Abstract
In pursuit of carbon neutrality, the demand for metals that are necessary for the development of clean energy technologies is rapidly increasing. Metallurgical waste, such as slag, presents a promising secondary source of these key metals. This research aims to develop an eco-friendly hydrometallurgical process to recover Cu, Ni, and Co from discarded copper/nickel slag. High-pressure acid leaching (HPAL) was used to selectively leach Ni, Cu, and Co from the fayalite slag, yielding high leaching efficiencies of 99.9%, 89.4%, and 99.9%, respectively, with low Fe and Si tenors to the pregnant leach solution (PLS). The solvent extraction (SX) technique utilizing LIX 984N was used to selectively extract and enrich copper from the dilute PLS to about 23 g/L Cu with a very low Fe concentration of 0.05 g/L. Potassium amyl xanthate (PAX) solution was used to form Ni and Co xanthate complexes from the raffinate solution. Nickel was selectively recovered using ammonia solution, while the cobalt xanthate complex was thermally decomposed and recovered as cobalt oxide solids of about 25 wt.% Co. A comprehensive process flowsheet is presented. Furthermore, to realize the real application of the developed slag cleaning process, a preliminary economic evaluation was performed.
Keywords:
slag; copper; nickel; cobalt; recovery; high-pressure leaching; solvent extraction; complexation; hydrometallurgy; waste 1. Introduction
As the world is shifting towards a carbon-neutral society, more emphasis is drawn to renewable sources of energy such as wind, solar, geothermal, hydro, and biomass. However, a clean energy transition would result in a great increase in demand for metals. For instance, solar panels utilize large quantities of copper, silicon, silver, and zinc; wind turbines require iron, copper, and aluminum; while a typical electric vehicle battery needs lithium, nickel, manganese, and cobalt. Countries worldwide have set targets to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 or 2060 [1,2]; therefore, a spike in demand for these key metals is inevitable. To sustain the supply of these metals in the future, secondary sources of metals are greatly important to support the declining primary ore resources. Metallurgical waste, such as slag, presents a promising secondary source of the key metals needed in low-carbon technologies such as Cu, Ni, Co, and Fe. Alongside the recovery of these valuable metals from slag waste, the process of cleaning the slag holds significant benefits in preventing environmental pollution. The slag dump sites generally undergo natural weathering; that is a wide range of chemical, biological, and environmental factors such as pH variations and microbial conditions [3]. Long-term exposure of slag to weathering may encourage the oxidation of entrained sulfur to sulfuric acid, which promotes the slow leaching of heavy metals into the environment and consequently contaminates soil and groundwater sources [4,5,6,7]. Therefore, when cleaning the slag, environmentally sensitive technologies that generate benign waste or zero waste should be primarily considered.
Slag cleaning technologies have widely been explored including the application of conventional methods such as flotation and pyrometallurgical approaches like re-smelting and roasting. However, some limitations associated with these methods have been noted. The flotation method is limited to the recovery of the metallic form and sulfide minerals, while other metals in the slag, such as cobalt, exist in the oxide form, making the flotation method ineffective for the recovery of Co and other metal oxides [8,9]. Additionally, a significant proportion of the sulfides are locked in the fayalite phase, requiring costly fine grinding to liberate the sulfides for effective recovery by flotation [8,10,11]. A common pyrometallurgical route in slag cleaning is the carbothermal reduction method at high temperatures of around 1400 °C using a DC arc furnace; however, high energy consumptions remain an associated challenge [9,12]. A combined pyro-hydrometallurgical method of roasting with subsequent leaching is a commonly studied method in slag treatment [8,13,14]. Nevertheless, comprehensive hydrometallurgical methods are preferred for the chemical extraction of valuable metals from low-grade materials such as slag. The common hydrometallurgical methods studied include atmospheric leaching and high-pressure acid leaching. Some limitations noted by some researchers during atmospheric leaching of slag include difficulty in solid–liquid separation due to silica gel formation, low metal extractions, and high iron co-extraction. Therefore, the addition of lixiviants such as dichromate compounds or hydrogen peroxide during leaching has largely been studied to address these challenges [15,16,17,18,19]. The high-pressure acid leaching (HPAL) process has been noted to be a robust process in achieving exceptionally high metal extractions and producing a benign residue that is most suitable for safe disposal [5,11,20,21]. However, low metal extractions have consistently been reported during the high-pressure leaching of amorphous slags when compared to crystalline (naturally cooled) slags with HPAL conditions of around 250 °C and oxygen overpressure of about 0.6 MPa [4,10,19].
The present study focuses on the process development of slag to recover cobalt, nickel, copper, and iron using hydrometallurgical methods. The slag sample utilized in this study is of an amorphous nature originating from a copper–nickel smelter in Botswana. The HPAL method is investigated at mild operating conditions, lower temperatures (~150 °C) and pressure (0.6 MPa), to selectively leach the finely dispersed metal sulfides from the slag. Leaching of low-grade material such as slag results in a dilute solution; therefore, to enrich the metal values after the leaching process, a combination of solvent extraction, selective precipitation, and xanthate complexation processes was employed to separate and upgrade the metal ions of Cu, Ni, and Co from the dilute pregnant leach solution (PLS) as well as separate the Fe impurity from the solution. The separation of Ni and Co from aqueous solutions is commonly conducted by solvent extraction; however, in this study, the xanthate complexation process was applied, utilizing potassium amyl xanthate (PAX) as a chelating agent. Alkali xanthates form xanthate complexes in the form of precipitates with various metal ions from the solution. The difference in the solubility product constant (Ksp) of these xanthate complexes allows for the selective separation of metal ions from the solution [22]. The utilization of the xanthate complexation method offers a cost-effective alternative to solvent extraction while demonstrating a high level of selectivity for the desired metal. Additionally, the widespread availability of PAX reagent further enhances its practicality and applicability.
The aim of this study is to present a comprehensive hydrometallurgical process flow to recover Co, Ni, Cu, and Fe from the smelter slag in Botswana. Currently, there is no slag cleaning process in place, and unfortunately, previous studies have demonstrated that the slag dump is causing significant environmental deterioration, especially in the surrounding water sources [23,24]. Additionally, the utilization of sulfuric acid as a leaching agent will encourage the copper/nickel smelter in Botswana to produce sulfuric acid from sulfur dioxide in the off-gas streams and cease venting SO2-containing off-gases to the atmosphere. So, a slag cleaning scheme will be beneficial in alleviating these environmental effects. Furthermore, in order to assess the practical implementation of the developed slag cleaning process, a preliminary economic evaluation was conducted. The establishment of a slag cleaning scheme is important as part of developing effective long-term processes to reduce the environmental footprint of the mining industry, especially in the numerous abandoned mines in the African region where effective mine remediation strategies are developing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
The slag sample was obtained from a copper–nickel smelter in Botswana. The sample was formed by granulation of the electric arc furnace slag melt in water resulting in a glassy material. The slag sample was analyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Rigaku Miniflex) (Figure 1), which showed that the dominant mineral composition is fayalite. The slag sample is amorphous, as demonstrated by an exceedingly high background of the XRD pattern. Several authors also confirmed that molten slags which are quenched in water produce an amorphous structure [4,10,19,25].
