Assessing the Impact of Engineering Measures and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Erosion: A Case Study in Osmancık, Türkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
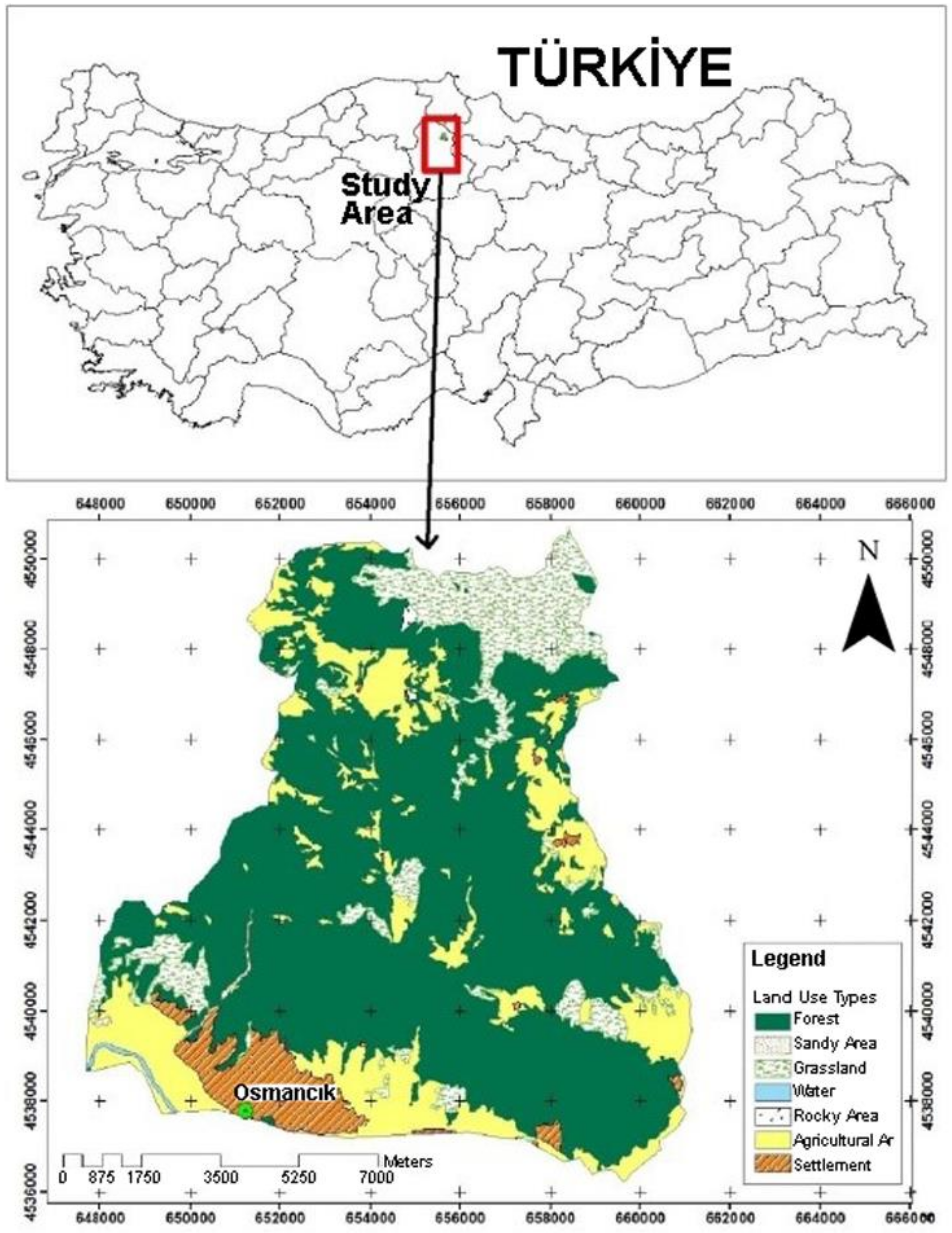
2.1. Study Site
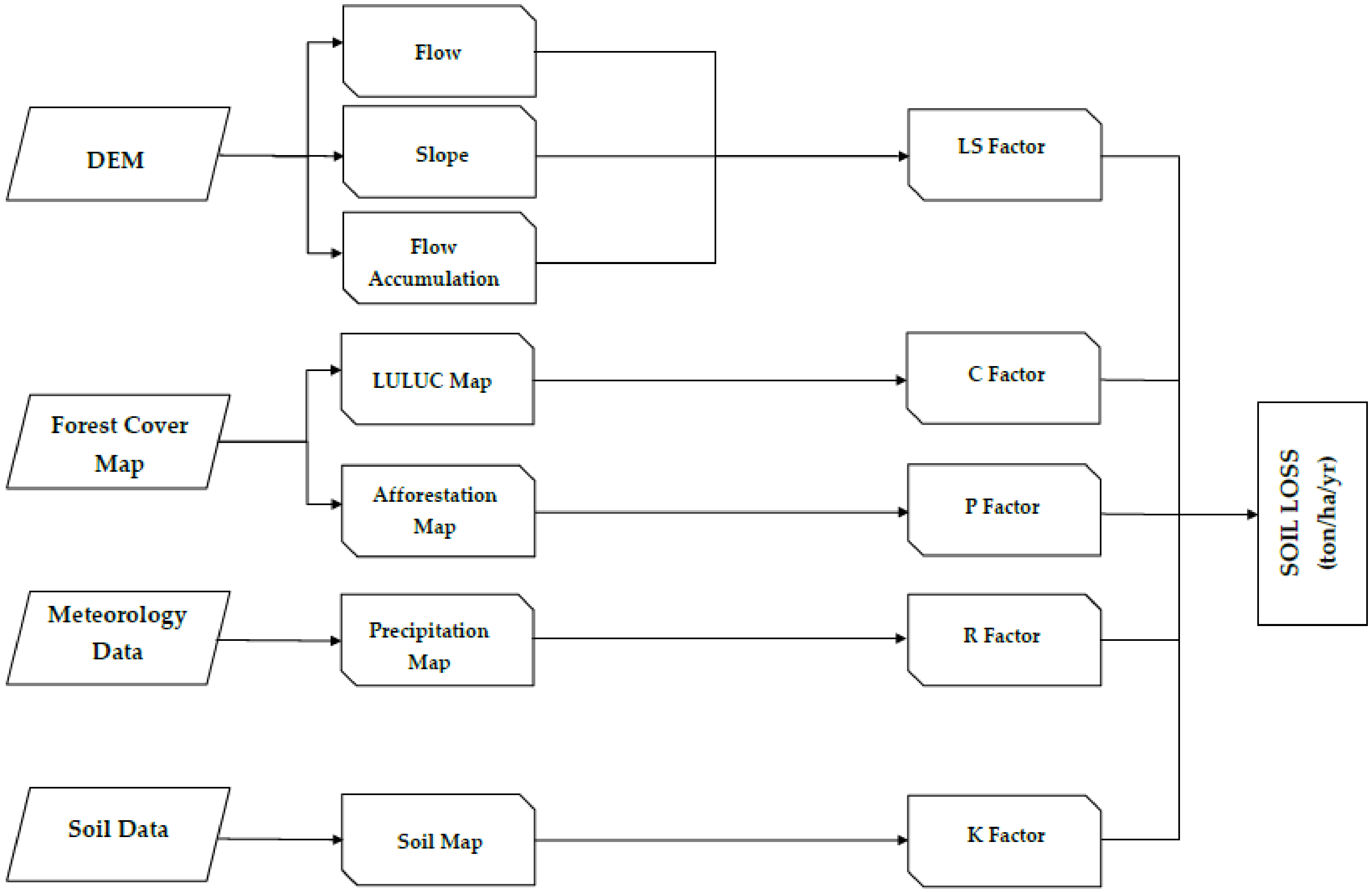
2.2. Methods
Soil Loss Estimation
3. Results
- -
- Forest areas (0–30% ground cover) increased by 3473 ha; the total potential soil loss decreased by 80.45 t ha−1 year−1.
- -
- Since forest areas with 30–100% ground cover did not exist in 1970, comparisons cannot be made between them.
- -
- Grassland areas decreased by 3611 ha, total potential soil loss in this class has increased by 66.37 t ha−1 year−1.
