Research on Combination of Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on MIBWOA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Optimization Model
2.1. DGP Objective Function
2.1.1. Accurate Active Power Loss
2.1.2. Voltage Deviation
2.1.3. Carbon Emissions
2.2. DNR Objective Function
2.2.1. Accurate Active Power Loss
2.2.2. Voltage Deviation
2.2.3. Carbon Emissions
2.3. Constraints
2.3.1. Flow Equation Constraint
2.3.2. Current Constraints
2.3.3. Voltage Constraints
2.3.4. Branch Capacity Constraint
2.3.5. Topological Constraints on the Distribution Network
2.3.6. Dynamic Constraint on the Number of Switch Operations in the Distribution Network
2.3.7. Transformer Constraint
2.4. Distributed Generation Model
2.4.1. PQ-Type Distributed Generation
2.4.2. PV-Type Distributed Power Generation
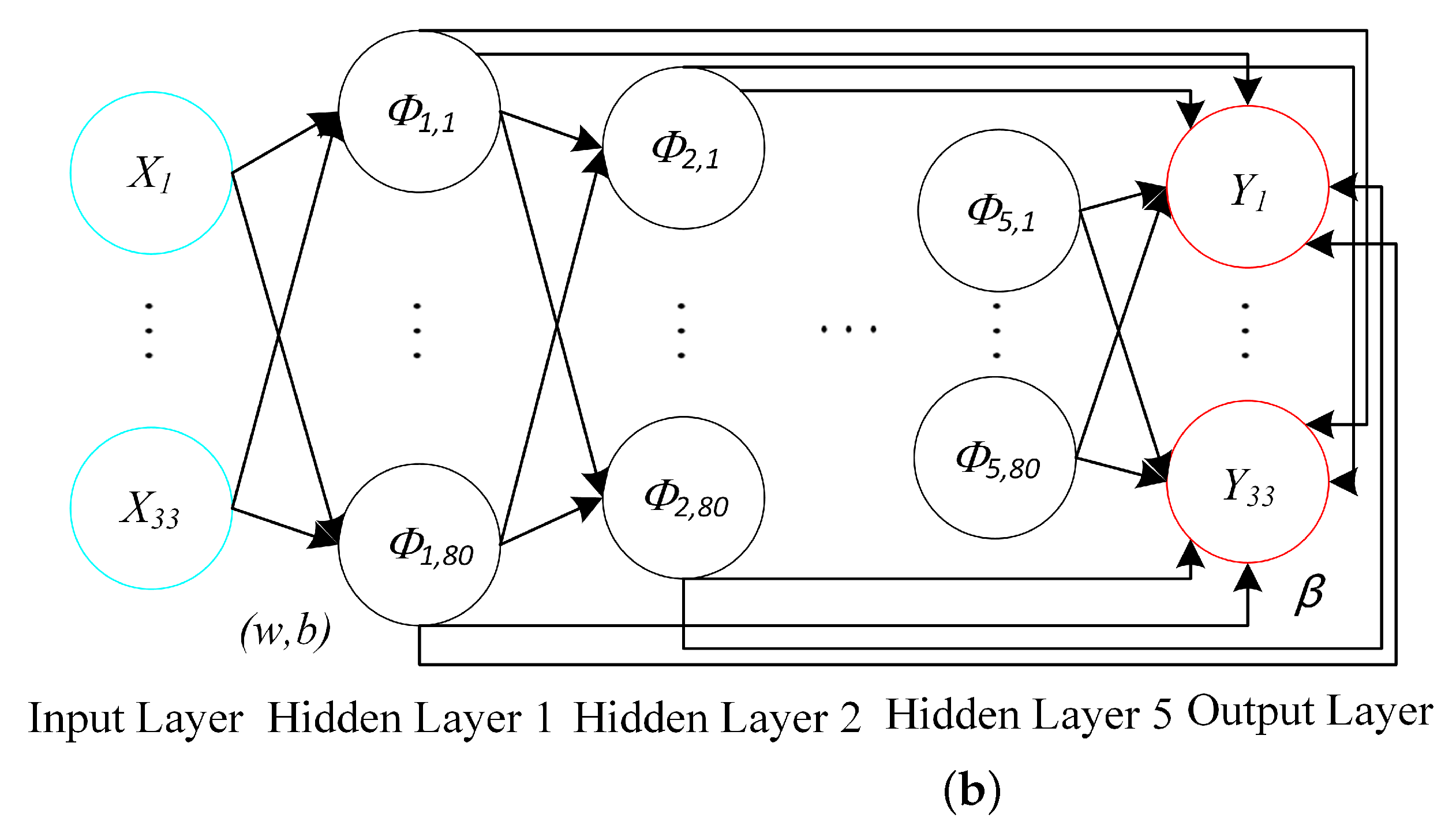
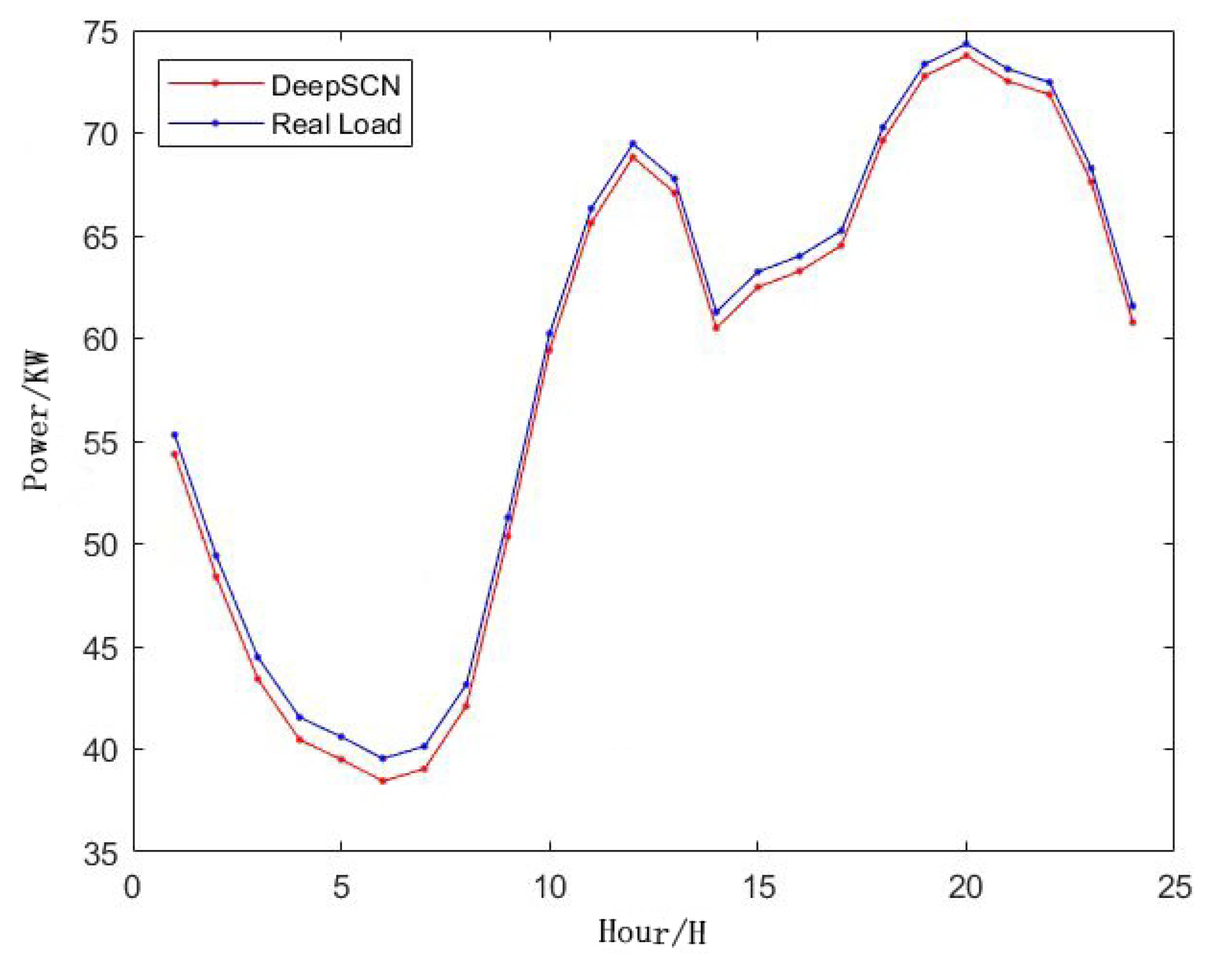
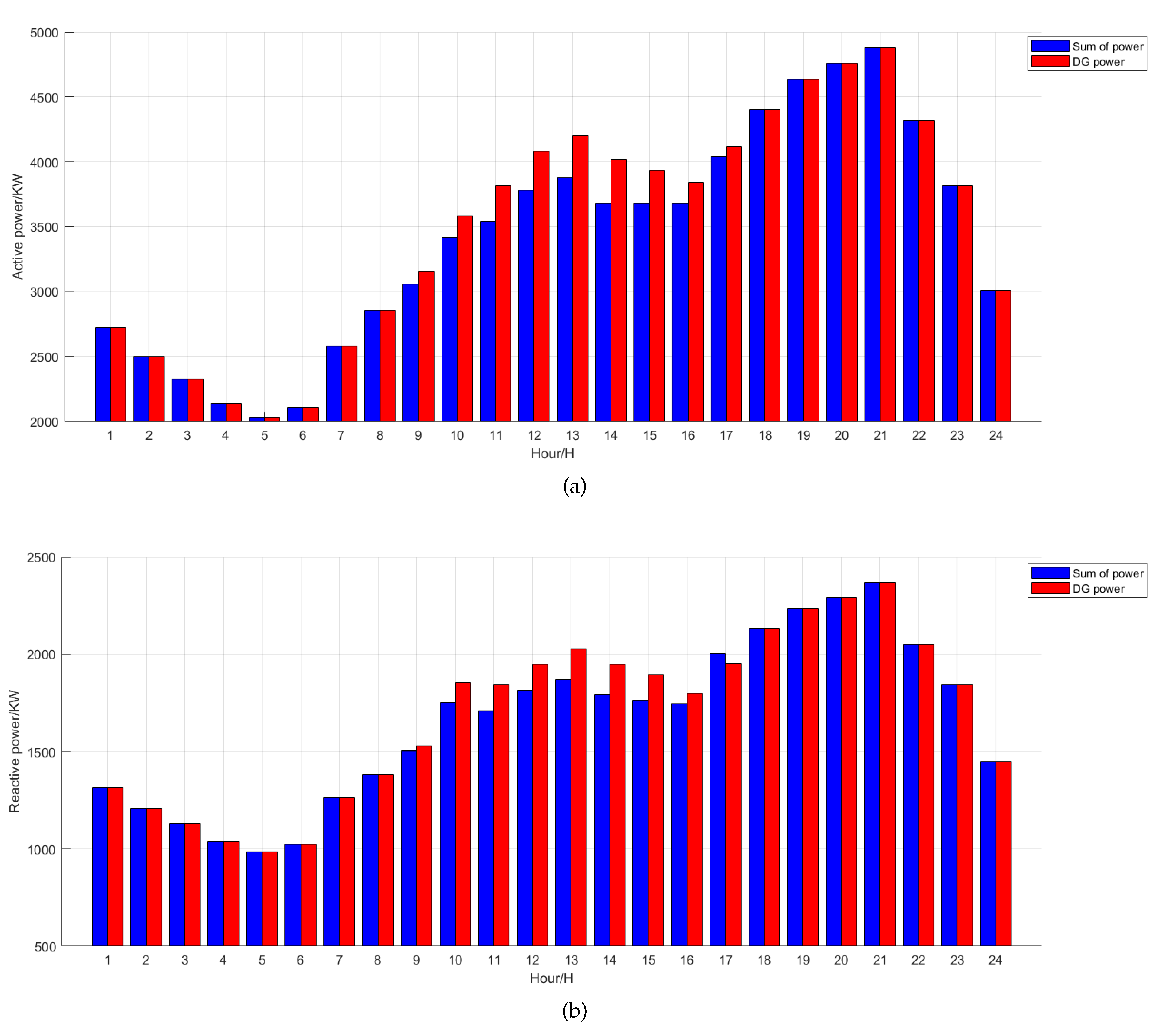
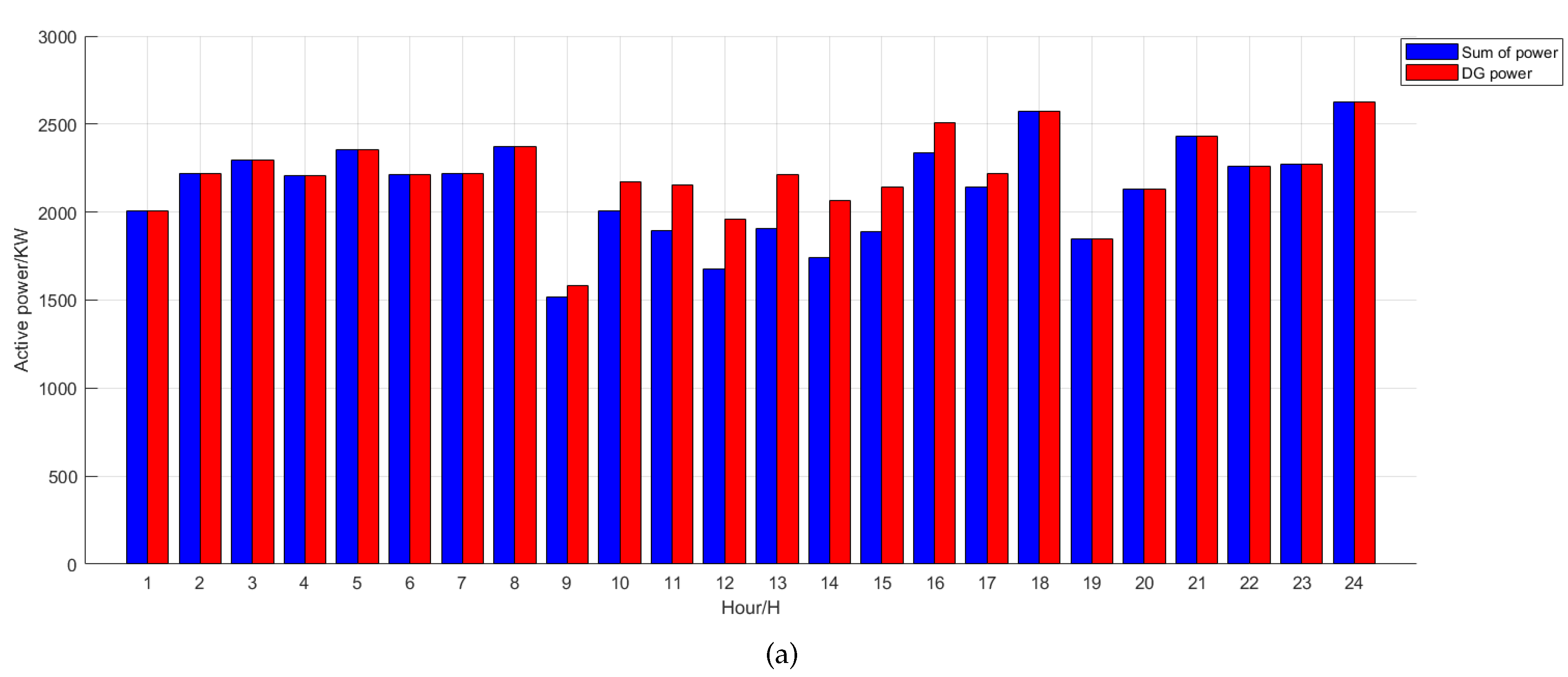
3. Prediction of DG and Load Power Based on DeepSCN
3.1. Introduction to DeepSCN
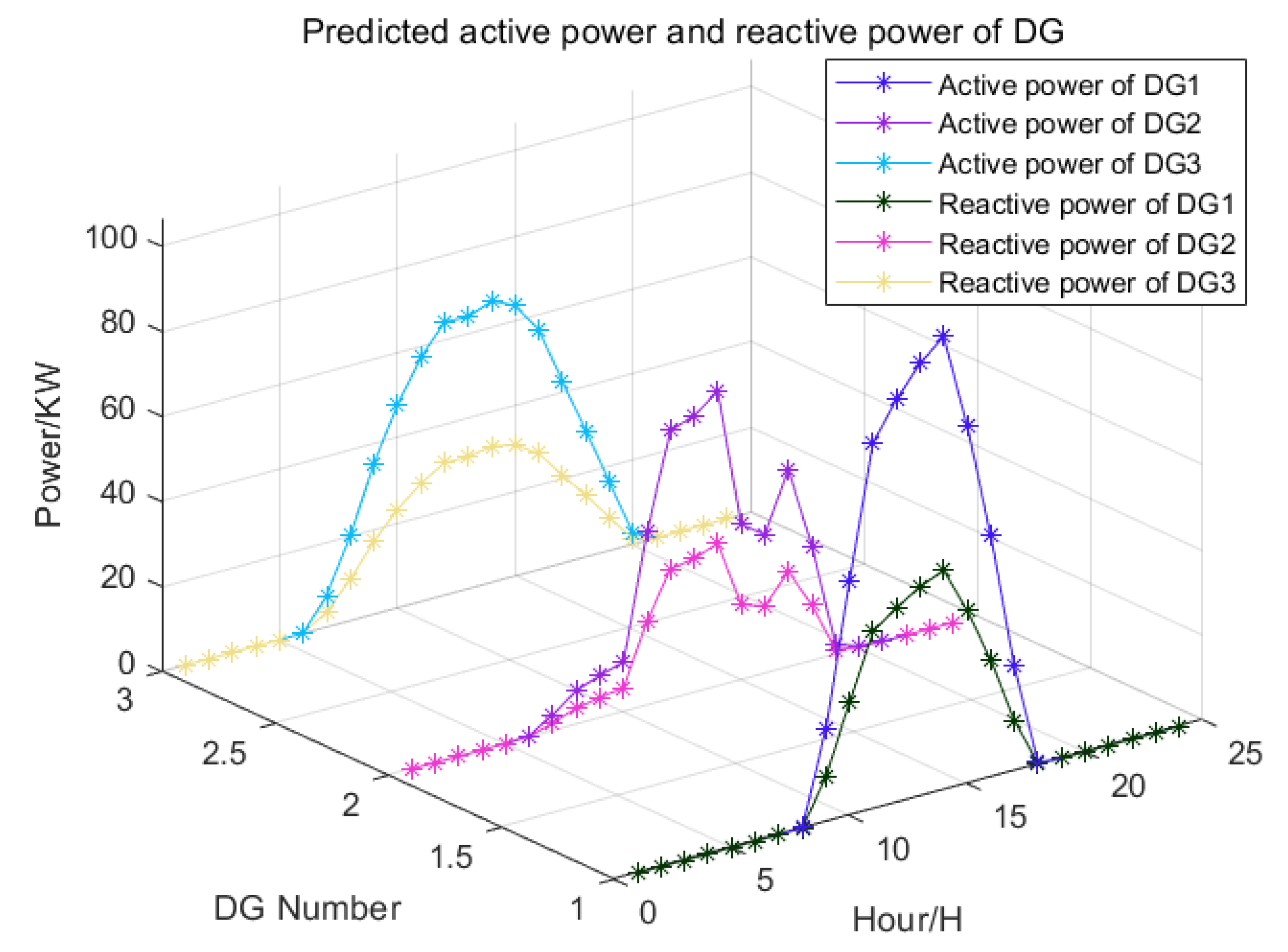
3.2. DG and Load Power Prediction Based on DeepSCN
4. Multi-Objective Improved Black Widow Optimization Algorithm
4.1. Standard Black Widow Algorithm
4.2. Multi-Objective Improved Black Widow Optimization Algorithm
4.2.1. Cubic–Tent Chaotic Mapping
4.2.2. Updating Formulas with the Fusion of Optimal Genes
4.2.3. Mutation Based on Adaptive Adjustment of Wald and Elite Reverse Learning
4.2.4. Multi-Objective Solution Set Selection Based on Pareto Theory
4.2.5. Discretization of Solutions in DGP-DNR Problem
4.2.6. Workflow of MIBWOA
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Optimization of Classic Test Functions
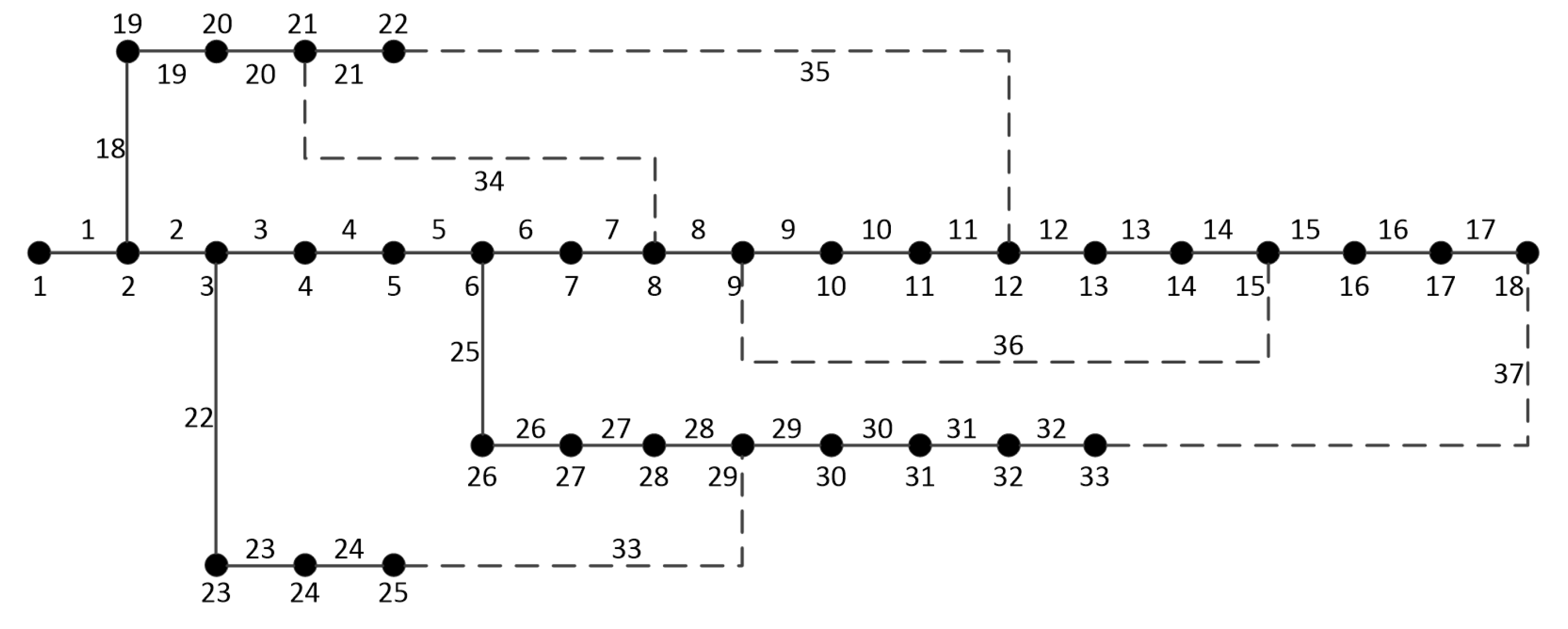
5.2. IEEE-33 DG Placement Experiment
5.3. IEEE-33 Distribution Network Reconfiguration Experiment
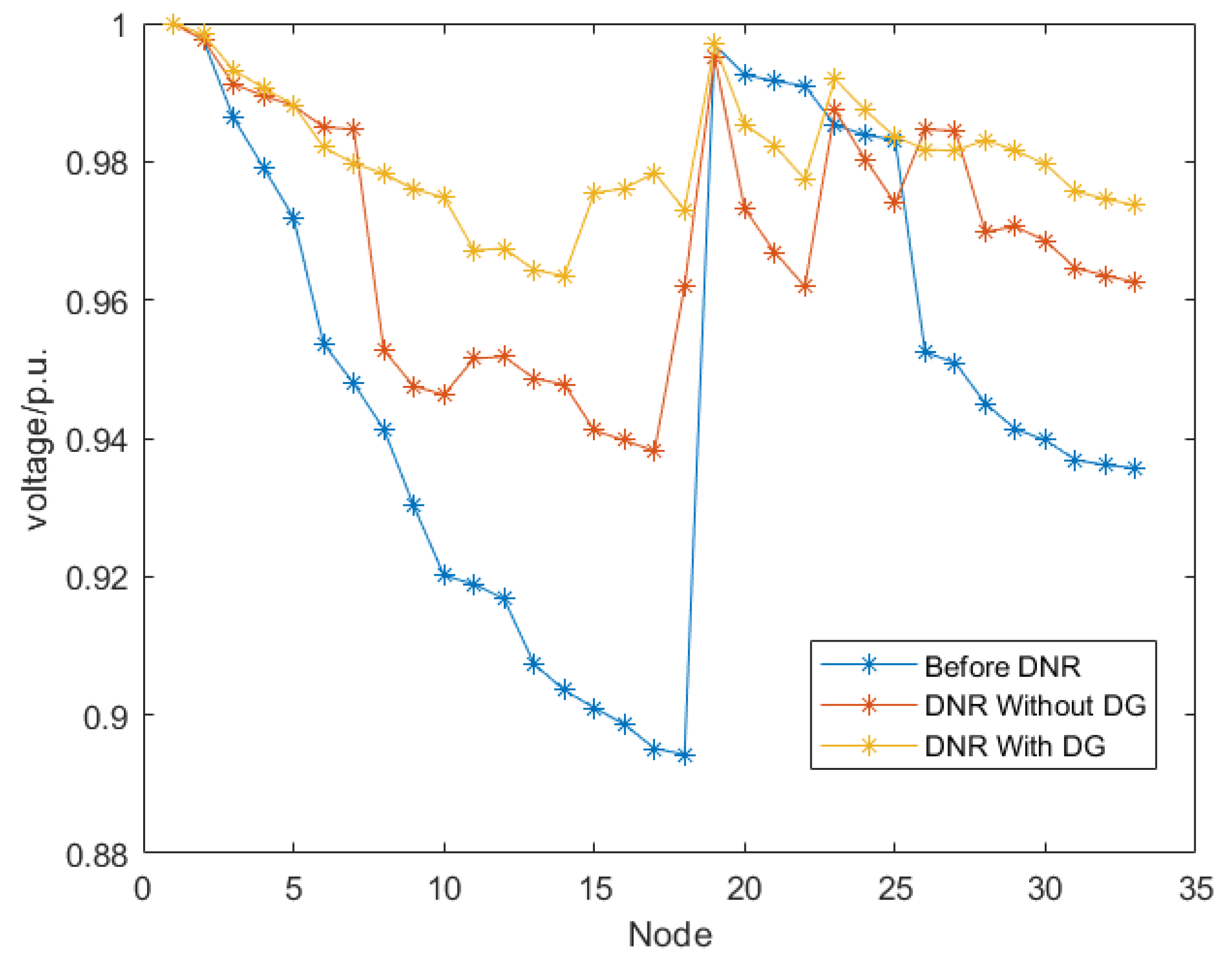
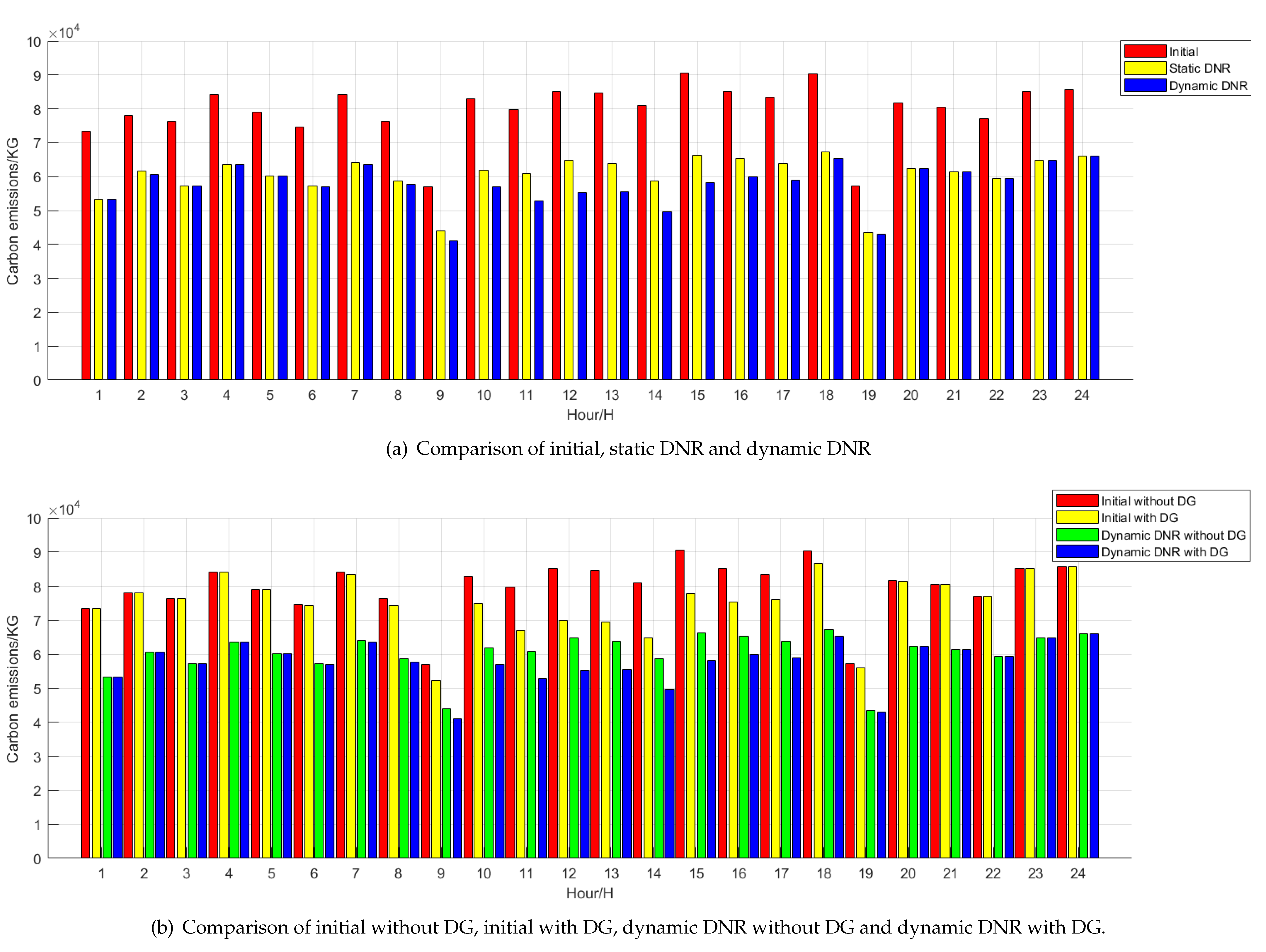
5.3.1. Static Distribution Network Reconfiguration
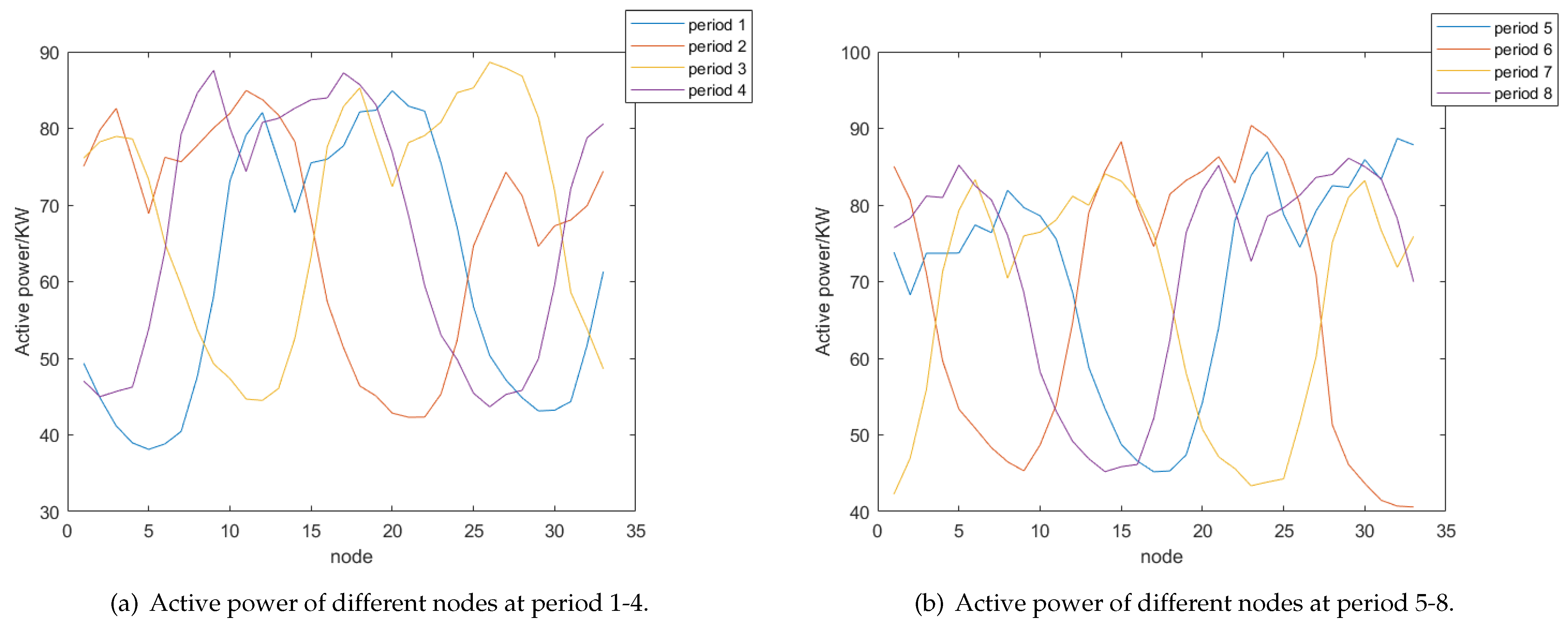
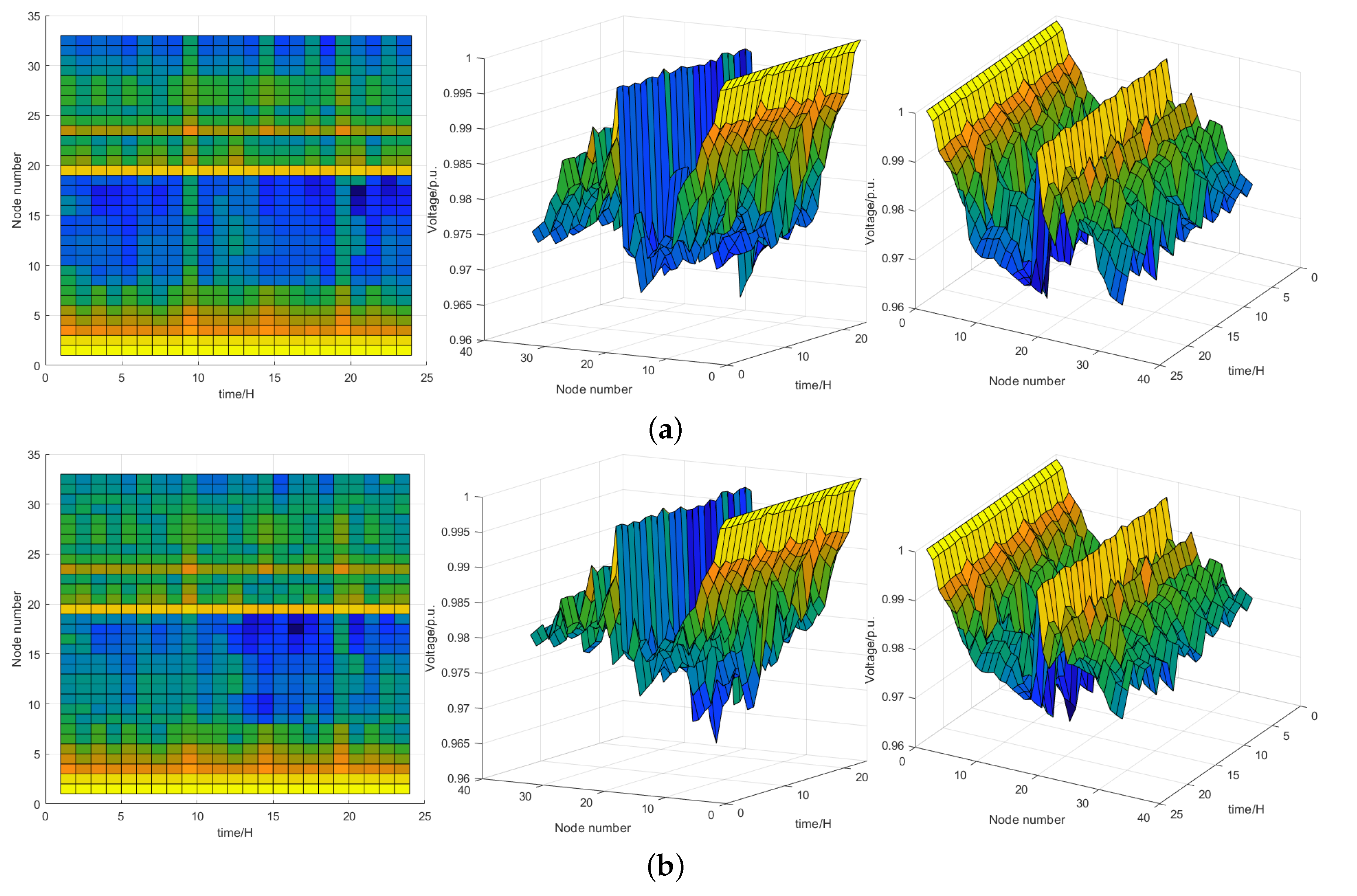
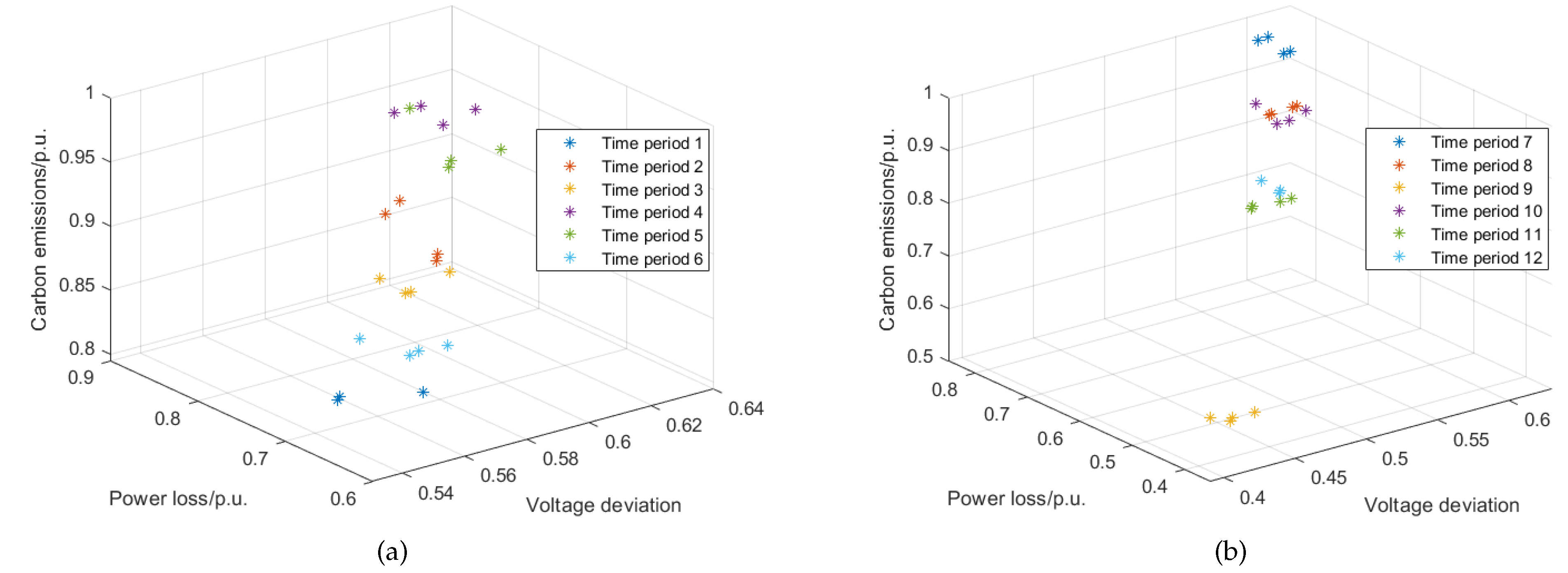
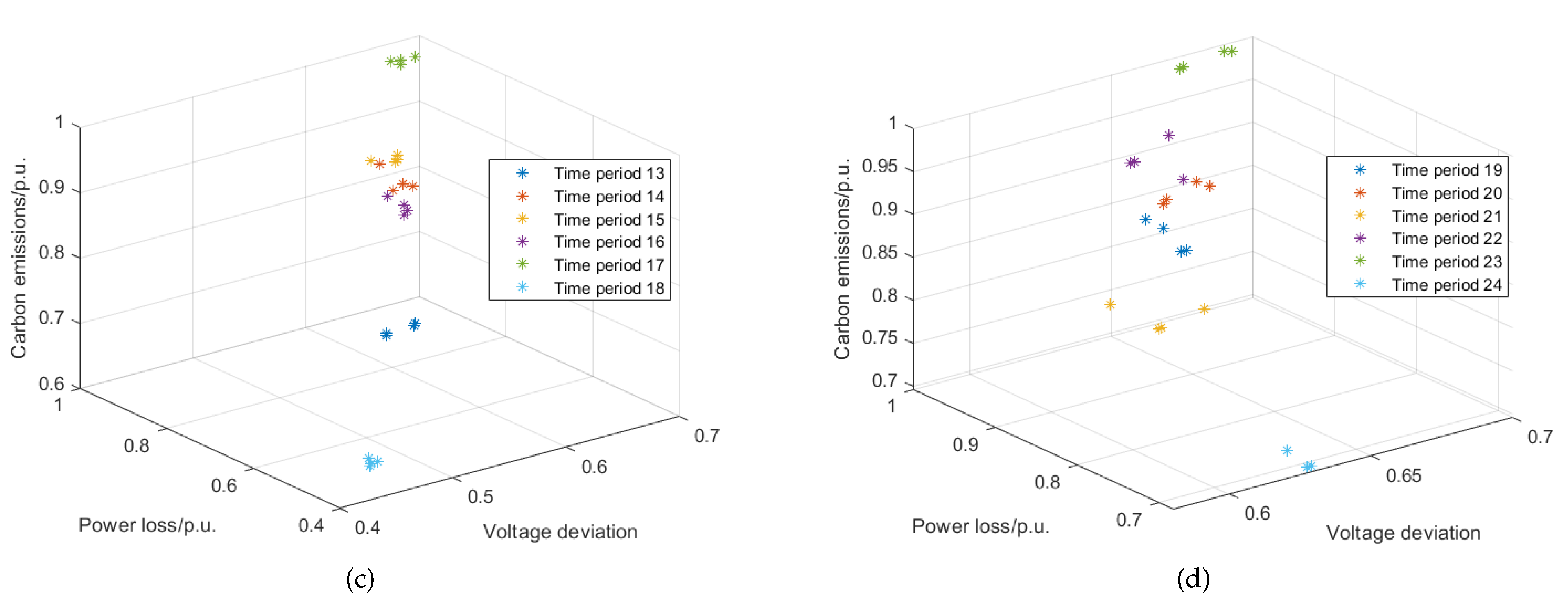
5.3.2. Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jabr, R.A.; Singh, R.; Pal, B.C. Minimum loss network reconfiguration using mixed-integer convex programming. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Song, D.; Deng, X.; Dong, M.; Yang, J.; Rizk-Allah, R.M.; Snášel, V. Dynamic Optimal Power Flow of Active Distribution Network Based on LSOCR and Its Application Scenarios. Electronics 2023, 12, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaaeldin, I.; Abdel Aleem, S.; El-Rafei, A.; Abdelaziz, A.; Zobaa, A.F. Optimal network reconfiguration in active distribution networks with soft open points and distributed generation. Energies 2019, 12, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntombela, M.; Musasa, K.; Leoaneka, M.C. Power Loss Minimization and Voltage Profile Improvement by System Reconfiguration, DG Sizing, and Placement. Computation 