Effect of Hydrothermal Curing on the Hydration and Strength Development of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Wastes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
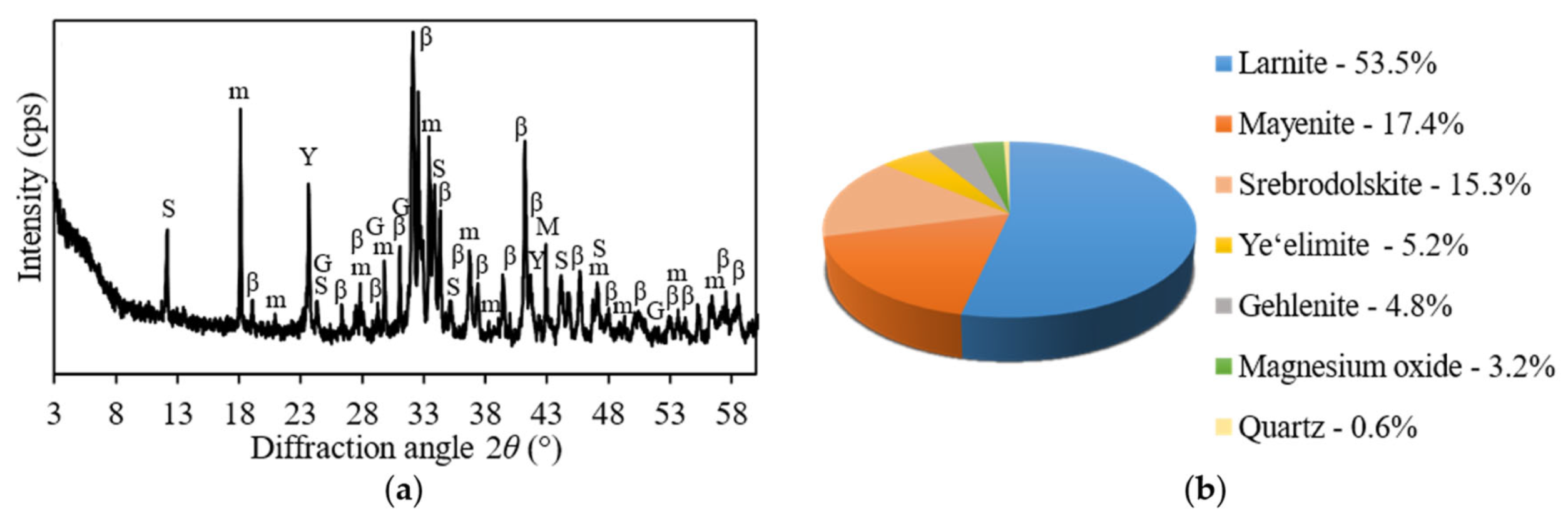
2.2. Production of Belite Cement
2.3. The Hardening of Samples
2.4. Analytical Techniques
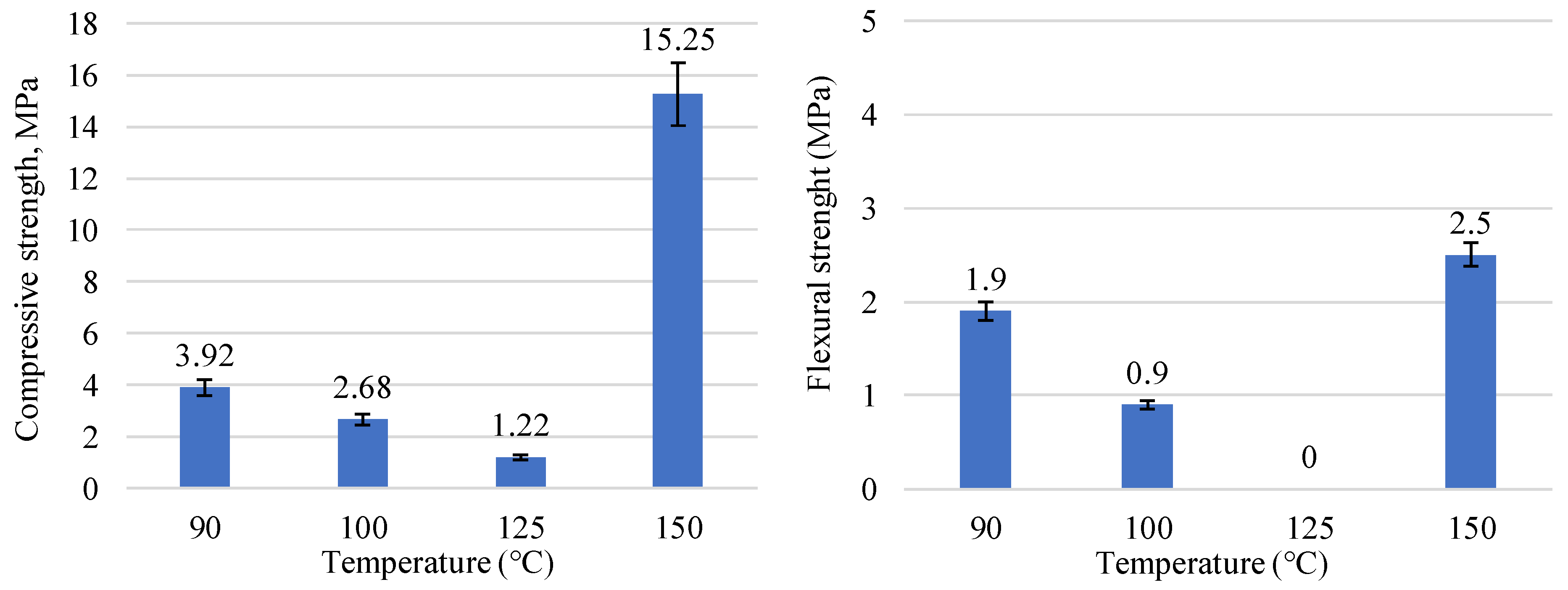
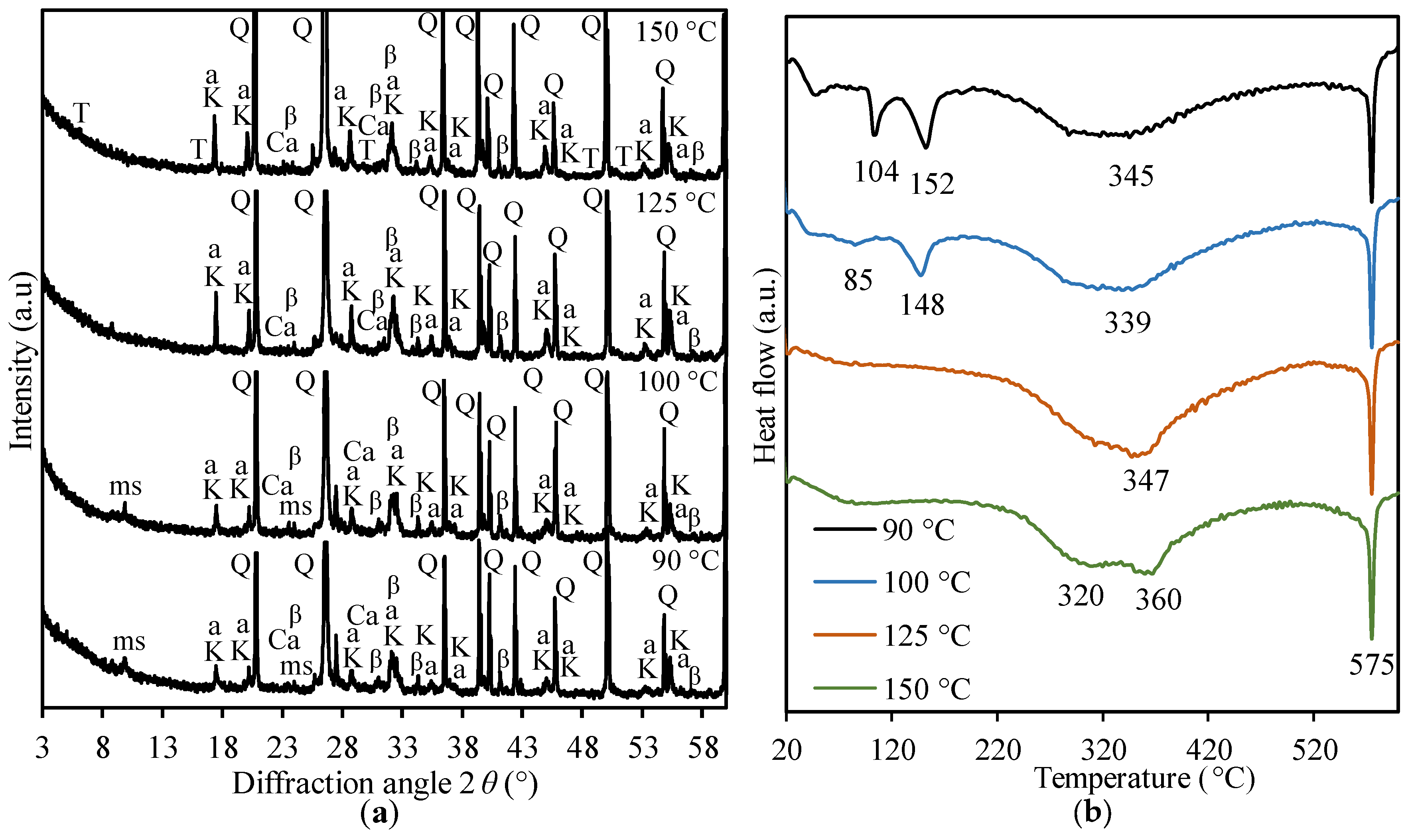
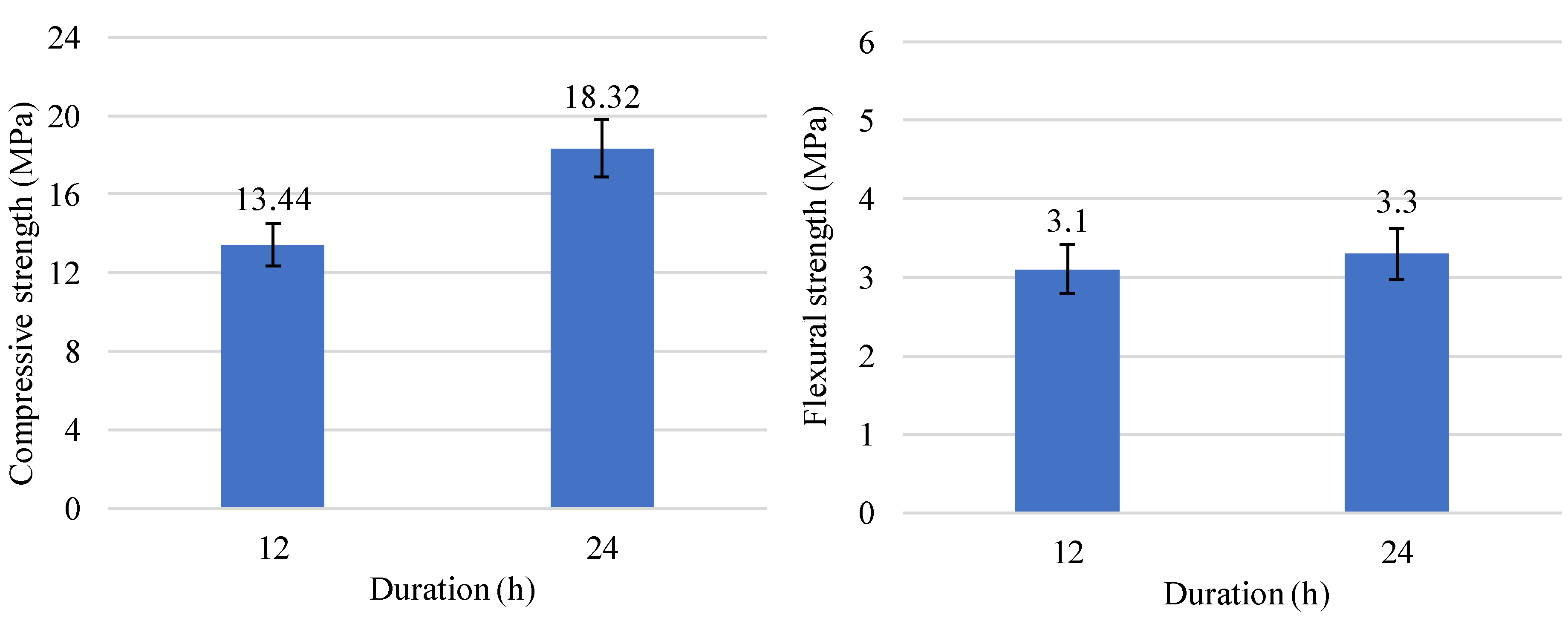
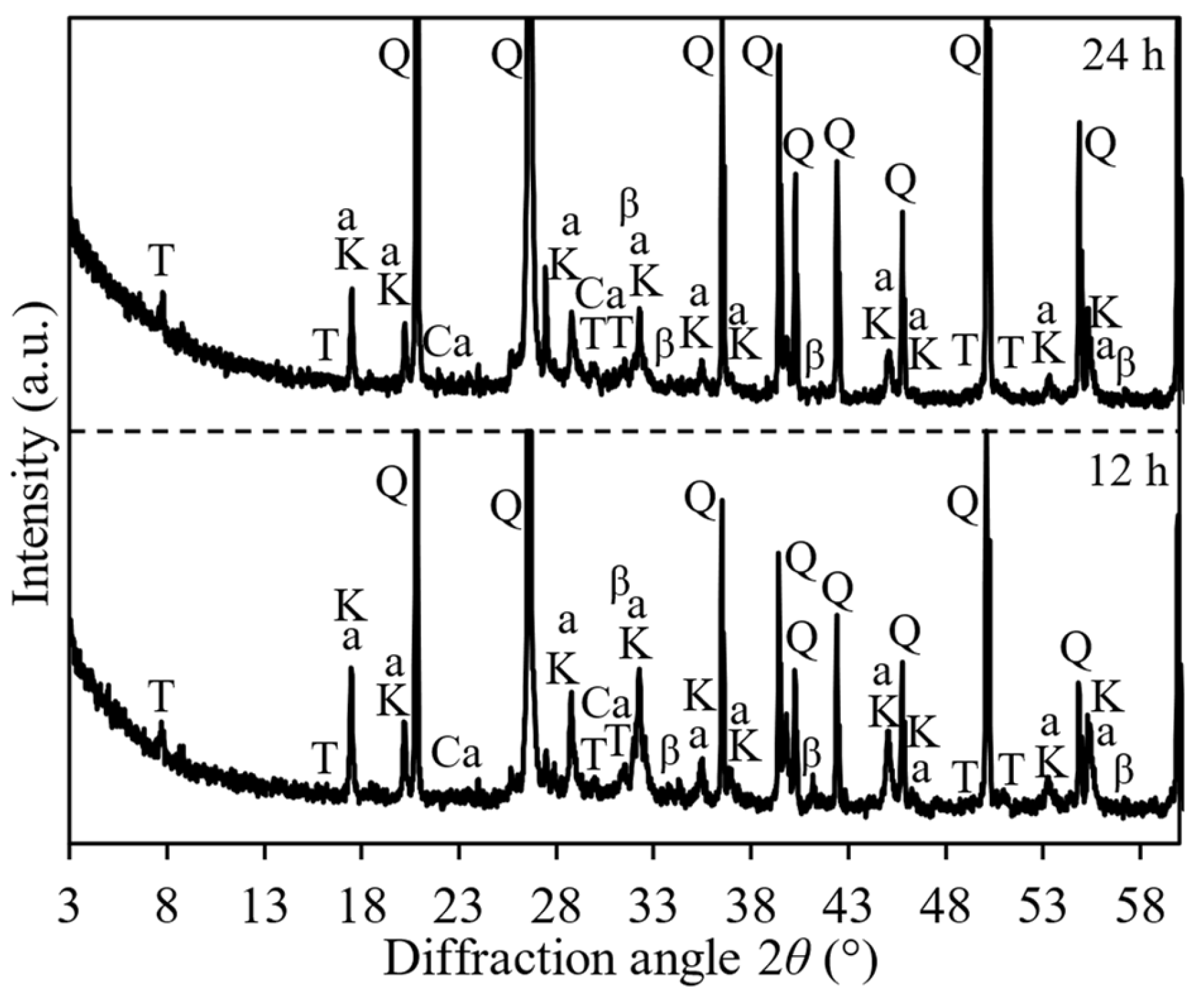
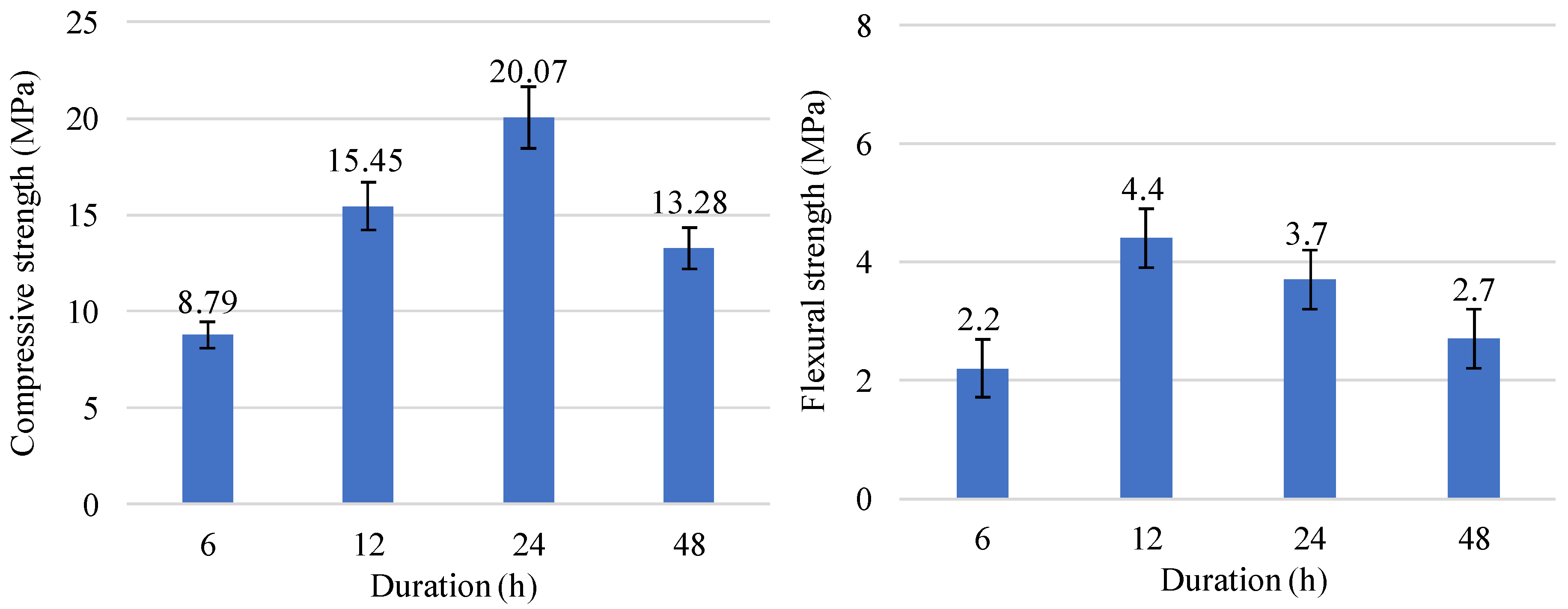
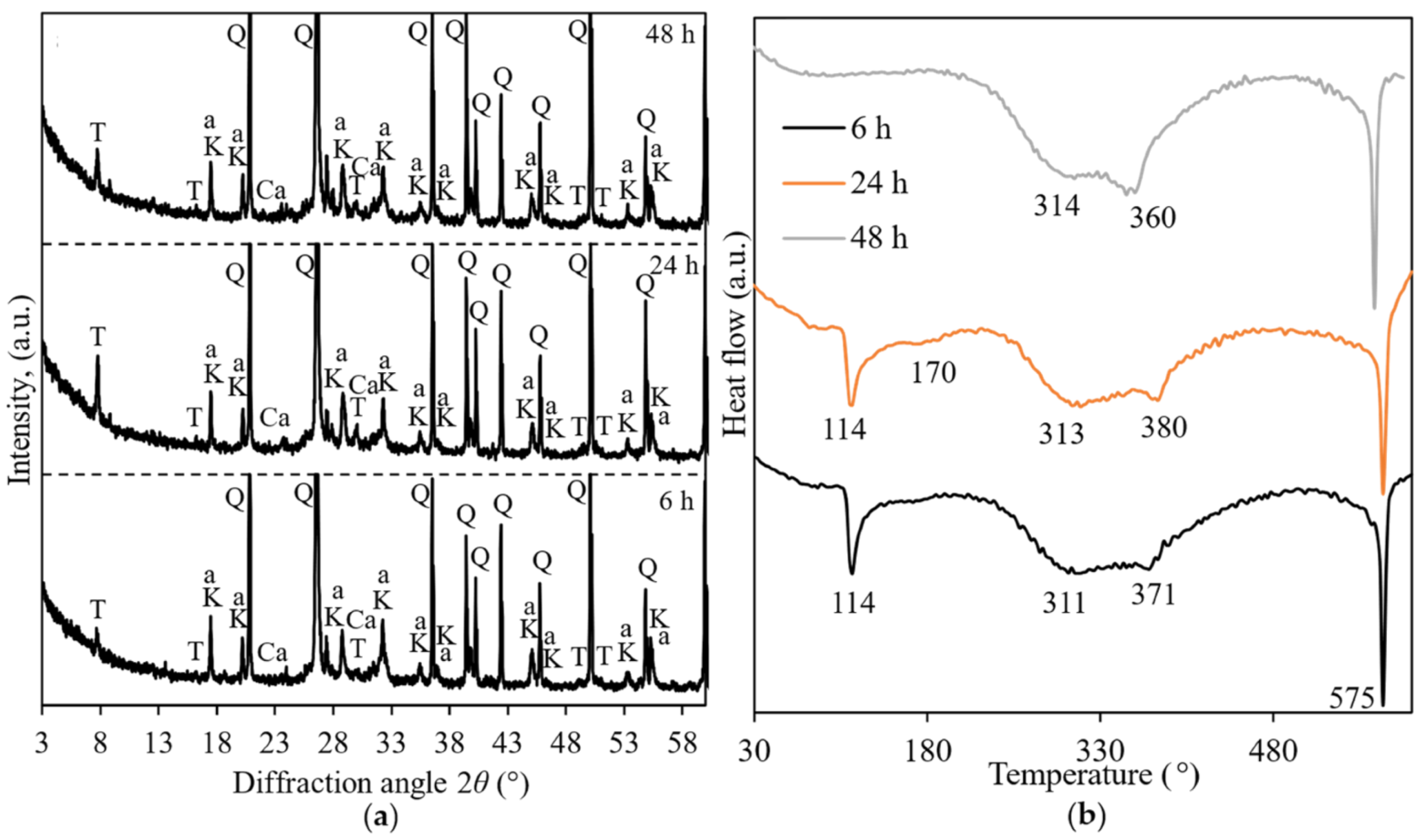
3. Results and Discussion
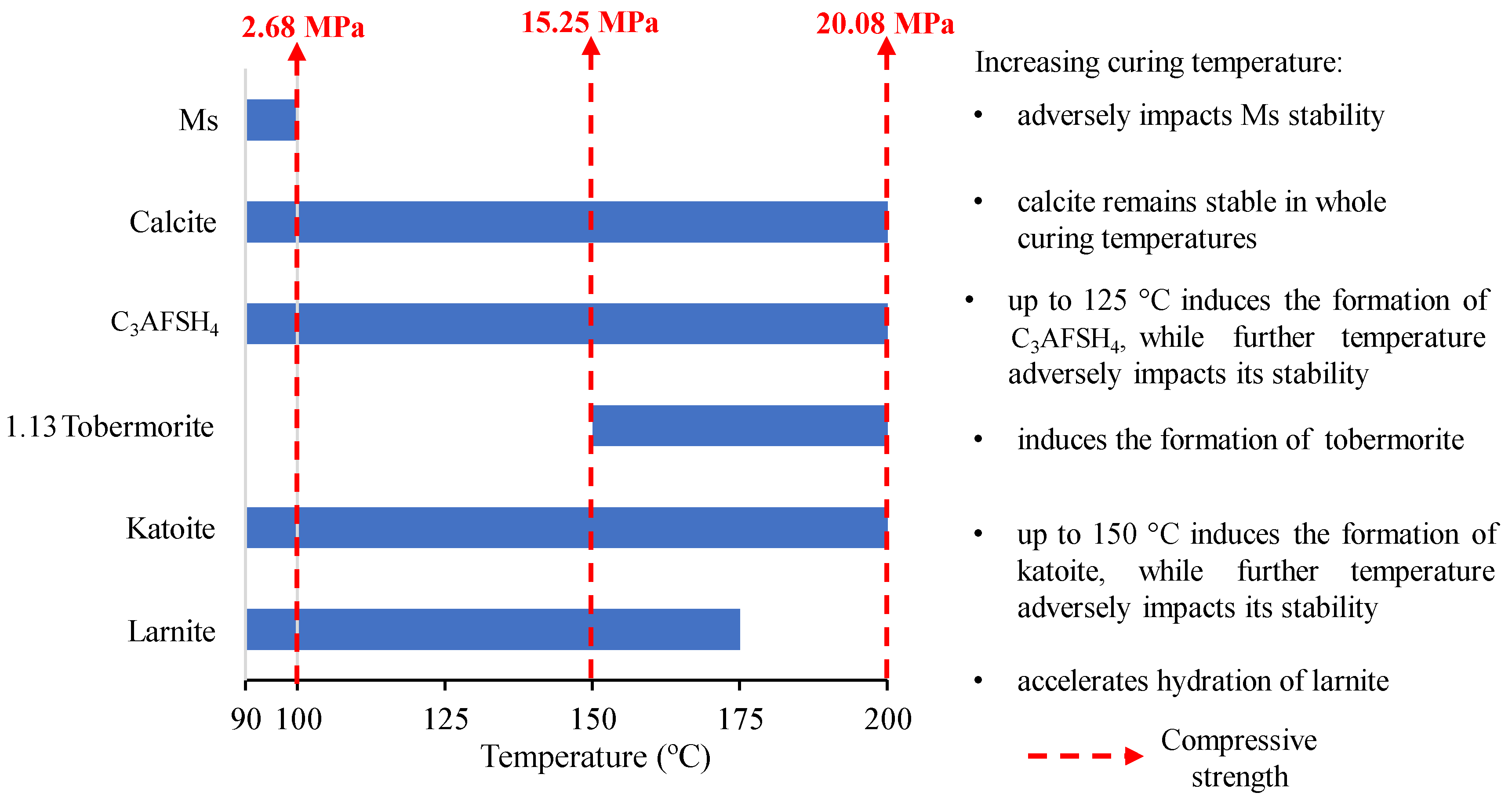
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pisoft, P.; Sacha, P.; Polvani, L.M.; Añel, J.A.; de La Torre, L.; Eichinger, R.; Foelsche, U.; Huszar, P.; Jacobi, C.; Karlicky, J.; et al. Stratospheric Contraction Caused by Increasing Greenhouse Gases. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 064038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. The European Green Deal, Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee of the Regions (COM (2019) 640 Final). 2019. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/default/files/european-green-deal-communication_en.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 Emissions from Cement Production, 1928–2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1675–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M. The Cement Industry on the Way to a Low-Carbon Future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Cen, K.; Geng, Y. Evaluation and Mitigation of Cement CO2 Emissions: Projection of Emission Scenarios toward 2030 in China and Proposal of the Roadmap to a Low-Carbon World by 2050. