Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Microbial Community Diversity and Soil Metabolism in Desert Grasslands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.2. Soil Physical and Chemical Property Index Measurement Methods
2.3. Soil DNA Sequence Extraction
2.4. Microbial Diversity Analysis
2.5. Soil Metabolites Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Physicochemical Properties in Grazing Exclusion
3.2. Influence of Grazing Exclusion on Soil Bacterial Diversity
3.3. Influence of Grazing Exclusion on Bacterial Community Composition
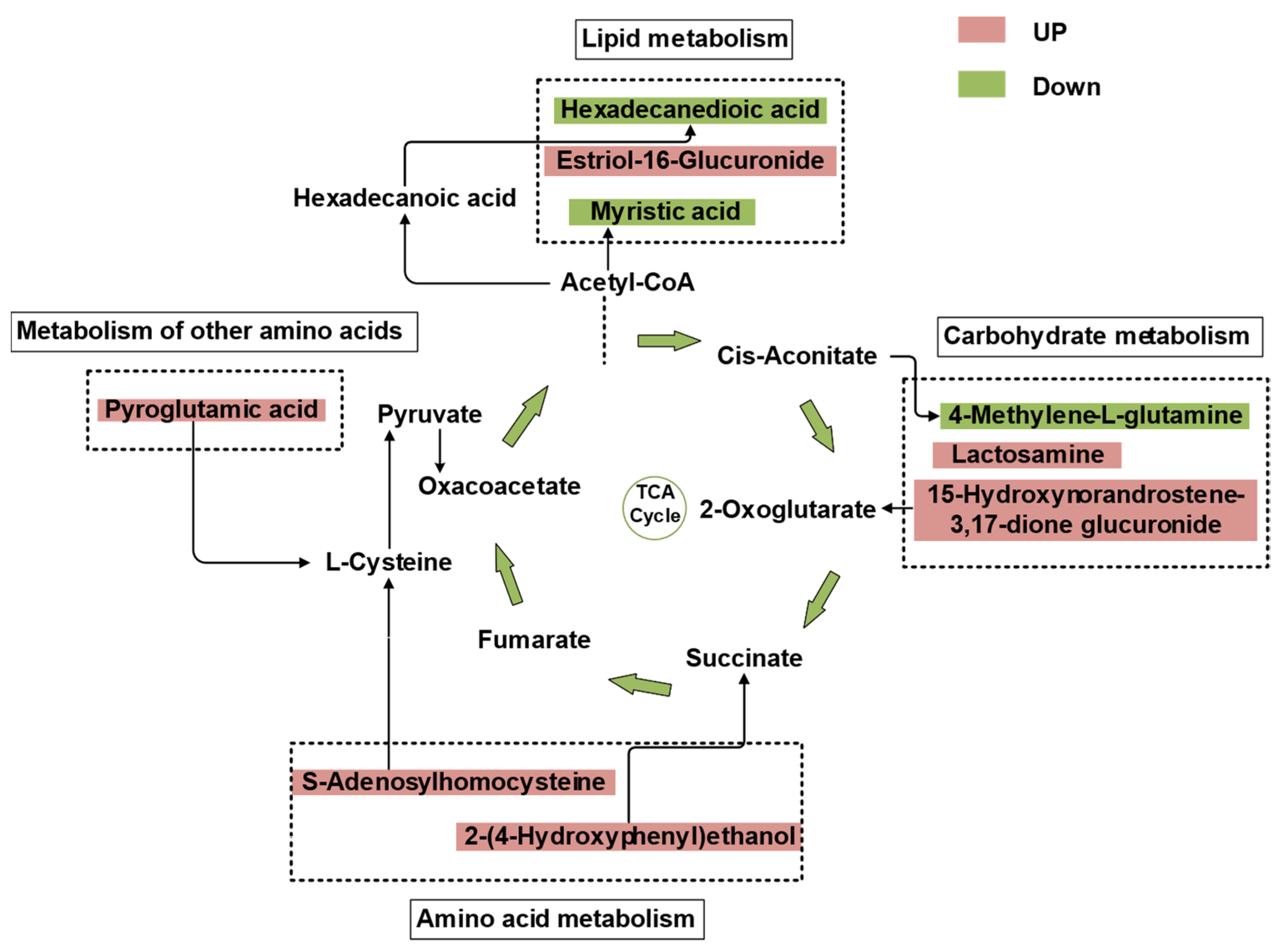
3.4. Impact of Grazing Exclusion on Soil Metabolites
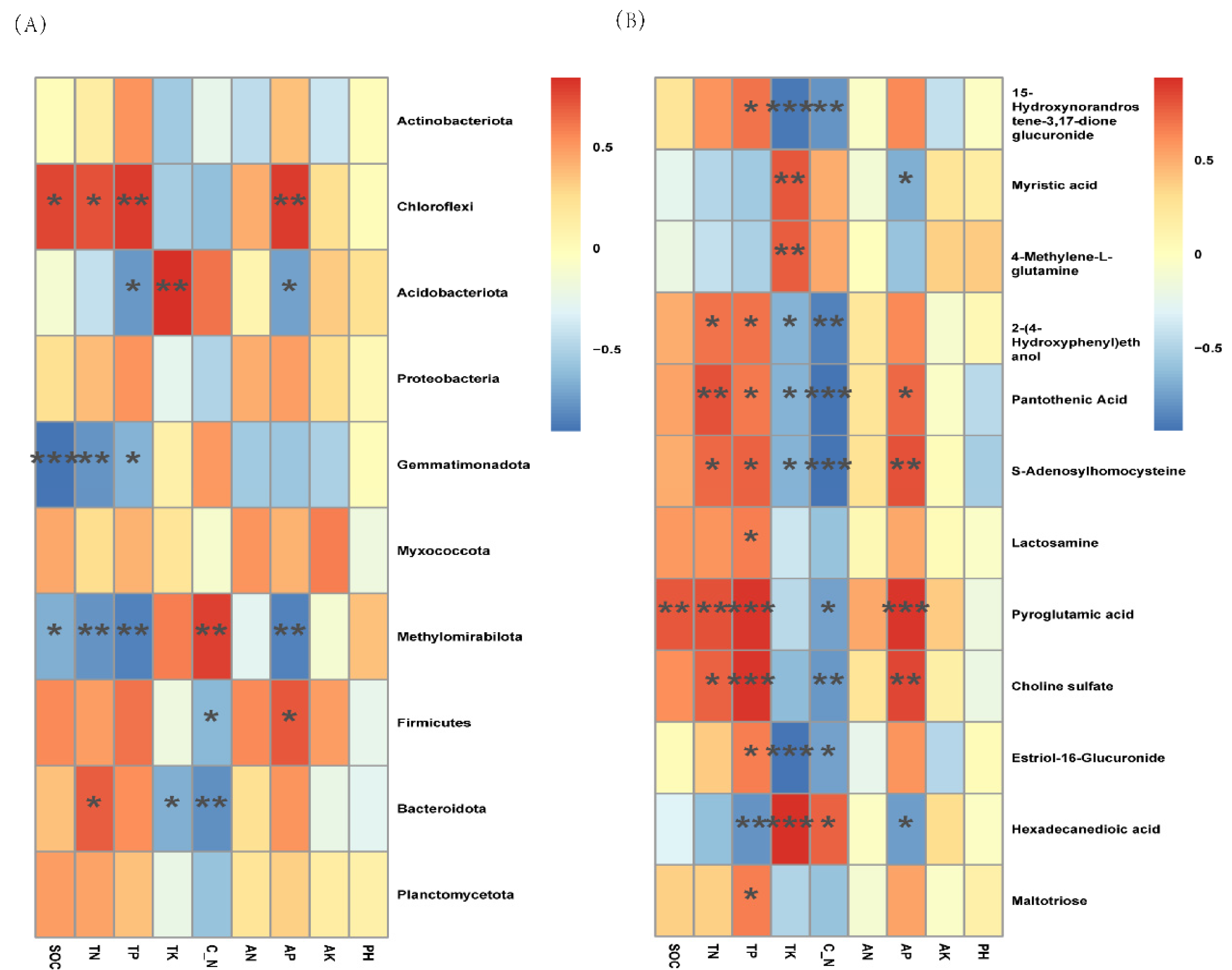
3.5. Metabolic Differentials and Bacterial Communities for Joint Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Grazing Exclusion on Soil Physicochemical Factors
4.2. Impact of Grazing Exclusion on Bacterial Communities and Their Drivers
4.3. Impact of Grazing Exclusion on Soil Metabolism and Its Drivers
4.4. Joint Analysis of Bacterial Communities and Differential Metabolites
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.M.; Jing, G.H.; Wei, L.; Jing, Z.B. Long-term grazing exclusion effects on vegetation characteristics, soil properties, and bacterial communities in the semi-arid grasslands of China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 97, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.T.; Bowatte, S.; Hou, F.J. Soil microbial communities and their relationships to soil properties at different depths in an alpine meadow and desert grassland in the Qilian mountain range of China. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 184, 104316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.L.; Barberan, A.; Danielson, R.E.; Fehmi, J.S.; Gornish, E.S. Disturbance is more important than seeding or grazing in determining soil microbial communities in a semiarid grassland. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, S335–S343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.S.; Shao, X.Q.; Li, H.; He, Y.X.; Sirimuji; Wang, B.J. Microbes require a relatively long time to recover in natural succession restoration of degraded grassland ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, S.K.; Gao, Q.Z.; Fan, C.; Fayiah, M.; Ganjurjav, H.; Hu, G.Z.; Wang, X.X.; Yan, Y.L.; Gao, X.X.; et al. Grazing changed plant community composition and reduced stochasticity of soil microbial community assembly of alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 864085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Yan, Q.Y.; Yang, S.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Wang, Z.R.; He, Z.L.; Zhou, J.Z.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y. Soil microbial beta-diversity is linked with compositional variation in aboveground plant biomass in a semi-arid grassland. Plant Soil 2018, 423, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.X.; Dong, Y.Q.; Liu, H.X.; Sun, Z.J. Short-term grazing exclusions reduced soil organic carbon but not bacterial diversity in the sagebrush desert, Northwest China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 31, e01872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Liu, J.; Yi, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.W.; Di, H.J. Grazing and enclosure alter the vertical distribution of organic nitrogen pools and bacterial communities in semiarid grassland soils. Plant Soil 2019, 439, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, W.; Cao, W.X.; Abalori, T.A.