Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
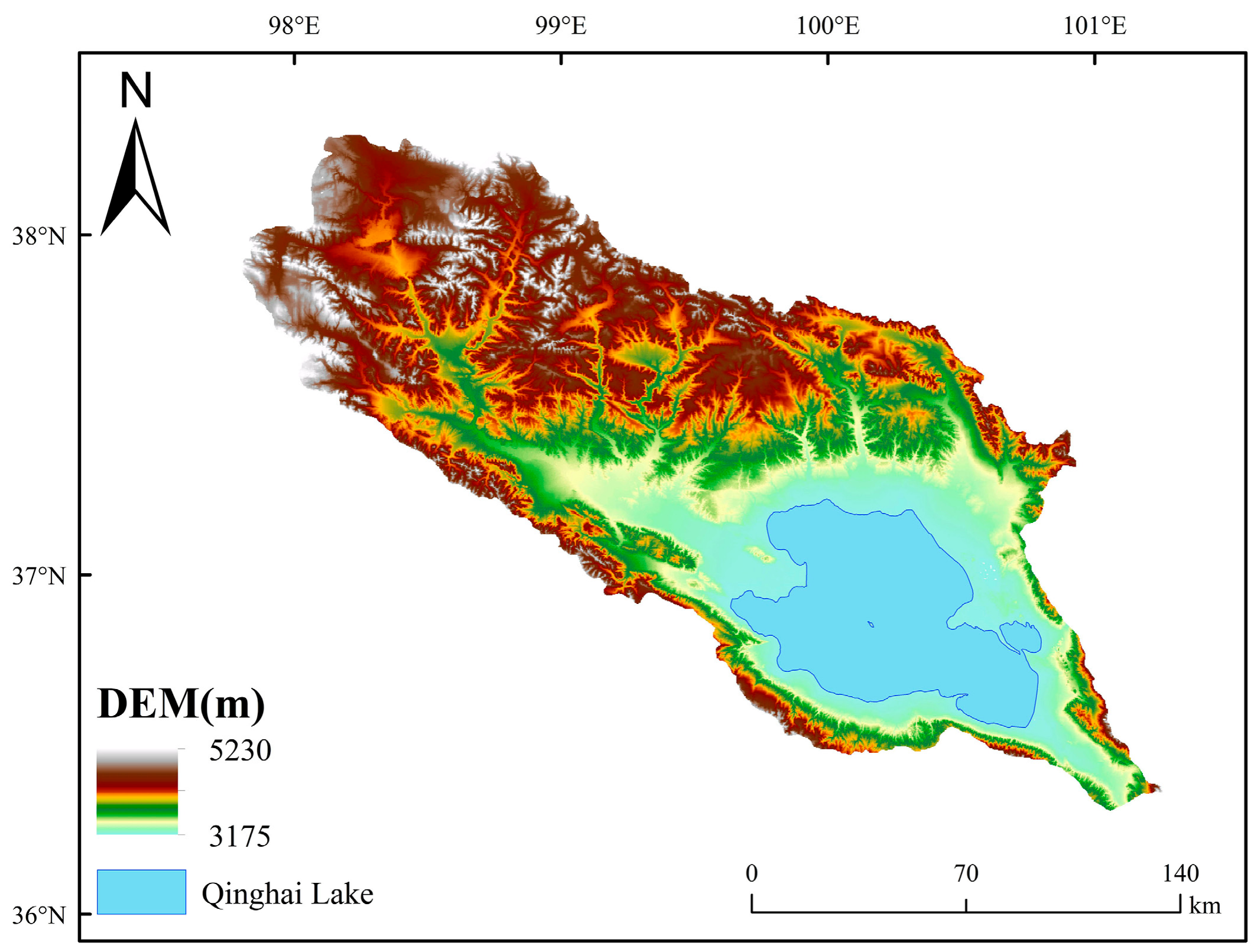
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Soil Retention
2.3.2. Habitat Quality
2.3.3. Carbon Storage
2.3.4. Water Conservation Capacity
2.3.5. Quantitative Measurements of Tradeoffs and Synergies between Ecosystem Services
2.3.6. Local Indicators of Spatial Association
