Research on the Impact of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Policies on Carbon Emission Efficiency of the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective of Policy Collaboration Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Measuring the Level of Collaboration of ESER Policies in the Yellow River Basin
2.1. Policy Quantitative Criteria Design
2.1.1. Policy Strength
2.1.2. Policy Objectives
2.1.3. Policy Measures
2.2. Policy Collaboration Model Construction
2.2.1. Policy Objectives Collaboration
2.2.2. Policy Measures Collaboration
2.3. Policy Collaboration Measurement of ESER
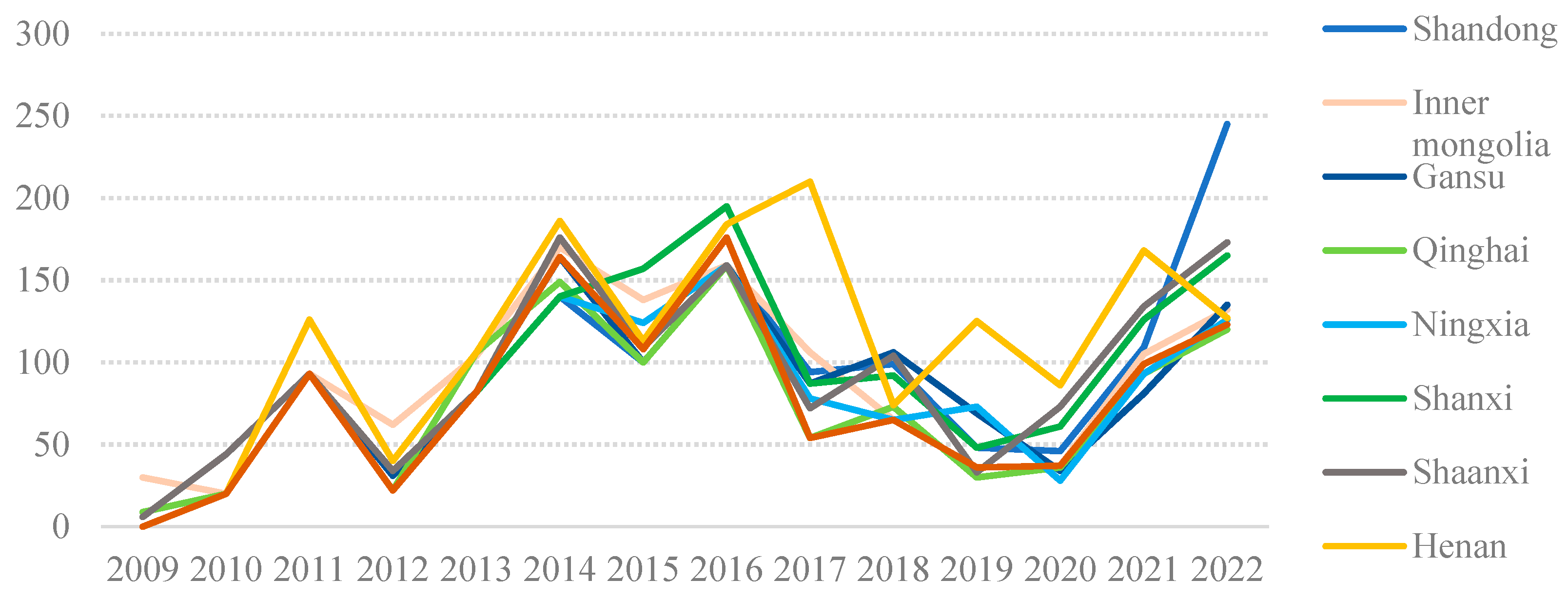
2.3.1. Collaboration Analysis of Policy Objectives
2.3.2. Collaboration Analysis of Policy Measures
3. Measurement and Analysis of Carbon Emission Efficiency of Prefecture-Level Cities in the Yellow River Basin
3.1. Measurement Index System Construction
3.2. Data Collection and Collation
3.3. Carbon Emission Efficiency Measurement
4. Impact of ESER Policies Collaboration on Carbon Emission Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin
4.1. Panel Data Model Construction
4.2. Initial Experience Judgment
4.3. Empirical Analysis
4.4. Model Testing
4.4.1. Test for Policy Lag Effect
4.4.2. Robustness Tests
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X. Where is the pathway to sustainable urban development? Coupling coordination evaluation and configuration analysis between low-carbon development and eco-environment: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z. Evaluation and prediction of the level of high-quality development: A case study of the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hou, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhai, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, J.; Zhang, B.; Xu, H. Coordination study on ecological and economic coupling of the yellow river basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.; Yue, L.; Ahmad, F.; Draz, M.U.; Chandio, A.A.; Ahmad, M.; Amin, W. Empirical investigation of urban land use efficiency and influencing factors of the Yellow River basin Chinese cities. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of ecological city and analysis of obstacle factors under the background of high-quality development: Taking cities in the Yellow River Basin as examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhou, Q. Study on coupling coordination and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment of cities along the Yellow River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6898–6912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fang, S.; Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Nan, D.; Yang, Y. Exploring the impact of urban form on urban land use efficiency under low-carbon emission constraints: A case study in China’s Yellow River Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 311, 114866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Y.; Song, S.; Wu, C. Carbon-efficient scheduling of flow shops by multi-objective optimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 248, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cheng, Z.; Tong, Y.; He, B. The Interaction Mechanism of Tourism Carbon Emission Efficiency and Tourism Economy High-Quality Development in the Yellow River Basin. Energies 2022, 15, 6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Kong, F.; Choi, Y.; Zhou, P. The effect of size-control policy on unified energy and carbon efficiency for Chinese fossil fuel power plants. Energy Policy 2014, 70, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, Z.; Sun, H. Analysis of Carbon Emission Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin in China: Spatiotemporal Differences and Influencing Factors. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Ahmad, M.; Xue, C. Analysis of influencing factors of carbon emissions in resource-based cities in the Yellow River basin under carbon neutrality target. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 23847–23860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission Efficiency in the Yellow River Basin of China: Comparative Analysis of Resource and Non-Resource-Based Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Gu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y. Research on carbon emission efficiency space relations and network structure of the Yellow River Basin City cluster. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Carbon emission efficiency measurement and influencing factor analysis of nine provinces in the Yellow River basin: Based on SBM-DDF model and Tobit-CCD model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33263–33280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y. Energy-saving and emission-reduction technology selection and CO2 emission reduction potential of China’s iron and steel industry under energy substitution policy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bao, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J. Circular Economy of Resource-Based Industries in Coastal Cities and the Influence on Sustainable Development. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 98 (Suppl. S1), 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. Impact of environmental regulation intensity on green innovation efficiency in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Impact of energy saving and emission reduction policy on urban sustainable development: Empirical evidence from China. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mi, J.J. Energy-saving and Emission Reduction Effects of China’s Auto Tax Policy. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 214, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Xu, C.; Lin, B. Does the Emission Trading Scheme achieve the dual dividend of reducing pollution and improving energy efficiency? Micro evidence from China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Kang, C.; Zhang, H. China’s efforts towards carbon neutrality: Does energy-saving and emission-reduction policy mitigate carbon emissions? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J. Effectiveness of the Coordination of Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Policies in China: From 1997 to 2011. Manag. Rev. 2015, 27, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Ye, Y.; Guan, X.; Yin, J.H.; Lv, X.L. Difference and collaboration in Jing-Jin-Ji’s energy saving and emission reduction policy measurers. J. Manag. Sci. China 2018, 21, 111–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Z. Positive or negative coordination? Spatiotemporal coupling analysis between economic growth and carbon neutrality in the Yellow River Basin. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z. An Analysis on the Effectiveness of Policy Objectives of Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction in China—Based on the Study of 1052 Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction Policies. East China Econ. Manag. 2015, 29, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Sun, W.; Zhong, W. The evolution of Chinese technological and innovational policies and the empirical research on the performance (1978–2006). Sci. Res. Manag. 2008, 29, 134–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Xiu, J.; Chai, J. Are energy-saving and emission reduction policy measures effective for industrial structure restructuring and upgrading? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 123–133. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in date envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, J. Energy efficiency analysis on Chinese industrial sectors: An improved Super-SBM model with undesirable outputs. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Jiang, H. Regional low-carbon economy efficiency in China: Analysis based on the Super-SBM model with CO2 emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhu, J. Is the implementation of energy saving and emission reduction policy really effective in Chinese cities? A policy evaluation perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Score | Policy Strength Scoring Criteria |