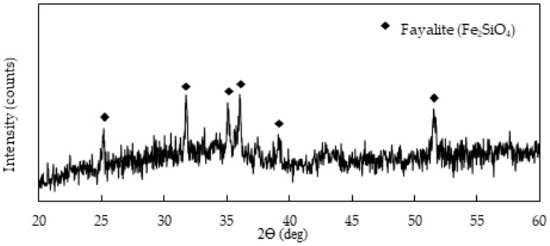
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of the granulated electric furnace copper/nickel slag.
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectrometry (Rigaku ZSX Primus II) was used to determine the elemental composition of the slag. The results in Table 1 show that the most abundant element is iron at 38.7 wt.% followed by silicon at 13.3 wt.%, while the content of valuable metals of interest, nickel, copper, and cobalt, was measured to be 0.36, 0.36, and 0.17 wt.%, respectively. Additionally, SEM-EDS (Scanning Electron Microscope–Energy Dispersion Spectroscopy) was used to characterize the slag sample. Figure 2 shows a SEM image of the slag particles, showing entrapped matte (MeS, where Me can be Ni, Cu, and/or Co). The matte which is the sulfide phase appears as visible bright dots (light grey), occurring as fine occlusions in the fayalite phase (dark grey). EDX spectrum analysis (Figure S1) was used to confirm the mineral phases present within the slag particle. Elemental mapping of SEM-EDS observations of the granulated electric furnace slag is shown in Figure 3. Nickel and copper exist in the slag as sulfides and occur as dispersed spherical matte inclusions, while cobalt exists predominantly in the oxide form which is homogeneously distributed in the fayalite phase. Several authors also found that typical slags from nickel and copper smelters contain Ni and Cu mostly in the form of sulfide, while Co exists in the oxide form [5,10,26,27].

Table 1.
The chemical composition of the electric furnace copper/nickel slag (wt.%).
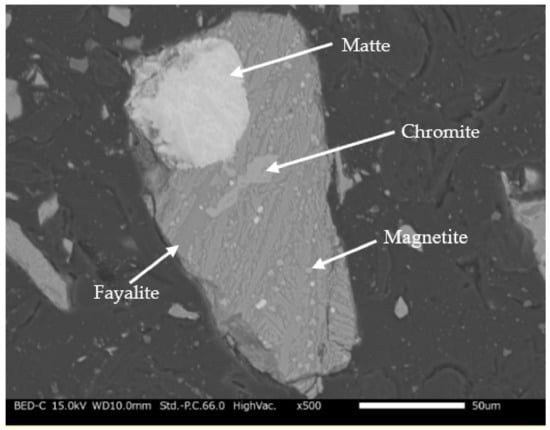

Figure 2.
SEM image of the granulated electric furnace copper/nickel slag.
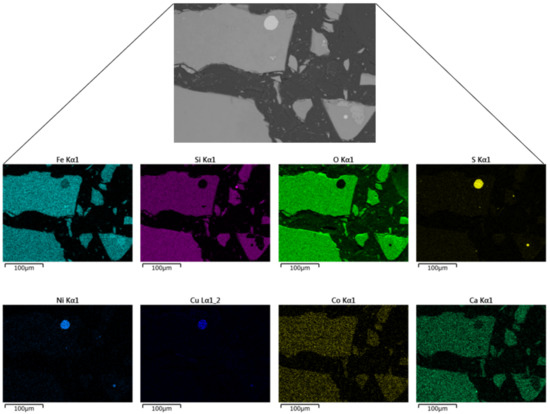
Figure 3.
SEM image and the respective elemental mapping of the granulated slag.
2.2. Procedure
2.2.1. High-Pressure Leaching
Leaching experiments were conducted on a ground slag sample using a sulfuric acid solution. The particle size of the sample was less than 125 µm with the average particle (D50) of 56 µm. A stainless steel autoclave reactor comprising a 200 mL capacity reaction vessel, heating mantle, temperature controller, and a variable speed stirrer was utilized. To obtain optimal leaching conditions, the sulfuric acid concentration was varied between 0 (distilled water) and 1 mol/L, while the leaching time and temperature were varied in the ranges of 0.5–2 h and 120–180 °C, respectively. The stirring speed and pulp density were kept constant at 700 rpm and 100 g/L, respectively. Once the intended temperature was reached, oxygen (O2) gas was injected into the slurry vessel at a controlled total pressure (Ptotal = Pvapor + Poxygen) of 0.6–1.5 MPa. The slurry pH was recorded before and after leaching. The obtained slurry was filtered to separate the pregnant leach solution (PLS) from the solid residue after leaching. The PLS was analyzed using a 4210 MP-AES (Agilent), while the solid residue was analyzed using an X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD, Rigaku RINT–2200V) to identify the mineral composition of the solid samples. The leaching tests were performed in triplicate, and the average values of the dissolved metals were utilized to calculate the leaching efficiency. About 0.3 g of the solid residue was dissolved by aqua regia and analyzed using MP-AES to determine the residual metal content.
2.2.2. Solvent Extraction
Batch solvent extraction tests were conducted using a countercurrent two-stage mixer settler extraction column on a simulated pregnant leach solution obtained from the optimized HPAL experiment. The concentration of metals in the PLS is displayed in Table 2, showing low metal concentrations of nickel, copper, and cobalt. A LIX 984N (10% v/v) with Isoper M as a diluent was used as a copper extractant. The initial pH of the PLS was measured to be 1, and the pH was adjusted between 1 and 2.5 using a 1 M NaOH solution. For each extraction test, 400 mL of solution and 100 mL of extractant (O/A = 0.25) were simultaneously fed by a pump into the extraction column at about 15 mL/s. The agitation speed was kept constant at 400 rpm. Once the extractant was filled into the extraction column, the respective pump was stopped to avoid air bubbles in the extraction column. The mixing and settling were allowed for 20 min to achieve clear phase separation. The copper-loaded organic phase was then collected at its respective outlet leaving behind the copper-barren aqueous phase (raffinate), which was collected afterward at the aqueous phase outlet. The raffinate solution was analyzed using MP-AES to determine the metal concentration and compute the extraction efficiency.

Table 2.
Metal concentration in the pregnant leach solution from HPAL.