3. Results
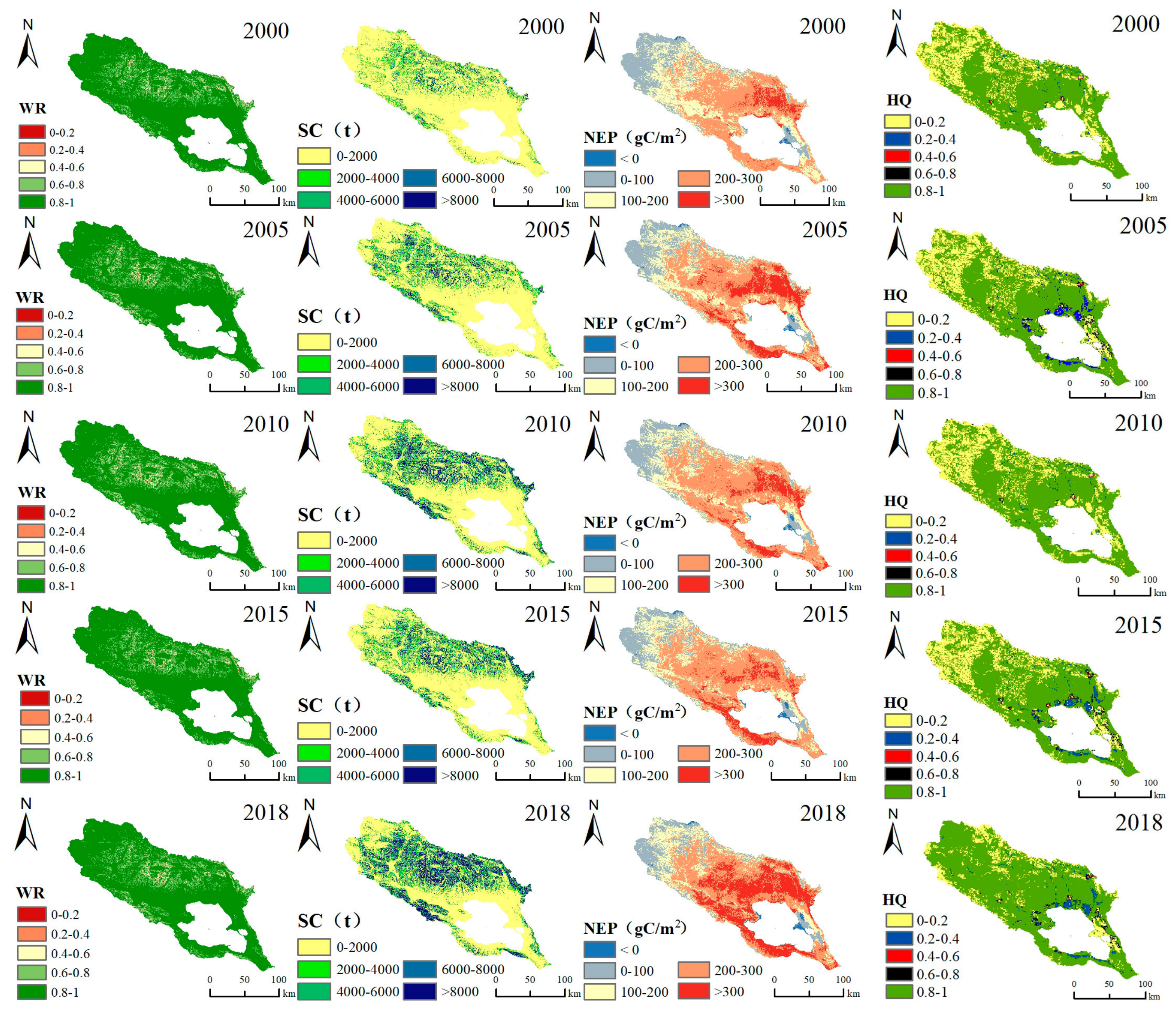
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in Ecosystem Services
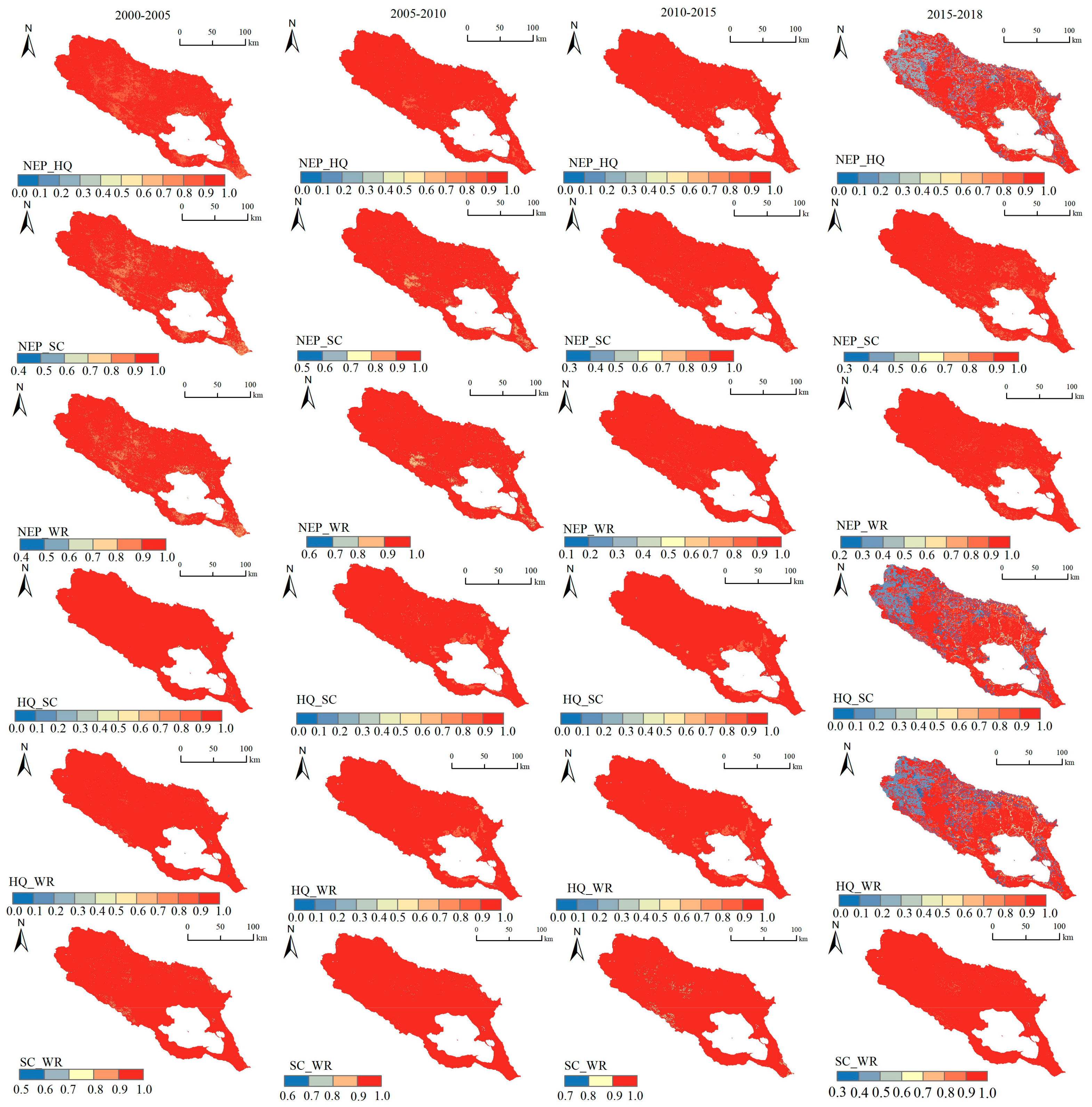
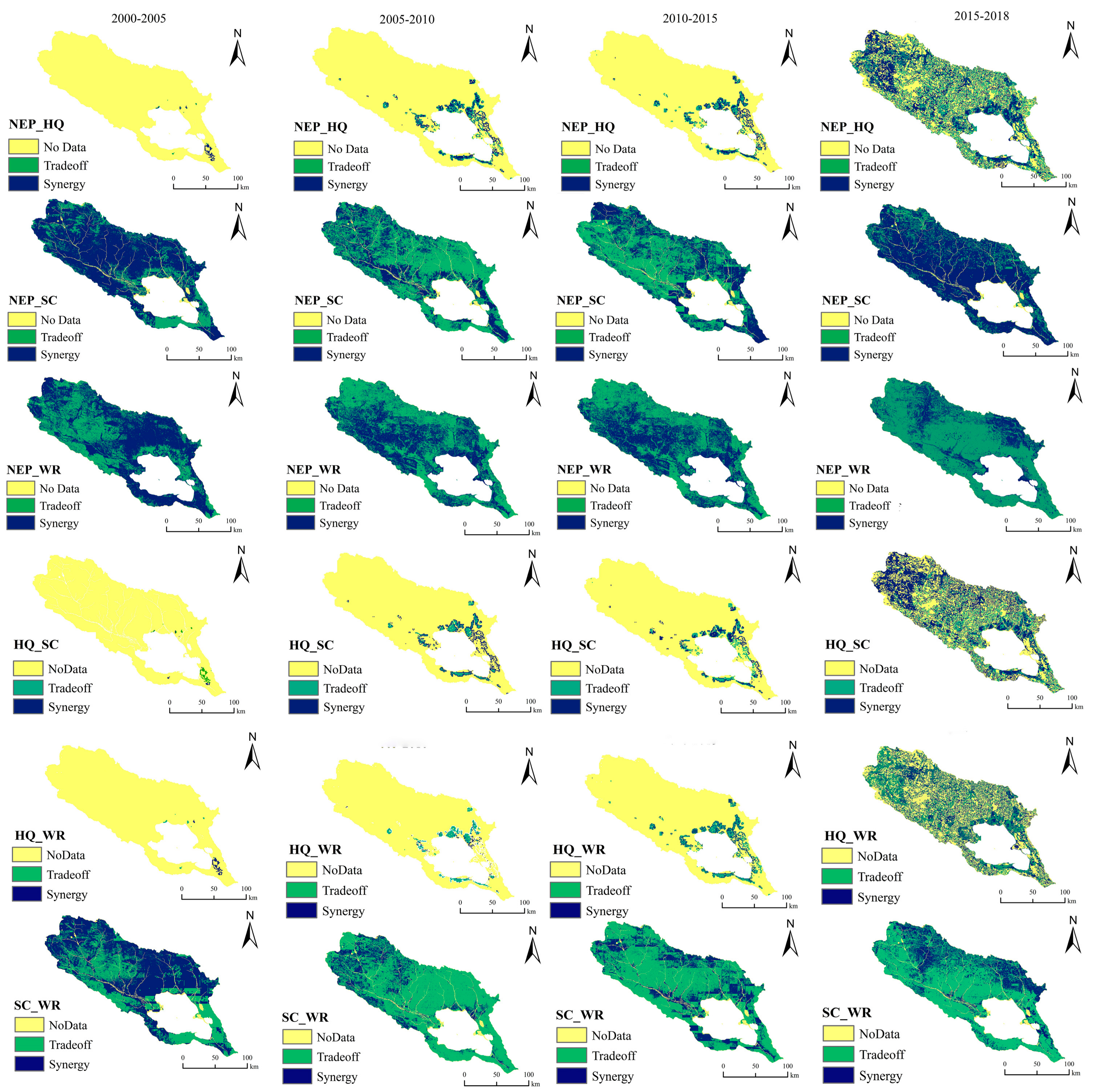
3.2. Spatial Characteristics of Ecosystem Services’ Tradeoffs and Synergies
3.2.1. Tradeoff/Synergy Criterion and Tradeoff–Synergy Index in the Watershed