- -
- Agricultural land decreased by 1102 ha over the past fifty years, and potential soil loss decreased by 97 t ha−1 year−1.
- -
- Although there was an expansion of the residential area by 520 hectares, the potential soil loss experienced a reduction of 158 t ha−1 year−1 (Table 6).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pimentel, D. Soil erosion: A food and environmental threat. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2006, 8, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Shi, Z.; Behrens, T.; Chappell, A.; Bui, E. Assimilating satellite imagery and visible-near infrared spectroscopy to model and map soil loss by water erosion in Australia. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 77, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L.; Tye, A.; Obst, C.G. Soil natural capital in Europe; A framework for state and change assessment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, H.; Kavvas, M.L. A review of hillslope and watershed scale erosion and sediment transport models. Catena 2005, 64, 247–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggelaar, C.D.; Lal, R.; Eswaran, H.; Breneman, V.E.; Reich, P.F. Land quality, agricultural productivity, and food security: Biophysical processes and economic choices at local, regional, and global levels. In Crop Yield Losses to Soil Erosion at Regional and Global Scales: Evidence from Plot-Level and GIS Data; Wiebe, K., Ed.; Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd.: Cheltenham, UK, 2003; pp. 262–279. [Google Scholar]
- Erpul, G.; İnce, K.; Demirhan, A.; Küçümen, A.; Akdağ, M.A.; Demirtaş, I.; Sarıhan, B.; Çetin, E.; Şahin, S. Water Erosion Provincial Statistics—Soil Erosion Control Strategies (Sustainable Land/Soil Management Practices and Approaches), 1st ed.; General Directorate of Combating with Desertification and Erosion: Ankara, Turkey, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Avcı, B.C.; Kesgin, E.; Atam, M.; Tan, R.I. Spatial-Temporal Response of Sediment Loads to Climate Change and Soil Conservation Practices in the Northern Aegean Watershed, Türkiye. Water 2023, 15, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H. Impacts of land use and soil conservation measures on runoff and soil loss from two contrasted soils in the black soil region, northeastern China. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, 14886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wei, W.; Chen, L. Effects of terracing practices on water erosion control in China: A meta-analysis. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, Z. Soil and Water Conservation Effects of Contour Reverse Slope Terraces on Red Clay Sloping Farmland against Short and Heavy Rainfall. Geofluids 2023, 2023, 9479632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggau, P.; Kuhwald, M.; Duttmann, R. Effects of contour farming and tillage practices on soil erosion processes in a hummocky watershed. A model-based case study highlighting the role of tramline tracks. Catena 2023, 228, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebabu, K.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsubo, M.; Adgo, E.; Fenta, A.A.; Meshesha, D.T.; Berihun, M.L.; Sultan, D.; Vanmaercke, M.; et al. Global analysis of cover management and support practice factors that control soil erosion and conservation. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhai, R.; An, Y.; Pereira, P. Quantifying the effects of contour tillage in controlling water erosion in China: A meta-analysis. Catena 2020, 195, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Meng, L. Effect of topographic variations and tillage methods on gully erosion in the black soil region: A case-study from Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3786–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Dahal, K. Problems associated with implementation of bioengineering in hill road construction in Nepal. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 70, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira-Caballero, V.G.; Martínez-Menez, M.R.; Romero-Manzanares, A.; García-Moya, E.; Ríos-Berber, J.D.; Rubio-Granados, E. Morphometry of gullies and bioengineering for sediment retention in the Mixteca Region of Oaxaca, Mexico. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2020, 20, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenhuber, P.L.W.; dos Santos Sousa, R.; Dewes, J.J.; Rauch, H.P.; Sutili, F.J.; Hörbinger, S. Performance assessment of a soil and water bioengineering work on the basis of the flora development and its associated ecosystem processes. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 186, 106840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Cui, L.; Niu, H.; Zu, P.; Cao, M. Synergistic effects of vegetation restoration and check dams on water erosion in a slope-gully system. L. Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 3581–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Mei, S.; Yang, M. Experimental study on predicting head-cut migration rate of check dams. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Chen, D.; Ran, L.; Fang, N.; Ni, L.; Shi, Z. Effects of soil and water conservation measures on sediment delivery processes in a hilly and gully watershed. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, G.; Van De Wiel, M.J.; De Clercq, W.P. Intersecting views of gully erosion in South Africa. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2023, 48, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S. Effects of Vegetation Root on Erosion Degree Under Different Arrangements of River Banks. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 23–28 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.; Alsafadi, K.; Talukdar, S.; Kiwan, S.; Hennawi, S.; Alshihabi, O.; Sharaf, M.; Harsanyie, E. Estimation of soil erosion risk in southern part of Syria by using RUSLE integrating geo informatics approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2020, 20, 100375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issaka, S.; Ashraf, M.A. Impact of soil erosion and degradation on water quality: A review. Geol. Ecol. Landscapes 2017, 1, 1301053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning (No. 537), 1st ed.; USA Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, D.K.M.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Zerihun, M.; Mohammedyasin, M.S.; Sewnet, D.; Adem, A.A.; Lakew, M. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE, GIS and remote sensing in NW Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg. 2018, 12, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.U.; Erpul, G.; Basaran, M.; Erdogan, H.E. Use of USLE/GIS technology integrated with geostatistics to assess soil erosion risk in different land uses of Indagi Mountain Pass—Çankiri, Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. Revised universal soil loss equation (Rusle). J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukharamova, S.; Saveliev, A.; Ivanov, M.; Gafurov, A.; Yermolaev, O. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at the european part of Russia. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.; Xie, S.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Nie, X. Long-term effect of soil and water conservation measures on runoff, sediment and their relationship in an orchard on sloping red soil of southern China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European scale. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K. Mapping spatio-temporal dynamics of the cover and management factor (C-factor) for grasslands in Switzerland. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, R.A.H. Understanding the Effect of Changing Land Use on Floods and Soil Erosion in the Cagayan De Oro Catchment. Ph.D. Thesis, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, A.U.; Aytaş, İ. Effects of soil erosion on doline lake degradation within karst landscapes: Bakkal Lake, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staff, S.S. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Yılmaz, E.; Çiçek, İ. Thornthwaite climate classification of Turkey<p>Türkiye Thornthwaite iklim sınıflandırması. J. Hum. Sci. 2016, 13, 3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; McCool, D.K.; Renard, K.G.; Moldenhauer, W.C. Conversion of the universal soil loss equation to SI metric units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1981, 36, 355–359. [Google Scholar]
- Erpul, G.; Bayramin, I.; Topcu Kaya, P.; Saygın, D.S. Determination of Rainfall Energy and Intensity for Water Erosion Studies Using Long-Term Meteorological Data at National Scale in Turkey; Ankara University/Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences: Ankara, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Toy, T.J.; Foster, G.R.; In, J.R. Guidelines for the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) Version 1.06 on Mined Lands, Construction Sites, and Reclaimed Lands. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1999, 54, 462–467. [Google Scholar]
- Erpul, G. Characteristics of Precipitation in Turkey and the Renewed Universal Soil Loss Equation (YETKE) R Factor, 1st ed.; General Directorate of Combating with Desertification and Erosion: Ankara, Turkey, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Erpul, G.; Şahin, S.; İnce, K.; Küçümen, A.; Akdağ, M.A.; Demirtaş, İ.; Çetin, E. Water Erosion Atlas of Turkey, 1st ed.; General Directorate of Combating with Desertification and Erosion: Ankara, Turkey, 2018; ISBN 9783540773405. [Google Scholar]
- Torri, D.; Poesen, J.; Borselli, L. Predictability and uncertainty of the soil erodibility factor using a global dataset. Catena 1997, 31, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinar, M.Ö.; Şahin, S.; Madenoğlu, S.; Erpul, G. Determining Severe Erosion Affected Areas and Estimation Reservoir Sediment Load in Derinöz Dam Basin. Su Kaynakları 2020, 5, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Romkens, M.J.M.; Prasad, S.N.; Poesen, J.W.A. Soil erodibility and properties. In Proceedings of the 13th Congress of the International Society of Soil Science, Hamburg, Germany, 13–20 August 1986; pp. 492–504. [Google Scholar]
- Cebel, H.; Akgül, S.; Doğan, O.; Elbaşı, F. K factor of Turkey big soil groups. Soil Water J. 2013, 2, 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.P.; Gallant, J.C. Digital Terrain Analysis. In Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications; Wilson, J.P., Gallant, J.C., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–28. ISBN 0-471-32188-590000. [Google Scholar]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): With a view to increasing its global applicability and improving soil loss estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, A.U.; Basaran, M.; Erpul, G.; Timur, O.B.; Dölarslan, M. Determining erosion resistance of the forest and its pasture in semiarid and arid region. In Proceedings of the Arid and Semiarid Regions Management Workshop, Nevsehir, Turkey, 5–8 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saygın, S.D.; Ozcan, A.U.; Basaran, M.; Timur, O.B.; Dolarslan, M.; Yılman, F.E.; Erpul, G. The combined RUSLE/SDR approach integrated with GIS and geostatistics to estimate annual sediment flux rates in the semi-arid catchment, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriels, D.; Ghekiere, G.; Schiettecatte, W.; Rottiers, I. Assessment of USLE cover-management C-factors for 40 crop rotation systems on arable farms in the Kemmelbeek watershed, Belgium. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 74, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenner, C.G. Soil conservation in Kenya, Nairobi, 1st ed.; Ministry of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Extension Unit: Nairobi, Kenya, 1981.