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2019, 24, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlool, N.A.; Saidur, R.; Hossain, M.S.; Rahim, N.A. A Critical Review on Energy Use and Savings in the Cement Industries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 2042–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Sharma, S. Impact of Alternative Fuels on the Cement Manufacturing Plant Performance: An Overview. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakrishna, A.; Adesina, A.; Awoyera, P.O.; Kumar, K.R. Green Concrete: A Review of Recent Developments. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 27, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsay, G.; Jaskulski, R. Kotsay and Jaskulski/Belite cement as an ecological alternative to Portland cement—A review. Mater. Struct. Technol. J. 2019, 2, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, E. Industrially Interesting Approaches to “Low-CO2” Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqi, A.; Jang, J.G. Recent Progress in Green Cement Technology Utilising Low-Carbon Emission Fuels and Raw Materials: A Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, J.J.; Bullard, J.W.; Sant, G.; Brown, K.; Glasser, F.P.; Jones, S.; Ley, T.; Livingston, R.; Nicoleau, L.; Olek, J.; et al. Cements in the 21st Century: Challenges, Perspectives, and Opportunities. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 2746–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Alfi, E.A.; Gado, R.A. Preparation of Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Belite Cement from Marble Sludge Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Maté, M.; de La Torre, A.G.; León-Reina, L.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Santacruz, I. Hydration Studies of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements Blended with Fly Ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 54, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telesca, A.; Matschei, T.; Marroccoli, M. Study of Eco-Friendly Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements Obtained from Special Wastes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Synergistic Use of Industrial Solid Wastes to Prepare Belite-Rich Sulphoaluminate Cement and Its Feasibility Use in Repairing Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullerjahn, F.; Zajac, M.; ben Haha, M. CSA Raw Mix Design: Effect on Clinker Formation and Reactivity. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2015, 48, 3895–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, V.; Termkhajornkit, P.; Huet, B.; Pham, G. Impact of Quantity of Anhydrite, Water to Binder Ratio, Fineness on Kinetics and Phase Assemblage of Belite-Ye’elimite-Ferrite Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 99, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadix, A.; James, S. Chapter 5—Cementing Additives. In Fluid Chemistry, Drilling