2022, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, M.; Yao, H.; Long, J. Multi-Objective Optimal Planning for Distribution Network Considering the Uncertainty of PV Power and Line-Switch State. Sensors 2022, 22, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, R.; Khenissi, I.; Guesmi, T.; Alshammari, B.M.; Alqunun, K.; Alshammari, A.S.; Tlijani, K.; Neji, R. Optimal Reconfiguration of Distribution Network Considering Stochastic Wind Energy and Load Variation Using Hybrid SAMPSO Optimization Method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Truong, A.V.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Phung, T.A. Multi-objective electric distribution network reconfiguration solution using runner-root algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 52, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsan, A.; Yang, Q. State-of-the-art techniques for modelling of uncertainties in active distribution network planning: A review. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, N. Dynamic distribution network reconfiguration using reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Beijing, China, 21–23 October 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kandasamy, M.; Thangavel, R.; Arumugam, T.; Jayaram, J.; Kim, W.W.; Geem, Z.W. Performance Enhancement of Radial Power Distribution Networks Using Network Reconfiguration and Optimal Planning of Solar Photovoltaic-Based Distributed Generation and Shunt Capacitors. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego Pareja, L.A.; López-Lezama, J.M.; Gómez Carmona, O. Optimal Feeder Reconfiguration and Placement of Voltage Regulators in Electrical Distribution Networks Using a Linear Mathematical Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alorf, A. A survey of recently developed metaheuristics and their comparative analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Optimal scheduling of cogeneration system with heat storage device based on artificial bee colony algorithm. Electronics 2022, 11, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, D.; Rajagopalan, A.; Montoya, O.D.; Arul, S.; Grisales-Noreña, L.F. Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on Hybrid Golden Flower Algorithm for Smart Cities Evolution. Energies 2023, 16, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Jing, R.; Zeng, Y.; Li, M. Credible capacity calculation method of distributed generation based on equal power supply reliability criterion. Renew. Energy 2022, 201, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, J. Optimization planning method of distributed generation based on steady-state security region of distribution network. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4209–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, M.; Mittal, A.; Kansal, S. Optimal placement of distributed generation using genetic algorithm approach. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Microelectronics, Computing & Communication Systems (MCCS 2017); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 587–597. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, D.; Lakshminarayana, C. Multiple DG placements in distribution system for power loss reduction using PSO algorithm. Procedia Technol. 2016, 25, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.D.P.; Reddy, V.V.; Manohar, T.G. Application of flower pollination algorithm for optimal placement and sizing of distributed generation in distribution systems. J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2016, 3, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Lakshminarayana, C. Multiple DG placements in radial distribution system for multi objectives using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2797–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Duran, M.J.; Candelo-Becerra, J.E.; Cabana-Jimenez, K. Distribution network reconfiguration with large number of switches solved by a modified binary bat algorithm and improved seed population. Teh. Vjesn. 2019, 26, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Salau, A.O.; Gebru, Y.W.; Bitew, D. Optimal network reconfiguration for power loss minimization and voltage profile enhancement in distribution systems. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, A.M.; Kowsalya, M. A new power system reconfiguration scheme for power loss minimization and voltage profile enhancement using fireworks algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 62, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, H.; Xu, H.; Bao, Y.; Di, H. Distribution network reconfiguration based on noisynet deep Q-learning network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 90358–90365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, A.; El-Sehiemy, R.; Kamel, S.; Selim, A. Optimal Operational Reliability and Reconfiguration of Electrical Distribution Network Based on Jellyfish Search Algorithm. Energies 2022, 15, 6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatkhah, M.H.; Haghifam, M.R.; Salehi, J.; Moser, A. Duration based reconfiguration of electric distribution networks using dynamic programming and harmony search algorithm. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Lin, L. Dynamic reconfiguration strategy based on partition of time intervals with improved fuzzy C-means clustering. In Proceedings of the 2018 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Tianjin, China, 17–19 September 2018; pp. 398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, A.; Ganjehlou, H.G.; Darbandi, F.B.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Abapour, M. Dynamic and multi-objective reconfiguration of distribution network using a novel hybrid algorithm with parallel processing capability. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 90, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.S.; Elnaghi, B.E.; Abd-Alwahab, M.; Ismail, M. Optimal Distribution Networks Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction Via Black Widow Optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2021 22nd International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Assiut, Egypt, 14–16 December 2021; pp. 672–677. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, T.; He, C. Day-ahead stochastic coordinated scheduling for thermal-hydro-wind-photovoltaic systems. Energy 2019, 187, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.P.; Suganthan, P.N.; Qu, B.Y.; Amaratunga, G.A. Multiobjective economic-environmental power dispatch with stochastic wind-solar-small hydro power. Energy 2018, 150, 1039–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgerd, O.I. Electric Energy Systems Theory: An Introduction. 1982. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5599996 (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Doagou-Mojarrad, H.; Gharehpetian, G.; Rastegar, H.; Olamaei, J. Optimal placement and sizing of DG (distributed generation) units in distribution networks by novel hybrid evolutionary algorithm. Energy 2013, 54, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lei, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y. Dynamic distribution network reconfiguration considering travel behaviors and battery degradation of electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsami, P.; King, R.T.A. Dynamic distribution network reconfiguration for distributed generation integration: A systematic review. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd China International Youth Conference on Electrical Engineering (CIYCEE), Chengdu, China, 15–17 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, P. Forecasting and Uncertainty Analysis of Day-Ahead Photovoltaic Power Based on WT-CNN-BiLSTM-AM-GMM. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pu, W.; Song, H. Planning Strategies for Distributed PV-Storage Using a Distribution Network Based on Load Time Sequence Characteristics Partitioning. Processes 2023, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, Z. Research on Multiple Load Short-Term Forecasting Model of Integrated Energy Distribution System Based on Mogrifier-Quantum Weighted MELSTM. Energies 2023, 16, 3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, M. Deep stochastic configuration networks with universal approximation property. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hayyolalam, V.; Kazem, A.A.P. Black widow optimization algorithm: A novel meta-heuristic approach for solving engineering optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 87, 103249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. Another look at a proposed cubic chaotic mapping. In Proceedings of the Cyberspace Safety and Security: 11th International Symposium, CSS 2019, Guangzhou, China, December 1–3 2019; Proceedings, Part I 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Han, M.; Guo, Q. Modified whale optimization algorithm based on tent chaotic mapping and its application in structural optimization. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3703–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Masuda, H.; Tanigaki, Y.; Nojima, Y. Modified distance calculation in generational distance and inverted generational distance. In Proceedings of the Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization: 8th International Conference, EMO 2015, Guimarães, Portugal, March 29–April 1 2015; Proceedings, Part II 8. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Coello, C.A.C.; Cortés, N.C. Solving multiobjective optimization problems using an artificial immune system. Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 2005, 6, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, A.P.; Fonseca, C.M.; Paquete, L. The hypervolume indicator: Computational problems and algorithms. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Thiele, L.; Laumanns, M.; Fonseca, C.M.; Da Fonseca, V.G. Performance assessment of multiobjective optimizers: An analysis and review. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2003, 7, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Qu, B.; Liang, J. A multiobjective particle swarm optimizer using ring topology for solving multimodal multiobjective problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 22, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Qu, B.; Yu, K.; Liang, J.; Li, X. A novel scalable test problem suite for multimodal multiobjective optimization. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 48, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, J. Capacitors Optimization Placement in Distribution Systems Based on Improved Seeker Optimization Algorithm. Sens. Transducers 2013, 155, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S. Dragonfly algorithm: A new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Kumar, V. Spotted hyena optimizer: A novel bio-inspired based metaheuristic technique for engineering applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Singh, S. Butterfly optimization algorithm: A novel approach for global optimization. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, E.; Rashedi, E.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H. A comprehensive survey on gravitational search algorithm. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 41, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




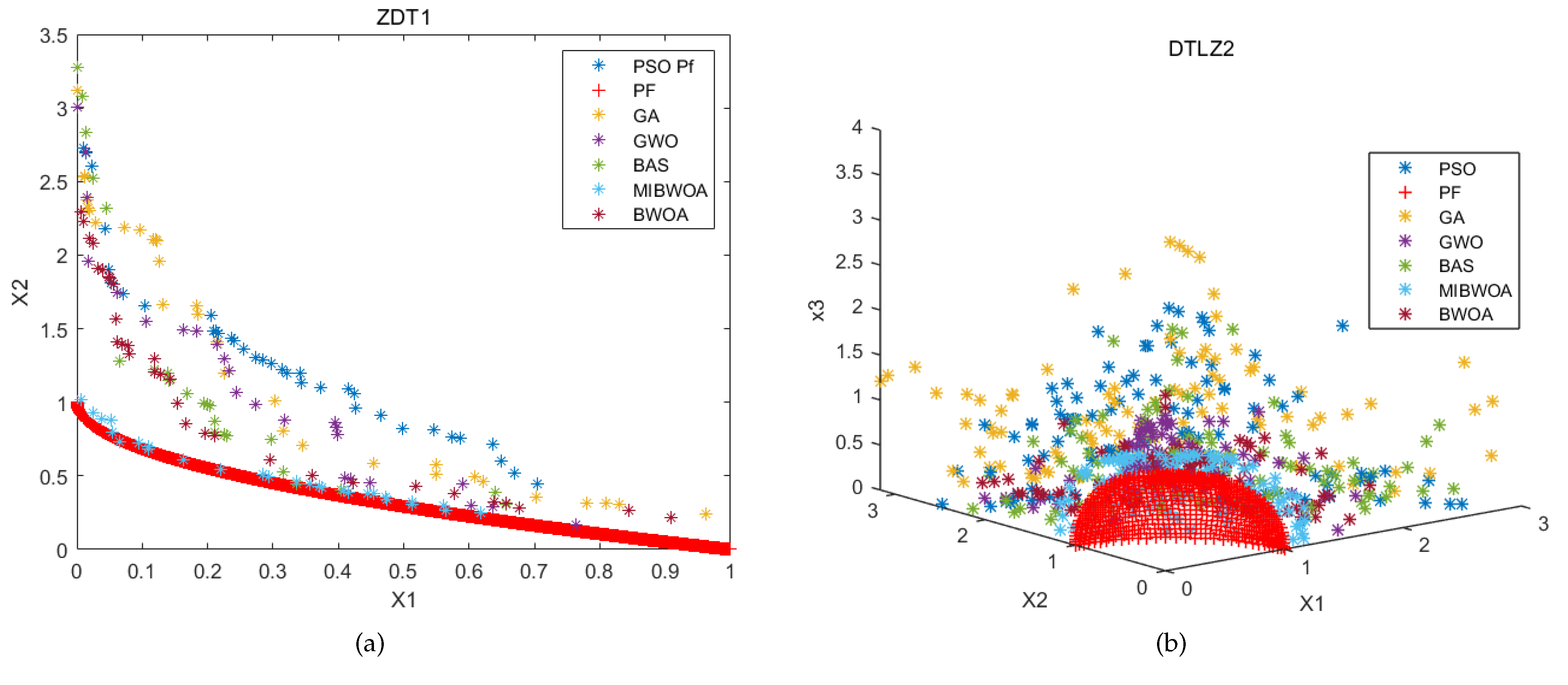



| Name | Function | Interval |
|---|---|---|
| F1 | ||
| F2 | ||
| F3 | ||
| F4 |
| Name | Algorithm | Optimum Value | Iterations | Time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | PSO | 3.27 × 10 | 167 | 118 |
| GA | 1.56 × 10 | 231 | 182 | |
| GWO | 5.61 × 10 | 104 | 82 | |
| BAS | 7.45 × 10 | 107 | 75 | |
| BWOA | 7.45 × 10 | 52 | 65 | |
| MIBWOA | 0 | 26 | 37 | |
| F2 | PSO | 6.51 × 10 | 198 | 125 |
| GA | 2.67 × 10 | 241 | 167 | |
| GWO | 8.10 × 10 | 127 | 77 | |
| BAS | 3.12 × 10 | 114 | 64 | |
| BWOA | 5.68 × 10 | 76 | 74 | |
| MIBWOA | 0 | 14 | 44 |
| Indicators | Name | PSO | GA | GWO | BAS | MIBWOA | BWOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGD | F3 | 0.3557 | 0.2072 | 0.1513 | 0.1664 | 0.0109 | 0.1284 |
| F4 | 0.85 | 1.0783 | 0.4347 | 0.2742 | 0.2470 | 0.3428 | |