The copper-loaded organic was subjected to stripping experiments using a sulfuric acid solution. The stripping column had a similar setup to the extraction column. The desired volume of the sulfuric acid solution (50–175 g/L H2SO4) and the copper-loaded organic was pumped into the stripping column at 15 mL/s and mixed at an agitation speed of 400 rpm. The organic/aqueous (O/A) phase ratio was investigated in the range of 0.25–4.0. After 20 min of contacting, the barren and the stripped solution were collected separately from their respective outlets. The strip solution was analyzed using MP-AES for copper concentration and determination of the stripping efficiency. For copper enrichment in the solution, a combination of two extraction stages and two stripping stages was employed where the strip solution from the first stripping stage was contacted again with the copper extractant. The operating conditions were kept the same as in the first extraction and stripping stages. The extraction and stripping tests were repeated three times and the average values were reported.
2.2.3. Iron Recovery
The raffinate solution obtained from the first extraction stage was further processed for iron removal. A prepared calcium carbonate emulsion of 200 g/L was added to the raffinate solution in a dropwise manner to achieve a pH of 4. The raffinate solution was then heated to 65 °C using a magnetic stirrer operating at 400 rpm. Once the temperature reached 65 °C, the reaction time was set to 20 min. The resulting precipitate and the residual solution were cooled, filtered, and the solution was taken for MP-AES analysis for the elemental analysis to determine the precipitation efficiency. The tests were repeated three times.
2.2.4. Ni/Co Complexation
For the recovery of nickel and cobalt from the raffinate solution obtained from the first copper extraction stage, a potassium amyl xanthate (PAX) solution of 55 g/L was prepared and dosed correspondingly to achieve the desired molar ratio of xanthate to nickel and cobalt. A 50 mL solution of the raffinate was utilized for each complexation test. The pH was investigated between 4 and 8, with a pH of 4 being the initial pH of the raffinate solution. A 1 mol/L NaOH solution was used to adjust the pH to the required pH. The mixture was then heated to 50 °C using a water bath shaker operating at 200 rpm. The complexation reaction was allowed to proceed for 2 h, after which the solution was cooled and filtered. The residual barren solution was analyzed using MP-AES to determine the amount of nickel and cobalt remaining in the solution and accordingly calculate the complexation efficiency. The tests were repeated three times and the average values were reported.
The Ni/Co xanthate precipitate was washed with 10 mL of a 28% analytical grade ammonia solution (NH3) and shaken at 400 rpm for 20 min at 30 °C. The solution was filtered and taken for MP-AES analysis to determine the amount of nickel dissolved, while the remaining cobalt xanthate was dried before the calcination process. The cobalt xanthate precipitate was roasted in a muffle furnace at 200 °C for 1.5 h. After the calcination process, the products were cooled to room temperature and analyzed using XRD for mineral identification. Part of the calcined product was dissolved using aqua regia and analyzed for elemental composition using MP-AES.
3. Discussion
3.1. High-Pressure Leaching
3.1.1. Effect of Sulfuric acid Concentration
The sulfuric acid concentration was varied between 0 mol/L (distilled water) and 1.0 mol/L under 0.6 MPa total pressure, 150 °C temperature, 1 h leaching time, 100 g/L pulp density, and a stirring speed of 700 rpm (Figure 4a). The metal extractions of Ni, Cu, and Co significantly increased as the sulfuric acid concentration was increased. The optimum leaching conditions were observed at 0.6 mol/L sulfuric acid concentration with Ni, Cu, and Co metal dissolutions of 91.81%, 83.36, and 98.36% respectively, beyond which there was no significant improvement in metal dissolution. Iron tenors in the PLS remained low at about 2%; however, the extent of Fe reporting to the PLS seems to significantly increase above 0.4 mol/L H2SO4 concentration. Liao et al. noted the possible re-dissolution of hematite from the solid residue, thus increasing the iron concentration in the PLS at high acid concentrations [21]. At 0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration, almost all the Co is extracted from the slag, while the Cu and Ni extractions began to decline. The highest Cu, Co, and Fe concentrations in the PLS were 0.30, 0.25, 0.11, and 7.22 g/L, respectively, under 0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration.
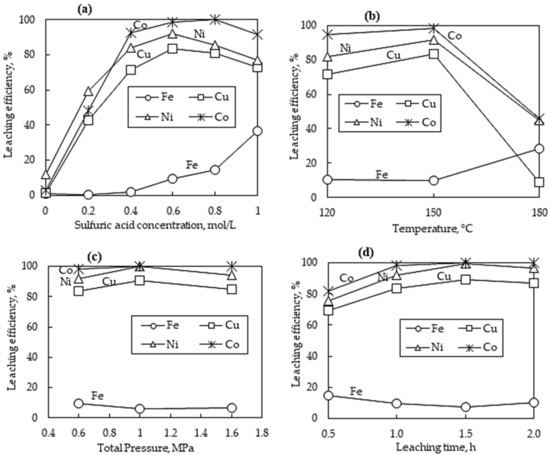
Figure 4.
Metals’ dissolution profiles versus (a) H2SO4 concentration at 150 °C, 1 h, and 0.6 MPa; (b) temperature at 0.6 mol/L H2SO4, 0.6 MPa, and 1 h; (c) total pressure at 0.6 mol/L H2SO4, 1 h, and 150 °C; (d) leaching time at 0.6 mol/L H2SO4, 0.6 MPa, and 150 °C. The particle size, pulp density, and stirring speed were kept constant at −125 µm, 100 g/L, and 700 rpm, respectively.
The residues obtained after leaching were analyzed using XRD (Figure 5); the main components observed were hematite, jarosite-natrojarosite, and goethite. At lower acid concentrations (0.2–0.4 mol/L), hematite and goethite are preferentially precipitated, while at increasing acid concentrations (0.6–1.0 mol/L), jarosite is preferentially precipitated due to a sulfate-rich environment. Therefore, the formation of iron phases is dependent on pH and/or free acidity. McDonald and Muir [28] and Han et al. [29] also observed that upon increasing the acid and sulfate concentrations, the predominant iron-containing residue formed as jarosite. The silica phase was not detected by XRD; however, XRF analysis (Table 3) indicates almost 90% silica removal in all the solid residues, and this suggests that silica may exist as amorphous silica, rather than in a crystalline form, which has also been confirmed by other studies [11,21].