- Lufafa, A.; Tenywa, M.M.; Isabirye, M.; Majaliwa, M.J.G.; Woomer, P.L. Prediction of soil erosion in a Lake Victoria basin catchment using a GIS-based Universal Soil Loss model. Agric. Syst. 2003, 76, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhao, W.W.; Chen, L.D.; Zhang, Q.J.; Lü, Y.H.; Gulinck, H.; Poesen, J. Assessment of soil erosion at large watershed scale using RUSLE and GIS: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2005, 16, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, O.; Antronico, L.; Coscarelli, R.; Iaquinta, P. Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: An application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 112, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, M.; Cecchi, S.; Orlandini, S.; Mugnai, G.; Zanchi, C.A. Simulation of field-measured soil loss in Mediterranean hilly areas (Chianti, Italy) with RUSLE. Catena 2016, 145, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S. The assessment of water-borne erosion at catchment level using GIS-based RUSLE and remote sensing: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Cruse, R.M.; Zhang, X. Gully erosion control practices in Northeast China: A review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özhan, S.; Balci, A.N.; Özyuvaci, N.; Hizal, A.; Gökbulak, F.; Serengil, Y. Cover and management factors for the Universal Soil-Loss Equation for forest ecosystems in the Marmara region, Turkey. For. Ecol. Manage 2005, 214, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe; European Commission Directorate General Jrc Joint Research Centre, Space Applications Institute European Soil Bureau: Luxembourg, 2000; Volume 19044. [Google Scholar]
- Ejaz, N.; Elhag, M.; Bahrawi, J.; Zhang, L.; Gabriel, H.F.; Rahman, K.U. Soil Erosion Modelling and Accumulation Using RUSLE and Remote Sensing Techniques: Case Study Wadi Baysh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramin, I.; Erpul, G.; Erdoǧan, H.E. Use of CORINE methodology to assess soil erosion risk in the semi-arid area of Beypazarι, Ankara. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2006, 30, 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulou, M.; Depountis, N.; Nikolakopoulos, K.; Boumpoulis, V. The Significance of Digital Elevation Models in the Calculation of LS Factor and Soil Erosion. Land 2022, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Nguyen, K.A. The New Island-Wide LS Factors of Taiwan, with Comparison with EU Nations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmani, O.; Khanchoul, K.; Boubehziz, S.; Bouguerra, H.; Benslama, A.; Navarro-Pedreno, J. Spatial Variability of Soil Erodibility at the Rhirane Catchment Using Geostatistical Analysis. Soil Sys. 2023, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, S.F.; Silva, Y.J.A.B.D.; Martins, V.; Boechat, C.L.; Araújo, A.S.F.; Dantas, J.S.; Costa, O.S.; Barbosa, R.S. Prediction