| HYP | F3 | 0.0657 | 0.0898 | 0.1885 | 0.3319 | 0.5501 | 0.3442 |
| F4 | 0.7834 | 0.2401 | 1.3808 | 1.7311 | 2.1317 | 1.5477 | |
| PSP | F3 | 1.7424 | 4.1285 | 5.2555 | 4.0525 | 6.1914 | 5.7467 |
| F4 | 1.1739 | 0.9251 | 2.2647 | 3.6361 | 4.0478 | 2.9134 |
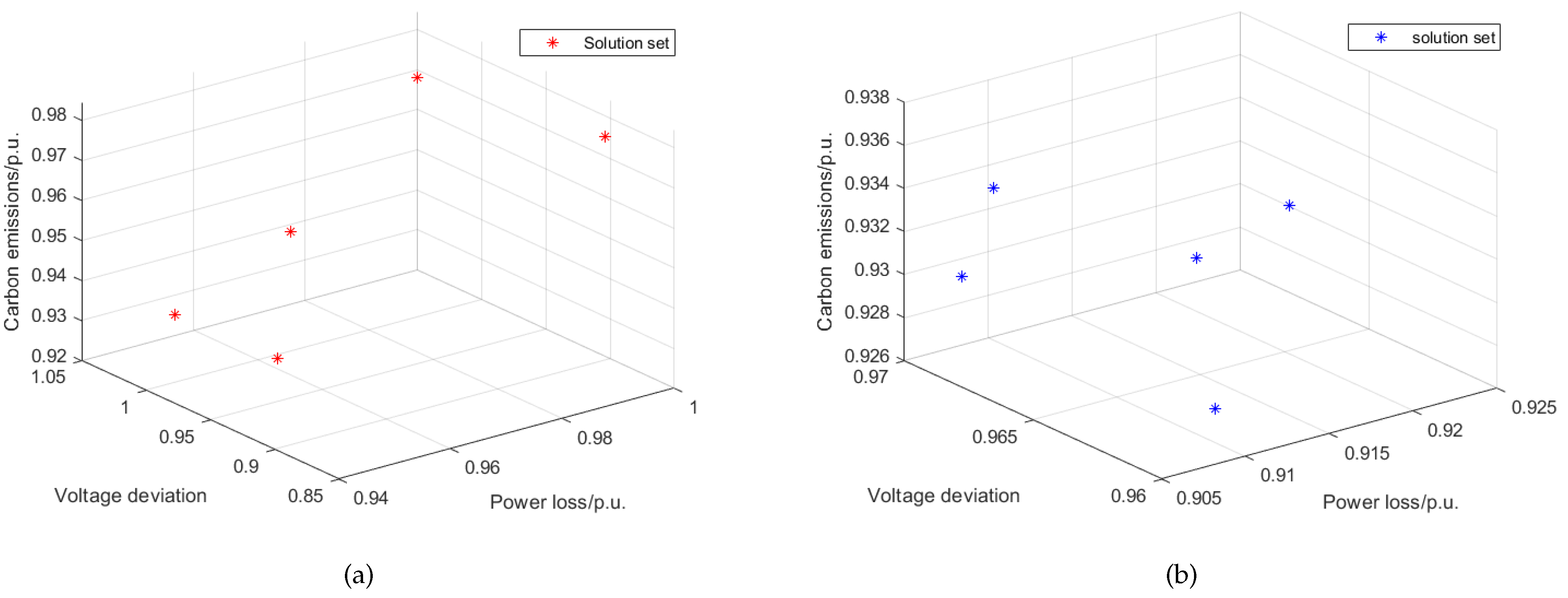
| Algorithm | Power Loss/kW | Voltage Deviation | Carbon Emissions/kg | Select Node |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 112.86 | 0.90 | 84,825 | 31, 28, 13 | |
| MIBWOA | 113.69 | 0.92 | 87,177 | 15, 32, 29 |
| Pareto | 114.52 | 1.04 | 83,485 | 13, 7, 31 |
| solution set | 118.07 | 0.98 | 88,604 | 32, 14, 11 |
| 119.06 | 0.87 | 88,442 | 11, 32, 16 | |
| BWOA | 126.54 | 0.93 | 97,336 | 15, 16, 30 |
| DA | 135.82 | 1.14 | 98,446 | 13, 11, 22 |
| SMA | 135.84 | 0.99 | 99,493 | 14, 17, 25 |
| SA | 144.47 | 0.94 | 104,000 | 14, 12, 11 |
| WOA | 139.06 | 0.99 | 102,060 | 10, 11, 12 |
| Algorithm | Power Loss/kW | Voltage Deviation | Carbon Emissions/kg | Select Node |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 63.57 | 0.96 | 74,289 | 13, 16, 17 | |
| MIBWOA | 64.57 | 0.97 | 74,169 | 15, 16, 17 |
| Pareto | 63.59 | 0.97 | 74,334 | 14, 15, 16 |
| solution set | 63.72 | 0.97 | 74,632 | 13, 14, 15 |
| 63.88 | 0.96 | 74,971 | 12, 13, 14 | |
| BWOA | 66.04 | 1.04 | 74,548 | 14, 17, 31 |
| DA | 66.52 | 1.01 | 76,238 | 13, 25, 30 |
| SMA | 66.38 | 0.98 | 75,223 | 13, 14, 29 |
| SA | 67.59 | 0.99 | 76,115 | 4, 9, 17 |
| WOA | 65.85 | 1.03 | 74,625 | 14, 11, 17 |
| Algorithm | Iterations | Time/s | Optimum Probability/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOA | 21 | 36.54 | 70 |
| SHO | 17 | 24.63 | 82 |
| GSA | 14 | 17.74 | 86 |
| BWOA | 10 | 21.55 | 84 |
| MIBWOA | 3 | 11.32 | 100 |
| Algorithm | Power Loss/kW | Voltage Deviation | Carbon Emissions/kg | Open Circuit Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 144.58 | 1.05 | 74,223 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 32 | |
| MIBWOA | 142.43 | 1.07 | 73,911 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| Pareto | 140.71 | 1.09 | 74,101 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 32 |
| solution | 141.92 | 1.06 | 74,110 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 37 |
| set | 139.98 | 1.08 | 74,296 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 32 |
| 139.55 | 1.15 | 74,387 | 33, 7, 9, 14, 32 | |
| BWOA | 149.64 | 1.19 | 76,581 | 28, 6, 10, 14, 32 |
| BOA | 152.98 | 1.19 | 74,855 | 27, 6, 9, 14, 37 |
| SHO | 147.28 | 1.21 | 74,433 | 28, 7, 11, 14, 37 |
| GSA | 145.03 | 1.23 | 81,658 | 28, 7, 10, 13, 32 |
| Initial state | 202.68 | 1.70 | 96,321 | 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 |
| Algorithm | Power Loss/kW | Voltage Deviation | Carbon Emissions/kg | Open Circuit Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95.62 | 0.66 | 42,223 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 32 | |
| MIBWOA | 99.26 | 0.72 | 40,911 | 26, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| Pareto | 94.34 | 0.67 | 41,073 | 27, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| solution | 94.22 | 0.67 | 41,147 | 27, 7, 10, 14, 17 |