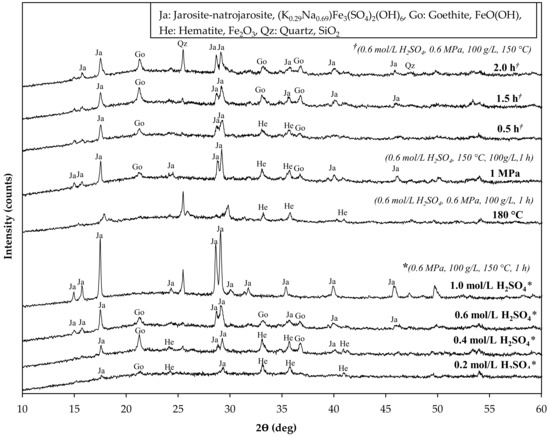
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of residues obtained after HPAL at different leaching conditions. Conditions; H2SO4 concentration 0.2–1.0 mol/L, total pressure 0.6–1.0 MPa, temperature 150–180 °C, and leaching time 0.5–2 h. The respective leaching conditions are indicated by * and † where applicable.

Table 3.
Metal distribution from slag to the solid leach residues after HPAL at different H2SO4 concentrations.
During the HPAL of slag, the following chemical Reactions (1)–(6) are considered [4,20,30,31,32]. The dissolution of fayalite via Reaction (1) consumes acid and yields ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) and silicic acid (H4SiO4). The ferrous sulfate is then oxidized to ferric sulfate (Fe2(SO4)3) as per Reaction (2), and the ferric sulfate is spontaneously hydrolyzed to form iron precipitates of hematite, goethite, and/or natrojarosite as per Reactions (3)–(5). Silicic acid is further dehydrated via Reaction (6), generating amorphous silica (SiO2), which was confirmed by XRF measurements used for calculations in Table 3. Dehydration of silicic acid has thermodynamically been found to be favored at temperatures above 109 °C [20]; therefore, leaching at 150 °C ensured that the majority of silicon is fixed in the solid residue as observed in Table 3. The pH of the pregnant leach solutions obtained after leaching with 0.4 mol/L and 0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration increased from the initial pH of 0.41 and 0.66 to 1.02 and 1.25, respectively. Though the Reactions (3)–(5) release sulfuric acid, it is in turn balanced by the acid consumption of the fayalite dissolution through Reaction (1).
Fe2SiO4 + 2H2SO4 → 2FeSO4 + H4SiO4
4FeSO4 + O2 + 2H2SO4 → 2Fe2(SO4)3 + 2H2O
3Fe2(SO4)3 + Na2SO4 + 12H2O → 2NaFe3(SO4)2(OH)6 + 6H2SO4
Fe2(SO4)3 + 4H2O → 2FeO(OH) + 3H2SO4
2Fe2(SO4)3 + 6H2O → 2Fe2O3 + 6H2SO4
H4SiO4 → SiO2 + 2H2O
3.1.2. Effect of Temperature
Figure 4b shows the metals’ dissolution profiles with respect to temperature, and other parameters were kept constant at 0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration, 1 h leaching time, 100 g/L pulp density, 700 rpm stirring speed, and 0.6 MPa total pressure. The results show that at temperatures below 150 °C, the slag was amendable for leaching; however, at elevated temperatures (180 °C), a negative effect on the metal dissolution of Ni, Cu, and Co is observed. Difficulty with filtration was also experienced with the 180 °C leached sample, indicating the presence of silica gel. This was attributed to the decreased stability of silicic acid at high temperatures, which re-polymerizes rapidly forming silica gel, resulting in closed dissolution pores and preventing further slag leaching [4]. At all investigated conditions, cobalt is preferentially leached from the slag when compared to Ni and Cu, mainly because cobalt exists in the oxide form as shown in the mineralogical analysis (Figure 3), and thus can easily be dissolved by acid. The percentage of the dissolved iron increased by about threefold when the temperature was increased from 150 °C to 180 °C. The increase in iron concentration could be attributed to the hindered oxygen diffusion resulting from the abundance of silica gel, thus hindering the oxidation of ferrous sulfate and or the hydrolysis of ferric sulfate. At lower leaching temperatures (120–150 °C), the main component in the solid residue is jarosite, while at elevated temperatures (180 °C), hematite was observed as the only iron precipitate (Figure 5).
3.1.3. Effect of Total Pressure
Figure 4c shows the metals’ leaching efficiencies as the total pressure varied between 0.6 MPa and 1.6 MPa. The total pressure was controlled by oxygen injection, while other parameters were fixed at 0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration, 1 h leaching time, 150 °C temperature, 100 g/L pulp density, and 700 rpm stirring speed. The leaching efficiency of Ni, Cu, and Co did not show a significant change when the total pressure of the leaching system was increased. The lower total pressure of 0.6 MPa was able to yield good leaching efficiency results of 91.81%, 83.36, and 98.36% for Ni, Cu, and Co, respectively, comparable to a higher total pressure of 1.6 MPa which yielded a similar leaching efficiency of 94.02%, 84.56, and 99.99% for Ni, Cu, and Co, respectively. Other scholars also confirmed that there was no benefit in increasing oxygen overpressure above 600 kPa when leaching slag [5,20]. The dissolved iron in the PLS remained low at all the investigated total pressures. Excess oxygen encouraged the precipitation of hematite alongside jarosite-natrojarosite and goethite (Figure 5). Additionally, the presence of oxygen promotes the dissolution of metal sulfides as per the reaction [20].
MeS(s) + 2O2 → MeSO4 (Me = Ni, Cu, and Co)
3.1.4. Effect of Leaching Time
The effect of leaching time on slag dissolution was investigated at different time intervals of 0.5–2 h, while other parameters were kept constant (0.6 mol/L H2SO4 concentration, 0.6 MPa total pressure, 150 °C temperature, 100 g/L pulp density, and 700 rpm stirring speed). The results are displayed in Figure 4d, showing that the dissolution of cobalt almost reached completion after 1 h of leaching, while nickel dissolution reached completion after 1.5 h. The rapid leaching rate of cobalt can be attributed to its presence in the oxide form within fayalite, in contrast to nickel and copper, which are predominantly found in sulfide form. On the other hand, the leaching rate of copper was lower than that of Ni and Co and reached a high of 89.42% after 1.5 h, and no further improvements in dissolution were noted. The lower leaching efficiency of copper is likely due to the re-precipitation of the dissolved copper, which has been previously noted [21]. The Fe tenors to the PLS remained around 10% after 1 h of leaching time. The XRD patterns of residues obtained after leaching at different intervals are shown in Figure 5. Hematite was only noted in the leach residue obtained after 0.5 h of leaching time, alongside goethite and jarosite-natrojarosite. The leach residues obtained after 1–2 h of leaching had a similar mineralogical composition, comprising mainly jarosite-natrojarosite and goethite. No hematite was detected in the residue obtained after 1 h of leaching time, indicating an iron phase conversion from hematite to jarosite as leaching progressed. Silica was not detected by XRD measurements in solid residues of less than 1.5 h, indicating its existence as amorphous silica. However, silica was detected by XRD in the leach residue obtained after 2 h of leaching, indicating a structural change from amorphous silica to crystalline silica as a function of time.