of Soil Erodibility by Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy in a Neotropical Dry Forest Biome. Land 2022, 11, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoǧlu, S. Variations of measured and simulated soil-loss amounts in a semiarid area in Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 165, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mati, B.M.; Morgan, R.P.C.; Gichuki, F.N.; Quinton, J.N.; Brewer, T.R.; Liniger, H.P. Assessment of erosion hazard with the USLE and GIS: A case study of the Upper Ewaso Ng’iro North basin of Kenya. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2000, 2, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamud, M.A.; Saad, N.A.; Zainal Abidin, R.; Yusof, M.F.; Zakaria, N.A.; Mohd Amiruddin Arumugam, M.A.R.; Desa, S.M.; Md. Noh, M.N. Determination of cover and land management factors for soil loss prediction in Cameron highlands, Malaysia. Agriculture 2022, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, S.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Xing, G.; et al. Soil Erosion Characteristics and Scenario Analysis in the Yellow River Basin Based on PLUS and RUSLE Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Ren, Y. Study on Soil Erosion Driving Forces by Using (R)USLE Framework and Machine Learning: A Case Study in Southwest China. Land 2023, 12, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Iqbal, F.; Humayun, M.; Umais Latif, M.; Javed, T.; Kebede Leta, M. Spatial Assessment of Soil Erosion Risk Using RUSLE Embedded in GIS Environment: A Case Study of Jhelum River Watershed. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkanou, K.; Karymbalis, E.; Bathrellos, G.; Skilodimou, H.; Tsanakas, K.; Papanastassiou, D.; Gaki-Papanastassiou, K. Soil Loss Potential Assessment for Natural and Post-Fire Conditions in Evia Island, Greece. Geoscience 2022, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özşahin, E. Climate change effect on soil erosion using different erosion models: A case study in the Naip Dam basin, Türkiye. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamurthi, S.; Ramya, M.; Saravanan, S.; Subramani, T. Estimation of soil erosion for a semi-urban watershed in Tamil Nadu, India using RUSLE and geospatial techniques. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getnet, T.; Mulu, A. Assessment of soil erosion rate and hotspot areas using RUSLE and multi-criteria evaluation technique at Jedeb watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yao, F.