|---|---|
| 5 | Laws and regulations promulgated by the National People’s Congress and its Standing Committee. |
| 4 | Various directives, regulations, provisions, as well as the orders of ministries and commissions promulgated by the State Council and local people’s congresses and their standing committees. |
| 3 | Provisional regulations and provisions, decisions, opinions, methods, standards and programs promulgated by the State Council, as well as regulations, provisions and decisions promulgated by ministries and provincial governments. |
| 2 | Action plans, opinions, approaches, guidelines, rules, programs, conditions, interim regulations and standards issued by various ministries and provincial government departments. |
| 1 | Simple notices, announcements and planning. |
| Type of Policy Objectives | Contents of Policy Objective |
|---|---|
| PP | Strengthen environmental monitoring, formulate environmental protection laws and regulations, and strengthen law enforcement, etc. |
| EC | Strengthen environmental education and guide the public and enterprises to raise awareness of energy conservation and emission reduction, etc. |
| IEE | Promote the use of energy-saving and environmental protection equipment, strengthen energy-saving management, promote the development of clean energy, adjust energy production and consumption patterns, etc. |
| PI | Technological innovation, product innovation, service upgrade and development of human resources, etc. |
| IE | Strengthen policy guidance, establish a sound responsibility system and assessment mechanism for ESER, etc. |
| PE | Promote cleaner production technologies, strengthen technological innovation and research and development, etc. |
| OE | Develop new energy sources, increase the use of clean and renewable energy, etc. |
| Score | Policy Objective Scoring Criteria |
|---|---|
| 5 | Clearly put forward energy conservation and emission reduction policies, from legislation, publicity, implementation and other aspects of a comprehensive and strong guidance. |
| 4 | Clearly put forward energy conservation and emission reduction from a legislative perspective, with detailed provisions for energy conservation and emission reduction in relevant areas. |
| 3 | Promote ESER in various sectors or areas and have specific measures. |
| 2 | Clearly put forward the corresponding ESER targets, but did not propose specific measures. |
| 1 | Only the targets related to ESER are involved. |
| Type of Policy Measures | Contents of Policy Measures |
|---|---|
| AM | Government administrative licensing, supervision and inspection and approval and other mandatory means. |
| GM | Publicity, promotion and project demonstration, etc. |
| FT | Financial taxes, subsidies, etc. |
| PM | Personnel training, rewards and punishments, scheduling arrangements, etc. |
| FM | Credit, finance, etc. |
| TM | The government encourages research and development, application and promotion of ESER-related technologies, etc. |
| OE | Related to accounting for expenses, costs, prices and depreciation. |
| Score | Policy Objective Scoring Criteria |
|---|---|
| 5 | Establishes very specific measures and methodological approaches and clearly requires the relevant subjects to enforce. |
| 4 | Relatively specific measures and methods have been developed and are mandatory, but the subject of compulsion is not specified. |
| 3 | Relatively specific measures and approaches are developed, but not required to be enforced. |
| 2 | Develop or involve relevant policies but measures and methods are not specific. |
| 1 | Only relevant policy objectives are addressed but no relevant measures and approaches are developed. |
| Guideline Layer | Indicator Name | Indicator Description |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Energy Input | Total energy consumption of prefecture-level cities (million tons of standard coal) |