3.2. Solvent Extraction and Stripping of Cu from PLS
3.2.1. Effect of pH on Copper Extraction
The first stage of copper extraction was conducted on the PLS whose metal concentration is displayed in Table 2. The pH of the pregnant leach solution (PLS) is one of the most important parameters affecting ion exchange reactions. Therefore, the pH was investigated in the range of 1–2.5 on metal extractions, with a pH of 1 being the initial solution pH. Other operating conditions were kept constant with an O/A ratio of 0.25 (100 mL to 400 mL), a 10% LIX984N extractant, agitation speed of 400 rpm, solution flow rate of 15 mL/s, and a residence time of 20 min. The results are displayed in Figure 6a, showing that as the pH was increased, the amount of copper extracted from the pregnant leach solution likewise increased, reaching a high of 98.3% when the pH was 2.5. The amount of Fe extracted along with Cu remained below 6% when the pH was 2 or lower; however, when the pH was increased to 2.5, the amount of Fe co-extracted with copper sharply increased to about 25%. Co-extractions of cobalt and nickel remained low at all the investigated pH values. Therefore, a pH of 2 was chosen as the optimal condition for the extraction of copper (96.3%) from the pregnant leach solution due to the good separation efficiency of copper from iron, nickel, and cobalt.
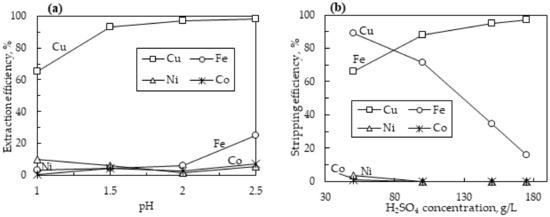
Figure 6.
(a) The extraction behavior of metals as a function of pH at O/A ratio 0.25, extractant LIX 984N 10%, agitation speed 400 rpm, flow rate 15 mL/s, and residence time 20 min. (b) Stripping behavior of metals as a function of sulfuric acid concentration at O/A ratio 0.25 (100 mL to 400 mL), stirring speed 400 rpm, flow rate 15 mL/s, and residence time 20 min.
3.2.2. Effect of Sulfuric Acid Concentration on Cu Stripping
The effect of sulfuric acid on the stripping of copper from the organic phase was investigated in the range of 50 g/L to 175 g/L H2SO4 concentration (Figure 6b). Operating conditions of the stripping column were kept identical to that in the extraction column (O/A ratio of 0.25, agitation speed 400 rpm, solution flow rate 15 mL/s, and a residence time of 20 min). As the concentration of sulfuric acid increased, so did the separation efficiency between copper and iron. Utilizing a sulfuric acid concentration of 175 g/L, a high copper stripping efficiency of 97.3% was achieved, with a lower iron stripping efficiency of 15.6%, yielding a good separation efficiency of 81.6% between copper and iron, while cobalt and nickel were undetectable in the strip solution.
3.2.3. Effect of Organic/Aqueous (O/A) Ratio
The organic/aqueous (O/A) ratio was investigated to achieve a higher copper concentration in the strip solution while maintaining a good copper stripping efficiency. The stripping conditions were as follows: 175 g/L H2SO4 concentration, 400 rpm stirring speed, 15 mL/s solution flow rate, and residence time of 20 min. Figure 7 shows that the copper concentration increased from 0.26 g/L to 4.18 g/L as the O:A volume ratio was increased from 1:4 to 4:1. The concentration of iron slightly increased as the O/A volume ratio was increased, reaching a high of 1.27 g/L when the O/A volume ratio was 4:1. This is attributed to the increased volume of the organic phase consequently presenting a higher amount of surface-active iron impurity, which is stripped alongside copper. The stripping efficiency of copper slightly declined from 97% to around 80% as the O/A volume ratio was increased beyond 0.25, but maintained a stripping efficiency of 86% when the O/A ratio was 4:1. The decline in stripping efficiency is attributed to an increase in the mass transfer resistance as the loading ratio is increased [33].
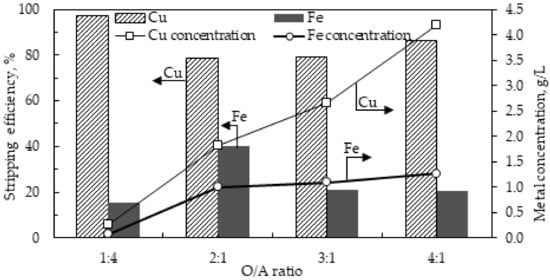
Figure 7.
The effect of the organic/aqueous (O/A) volume ratio on the concentration of metals in the stripped copper solution. Conditions: H2SO4 concentration 175 g/L, agitation speed 400 rpm, solution flow rate 15 mL/s, and residence time 20 min).
3.2.4. The Second Stage of Solvent Extraction
To increase copper production, solvent extraction circuits are oftentimes arranged in parallel or series-parallel in the industry [34]. The strip solution (4.18 g/L Cu, 1.27 g/L Fe) obtained under the copper stripping conditions of O/A ratio 4:1 was further contacted with a fresh extractant to employ the second stage of extraction and stripping stages for further solution upgrade. The conditions of extraction and stripping in the second stages were kept the same as in the first extraction and stripping stages. By employing two stages of copper loading and stripping, the copper concentration was successfully upgraded from 4.2 g/L in the first extraction and stripping stages to 22.9 g/L in the second extraction and stripping stages. Moreover, iron concentration was further minimized in the final strip solution, decreasing from 1.27 g/L to 0.05 g/L in the first and second strip solutions, respectively. The raffinate 2 obtained from the second stage after copper extraction had a copper and iron concentration of 0.4 g/L and 1.57 g/L, respectively, which can be recycled back to the first stage of copper extraction to be blended with the PLS (0.3 g/L Cu and 2.96 g/L Fe) feed solution.
3.3. Recovery of Ni and Co
3.3.1. Iron Recovery
Iron was removed from the raffinate 1 solution (2.52 g/L Fe, 0.3 g/L Ni, and 0.13 g/L Co) that was obtained from the first SX stage before Ni and Co can be recovered. A 200 g/L calcium carbonate (CaCO3) emulsion was used to selectively precipitate iron from the solution at pH 4, 65 °C, and 400 rpm for 20 min. A CaCO3 emulsion is commonly used to achieve excellent removal of iron from solutions at a pH of around 3.5 [19]. Likewise, excellent removal of iron (99%) from the raffinate solution was achieved in this study, with no residual iron detected by MP-AES analysis. Ferric iron is known to precipitate as hydroxides at pH values above 3, and Bhattacharjee et al. also noted that the precipitation of iron using calcium carbonate forms a mixture of calcium-iron hydroxides (Ca3Fe2(OH)12) [35]. However, an XRD analysis of the obtained precipitate showed the main mineral component as gypsum, while the iron mineral components could not be detected by XRD, suggesting that Fe precipitates are not in a crystalline structure. Low co-precipitation of nickel and cobalt of 3.68% and 2.27%, respectively, were obtained. The concentration of metals in the residual Ni/Co solution was 0.3 g/L Ni and 0.12 g/L Co. However, utilization of CaCO3 reagent results in an increased content of calcium in solutions, which has been noted to cause difficulties in the subsequent recovery processes of nickel and cobalt [36,37]. Therefore, the following separation process of xanthate complexation utilized in this study is a promising way to separate nickel and cobalt as it does not require prior removal of calcium impurity from the solution, as compared to the solvent extraction process commonly used for the separation of nickel and cobalt.