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Geng, X. Estimating the Soil Erosion Response to Land-Use Change Using GIS-Based RUSLE and Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Heilongjiang Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J. Assessing Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Soil Erosion Caused by Water in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, R.; Chen, L. Assessing the accuracy of large-scale rainfall erosivity estimation based on climate zones and rainfall patterns. Catena 2022, 217, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tang, Z.; Shangguan, Z.; Peng, C.; Deng, L. Factors Affecting the Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Erodibility of China. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari Damaneh, H.; Khosravi, H.; Habashi, K.; Eskandari Damaneh, H.; Tiefenbacher, J.P. The impact of land use and land cover changes on soil erosion in western Iran. Nat. Hazards 2022, 110, 2185–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Igwe, O.; Ifediegwu, S.I. Erosion risk mapping of Anambra State in southeastern Nigeria: Soil loss estimation by RUSLE model and geoinformatics. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, D.; Sadaoui, M.; Ludwig, W.; Méndez, W. Spatio-temporal assessment of rainfall erosivity in Ecuador based on RUSLE using satellite-based high frequency GPM-IMERG precipitation data. Catena 2022, 219, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, A.; Shaw, R.; Mallick, K.; Patel, P.P. Towards improved USLE-based soil erosion modelling in India: A review of prevalent pitfalls and implementation of exemplar methods. Earth Sci. Rev. 2021, 221, 103786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Months | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | Annual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∑R a | 0.00 | 29.43 | 15.40 | 187.67 | 1743.77 | 2594.65 | 1236.99 | 574.95 | 310.88 | 117.09 | 44.26 | 69.01 | 6924.11 |
| Rk b | 0.00 | 2.94 | 1.54 | 18.77 | 174.38 | 288.29 | 123.70 | 63.88 | 31.09 | 13.01 | 4.92 | 7.67 | 730.19 |
| %R c | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.21 | 2.57 | 23.88 | 39.48 | 16.94 | 8.75 | 4.26 | 1.78 | 0.67 | 1.05 | 100.00 |
| R d | 0.00 | 2.94 | 4.48 | 23.25 | 197.63 | 485.92 | 609.62 | 673.51 | 704.59 | 717.60 | 722.52 | 730.19 | 730.19 |
| Land Use Type/Land Cover (LUT/LC) | C Factor Value |
| Forest (0–30% ground cover) | 0.15 |
| Forest (30–70% ground cover) | 0.1 |
| Forest (70–100% ground cover) | 0.05 |
| Grassland | 0.3 |
| Agriculture | 0.5 |
| Water | 1 |
| Sandy Area | 0.5 |
| Rocky Area | 1 |
| Settlement | 1 |
| Factor | Min | Mean | Max | Std. dev |
| R factor [MJ mm ha−1 h−1 y−1] | 683.50 | 745.02 | 919.42 | 51.42 |
| K factor [t ha h ha−1 MJ−1 mm−1] | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.00 |
| LS factor | 0 | 73.94 | 430.64 | 61.50 |
| C factor (1970) | 0.15 | 0.32 | 1 | 0.14 |
| C factor (2020) | 0.05 | 0.28 | 1 | 0.22 |
| P factor (2020) | 0.20 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.37 |
| Land Use Type/ Land Cover (LUT/LC) | C Factor | 1970 | 2020 | Differences | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | Area (ha) | Area (%) | ||
