecosystem Service and their Threshold in the Loess Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 75, 949–960. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, T.W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Q.Q.; Liu, D. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Ecosystem Service Value and its Influencing Factors in Shaanxi Province based on GWR. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Lv, Y.H.; Fu, B.J.; Hu, W.Y. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment Under the Influence of Typical Human Activities in Loess Plateau, Northern Shaanxi. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2019, 35, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary Indicators | Specific Indicators | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| natural factors | temperature (X1) | China Meteorological Data Sharing Network (http://data.cma.cn/) (accessed on 3 January 2023) DEM data from Geospatial Data Cloud (http://www.gscloud.cn/) (accessed on 3 January 2023) |
| slope (X2) | ||
| precipitation (X3) | ||
| elevation (X4) | ||
| socio-economic factors | GDP per land (X5) | Statistical Yearbook of Shaanxi Province, Statistical Yearbook of Yan’an City, Statistical Yearbook of Yulin City; Calculated with reference to the relevant literature [50] |
| urbanization rate (X6) | ||
| population density (X7) | ||
| human activity intensity (X8) | ||
| landscape pattern factors | landscape diversity (X9) | SHDI and AI indices were selected in Fragstats 4.2 landscape categories to represent landscape diversity and landscape connectivity, respectively [51] |
| landscape connectivity (X10) | ||
| policy factor | afforestation area (X11) | Statistical Yearbook of Shaanxi Province, Statistical Yearbook of Yan’an City, Statistical Yearbook of Yulin City |
| Service Type | Land Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Type | Secondary Type | Arable Land | Forest Land | Grassland | Water Area | Unused Land |
| supply services | food production | 1088 | 323 | 299 | 839 | 13 |
| raw material production | 512 | 743 | 440 | 467 | 38 | |
| water resource supply | 26 | 384 | 243 | 6966 | 26 | |
| regulation services | gas regulation | 858 | 2443 | 1545 | 1710 | 141 |
| climate regulation | 461 | 7309 | 4085 | 3771 | 128 | |
| environmental purification | 128 | 2142 | 1349 | 5858 | 397 | |
| hydrological regulation | 346 | 4783 | 2992 | 80,974 | 269 | |
| support services | soil conservation | 1319 | 2974 | 1882 | 2074 | 166 |
| nutrient cycling maintenance | 154 | 227 | 145 | 160 | 13 | |
| biodiversity | 166 | 2708 | 1712 | 6672 | 154 | |
| cultural services | aesthetic landscape | 77 | 1188 | 756 | 4239 | 64 |
| Land Type | Parameter | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arable land | area/hm2 | 329,423.22 | 328,995.02 | 242,727.01 | 238,988.24 |
| proportion | 43.11% | 43.05% | 31.76% | 31.27% | |
| forest land | area/hm2 | 81,979.47 | 85,135.25 | 112,421.75 | 112,809.56 |
| proportion | 10.73% | 11.14% | 14.71% | 14.76% | |
| grassland | area/hm2 | 347,502.87 | 344,613.32 | 401,803.35 | 400,981.28 |
| proportion | 45.47% | 45.09% | 52.58% | 52.47% | |
| water area | area/hm2 | 2694.06 | 2511.12 | 2415.63 | 2552.97 |
| proportion | 0.35% | 0.33% | 0.32% | 0.33% | |
| construction land | area/hm2 | 2382.39 | 2698.75 | 4718.36 | 7678.23 |
| proportion | 0.31% | 0.35% | 0.62% | 1.00% | |
| unused land | area/hm2 | 249.39 | 248.88 | 114.57 | 1183.85 |
| proportion | 0.03% | 0.03% | 0.01% | 0.15% | |
| information entropy H | 0.4348 | 0.4377 | 0.4496 | 0.4602 | |
| equilibrium degree J | 0.5587 | 0.5625 | 0.5777 | 0.5914 | |