3.3.2. Ni/Co Xanthate Complexation
Effect of pH
The solution pH is an important parameter that significantly influences the Ksp and the stability of xanthates [38], consequently affecting the selective extraction of metals from the solution. Therefore, the effect of pH on the co-extraction of nickel and cobalt from the solution using PAX as a complexing agent was investigated. Figure 8 shows the complexation behavior of nickel and cobalt under different pH conditions, at 50 °C, 2 h, 400 rpm, and a 1.5 molar ratio of xanthate to nickel and cobalt. The results show that a pH of about 6 is conducive for complexing Ni and Co from solution using PAX, yielding a complexation efficiency of 83.6% and 99.4% for nickel and cobalt, respectively. At lower pH values, the xanthate complexation efficiency of nickel and cobalt is low, which is attributed to the decomposition of xanthate in acidic conditions, thus resulting in insufficient xanthate ions to form nickel and cobalt complexes. A further increase in pH resulted in a decline in the formation of nickel xanthate precipitate; however, cobalt complexation efficiency was not affected by an increase in pH above 6 and maintained complete extraction from the solution. A lower complexation of Ni than Co may be attributed to a lower Ksp of nickel xanthate (Ni(C2H5OCSS)2) as compared to cobalt xanthate (Co(C2H5OCSS)2) [39], making Ni(C2H5OCSS)2 more unstable than Co(C2H5OCSS)2, and therefore, it easily re-dissolves. At high pH values, hydroxide ions have also been noted to compete with xanthates for metal ions [38], and this also may have contributed to the low nickel xanthate complexation efficiency. The complexation of nickel and cobalt from solution using PAX is suggested to follow Reactions (8) and (9), respectively [22,40].
Ni2+ + 2CH3(CH2)4OCS2K → Ni(CH3(CH2)4OCSS)2 + 2K+
Co2+ + 2CH3(CH2)4OCS2K → Co(CH3(CH2)4OCSS)2 + 2K+
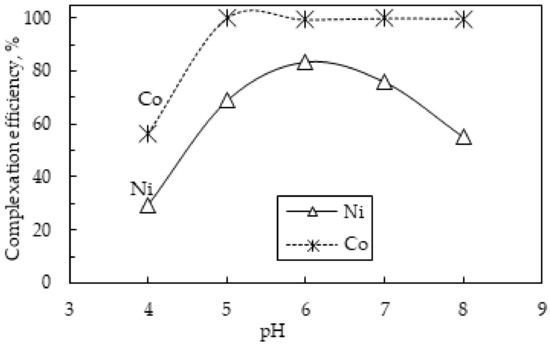
Figure 8.
The effect of pH on the Ni/Co complexation using PAX. Conditions: 50 °C, 2 h, 400 rpm.
Effect of Xanthate to Ni/Co Molar Ratio
The molar ratio of xanthate to nickel and cobalt ions was investigated between 1 and 2.5 by varying the PAX dosage. Other complexation conditions were kept constant at 50 °C, a pH of 6, 400 rpm, and a reaction time of 2 h. The results are displayed in Figure 9, showing that as the xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratio was increased, the complexation efficiency of nickel and cobalt likewise increased. At a xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratio of 2, almost all the nickel (99.3%) and the cobalt (99.9%) were complexed out of the raffinate solution, which is in agreement with Reactions (8) and (9). A xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratio of less than 2 results in insufficient xanthate ions required to form complexes with Ni and Co, while a molar ratio beyond 2 provides excess xanthate ions that enable complete complexation of Ni and Co from the solution. The tendency of xanthate to form metal complexes with cobalt was preferred over nickel as observed by a consistent complexation efficiency of more than 99.9% even at xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratios of less than 2. This indicates that cobalt may have a stronger affinity to xanthate than nickel, and thus rapidly binds and forms stable cobalt xanthate complexes. The barren solution was confirmed to have almost no residual metals and can potentially be recycled to the slag leaching stage to be used as a leaching medium with the addition of sulfuric acid.
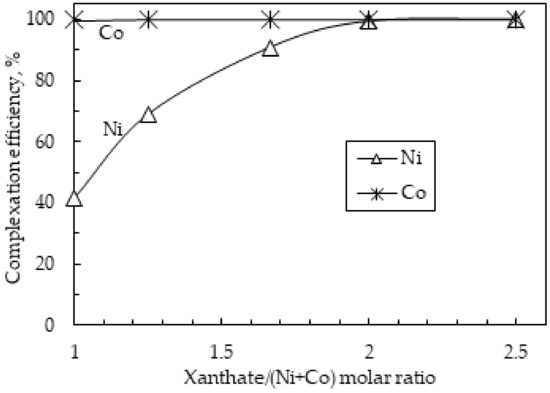
Figure 9.
The effect of xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratio on the Ni/Co complexation using PAX. Conditions: 50 °C, pH 6, 2 h, 400 rpm.
3.3.3. Separation of Ni and Co
For the separation of nickel and cobalt xanthate complexes, the difference in their solubility product (Ksp) was explored. Because nickel xanthate has a lower solubility product than cobalt xanthate [22], nickel xanthate can therefore be easily dissolved, while cobalt remains in the solid form. Additionally, nickel is known to form stable complexes with ammonia [39], therefore, an analytical grade 28% ammonia solution (NH3) was directly used to selectively dissolve the nickel xanthate complex while cobalt xanthate remained in solid form. The dissolution of the nickel xanthate complex using 10 mL ammonia solution, at 30 °C and 400 rpm for 20 min, was anticipated to follow Reaction (10). The nickel xanthate dissolution percentage of 75.4% was obtained, yielding a nickel ammine solution of 1.2 g/L Ni. Cobalt was not detected in the wash solution by MP-AES analysis, confirming that almost all cobalt xanthate remained in solid form due to its higher Ksp. The incomplete dissolution of nickel xanthate may be attributed to the easy hydrolysis of NH3 to NH4+ in an aqueous solution, resulting in insufficient ammonia to react with Ni in the solution [39].