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xin, Y.Q.; Wang, S.L.; Zhang, D.G. Soil bacterial community responses to short-term grazing exclusion in a degraded alpine shrubland–grassland ecotone. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Jin, K.; Struik, P.C.; Sun, S.X.; Ji, B.M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, X.L. Soil bacterial and fungal communities are linked with plant functional types and soil properties under different grazing intensities. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Tasnim, R.; Capobianco, V.; Coo, J.L. Influence of soil nutrients on plant characteristics and soil hydrological responses. Géotechnique Lett. 2018, 8, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q. Effects of Vegetation Degradation on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities of Gahai Wet Meadow. Ph.D. Thesis, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Nian, Y.P.; Lui, L.X.; Yi, L.C.; Wei, D.C. Response of soil microbial diversity to long-term enclosure in degraded patches of alpine meadow in the source zone of the yellow river. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, B.; Shi, Y.X.; Zhang, G.X.; Wang, J.; Si, G.C.; Han, C.H.; Yuan, Y.L.; Hu, A. The response of alpine grasslands ecosystem in the north Tibet to short-term enclosure. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 4366–4374. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.N. Effects of Grazing Prohibition on Grassland Soil Microbial Community Structure and Function in Yunwu Mountain. Master’s Thesis, North West Agriculture and Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, S.X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ma, Y.S.; Bao, G.S. Soil microbial character response to plant community variation after grazing prohibition for 10 years in a Qinghai-Tibetan alpine meadow. Plant Soil 2021, 458, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Travers, S.K.; Val, J.; Wang, J.T.; Liu, H.W.; Singh, B.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M. Grazing regulates the spatial heterogeneity of soil microbial communities within ecological networks. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.B.; Song, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Interactions of soil bacteria and fungi with plants during long-term grazing exclusion in semiarid grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenster-Jordan, S.; Ingold, M.; Jannoura, R.; Buerkert, A.; Joergensen, R.G. Soil microbial properties of subalpine steppe soils at different grazing intensities in the Chinese Altai Mountains. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, L.J.; Wang, H.T.; Xu, Q.S.; Jiang, Y.J.; Sun, B. Coupling bacterial community assembly to microbial metabolism across soil profiles. Msystems 2020, 5, e00298-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Staley, C.; Gao, H.L.; Ishii, S.; Wei, X.R.; Liu, J.; Cheng, J.M.; Hao, M.D.; Sadowsky, M.J. Impact of long-term grazing exclusion on soil microbial community composition and nutrient availability. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.P.D.; Lima, L.A.L.; Bezerra, W.M.; Pereira, M.L.; Normando, L.R.O.; Mendes, L.W.; de Oliveira, J.G.B.; Araujo, A.S.F.; Melo, V.M.M. Grazing exclusion regulates bacterial community in highly degraded semiarid soils from the Brazilian Caatinga biome. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2210–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Du, Q.F.; Li, G.D.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, W.B.; Hou, X.Y. Soil phosphorus fractions and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity following long-term grazing exclusion on semi-arid steppes in Inner Mongolia. Geoderma 2016, 269, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Laborda, P.; Xie, X.L.; Zhou, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Pu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Deng, Z.F. Spartina alterniflora invasion alters soil microbial metabolism in coastal wetland of China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 245, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.L.; Bing, H.J.; Chang, R.Y.; Cui, Y.X.; Shen, G.T.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, S.P.; Fang, L.C. Microbial metabolic limitation response to experimental warming along an altitudinal gradient in alpine grasslands eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2022, 214, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Fei, H.Y.; Pan, R.P.; Han, F.P. Plants use rhizosphere metabolites to regulate soil microbial diversity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5267–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.A.H.; Sdepanian, S.; Lofts, S.; Svendsen, C.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Maguire, M.L.; Griffin, J.L. Metabolomic analysis of soil communities can be used for pollution assessment. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.P.; Li, W.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhu, Y.F.; Feng, Y.Z.; Yang, G.H.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.H. Soil eco-enzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Y.X.; Zhang, X.C.; Ju, W.L.; Duan, C.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Fang, L.C. A novel extracellular enzyme stoichiometry method to evaluate soil heavy metal contamination: Evidence derived from microbial metabolic limitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, E.; Hill, P.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Use of untargeted metabolomics for assessing soil quality and microbial function. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, F. Systems-based approaches to unravel multi-species microbial community functioning. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.N.; Yao, S.; Yang, X.L.; Jiang, X. Correlations between soil metabolomics and bacterial community structures in the pepper rhizosphere under plastic greenhouse cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, T.X.; Huang, Y.Y.; Xie, X.N.; Huo, X.; Shahid, M.Q.; Tian, L.; Lan, T.; Jin, J. Rice SST variation shapes the rhizosphere bacterial community, conferring tolerance to salt stress through regulating soil metabolites. MSystems 2021, 5, e00721-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magoc, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberan, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero Rioseras, A.; Singh, K.D.; Nowak, N.; Gaugg, M.T.; Bruderer, T.; Zenobi, R.; Sinues, P.M.L. Real-time monitoring of tricarboxylic acid metabolites in exhaled breath. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6453–6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q. Effects of Long-Term Enclosing on Vertical Distributions of Soil Physical Properties and Nutrient Stocks in Grassland of Inner Mongolia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Li, Y.L.; Cui, J.Y. Effects of grazing and livestock exclusion on soil physical and chemical properties in desertified sandy grassland, Inner Mongolia, northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Niu, K.C.; Collins, C.G.; Yan, X.B.; Ji, Y.G.; Ling, N.; Zhou, X.H.; Du, G.Z.; Guo, H.; Hu, S.J. Grazing practices affect the soil microbial community composition in a Tibetan alpine meadow. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, L.L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, M.; Cao, J.X.; Wu, S.H.; Lei, G.C. Effects of different grazing intensities on soil C, N, and P in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai—Tibetan Plateau, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.S.; Fu, B.J.; Zhou, W.M.; Liu, H.F.; Liu, G.H. Restoration of ecosystem carbon and nitrogen storage and microbial biomass after grazing exclusion in semi-arid grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Roy, S.; Maitra, A.; Sran, R.S. Herbivores suppress soil microbes to influence carbon sequestration in the grazing ecosystem of the Trans-Himalaya. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 239, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Kan, H.M.; Lin, L.J. Impact of grazing on soil carbon and microbial biomass in typical steppe and desert steppe of Inner Mongolia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Kan, H.M.; Lin, L.J. Phylogenetic and functional changes in the microbial community of long-term restored soils under semiarid climate. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.J.; Polson, S.W.; Hanson, T.E.; Mack, M.C.; Schuur, E.A.G. The effect of nutrient deposition on bacterial communities in Arctic tundra soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1842–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stach, J.E.M.; Maldonado, L.A.; Ward, A.C.; Goodfellow, M.; Bull, A.T. New primers for the class Actinobacteria: Application to marine and terrestrial environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 828–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Adamowski, J.F.; Biswas, A.; Holden, N.M.; Hu, Z.Y. Grassland grazing management altered soil properties and microbial β-diversity but not α-diversity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 167, 104032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, L.A.; Castelle, C.