3.2.2. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation of Watershed Ecosystem Services
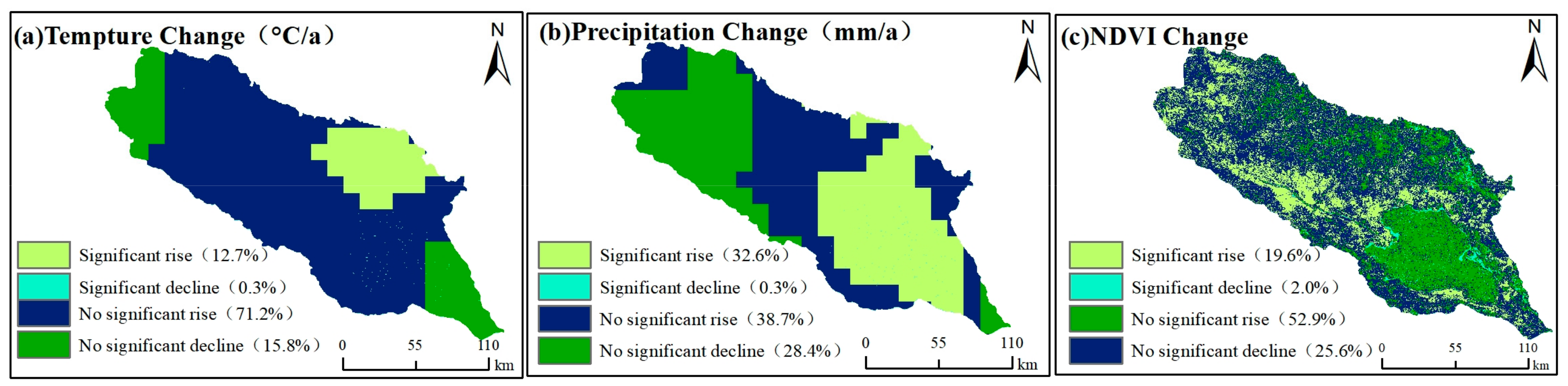
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The four ESs—water conservation capacity, soil retention services, habitat quality, and carbon storage—in the Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2018 showed upward trends. The basin had a high water conservation capacity. The soil retention had an annual growth rate of 130.80 t/a. Carbon storage’s average annual growth rate was 1.63 gC/m2·a−1. Habitat quality showed a fluctuating upward trend represented by an increase of 22.2%.
- During the period 2000–2018, there was a consistent synergetic relationship between habitat quality and soil retention, as well as habitat quality and carbon storage, while carbon storage services and water conservation capacity and soil retention and water conservation capacity mainly had tradeoff-based relationships. The relationships between carbon storage and soil retention and habitat quality and water conservation are not clear.