Ni(CH3(CH2)4OCSS)2 (s) + 6NH3(aq) → Ni(NH3)62+(aq) + 2CH3(CH2)4OCSS−(aq)
The cobalt xanthate precipitate was thermally decomposed in a muffle furnace for 1.5 h at 200 °C and the XRD pattern of the calcined product is shown in Figure 10, showing that the main composition of the calcined product was cobalt oxide (CoO). The chemical analysis of the CoO product using MP-AES determined the cobalt grade to be 25 wt.%.
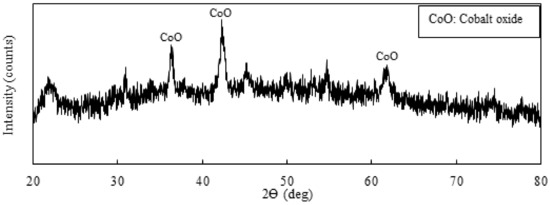
Figure 10.
An XRD pattern of the calcined product obtained after cobalt xanthate precipitate calcination.
3.4. Economic Evaluation
A preliminary economic evaluation for processing the slag by the proposed technologies was evaluated as shown in Table 4 and Table 5. Table 4 shows the financial benefit from the metal values utilizing the current market prices and the estimated tonnage of metal content in slag that could be recovered. The recoveries were calculated based on the waste streams. The slag pile that accumulated over the 41 years of continuous smelter operation at a slag generation rate of 120 t/h was estimated to be about 32 million tons taking into consideration maintenance and smelter shutdowns. The total amount of metals was valued at around USD 8.6 billion. The value of Fe was derived from the price of iron ore (62% Fe). The leach residue and the precipitated solids were regarded as Fe resources due to the possibility of further utilization as feed in the steel industry after additional processing.

Table 4.
The estimated economic benefit of metal values from slag.

Table 5.
The estimated processing cost of slag per year.
The cost of processing the slag was estimated based on the yearly production of Cu, Ni, and Co when the throughput of slag is around 800,000 tons, which was equivalent to the yearly generation of slag by the smelter in Botswana. Table 5 displays the cost of processing slag with respect to the methodologies proposed. In the current study, other factors, such as depreciation values, labor costs, transportation, administrative, and other miscellaneous expenses, were not taken into account during the economic evaluation estimation. High-pressure leaching capital costs were estimated to be 50,000 USD/annual tons of nickel produced, while the operating cost was estimated to be 8000 USD/ton of nickel produced [41]. The sulfuric acid was considered to be readily supplied by the sulfuric acid plant from an operating smelter. The solvent extraction capital costs were estimated to be 500 USD/annual tons of Cu produced, while the operational costs and reagent costs were each estimated to be 0.05 USD/kg Cu produced [34]. Based on this preliminary cost evaluation, cleaning the Botswana copper nickel slag will have an economic benefit of about USD 60 million per year after the settlement of the capital costs in the first year of operation. In addition to the economic benefit, environmental advantages are also realized. Processing the slag will disrupt the natural weathering process and prevent further metal elution into the environment; additionally, by manufacturing sulfuric acid for this leaching process, less SO2 emissions will be realized.
4. Conclusions
A hydrometallurgical process for the recovery of copper, nickel, and cobalt from smelter slag was developed and the process flow chart is presented in Figure 11. The key methods utilized were high-pressure acid leaching, solvent extraction, xanthate complexation, ammonia leaching, and calcination. The main findings from this study are highlighted below.
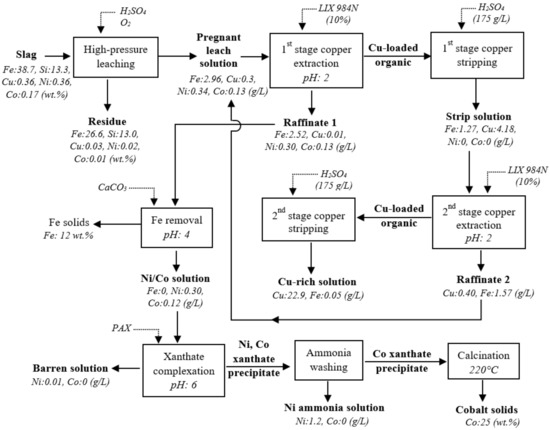
Figure 11.
Process flow chart for recovery of copper, nickel, and cobalt from smelter slag by HPAL, solvent extraction, precipitation, and xanthate complexation.
Under optimized HPAL conditions, selective extraction of Ni, Cu, and Co from the smelter slag was achieved, yielding high leaching efficiencies of 99.9%, 89.4%, and 99.9%, respectively. Low Fe and Si tenors to the PLS of 7.2% and 2.5%, respectively, were obtained, with a final solution pH of 1. Employing two-stage extraction and stripping stages, copper in the PLS was successfully enriched from 0.3 g/L to 23 g/L Cu, while iron concentration was remarkably reduced from 2.96 g/L to 0.05 g/L Fe in the final Cu-rich solution. After the complete removal of iron from the raffinate solution, PAX was successfully used to selectively extract 99.3% of nickel and 99.9% of cobalt from the raffinate solution through chemical complexation at pH 6 and a xanthate/(Ni+Co) molar ratio of 2. Cobalt showed a stronger affinity to xanthate ions than nickel. Selective dissolution of nickel xanthate using ammonia solution yielded 75.4% nickel dissolution (1.2 g/L Ni), while more than 99% of Co remained as cobalt xanthate solids due to the difference in the Ksp of nickel and cobalt xanthates. The thermal decomposition of cobalt xanthate precipitate at 200 °C for 1 h was converted to a cobalt oxide (CoO) product, which was assayed at 25 wt.% Co.
