Sustainable Soundscape Monitoring of Modified Psycho-Acoustic Annoyance Model with Edge Computing for 5G IoT Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zwicker’s Model and Tonality
2.2. Study of JNDs in Sound-Quality Metrics
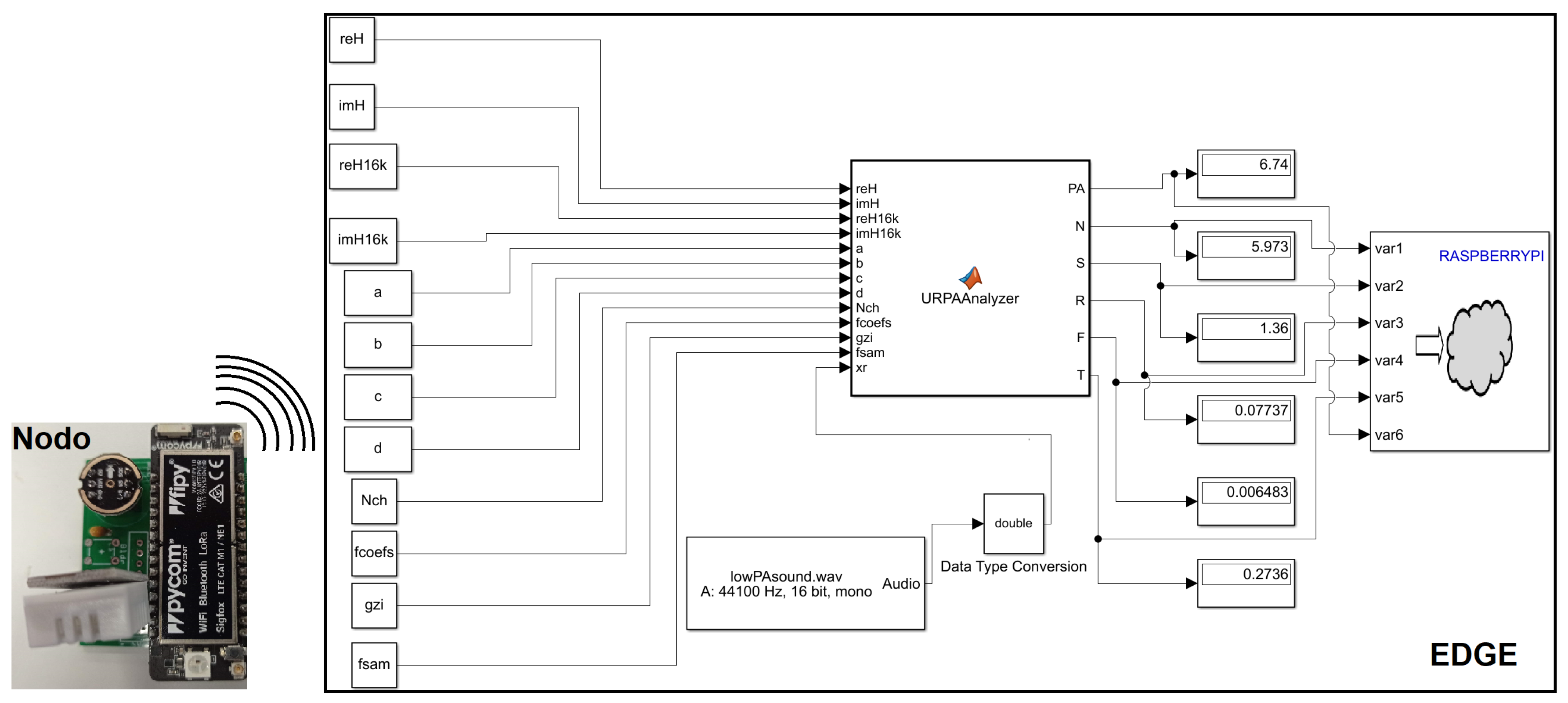
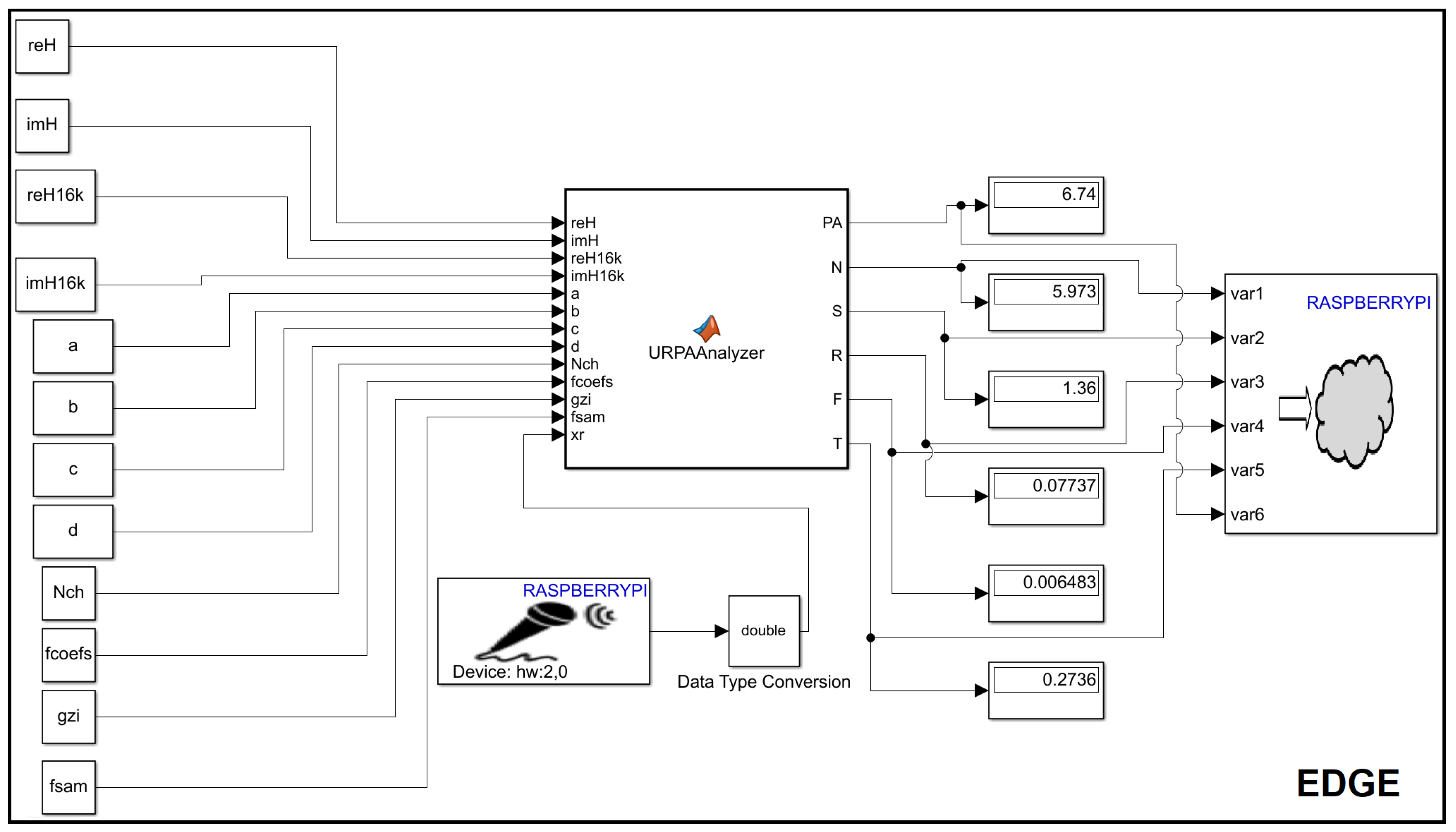
2.3. Implementation of the Architecture of the System
2.4. Calibration Procedure
2.5. Experiments to Evaluate the Model
3. Results and Discussion
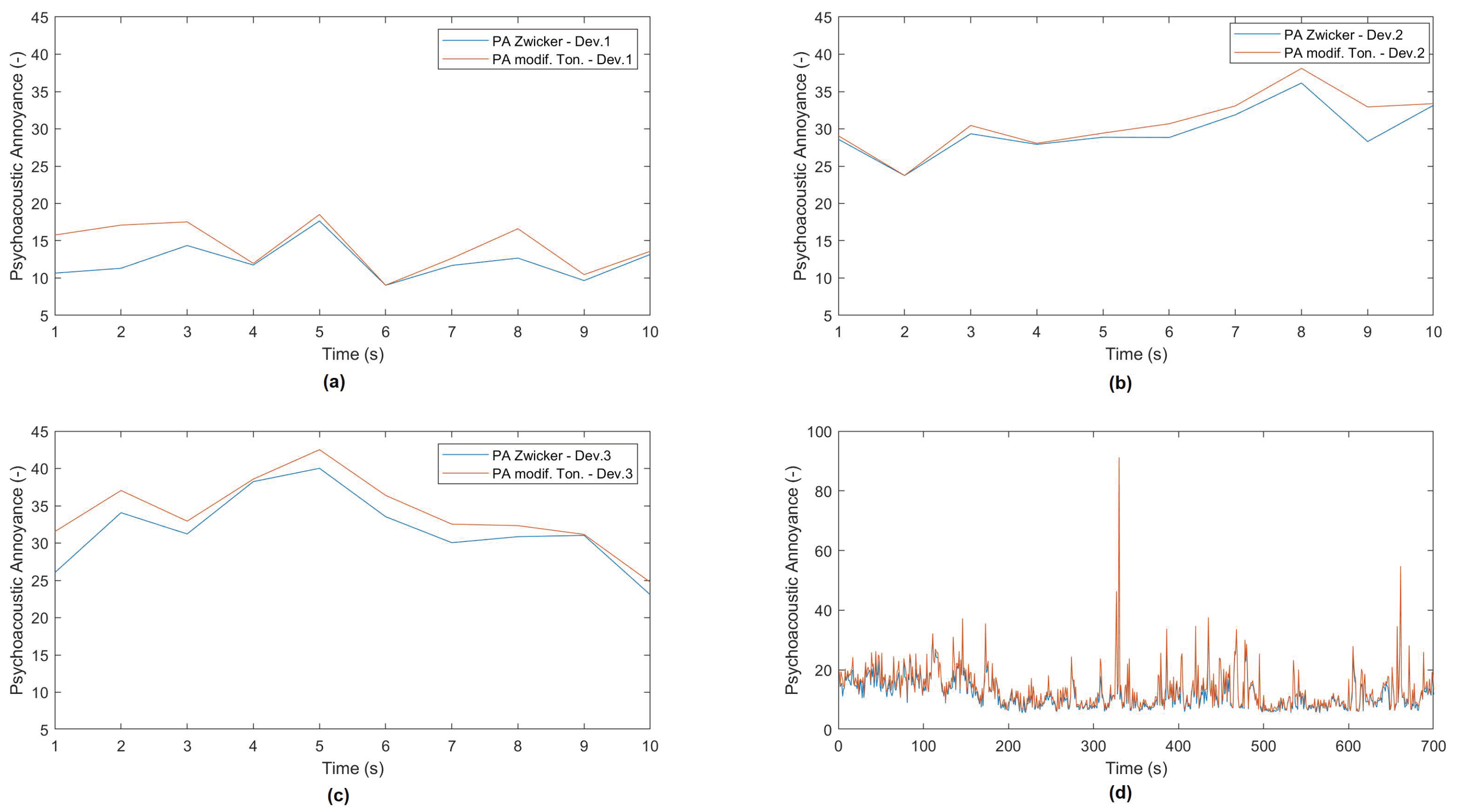
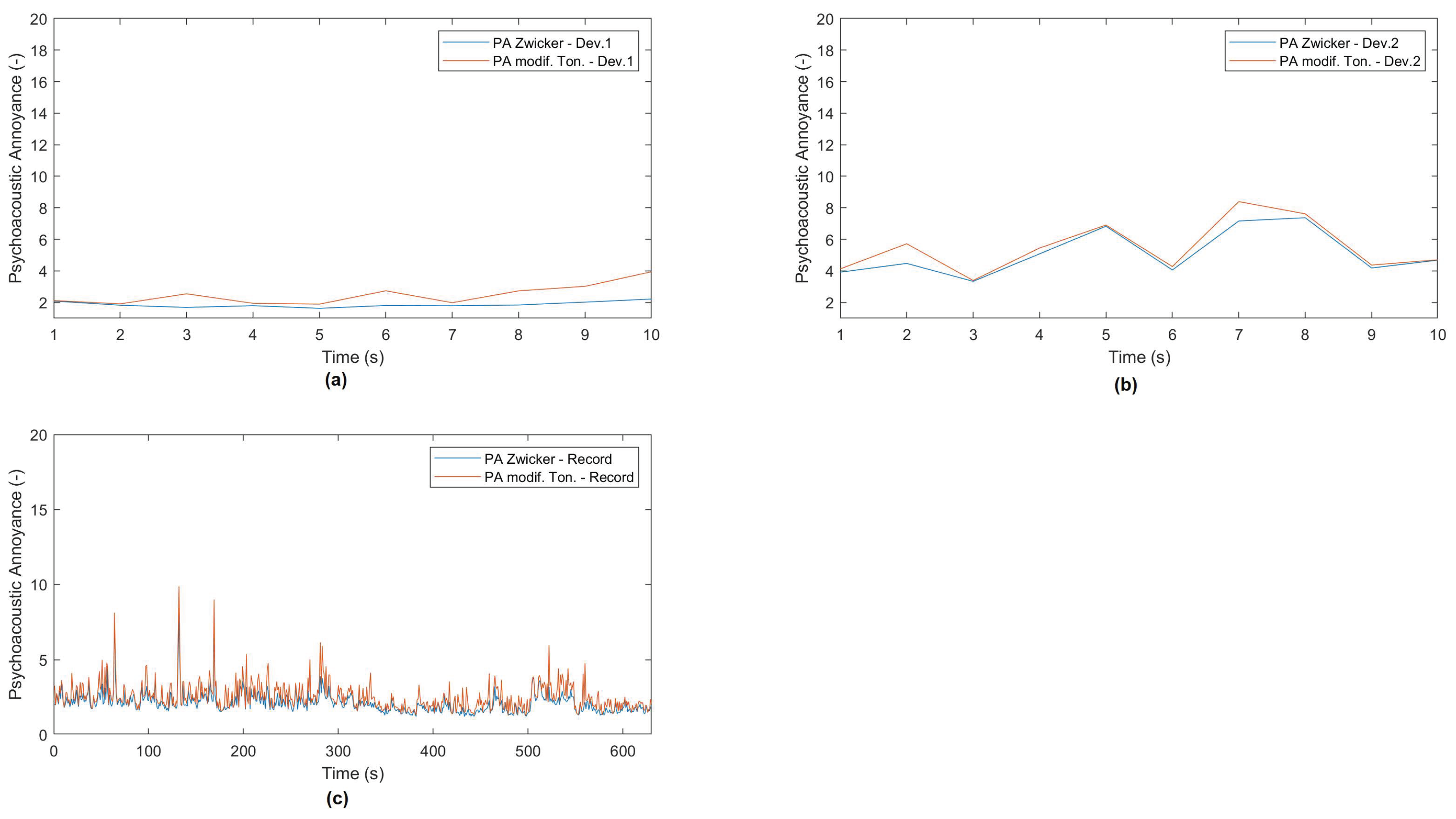
3.1. Application of the System to Compare Models’ Results
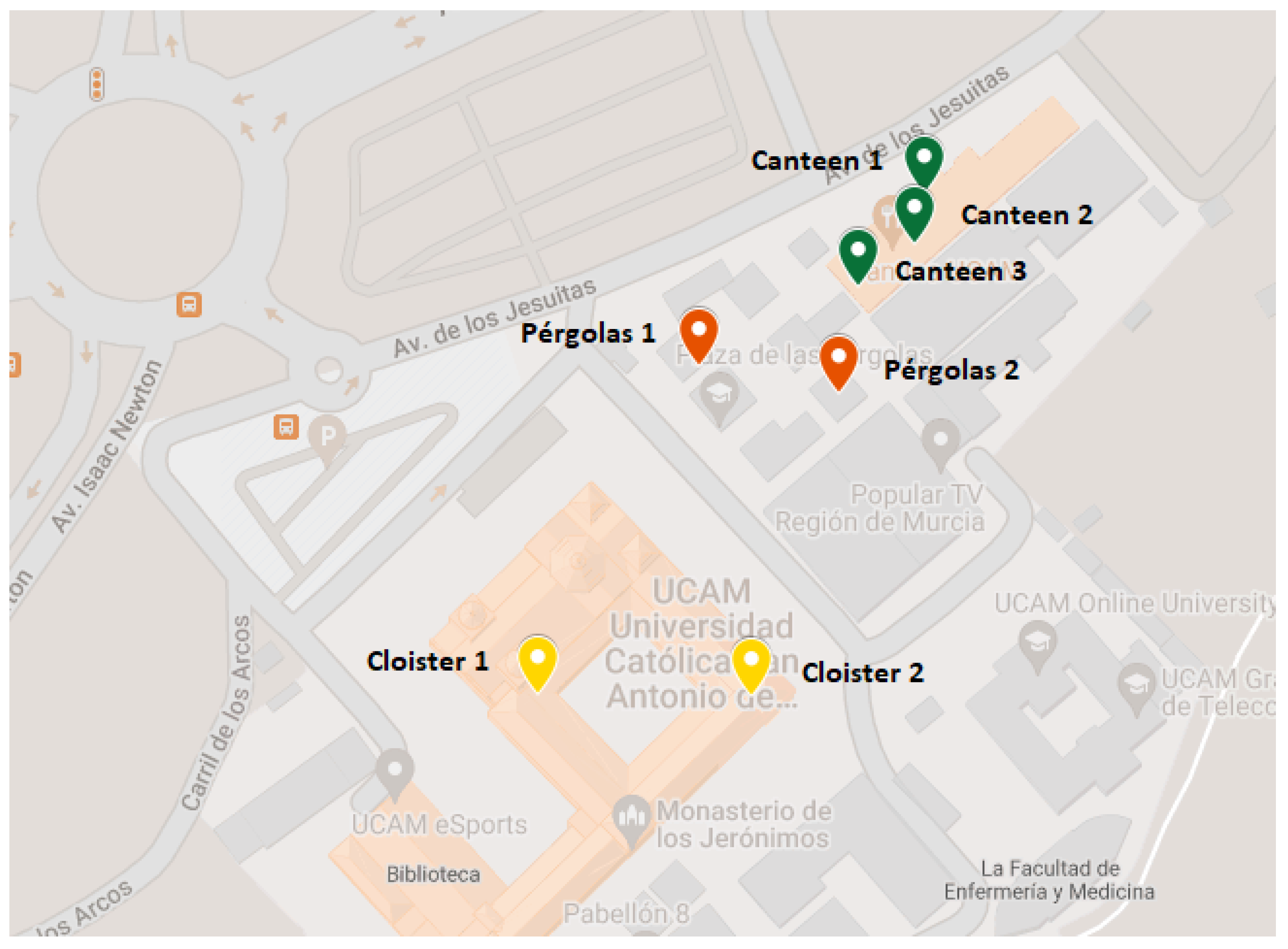
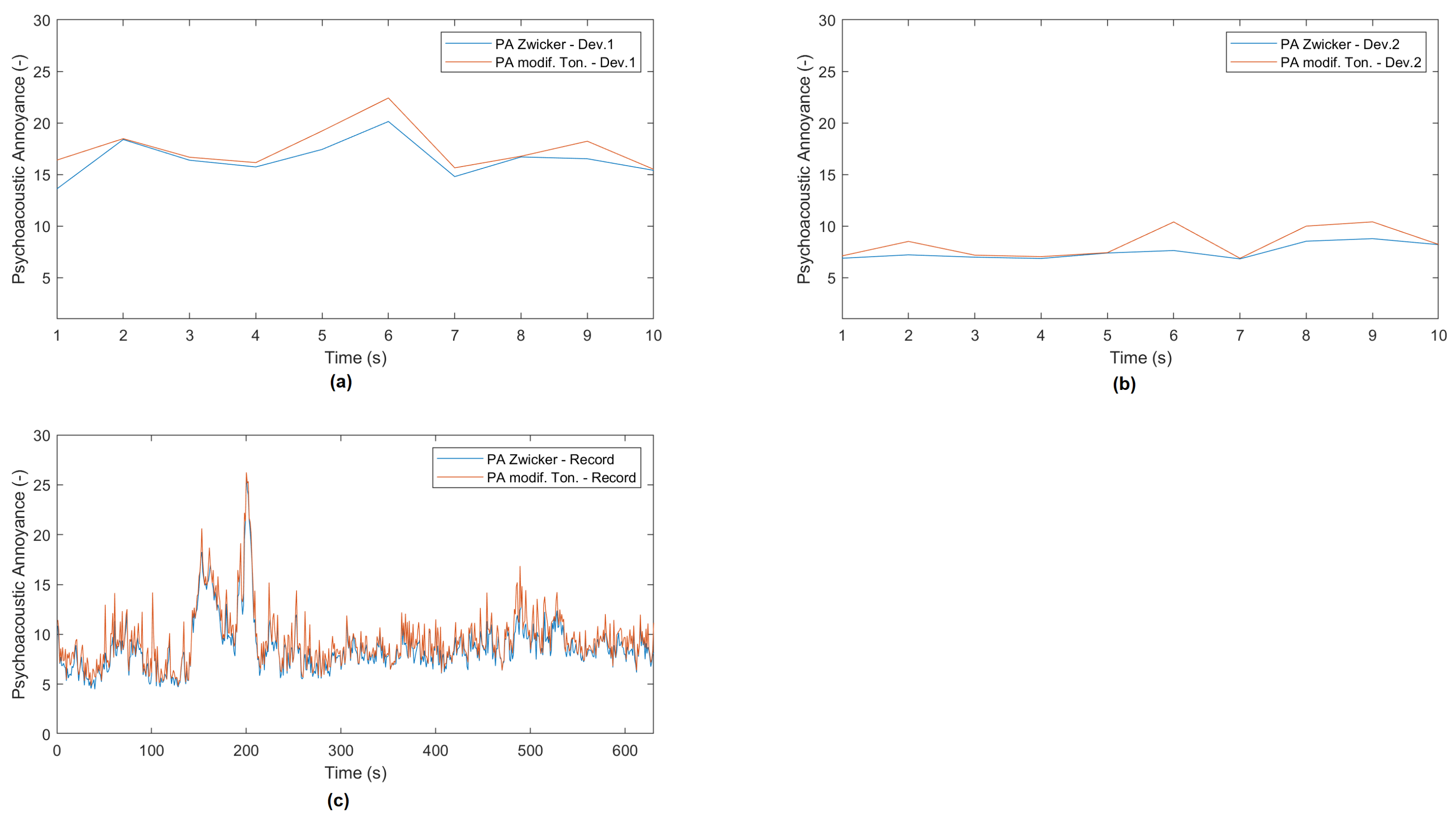
3.2. Application of the System to a Real Scenario: UCAM Campus
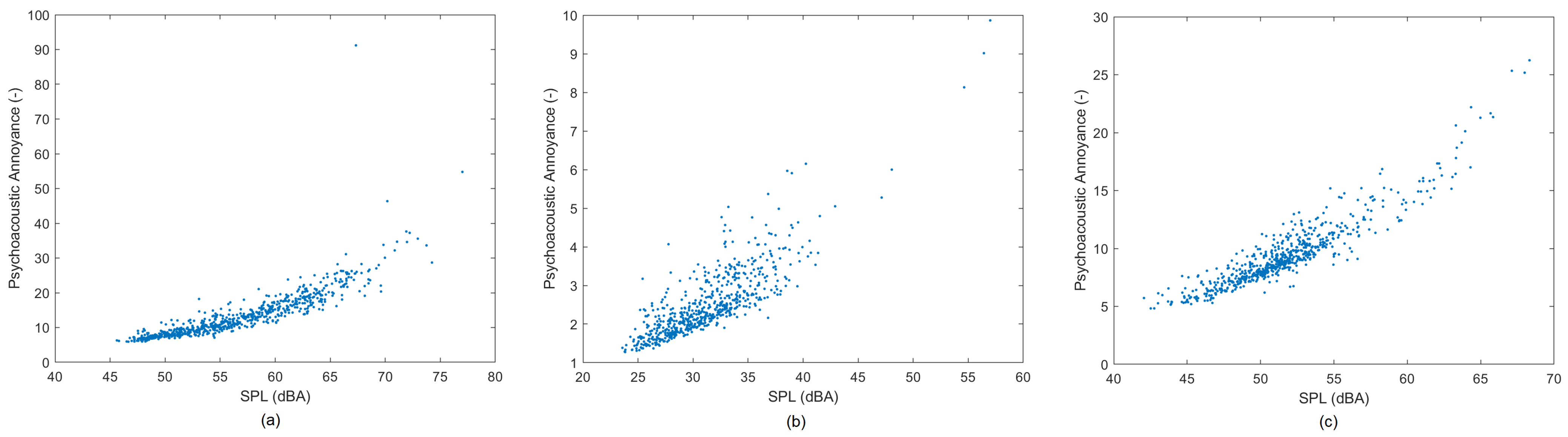
3.3. JND in the UCAM Campus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO 12913-1:2014; Acoustics—Soundscape—Part 1: Definition and Conceptual Framework. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- ISO 12913-2:2018; Acoustics—Soundscape—Part 2: Data Collection and Reporting Requirements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Dunbavin, P. ISO/TS 12913-2:2018—Soundscape—Part 2: Data collection and reporting requirements—What’s it all about? Acoust. Bull. 2018, 