| set | 97.82 | 0.70 | 40,819 | 27, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| 89.8 | 0.62 | 43,820 | 28, 34, 10, 14, 17 | |
| BWOA | 106.04 | 0.82 | 52,659 | 28, 6, 10, 14, 32 |
| BOA | 105.58 | 0.75 | 52,762 | 27, 6, 9, 14, 37 |
| SHO | 104.98 | 0.76 | 51,550 | 28, 7, 11, 13, 37 |
| GSA | 111.11 | 0.78 | 47,257 | 28, 7, 9, 13, 32 |
| Initial state | 149.78 | 1.07 | 81,073 | 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 |
| Algorithm | Iterations | Time/s | Optimum Probability/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOA | 33 | 28.47 | 66 |
| SHO | 26 | 22.83 | 78 |
| GSA | 15 | 13.87 | 82 |
| BWOA | 12 | 15.73 | 80 |
| MIBWOA | 5 | 5.83 | 100 |
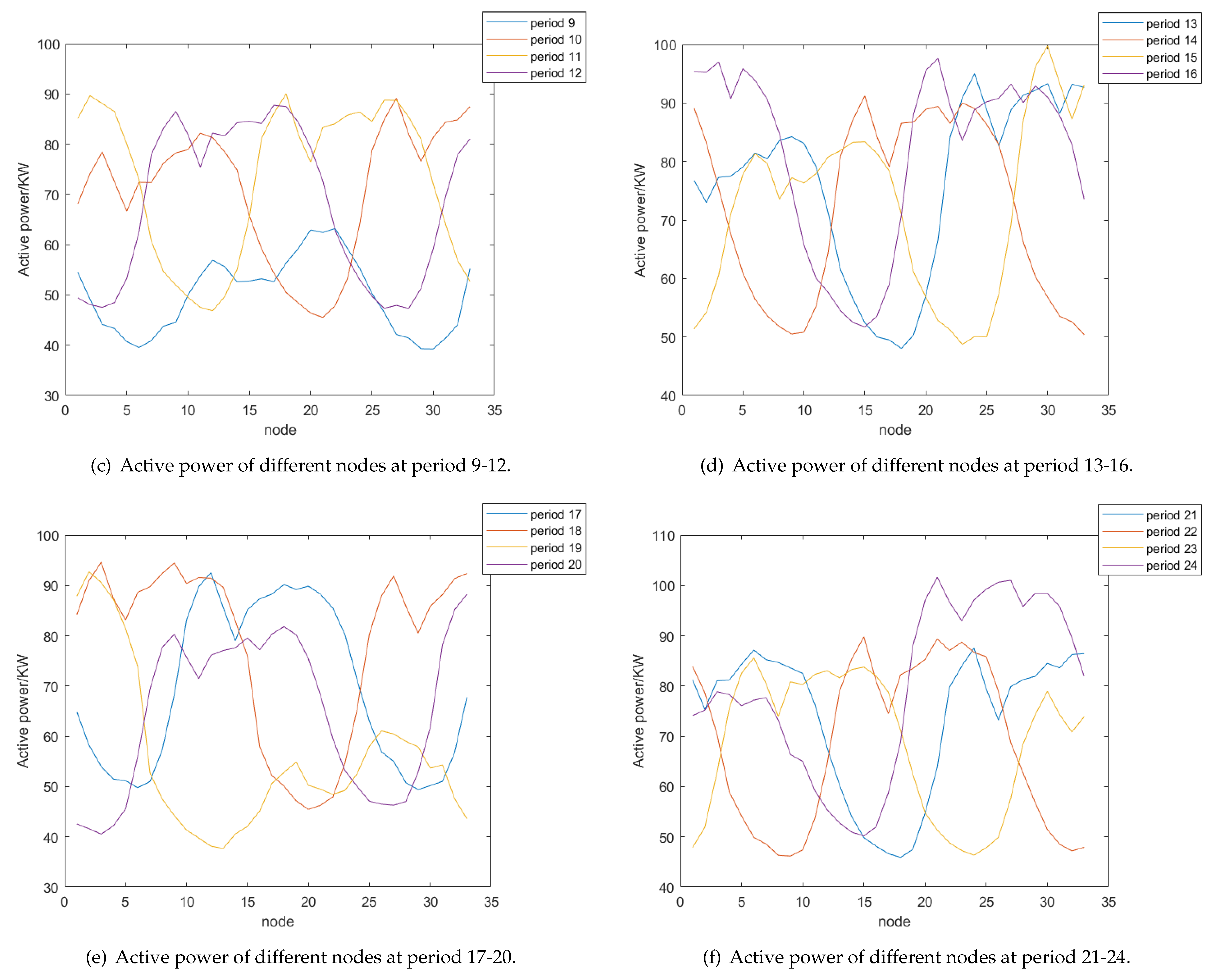
| Period | Power Loss/kW | Voltage Deviation | Carbon Emissions/kg | Open Circuit Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| period 1 | 30.63 | 0.53 | 55,973.76 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 58.72 | 1.08 | 83,400.96 | 33, 34, 35, 36, 37 |
| period 2 | 36.65 | 0.58 | 60,639.92 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 36.65 | 0.58 | 60,639.92 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 16 |
| period 3 | 35.28 | 0.57 | 58,325.40 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 36.41 | 0.57 | 60,504.42 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 16 |
| period 4 | 39.62 | 0.6 | 63,719.06 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 43.38 | 0.65 | 59,969.61 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 16 |
| period 5 | 39.9 | 0.62 | 60,236.38 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 40.34 | 0.6 | 62,923.73 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 17 |
| period 6 | 32.95 | 0.55 | 57,093.81 | 27, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 34.85 | 0.58 | 54,383.97 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 7 | 39.91 | 0.6 | 63,535.58 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 40.88 | 0.61 | 63,668.84 | 27, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 8 | 36 | 0.58 | 57,810.34 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 38.45 | 0.58 | 61,374.55 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 9 | 16.79 | 0.39 | 41,052.65 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 20.34 | 0.45 | 41,856.58 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 10 | 35.56 | 0.58 | 56,877.09 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 41.8 | 0.62 | 64,542.37 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 11 | 29.94 | 0.52 | 52,874.29 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 38.66 | 0.6 | 60,677.02 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| period 12 | 30.43 | 0.53 | 55,337.45 | 28, 34, 10, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 43.1 | 0.64 | 61,941.51 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 16 |
| period 13 | 34.37 | 0.56 | 55,509.76 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 47.64 | 0.66 | 67,773.87 | 28, 34, 10, 14, 17 |