and Completion; Wang, Q., Ed.; Oil and Gas Chemistry Management Series; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2022; Volume 187–254, ISBN 978-0-12-822721-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta, A.; Ayuela, A.; Aranda, M.A.G. Belite Cements and Their Activation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tighare, P.; Singh, M.R.C. Study of Different Methods of Curing of Concrete & Curing Periods. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Borštnar, M.; Lengauer, C.L.; Dolenec, S. Quantitative in Situ X-ray Diffraction Analysis of Early Hydration of Belite-calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement at Various Defined Temperatures. Minerals 2021, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, N.; Peng, Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, P. Retardation Effect of Elevated Temperature on the Setting of Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cement Clinker. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, S.; Cuesta, A.; Morales-Cantero, A.; de la Torre, A.G.; Olbinado, M.P.; Aranda, M.A.G. Influence of Curing Temperature on Belite Cement Hydration: A Comparative Study with Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 147, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borštnar, M.; Daneu, N.; Dolenec, S. Phase Development and Hydration Kinetics of Belite-Calcium Sulfoaluminate Cements at Different Curing Temperatures. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 29421–29428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinaite, D.; Dambrauskas, T.; Baltakys, K.; Siauciunas, R. Investigation on the Hydration and Strength Properties of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Waste. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 148, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltakys, K.; Dambrauskas, T.; Rubinaite, D.; Siauciunas, R.; Grineviciene, A. Formation and Hydration of Eco-Friendly Cement Using Industrial Wastes as Raw Materials. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartner, E.; Sui, T. Alternative Cement Clinkers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-1:2015; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
- EN-12390-6:2000; Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 6: Tensile Splitting Strength of Test Specimens. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Chen, I.A.; Juenger, M.C.G. Synthesis and Hydration of Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Belite Cements with Varied Phase Compositions. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2568–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungchet, A.; Chindaprasirt, P.; Wansom, S.; Pimraksa, K. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Calcium Sulfoaluminate-Belite Cement from Industrial Waste Materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 115, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkeo, W.; Thongsanitgarn, P.; Pimraksa, K.; Chaipanich, A. Compressive Strength, Flexural Strength and Thermal Conductivity of Autoclaved Concrete Block Made Using Bottom Ash as Cement Replacement Materials. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, B.; Lv, Y. The Slurry and Physical-Mechanical Performance of Autoclaved Aerated Concrete with High Content Solid Wastes: Effect of Grinding Process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.F.; Oliveira, I.R.; Salomão, R.; Frollini, E.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Temperature and Common-Ion Effect on Magnesium Oxide (MgO) Hydration. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sedeño, M.C.; Cuberos, A.J.M.; de la Torre, Á.G.; Álvarez-Pinazo, G.; Ordónez, L.M.; Gateshki, M.; Aranda, M.A.G. Aluminum-Rich Belite Sulfoaluminate Cements: Clinkering and Early Age Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londono-Zuluaga, D.; Tobón, J.I.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Santacruz, I.; de la Torre, A.G. Clinkering and Hydration of Belite-Alite-Ye’elimite Cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 80, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, D.S.; Ray, A.; Guerbois, J.-P. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Evaluation of Autoclaved Cement Based Building Materials Made with Construction and Demolition Waste. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 389, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquerizo, L.G.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K.L. Impact of Water Activity on the Stability of Ettringite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquerizo, L.G.; Matschei, T.; Scrivener, K.L.; Saeidpour, M.; Thorell, A.; Wadsö, L. Methods to Determine Hydration States of Minerals and Cement Hydrates. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 65, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Kikuma, J.; Tsunashima, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Matsuno, S.Y.; Ogawa, A.; Sato, M. In Situ Time-Resolved X-ray Diffraction of Tobermorite Formation in Autoclaved Aerated Concrete: Influence of Silica Source Reactivity and Al Addition. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prospective Composition, wt.% | |
|---|---|
| 2CaO·SiO2 | 60 |
| 4CaO·3Al2O3·SO3 | 20 |
| 4CaO·3Al2O3·Fe2O3 | 20 |
| Oxide composition, % | |
| CaO | 55.63 |
| SiO2 | 20.93 |
| Al2O3 | 14.23 |
| SO3 | 2.62 |
| Fe2O3 | 6.58 |
| Raw material, wt% | |
| Calcium carbonate | 66.67 |
| Hemihydrate gypsum | 3.17 |
| Granite cutting waste | 14.35 |
| Iron (III) oxide | 2.50 |
| Aluminium hydroxide | 9.47 |
| Silica gel waste | 3.81 |
| Conditions | Intensity (cps) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | 90 °C | 100 °C | 125 °C | 150 °C | |
| Larnite (0.279 nm) | 389 | 386 | 385 | 343 | |
| Katoite (0.505 nm) | 311 | 353 | 593 | 561 | |
| 1.13 tobermorite (1.139 nm) | - | - | - | 380 | |
| Calcium aluminium iron silicate hydroxide (0.438 nm) | 302 | 346 | 454 | 430 | |
| Calcite (0.304) | 193 | 197 | 203 | 190 | |
| Calcium monosulfoaluminate (0.893) | 248 | 142 | - | - | |
| Conditions | Intensity (cps) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compond | 175 °C 12 h | 175 °C 24 h | 200 °C 6 h | 200 °C 12 h | 200 °C 24 h | 200 °C 48 h | |