| Labor Input | Year-end employment in prefecture-level cities (10,000 people) | |
| Capital Investment | Fixed asset investment in prefecture-level cities (million yuan) | |
| Expected Outputs | Gross Regional Product | GDP of prefecture-level cities (million yuan) |
| Non-desired Outputs | Carbon Emissions | CO2 emissions from prefecture-level cities (million tons) |
| Variables | Obs | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 627 | 0.613 | 0.306 | 0.138 | 1.456 |
| DOC | 627 | 14.109 | 6.61 | 0 | 32 |
| MOC | 627 | 67.15 | 42.588 | 28.2 | 485.625 |
| DMC | 627 | 15.509 | 9.052 | 0 | 41 |
| MMC | 627 | 129.443 | 197.892 | 22.667 | 1482.333 |
| ECO | 627 | 50.69 | 10.184 | 15.93 | 73.92 |
| POP | 627 | 448.372 | 273.106 | 74 | 1259 |
| Tech | 627 | 48,594.643 | 73,572.207 | 1338 | 668,363 |
| DOC | MOC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (1) | (2) | |
| CE | 0.00474 ** (2.03) | 0.00434 * (1.85) | −0.0000962 (−0.54) | −0.000126 (−0.71) |
| POP | −0.000178 (−0.62) | −0.000161 (−0.56) | ||
| ECO | 0.00166 (0.88) | 0.00207 (1.09) | ||
| Tech | 0.000000261 * (1.78) | 0.000000282 * (1.92) | ||
| MDC | MMC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (1) | (2) | |
| CE | 0.00413 ** (2.54) | 0.00435 *** (2.67) | 0.000120 *** (3.42) | 0.000121 *** (3.45) |
| POP | −0.000240 (−0.84) | −0.000163 (−0.57) | ||
| ECO | 0.00217 (1.16) | 0.00183 (0.98) | ||
| Tech | 0.000000292 ** (2.01) | 0.000000289 ** (1.99) | ||
| MDC | MMC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EEP(0) | 0.00434 * (1.85) | −0.000126 (−0.71) | 0.00435 *** (2.67) | 0.000121 *** (3.45) |
| EEP(1) | 0.00180 (0.73) | 0.0000239 (0.13) | 0.00174 (1.01) | −0.0000304 (−0.25) |
| EEP(2) | 0.00304 (1.22) | 0.0000858 (0.47) | 0.000621 (0.35) | −0.000256 (−1.35) |
| EEP(3) | 0.00557 ** (2.20) | 0.000258 (1.38) | 0.00167 (0.91) | 0.0000406 (0.21) |
| Original Control Variables | Substitution of Control Variables | Adding Control Variables | Tailoring Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOC | 0.00434 * (1.85) | 0.00491 ** (2.13) | 0.00411 * (1.74) | 0.00427 * (1.82) |
| MOC | −0.000126 (−0.71) | −0.0000980 (−0.56) | −0.000103 (−0.57) | −0.000695 (−1.55) |
| DMC | 0.00435 *** (2.67) | 0.00449 *** (2.81) | 0.00405 ** (2.42) | 0.00420 ** (2.58) |
| MMC | 0.000121 *** (3.45) | 0.000105 *** (3.01) | 0.000117 *** (3.16) | 0.000118 *** (3.38) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, L.; Yi, N.; Li, Z.; Su, Z. Research on the Impact of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Policies on Carbon Emission Efficiency of the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective of Policy Collaboration Effect. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12051. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512051
Ren L, Yi N, Li Z, Su Z. Research on the Impact of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Policies on Carbon Emission Efficiency of the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective of Policy Collaboration Effect. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):12051. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512051
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Lingzhi, Ning Yi, Zhiying Li, and Zhaoxian Su. 2023. "Research on the Impact of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Policies on Carbon Emission Efficiency of the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective of Policy Collaboration Effect" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 12051. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512051
APA StyleRen, L., Yi, N., Li, Z., & Su, Z. (2023). Research on the Impact of Energy Saving and Emission Reduction Policies on Carbon Emission Efficiency of the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective of Policy Collaboration Effect. Sustainability, 15(15), 12051. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512051