- LISA showed that the relationship between ESs is mainly based on high–high clusters that concentrate in the middle of the basin. The analysis also revealed obvious spatial heterogeneity. LISA validates the TSC results in another way, as carbon storage and soil retention and carbon storage and habitat quality show the same trends in LISA and TSC, as do habitat quality and soil retention. In addition, LISA reveals the result of synergy between HQ and WR, which is more scientific than that of TSC.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| InVest | Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs |
| CASA | Carnegie–Ames–Stanford Approach |
| TSC | Tradeoff–Synergy Criterion |
| TSI | Tradeoff–Synergy Index |
| LISA | Local Indicators of Spatial Association |
| QTP | Qinghai–Tibet Plateau |
| NEP | Carbon Storage |
| NPP | Net Primary Productivity |
| HQ | Habitat Quality |
| SC | Soil Retention |
| WR | Water Conservation Capacity |
| ESs | Ecosystem Services |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Clarke, K.C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Jia, X.; Li, J. Spatial Correlations among Ecosystem Services and Their Socio-Ecological Driving Factors: A Case Study in the City Belt along the Yellow River in Ningxia, China. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 108, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J. Ecosystem service trade-off and synergy on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Q.; Tong, K.; Hu, B. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Hot-Spots of the Trade-off and Synergy Relationship Among Ecosystem Services in Nanliujiang River Basin. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkelboom, F.; Leone, M.; Jacobs, S.; Kelemen, E.; García-Llorente, M.; Baró, F.; Termansen, M.; Barton, D.N.; Berry, P.; Stange, E.; et al. When we cannot have it all: Ecosystem services trade-offs in the context of spatial planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Moran, E.F. Evolution and effects of the social-ecological system over a millennium in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc0276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.R.; Friess, D.A. Characterizing Coastal Ecosystem Service Trade-offs with Future Urban Development in a Tropical City. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, P.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Spatial and Temporal Distribution and Trade-off of Water Conversation, Soil Conservation and NPP Services in Ecosystems of the Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2015. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 114–121+128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Pei, T. Trade-off and synergy of ecosystem services in Gansu-Qinghai section of the Yellow River Basin. J. Lanzhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2022, 58, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, D.; O’Connor, P.; Wu, T.; Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Guo, R.; Lin, J. Dynamic characteristics and synergistic effects of ecosystem services under climate change scenarios on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, L. Study on ecological health evaluation of Qinghai Lake Basin under climate change. Ecol. Sci. 2022, 41, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Sun, G. Watershed Ecosystem Processes and Management; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Lian, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R. Dynamic mechanism between human activities and ecosystem services: A case study of Qinghai lake watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chen, K.; Yu, D. Evaluation on the impact of land use change on habitat quality in Qinghai Lake Basin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhong, J.; Wang, B.; Mi, W. Spatiotemporal change and driving factor analysis of the Qinghai Lake Basin based on InVEST model. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2023, 43, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ren, Z.; Hao, M.; Duan, Y. Spatial and temporal changes in the synergy and trade-off between ecosystem services, and its influencing factors in Yanan, Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar]
- Vallet, A.; Locatelli, B.; Levrel, H.; Wunder, S.; Seppelt, R.; Scholes, R.J.; Oszwald, J. Relationships Between Ecosystem Services: Comparing Methods for Assessing Tradeoffs and Synergies. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 150, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Spatial-temporal evolution of ecosystem services and its potential drivers: A geospatial perspective from Bairin Left Banner, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Scale effect and spatially explicit drivers of interactions between ecosystem services—A case study from the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Spatio-temporal quantification of the trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services based on grid-cells: A case study of Guanzhong Basin, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Qian, K.; Yan, W.; Yang, X.; Ma, X. Trade-offs and synergistic relationships of ecosystem services under land use change in Xinjiang from 1990 to 2020: A Bayesian network analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Xu, C.; Gong, J. Ecological risk identification and management based on ecosystem service supply and demand relationship in the Bailongjiang River Watershed of Gansu Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2023, 43, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, R.; Gong, J. Evaluation and trade-offs of ecosystem services in GuangdongHong-Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area under multi-scenario simulation. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Hao, S.; Lv, L.; Xu, W.Y.; Wang, H. Spatial-temporal change and trade-off/synergy relationships among multiple ecosystem services in Three-River-Source National Park. Geogr. Res. 2020, 39, 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- Aryal, K.; Maraseni, T.; Apan, A. Preference, perceived change, and professed relationship among ecosystem services in the Himalayas. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zeng, H.; Guo, C.; You, W.; Xu, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. Spatial heterogeneity and management challenges of ecosystem service trade-offs: A case study in Guangdong Province, China. Environ. Manag. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, K. Microclimate in an Alpine Wetlands in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Arid Zone Res. 2019, 36, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L. Spatialtemporal dynamics of the vegetation coverage in Qinghai Lake Basin. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 1318–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, J. Estimating grassland yield and carrying capacity in Qinghai Lake Basin based on MODIS NPP data. Ecol. Sci. 2019, 38, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; He, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. China Meteorological Forcing Dataset (1979–2018). 2015. Available online: https://doi.org/10.11888/AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Impacts of human activities on ecosystem services in national parks: A case study of Qilian Mountain National Park. J. Nat. Resour. 2023, 38, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, C. Temporal and spatial distribution of net ecosystem productivity in the Bailongjiang Watershed of Gansu Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 5121–5128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Long, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, H. Estimating Net Primary Productivity of Terrestrial Vegetation Based on GIS and RS: A Case Study in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 3, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zeng, Y. Analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of vegetation carbon source/sink in Qinghai Plateau from 2000–2015. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5792–5803. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, L. Importance evaluation and spatial distribution analysis of ecosystem services in Min triangle area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 7254–7268. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.; Chen, X.; Xue, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, D. Modeling the spatially heterogeneous relationships between tradeoffs and synergies among ecosystem services and potential drivers considering geographic scale in Bairin Left Banner, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Spatial distribution pattern of NPP of Xinjiang grassland and its response to climate changes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 5318–5326. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Labzovskii, L. Challenging the land degradation in China’s Loess Plateau: Benefits, limitations, sustainability, and adaptive strategies of soil and water conservation. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Lü, Y.; He, C.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, B. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecol. Complex. 2011, 8, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, M. The study of ecosystem services and the comparison of trade-off and synergy in Yangtze River Basin and Yellow River Basin. Geogr. Res. 2021, 40, 821–838. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, S.; Cao, G.; Chen, K.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, T.; Han, G.; Lin, Y. Variation of Soil Conservation Quantity in Qinghai Lake Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 326–331+350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, R. Spatial pattern of ecosystem services under the influence of human activities in Qinghai Lake watershed. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2019, 41, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, X.J.; Tui, S.W.; Xie, X.L.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y. Spatial Distribution and Changing trends of Net Ecosystem Productivity in China. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 36, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W. Water and soil conservation and their trade-off and synergistic relationship under changing environment in Zhangjiakou-Chengde Area. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 5391–5403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y. Multi-scale analysis of trade-off/synergy effects of forest ecosystem services in the Funiu Mountain Region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 975–988. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Ma, X. Change and tradeoffs-synergies analysis on watershed ecosystem services: A case study of Bailong Watershed, Gansu. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 868–879. [Google Scholar]
- Maes, J.; Egoh, B.; Willemen, L.; Liquete, C.; Vihervaara, P.; Schägner, J.P.; Grizzetti, B.; Drakou, E.G.; Notte, A.L.; Zulian, G.; et al. Mapping ecosystem services for policy support and decision making in the European Union. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Feng, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.; Tu, Y.; Sun, Z. Changes and driving factors of ecosystem services supply and demand on the Tibetan plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhong, S.; Long, Y.; Yan, D. Spatiotemporal variation of ecosystem services and their drivers in the Yellow River Basin, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2023. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20230410.1449.016.html (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Liu, J. Spatial and temporal effect and driving factors of ecosystem service trade-off in the Qingjiang River Basin. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 34, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mu, Q.; Luo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qu, Z. Spatial and temporal variations of ecosystem service synergy and trade-off in the Qinling Mountains, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Fu, B. Evolution of ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau under climatic and land use changes. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 101, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, P. Spatio-temporal pattern and functional zoning of ecosystem services in the karst mountains areas of southeastern Yunnan. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 736–756. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511711
Wu X, Zhang L, Gao L, Li Y, Liu X. Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511711
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xueqing, Lele Zhang, Liming Gao, Yankun Li, and Xuanchen Liu. 2023. "Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511711
APA StyleWu, X., Zhang, L., Gao, L., Li, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Change and Tradeoff/Synergy Analysis of Watershed Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability, 15(15), 11711. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511711