| Larnite (0.279 nm) | 341 | 245 | 276 | 264 | - | - | |
| Katoite (0.505 nm) | 573 | 460 | 519 | 479 | 484 | 462 | |
| 1.13 tobermorite (1.139 nm) | 394 | 455 | 423 | 457 | 695 | 557 | |
| Calcium aluminium iron hydrosilicate (0.438 nm) | 400 | 345 | 423 | 396 | 438 | 405 | |
| Calcite (0.304) | 215 | 197 | 207 | 207 | 200 | 219 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubinaite, D.; Dambrauskas, T.; Baltakys, K.; Siauciunas, R. Effect of Hydrothermal Curing on the Hydration and Strength Development of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Wastes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129802
Rubinaite D, Dambrauskas T, Baltakys K, Siauciunas R. Effect of Hydrothermal Curing on the Hydration and Strength Development of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Wastes. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129802
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubinaite, Dovile, Tadas Dambrauskas, Kestutis Baltakys, and Raimundas Siauciunas. 2023. "Effect of Hydrothermal Curing on the Hydration and Strength Development of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Wastes" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129802
APA StyleRubinaite, D., Dambrauskas, T., Baltakys, K., & Siauciunas, R. (2023). Effect of Hydrothermal Curing on the Hydration and Strength Development of Belite Cement Mortar Containing Industrial Wastes. Sustainability, 15(12), 9802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129802