| Forest (0–30% ground cover) | 0.05 | 3324.12 | 27.41 | 6797.56 | 56.05 | 3473.44 | 28.64 |
| Forest (30–70% ground cover) | 0.10 | 0 | 0 | 387.89 | 3.20 | 387.89 | 3.20 |
| Forest (70–100% ground cover) | 0.15 | 0 | 0 | 331.90 | 2.74 | 331.90 | 2.74 |
| Grassland | 0.3 | 5314.62 | 43.82 | 1703.58 | 14.05 | −3611.04 | −29.78 |
| Agriculture | 0.5 | 3395.71 | 28.00 | 2293.64 | 18.91 | −1102.07 | −9.09 |
| Settlement | 1 | 92.96 | 0.77 | 612.84 | 5.05 | 519.88 | 4.29 |
| TOTAL | 12,127.41 | 100.00 | 12,127.41 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Factor | Min | Mean | Max | Std. dev |
| Soil Losses (1970) [t ha−1 year−1] | 0 | 417.01 | 4265.09 | 398.11 |
| Soil Losses (2020) [t ha−1 year−1] | 0 | 256.24 | 3023.14 | 353.03 |
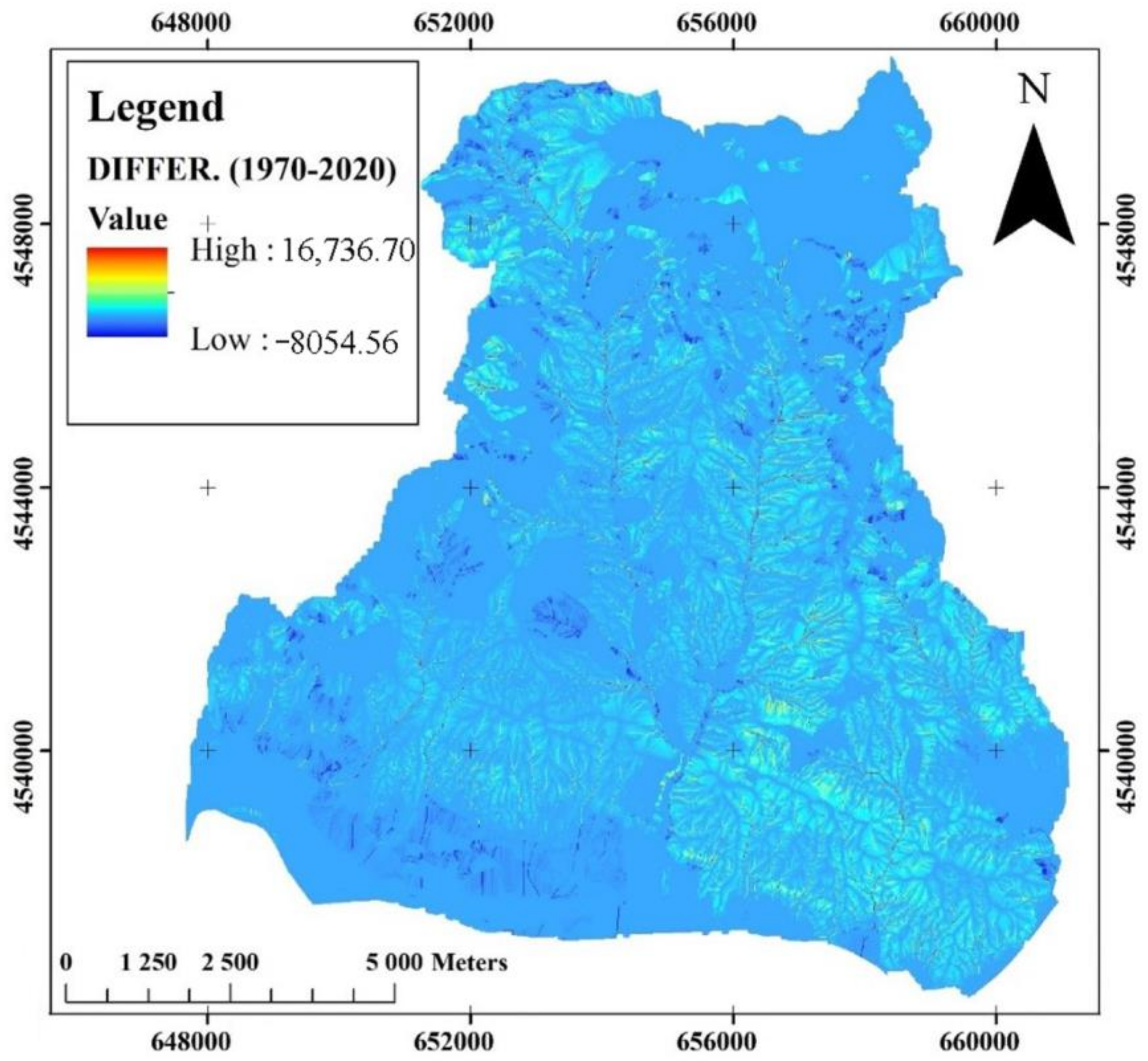
| Differences [(1970)–(2020)] | −3625.32 | −160.77 | 1768.76 | 272.47 |
| RKLS (without C and P factors) | 0 | 1474.10 | 10,077.12 | 1277.87 |
| Land Use Type/ Land Cover (LUT/LC) | Area (ha) 1970 | Soil Loss 1970 | Area (ha) 2020 | Soil Loss 2020 | C-Value |
| Forest (0–30% ground cover) | 3324.12 | 272.25 | 6797.56 | 191.8 | 0.15 |
| Forest (30–70% ground cover) | 0 | 0 | 387.89 | 88.14 | 0.1 |
| Forest (70–100% ground cover) | 0 | 0 | 331.9 | 17.35 | 0.05 |
| Grassland | 5314.62 | 506.5 | 1703.58 | 572.87 | 0.3 |
| Agriculture | 3395.71 | 422.41 | 2293.64 | 325.42 | 0.5 |
| Settlement | 92.96 | 247.89 | 612.84 | 89.92 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 12,127.41 | 1449.05 | 12,127.41 | 1285.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ediş, S.; Timur, Ö.B.; Tuttu, G.; Aytaş, İ.; Göl, C.; Özcan, A.U. Assessing the Impact of Engineering Measures and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Erosion: A Case Study in Osmancık, Türkiye. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12001. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512001
Ediş S, Timur ÖB, Tuttu G, Aytaş İ, Göl C, Özcan AU. Assessing the Impact of Engineering Measures and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Erosion: A Case Study in Osmancık, Türkiye. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):12001. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512001
Chicago/Turabian StyleEdiş, Semih, Özgür Burhan Timur, Gamze Tuttu, İbrahim Aytaş, Ceyhun Göl, and Ali Uğur Özcan. 2023. "Assessing the Impact of Engineering Measures and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Erosion: A Case Study in Osmancık, Türkiye" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 12001. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512001
APA StyleEdiş, S., Timur, Ö. B., Tuttu, G., Aytaş, İ., Göl, C., & Özcan, A. U. (2023). Assessing the Impact of Engineering Measures and Vegetation Restoration on Soil Erosion: A Case Study in Osmancık, Türkiye. Sustainability, 15(15), 12001. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512001