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Sharon, I.; Frischkorn, K.R.; Williams, K.H.; Tringe, S.G.; Banfield, J.F. Community genomic analyses constrain the distribution of metabolic traits across the Chloroflexi phylum and indicate roles in sediment carbon cycling. Microbiome 2013, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.L.; Xu, Z.C.; Zou, P.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.Q.; You, X.W.; Zhang, C.S. Coastal halophytes alter properties and microbial community structure of the saline soils in the yellow river delta, china. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, K.C.; Karaoz, U.; Hanson, C.A.; Santee, C.A.; Bradford, M.A.; Treseder, K.K.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Brodie, E.L. Differential growth responses of soil bacterial taxa to carbon substrates of varying chemical recalcitrance. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.; Chen, D.M.; Guo, H.; Wei, J.X.; Bai, Y.F.; Shen, Q.R.; Hu, S.J. Differential responses of soil bacterial communities to long-term n and p inputs in a semi-arid steppe. Geoderma 2017, 292, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Bai, Y.; Hou, J.F.; Li, F.; Li, X.Q.; Cao, R.; Deng, Y.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Jiang, Y.R.; Yang, W.Q. The changes in soil microbial communities across a subalpine forest successional series. Forests 2022, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.L.; Ji, B.M.; Struik, P.C.; Jin, K.; Tang, S.M. Coupling between the responses of plants, soil, and microorganisms following grazing exclusion in an overgrazed grassland. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 640789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lai, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.G.; Han, M.W.; Zhao, S.P. Microbial community structure and metabolome profiling characteristics of soil contaminated by TNT, RDX, and HMX. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Long, F.Y.; Liu, J.B.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, H.Y. Effects of organic planting on metabolites in maize rhizosphere soil. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. 2022, 53, 30–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, R.; Liu, W.T.; Piao, M.Y.; Zhu, H. A review of the relationship between the gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Sun, H.W.; Liang, A.P.; Liu, J.; Song, L.H.; Lv, M.; Zhu, D. Testosterone amendment alters metabolite profiles of the soil microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Zou, J.; Zhu, H.H.; He, J.Q.; Setter, T.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Meng, Y.L.; Chen, B.L.; Zhao, W.Q.; Wang, S.S. Drought deteriorated the nutritional quality of cottonseed by altering fatty acids and amino acids compositions in cultivars with contrasting drought sensitivity. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 194, 104747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Qu, C.S.; Bian, Y.R.; Gu, C.G.; Jiang, X.; Song, Y. New insights into the responses of soil microorganisms to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon stress by combining enzyme activity and sequencing analysis with metabolomics. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.K.; McInroy, J.A.; Kloepper, J.W. The interactions of rhizodeposits with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in the rhizosphere: A review. Agriculture 2019, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Rehman, S.A.A.; Tarique, K.F.; Gourinath, S. Structural characterization and functional analysis of cystathionine β-synthase: An enzyme involved in the reverse transsulfuration pathway of Bacillus anthracis. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 3862–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | GE (Grazing Exclusion) | G (Grazing) | Test (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cover (%) | 80 | 50 | --- |
| Aboveground biomass of shrub (g/m2) | 285.48 ± 22.23 | 161.33 ± 14.50 | 0.002 |
| Aboveground biomass of herbs (g/m2) | 165.70 ± 14.59 | 43.74 ± 4.50 | 0.000 |
| Litter aboveground biomass (g/m2) | 145.56 ± 4.83 | 39.83 ± 2.74 | 0.000 |
| Belowground biomass (g/m2) | 264.38 ± 19.73 | 88.08 ± 5.03 | 0.000 |
| Parameters | GE (Grazing Exclusion) | G (Grazing) | t-Test (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOC (g/kg) | 27.90 ± 2.63 | 23.05 ± 5.35 | 0.107 |
| TN (g/kg) | 2.53 ± 0.18 | 1.87 ± 0.51 | 0.040 |
| TP (g/kg) | 1.13 ± 0.10 | 0.81 ± 0.08 | 0.000 |
| TK (g/kg) | 17.38 ± 1.05 | 20.62 ± 0.41 | 0.001 |
| C/N | 11.02 ± 0.74 | 12.42 ± 0.49 | 0.008 |
| AN (mg/kg) | 35.93 ± 4.47 | 38.11 ± 9.87 | 0.665 |
| AP (mg/kg) | 7.69 ± 2.39 | 3.48 ± 0.86 | 0.014 |
| AK (mg/kg) | 201.6 ± 37.73 | 231.60 ± 73.34 | 0.447 |
| pH | 8.10 ± 0.06 | 8.12 ± 0.06 | 0.511 |
| Estimators | GE-Mean | GE-Sd | G-Mean | G-Sd | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ace | 3371.60 | 130.60 | 2967.60 | 164.32 | 0.022 |
| Sobs | 2868.00 | 111.43 | 2558.20 | 130.65 | 0.022 |
| Chao | 3374.80 | 140.67 | 2943.30 | 150.25 | 0.012 |
| Shannon | 6.55 | 0.08 | 6.49 | 0.06 | 0.296 |
| Simpson | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.144 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Lv, P. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Microbial Community Diversity and Soil Metabolism in Desert Grasslands. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411263
Geng M, Wang X, Liu X, Lv P. Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Microbial Community Diversity and Soil Metabolism in Desert Grasslands. Sustainability. 2023; 15(14):11263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411263
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Meiju, Xinhui Wang, Xiaoying Liu, and Pei Lv. 2023. "Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Microbial Community Diversity and Soil Metabolism in Desert Grasslands" Sustainability 15, no. 14: 11263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411263
APA StyleGeng, M., Wang, X., Liu, X., & Lv, P. (2023). Effects of Grazing Exclusion on Microbial Community Diversity and Soil Metabolism in Desert Grasslands. Sustainability, 15(14), 11263. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151411263