This study demonstrates that copper/nickel smelter slags present a potential source of secondary raw material for copper, nickel, and cobalt production. A preliminary economic evaluation of the proposed process showed a positive income after the second year of operation, in addition to the unquantifiable environmental benefits that will be realized.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su151310496/s1, Figure S1: EDX spectrum analysis of different spots in the slag particle.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L.G., K.H. and A.S.; methodology, L.L.G., K.H., G.D. and A.S.; validation, L.L.G., B.A. and A.S.; formal analysis, L.L.G. and K.H.; investigation, L.L.G., K.H., G.D. and A.S.; resources, G.D., K.H. and A.S.; data curation, L.L.G., B.A., S.J. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.L.G.; writing—review and editing, L.L.G., K.H., B.A., S.J., G.D. and A.S.; visualization, L.L.G., K.H., B.A., S.J., G.D. and A.S.; supervision, A.S.; project administration, A.S.; funding acquisition, K.H. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to appreciate the former BCL Mine and the Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST) for their kind support, cooperation, and provision of the smelter slag sample. The authors are grateful for the financial support of the Program for Leading Graduate Schools “New Frontier Leader Program for Rare Metals and Resources” and Akita University Support for Fostering Research Project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, J.M. Carbon neutrality: Toward a sustainable future. Innovation 2021, 2, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Msigwa, G.; Yang, M.; Osman, A.I.; Fawzy, S.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Strategies to achieve a carbon neutral society: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2277–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potysz, A.; Mikoda, B.; Napieraj, M. (Bio)dissolution of Glassy and Diopside-Bearing Metallurgical Slags: Experimental and Economic Aspects. Minerals 2021, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perederiy, I.; Papangelakis, V.G. Why amorphous FeO-SiO2 slags do not acid-leach at high temperatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Perederiy, I.; Papangelakis, V.G. Cleaning of waste smelter slags and recovery of valuable metals by pressure oxidative leaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tang, C.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, P.; Tang, M. A cleaner process for valuable metals recovery from hydrometallurgical zinc residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, G.; Perek, K.T.; Gül, A.; Arslan, F.; Önal, G. Recovery of metal values from copper slags by flotation and roasting with pyrite. Min. Metall. Explor. 2007, 24, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, T.C.; Singh, P.; Nikoloski, A.N. The potential for copper slag waste as a resource for a circular economy: A review–Part II. Miner. Eng. 2021, 172, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalha, M.; Papangelakis, V.G.; Curlook, W. Factors affecting the leachability of Ni/Co/Cu slags at high temperature. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 85, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Papangelakis, V.G.; Perederiy, I. High pressure oxidative acid leaching of nickel smelter slag: Characterization of feed and residue. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 97, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, C.; Gao, W.; Lu, M. Recovery of Iron from Copper Slag Using Coal-Based Direct Reduction: Reduction Characteristics and Kinetics. Minerals 2020, 10, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadirov, R.K.; Syzdykova, L.I.; Zhussupova, A.K.; Usserbaev, M.T. Recovery of value metals from copper smelter slag by ammonium chloride treatment. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 124, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundoǧan, H.S.; Tümen, F. Metal recovery from copper converter slag by roasting with ferric sulphate. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 44, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Rui-lin, M.; Wang-dong, N.; Hui, W. Selective leaching of base metals from copper smelter slag. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijevic, M.; Urosevic, D.; Milic, S.; Sokic, M.; Markovic, R. Dissolution of copper from smelting slag by leaching in chloride media. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2017, 53, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altundogan, H.S.; Boyrazli, M.; Tumen, F. A study on the sulphuric acid leaching of copper converter slag in the presence of dichromate. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyrazli, M.; Altundogan, H.S.; Tumen, F. Recovery of metals from copper converter slag by leaching with K2Cr2O7-H2SO4. Can. Metall. Q. 2006, 45, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banza, A.N.; Gock, E.; Kongolo, K. Base metals recovery from copper smelter slag by oxidizing leaching and solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 67, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Selective recovery of valuable metals from nickel converter slag at elevated temperature with sulfuric acid solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ji, G.; Shi, G.; Xi, J. A Study on the Selective Leaching of Valuable Metals and the Configuration of Iron Silicon Phases in Copper Smelting Slag by Oxidative Pressure Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakylabad, A.B.; Darezereshki, E.; Hassanzadeh, A. Selective Recovery of Cobalt and Fabrication of Nano-Co3S4 from Pregnant Leach Solution of Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1027–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motswaiso, F.S.; Nakamura, K.; Watanabe, N.; Komai, T. Geochemical Investigation of Metals and Trace Elements around the Abandoned Cu-Ni Mine Site in Selibe Phikwe, Botswana. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2019, 07, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moagi, L. Sulphur and heavy metals contents in soils and Grewia bicolor leaves around the Selibe Pikwe Cu-Ni mine (BCL), Botswana. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2016, 8, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatak, N.M.; Parsons, M.B.; Seal, R.R. Characteristics and environmental aspects of slag: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 236–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perederiy, I. Dissolution of Valuable Metals from Nickel Smelter Slags by Means of High Pressure Oxidative Acid Leaching; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gabasiane, T.S.; Danha, G.; Mamvura, T.A.; Mashifana, T.; Dzinomwa, G. Characterization of copper slag for beneficiation of iron and copper. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.G.; Muir, D.M. Pressure oxidation leaching of chalcopyrite. Part II: Comparison of medium temperature kinetics and products and effect of chloride ion. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 86, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Altansukh, B.; Haga, K.; Takasaki, Y.; Shibayama, A. Leaching and Kinetic Study on Pressure Oxidation of Chalcopyrite in H2SO4 Solution and the Effect of Pyrite on Chalcopyrite Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Ning, P. Leaching of iron from copper tailings by sulfuric acid: Behavior, kinetics and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 5741–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, U.; Rintala, L.; Halli, P.; Taskinen, P.; Lundström, M. Hydrometallurgical Approach for Leaching of Metals from Copper Rich Side Stream Originating from Base Metal Production. Metals 2018, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aracena, A.; Fernández, F.; Jerez, O.; Jaques, A. Converter slag leaching in ammonia medium/column system with subsequent crystallisation with NaSH. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 188, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Nii, S. Behaviour of multistage mixer-settler extraction column. Mem. Sch. Eng. Nagoya Univ. 1999, 51, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, M.E.; King, M.J.; Sole, K.C.; Davenport, W.G. Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 5th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Gupta, K.K.; Chakravarty, S.; Thakur, P.; Bhattacharyya, G. Separation of Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt from Sulphated Leach Liquor of Low Nickel Lateritic Oxide Ore. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, Q.-w.; Chen, J. Recovery of copper, nickel and cobalt from acidic pressure leaching solutions of low-grade sulfide flotation concentrates. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursunoglu, S.; Ichlas, Z.T.; Kaya, M. Solvent extraction process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from Caldag laterite leach solution: The first bench scale study. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Wu, L.-M.; Huang, P.-P.; Shen, Q.; Sun, Z.-X. Determination and application of the solubility product of metal xanthate in mineral flotation and heavy metal removal in wastewater treatment. Miner. Eng. 2018, 127, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Song, S.; Tang, H.; Ding, S.; Sun, W.; Lei, S.; Xu, S. Recovering valuable metals from the leaching liquor of blended cathode material of spent lithium-ion battery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darezereshki, E.; Vakylabad, A.B.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Niedoba, T.; Surowiak, A.; Koohestani, B. Hydrometallurgical Synthesis of Nickel Nano-Sulfides from Spent Lithium-Ion Batteries. Minerals 2021, 11, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, M. Commodities: Nickel laterites in the ascendant. Aust. J. Min. 2010, 12–13, 13. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).