43, 55–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Ballester, J.; Pastor-Aparicio, A.; Felici-Castell, S.; Segura-Garcia, J.; Cobos, M. Enabling Real-Time Computation of Psycho-Acoustic Parameters in Acoustic Sensors Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 11429–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Belmonte, J.; Navarro, J.M. Long-Term Temporal Analysis of Psychoacoustic Parameters of the Acoustic Environment in a University Campus Using a Wireless Acoustic Sensor Network. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.L.; Brambilla, G.; Iarossi, S.; Fredianelli, L. The LIFE NEREiDE project: Psychoacoustic parameters and annoyance of road traffic noise in an urban area. In Proceedings of the Euronoise Conference (Euronoise 2018), Heraklion, Greece, 27–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y. Physical and Psychoacoustic Characteristics of Typical Noise on Construction Site: “How Does Noise Impact Construction Workers’ Experience?”. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 532:2017; Acoustics—Methods for Calculating Loudness—Part 1: Zwicker Method; Part 2: Moore-Glasberg Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Pastor-Aparicio, A.; Segura-Garcia, J.; Lopez-Ballester, J.; Felici-Castell, S.; García-Pineda, M.; Pérez-Solano, J.J. Psychoacoustic Annoyance Implementation With Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks for Monitoring in Smart Cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, M.; Fiebig, A.; Pfaffenbach, C.; Fels, J. A Review of the Use of Psychoacoustic Indicators on Soundscape Studies. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arce, P.; Salvo, D.; Piñero, G.; Gonzalez, A. FIWARE based low-cost wireless acoustic sensor network for monitoring and classification of urban soundscape. Comput. Netw. 2021, 196, 108199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y. Monitoring time-varying noise levels and perceived noisiness in hospital lobbies. Build. Acoust. 2021, 28, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet-Solà, D.; Martínez-Suquía, C.; Alsina-Pagès, R.M.; Bergadà, P. The Soundscape of the COVID-19 Lockdown: Barcelona Noise Monitoring Network Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y. Influence of urban contexts on soundscape perceptions: A structural equation modeling approach. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 141, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.I.; Jeon, J.Y. Overall environmental assessment in urban parks: Modelling audio-visual interaction with a structural equation model based on soundscape and landscape indices. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masullo, M.; Toma, R.A.; Maffei, L. Effects of Industrial Noise on Physiological Responses. Acoustics 2022, 4, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohare, M.; Garg, B.; Rajasekar, E.; Parida, M. Evaluation of change in heart rate variability due to different soundscapes. Noise Mapp. 2022, 9, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, J. Sensitivity analysis of changes in human physiological indicators observed in soundscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 190, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastl, H.; Zwicker, E. Psychoacoustics: Facts and Models; Springer Series in Information Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.C.J.; Glasberg, B.R.; Baer, T. A Model for the Prediction of Thresholds, Loudness, and Partial Loudness. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1997, 45, 224–240. [Google Scholar]
- Caniato, M.; Zaniboni, L.; Marzi, A.; Gasparella, A. Evaluation of the main sensitivity drivers in relation to indoor comfort for individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Part 1: Investigation methodology and general results. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caniato, M.; Zaniboni, L.; Marzi, A.; Gasparella, A. Evaluation of the main sensitivity drivers in relation to indoor comfort for individuals with autism spectrum disorder. Part 2: Influence of age, co-morbidities, gender and type of respondent on the stress caused by specific environmental stimuli. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 2989–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettarello, F.; Caniato, M.; Scavuzzo, G.; Gasparella, A. Indoor Acoustic Requirements for Autism-Friendly Spaces. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, M.; Lee, H.; Sakamoto, S. Subjective Evaluation on the Annoyance of Environmental Noise Containing Low-Frequency Tonal Components. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.Q.; Chen, X.W.; Song, K.; Zhou, B.; Pei, C.M. Improvement of Zwicker’s psychoacoustic annoyance model aiming at tonal noises. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 105, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Zhong, Z. Sound Quality User-Defined Cursor Reading Control-Tonality Metric. Master’s Thesis, IMM (Informatics and Mathematical Modelling), DTU (Technical University of Denmark), Brüel & Kjær, Naerum, Denmark, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Estreder, J.; Piñero, G.; de Diego, M.; Rämö, J.; Välimäki, V. Improved Aures tonality metric for complex sounds. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 204, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN45631/A1:2010; Calculation of Loudness Level and Loudness from the Sound Spectrum-Zwicker Method-Amendment 1: Calculation of the Loudness of Time-Variant Sound. Deutsches Institut Fur Normung E.V. (German National Standard), Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- DIN45692/A1:2009; Measurement Technique for the Simulation of the Auditory Sensation of Sharpness. Deutsches Institut Fur Normung E.V. (German National Standard), Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2009.
- Jourdes, V. Estimation of Perceived Roughness. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, P.; Weber, R. Psychoacustical Roughness: Implementation of an Optimized Model. Acustica 1997, 83, 113–123. [Google Scholar]
- Aures, W. Procedure for Calculating the Sensory Euphony of Arbitrary Sound Signals. Acustica 1985, 59, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Terhardt, E.; Stoll, G.; Seewann, M. Algorithm for extraction of pitch and pitch salience from complex tonal signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 71, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, L.N.; Davis, R. Understanding Sound Sensitivity in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2010, 25, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucker, J.R. Auditory Hypersensitivity in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2013, 28, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just Noticeable Difference. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Just-noticeable_difference (accessed on 18 April 2023).
- You, J.; Jeon, J.Y. Just noticeable differences in sound quality metrics for refrigerator noise. Noise Control Eng. J. 2008, 56, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Garcia, J.; Felici-Castell, S.; Perez-Solano, J.J.; Cobos-Serrano, M.; Navarro, J.M. Low-Cost Alternatives for Urban Noise Nuisance Monitoring Using Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pycom.io. Fipy, Five Network Development Board for IoT. 2022. Available online: https://pycom.io/product/fipy/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- ThingSpeak. IoT Analytics-ThingSpeak Internet of Things. 2023. Available online: https://thingspeak.com/ (accessed on 13 April 2023).