| period 14 | 27.88 | 0.51 | 50,240.60 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 27.88 | 0.51 | 50,240.60 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| period 15 | 37.22 | 0.59 | 58,199.42 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 37.34 | 0.6 | 58,548.97 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 37 |
| period 16 | 39.21 | 0.61 | 59,878.33 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 39.67 | 0.6 | 59,966.68 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| period 17 | 35.24 | 0.57 | 59,063.16 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 39.92 | 0.64 | 55,480.01 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 37 |
| period 18 | 46.25 | 0.66 | 65,336.85 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| Initial state | 47.42 | 0.66 | 68,341.25 | 28, 34, 9, 14, 37 |
| period 19 | 19.6 | 0.43 | 42,968.27 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 19.84 | 0.43 | 43,463.57 | 28, 7, 10, 14, 16 |
| period 20 | 39.41 | 0.61 | 62,370.93 | 27, 34, 10, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 40.29 | 0.63 | 58,356.08 | 28, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 21 | 41.51 | 0.63 | 61,445.81 | 7, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 44 | 0.64 | 64,484.53 | 6, 34, 10, 14, 37 |
| period 22 | 36.47 | 0.58 | 59,390.08 | 6, 34, 9, 14, 37 |
| Initial state | 36.8 | 0.6 | 56,262.97 | 7, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| period 23 | 41.69 | 0.62 | 64,852.93 | 7, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 43.03 | 0.64 | 64,916.33 | 6, 34, 9, 14, 37 |
| period 24 | 43.5 | 0.62 | 51,392.00 | 7, 7, 9, 14, 17 |
| Initial state | 44.79 | 0.78 | 53,482.00 | 7, 34, 9, 14, 17 |
| Algorithm | Iterations | Time/s | Optimum Probability/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOA | 35 | 216.43 | 52 |
| SHO | 27 | 205.38 | 66 |
| GSA | 31 | 142.34 | 70 |
| BWOA | 21 | 150.22 | 64 |
| MIBWOA | 6 | 63.11 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Zhang, Q. Research on Combination of Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on MIBWOA. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9580. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129580
Yan X, Zhang Q. Research on Combination of Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on MIBWOA. Sustainability. 2023; 15(12):9580. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129580
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xin, and Qian Zhang. 2023. "Research on Combination of Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on MIBWOA" Sustainability 15, no. 12: 9580. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129580
APA StyleYan, X., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Research on Combination of Distributed Generation Placement and Dynamic Distribution Network Reconfiguration Based on MIBWOA. Sustainability, 15(12), 9580. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129580