| dominance degree I | 0.5652 | 0.4375 | 0.4223 | 0.4086 | |
| Land Type | ESVs/Million | Rate of Change/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 1990–2020 | |
| arable land | 169,156.36 | 168,942.07 | 124,705.76 | 122,775.06 | −0.13 | −26.18 | −1.55 | −27.42 |
| forest land | 206,778.78 | 214,937.26 | 283,831.14 | 284,811.82 | 3.95 | 32.05 | 0.35 | 37.74 |
| grassland | 536,803.68 | 532,217.03 | 620,347.87 | 619,120.54 | −0.85 | 16.56 | −0.20 | 15.33 |
| water area | 30,639.62 | 28,550.51 | 27,440.95 | 28,998.83 | −6.82 | −3.89 | 5.68 | −5.36 |
| unused land | 35.13 | 35.10 | 16.07 | 166.52 | −0.08 | −54.20 | 935.88 | 374.02 |
| Mode | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land-Use Conversion | ESVs Change/Billion Yuan | Contribution/% | Land-Use Conversion | ESVs Change/Billion Yuan | Contribution/% | Land-Use Conversion | ESVs Change/Billion Yuan | Contribution/% | |
| improvement | 1→3 | 4951.7 | 81.1 | 1→3 | 30,578.7 | 44.29 | 1→3 | 4172.1 | 79.00 |
| 2→3 | 254.4 | 4.2 | 1→2 | 2918.6 | 4.23 | 2→3 | 519.6 | 9.84 | |
| 1→2 | 113.7 | 1.9 | 2→3 | 266.3 | 0.39 | 1→2 | 245.0 | 4.64 | |
| 4→3 | 70.3 | 1.2 | 6→3 | 84.5 | 0.12 | 5→3 | 150.1 | 2.84 | |
| 4→1 | 29.00 | 0.5 | 4→3 | 41.9 | 0.06 | 4→3 | 30.0 | 0.57 | |
| Total | 5419.1 | 88.7 | Total | 33,890.1 | 49.09 | Total | 5116.8 | 96.89 | |
| degradation | 3→1 | 5101.1 | 63.5 | 3→1 | 2893.2 | 19.41 | 3→1 | 3439.4 | 49.27 |
| 3→2 | 1118.5 | 13.9 | 3→2 | 942.3 | 6.32 | 3→5 | 878.1 | 12.58 | |
| 2→1 | 75.4 | 0.9 | 1→5 | 262.1 | 1.76 | 3→2 | 634.7 | 9.09 | |
| 1→5 | 56.1 | 0.7 | 3→5 | 252.1 | 1.69 | 3→6 | 461.2 | 6.61 | |
| 3→4 | 44.2 | 0.6 | 2→1 | 107.7 | 0.72 | 1→5 | 218.0 | 3.12 | |
| Total | 6395.3 | 79.6 | Total | 4457.3 | 29.90 | Total | 5631.4 | 80.67 | |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.202 | ||||||||||
| X2 | 0.227 ** | 0.115 | |||||||||
| X3 | 0.265 ** | 0.268 * | 0.022 | ||||||||
| X4 | 0.959 * | 0.492 ** | 0.999 * | 0.455 | |||||||
| X5 | 0.979 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.965 | ||||||
| X6 | 0.2279 ** | 0.227 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.959* | 1 ** | 0.205 | |||||
| X7 | 0.979 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.966 ** | 1 ** | 0.965 | ||||
| X8 | 0.268 ** | 0.181 ** | 0.268 * | 0.533 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.157 | |||
| X9 | 0.268 ** | 0.268 * | 0.053 ** | 0.999 * | 0.999 ** | 0.268 ** | 0.999 ** | 0.268 * | 0.025 | ||
| X10 | 1 * | 0.971 * | 1 * | 1 ** | 0.971 ** | 1 * | 0.971 ** | 0.971 * | 1 * | 0.565 | |
| X11 | 0.979 ** | 1 ** | 1 * | 0.948 ** | 0.979 ** | 1 ** | 0.979 ** | 1 ** | 1 * | 1 ** | 0.924 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, W.; Zhang, J. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values and Driving Mechanism in the Yan River Basin from 1990 to 2020. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612550
Zheng W, Zhang J. Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values and Driving Mechanism in the Yan River Basin from 1990 to 2020. Sustainability. 2023; 15(16):12550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612550
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Wenxin, and Jian Zhang. 2023. "Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values and Driving Mechanism in the Yan River Basin from 1990 to 2020" Sustainability 15, no. 16: 12550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612550
APA StyleZheng, W., & Zhang, J. (2023). Study on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values and Driving Mechanism in the Yan River Basin from 1990 to 2020. Sustainability, 15(16), 12550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612550