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segura-Garcia, J.; Pérez-Solano, J.J.; Felici-Castell, S.; Montoya-Belmonte, J.; Lopez-Ballester, J.; Navarro, J.M. Sustainable Soundscape Monitoring of Modified Psycho-Acoustic Annoyance Model with Edge Computing for 5G IoT Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310016
Segura-Garcia J, Pérez-Solano JJ, Felici-Castell S, Montoya-Belmonte J, Lopez-Ballester J, Navarro JM. Sustainable Soundscape Monitoring of Modified Psycho-Acoustic Annoyance Model with Edge Computing for 5G IoT Systems. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310016
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegura-Garcia, Jaume, Juan J. Pérez-Solano, Santiago Felici-Castell, José Montoya-Belmonte, Jesus Lopez-Ballester, and Juan Miguel Navarro. 2023. "Sustainable Soundscape Monitoring of Modified Psycho-Acoustic Annoyance Model with Edge Computing for 5G IoT Systems" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310016
APA StyleSegura-Garcia, J., Pérez-Solano, J. J., Felici-Castell, S., Montoya-Belmonte, J., Lopez-Ballester, J., & Navarro, J. M. (2023). Sustainable Soundscape Monitoring of Modified Psycho-Acoustic Annoyance Model with Edge Computing for 5G IoT Systems. Sustainability, 15(13), 10016. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310016









